Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in Image Perception of High-Quality Tourism Destinations in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
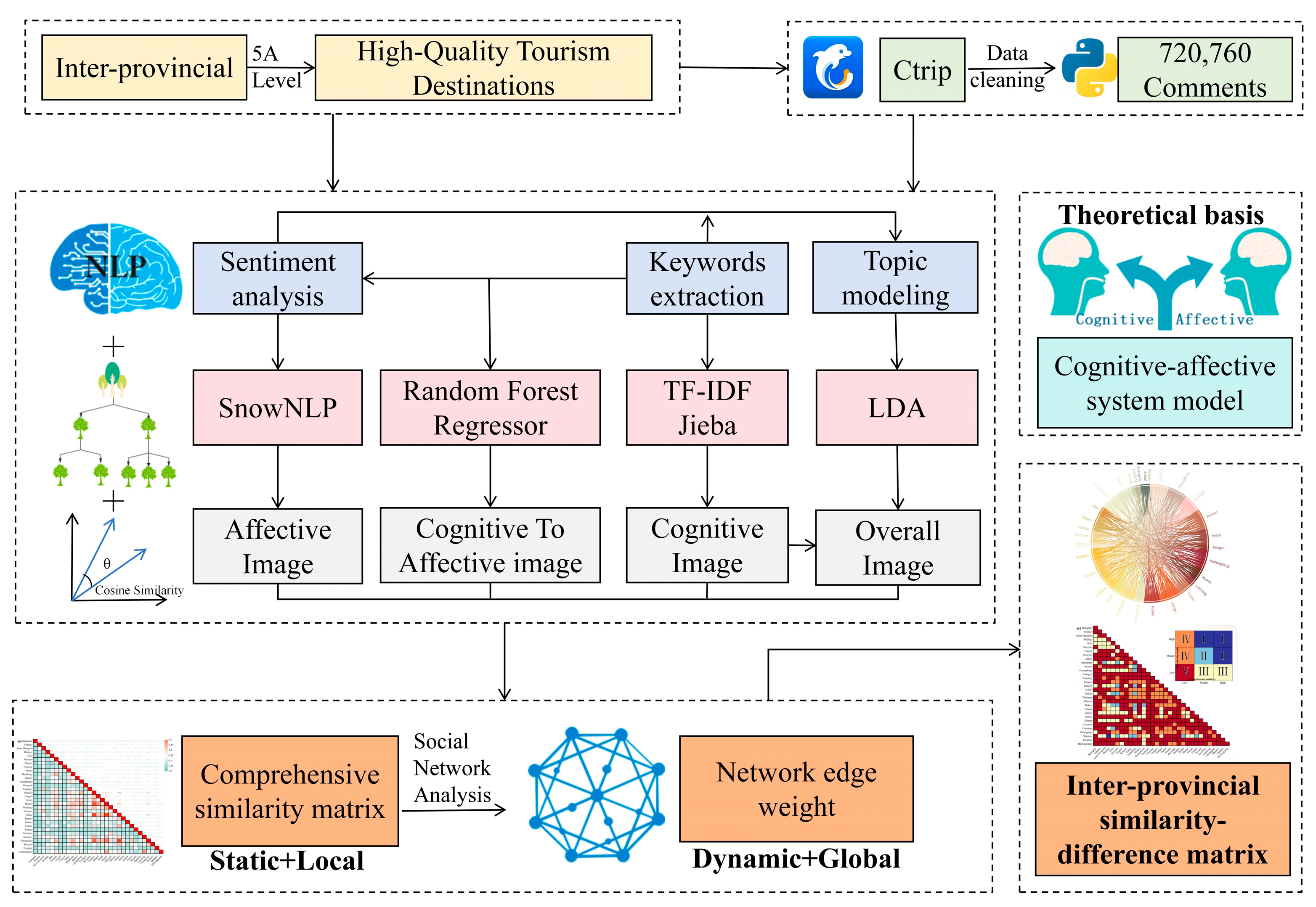
2.1. Research Framework
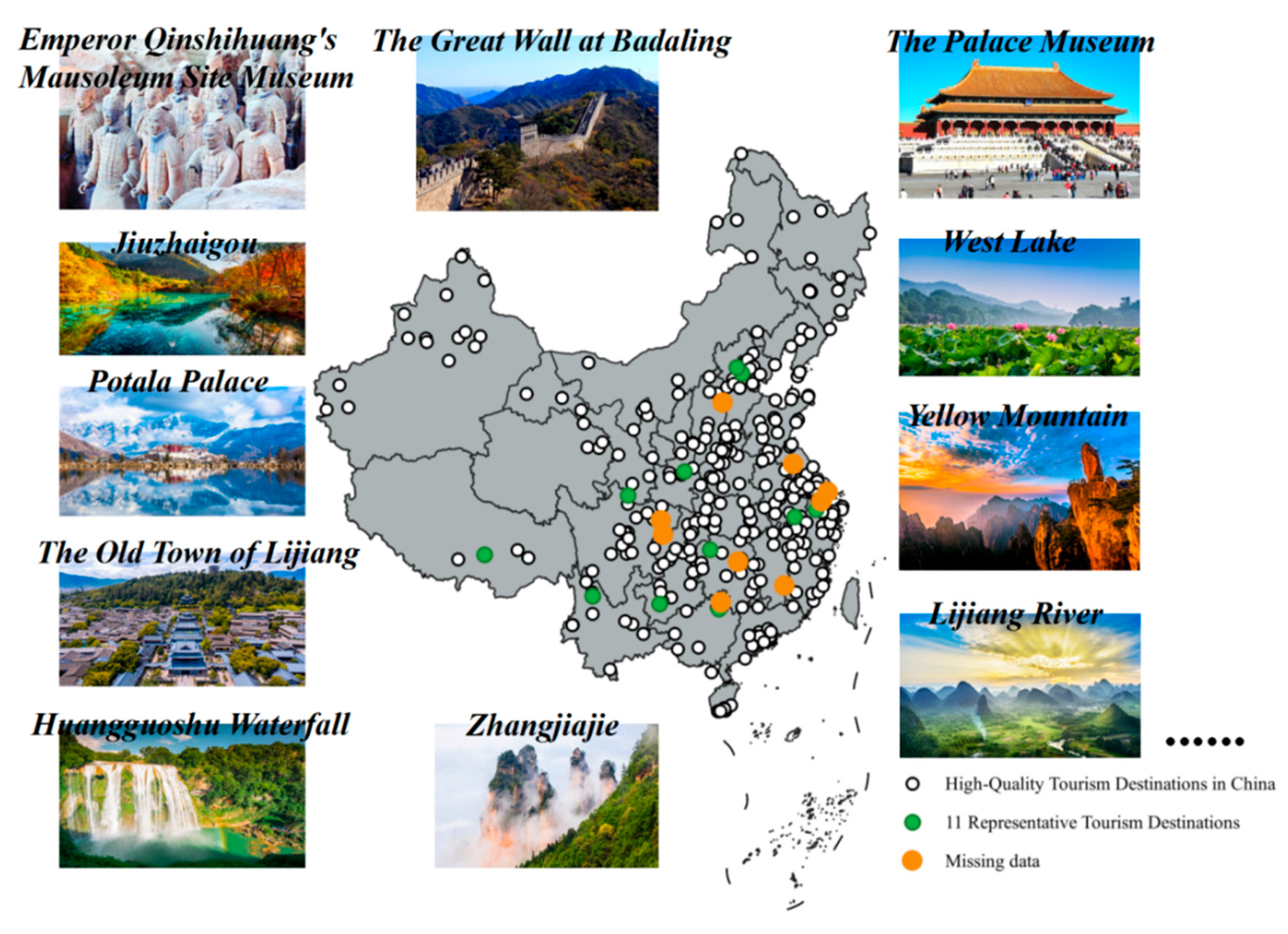
2.2. Data
2.3. Natural Language Processing
2.3.1. Sentiment Analysis
2.3.2. Keyword Extraction
2.3.3. Topic Modeling
2.4. Random Forest Regression
2.5. Cosine Similarity
2.6. A Network Analysis of Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in High-Quality Tourism Destinations
3. Results
3.1. Affective Image Analysis
3.2. Cognitive Image Analysis
3.3. Overall Image Analysis
3.4. Analysis of the Relationship Between Cognitive and Affective Image
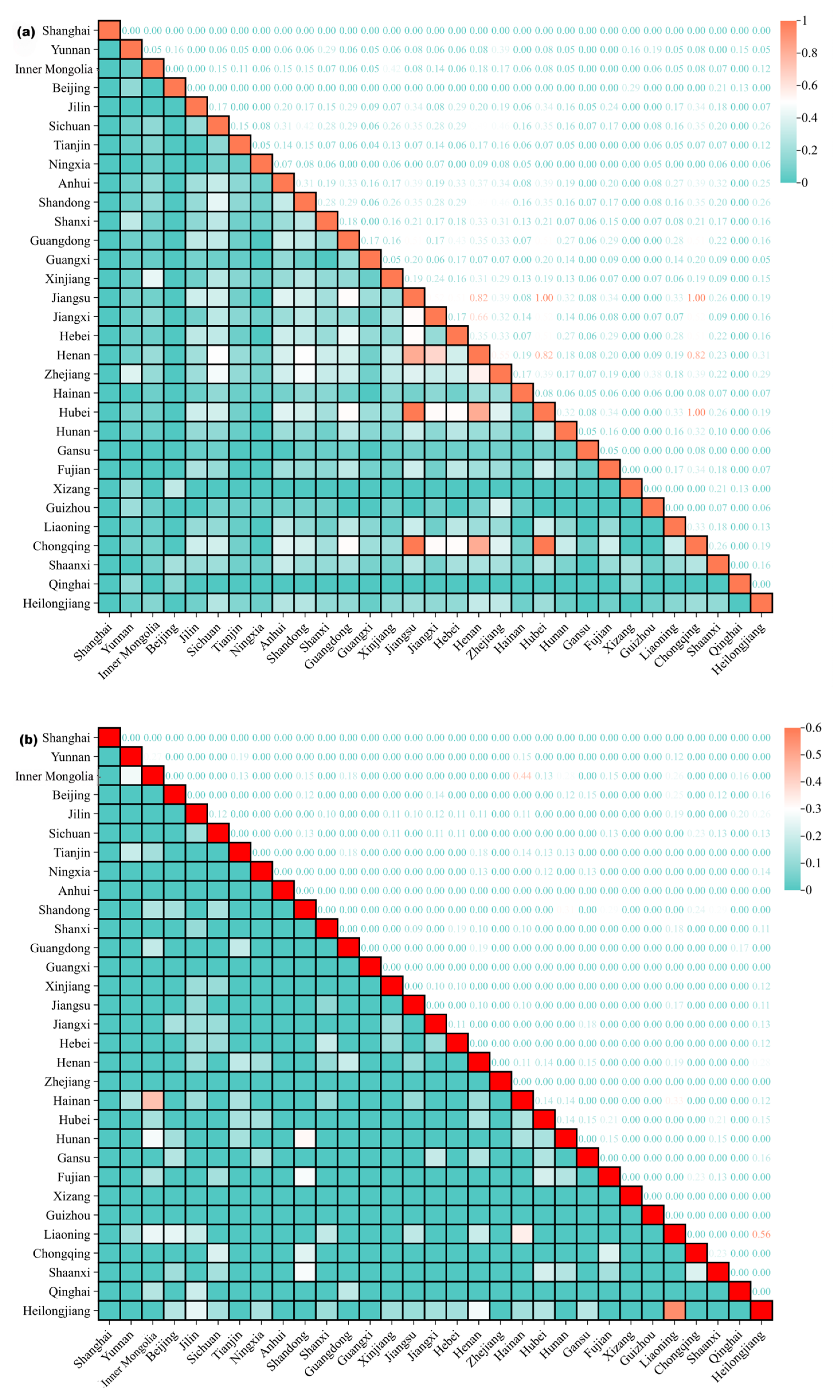
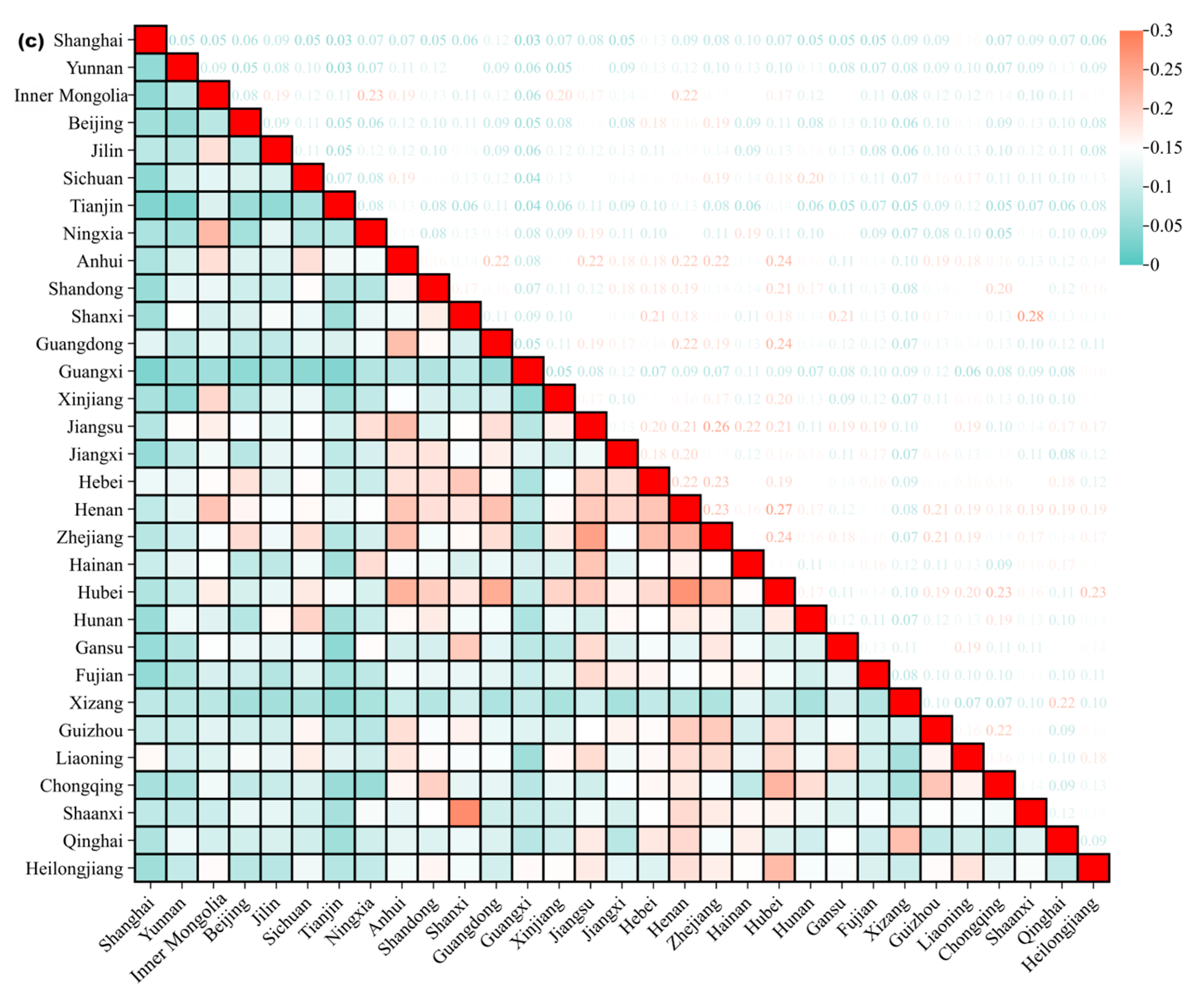
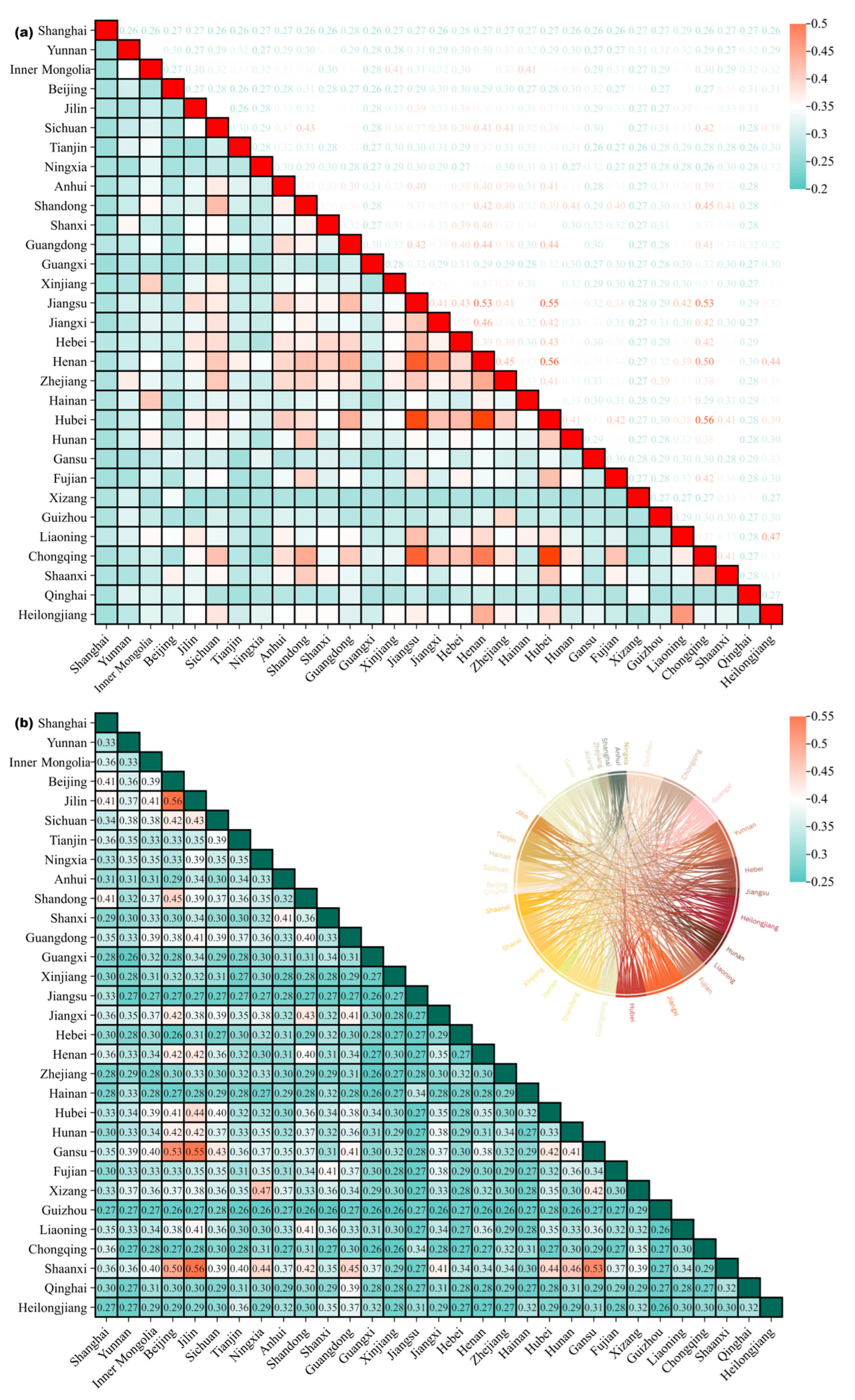
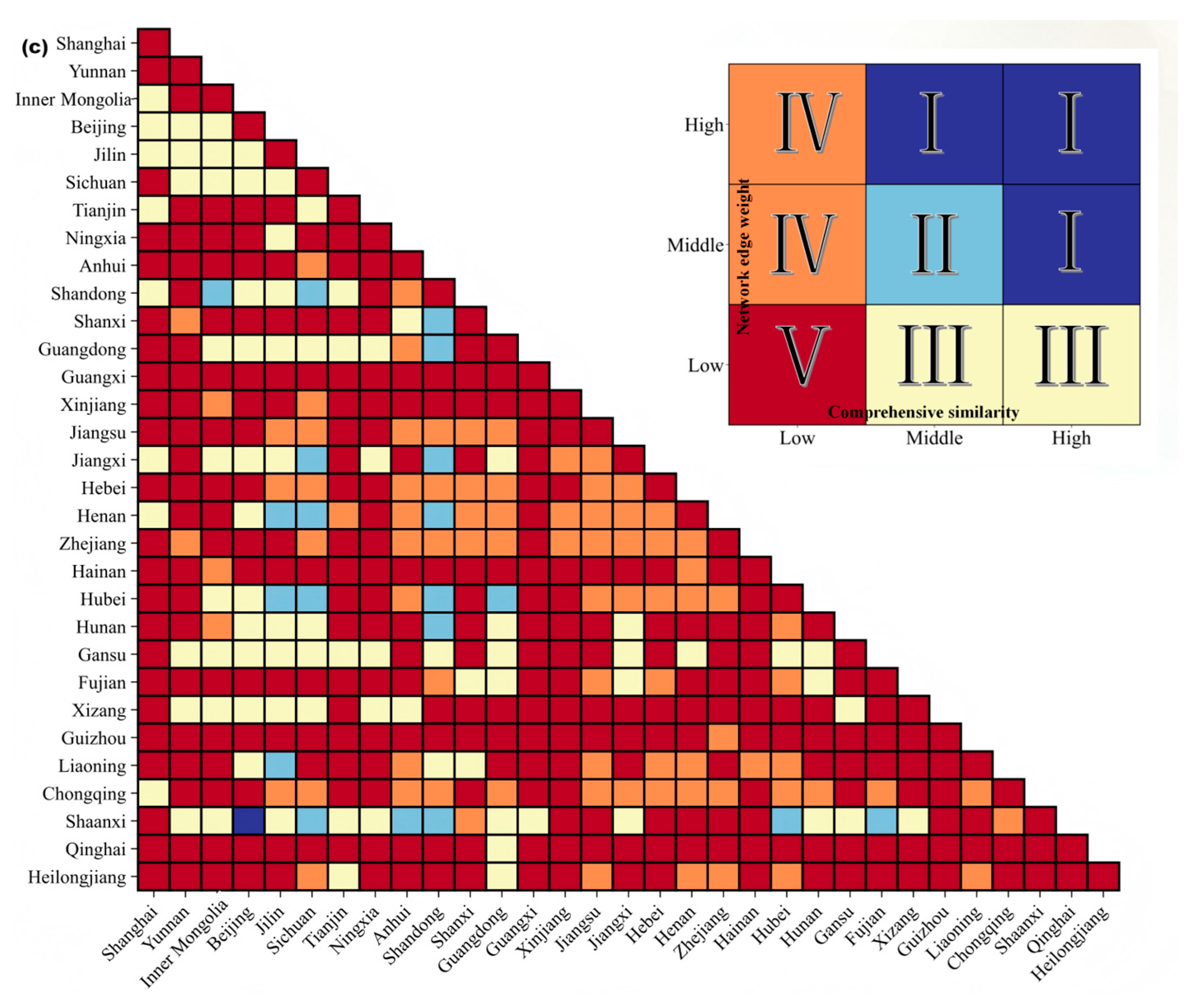
3.5. Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in High-Quality Tourism Destinations
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpreting the Patterns of High-Quality Tourism Destination Images: Homogeneity in Diversity
4.2. Deconstructing the Cognitive–Affective Linkage: Insights from Machine Learning
4.3. Implications for Tourism Image Theory
5. Recommendations for Inter-Provincial Tourism Management and Development Under the Similarity–Difference Matrix
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations and Further Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, H.; Zou, J. Impacts of Official High-Standard Scenic Spots on Environment and Growth—Evidence from China’s 5A Scenic Spots at the City Level. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 201, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, H. Does the Selection of High-Quality Scenic Spots Promote the Growth of Tourism Economy? Evidence from China’s 5A-Rated Tourist Attractions. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Duan, Y.; Wu, X. Evaluation of the Coupling and Coordination Degree of Eco-Cultural Tourism System in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang-Shanghai-Anhui Region. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S. Roles and Functions of Tourism Destinations in Tourism Region of South Anhui: A Tourist Flow Network Perspective. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Di, Q.; Liu, Y. Perceived Differences in Coastal Tourism Image under Tourist Experience-IPA Analysis Based on UGC Data of 12 Coastal Cities. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Gong, P. Unveiling Interprovincial Geographic Patterns of 5A-Level Tourism Cultural Ecosystem Service Flows and Tourist Preferences in China’s Metacoupled Systems. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 172, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wen, X.