Power Spectra’s Perspective on Meteorological Drivers of Snow Depth Multiscale Behavior over the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
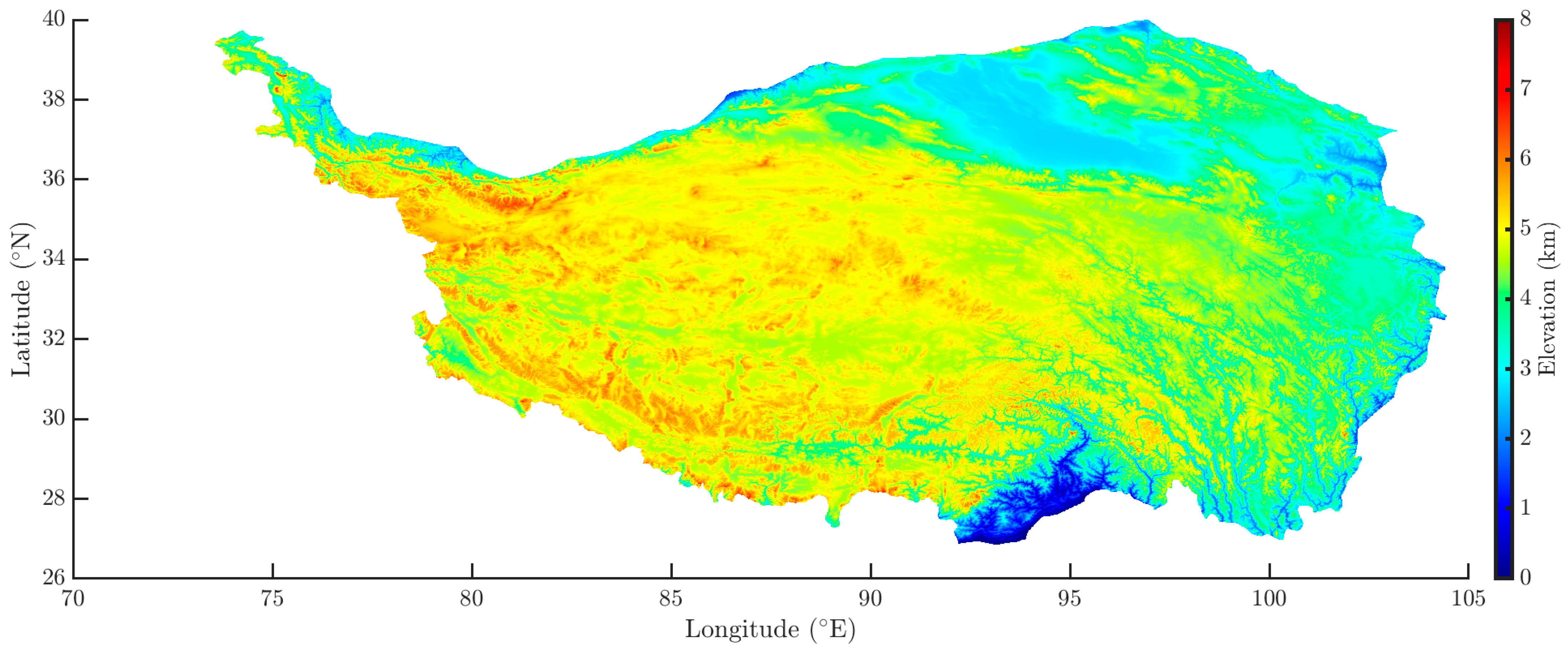
2.1. Tibetan Plateau
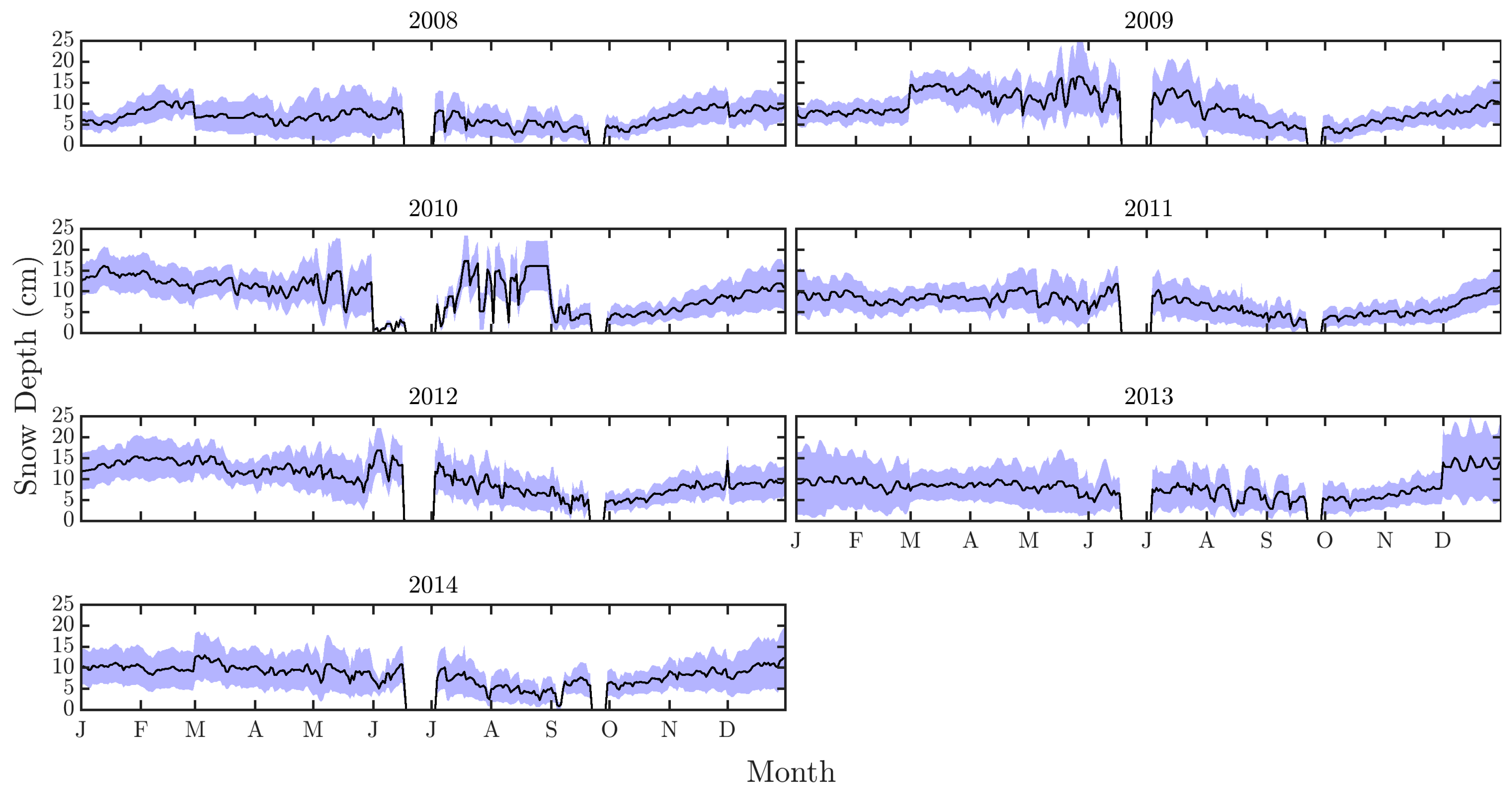
2.2. Snow Depth Product
2.3. Meteorological Reanalysis
2.4. Scaling Analysis
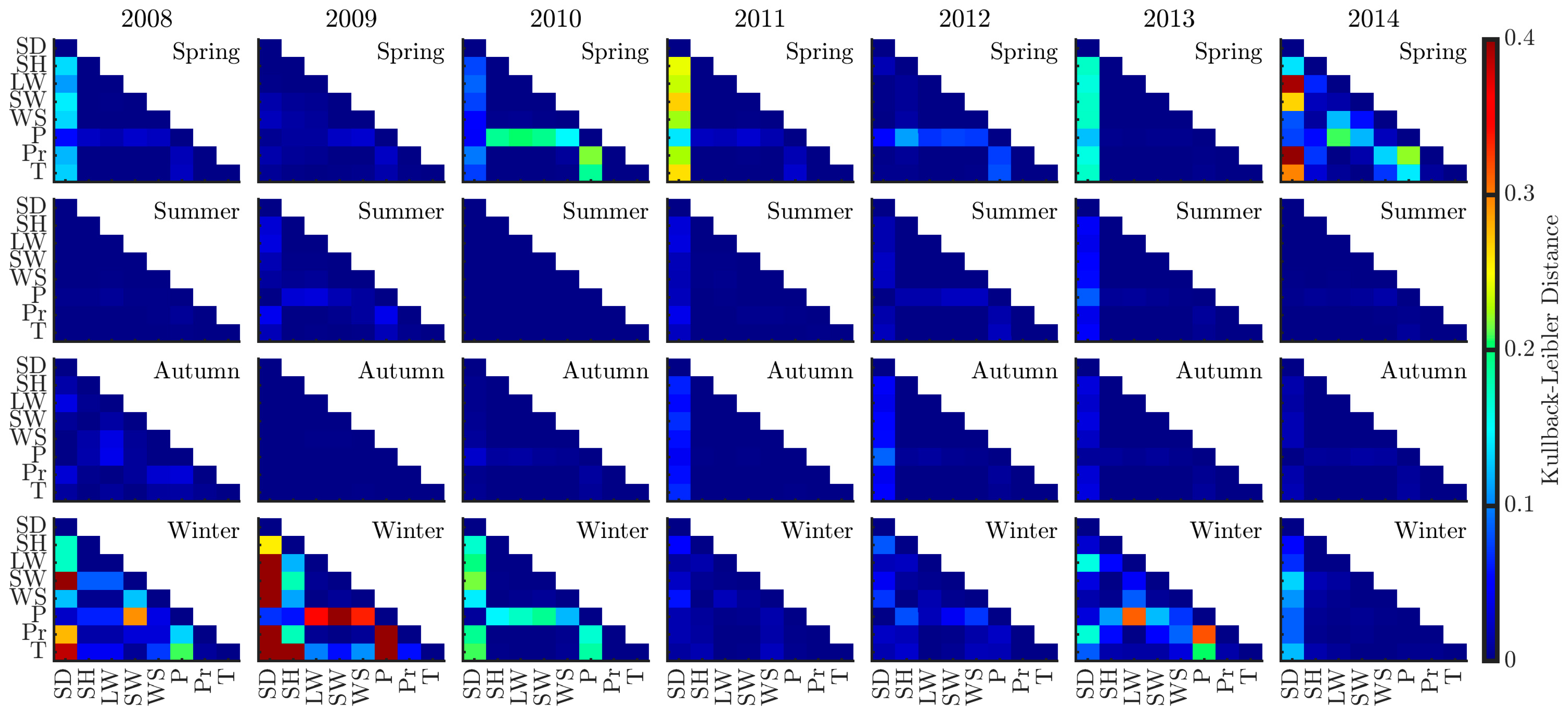
2.5. Kullback–Leibler Distance
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Variations
3.2. Power Spectra
3.3. Spectral Divergence
3.4. Spatial Heterogeneity Across Scales
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J. China: The Third Pole. Nature 2008, 454, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-W.; Qian, Z.-A. The Relation between the Tibetan Winter Snow and the Asian Summer Monsoon and Rainfall: An Observational Investigation. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2038–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate Change Will Affect the Asian Water Towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Feng, L.; Kuang, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Tian, Y.; Yao, Y. Divergent and Changing Importance of Glaciers and Snow as Natural Water Reservoirs in the Eastern and Southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, N.; Dai, Y.; Yao, T. Reversal in Snow Mass Trends on the Tibetan Plateau and Their Climatic Causes. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ma, L.; Ma, M.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, W. Spatial–Temporal Variability of Snow Cover and Depth in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Pepin, N.; Yang, K.; Sun, J.; Li, D. Local Changes in Snow Depth Dominate the Evolving Pattern of Elevation-Dependent Warming on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, Y.; Wegmann, M.; Dutra, E.; Liu, B.; Balsamo, G.; Yang, K.; de Rosnay, P.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W.; Senan, R.; et al. Evaluation of Snow Depth and Snow Cover over the Tibetan Plateau in Global Reanalyses Using in Situ and Satellite Remote Sensing Observations. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2221–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Ren, G.; Fraedrich, K.; Pepin, N.; Yan, Y.; Ma, L. Observed Changes in Snow Depth and Number of Snow Days in the Eastern and Central Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhao, P.; Yao, S.; Jia, X. Formation of Snow Cover Anomalies Over the Tibetan Plateau in Cold Seasons. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4873–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.D.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.S.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.J.; Yang, X.X.; Duan, K.Q.; Zhao, H.B.; Xu, B.Q.; et al. Different Glacier Status with Atmospheric Circulations in Tibetan Plateau and Surroundings. