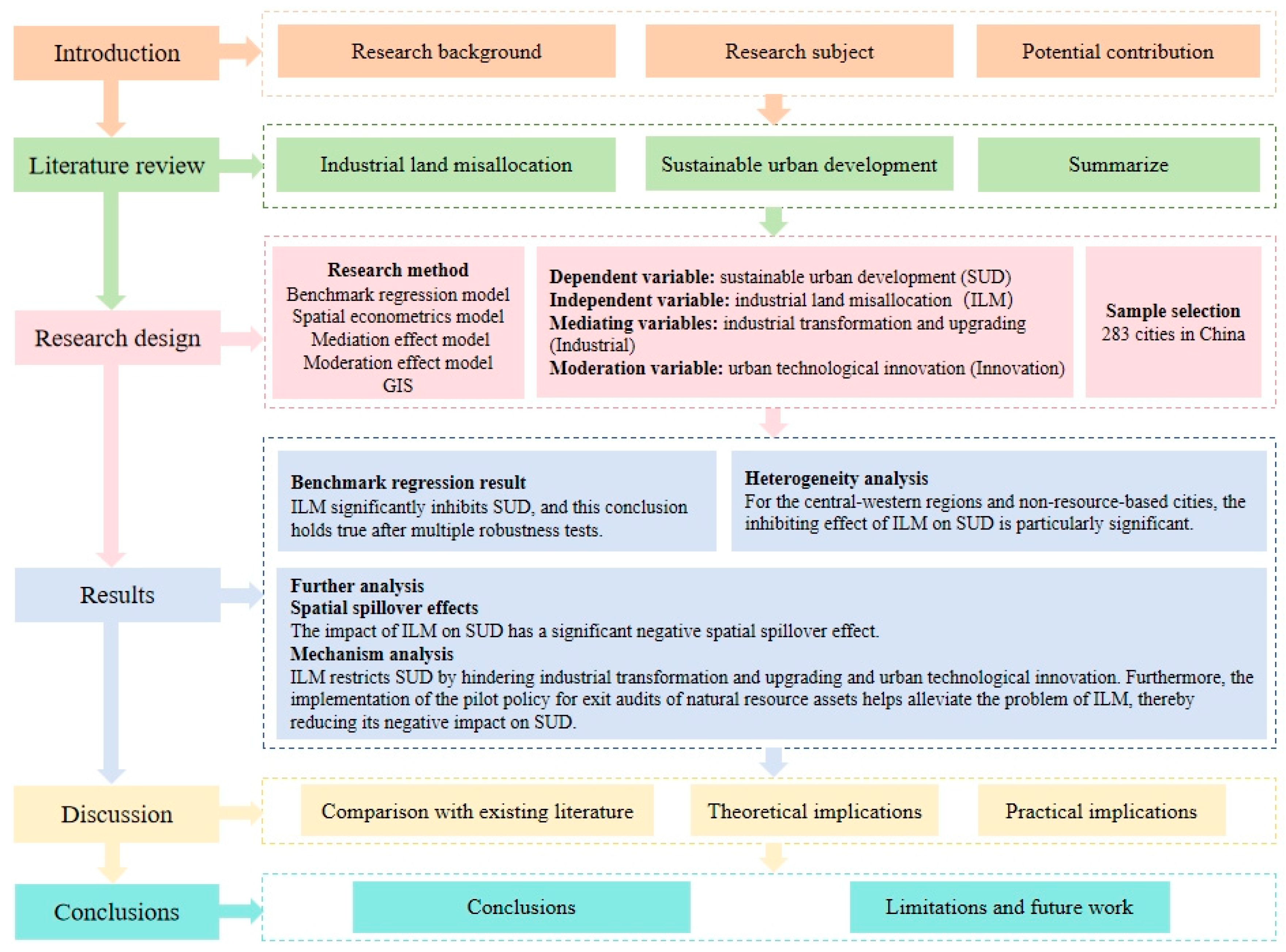
The Impact of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development: Mechanisms and Spatial Spillover Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
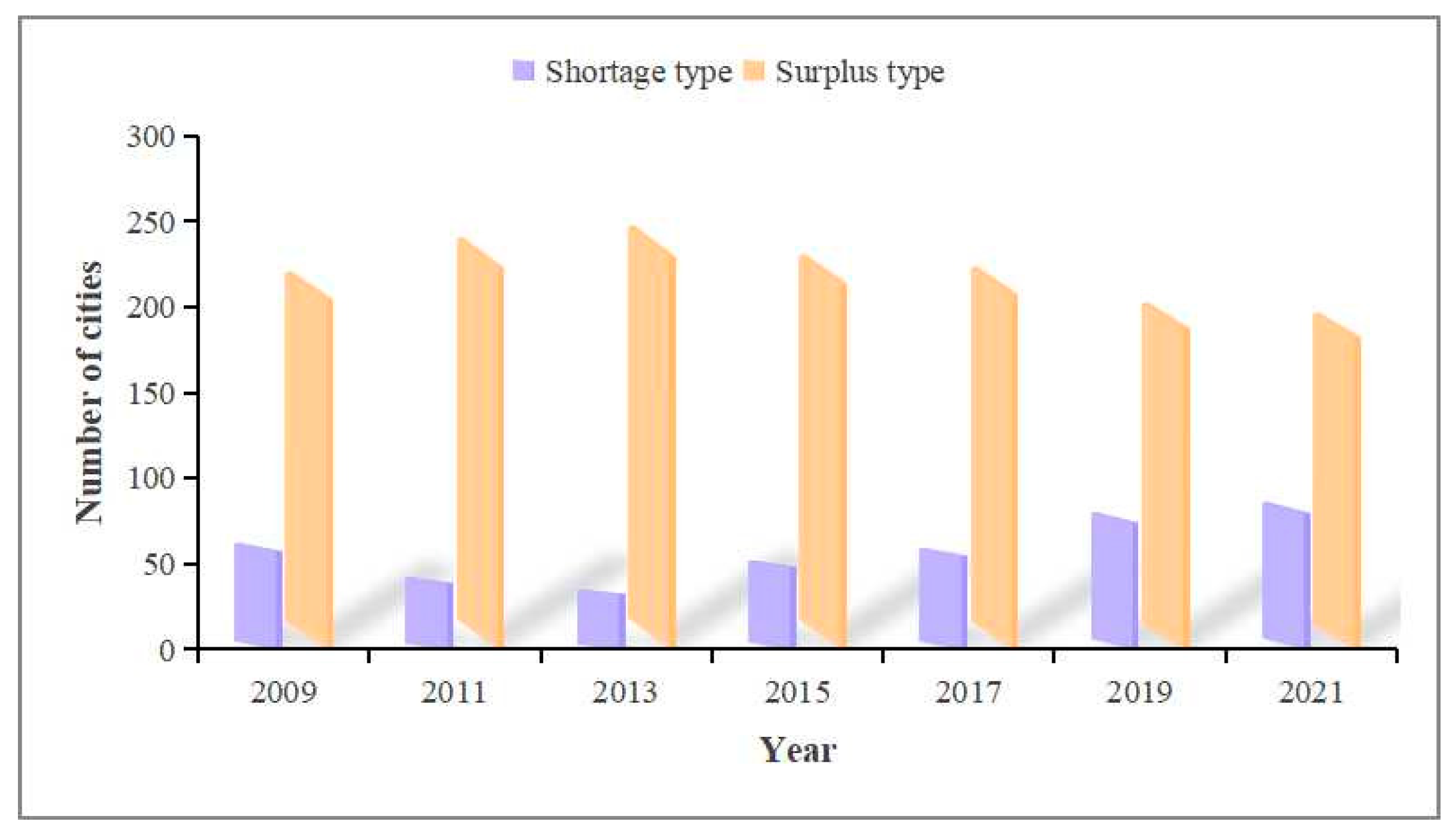
2.1.1. Industrial Land Misallocation
2.1.2. Sustainable Urban Development
2.2. Theoretical Analysis
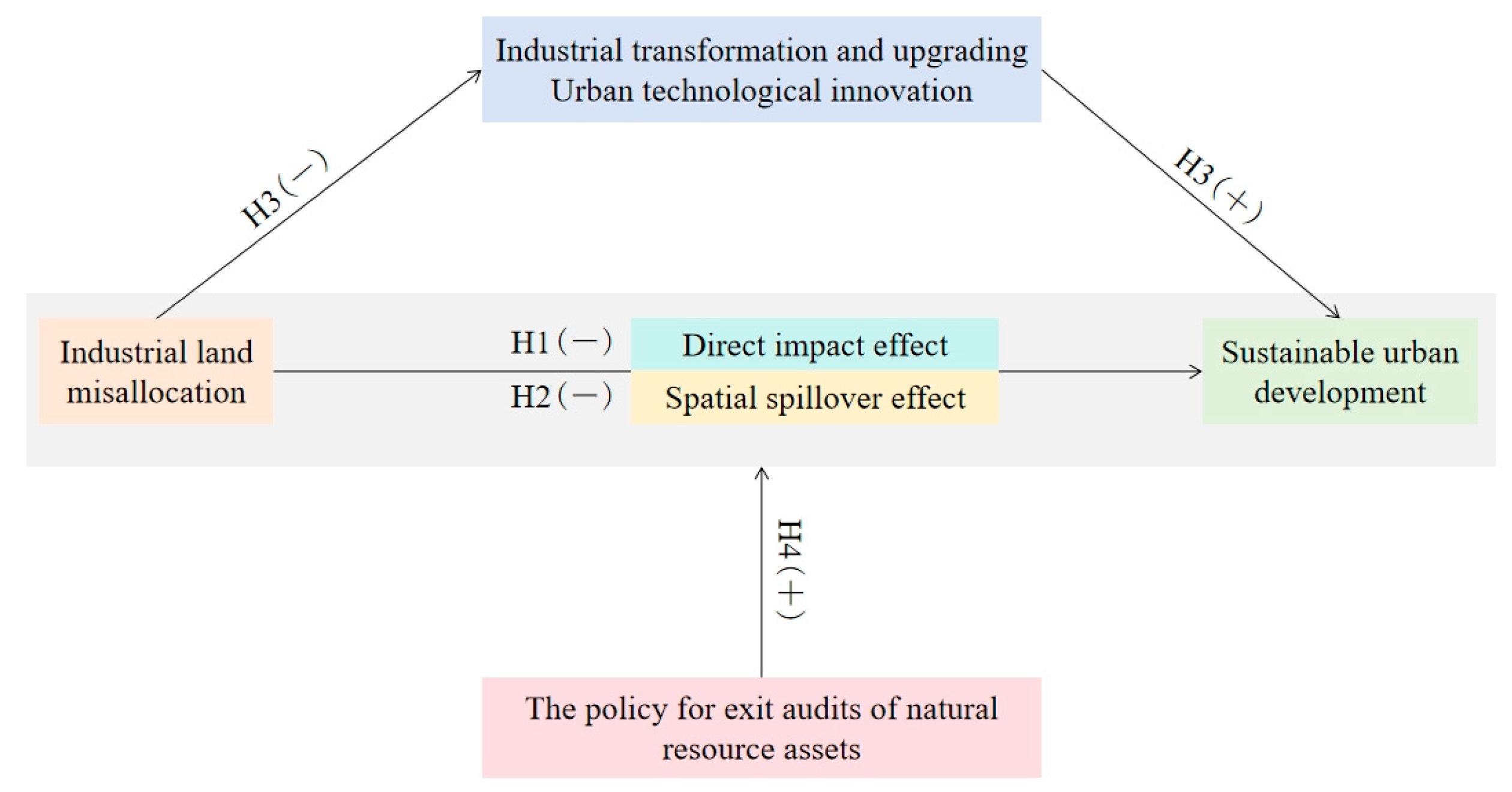
2.2.1. Industrial Land Misallocation and Sustainable Urban Development
2.2.2. The Impact of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development Has a Spatial Spillover Effect
2.2.3. The Impact Mechanism of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development
3. Research Design
3.1. Model Construction
3.1.1. Benchmark Regression Model
3.1.2. Spatial Econometrics Model
3.1.3. Mediation Effect Model
3.1.4. Moderation Effect Model
3.2. Variables
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Independent Variable
3.2.3. Control Variables
3.2.4. Mediating Variables
3.2.5. Moderation Variable
3.3. Data Source
4. Empirical Analysis Results
4.1. Benchmark Regression Result
4.2. Robustness Tests
4.3. Endogeneity Test
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4.1. Regional Heterogeneity
4.4.2. Heterogeneity of Resource Endowments
5. Further Analysis
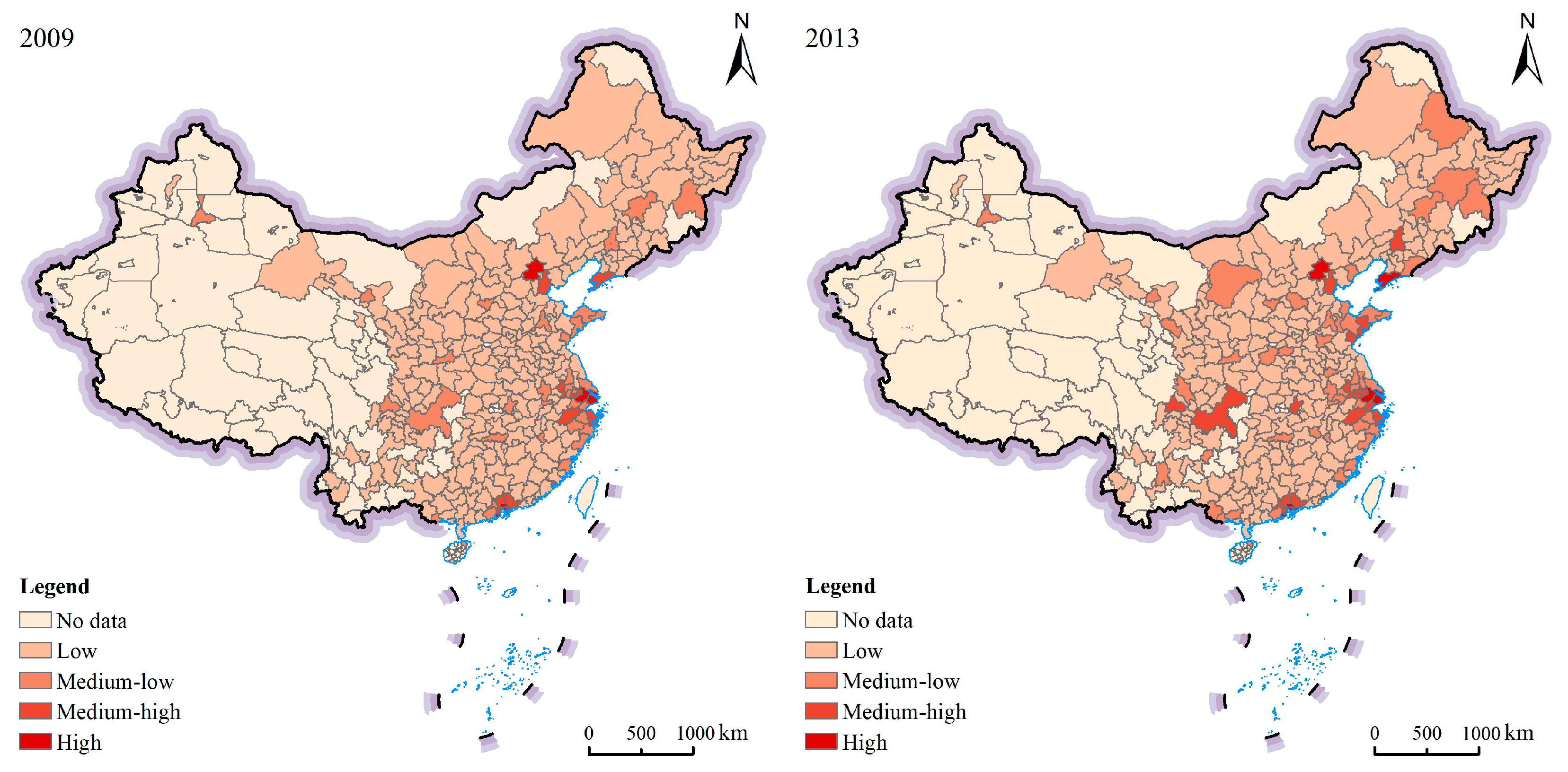
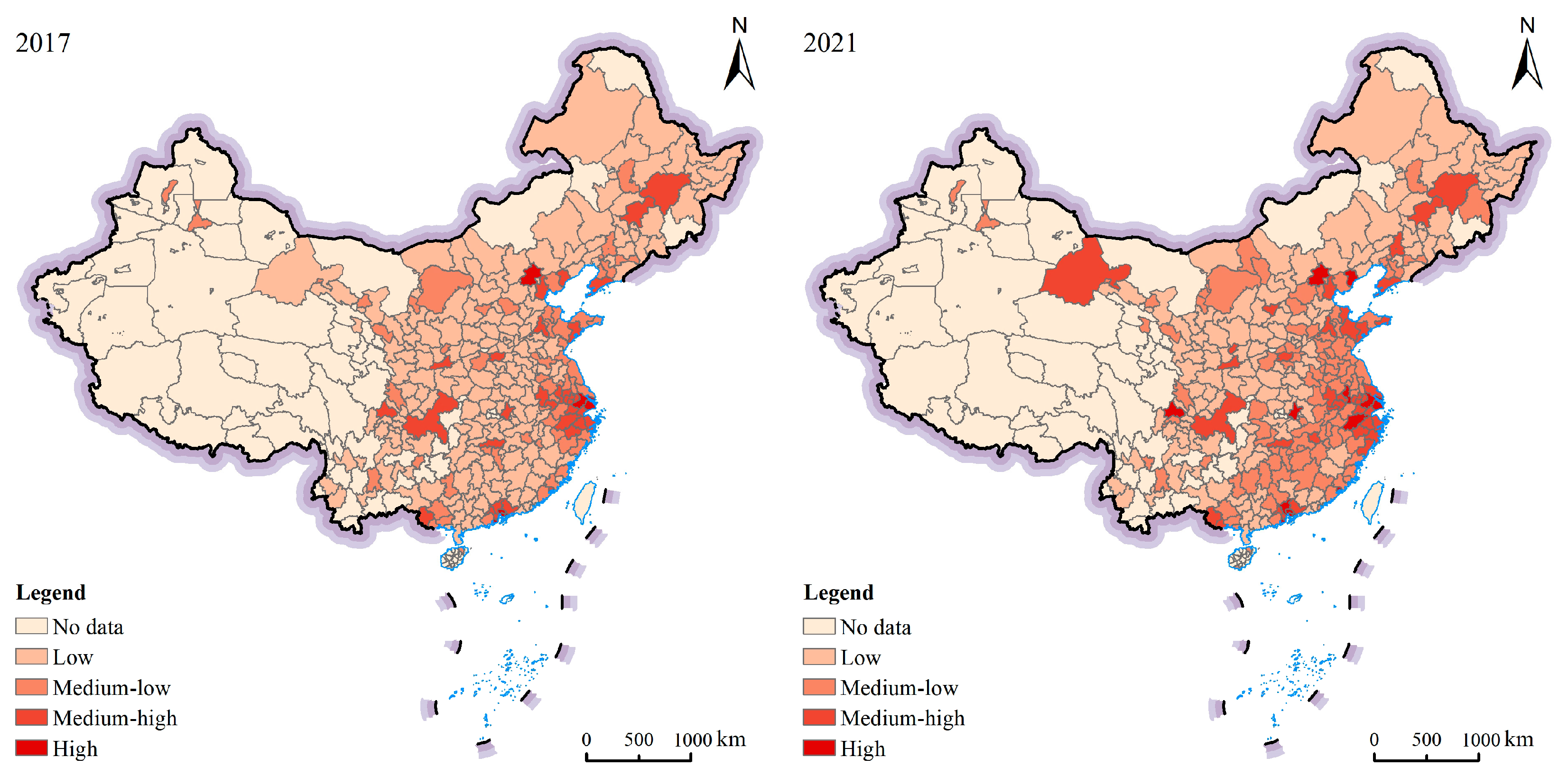
5.1. Spatial Spillover Effects
5.2. Mechanism Analysis
6. Discussion
6.1. Comparison with Existing Literature
6.2. Theoretical Implications
6.3. Practical Implications
7. Conclusions and Future Research
7.1. Conclusions
7.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Feng, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, L.; Niu, Q.; Mao, X. Is the assessment approach of sustainable development goal 11.3.1 justified? Evidence from the drivers of future urban land use efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Prediction and evaluation of industrial land intensive use: Adding policy impact to system dynamics model. Systems 2024, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. The Governance of Land Use in OECD Countries: Policy Analysis and Recommendations; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.; Huang, J.; Gao, F.; Meng, H.; Peng, C. Regional allocation of industrial land in industrializing China: Does spatial mismatch exist? Landscape Res. 2023, 48, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, J. Marketization and resource mismatches: Evidence from China’s land resource allocation. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Li, M. The impact of land resource mismatch and land marketization on pollution emissions of industrial enterprises in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Song, K.; Bai, J. Market segmentation, resource misallocation and environmental pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, L.; Bao, H.; Wong, S.; Du, X.; Wei, X. An empirical study on the mismatch phenomenon in utilizing urban land resources in China. Land 2023, 12, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xie, D. Land resource mismatch and energy efficiency: Evidence from 243 cities in China. Energ. Policy 2023, 183, 113800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, J.E.; Lathrop, R.G. Land resource impact indicators of urban sprawl. Appl. Geogr. 2003, 23, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtonen, E.; Falkenbach, H.; Viitanen, K. Securing public objectives in large-scale urban development: Comparison of public and private land development. Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britos, B.; Hernandez, M.A.; Robles, M.; Trupkin, D.R. Land market distortions and aggregate agricultural productivity: Evidence from Guatemala. J. Dev. Econ. 2022, 155, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, H. The impact of industrial land mismatch on carbon emissions in resource-based cities under environmental regulatory constraints—Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2024, 31, 56860–56872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ren, C.R.; Zhou, T. Understanding the impact of land finance on industrial structure change in China: Insights from a spatial econometric analysis. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Huang, M. Land Misallocation and Carbon Emissions: Evidence from China. Land 2022, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvin, M.B.; Pradhan, R.P.; Norman, N.R. Transportation intensity, urbanization, economic growth, and CO2 emissions in the G-20 countries. Util. Policy 2015, 35, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Y.F.; Li, X.R.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Xue, P.; Gong, H.B.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effects of land use patterns on the interannual variations of carbon sinks of terrestrial ecosystems in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Q.