Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
2.3. Technical Framework and Methods
2.3.1. Development Scenarios
2.3.2. SD-PLUS Model
2.3.3. InVEST-HQ Model
2.3.4. Spatial Autocorrelation and Hot-spot Analysis of HQ
2.3.5. GeoDetector
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Simulation Accuracy Using Different Land-Use Data
3.2. Characteristics of Land-Use Change
3.2.1. Spatiotemporal Changes of LULC (Historical Period)
3.2.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in LULC (Simulation Period)
3.3. Change and Response of HQ
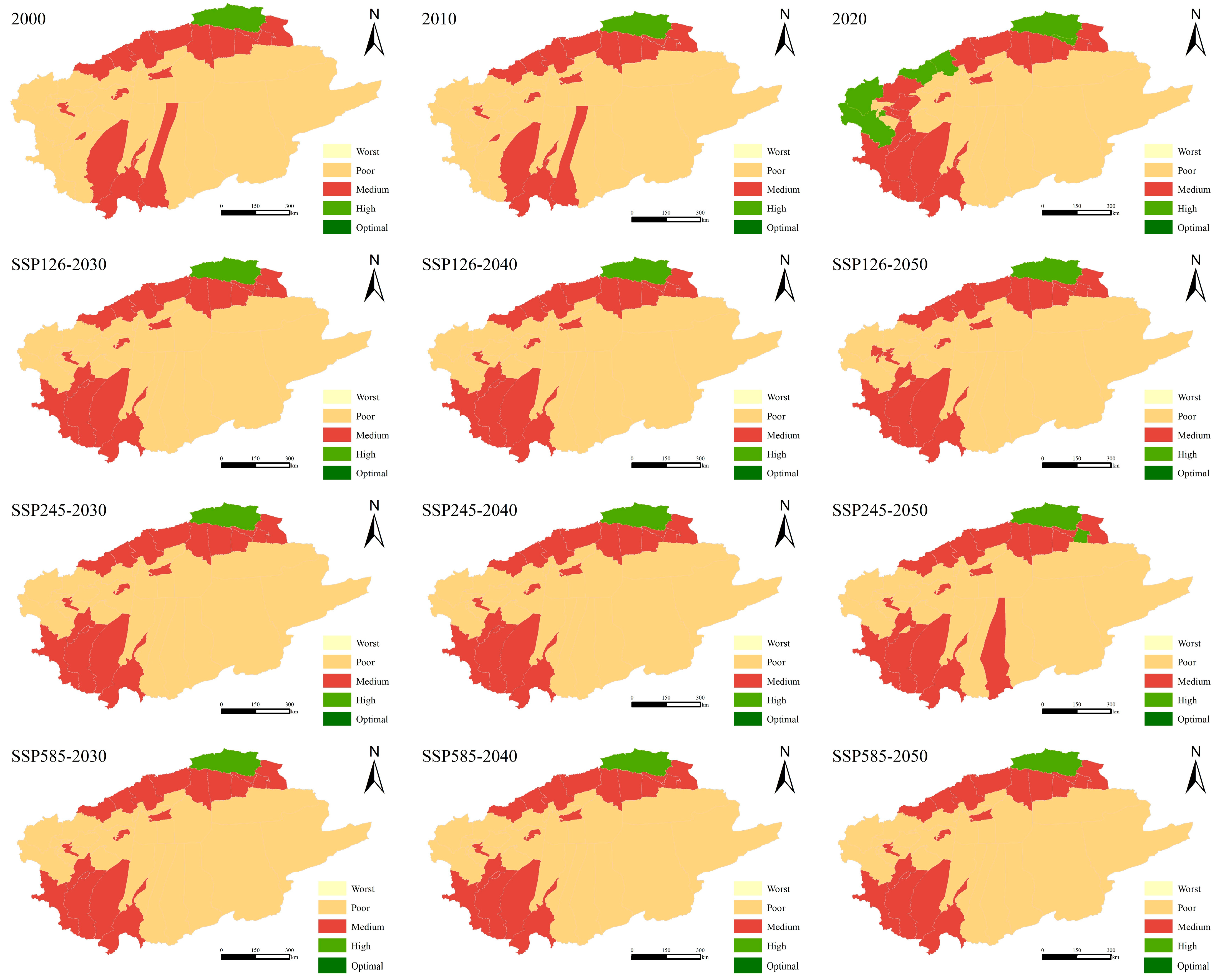
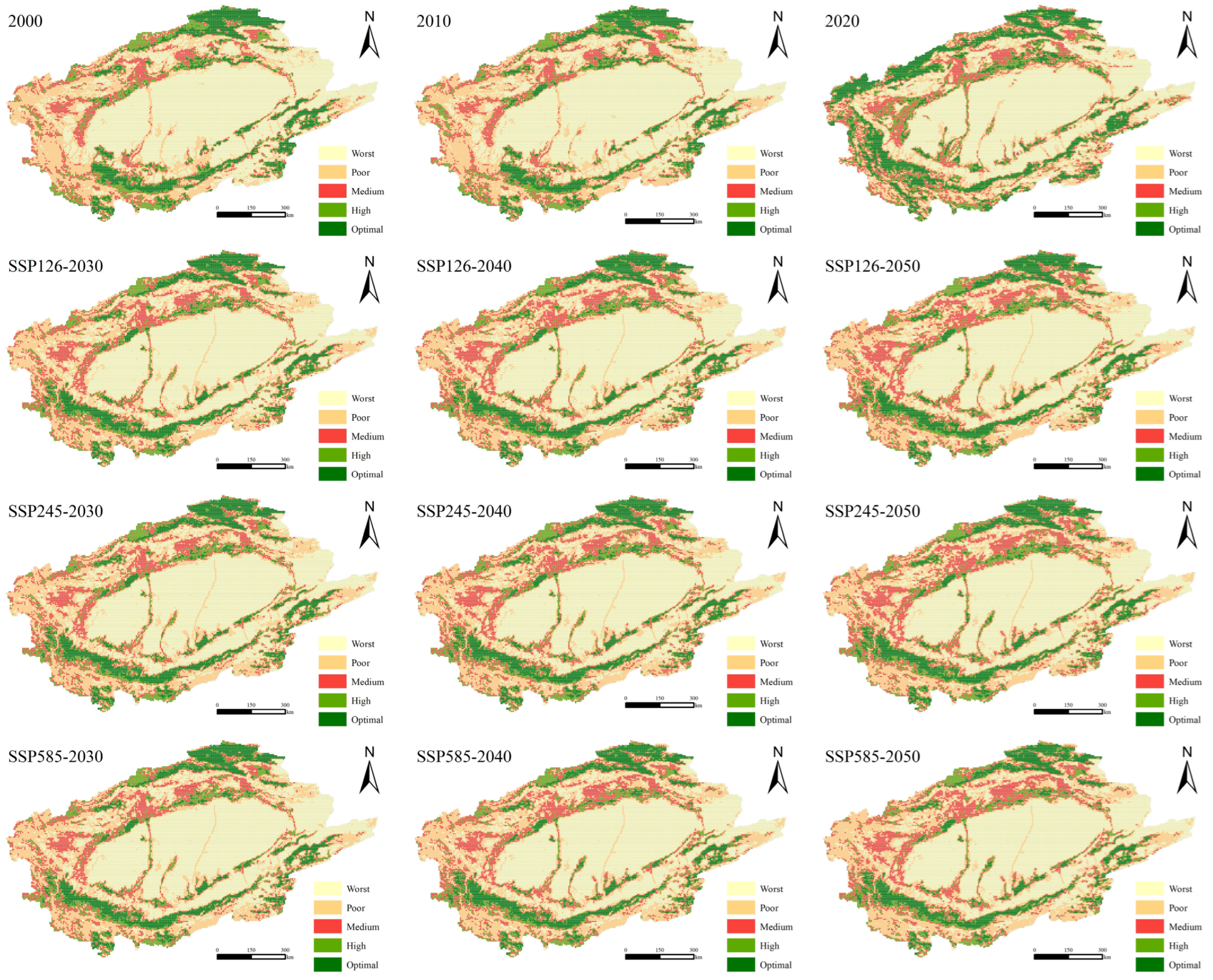
3.3.1. HQ Distribution and Evolution Under Different Scales
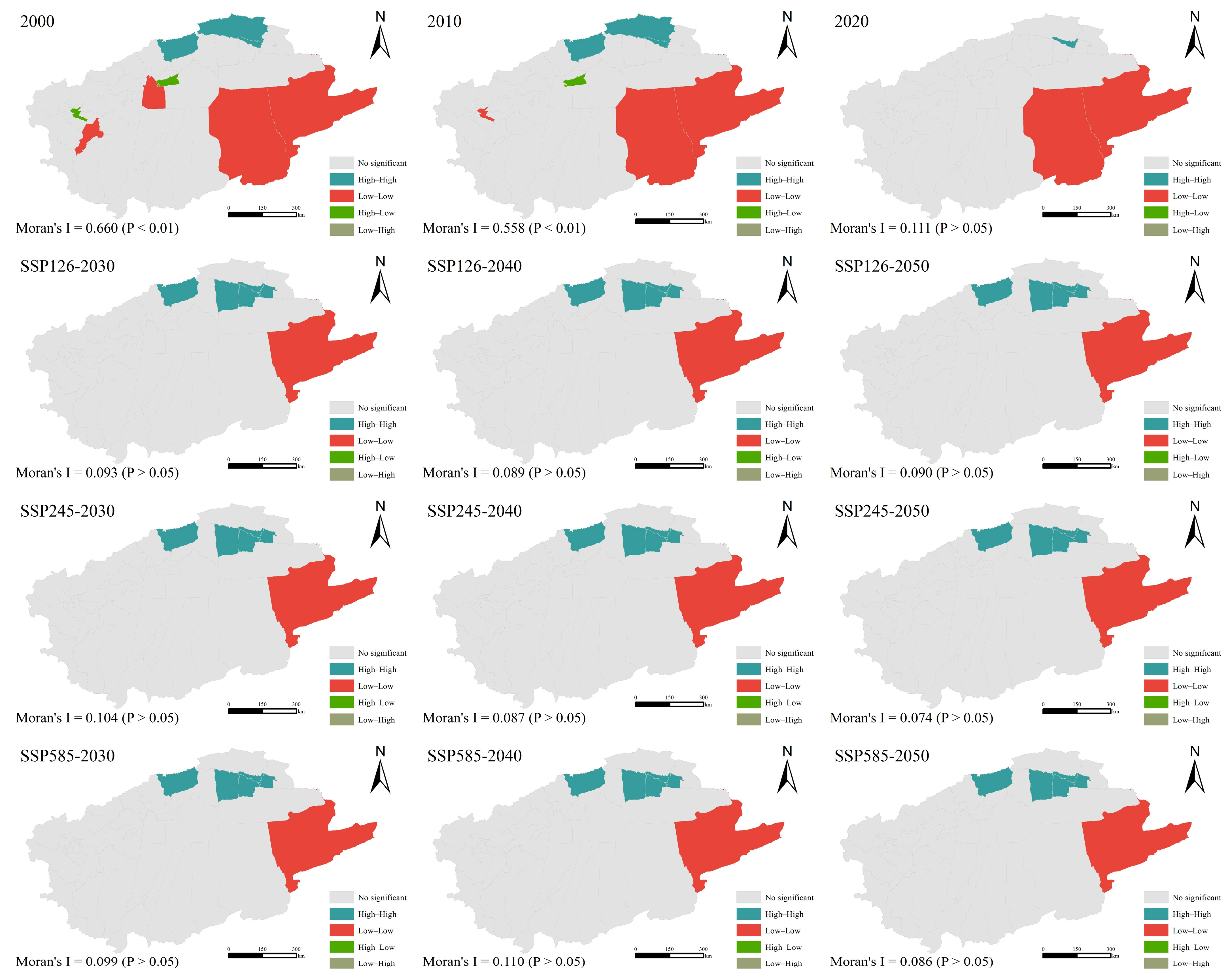
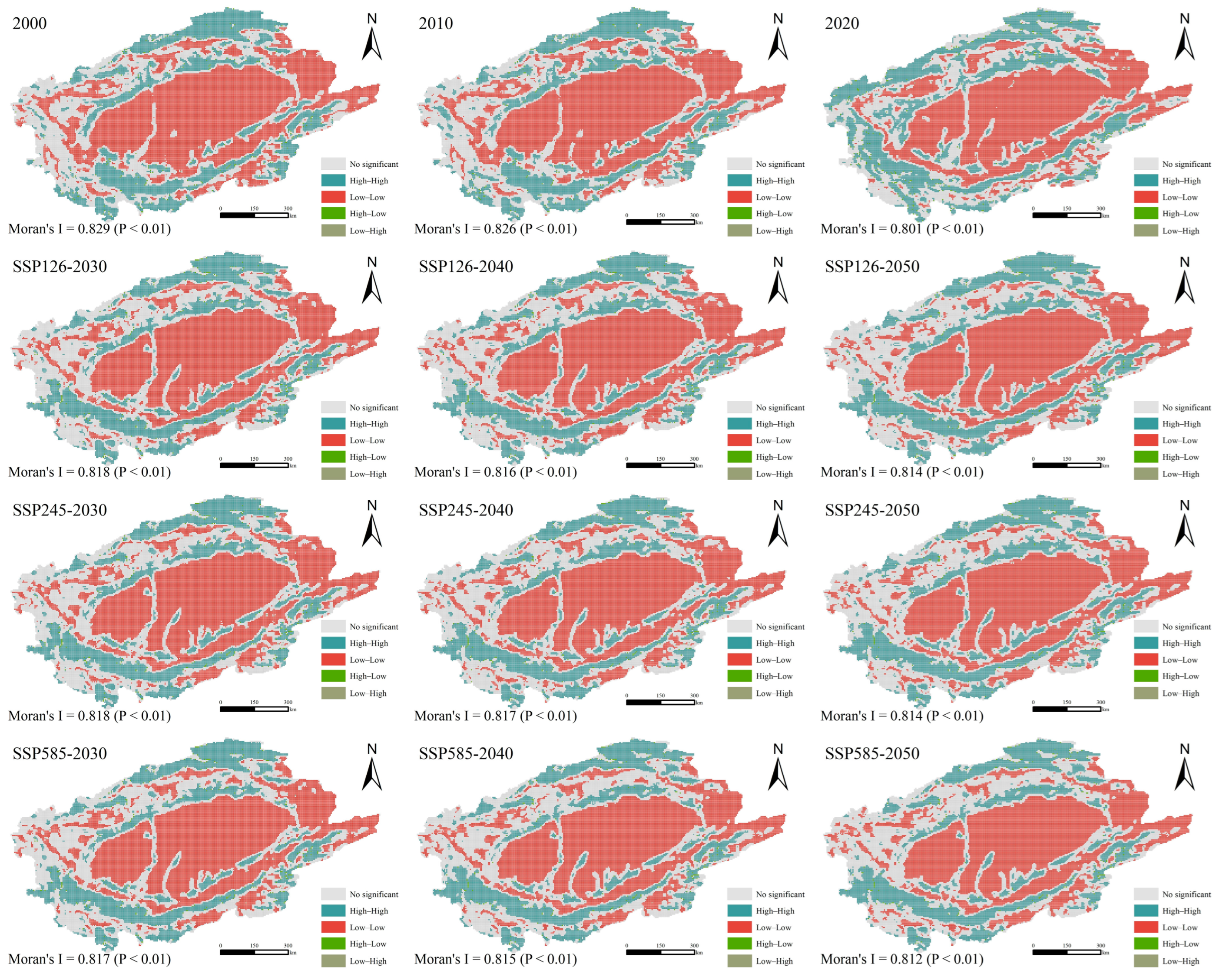
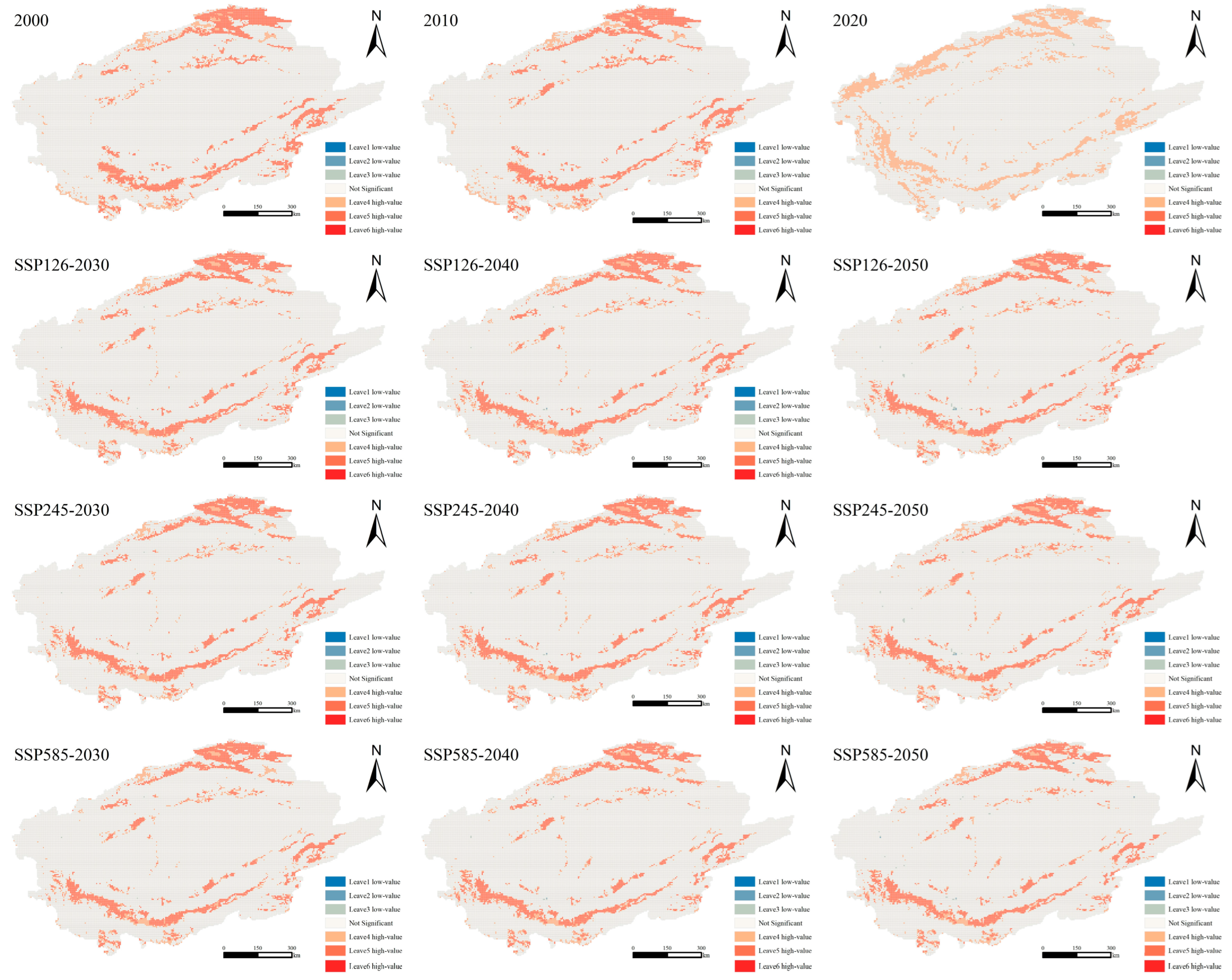
3.3.2. HQ Clustering under Different Scales
4. Discussion
4.1. Response Characteristics of LULC and Data Selection Principles
4.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of HQ
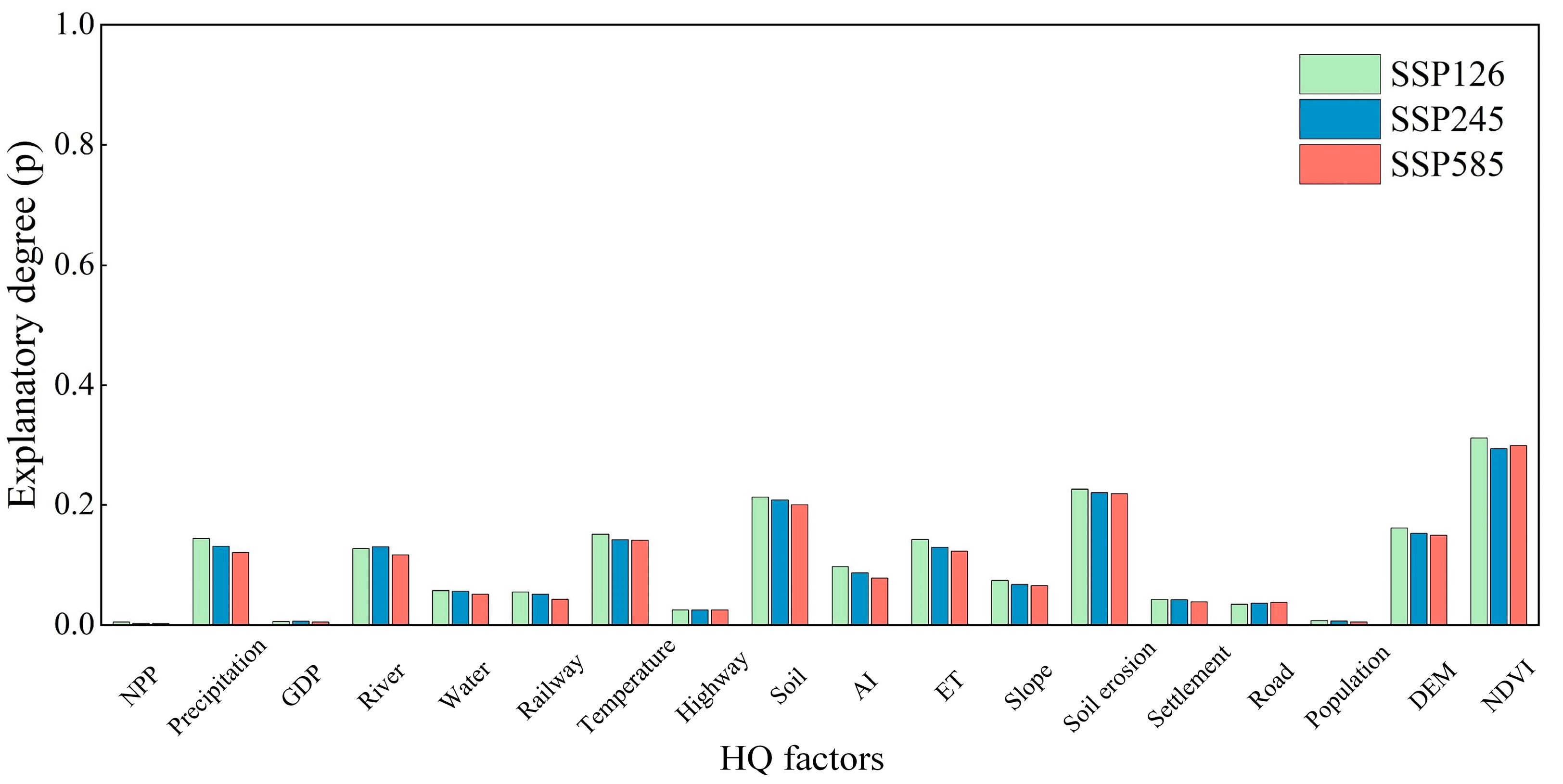
4.3. Driving Factors and the Impact of HQ
4.4. Comparison of HQ with Other Regions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Feyisa, G.L. Landscape change effects on habitat quality in a forest biosphere reserve: Implications for the conservation of native habitats. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Feng, Q.; Li, Z.X.; Lu, Z.X.; Zhang, B.J.; Cheng, W.J. Land Use/Cover-Related Ecosystem Service Value in Fragile Ecological Environments: A Case Study in Hexi Region, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, E.; Inácio, M.; Bogdzevic, K.; Kalinauskas, M.; Karnauskait, D.; Pereira, P. Future scenarios impact on land use change and habitat quality in Lithuania. