Codesigning More-than-Human Ecosystems with Social and Environmental Systems: The Gamification of NetWall and BioDiveIn
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Mapping
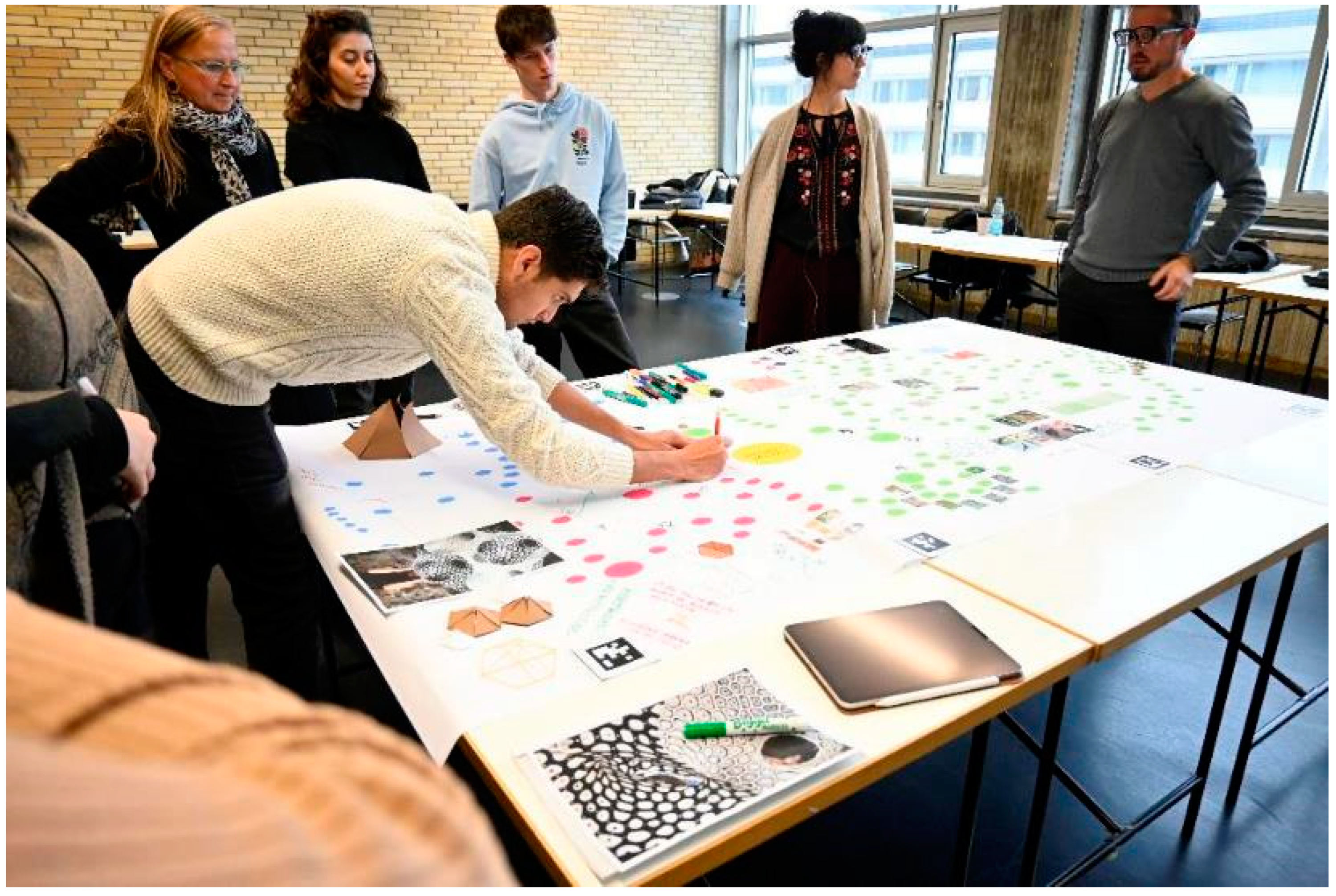
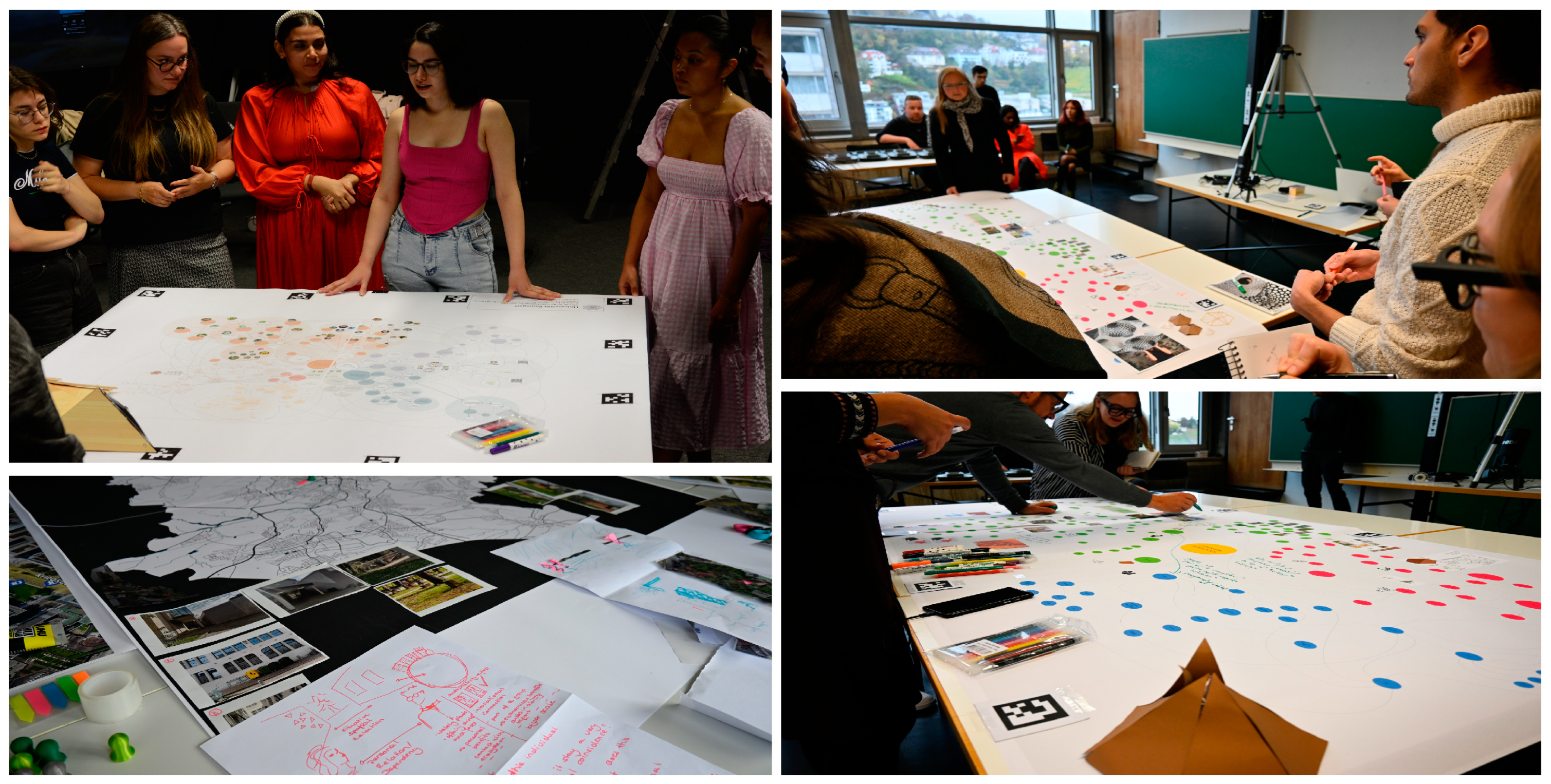
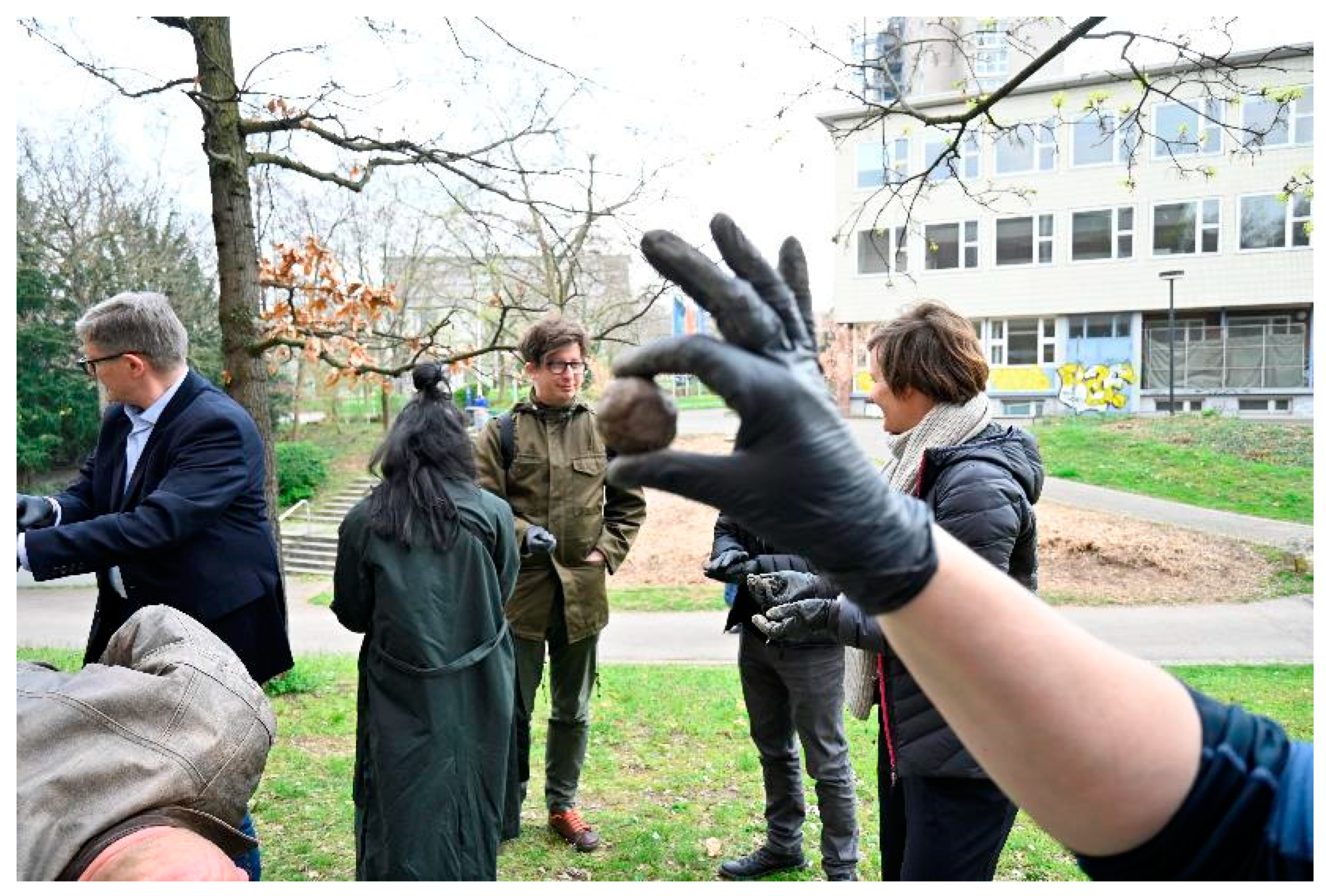
2.2. The Real Life CoDesign Laboratory
2.2.1. Tangible and Non-Tangible Interventions
- QR Codes: Embedded on the interventions, the codes provided access to supplementary blogs with detailed information and DIY guides.
- Citizen Science Application (Spot-a-Bee): Developed by Cardiff University and the University of Glasgow [13], this platform encouraged public participation in ecological monitoring by allowing users to upload images of pollinators. These user-contributed images trained image recognition algorithms to identify and assign value to pollination activities, fostering a new ecology of shared living through technology [24].