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, F. Exploring the effects of market-oriented reforms on industrial land use eco-efficiency in China: Evidence from a spatial and non-linear analysis. Environ. Impact Asses 2023, 102, 107211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.Y. Can the performance evaluation change from central government suppress illegal land use in local governments? A new interpretation of Chinese decentralisation. Land. Use Policy 2021, 108, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.C.; Wang, S.; Ahmad, F.; Chandio, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Xue, D. The nexus between misallocation of land resources and green technological innovation: A novel investigation of Chinese cities. Clean. Technol. Envir 2021, 23, 2101–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.R.; Feng, Y.J.; Tong, X.H.; Liu, S.; Xie, H.; Gao, C.; Lei, Z.K. Modeling ESV losses caused by urban expansion using cellular automata and geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Nakicenovic, N.; Visbeck, M.; Stevance, A.S. Policy: Five priorities for the un sustainable development goals. Nature 2015, 520, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S. Developing Sustainability Indicators and Indices. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secundo, G.; Ndou, V.; Del Vecchio, P.; De Pascale, G. Sustainable development, intellectual capital and technology policies: A structured literature review and future research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2020, 153, 119917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijering, J.V.; Tobi, H.; Kern, K. Defining and measuring urban sustainability in Europe: A Delphi study on identifying its most relevant components. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, R.F.M.; Mourshed, M. Urban sustainability assessment framework development: The ranking and weighting of sustainability indicators using analytic hierarchy process. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shuai, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.R.; Zhao, B. Toward sustainable urban development: Identifying principal SDG indicators for Chinese cities. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2025, 9, 2400894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xu, W.; Kung, C.-C. The impact of data elements on urban sustainable development: Evidence from the big data policy in China. Technol. Soc. 2025, 81, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J. Spatiotemporal characteristics and interactive effect between urbanization and sustainable urban development: Evidence from Yangtze River delta. Land 2024, 13, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.P.; Shen, Q.Q. Exploring impact of digital economy on sustainable urban development by panel data of 30 underdeveloped cities in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenaker, N.; Hoekstra, R.; Smits, J.P. Comparison of measurement systems for sustainable development at the national level. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.L.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y.X. Exploring the dynamics of urban digital intelligent transformation: Sustainable development through the national AI innovation pilot zone. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wang, L.G. Can the relationship between atmospheric environmental quality and urban industrial structure adjustment achieve green and sustainable development in China? A Case of Taiyuan City. Energies 2022, 15, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Zhang, W.K. Green finance: The catalyst for artificial intelligence and energy efficiency in Chinese urban sustainable development. Energ. Econ. 2024, 139, 107883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masha, M.; Tadila, G.; Bojago, E. GIS-based analysis of urban expansion in Wolaita Sodo, South Ethiopia: Implications for sustainable development. Discov. Sustain. 2025, 6, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounoua, L.; Bachir, N.; Souidi, H.; Bahi, H.; Lagmiri, S.; Khebiza, M.Y.; Nigro, J.; Thome, K. Sustainable development in Algeria’s urban areas: Population growth and land consumption. Urban. Sci. 2023, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.H.; Shi, Z.X.; Li, J.; Dong, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Hou, J. Research on the impact of factor flow on urban land use efficiency from the perspective of urbanization. Land 2022, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Guo, G.; Li, C. Treating the symptoms as well as the root causes: How the digital economy can mitigate the negative impacts of land resource mismatches on urban ecological resilience. Land 2024, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Xiao, D.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Can the digital economy address the loss of green development efficiency due to resource mismatch? Evidence from China’s land transaction markets. J. Environ. Plann Man. 2025, 68, 406–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ma, R.; Du, M.; Ding, X.; Feng, J.; Jing, Y. The impact of land resource mismatch and environmental regulation on carbon emissions: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Plann Man. 2025, 68, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, M. How does land resource mismatch affect urban energy low-carbon transition? Urban. Clim. 2024, 58, 102236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ran, Q.