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehring, M.; Ott, E.; Hummel, D. Ecosystem services supply and demand assessment: Why social-ecological dynamics matter. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, A.L.; Evans, J.P.; De Kauwe, M.G. Anthropogenic climate change has driven over 5 million km2 of drylands towards desertification. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.J.; Chen, Y.N. The effects of landscape change on habitat quality in arid desert areas based on future scenarios: Tarim River Basin as a case study. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1031859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, Q.; Li, L. A new approach to land use optimization and simulation considering urban development sustainability: A case study of Bortala, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Z.J. Evaluating potential impacts of land use changes on water supply-demand under multiple development scenarios in dryland region. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerten, D.; Heck, V.; Jäegermeyr, J.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Fetzer, I.; Jalava, M.; Kummu, M.; Lucht, W.; Rockström, J.; Schaphoff, S.; et al. Feeding ten billion people is possible within four terrestrial planetary boundaries. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdugo, M.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Soliveres, S.; Hernández-Clemente, R.; Zhao, Y.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Gross, N.; Saiz, H.; Maire, V.; Lehman, A.; et al. Global ecosystem thresholds driven by aridity. Science 2020, 367, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.A.; Wu, H.F.; Han, H.R.; Cheng, X.Q.; Kang, F.F. Dramatic shift in the drivers of ecosystem service trade-offs across an aridity gradient: Evidence from China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Betz, F.; Aishan, T.; Halik, U.; Abliz, A. Impact of water supply on the restoration of the severely damaged riparian plants along the Tarim River in Xinjiang, Northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Aishan, T.; Halik, Ü.; Wei, Z.C.; Wumaier, M. A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis of Research Progress and Trends on Decay and Cavity Trees in Forest Ecosystem over 20 Years: An Application of the CiteSpace Software. Forests 2022, 13, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halik, Ü.; Aishan, T.; Betz, F.; Kurban, A.; Rouzi, A. Effectiveness and challenges of ecological engineering for desert riparian forest restoration along China’s largest inland river. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, P.L.; Hu, S.G.; Frazier, A.E.; Yang, S.F.; Song, X.Y.; Qu, S.J. The dynamic relationships between landscape structure and ecosystem services: An empirical analysis from the Wuhan metropolitan area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourado, G.F.; Rallings, A.M.; Viers, J.H. Overcoming persistent challenges in putting environmental flow policy into practice: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyka, I.; Hysa, A.; Dervishi, S.; Solomun, M.K.; Kuriqi, A.