Optimizing the Layout of Service Facilities for Older People Based on POI Data and Machine Learning: Guangzhou City as an Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
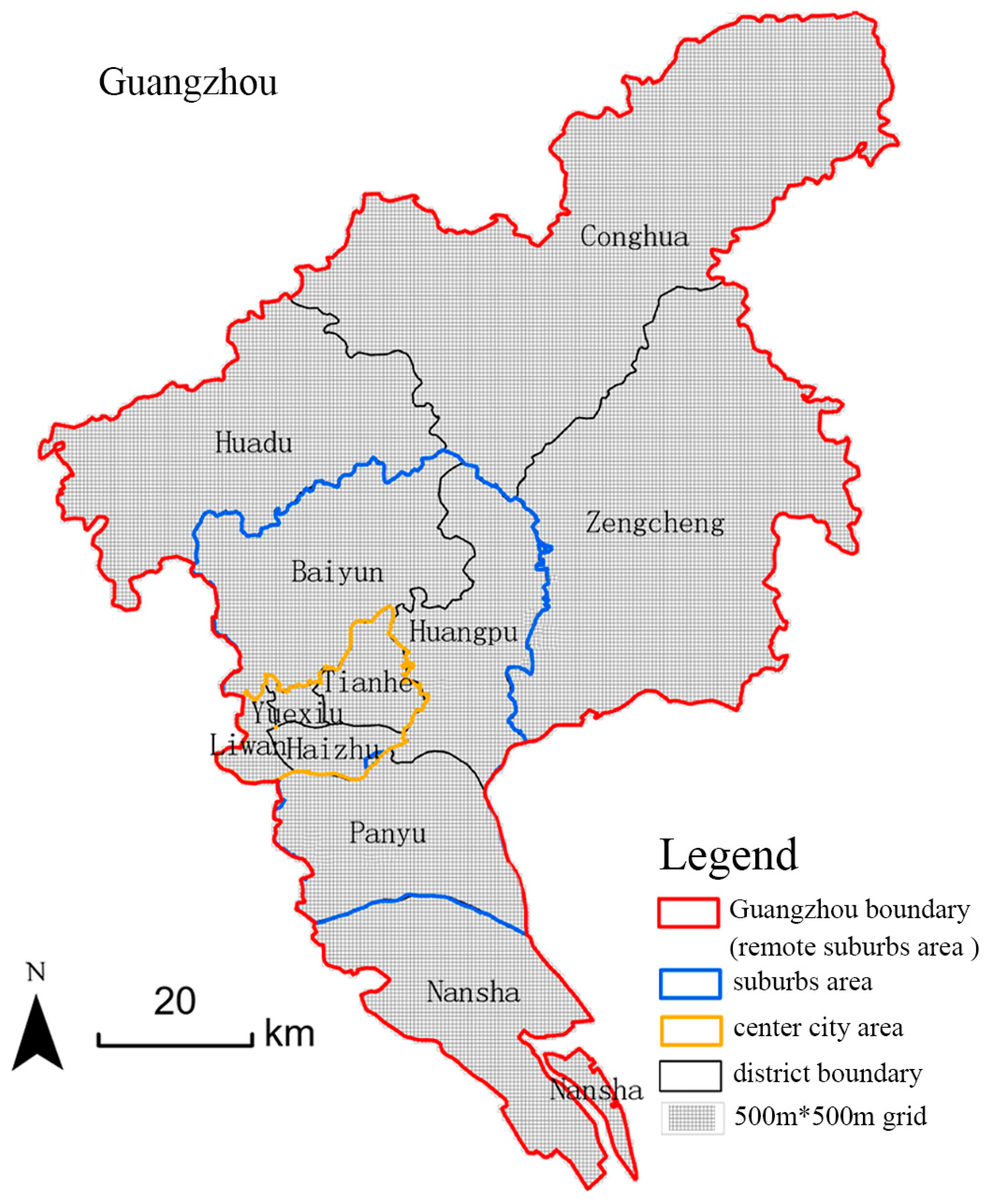
2.1. Study Area
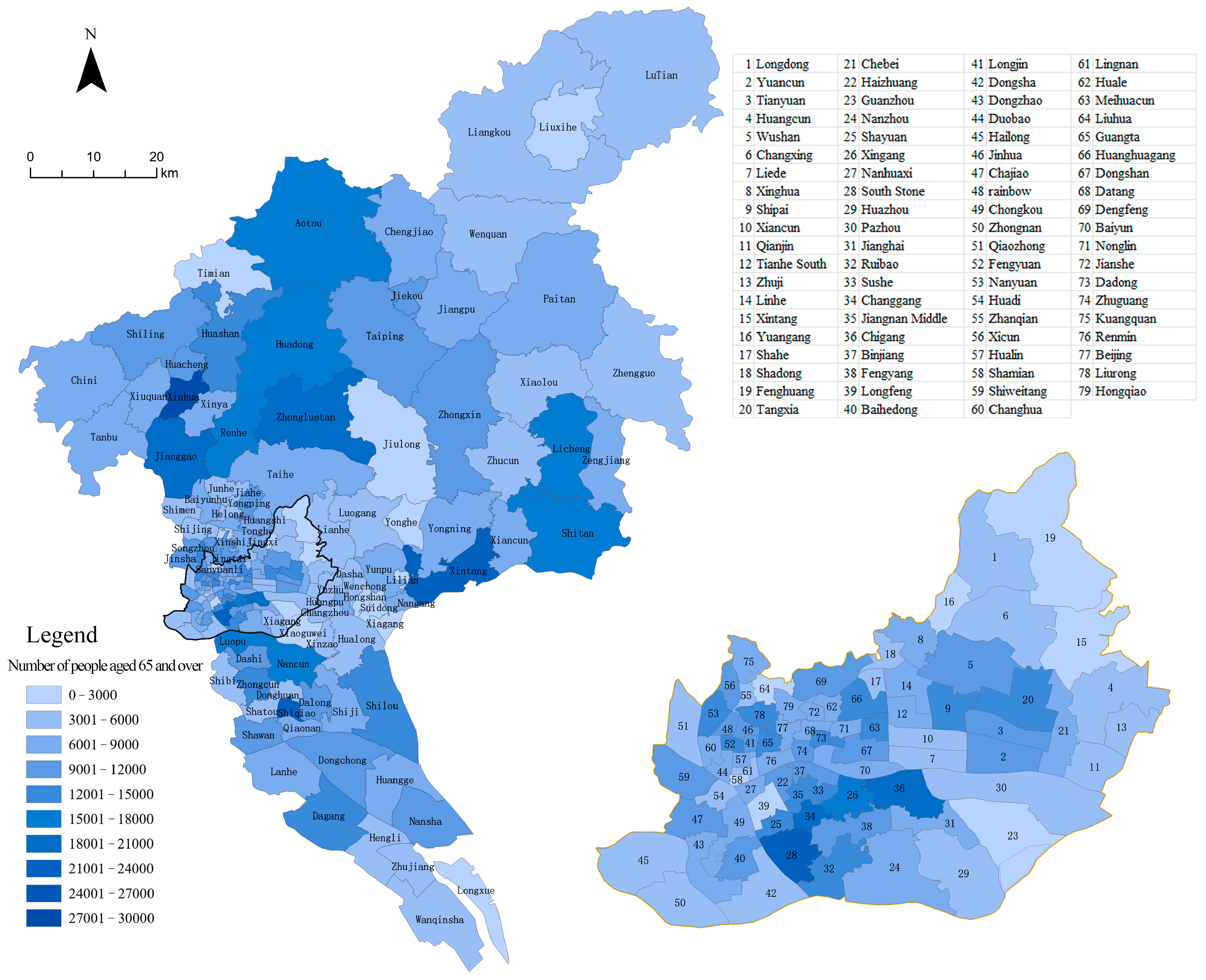