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Zhu, M. TriPlan: An Interactive Visual Analytics Approach for Better Tourism Route Planning. J. Vis. 2023, 26, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Cao, F.; Jin, C.; Yu, Z.; Huang, R. Carbon Emission Flow from Self-Driving Tours and Its Spatial Relationship with Scenic Spots—A Traffic-Related Big Data Method. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Cui, F.; Meng, Y.; Lian, T.; Yu, C. Opinion Mining from Online Travel Reviews: A Comparative Analysis of Chinese Major OTAs Using Semantic Association Analysis. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloglu, S.; McCleary, K.W. A Model of Destination Image Formation. Ann. Tour. Res. 1999, 26, 868–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, X.; Zhou, Y. A Comparative Study of Relative Roles and Sequences of Cognitive and Affective Attitudes on Tourists’ pro-Environmental Behavioral Intention. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinejad, A.; Gardiner, S.; Kralj, A.; Scott, N.; Moyle, B.D. Cognition, Metacognition and Attitude to Tourism Destinations: The Impact of Emotional Arousal and Source Credibility. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2022, 51, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghermandi, A.; Sinclair, M. Passive Crowdsourcing of Social Media in Environmental Research: A Systematic Map. Glob. Environ. Change 2019, 55, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Carmona, M.Á.; Aranda, R.; Rodríguez-Gonzalez, A.Y.; Fajardo-Delgado, D.; Sánchez, M.G.; Pérez-Espinosa, H.; Martínez-Miranda, J.; Guerrero-Rodríguez, R.; Bustio-Martínez, L.; Díaz-Pacheco, Á. Natural Language Processing Applied to Tourism Research: A Systematic Review and Future Research Directions. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 10125–10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles Da Mota, V.; Pickering, C. Using Social Media to Assess Nature-Based Tourism: Current Research and Future Trends. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2020, 30, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confente, I.; Mazzoli, V.; Camatti, N.; Bertocchi, D. Integrating Tourists’ Walk and Talk: A Methodological Approach for Tracking and Analysing Tourists’ Real Behaviours for More Sustainable Destinations. J. Sustain. Tour. 2024, 32, 2323–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ctrip.com. Available online: https://www.ctrip.com/ (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, B.; Peng, S.; Li, K.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of Cultural Landscape Service Features in National Forest Parks on Visitors’ Sentiments: A Nationwide Social Media-Based Analysis in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 67, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Y. Sensing Tourist Distributions and Their Sentiment Variations Using Social Media: Evidence from 5A Scenic Areas in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Jia, G. Systematic Investigation of Keywords Selection and Processing Strategy on Search Engine Forecasting: A Case of Tourist Volume in Beijing. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2022, 24, 547–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taecharungroj, V.; Mathayomchan, B. Traveller-generated Destination Image: Analysing Flickr Photos of 193 Countries Worldwide. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 23, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canoy, N.A.; Roxas, G.K.T.; Robles, A.M.Q.; Alingasa, A.P.T.; Ceperiano, A.M. From Cesspool to Fortified Paradise: Analyzing News Media Territorial Assemblages of Rehabilitating Boracay Island, Western Philippines. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 1138–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grömping, U. Variable Importance Assessment in Regression: Linear Regression versus Random Forest. Am. Stat. 2009, 63, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, H.; Fang, S.; Chen, W. Predicting the Success of Internet Social Welfare Crowdfunding Based on Text Information. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsudais, A.; Alotaibi, W.; Alomary, F. Similarities between Arabic Dialects: Investigating Geographical Proximity. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wei, Y.D.; Wang, T. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Urban Innovation Network in China. Habitat Int. 2015, 49, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Gao, C. Comparative Study on Tourism Image Perception Between Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and Yangtze River Delta Agglomerations. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 194–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Ma, Y.; Ren, J. Influencing Factors and Mechanism of Tourists’ pro-Environmental Behavior—Empirical Analysis of the CAC-MOA Integration Model. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1060404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wei, D.; Qiu, Y.; Xinyuan, L.; Zhang, T. Strategies for Enhancing Tourism Efficiency in Guizhou, China: Based on Spatiotemporal Dynamic Analysis and Driving Force Decomposition. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, D. The Dynamic Analysis and Evaluation on Tourist Ecological Footprint of City: Take Shanghai as an Instance. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, N.; Yuan, R.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Makkonen, T. Exploring Spatio-Temporal Changes of City Inbound Tourism Flow: The Case of Shanghai, China. Tour. Manag. 2020, 76, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, N. Effects of Destination Resource Combination on Tourist Perceived Value: In the Context of Chinese Ancient Towns. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 40, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Social Inequality among Elderly Individuals Caused by Climate Change: Evidence from the Migratory Elderly of Mainland China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, E.; Liu, J. The Influence of High-Speed Rail on Ice–Snow Tourism in Northeastern China. Tour. Manag. 2020, 78, 104070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Yu, J.-G. Sustaining Sporting Destinations through Improving Tourists’ Mental and Physical Health in the Tourism Environment: The Case of Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, J.; Olya, H.G. Canal Boat Tourism: Application of Complexity Theory. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 53, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosnam, K.M.; Stylidis, D.; Ivkov, M. Explaining Conative Destination Image through Cognitive and Affective Destination Image and Emotional Solidarity with Residents. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozili, P.K. The Acceptable R-Square in Empirical Modelling for Social Science Research. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, M.; Rao, A.C.S.; Kulkarni, C. A Survey on Sentiment Analysis Methods, Applications, and Challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5731–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeboah, R.; Ashie, D. Promotion of Local Food as Tourism Product in the Cape Coast Metropolis: An Explorative Research. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhong, H. Study on Forming Factors and Affecting Paths of Tourist Crowding Events. Hum. Geogr. 2021, 36, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, M. Holiday Travel Behavior Analysis and Empirical Study with Integrated Travel Reservation Information Usage. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2020, 134, 130–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Cao, X.; Ge, H.; Liu, Y. How Does National Image Affect Tourists’ Civilized Tourism Behavior? The Mediating Role of Psychological Ownership. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 47, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, L.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Nader, M.; Sianes, A.; Law, R. Exploring Preferences and Sustainable Attitudes of Airbnb Green Users in the Review Comments and Ratings: A Text Mining Approach. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 1134–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, C.; Surdeanu, M.; Bauer, J.; Finkel, J.; Bethard, S.; McClosky, D. The Stanford CoreNLP Natural Language Processing Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Baltimore, Maryland, 23–24 June 2014; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Nayak, J.K. Do Tourists’ Emotional Experiences Influence Images and Intentions in Yoga Tourism? Tour. Rev. 2019, 74, 646–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Province | Number of Positive Comments | Percentage of Positive Comments | Number of Neutral Comments | Percentage of Neutral Comments | Number of Negative Comments | Percentage of Negative Comments | Average Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | 7036 | 85.06% | 487 | 5.89% | 749 | 9.05% | 0.875 |
| Yunnan | 19,496 | 73.26% | 2929 | 11.01% | 4186 | 15.73% | 0.779 |
| Inner Mongolia | 8153 | 74.25% | 1369 | 12.47% | 1458 | 13.28% | 0.793 |
| Beijing | 20,594 | 84.57% | 1737 | 7.13% | 2020 | 8.30% | 0.874 |
| Jilin | 10,357 | 79.14% | 1423 | 10.87% | 1307 | 9.99% | 0.832 |
| Sichuan | 28,063 | 77.54% | 3705 | 10.24% | 4422 | 12.22% | 0.817 |
| Tianjin | 4305 | 74.33% | 834 | 14.40% | 653 | 11.27% | 0.800 |
| Ningxia | 9469 | 84.79% | 925 | 8.28% | 773 | 6.92% | 0.878 |
| Anhui | 19,886 | 77.91% | 2971 | 11.64% | 2666 | 10.45% | 0.825 |
| Shandong | 24,392 | 75.12% | 3526 | 10.86% | 4552 | 14.02% | 0.794 |
| Shanxi | 16,281 | 72.55% | 2639 | 11.76% | 3522 | 15.69% | 0.773 |
| Guangdong | 20,625 | 77.26% | 3359 | 12.58% | 2713 | 10.16% | 0.820 |
| Guangxi | 13,870 | 74.42% | 2013 | 10.80% | 2754 | 14.78% | 0.789 |
| Xinjiang | 18,461 | 75.93% | 2991 | 12.30% | 2861 | 11.77% | 0.809 |
| Jiangsu | 54,578 | 80.53% | 6843 | 10.10% | 6356 | 9.38% | 0.845 |
| Jiangxi | 17,213 | 73.57% | 2679 | 11.45% | 3506 | 14.98% | 0.781 |
| Hebei | 12,287 | 74.16% | 2118 | 12.78% | 2164 | 13.06% | 0.793 |
| Henan | 26,669 | 80.31% | 3155 | 9.50% | 3382 | 10.18% | 0.840 |
| Zhejiang | 39,253 | 80.10% | 4771 | 9.74% | 4983 | 10.17% | 0.839 |
| Hainan | 17,175 | 84.96% | 1526 | 7.55% | 1514 | 7.49% | 0.877 |
| Hubei | 30,636 | 75.55% | 5089 | 12.55% | 4826 | 11.90% | 0.805 |
| Hunan | 20,638 | 76.92% | 3021 | 11.26% | 3171 | 11.82% | 0.814 |
| Gansu | 9757 | 77.09% | 1293 | 10.22% | 1607 | 12.70% | 0.813 |
| Fujian | 15,210 | 76.49% | 2297 | 11.55% | 2377 | 11.95% | 0.811 |
| Xizang | 8998 | 81.62% | 1009 | 9.15% | 1017 | 9.23% | 0.851 |
| Guizhou | 12,628 | 68.16% | 2334 | 12.60% | 3564 | 19.24% | 0.735 |
| Liaoning | 12,900 | 80.04% | 1669 | 10.36% | 1548 | 9.60% | 0.839 |
| Chongqing | 14,350 | 71.97% | 2847 | 14.28% | 2741 | 13.75% | 0.777 |
| Shaanxi | 28,325 | 77.79% | 3537 | 9.71% | 4550 | 12.50% | 0.818 |
| Qinghai | 5029 | 81.06% | 587 | 9.46% | 588 | 9.48% | 0.848 |
| Heilongjiang | 5469 | 71.07% | 1159 | 15.06% | 1067 | 13.87% | 0.772 |
| Province | Theme 1 Label | Theme 2 Label | Theme 3 Label | Theme 4 Label | Theme 5 Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | Wild Animals | Landmarks/The Bund/Lujiazui | Shanghai | Education/Science Popularization/China | Night View/Hours |
| Yunnan | Cable Car | Eastern District | Hot Springs | Scenic Area/Nature | |