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Sestras, P. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Landscape Transformation in Western Balkans’ Metropolitan Areas. Land 2022, 11, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.Y.; Hu, Y.F.; Lei, Z.Y.; Yan, H.M.; Ye, J.Z.; Wang, H. Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics and Its Driving Mechanism of Land Use/Cover in Vietnam from 2000 to 2020. Land 2022, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.Y.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.C.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.G.; Li, J.; Zhan, C.S. Land use/land cover prediction and analysis of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under different scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Mankin, J.S.; Marvel, K.; Williams, A.P.; Smerdon, J.E.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Twenty-First Century Drought Projections in the CMIP6 Forcing Scenarios. Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, P.H.; Tian, Y.S.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, Y.Y. Exploring the impact of integrated spatial function zones on land use dynamics and ecosystem services tradeoffs based on a future land use simulation (FLUS) model. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.C.; Halik, U.; Aishan, T.; Abliz, A.; Welp, M. Spatial distribution patterns of trunk internal decay of Euphrates poplar riparian forest along the Tarim River, northwest China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 522, 120434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusup, A.; Halik, Ü.; Abliz, A.; Aishan, T.; Keyimu, M.; Wei, J.X. Population Structure and Spatial Distribution Pattern of Populus euphratica Riparian Forest Under Environmental Heterogeneity Along the Tarim River, Northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 844819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishan, T.; Mumin, R.; Halik, U.; Jiang, W.; Sun, Y.X.; Yusup, A.; Chen, T.Y. Patterns in Tree Cavities (Hollows) in Euphrates Poplar (Populus euphratica, Salicaceae) along the Tarim River in NW China. Forests 2024, 15, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.F.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.P.; Sun, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.Q. Land Use Dynamic Changes in an Arid Inland River Basin Based on Multi-Scenario Simulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Sun, F.B. Global gridded GDP data set consistent with the shared socioeconomic pathways. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Guo, F.; Wang, J.C.; Cai, W.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.C. Provincial and gridded population projection for China under shared socioeconomic pathways from 2010 to 2100. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Aishan, T.; Ma, X. Coupled water-habitat-carbon nexus and driving mechanisms in the Tarim River Basin: A multi-scenario simulation perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2024, submitted.