2.2.2. Iterative Feedback and Community Engagement
- Ecological Interactions: observations of how local ecosystems interacted with the prototypes, such as which species utilized the modules, informed adjustments to their design and placement.
- Public Engagement: Activities such as ecological checks and community gatherings provided insights into public perceptions and usability. These events also fostered a sense of ownership among participants.
- Technology Integration: tools like Spot-a-Bee and urban games generate data that could inform both ecological research and community engagement strategies.
3. Outcomes
3.1. The Tangible Interventions
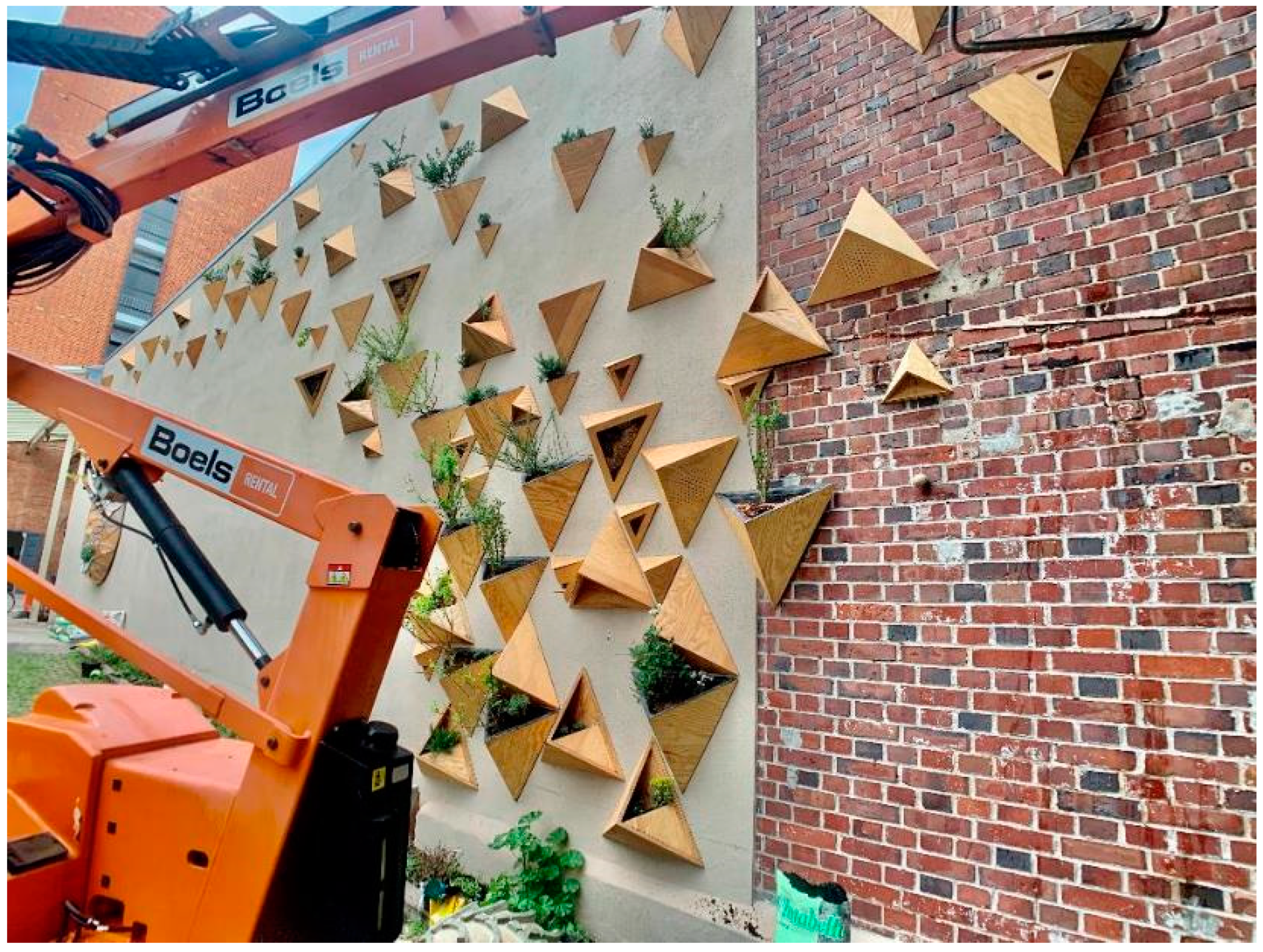
3.1.1. BioDiveIn
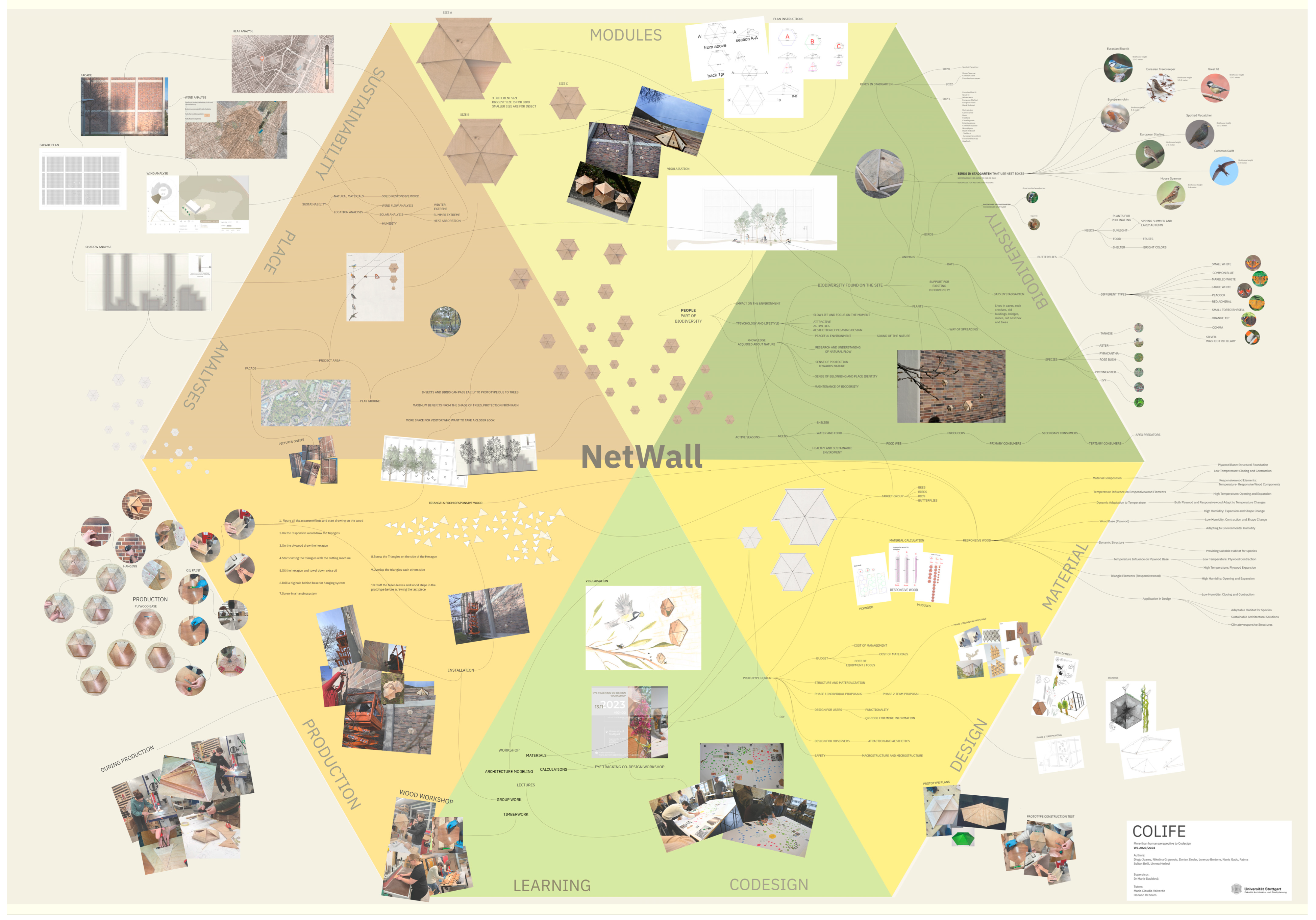
3.1.2. NetWall
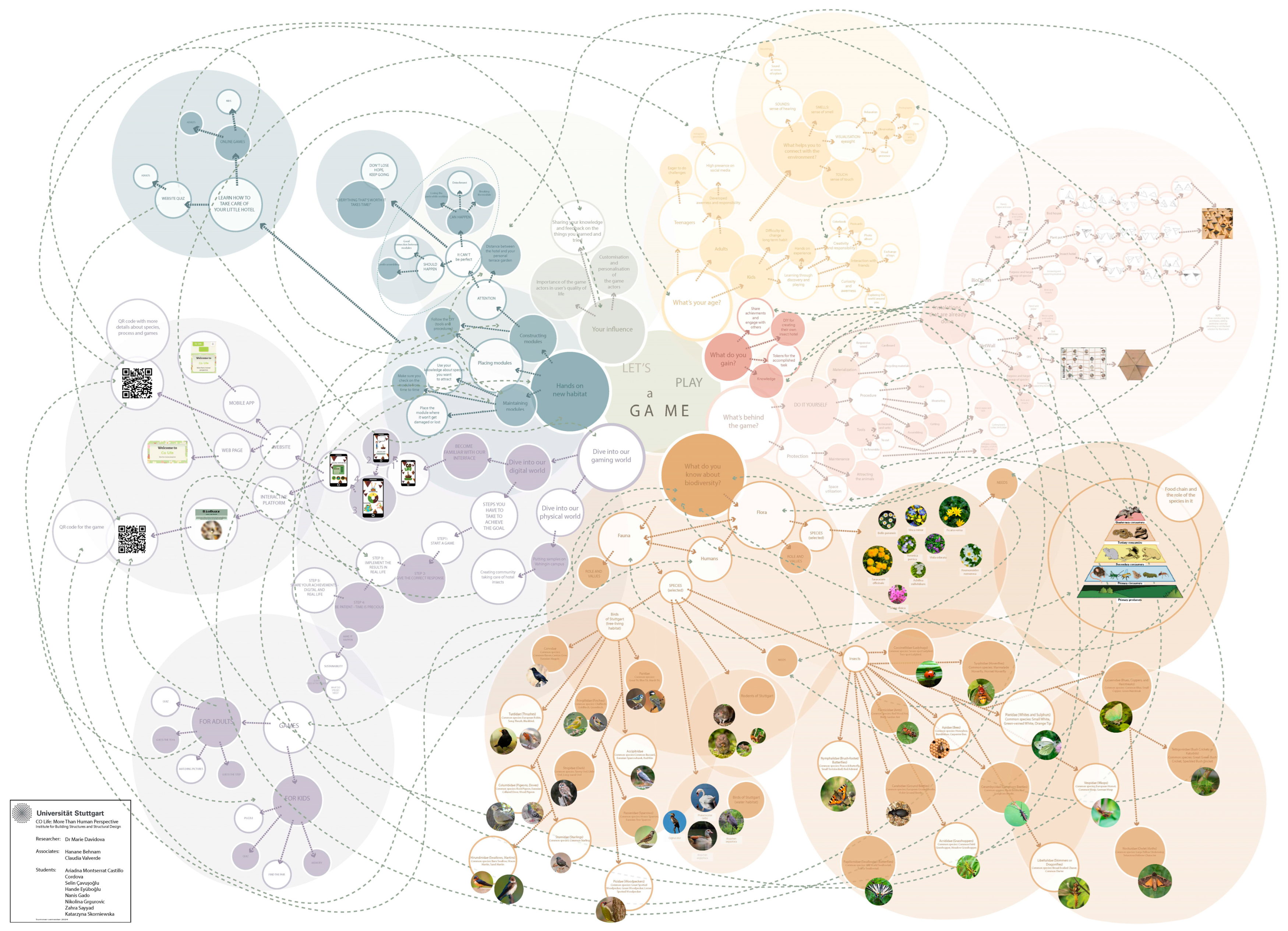
3.2. Gamification of Prototypes
3.2.1. GoCOLife Game
3.2.2. CoLife Web-Based Game
3.3. Evaluation of Codesigned Interventions
3.4. Events
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bateson, G. Mind and Nature: A Necessary Unity (Issue June); E.P. Dupton: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ingaramo, R.; Negrello, M.; Khachatourian Saradehi, L.; Khachatourian Saradhi, A. View of Transcalar project of nature-based solutions for the 2030 Agenda. Innovations and interconnections. AGATHÓN Int. J. Arch. Art Des. 2023, 13, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Spotswood, E.N.; Beller, E.E.; Grossinger, R.; Grenier, J.L.; Heller, N.E.; Aronson, M.F.J. The Biological Deserts Fallacy: Cities in Their Landscapes Contribute More than We Think to Regional Biodiversity. Bioscience 2021, 71, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruford, M.; Baillie, L.; Sanderson Bellamy, A.; Cuff, J.; Davidová, M.; Henderson, K.; Hutchinson, N.; James, C.; Jenkins, J.; Komar, J.; et al. Cardiff University Ecosystem Resilience and Biodiversity Action Plan (ERBAP) 2021–2023; Cardiff University: Cardiff, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Meadows, D. Dancing with systems. Syst. Think. 