How Does Urban Scale Influence Carbon Emissions?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data
3.3. Methods
4. Results
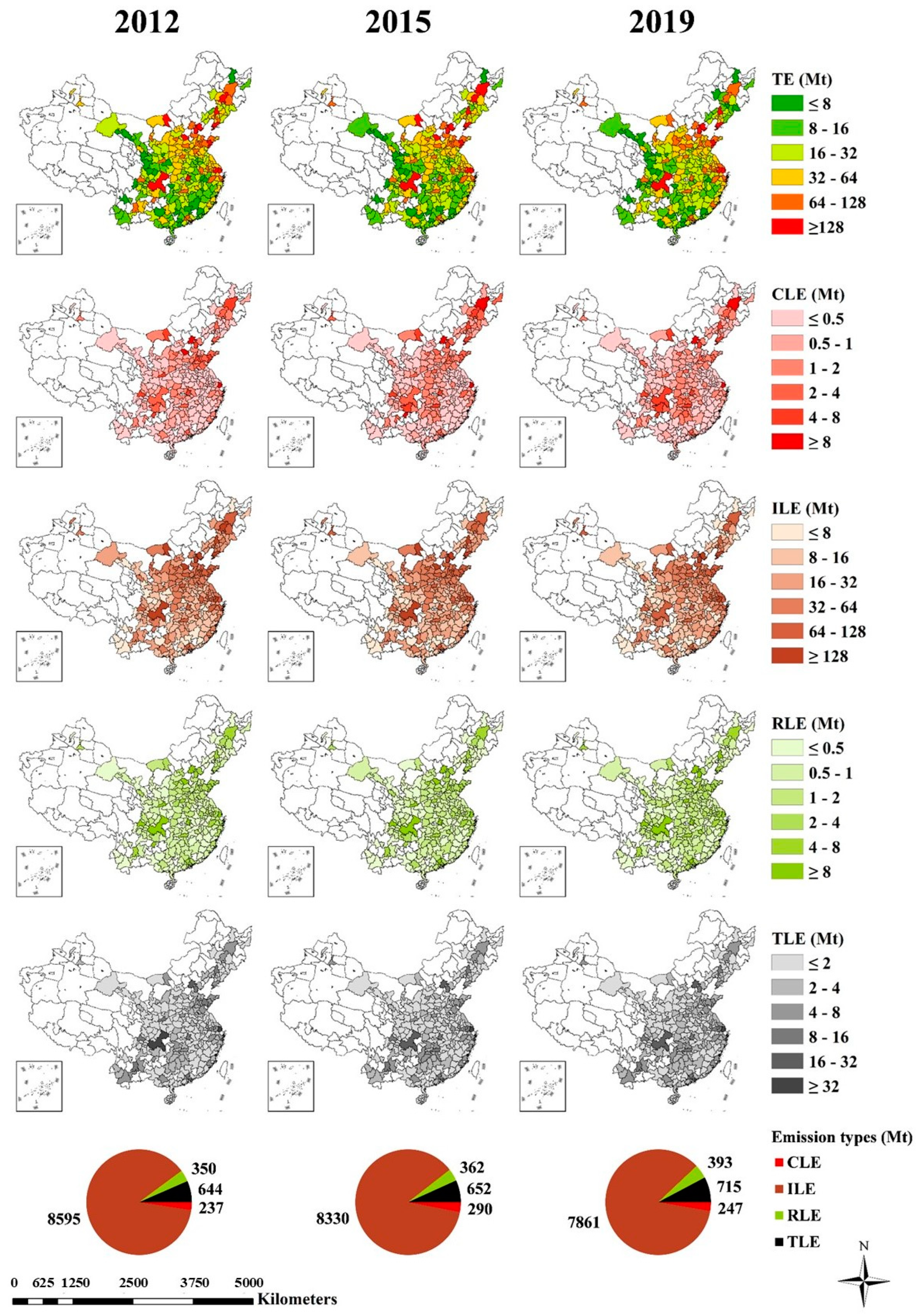
4.1. Spatial–Temporal Pattern of Carbon Emissions
4.2. Relationship between Carbon Emissions and Urban Scale
4.3. Detailed Analysis of Emissions on Four Types of Urban Construction Land
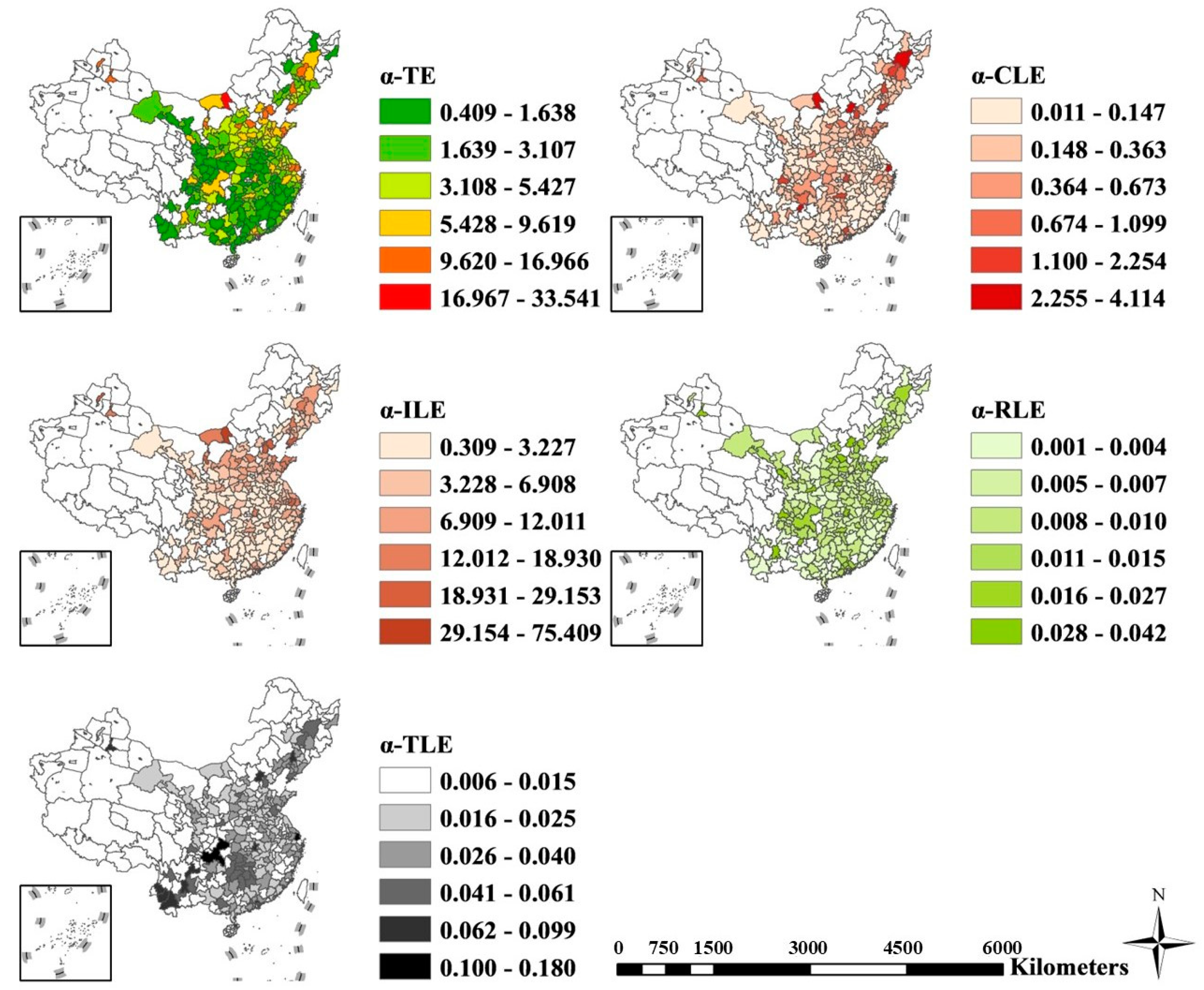
4.4. Distribution of Multiplier α of Carbon Emissions
5. Discussion
5.1. Implications for Developing a Low-Carbon Land-Use Layout
5.2. Impact of Urban Scale on Carbon Emissions
5.3. Multiplier Effect of Urban Expansion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muneer, T.; Celik, A.N.; Caliskan, N. Sustainable transport solution for a medium-sized town in Turkey—A case study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2011, 1, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, A. The Metabolism of Cities. Sci. Am. 1965, 213, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, K.; Yuan, W. Spatial heterogeneity and driving mechanisms of carbon emissions in urban expansion areas: A research framework coupled with patterns and functions. Land Use Policy. 2024, 143, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Loganathan, N.; Muzaffar, A.T.; Ahmed, K.; Jabran, M.A. How urbanization affects CO2 emissions in Malaysia? The application of STIRPAT model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Hua, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Q. The process of peak CO2 emissions in developed economies: A perspective of industrialization and urbanization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Salim, R.; Nielsen, I. Urbanization, openness, emissions, and energy intensity: A study of increasingly urbanized emerging economies. Energy Econ. 2016, 56, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridzuan, N.H.A.M.; Marwan, N.F.; Khalid, N.; Ali, M.H.; Tseng, M.L. Effects of agriculture, renewable energy, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions: Evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Huang, C.C. How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B.Q. How industrialization and urbanization process impacts on CO2 emissions in China: Evidence from nonparametric additive regression models. Energy Econ. 2015, 48, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, R.R. Does income inequality reshape the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis? A nonlinear panel data analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Yang, Y. Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions in China: A spatial panel data approach. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özokcu, S.; Özdemir, Ö. Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.M. Driving Factors of Transportation CO2 Emissions in Beijing: An Analysis from the Perspective of Urban Development. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2020, 8, 2050013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, G.B.; Brown, J.H.; Enquist, B.J. A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 1997, 276, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louf, R.; Barthelemy, M. How congestion shapes cities: From mobility patterns to scaling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Phibbs, P.; Simpson, R.; Wasnik, S. The scaling of income distribution in Australia: Possible relationships between urban allometry, city size, and economic inequality. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 603–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axtell, R.L. Zipf Distribution of U.S. Firm Sizes. Science 2001, 293, 1818–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neale, D.R.J.; Hendy, S.C. Power law distributions of patents as indicators of innovation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alves, L.G.A.; Ribeiro, H.V.; Lenzi, E.K.; Mendes, R.S. Empirical analysis on the connection between power-law distributions and allometries for urban indicators. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 409, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, M.; Reckien, D.; Pietrapertosa, F.; Eckersley, P.; Spyridaki, N.-A.; Krook-Riekkola, A.; Olazabal, M.; De Gregorio Hurtado, S.; Simoes, S.G.; Geneletti, D.; et al. Will climate mitigation ambitions lead to carbon neutrality? An analysis of the local-level plans of 327 cities in the EU. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, B. Coupling of carbon and energy flows in cities: A meta-analysis and nexus modelling. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.; Matsumoto, H.; Lun, Y. Establishment of City Level Carbon Dioxide Emission Baseline Database and Carbon Budgets for Developing Countries with Data Constraints. J. Asian Arch. Build. Eng. 2008, 7, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, S.S.B. Is there more traffic congestion in larger cities? -Scaling analysis of the 101 largest U.S. urban centers-. Transp. Policy 2017, 59, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, B. How does new-type urbanization affect air pollution? Empirical evidence based on spatial spillover effect and spatial Durbin model. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.B. Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.S.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Streets, D.G.; Wang, C. Direct and spillover effects of new-type urbanization on CO2 emissions from central heating sector and EKC analyses: Evidence from 144 cities in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 192, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Gao, S.; Li, S.J.; Feng, K.S. Strategizing the relation between urbanization and air pollution: Empirical evidence from global countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Xu, N.; Ji, M.; Zeng, J. Promoting or inhibiting? New-type urbanization and urban carbon emissions efficiency in China. Cities 2023, 140, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Jiao, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, G. Scaling of urban economic outputs: Insights both from urban population size and population mobility. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 88, 101657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.; West, G. A unified theory of urban living. Nature 2010, 467, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, H. Effects of land urbanization and land finance on carbon emissions: A panel data analysis for Chinese provinces. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 2013, 57, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapola, D.M.; Martinelli, L.A.; Peres, C.A.; Ometto, J.P.H.B.; Ferreira, M.E.; Nobre, C.A.; Aguiar, A.P.D.; Bustamante, M.M.C.; Cardoso, M.F.; Costa, M.H.; et al. Pervasive transition of the Brazilian land-use system. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kafy, A.; Faisal, A.-A.; Al Rakib, A.; Fattah, A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Sattar, G.S. Impact of vegetation cover loss on surface temperature and carbon emission in a fastest-growing city, Cumilla, Bangladesh. Build. Environ. 2022, 208, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Li, C.L.; Shi, K.F.; Liu, S.R.; Chang, Z.J. Exploring the effect of urban sprawl on carbon dioxide emissions: An urban sprawl model analysis from remotely sensed nighttime light data. Environ. Impact Asses. Rev. 2022, 93, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Brandt, M.; Tong, X.W.; Ciais, P.; Yue, Y.M.; Xiao, X.M.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, K.L.; Fensholt, R. A large but transient carbon sink from urbanization and rural depopulation in China. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, P.R.; Holdren, J.P. Impact of population growth. Science 1971, 171, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkias, M.; Lobo, J.; Strumsky, D.; Seto, K.C. Does size matter? Scaling of CO2 emissions and US urban areas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B.Q. Investigating spatial variability of CO2 emissions in heavy industry: Evidence from a geographically weighted regression model. Energy Policy 2021, 149, 112011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.H.; Hu, X.W. The effects of urbanization and urban sprawl on CO2 emissions in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 1792–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, B. The impact of urbanization on residential energy consumption in China: An aggregated and disaggregated analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.F.; Cao, R.J.; Du, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, W.G.; Liu, B.S. Nonlinear influence of urbanization on China’s urban residential building carbon emissions: New evidence from panel threshold model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, T.F.; Li, X.H.; Cai, W.G.; Zuo, J.; Jia, F.Y.; Wei, H.F. Exploring the impact of urbanization on urban building carbon emissions in China: Evidence from a provincial panel data model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, E.; He, C.; Lei, K.; Gao, W. Impact of urban land development on carbon emission performance based on a multidimensional framework. Environmental Impact Assessment Review. 2024, 105, 107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.V.; Rybski, D.; Kropp, J.P. Effects of changing population or density on urban carbon dioxide emissions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabani, A.E.; Silitonga, A.S.; Ong, H.C.; Mahlia, T.; Masjuki, H.H.; Badruddin, I.A.; Fayaz, H. Non-edible vegetable oils: A critical evaluation of oil extraction, fatty acid compositions, biodiesel production, characteristics, engine performance and emissions production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 211–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Zeng, J.Y.; Liu, X.P. Examining the multiple impacts of technological progress on CO2 emissions in China: A panel quantile regression approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.; Alnour, M.; Jahanger, A.; Onwe, J.C. Do technological innovation