- Song, J. Modeling of Land Use/Cover Changes and Ecosystem Services Based on PLUS and InVEST Models—A Case Study of the Tarim River Basin. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China, 2 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, X.; Mao, Y.T.; Li, L.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, Q. Dynamic simulation of land use change and assessment of carbon storage based on climate change scenarios at the city level: A case study of Bortala, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, H.; Keenan, R.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Stork, N.E.; Kasel, S. Spatial assessment and mapping of biodiversity and conservation priorities in a heavily modified and fragmented production landscape in north-central Victoria, Australia. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Sun, Y.L.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.W.; Li, K. Land use and habitat quality change in the Yellow River Basin: A perspective with different CMIP6-based scenarios and multiple scales. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Halik, U.; Shi, L.; Welp, M. Multi-scenario dynamic prediction of ecological risk assessment in an arid area of northwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.J.; Qin, Q.T.; You, H.T.; Han, X.W.; Zhou, G.Q. Patch Pattern and Ecological Risk Assessment of Alpine Grassland in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Li, X.P.; Yu, J.J.; Li, H. The impact of the spatial agglomeration of foreign direct investment on green total factor productivity of Chinese cities. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.A.; Tao, F.; Liu, R.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Leng, H.J.; Zhou, T. Multi-scenario simulation and ecological risk analysis of land use based on the PLUS model: A case study of Nanjing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.J.; Wu, H.Q.; Jiang, P.A.; Zheng, K.; Liu, Z.; Dong, T.; He, P.X.; Fan, X. Food-water-land-ecosystem nexus in typical Chinese dryland under different future scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.B.; Xu, H.L.; Guo, B.; Deng, X.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.Y. Regulating water disturbance for mitigating drought stress to conserve and restore a desert riparian forest ecosystem. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Q.; Jiang, E.H.; Yin, H.J.; Wu, K.; Dong, G.T. Ultrashort-term responses of riparian vegetation restoration to adjacent cycles of ecological water conveyance scheduling in a hyperarid endorheic river basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, J.; Ordens, C.M.; Barnett, S.; Djordjevic, S.; Chen, A.S. Small-scale land use change modelling using transient groundwater levels and salinities as driving factors—An example from a sub-catchment of Australia’s Murray-Darling Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagib, N.A.; Khalifa, M.; Rahma, A.E.; Babker, Z.; Gamaledin, S.I. Performance of major mechanized rainfed agricultural production in Sudan: Sorghum vulnerability and resilience to climate since 1970. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, D.; Dube, T.; Mazvimavi, D. Use of multi-temporal satellite data for monitoring pool surface areas occurring in non-perennial rivers in semi-arid environments of the Western Cape, South Africa. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Ma, X.F.; Huo, T.C.; Zhu, J.T.; Zhao, C.Y. Assessment of the environmental effects of ecological water conveyance over 31 years for a terminal lake in Central Asia. Catena 2022, 208, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Chavez, H.M.; Kissling, W.D.; Veen, L.E.; Swenson, N.G.; van Bodegom, P.M. Spatial scale dependence of factors driving climate regulation services in the Americas. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Xie, B.G.; Gao, C.; Zhou, K.C.; Liu, C.C.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, J.Y.; Xie, J. Impacts of natural and human factors on water-related ecosystem services in the Dongting Lake Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Hu, H.F.; Sun, W.J.; Zhu, J.J.; Liu, G.B.; Zhou, W.M.; Zhang, Q.F.; Shi, P.L.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, X.; et al. Effects of national ecological restoration projects on carbon sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Song, W. Integrating potential ecosystem services losses into ecological risk assessment of land use changes: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Hu, B.F.; Peng, J.; Bourennane, H.; Biswas, A.; Opitz, T.; Shi, Z. Spatio-temporal variation and dynamic scenario simulation of ecological risk in a typical artificial oasis in northwestern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.C.; Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, Y.Z.; Tao, F.L.; Hu, J. A coupled human-natural system analysis of water yield in the Yellow River basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Peng, J.; Dong, J.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Q.Y.; Lyu, D.N.; Qiao, R.L.; Zhang, Z.M. Spatial correlation between the changes of ecosystem service supply and demand: An ecological zoning approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 217, 104258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.L.; Ding, J.L.; Han, L.J.; Li, J.; Ge, X.Y. Predicting land change trends and water consumption in typical arid regions using multi-models and multiple perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Xie, F.; Ling, F.; Du, Y. Monitoring Surface Water Inundation of Poyang Lake and Dongting Lake in China Using Sentinel-1 SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.F. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanisms of Ecosystem Service Value in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