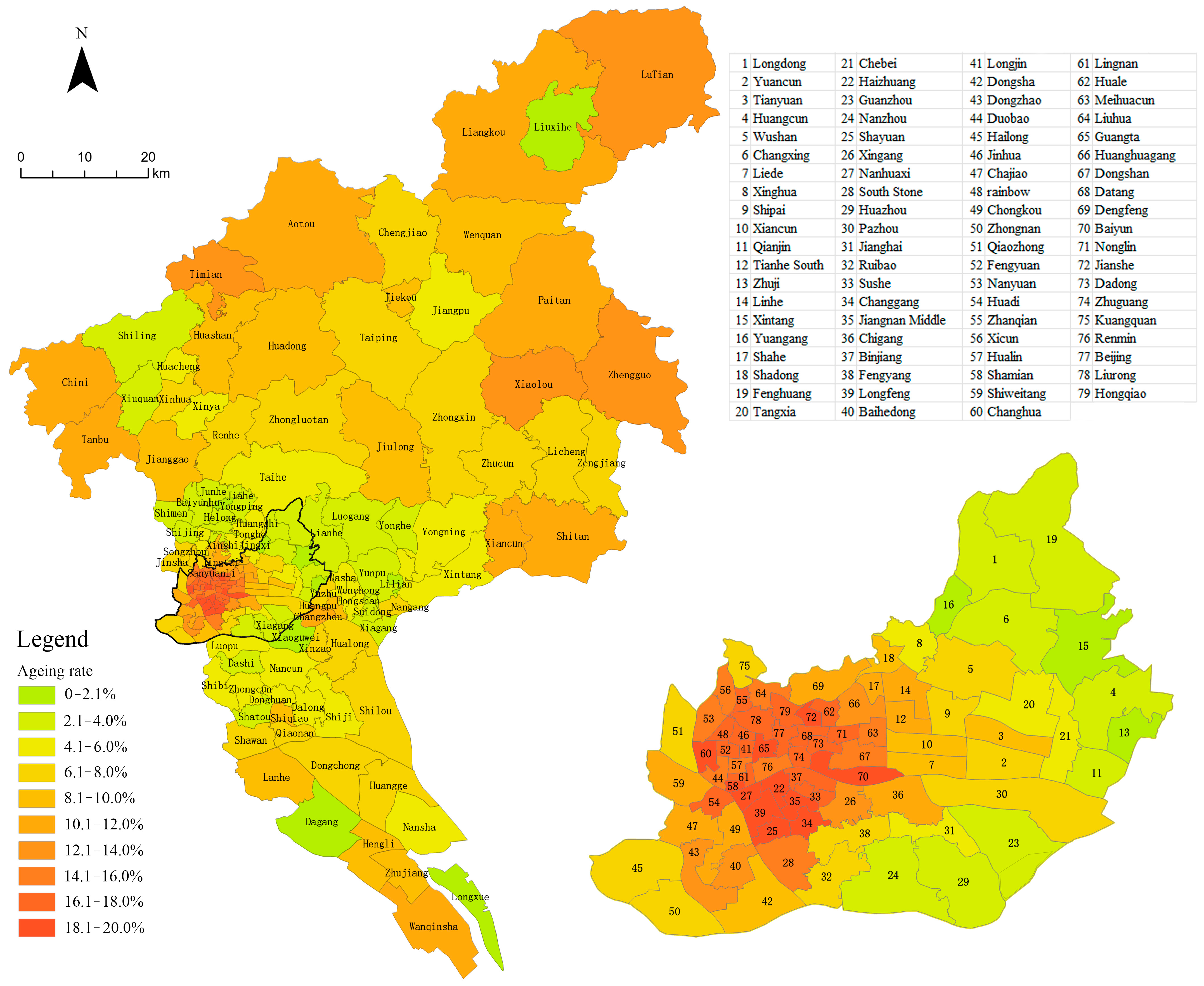
2.2. Research Data
3. Methodology
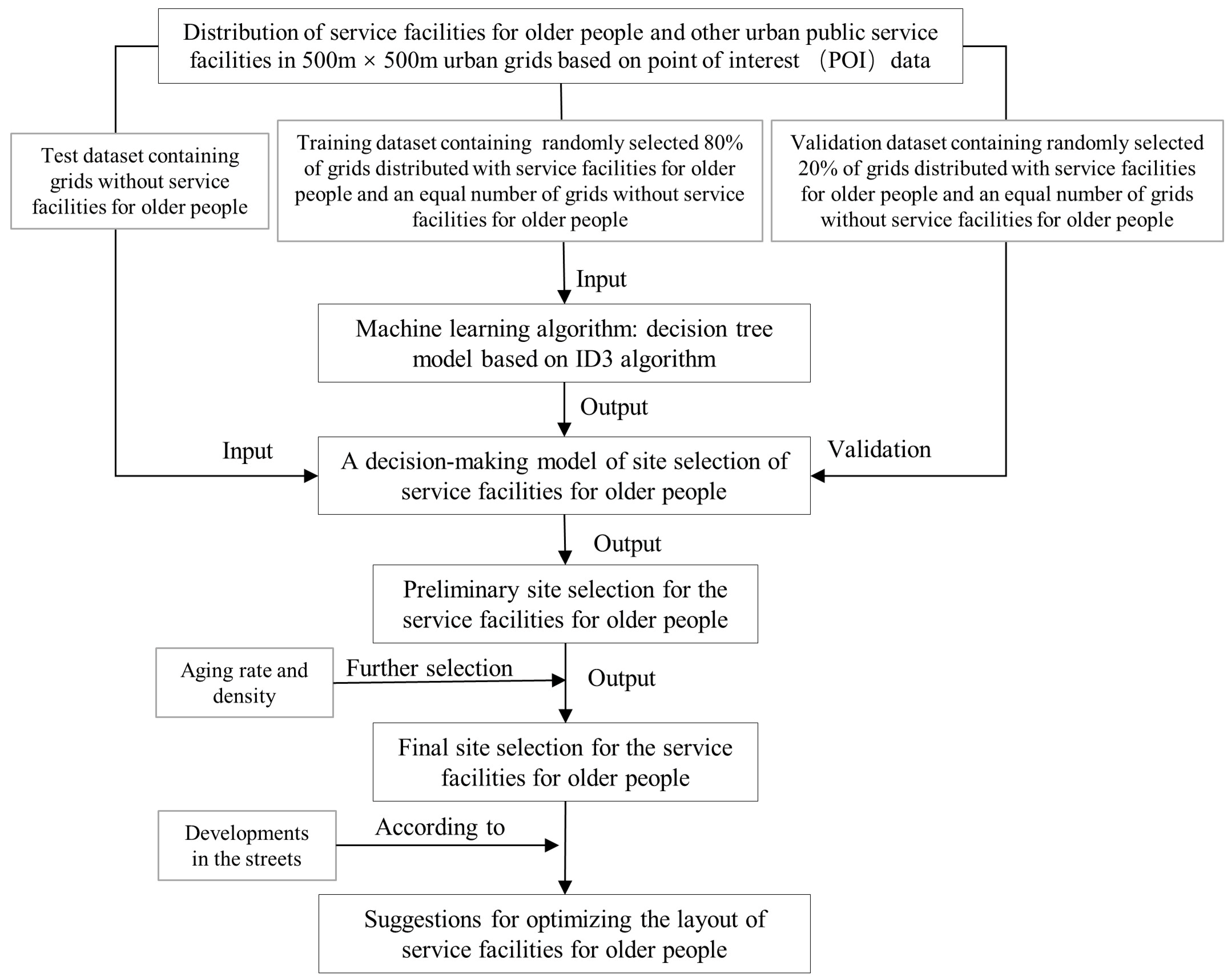
3.1. Gridding the Distribution of Urban Public Service Facilities
3.2. Training of the Prediction Model for the Siting of Service Facilities for Older People