| Inner Mongolia | Erdao Bridge/Most Beautiful/Places | Recommendation | Time | Scenery | |
| Beijing | Heshen | China/Beijing | Scenic Area/Convenience/Beijing | Tickets/Places/Attractions | Ancient China/Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests |
| Jilin | Children | Scenery/Changchun | Commentary/Places | West Slope/World/Attractions | |
| Sichuan | World Heritage | Jiuzhaigou | Scenery/Attractions/Pandas | Snow Mountain/Guangwu | Commentary |
| Tianjin | Clay Figurine Zhang | Clay Figurine Zhang | Scenery/Scenic Area/Jixian | Children/Hiking/Cost-Effectiveness | |
| Ningxia | Scenery/Service | Tickets | Experience/Heritage Site | Filming/Scenes/Zhenbeibao | |
| Anhui | Scenic Area/Hours/Descent | Bodhisattva/Tiantai | Ancient Villages/Huizhou/Nanhu | Recommendation/Places | |
| Shandong | Cable Car/Ropeway/Hours | Recommendation/Attractions/Liugong Island | Convenience/Qingdao/Evening | Confucius Mansion | Tickets |
| Shanxi | Buddha Statues | Shanxi/Architecture | Places | Queuing/Mianshan | Hukou Waterfall |
| Guangdong | Places/West Lake | Children | Time | Xiqiao Mountain/Huizhou | Environment/Stone Towers/Scenery |
| Guangxi | Scenery/Cross-Border/Scenery | Bamboo Raft/Landscape/Dock | Lijiang River/Night Tour/Duxiu Peak | Culture/Experience/History | Scenery/Tickets |
| Xinjiang | Scenery/Grand Canyon/Keketuohai | Scenery | Tianshan/Bayanbulak | Clear/Lakes | Time/Shuttle Bus |
| Jiangsu | Tickets | Giant Buddha/Places | Linggu/Meiling Palace/Nanjing | Suzhou/Yuantouzhu | Jinshan/Confucius Temple |
| Jiangxi | Convenience | World/Lushan/Scenery | China/Jiangnan | Mountain Climbing/Sanqingshan/Attractions | |
| Hebei | Cable Car/Scenery | Scenery | Underground Palace/Mausoleum | Architecture/Summer Resort/Ancient City | |
| Henan | Shaolin | Grand Canyon/Taihang | Tickets | Children/Places/Attractions | Shows/Evening |
| Zhejiang | Tickets | Ningbo/Yandang Mountain/Hometown | Hangzhou | Water Town/Scenic Area/Jiangnan Water Town | Qiandao Lake |
| Hainan | Sanya | Scenery | Sanya | Small Cave/Places | |
| Hubei | Convenience/Fun/Recommendation | Park/Chibi | Tickets | Scenery/Suitable/Places | People/Dam/Scenery |
| Hunan | Glass/Mountain/Boardwalk | Convenience | Like/Recommendation | Scenery/Chairman Mao/Places | Night View |
| Gansu | Convenience | Dunhuang/Tickets | Kongtong Mountain/China | Desert/First Pass Under Heaven/Fortress | |
| Fujian | Gulangyu/Wuyi Mountain | Attractions/Mazu | Rafting | Recommendation/Suitable/Fun | |
| Xizang | Devotion | Linzi/Tibet | Monasteries/Tibetan Buddhism | Lake | Time |
| Guizhou | Attractions | Guizhou/Characteristics | Mountain Climbing/Weather | Guizhou/Magnificent | Time/Tianxingqiao/Hours |
| Liaoning | Convenience/Animals | Places/Scenic Area | Scenic Area | Places | |
| Chongqing | Places | Attractions/Tourists | Chongqing/Attractions/Wulong | Waterfall/Baidicheng | Art/Grottoes/Beishan |