2002, 13, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Meadows, D. Leverage Points: Places to Intervene in a System; The Sustainability Institut: Hartland, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M.; Behnam, H.; Valverde Rojas, M.C.; Juarez, D.; Grgurovic, N.; Herlevi, L.; Zinder, D.; Bortone, L.; Belli, F.S.; Gado, N. COLife_03—Gigamap and DIY; University of Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidová, M.; Rojas Valverde, M.C.; Behnam, H. BioDiveIn: Leveraging the ecosystem through social and environmental systems Presentation introduction. In Relating Systems Thinking and Design 2023 Symposium; May, C., Barba, E., Eds.; Systemic Design Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M.; Valverde Rojas, M.C.; Behnam, H.; Fischer, L.K.; Fadini, T.; Haueise, J.; Hauke, A.; Florescu, M.; Ferrari, V.; Ros, A.P.; et al. COLife_01—Gigamap and DIY Files; University of Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clatworthy, S. Service innovation through touch-points: Development of an innovation toolkit for the first stages of new service development. Int. J. Des. 2011, 5, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M.; Behnam, H.; Valverde Rojas, M.C.; Guerriero, C.; Yeh, H.; Huang, J.; Köse, M. COLife_02—Gigamap and Game Design; University of Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidova, M.; Valverde Rojas, M.C.; Behnam, H.; Montserrat Castillo Cordova, A.; Çavuşoğlu, S.; Eyüboğlu, H.; Gado, N.; Grgurovic, N.; Sayyad, Z.; Skorniewska, K. COLife_05: Gigamap and Game Introduction; University of Stuttgart: Stuttgart, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff University, University of Glasgow. Spot-a-Bee 2021. Available online: https://www.spotteron.net/apps/global-community-science-projects/spot-a-bee-citizen-science-app (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Davidová, M.; Sharma, S.; McMeel, D.; Loisides, F. Co-De|GT: The Gamification and Tokenisation of More-Than-Human Qualities and Values. Sustainability 2022, 13, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüter, C. Importance