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Ge, W. Regional differentiation of the pollution reduction effect of accountability audit of natural resource under the perspective of spatial mismatch in land supply: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manage 2025, 384, 125554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zou, W.; Huang, Y. Urban sustainable development goals and ecosystem services: Pathways to achieving coordination. Land. Use Policy 2024, 146, 107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.X. Industrial and financial cooperation, heterogeneous green technological innovation, and urban low carbon transformation. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 102, 104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Du, R.; He, J.X. Fluctuating development traits of industrial land mismatch and its influence on urban ecological modernization. Land 2025, 14, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Ren, Z.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Q. Urban industrial land misallocation and green total factor productivity: Evidence from China’s Yellow River basin regions. Aust. Econ. Pap. 2024, 63, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Lee, W.-S.; Woo, S. Impact of land resource misallocation on carbon emission efficiency: Empirical evidence from 274 cities in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1652558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zeng, L.; Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Gu, X. The impact of land marketization on urban resilience: Empirical evidence from Chinese cities. Land 2024, 13, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| System | Indicator | SDG Type | Target | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economy | Regional GDP per capita (10,000 RMB/person) | SDG 8-Economic Growth | 8.1 | + |
| Regional GDP growth rate (%) | SDG 8-Economic Growth | 8.1 | + | |
| Number of invention patents granted per 1 billion RMB of regional GDP (units/billion RMB) | SDG 9-Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.5 | + | |
| R&D expenditure as a percentage of regional GDP (%) | SDG 9-Innovation and Infrastructure | 9.5 | + | |
| Amount of actual foreign investment used (billion USD) | SDG 17-Partnerships for the Goals | 17.3 | + | |