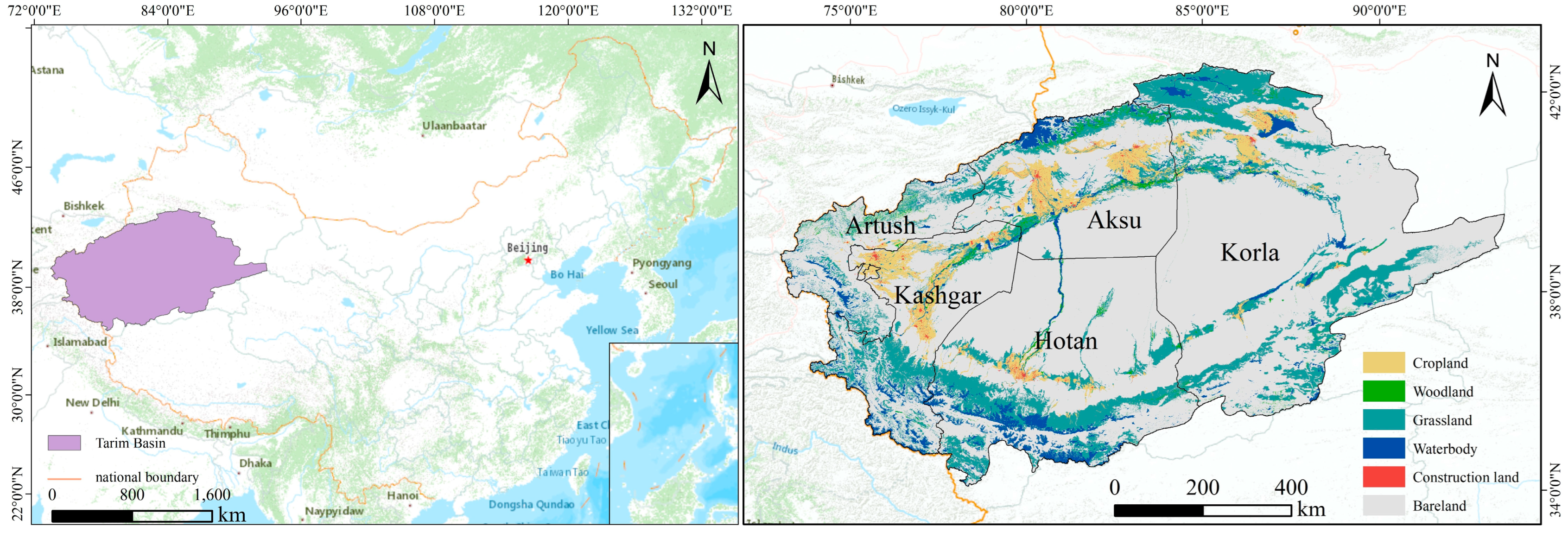


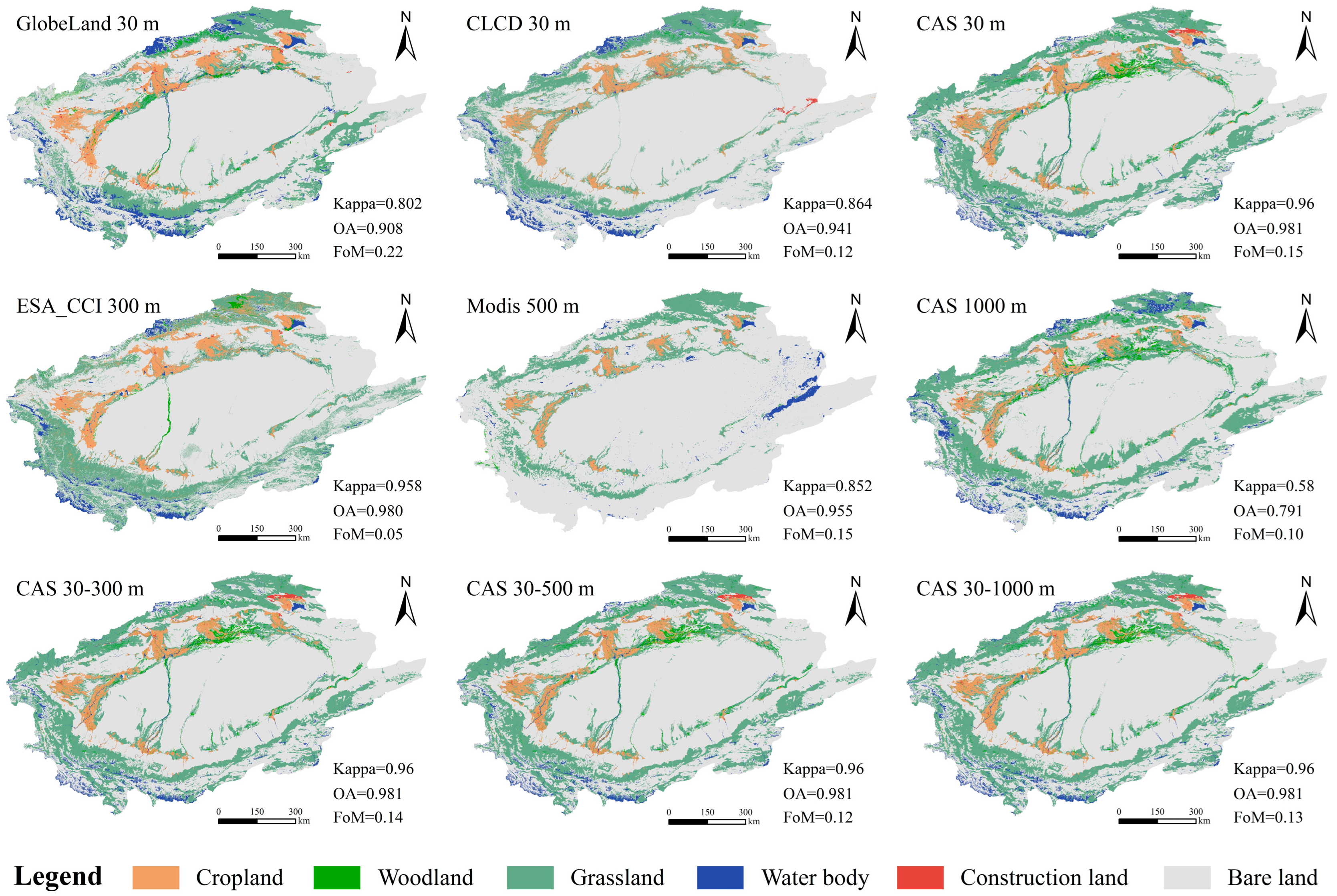

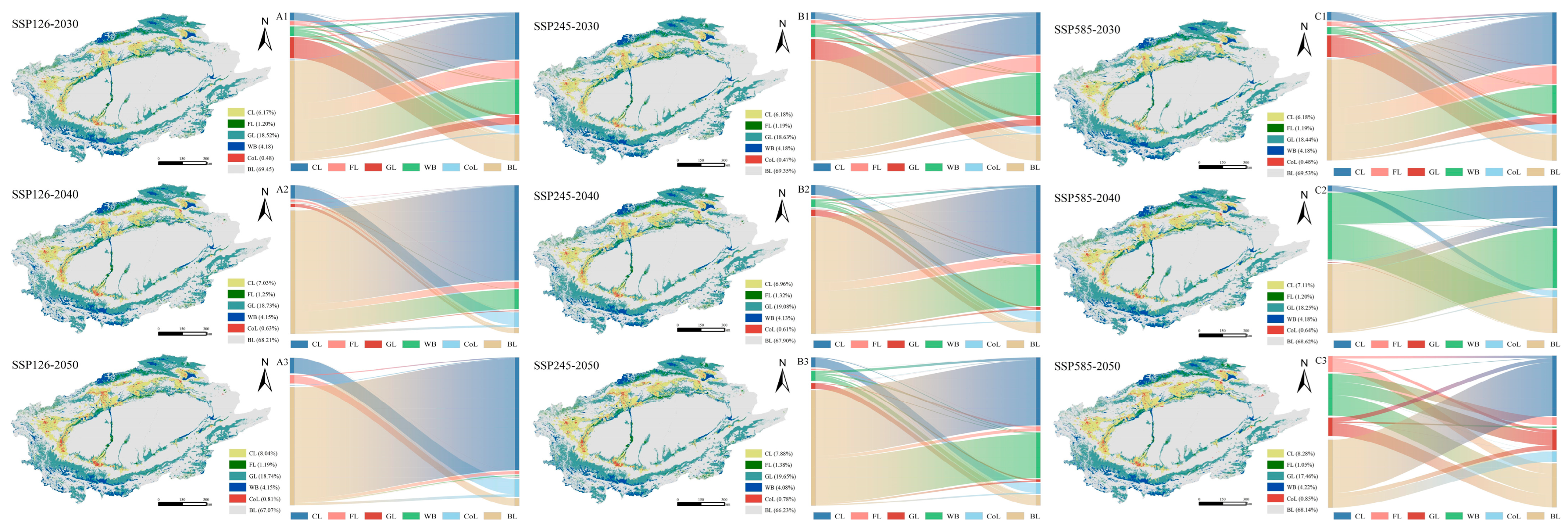
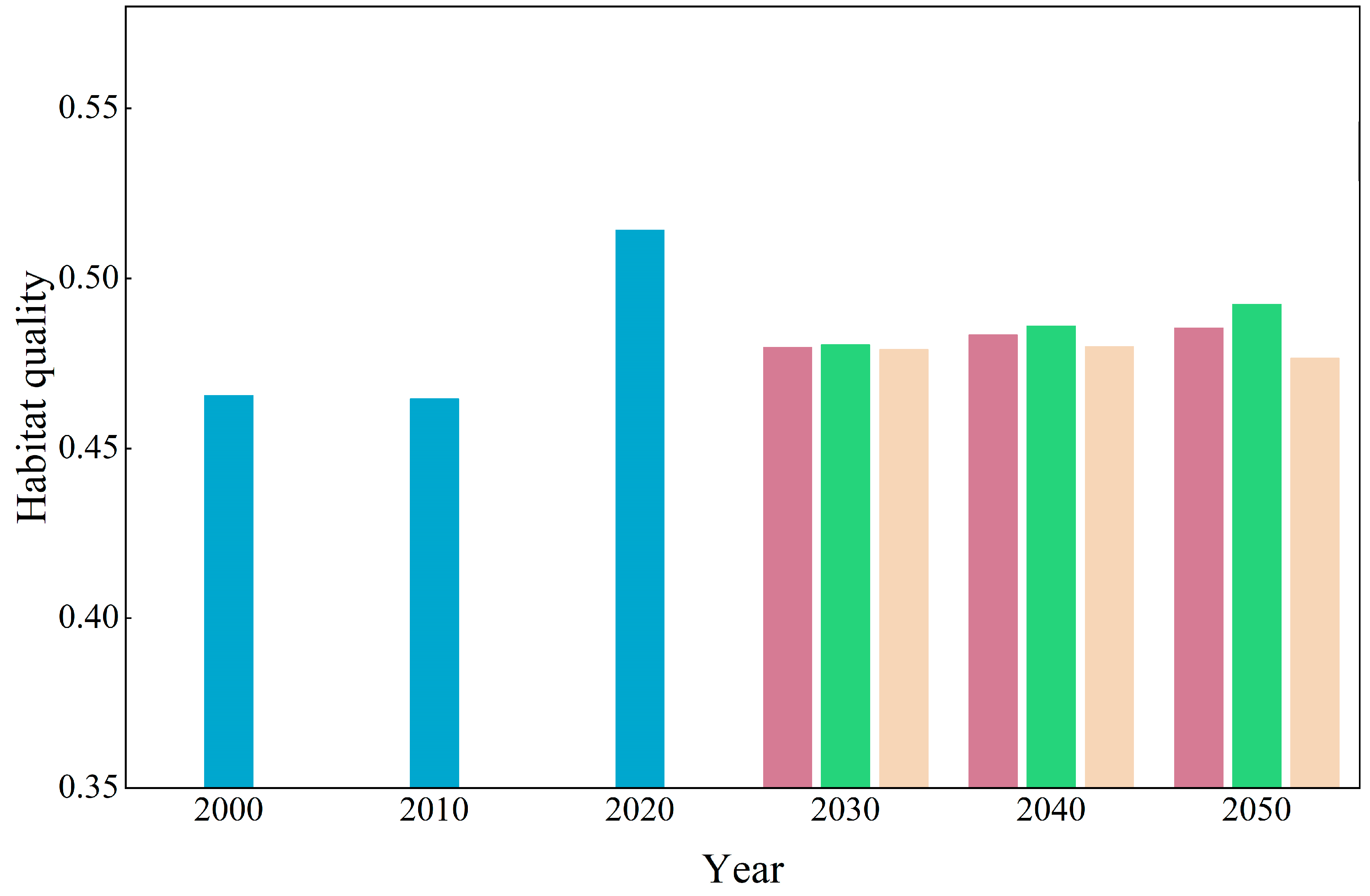

| Sub-Data | Year (s) | Resolution | Database Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| LULC | 2000–2020 | 30 m 300 m 500 m 1 km | National Catalogue Service For Geographic Information (https://www.webmap.cn), China’s 30 m annual land-cover product (https://essd.copernicus.org), National Ecological Science Data Center (http://www.nesdc.org.cn), Climate Data Store (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu), and Earth Data (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov) |
| DEM/Slope | 2020 | 30 m | Earth Data (https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov) |
| NDVI | 2020 | 30 m | National Ecological Science Data Center (http://www.nesdc.org.cn) |
| Night light data | 2020 | 500 m | Resource and Environmental Science Data Platform (https://www.resdc.cn) |
| GDP/Population | 2019 | 1 km | |
| Soil | 1995 | 1 km | |
| Erosion | 2010 | 1 km | |
| ET | 2000 | 1 km | Plant Science Data Center (https://www.plantplus.cn) |
| AI | |||
| Precipitation | 2020 | 1 km | A Big Earth Data for Three Poles (https://poles.tpdc.ac.cn) |
| Temperature | |||
| Railway | 2023 | OpenStreetMap (https://www.openstreetmap.org) | |
| Highway | |||
| Road | |||
| Settlement | |||
| River | |||
| Water | |||
| Socioeconomic data | 2000–2020 | Statistic Bureau of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (https://tjj.xinjiang.gov.cn) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aishan, T.; Song, J.; Halik, Ü.; Betz, F.; Yusup, A. Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales. Land 2024, 13, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081146
Aishan T, Song J, Halik Ü, Betz F, Yusup A. Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales. Land. 2024; 13(8):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081146
Chicago/Turabian StyleAishan, Tayierjiang, Jian Song, Ümüt Halik, Florian Betz, and Asadilla Yusup. 2024. "Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales" Land 13, no. 8: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081146
APA StyleAishan, T., Song, J., Halik, Ü., Betz, F., & Yusup, A. (2024). Predicting Land-Use Change Trends and Habitat Quality in the Tarim River Basin: A Perspective with Climate Change Scenarios and Multiple Scales. Land, 13(8), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081146