for Pollination; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevaldson, B. Beyond User Centric Design. In Proceedings of the RSD7, Relating Systems Thinking and Design 7, Turin, Italy, 23–26 October 2018; Barbero, S., Ed.; Systemic Design Association: Torino, Italy, 2018; pp. 516–525. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M. Generating the Design Process with GIGA-map: The Development of the Loop Pavilion. In Proceedings of the RSD3, Third Symposium of Relating Systems Thinking to Design, Oslo, Norway, 15–17 October 2014; Sevaldson, B., Jones, P., Eds.; Oslo School of Architecture and Design: Oslo, Norway, 2014; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M. Multicentred Systemic Design Pedagogy Through Real-Life Empathy: Integral and Inclusive Practice-Based Education in the Research-by-Design Context. FormAkademisk Res. J. Des. Des. Educ. 2020, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro. Miro|Online Whiteboard for Visual Collaboration 2023. Available online: https://miro.com/app/dashboard/ (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Sevaldson, B. Designing Complexity: The Methodology and Practice of Systems Oriented Design; Common Ground Publishing: Champaign, IL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidová, M. Synergy in the systemic approach to architectural performance: The integral multi- and cross-layered agencies in ecosystemic generative design processes of the post-anthropocene. FormAkademisk Res. J. Des. Des. Educ. 2020, 13, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COLife Studio Summer 2023. GOCOLIFE—Let the Fun Begin!|Interacty Project 2023. Available online: https://interacty.me/projects/d4d916f6b1a8609b (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- COLife Studio Summer 2024. CoLife 1 2024. Available online: https://colifebiodiversity.wixsite.com/co-life-1 (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Bellini Oscar, E.; Ruscica, G.; Paris, V. View of Towards a new ecology of shared living. Technological greenery and the Internet of Nature. ATHÓN Int. J. Archit. Art Des. 2022, 11, 124–135. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M. Wood as a Primary Medium to Architectural Performance: A Case Study in Performance Oriented Architecture Approached through Systems Oriented Design, 1st ed.; Technical University of Liberec: Liberec, Czech Republic, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sevaldson, B. Developing Digital Design Techniques: Investigations on Creative Design Computing, 1st ed.; Oslo School of Architecture and Design: Oslo, Norway, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M.; Prokop, Š. TreeHugger: The Ecosystemic Prototypical Urban Intervention. In Proceedings of the 6th eCAADe RIS, Nicosia, Cyprus, 24–25 May 2018; Kontovourkis, O., Ed.; University of Cyprus: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2018; pp. 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Davidová, M.; Zímová, K. COLridor: Co-Design and Co-Living Urban Adaptation. FormAkademisk Res. J. Des. Des. Educ. 2018, 11, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deterding, S.; Dixon, D.; Khaled, R.; Nacke, L. From game design elements to gamefulness: Defining “gamification. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, Tampere, Finland, 29–30 September 2011; MindTrek: Tampere, Finland, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamari, J.; Koivisto, J.; Sarsa, H. Does gamification work?—A literature review of empirical studies on gamification. In Proceedings of the 2014 47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 6–9 January 2014; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 3025–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Deterding, S.; Kuhn, K.A.; Staneva, A.; Stoyanov, S.; Hides, L. Gamification for health and wellbeing: A systematic review of the literature. Internet Interv. 2016, 6, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.H. Why do we like or dislike animals? Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2009, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschheuser, B.; Hamari, J.; Maedche, A. Cooperation or competition—When do people contribute more? A field experiment on gamification of crowdsourcing. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2019, 127, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, D.A. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development; Prentice Hall, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, M.C.; Andrews, E.; Biedenweg, K. A framework for environmental education strategies. Appl. Environ. Educ. Commun. 2007, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, H.; Luthe, T.; Sevaldson, B. Methodological Pluralism in Practice: A systemic design approach for place-based sustainability transformations. Context. Syst. Des. J. 2024, 2, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, G. Prototypes in Pinkenba; Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts, School of Architecture: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davidová, M.; Valverde Rojas, M.C.; Behnam, H. Codesigning More-than-Human Ecosystems with Social and Environmental Systems: The Gamification of NetWall and BioDiveIn. Land 2025, 14, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010165
Davidová M, Valverde Rojas MC, Behnam H. Codesigning More-than-Human Ecosystems with Social and Environmental Systems: The Gamification of NetWall and BioDiveIn. Land. 2025; 14(1):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010165
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavidová, Marie, María Claudia Valverde Rojas, and Hanane Behnam. 2025. "Codesigning More-than-Human Ecosystems with Social and Environmental Systems: The Gamification of NetWall and BioDiveIn" Land 14, no. 1: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010165
APA StyleDavidová, M., Valverde Rojas, M. C., & Behnam, H. (2025). Codesigning More-than-Human Ecosystems with Social and Environmental Systems: The Gamification of NetWall and BioDiveIn. Land, 14(1), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14010165