| Total import and export as a percentage of regional GDP (%) | SDG 17-Partnerships for the Goals | 17.11 | + | |
| Society | Per capita disposable income (10,000 RMB) | SDG 1-No Poverty /SDG 10-Reduced Inequality | 1.1/10.1 | + |
| Education expenditure as a percentage of fiscal expenditure (%) | SDG 4-Quality Education | 4.1 | + | |
| Number of books per 100 people in public libraries (volumes) | SDG 4-Quality Education | 4.2 | + | |
| Number of hospital beds per 10,000 people (beds) | SDG 3-Good Health and Well-being | 3.8 | + | |
| Environment | Road area per capita (m2/person) | SDG 11-Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.2 | + |
| Green coverage rate of built-up areas (%) | SDG 11/SDG 15 | 11.7/15.1 | + | |
| Centralized treatment rate of sewage treatment plants (%) | SDG 12-Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2 | + | |
| Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste (%) | SDG 12-Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.5 | + | |
| Utilization rate of industrial solid waste (%) | SDG 12-Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.5 | + | |
| Industrial wastewater discharge per unit of industrial output (tons/10,000 RMB) | SDG 6-Clean Water and Sanitation | 6.3 | – | |
| Industrial sulfur dioxide emissions per unit of industrial output (tons/10,000 RMB) | SDG 13-Climate Action | 13.2 | – | |
| Industrial smoke and dust emissions per unit of industrial output (tons/10,000 RMB) | SDG 13-Climate Action | 13.2 | – |
| Variable | Observation | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUD | 3679 | 0.059 | 0.041 | 0.020 | 0.252 |
| ILM | 3679 | 7.515 | 12.281 | 0.047 | 73.691 |
| Fis | 3679 | 0.456 | 0.221 | 0.092 | 1.006 |
| Con | 3679 | 6.304 | 1.063 | 3.864 | 8.984 |
| Emp | 3679 | 3.592 | 0.835 | 1.963 | 6.225 |
| Pop | 3679 | 5.590 | 5.214 | −8.050 | 21.300 |
| Fin | 3679 | 2.434 | 1.121 | 0.978 | 6.725 |
| Urb | 3679 | 0.549 | 0.154 | 0.245 | 0.949 |
| Policy | 3679 | 0.375 | 0.484 | 0 | 1 |
| Industrial | 3679 | 1.016 | 0.580 | 0.108 | 5.348 |
| Innovation | 3679 | 1.649 | 1.675 | 0.057 | 20.683 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | SUD | SUD | SUD | SUD | SUD | SUD | SUD |
| lnILM | −1.000 *** (−22.99) | −0.486 *** (−14.22) | −0.425 *** (−12.97) | −0.405 *** (−12.66) | −0.417 *** (−12.80) | −0.278 *** (−8.24) | −0.188 *** (−5.61) |
| Fis | 11.88 *** (52.92) | 8.788 *** (32.45) | 8.191 *** (30.61) | 8.183 *** (30.58) | 7.908 *** (30.10) | 5.125 *** (15.73) | |
| Con | 1.103 *** (18.75) | −0.180 * (−1.65) | −0.179 * (−1.65) | 0.108 (0.99) | 0.376 *** (3.47) | ||
