Innovative Multi-Type Identification System for Cropland Abandonment on the Loess Plateau: Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Driver Shifts (2000–2023) and Implications for Food Security
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
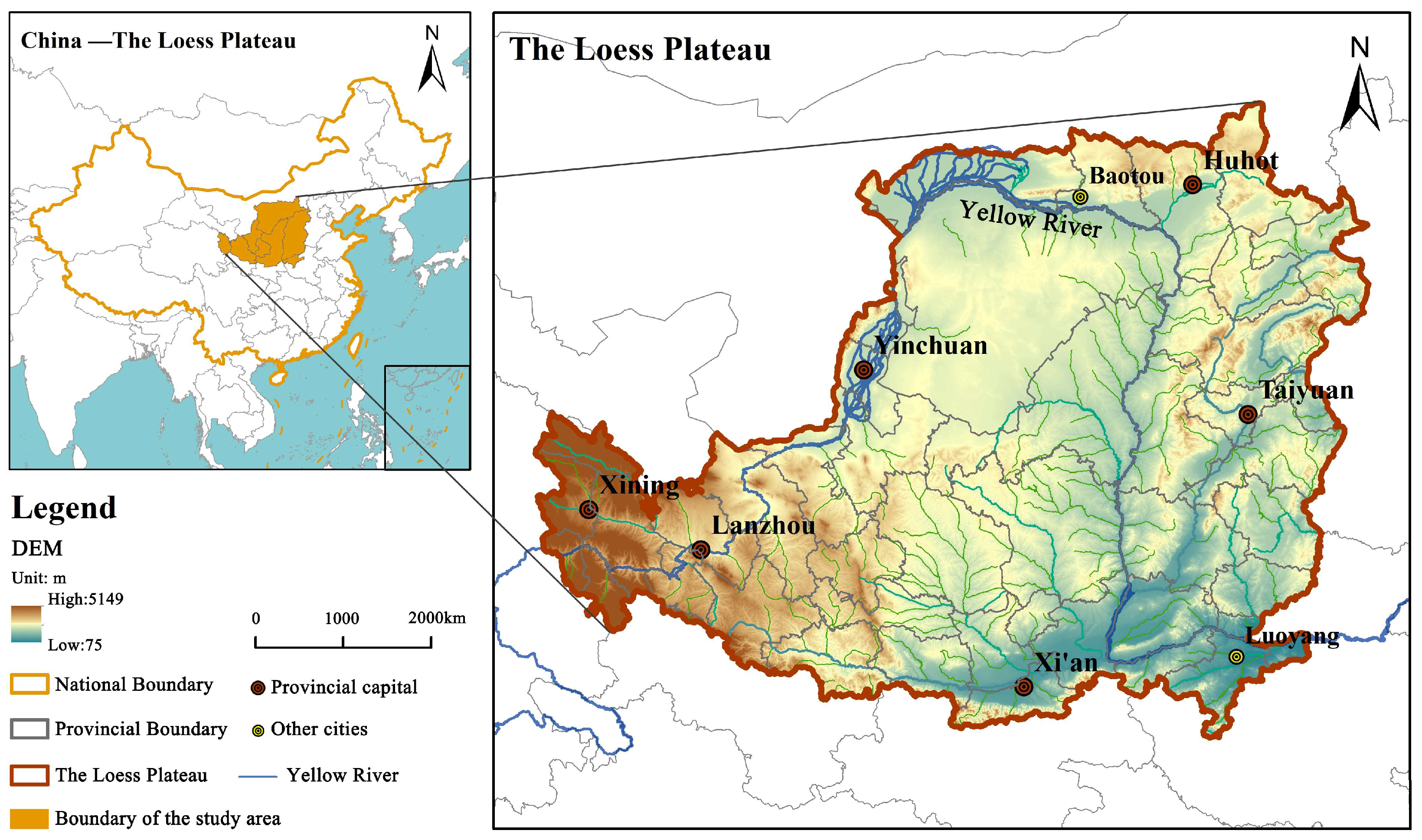
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3. Methods
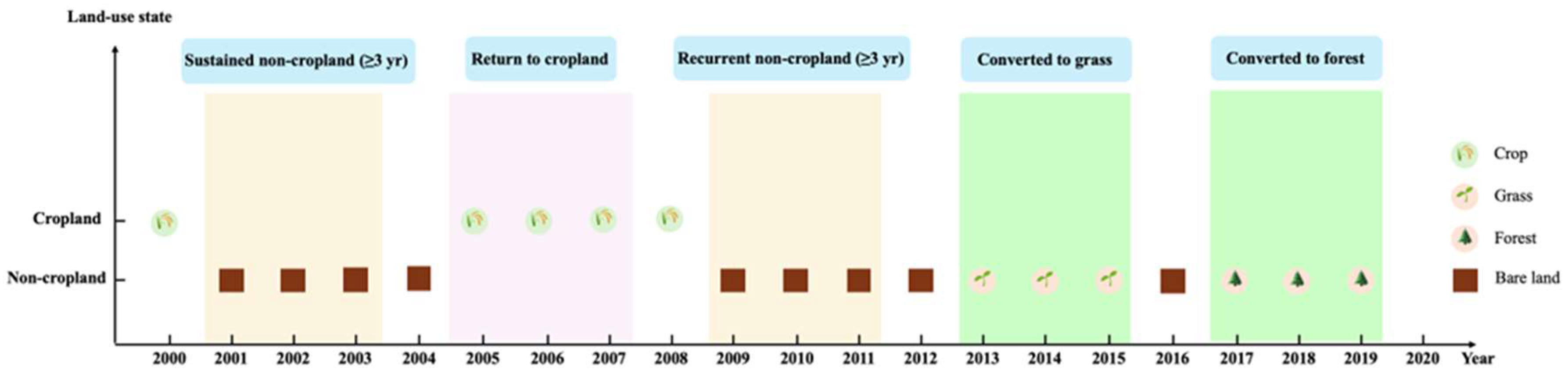
3.1. Identification of Cropland Abandonment
3.1.1. Interannual Cropland Abandonment
3.1.2. Multiyear Cropland Abandonment
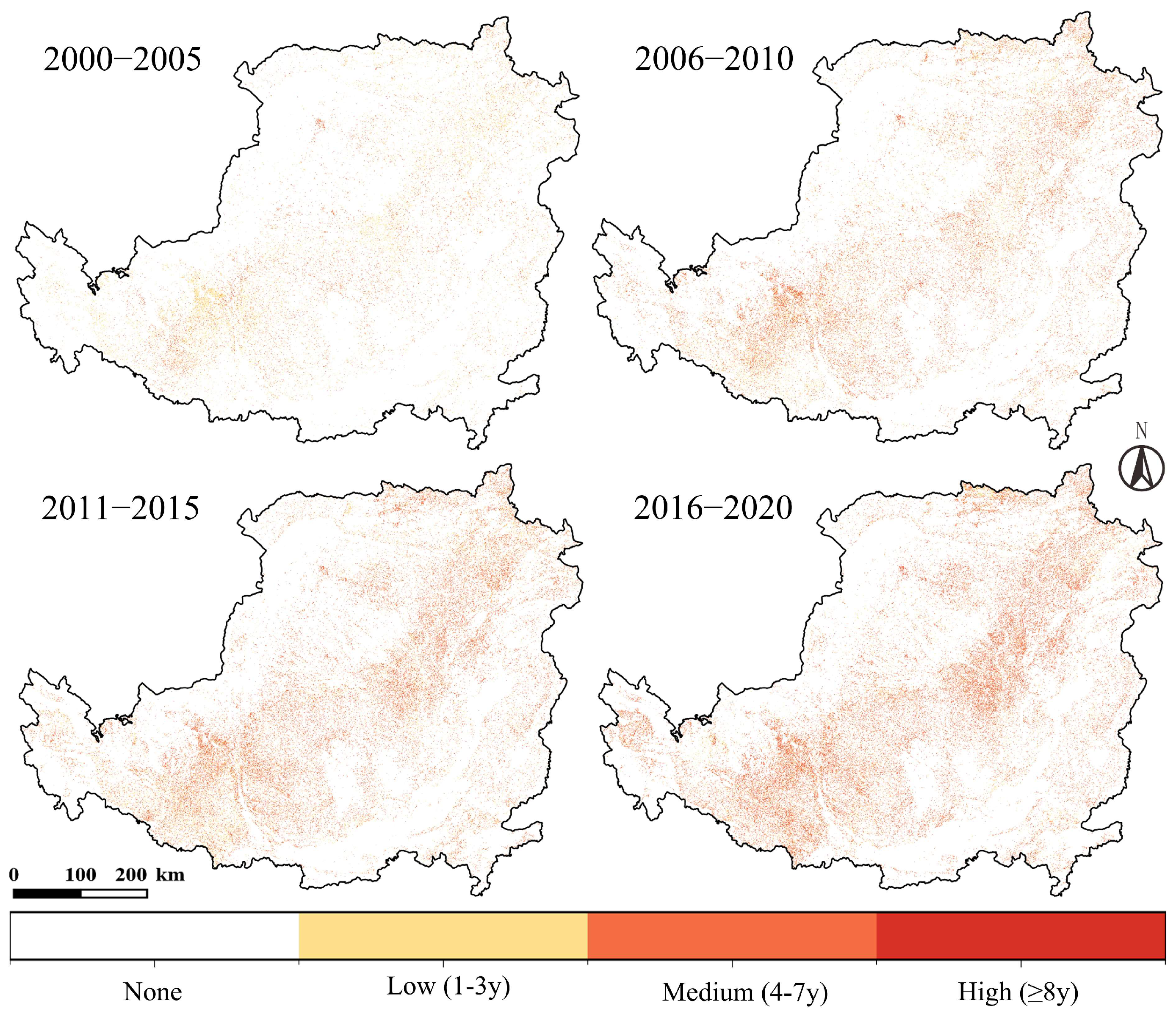
- Interannual abandonment distribution—Based on four stages (2000–2005, 2006–2010, 2011–2015, and 2016–2020). Pixels that experienced abandonment in any year within a stage were marked, and Boolean overlay was used to calculate the total abandoned area for each stage.