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Che, T.; Xie, H.; Wu, X. Estimation of Snow Depth over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Based on AMSR-E and MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Che, T.; Ding, Y.; Hao, X. Evaluation of Snow Cover and Snow Depth on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Derived from Passive Microwave Remote Sensing. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Development of a Fine-Resolution Snow Depth Product Based on the Snow Cover Probability for the Tibetan Plateau: Validation and Spatial–Temporal Analyses. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127027. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X.; Yi, G.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Wen, B. Reconstruction of Snow Depth Data at Moderate Spatial Resolution (1 Km) from Remotely Sensed Snow Data and Multiple Optimized Environmental Factors: A Case Study over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Dong, H.; Dai, Y.; Mou, N.; Wei, W. Contrasting Changes of Snow Cover between Different Regions of the Tibetan Plateau during the Latest 21 Years. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1075988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, X.-D.; Yang, X.-L.; Li, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-L.; Liang, T.-G. Mapping Snow Depth Distribution from 1980 to 2020 on the Tibetan Plateau Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and Downscaling Techniques. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 205, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Liang, T. AMSR2 Snow Depth Downscaling Algorithm Based on a Multifactor Approach over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, E.; Ramírez, J.A.; Elder, K.J. Topographic, Meteorologic, and Canopy Controls on the Scaling Characteristics of the Spatial Distribution of Snow Depth Fields. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W07409. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ullah, S.; Pepin, N.; Ma, Q. Changes in Snow Depth under Elevation-dependent Warming over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2021, 22, e1041. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, R.; Huang, G. Low-Frequency Snow Changes over the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; You, Q. How Do Westerly Jet Streams Regulate the Winter Snow Depth over the Tibetan Plateau? Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Gao, Y.; He, C.; Barlage, M.; Huang, W. Assessment of Uncertainty Sources in Snow Cover Simulation in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Pan, J.; Xiong, C.; Jiang, L.; Shi, J. Snow Depth and Snow Cover over the Tibetan Plateau Observed from Space in against ERA5: Matters of Scale. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 1523–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, P.A.; Musselman, K.N.; Revuelto, J.; Deems, J.S.; López-Moreno, J.I.; McPhee, J. Interannual and Seasonal Variability of Snow Depth Scaling Behavior in a Subalpine Catchment. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Z.S.; Peitzsch, E.H.; Sproles, E.A.; Birkeland, K.W.; Palomaki, R.T. Assessing the Seasonal Evolution of Snow Depth Spatial Variability and Scaling in Complex Mountain Terrain. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 4907–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.-H.; Shrestha, B.; Li, Z.-L.; Liu, G.; Ouyang, H.; Gurung, D.R.; Giriraj, A.; Aung, K.S. Determination of Snow Cover from MODIS Data for the Tibetan Plateau Region. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D. A Daily, 0.05° Snow Depth Dataset for Tibetan Plateau (2000–2018); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center, 2021; Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/0515ce19-5a69-4f86-822b-330aa11e2a28 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Yang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, W.; He, J.; Shao, C.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, J. A High-Resolution Near-Surface Meteorological Forcing Dataset for the Third Pole Region (TPMFD, 1979–2022); National Tibetan Plateau Data Center, 2023; Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/44a449ce-e660-44c3-bbf2-31ef7d716ec7 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, X.; He, J.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, B.; et al. TPHiPr: A Long-Term (1979–2020) High-Accuracy Precipitation Dataset (1/30°, Daily) for the Third Pole Region Based on High-Resolution Atmospheric Modeling and Dense Observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Barros, A.P. Topographic Controls on Active Microwave Behavior of Mountain Snowpacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindlish, R.; Barros, A.P. Aggregation of Digital Terrain Data Using a Modified Fractal Interpolation Scheme. Comput. Geosci. 1996, 22, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Barros, A.P. Space–Time Characterization of Soil Moisture from Passive Microwave Remotely Sensed Imagery and Ancillary Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Review of Snow Cover Variation over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Influence on the Broad Climate System. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory. In Wiley Series in Telecommunications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 978-0-471-06259-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On Information and Sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Zhou, S.; Sun, P.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, Z. Spatiotemporal Variations in Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau from 2003 to 2020. Water 2024, 16, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mou, N.; Niu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F. Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of Snow Depth and Snow Cover Days over the Tibetan Plateau. Water 2021, 13, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Li, X.; Jin, R.; Armstrong, R.; Zhang, T. Snow Depth Derived from Passive Microwave Remote-Sensing Data in China. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Xu, L.; Salomonson, V.V. MODIS/Terra Observed Seasonal Variations of Snow Cover over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L06706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yan, L.; Yin, Z.-Y. Elevation Dependency of Recent and Future Minimum Surface Air Temperature Trends in the Tibetan Plateau and Its Surroundings. Glob. Planet. Change 2009, 68, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangwala, I.; Miller, J.R.; Xu, M. Warming in the Tibetan Plateau: Possible Influences of the Changes in Surface Water Vapor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L06703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leathers, D.J.; Ellis, A.W.; Robinson, D.A. Characteristics of Temperature Depressions Associated with Snow Cover across the Northeast United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1995, 34, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Keyimu, M.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Zeng, F.; Lin, L. Climate and Elevation Control Snow Depth and Snow Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Tanaka, K.; Tsutsui, H.; Li, M. Snow Cover Conditions in the Tibetan Plateau Observed during the Winter of 2003/2004. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2007, 39, 152–164. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, M.; Qian, Q. The Impact of Tibetan Plateau Snow Cover on the Summer Temperature in Central Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Hu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Jia, B.; Sun, G.; Du, Y.; Song, H. Impact of the Snow Cover Scheme on Snow Distribution and Energy Budget Modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 131, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wu, Q. Relationship between the Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Snow Depth and the Terrain over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2015, 27, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J. The Impacts of Moisture Transport on Drifting Snow Sublimation in the Saltation Layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7523–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. The First High-Resolution Meteorological Forcing Dataset for Land Process Studies over China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, F. Lead-Lag Correlations between Snow Cover and Meteorological Factors at Multi-Time Scales in the Tibetan Plateau under Climate Warming. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2021, 146, 1459–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, S.; Yu, B.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y. Temperature-Dominated Spatiotemporal Variability in Snow Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau from 2002 to 2022. Cryosphere 2024, 18, 1817–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basang, D.; Barthel, K.; Olseth, J.A. Satellite and Ground Observations of Snow Cover in Tibet during 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z. Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau and Topographic Controls. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 33.43°N–36.13°N 75.88°E–78.58°E (55 × 55) | 35.68°N–36.63°N 76.08°E–77.03°E (20 × 20) | 35.43°N–36.88°N 75.63°E–77.08°E (30 × 30) | 35.68°N–38.13°N 70.98°E–73.43°E (50 × 50) |
| 2009 | 36.43°N–38.98°N 71.13°E–73.68°E (52 × 52) | 38.08°N–39.48°N 71.88°E–73.28°E (29 × 29) | 35.43°N–36.88°N 75.88°E–77.33°E (30 × 30) | 34.73°N–37.78°N 73.38°E–76.43°E (62 × 62) |
| 2010 | 36.68°N–38.98°N 71.63°E–73.93°E (47 × 47) | 35.43°N–35.63°N 80.63°E–80.83°E (5 × 5) | 35.93°N–37.08°N 74.88°E–76.03°E (24 × 24) | 36.88°N–39.03°N 70.98°E–73.13°E (44 × 44) |
| 2011 | 36.43°N–38.63°N 71.38°E–73.58°E (45 × 45) | 38.48°N–39.43°N 71.88°E–72.83°E (20 × 20) | 35.68°N–36.88°N 75.88°E–77.08°E (25 × 25) | 35.68°N–38.98°N 70.98°E–74.28°E (67 × 67) |
| 2012 | 36.43°N–38.98°N 71.38°E–73.93°E (52 × 52) | 38.43°N–39.38°N 71.63°E–72.58°E (20 × 20) | 35.43°N–36.38°N 76.38°E–77.33°E (20 × 20) | 35.68°N–38.98°N 70.98°E–74.28°E (67 × 67) |
| 2013 | 32.93°N–35.13°N 76.38°E–78.58°E (45 × 45) | 35.43°N–36.38°N 76.38°E–77.33°E (20 × 20) | 35.68°N–36.88°N 75.63°E–76.83°E (25 × 25) | 29.68°N–32.03°N 93.18°E–95.53°E (48 × 48) |
| 2014 | 36.53°N–38.98°N 71.38°E–73.83°E (50 × 50) | 38.53°N–39.48°N 71.88°E–72.83°E (20 × 20) | 35.68°N–36.88°N 76.13°E–77.33°E (25 × 25) | 34.68°N–37.43°N 73.33°E–76.08°E (56 × 56) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Jiang, L. Power Spectra’s Perspective on Meteorological Drivers of Snow Depth Multiscale Behavior over the Tibetan Plateau. Land 2025, 14, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040790
Cao Y, Jiang L. Power Spectra’s Perspective on Meteorological Drivers of Snow Depth Multiscale Behavior over the Tibetan Plateau. Land. 2025; 14(4):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040790
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yueqian, and Lingmei Jiang. 2025. "Power Spectra’s Perspective on Meteorological Drivers of Snow Depth Multiscale Behavior over the Tibetan Plateau" Land 14, no. 4: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040790
APA StyleCao, Y., & Jiang, L. (2025). Power Spectra’s Perspective on Meteorological Drivers of Snow Depth Multiscale Behavior over the Tibetan Plateau. Land, 14(4), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040790