| Shaanxi | Mountain/Cable Car | Convenience/Attractions | Park/Bicycle/Lishan | Experience/Famen Temple/Architecture | Recommendation |
| Qinghai | Saltwater Lakes/Beautiful | Commentary | Temple/Gelugpa | Driver/Time | Niuxin Mountain/Faith |
| Heilongjiang | Ice and Snow/Songhua River | Tickets | 5A | Places | Scenic Area/Scenery/Magnificent |
| Shanghai | Queuing | Too Many People | Ctrip | 160 | Buy Tickets | Oriental Pearl Tower | Go Up | ID Card | Animals | Science and Technology Museum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yunnan | Lijiang | Ancient Town | Scenic Area | Inn | Ancient Town | Scenery | Eggs | Tickets | Hot Springs | Electric Cart |
| Inner Mongolia | Package Tickets | Scenic Area | Queuing | Scenery | Grassland | Ctrip | Collect Tickets | Attractions | Not Bad | Tickets |
| Beijing | ID Card | 877 | Ctrip | Great Wall | Queuing | Tour Guide | Buy Tickets | Cable Car | Echo Wall | 20 |
| Jilin | Ctrip | Queuing | Buy Tickets | Tickets | Book Tickets | Scenic Area | Tianchi | Not Bad | Changchun Film Studio | Scenery |
| Sichuan | Scenic Area | Collect Tickets | ID Card | Queuing | Ctrip | Scenery | Attractions | Cable Car | Dujiangyan | Tickets |
| Tianjin | Jianbing Guozi | Scenic Area | Not Bad | Scenery | Ancient Culture | Tianjin | 60 | Panshan | Queuing | Ear Hole Fried Cake |
| Ningxia | Scenic Area | Ctrip | Package Tickets | Tickets | Journey to the West | Shapotou | Queuing | QR Code | Play | Desert |
| Anhui | Collect Tickets | Scenic Area | Tickets | Ctrip | Not Bad | Scenery | Hongcun | Attractions | Cable Car | Huangshan |
| Shandong | Scenic Area | Not Bad | Queuing | 10 | Scenery | Penglai Pavilion | Attractions | Rafting | Tickets | Buy Tickets |
| Shanxi | Pingyao | Hukou Waterfall | Scenic Area | Ancient Town | Waterfall | Collect Tickets | Not Bad | Ctrip | Attractions | Tickets |
| Guangdong | Not Bad | Scenery | Queuing | Tickets | Scenic Area | Fees | Collect Tickets | Attractions | Ctrip | Buy Tickets |
| Guangxi | Lijiang River | Guilin | Elephant Trunk Hill | Scenic Area | Collect Tickets | Ctrip | Scenery | Waterfall | Bamboo Raft | Duxiu Peak |
| Xinjiang | Scenic Area | Shuttle Bus | Scenery | Queuing | Grassland | Collect Tickets | Attractions | Ctrip | Tickets | Too Hot |
| Jiangsu | ID Card | Scenic Area | Ctrip | Attractions | Queuing | Ancient Town | Collect Tickets | Tickets | Not Bad | Scenery |
| Jiangxi | Tengwang Pavilion | Queuing | Collect Tickets | Scenic Area | Scenery | Cable Car | ID Card | Not Bad | Ctrip | Attractions |
| Hebei | Scenery | Scenic Area | Not Bad | Ctrip | 10 | Buy Tickets | Attractions | Tickets | First Pass Under Heaven | Collect Tickets |
| Henan | Scenic Area | Collect Tickets | Attractions | Ctrip | Queuing | Cable Car | Tickets | Not Bad | Scenery | Parking Lot |