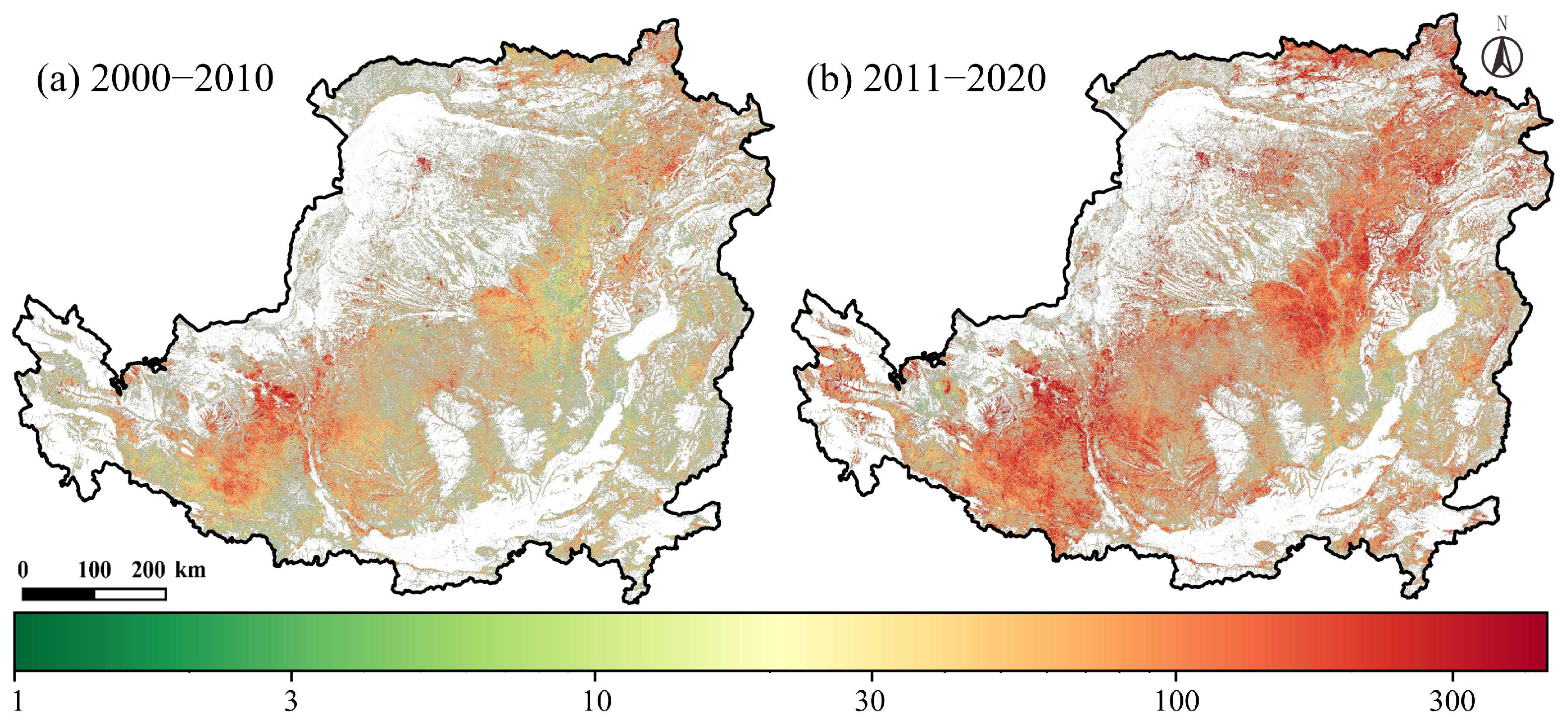
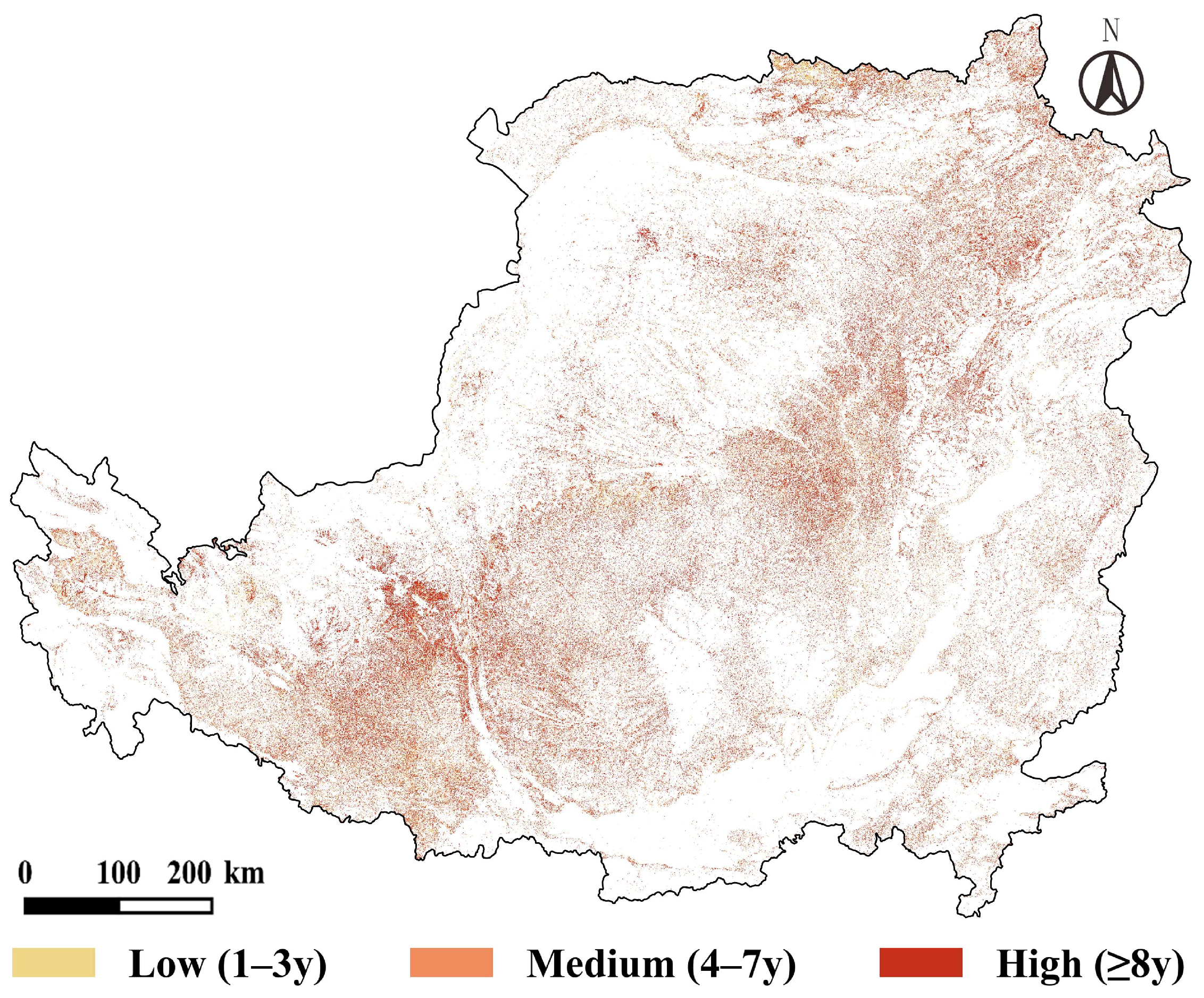
- Multiyear abandonment grade distribution—Based on the entire period of 2000–2020. Pixels were classified into low, medium, and high-grade abandonment according to their cumulative duration of abandonment.