and urbanization mitigate carbon dioxide emissions from the transport sector? Technol. Soc. 2022, 71, 102128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Gao, M.; Mangla, S.K.; Song, M.L.; Wen, J. Effects of technological changes on China’s carbon emissions. Technol. Forecast Soc. Change 2020, 153, 119938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Deng, X.Z.; Phillips, F.; Fang, C.L.; Wang, C. Impacts of industrial structure and technical progress on carbon emission intensity: Evidence from 281 cities in China. Technol. Forecast Soc. Change 2020, 154, 119949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.L.; Salman, M.; Dauda, L. Effect of urbanization and international trade on CO2 emissions across 65 belt and road initiative countries. Energy 2020, 196, 117102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Zhu, J.P. Impact of China’s new-type urbanization on energy intensity: A city-level analysis. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Xie, R.; Lu, Y.; Fang, J.Y.; Liu, Y. The effects of urban agglomeration economies on carbon emissions: Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, C. Decouple transport CO2 emissions from China’s economic expansion: A temporal-spatial analysis. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 79, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.C.; Wen, C.; Clarke, G.; Turner, A.; Ke, X.L.; You, L.Z.; Tang, L.P. Cropland displacement contributed 60% of the increase in carbon emissions of grain transport in China over 1990–2015. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendrill, F.; Persson, U.M.; Godar, J.; Kastner, T.; Moran, D.; Schmidt, S.; Wood, R. Agricultural and forestry trade drives large share of tropical deforestation emissions. Glob. Environ. Change 2019, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Industrial structure, technical progress and carbon intensity in China’s provinces. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Wang, F. How does digital inclusive finance affect carbon intensity? Econ. Anal. Policy 2022, 75, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Sharif, A.; Ahmad, P.; Jermsittiparsert, K. Asymmetric role of tourism development and technology innovation on carbon dioxide emission reduction in the Chinese economy: Fresh insights from QARDL approach. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Guan, D.; Hubacek, K.; Zheng, B.; Davis, S.J.; Jia, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Fromer, N.; Mi, Z.; et al. City-level climate change mitigation in China. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq0390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.A.; Andrade, J.S., Jr.; Makse, H.A. Large cities are less green. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.R. Scaling. Why is animal size so important? Endeavour 1985, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, N.; Gudmundsson, A.; French, J.R. CO2 emissions in relation to street-network configuration and city size. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 35, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.; Lobo, J.; Helbing, D.; Kuhnert, C.; West, G.B. Growth, innovation, scaling, and the pace of life in cities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7301–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, V. Zipf zipped. J. Urban Econ. 2005, 57, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broxterman, D.; Yezer, A. Human capital divergence and the size distribution of cities: Is Gibrat’s law obsolete? Urban Stud. 2021, 58, 2549–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Val, R.; Ximénez-de-Embún, D.P.; Sanz-Gracia, F. A long-term, regional-level analysis of Zipf’s and Gibrat’s laws in the United States. Cities 2024, 149, 104946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Cheng, H. Exploring the temporal and spatial effects of city size on regional economic integration: Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Qu, Y.; Shu, B.; Huang, T. Decoupling relationship between urban land use morphology and carbon emissions: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Linlin, X.; Weining, X. Analyzing spatial patterns of urban carbon metabolism: A case study in Beijing, China. Landsc. Urban Plan 2014, 130, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing urban forms and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Hu, J.; Ou, J. Examining the impacts of socioeconomic factors, urban form, and transportation networks on CO2 emissions in China’s megacities. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Bi, J. The carbon emissions of Chinese cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6197–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, P.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Taheri, M.M.; Gohari, M.; Abd Majid, M.Z. A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an overview of the top ten CO2 emitting countries). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayao, M.M.; Blackhurst, M.F.; Matthews, H.S. Do US metropolitan core counties have lower scope 1 and 2 CO2 emissions than less urbanized counties? Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; He, Z.; Long, R. Factors that influence carbon emissions due to energy consumption in China: Decomposition analysis using LMDI. Appl. Energy 2014, 127, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Z. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, influencing factors of land use carbon emissions, and low-carbon development in Hubei Province, China. Ecol. Inf. 2024, 81, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Jiang, X.; Gouldson, A.; Sudmant, A.; Guan, D.; Colenbrander, S.; Xue, T.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q. Climate change mitigation in Chinese megacities: A measures-based analysis of opportunities in the residential sector. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Long, Y. Urban-scale carbon footprint evaluation based on citizen travel demand in Japan. Appl. Energy 2021, 286, 116462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Shuai, C.; Shen, L.; Ye, G. Peaks of transportation CO2 emissions of 119 countries for sustainable development: Results from carbon Kuznets curve. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 550–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Dai, S.; Ren, Y. More fragmentized urban form more CO2 emissions? A comprehensive relationship from the combination analysis across different scales. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Chuai, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Thompson, J.R. Carbon emissions from land-use change and management in China between 1990 and 2010. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C. Land use, total carbon emissions change and low carbon land management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moomaw, R.L. Productivity and City Size: A Critique of the Evidence. Q. J. Econ. 1981, 96, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.W. How urbanization affects energy use in developing countries. Energy Policy 1991, 19, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, Y. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Evolution between Carbon Emissions, Industrial Structure, and Regional Innovation of Counties in Shandong Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Xia, C.; Xiang, M.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J. The impact of urban scale on carbon metabolism—A case study of Hangzhou, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X. China’s city-level energy-related CO2 emissions: Spatiotemporal patterns and driving forces. Appl. Energy 2017, 200, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. What is Special About Spatial Data Alternative Perspectives on Spatial Data Analysis; NCGIA Technical Report; University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Shang, Y. Multiscale analysis on spatiotemporal dynamics of energy consumption CO2 emissions in China: Utilizing the integrated of DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China’s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, J. Impact of urban density on carbon emissions in China. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 6153–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variable | Original Model | Revised Model |
| Constant | 3.41 *** | 0.898 |
| LAND | −0.043 * | −0.179 *** |
| POP | / | 0.311 ** |
| ECON | / | 0.174 *** |
| Adjusted R-squared | 0.934 | 0.950 |
| F-statistic | 113.504 *** | 113.933 *** |
| Emissions Type | CLE | ILE | RLE | TLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −0.724 *** | 3.13 *** | −0.627 *** | 0.253 *** |
| LAND | −0.013 | −0.03 * | 0.091 *** | 0.075 *** |
| Adjusted R-squared | 0.897 | 0.924 | 0.914 | 0.963 |
| F-statistic | 70.909 *** | 97.889 *** | 85.488 *** | 210.823 *** |
| Emissions Type | CLE | ILE | RLE | TLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | −1.928 | 1.160 | −5.086 *** | −3.813 *** |
| LAND | −0.005 | −0.024 | −0.128 ** | −0.074 *** |
| POP | 0.554 ** | 0.528 ** | 0.147 | 0.033 |
| ECON | −0.280 *** | −0.158 ** | 0.581 *** | 0.571 *** |
| Adjusted R-squared | 0.894 | 0.907 | 0.905 | 0.951 |
| F-statistic | 70.782 *** | 97.494 *** | 87.614 *** | 223.785 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; He, C.; Wang, S.; Li, F. How Does Urban Scale Influence Carbon Emissions? Land 2024, 13, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081254
Yang J, Feng X, Li Y, He C, Wang S, Li F. How Does Urban Scale Influence Carbon Emissions? Land. 2024; 13(8):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081254
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiayu, Xinhui Feng, Yan Li, Congying He, Shiyi Wang, and Feng Li. 2024. "How Does Urban Scale Influence Carbon Emissions?" Land 13, no. 8: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081254
APA StyleYang, J., Feng, X., Li, Y., He, C., Wang, S., & Li, F. (2024). How Does Urban Scale Influence Carbon Emissions? Land, 13(8), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081254