| Zhejiang | Scenic Area | ID Card | Tickets | Ctrip | Attractions | Collect Tickets | Ancient Town | Not Bad | West Lake | 10 |
| Hainan | Scenic Area | Ctrip | Electric Cart | Attractions | Queuing | Collect Tickets | Small Cave | Book Tickets | Wuzhizhou Island | Tour Bus |
| Hubei | Scenic Area | Not Bad | Scenery | Attractions | Collect Tickets | Waterfall | Ctrip | ID Card | Tickets | Tourists |
| Hunan | Queuing | Collect Tickets | Scenic Area | Yueyang Tower | Not Bad | Orange Island | Scenery | Attractions | Ctrip | Tianmen Mountain |
| Gansu | Scenic Area | Crescent Moon Spring | Jiayuguan | Tickets | Attractions | ID Card | Enter | Danxia | Mingsha Mountain | Queuing |
| Fujian | Scenic Area | Collect Tickets | Bamboo Raft | Ctrip | Not Bad | Wuyi Mountain | Gulangyu | Attractions | Tickets | Tulou |
| Xizang | Lhasa | Reservation | Tickets | Potala Palace | Tour Guide | Jokhang Temple | Queuing | Commentary | Ctrip | Attractions |
| Guizhou | Waterfall | Scenic Area | Queuing | Tianxingqiao | Huangguoshu | Scenery | Not Bad | Attractions | Ancient Town | Collect Tickets |
| Liaoning | Ctrip | Queuing | Buy Tickets | Scenery | Scenic Area | Collect Tickets | Water Cave | Not Bad | ID Card | Book Tickets |
| Chongqing | Not Bad | Scenery | Scenic Area | ID Card | Collect Tickets | Tiankeng | Ctrip | Queuing | Scenery | Hours |
| Shaanxi | Hukou Waterfall | Scenic Area | Collect Tickets | Waterfall | Buy Tickets | Cable Car | Ctrip | Commentary | Queuing | Tour Guide |
| Qinghai | Kumbum Monastery | Qinghai Lake | Scenic Area | Buy Tickets | 20 | Collect Tickets | Ctrip | Enter | Parking Lot | Tibetan Buddhism |
| Heilongjiang | Waterfall | Scenery | 100 | Not Bad | Scenic Area | ID Card | Ctrip | Tickets | Attractions | Sun Island |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, F.; Zhu, Z.; Zhengchen, R. Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in Image Perception of High-Quality Tourism Destinations in China. Land 2025, 14, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101999
Zhao W, Liu J, Zhu H, Li F, Zhu Z, Zhengchen R. Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in Image Perception of High-Quality Tourism Destinations in China. Land. 2025; 14(10):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101999
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wudong, Jiaming Liu, He Zhu, Fengjiao Li, Zehui Zhu, and Rouyu Zhengchen. 2025. "Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in Image Perception of High-Quality Tourism Destinations in China" Land 14, no. 10: 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101999
APA StyleZhao, W., Liu, J., Zhu, H., Li, F., Zhu, Z., & Zhengchen, R. (2025). Inter-Provincial Similarities and Differences in Image Perception of High-Quality Tourism Destinations in China. Land, 14(10), 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101999