| Emp | 1.813 *** (13.79) | 1.804 *** (13.72) | 1.326 *** (9.89) | 1.157 *** (8.82) | |||
| Pop | 0.017 * (1.95) | 0.020 ** (2.37) | 0.030 *** (3.55) | ||||
| Fin | 0.600 *** (12.72) | 0.455 *** (9.64) | |||||
| Urb | 5.999 *** (13.83) | ||||||
| Constant | 7.076 *** (89.27) | 1.074 *** (8.39) | −4.536 *** (−14.03) | −2.703 *** (−7.90) | −2.753 *** (−8.03) | −4.366 *** (−12.17) | −7.283 *** (−17.83) |
| Observations | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Number of cities | 283 | 283 | 283 | 283 | 283 | 283 | 283 |
| R-squared | 0.266 | 0.457 | 0.543 | 0.533 | 0.533 | 0.578 | 0.619 |
| (1) One-Period Lag | (2) Two-Period Lag | (3) 5% Winsorization | (4) 5% Trimming | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | SUD | SUD | SUD | SUD |
| L1.lnILM | −0.189 *** (−5.31) | |||
| L2.lnILM | −0.203 *** (−5.39) | |||
| lnILM | −0.187 *** (−7.08) | −0.242 *** (−6.97) | ||
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | −7.308 *** (−16.79) | −7.218 *** (−15.43) | −5.583 *** (−18.00) | −2.440 *** (−5.83) |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3396 | 3113 | 3679 | 2010 |
| R-squared | 0.617 | 0.617 | 0.666 | 0.499 |
| (1) IV-Ⅰ | (2) IV-Ⅱ | |
|---|---|---|
| Variable | lnILM | SUD |
| lnILM | −0.644 *** (−5.14) | |
| IV | 0.062 *** (17.21) | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM | 275.368 [0.000] | |
| Cragg–Donald Wald F | 296.028 [16.38] | |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3679 | 3679 |
| (1) Eastern | (2) Western-Central | (3) Resource -Based Cities | (4) Non-Resource-Based Cities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | SUD | SUD | SUD | SUD |
| lnILM | −0.085 (−1.24) | −0.198 *** (−6.63) | −0.154 (−1.46) | −0.200 *** (−8.08) |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 1300 | 2379 | 1469 | 2210 |
| R-squared | 0.708 | 0.467 | 0.371 | 0.641 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z-Values | Year | Moran’s I | Z-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 0.445 *** | 11.216 | 2010 | 0.430 *** | 10.806 |
| 2011 | 0.404 *** | 10.134 | 2012 | 0.395 *** | 9.912 |
| 2013 | 0.381 *** | 9.550 | 2014 | 0.395 *** | 9.897 |
| 2015 | 0.395 *** | 9.897 | 2016 | 0.402 *** | 10.028 |
| 2017 | 0.399 *** | 9.940 | 2018 | 0.398 *** | 9.921 |
| 2019 | 0.352 *** | 8.786 | 2020 | 0.339 *** | 8.438 |
| 2021 | 0.340 *** | 8.453 |
| Test | Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| LM-lag | 556.690 | 0.000 |
| Robust LM-lag | 12.511 | 0.000 |
| LM-error | 1750.105 | 0.000 |