3.1.3. Conversion of Cropland to Forest/Grassland
3.1.4. Cropland Reclamation
3.2. Grain Yield Assessment
3.2.1. Grain Production Estimation
3.2.2. Mann–Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope
3.3. Random Forest Analysis of Driving Factors
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Cropland Abandonment
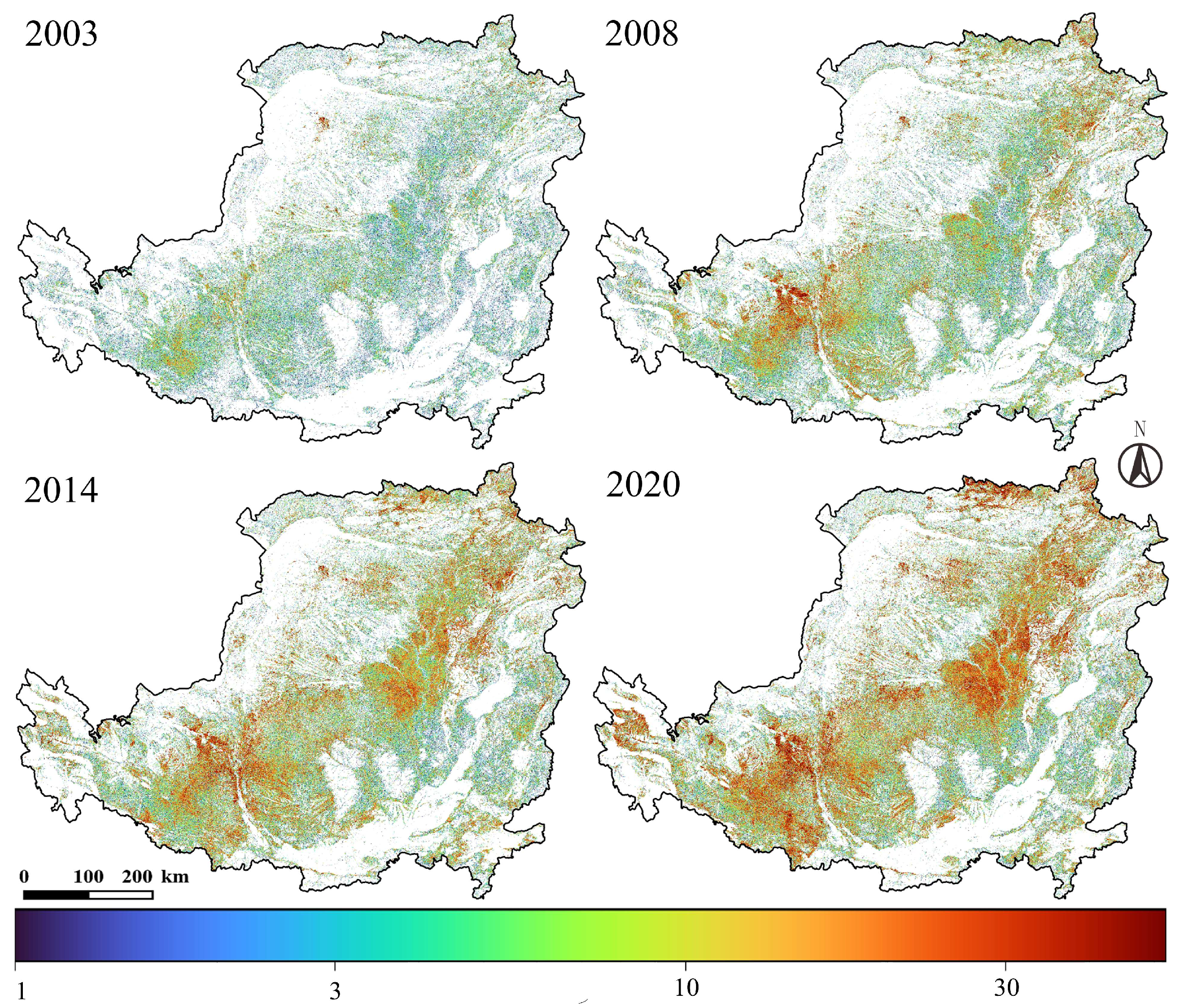
4.1.1. Interannual Spatiotemporal Fluctuations
4.1.2. Spatiotemporal Fluctuations of Multiyear Abandonment
4.2. Policy Effects on Cropland Abandoned
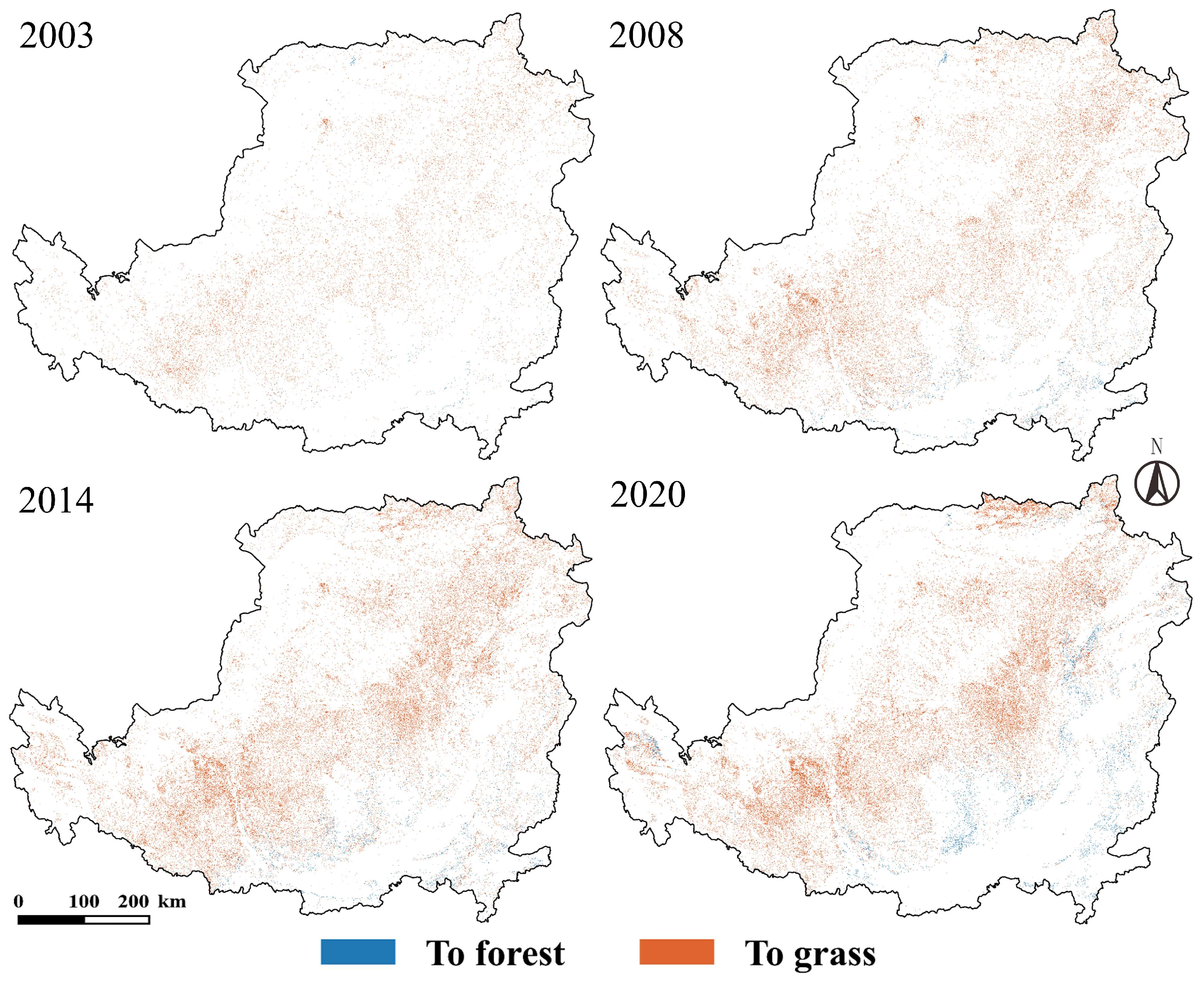
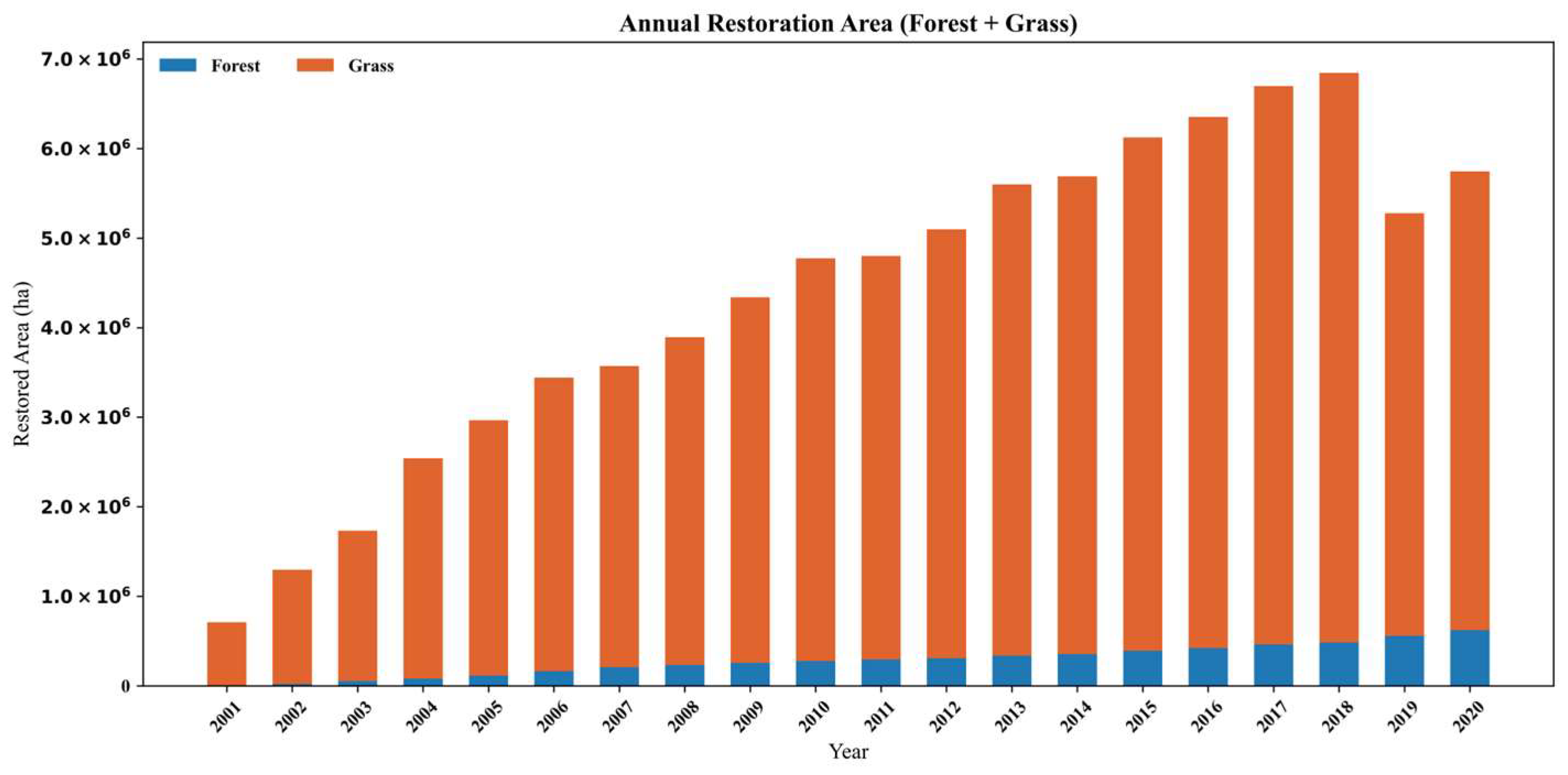
4.2.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Conversion to Forest and Grassland
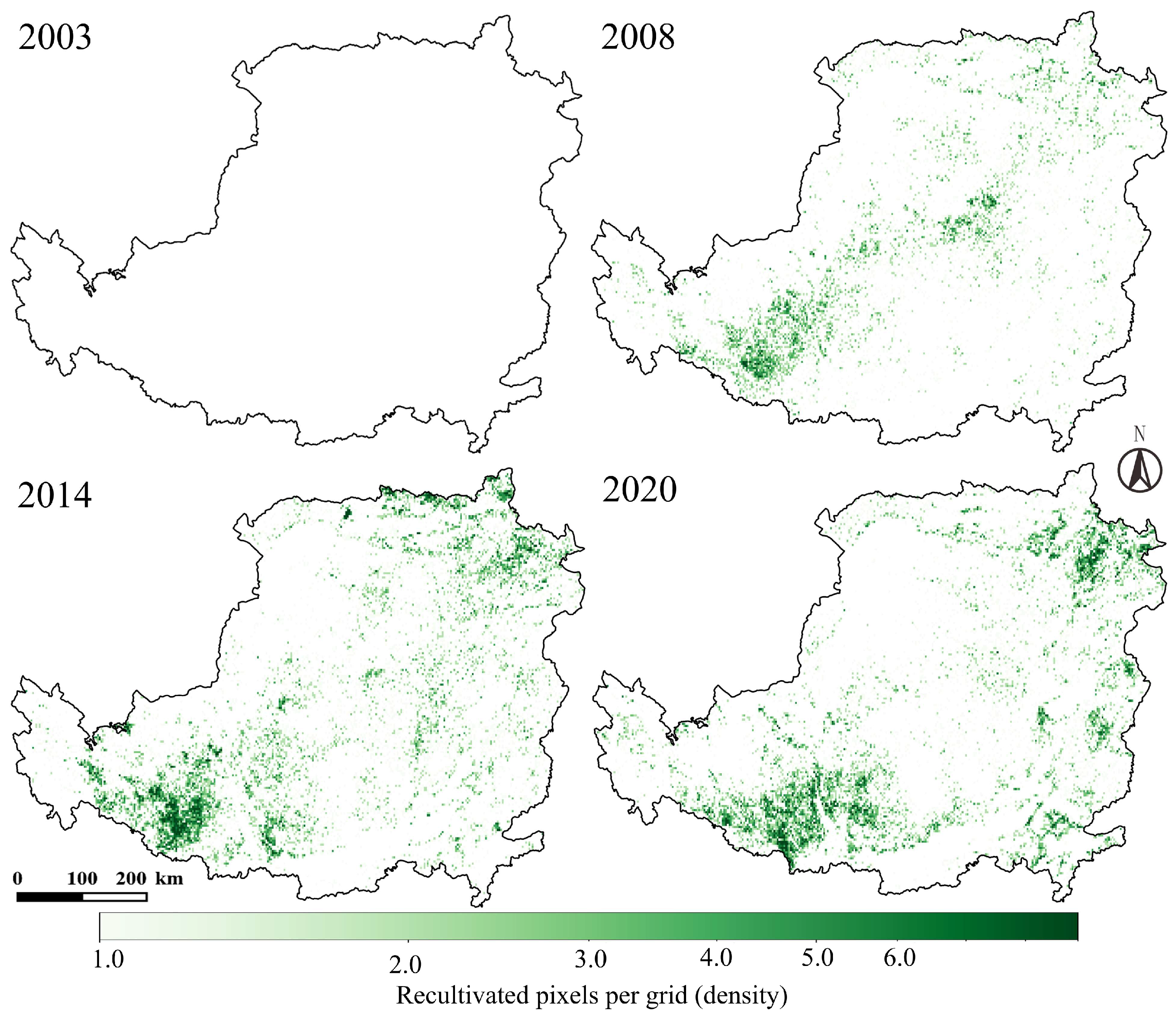
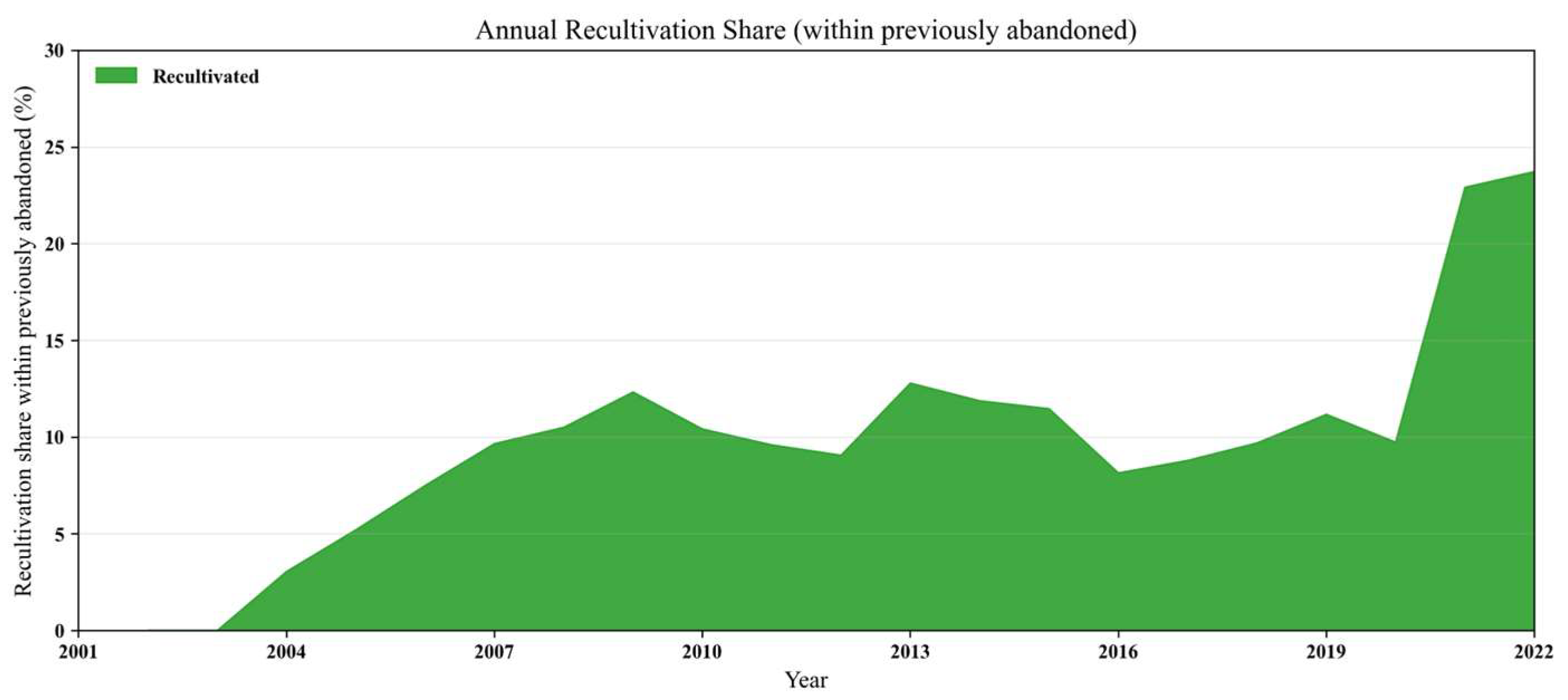
4.2.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Cropland Reclamation
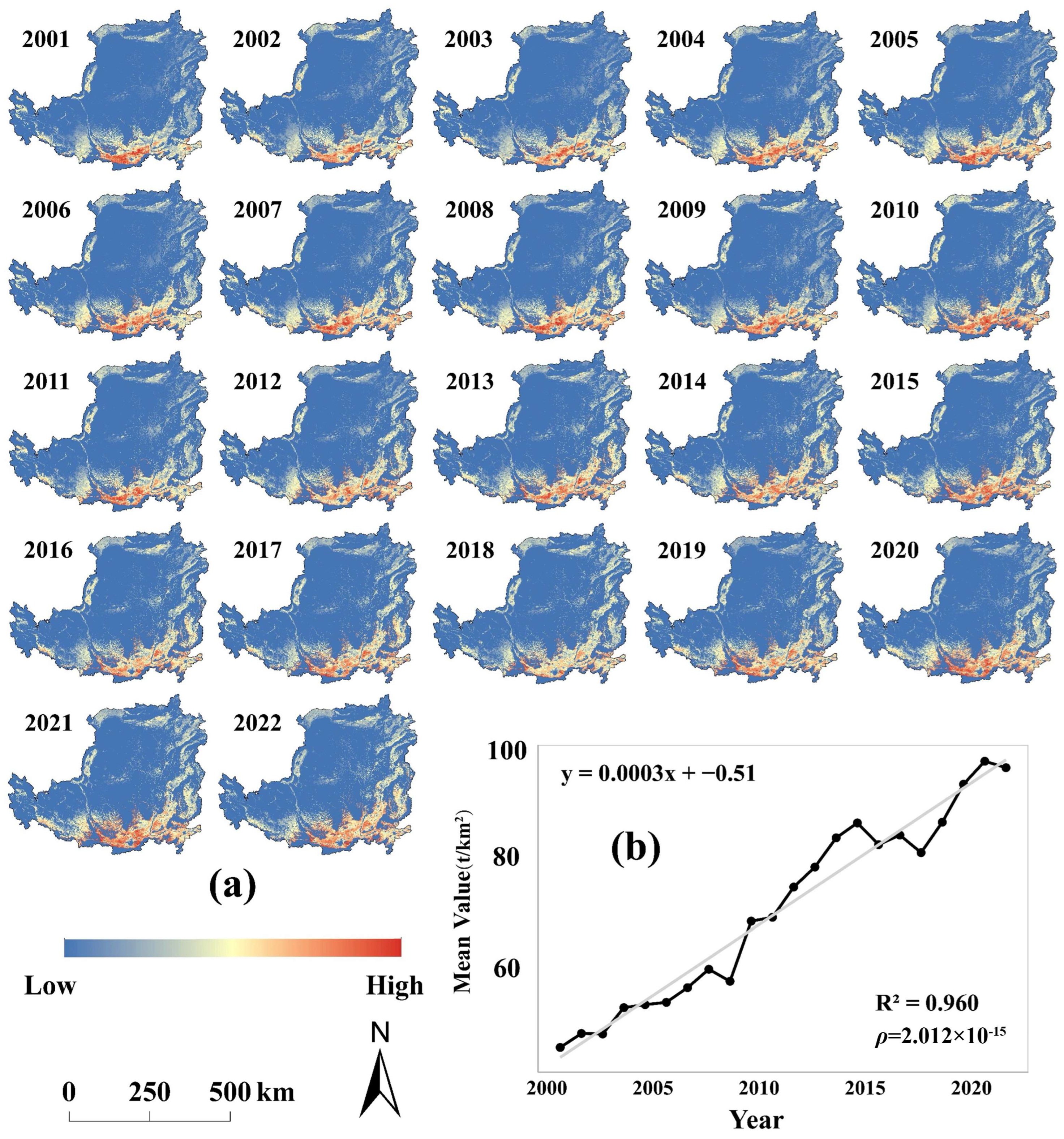
4.3. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Grain Production
4.3.1. Temporal Fluctuations of Grain Production
4.3.2. Spatial Pattern of Grain Production
4.4. Impacts of Cropland Abandonment on Grain Production
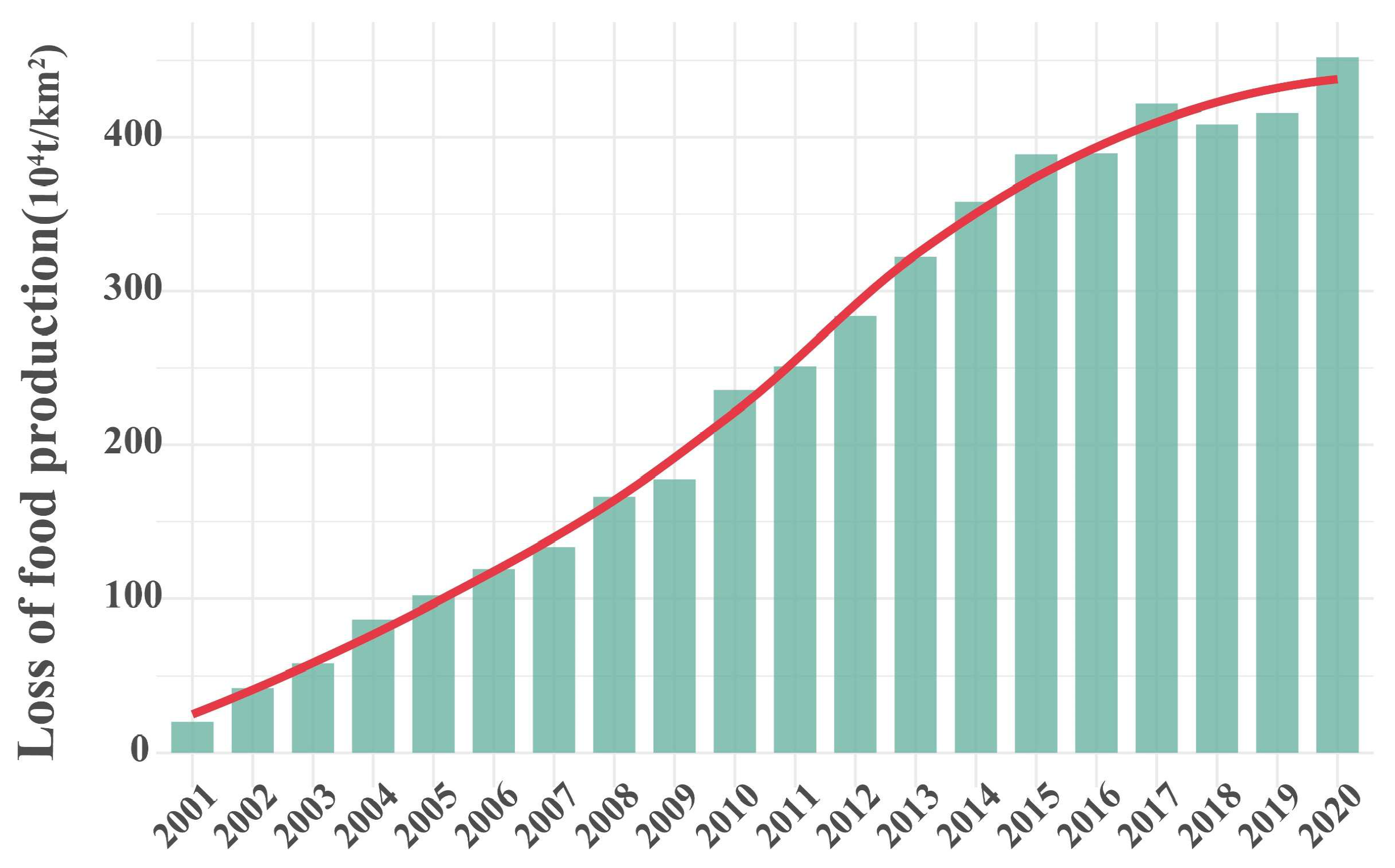
4.4.1. Mechanism of Grain Yield Loss
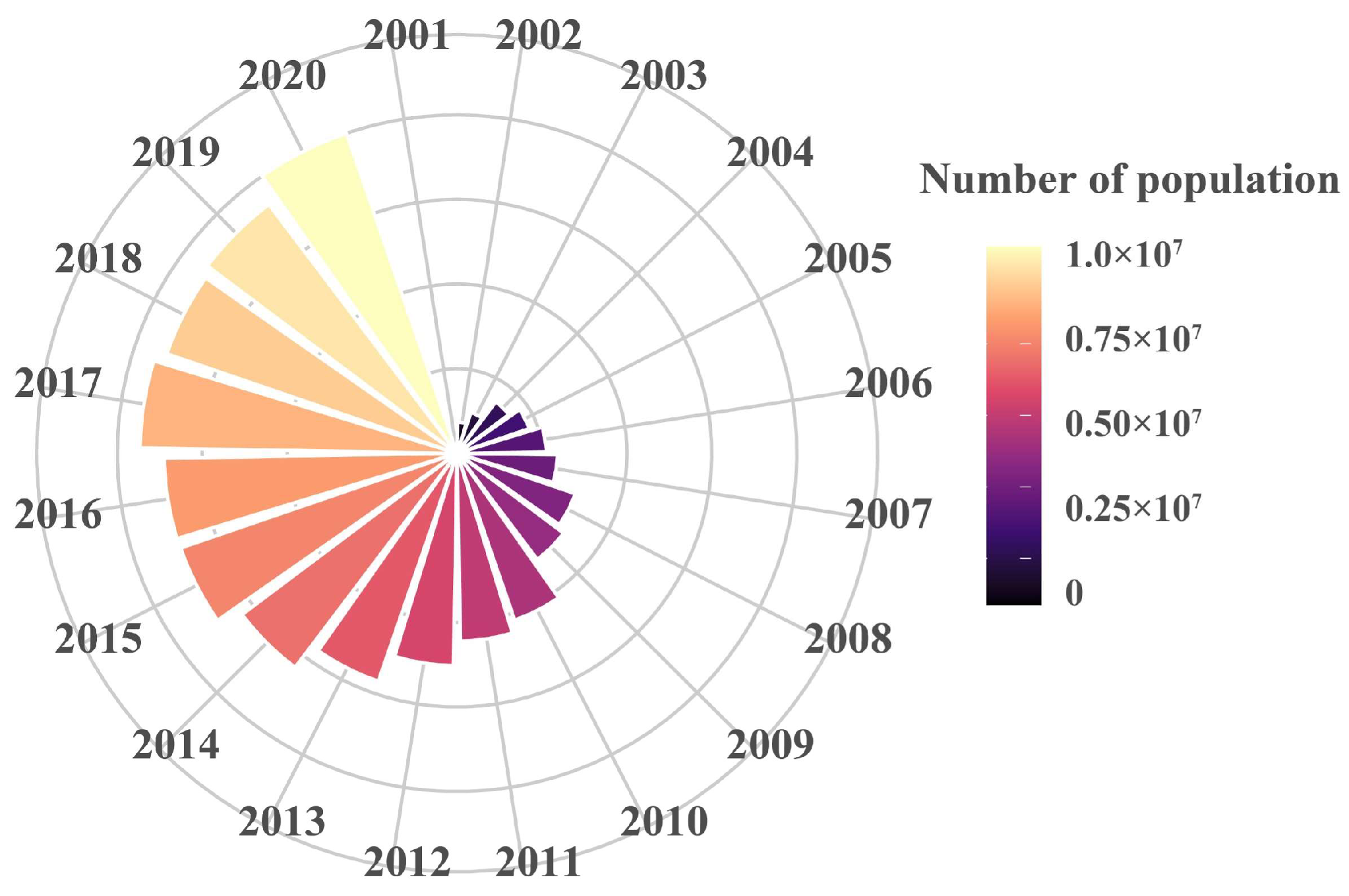
4.4.2. Impacts on per Capita Carrying Capacity
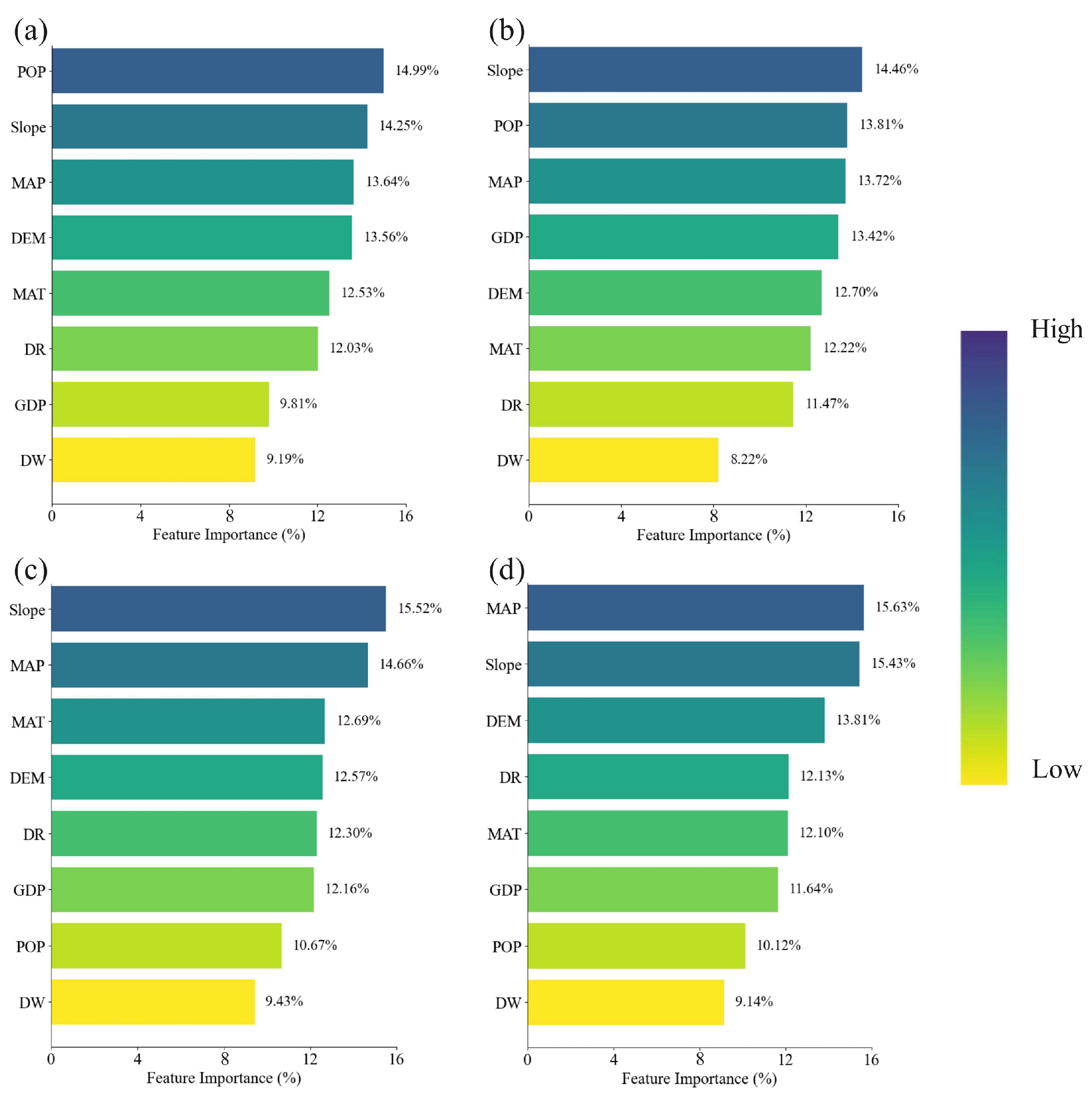
4.5. Driving Mechanisms of Cropland Abandonment
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Cropland Abandonment and Its Impacts on Grain Production
5.2. Policy Optimization Pathways for Agricultural Sustainability
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, H.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Dong, S.; Wang, X. Conflicts between ecological and agricultural production functions: The impact of the Grain for Green Program and wildlife damage on cropland abandonment in China’s mountainous areas. Land Use Policy 2025, 153, 107552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Xu, X. The spatial distribution of CA and its influential factors at the township level: A case study in the mountainous area of China. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, X.; Leng, J.; Xu, X.; Liao, W.; Qiu, Y.A.; Wu, Q. Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Yi, L.; Xu, J.; Hu, S.; Liu, B. Chinese cropland losses due to urban expansion in the past four decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juknelienė, D.; Narmontienė, V.; Valčiukienė, J.; Mozgeris, G. Driving Forces of Agricultural Land Abandonment: A Lithuanian Case. Land 2025, 14, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, H.; Tang, Z.; Chen, C.; Berry, J. How cropland losses shaped by unbalanced urbanization process? Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Yue, W.; Yang, J.; Xue, B.; Xiao, W.; Li, M.; He, T.; Zhang, M.; Jin, X.; Zhou, Q. Cropland abandonment in China: Patterns, drivers, and implications for food security. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Song, W. Abandoned cropland: Patterns and determinants within the Guangxi karst mountainous area, China. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 122, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, Z.; Guo, S.; Deng, X.; Song, J.; Xu, D. How does farmers’ differentiation affect CA from the perspective of land attachment and generational differences? Evidence from Sichuan Province, China. Environ. Dev. 2023, 48, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, X.; Xin, L.; Wang, X. Improving mechanization conditions or encouraging non-grain crop production? Strategies for mitigating CA in China’s mountainous areas. Land Use Policy 2025, 149, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Cao, G.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S. An estimation of the extent of cropland abandonment in mountainous regions of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Miao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, X. Address the challenge of cultivated land abandonment by cultivated land adoption: An evolutionary game perspective. Land Use Policy 2025, 149, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolecka, N. Height of successional vegetation indicates moment of agricultural land abandonment. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Kuemmerle, T.; Bleyhl, B.; Buchner, J.; Radeloff, V.C. Mapping agricultural land abandonment from spatial and temporal segmentation of Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Su, K.; Wang, Z.; Hou, M.; Li, X.; Lin, A.; Yang, Q. Patterns and drivers of terrace abandonment in China: Monitoring based on multi-source remote sensing data. Land Use Policy 2025, 148, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W. Mapping cropland abandonment in mountainous areas using an annual land-use trajectory approach. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Song, W. A land-use spatial optimum allocation model coupling a multi-agent system with the shuffled frog leaping algorithm. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 77, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prishchepov, A.V.; Radeloff, V.C.; Dubinin, M.; Alcantara, C. The effect of Landsat ETM/ETM+ image acquisition dates on the detection of agricultural land abandonment in Eastern Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 126, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yang, J. Cropland abandonment mapping at sub-pixel scales using crop phenological information and MODIS time-series images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löw, F.; Prishchepov, A.V.; Waldner, F.; Dubovyk, O.; Akramkhanov, A.; Biradar, C.; Lamers, J.P. Mapping cropland abandonment in the Aral Sea Basin with MODIS time series. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, D.; Guo, L. Mapping abandoned cropland in China using time series MODIS NDVI. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, W. Mapping abandoned cropland using Within-Year Sentinel-2 time series. Catena 2023, 223, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, L.T.; Timmermans, J.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; van Bodegom, P.M. Linking land use and plant functional diversity patterns in sabah, borneo, through large-scale spatially continuous sentinel-2 inference. Land 2022, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y. Integrating an abandoned cropland simulation model (AFSM) using system dynamics and CLUE-S for sustainable agriculture. Agric. Syst. 2024, 219, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; Buerkert, A.; Plieninger, T. Effects of land abandonment on nature contributions to people and good quality of life components in the Mediterranean region: A review. Land Use Policy 2022, 116, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, B.; Holden, S.T. Policy instruments for sustainable land management: The case of highland smallholders in Ethiopia. Agr. Econ.-Blackwell 2000, 22, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Kang, Q.; Li, F.; Li, L.; Qiao, H. What psychological factors lead to the abandonment of cultivated land by coastal farmers? An interpretation based on the psychological distance. J. Risk Res. 2023, 26, 947–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, W.; Yue, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. The potential role of abandoned cropland for food security in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, A.; Yang, Q. The extent, drivers and production loss of CA in China: Evidence from a spatiotemporal analysis of farm households survey. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, L.; Yao, A.; Chen, Z.; Feng, H.; Wu, S.; Siddique, K.H. Abandoned terrace recognition based on deep learning and change detection on the Loess Plateau in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Understanding the impacts of ‘Grain for Green’land management practice on land greening dynamics over the Loess Plateau of China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.; Sweeney, S. Changes in soil carbon and nitrogen following land abandonment of cropland on the Loess Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, W. Mapping abandoned cropland changes in the hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau in China. Land 2021, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Gu, P.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Xin, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Understanding the spatial distribution patterns and dominant determinants of CA in China. Habitat Int. 2025, 156, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Can agricultural machinery harvesting services reduce cropland abandonment? Evidence from rural China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hou, X.; Guo, Q.; Yue, Y.; Wu, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Fan, X. Switchgrass establishment can ameliorate soil properties of the abandoned cropland in northern China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, W.; Jia, Y.; Wang, N. Assessing the Ecological Success of Restoration by Afforestation on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Restor. Ecol. 2012, 20, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Quine, T.A.; Yu, H.Q.; Govers, G.; Six, J.; Gong, D.Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Van Oost, K. Sustained high magnitude erosional forcing generates an organic carbon sink: Test and implications in the Loess Plateau, China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 411, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Anomaly detection using causal sliding windows. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3260–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulanuwat, L.; Chantrapornchai, C.; Maleewong, M.; Wongchaisuwat, P.; Wimala, S.; Sarinnapakorn, K.; Boonya-Aroonnet, S. Anomaly detection using a sliding window technique and data imputation with machine learning for hydrological time series. Water 2021, 13, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, G.; He, T.; Zhai, G.; Guo, A.; Chen, H.; Wu, C. Reveal the severe spatial and temporal patterns of abandoned cropland in China over the past 30 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.H.; Chen, F.; Yang, B.; Jiang, F.; Ma, J.; Zhu, X. Identification of spatial relationship and imbalance attribution between cropland supplementation and abandonment in China. China Land Sci. 2024, 38, 120–132. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Huang, G.; Tian, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, F. Delineating and identifying risk zones of soil heavy metal pollution in an industrialized region using machine learning. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Qian, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Su, F.; Ma, H.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, T. Water conservation assessment and its influencing factors identification using the InVEST and random forest model in the northern piedmont of the Qinling Mountains. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Cao, W.; Cai, Y. Carbon potential of China’s Grain to Green Program and its contribution to the carbon target. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 200, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Qiao, J. The role of multi-category subsidies in cultivated land transfer decision-making of rural households in China: Synergy or trade-off? Appl. Geogr. 2023, 160, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pei, B. Spatial-temporal variations of cultivated land compensation and its compensation mechanism in mainland China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 110, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zeng, T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Jin, S. Rural transformation in the hilly and mountainous region of southern China: Livelihood trajectory and cross-scale effects. Habitat Int. 2024, 144, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Ma, L.; Chen, Z. Assessing sustainable transformation and development strategies for gully agricultural production: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jin, S.; Su, L. Of nothing comes nothing: The impact of agricultural comparative return on cropland abandonment. J. Rural. Stud. 2025, 119, 103759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Type | Variant | Years | Description | Spatial Resolution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land-Use Type | LUCC | 2000–2023 | For Identifying Cropland Abandonment | 30 m | https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-13-3907-2021 [39] |
| Crop production | NDVI | 2001–2022 | For Crop Growth Analysis | 1000 m | https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 11 September 2025 |
| Physical geographic factors | Elevation | 2020 | Elevation value of each raster cell | 250 m | https://www.gscloud.cn/, accessed on 11 September 2025 |
| Slope | 2020 | Slope value of each raster cell | 250 m | ||
| Precipitation | 2005/2010/2015/2020 | Precipitation of each raster cell | 1000 m | https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 11 September 2025 | |
| Temperature | 2005/2010/2015/2020 | Temperature of each raster cell | 1000 m | ||
| Socio-economic factors | Population density | 2005/2010/2015/2020 | Population density of each raster cell | 1000 m | https://earthengine.google.com/, accessed on 11 September 2025 |
| GDP | 2005/2010/2015/2020 | GDP of each raster cell | 1000 m | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 11 September 2025 | |
| Accessibility factors | County roads | 2005/2010/2015/2020 | Distance from each raster cell center to the nearest county road | 1000 m | |
| River | Distance from the river | 1000 m | https://www.openstreetmap.org/, accessed on 11 September 2025 |
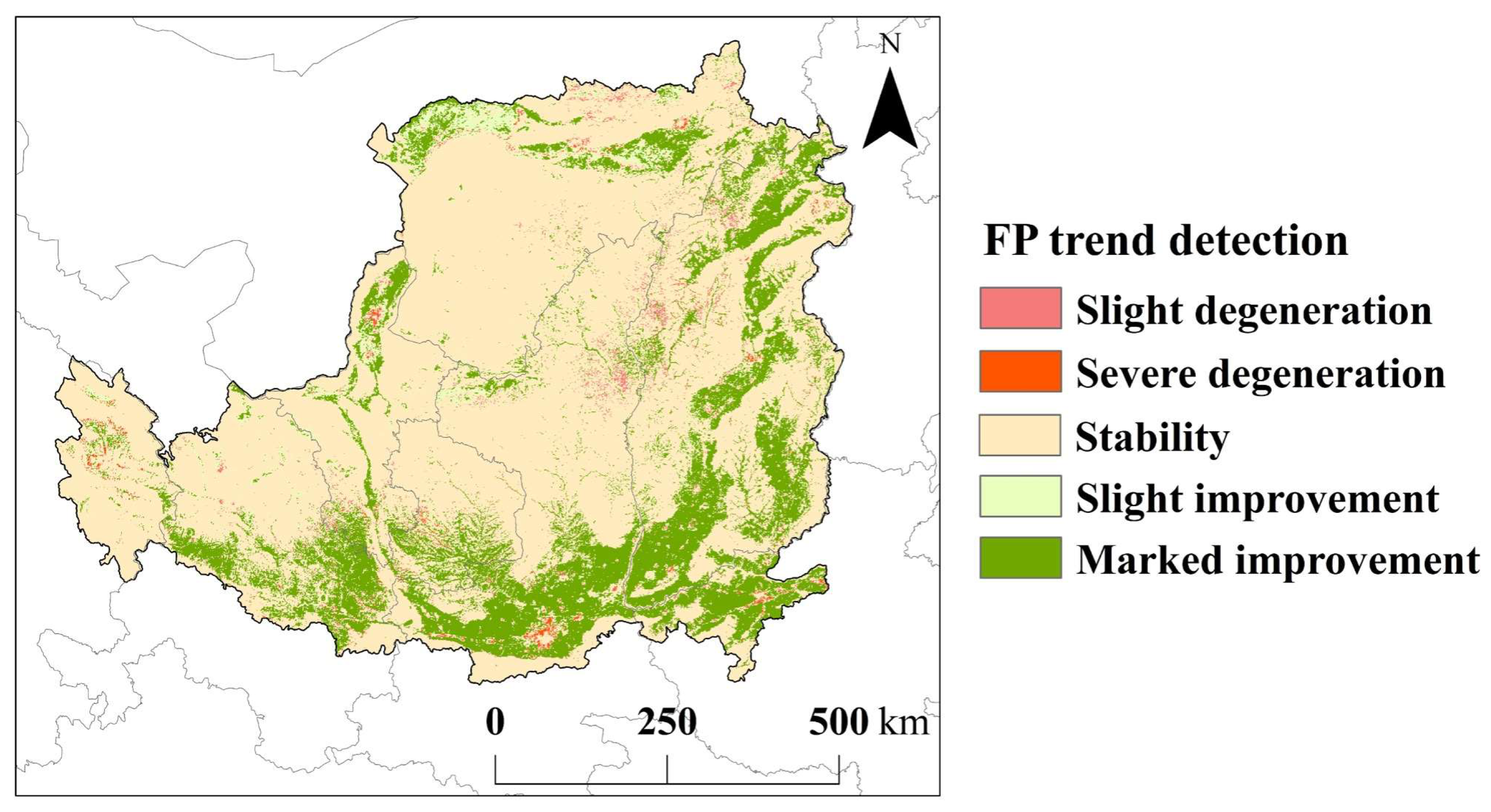
| SFP | ZS | FP Trend | Area Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marked improvement | 21.14% | ||
| −1.96–1.96 | Slight improvement | 4% | |
| −1.96–1.96 | Stability | 72.78% | |
| −1.96–1.96 | Slight degeneration | 1.55% | |
| Severe degradation | 0.52% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W. Innovative Multi-Type Identification System for Cropland Abandonment on the Loess Plateau: Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Driver Shifts (2000–2023) and Implications for Food Security. Land 2025, 14, 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102062
Song W. Innovative Multi-Type Identification System for Cropland Abandonment on the Loess Plateau: Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Driver Shifts (2000–2023) and Implications for Food Security. Land. 2025; 14(10):2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102062
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Wei. 2025. "Innovative Multi-Type Identification System for Cropland Abandonment on the Loess Plateau: Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Driver Shifts (2000–2023) and Implications for Food Security" Land 14, no. 10: 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102062
APA StyleSong, W. (2025). Innovative Multi-Type Identification System for Cropland Abandonment on the Loess Plateau: Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Driver Shifts (2000–2023) and Implications for Food Security. Land, 14(10), 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14102062