| Robust LM-error | 1205.926 | 0.000 |
| LR-lag | 49.06 | 0.000 |
| LR-error | 220.14 | 0.000 |
| WALD-lag | 66.87 | 0.000 |
| WALD-error | 207.27 | 0.000 |
| (1) Adjacent Matrix | (2) Economic Distance Matrix | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect Decomposition | Effect Decomposition | |||||
| Variable | SUD | Average Direct Effect | Average Indirect Effect | SUD | Average Direct Effect | Average Indirect Effect |
| lnILM | −0.120 *** (−3.71) | −0.139 *** (−4.18) | −0.269 *** (−3.70) | −0.163 *** (−5.18) | −0.172 *** (−5.32) | −0.287 ** (−2.39) |
| W × lnILM | −0.112 ** (−2.28) | −0.132 (−1.60) | ||||
| ρ | 0.428 *** (22.37) | 0.352 *** (12.29) | ||||
| sigma2_e | 5.175 *** (42.08) | 5.429 *** (42.57) | ||||
| Observations | 3679 | 3679 | ||||
| Number of cities | 283 | 283 | ||||
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | ||||
| R-squared | 0.630 | 0.628 | ||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Industrial | SUD | Innovation | SUD | SUD |
| lnILM | −0.064 *** (−11.57) | −0.144 *** (−4.25) | −0.033 ** (−2.00) | −0.163 *** (−5.24) | −1.164 *** (−20.68) |
| Industrial | 0.682 *** (6.89) | ||||
| Innovation | 0.741 *** (24.15) | ||||
| lnILM × Policy | 0.357 *** (4.45) | ||||
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | 0.644 *** (9.51) | −7.723 *** (−18.79) | −2.595 *** (−12.70) | −5.359 *** (−13.82) | 7.133 *** (46.39) |
| City FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 | 3679 |
| Number of cities | 283 | 283 | 283 | 283 | 283 |
| R-squared | 0.431 | 0.626 | 0.416 | 0.674 | 0.540 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Cao, X. The Impact of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development: Mechanisms and Spatial Spillover Effects. Land 2025, 14, 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101976
Zhang S, Cao X. The Impact of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development: Mechanisms and Spatial Spillover Effects. Land. 2025; 14(10):1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101976
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shijia, and Xiaojuan Cao. 2025. "The Impact of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development: Mechanisms and Spatial Spillover Effects" Land 14, no. 10: 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101976
APA StyleZhang, S., & Cao, X. (2025). The Impact of Industrial Land Misallocation on Sustainable Urban Development: Mechanisms and Spatial Spillover Effects. Land, 14(10), 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14101976