3.3. Prediction of the Siting of Service Facilities for Older People and Recommendations for the Optimization of the Layout
4. Results
4.1. Preliminary Site Selection for Service Facilities for Older People
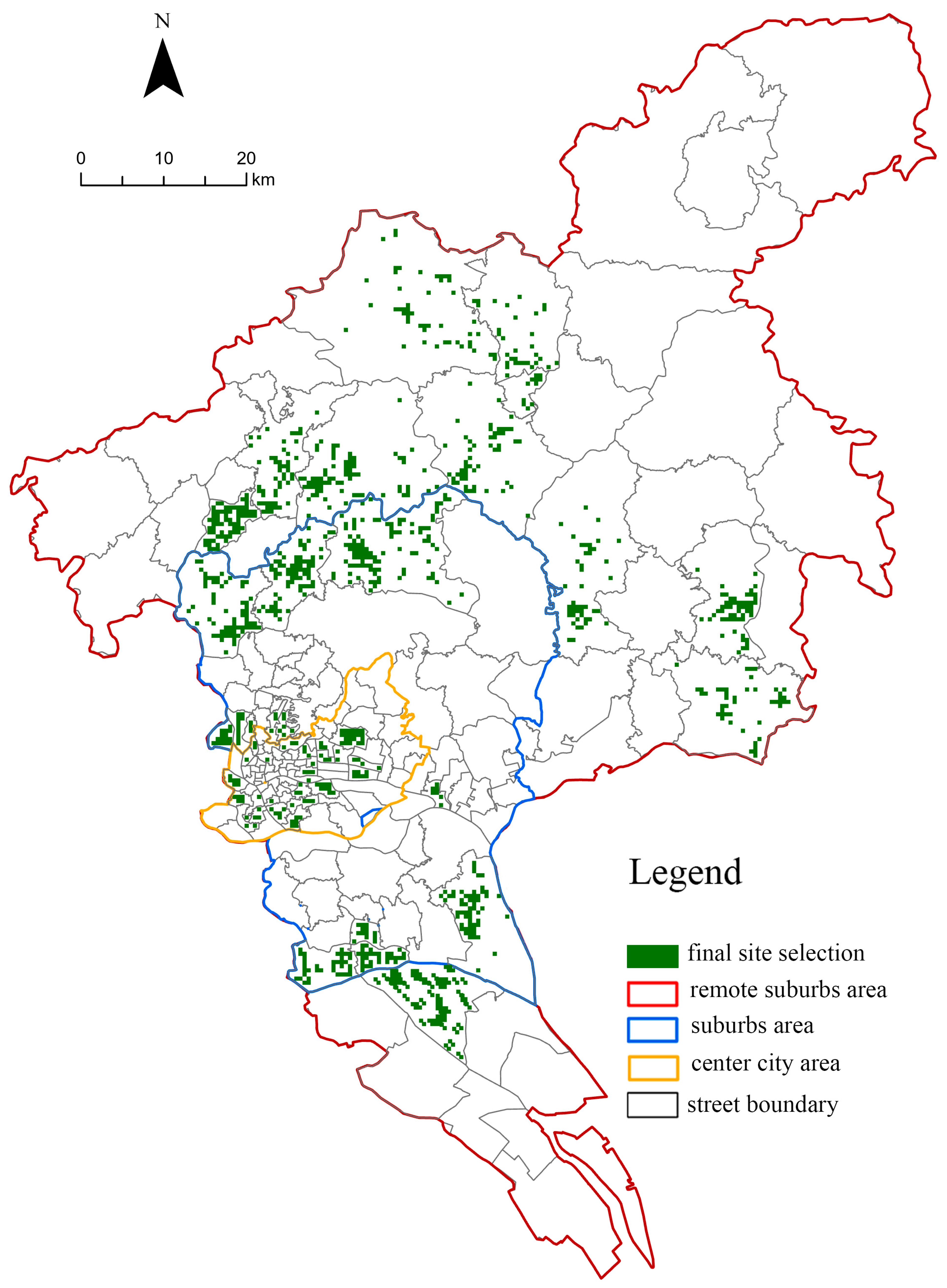
4.2. Final Site Selection for Service Facilities for Older People
4.3. Suggestions for the Optimization of the Layout of Service Facilities for Older People
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations World Population Prospects. 2022. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/ (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- China National Bureau of Statistics Seventh Population Census Data. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/pcsj/rkpc/d7c/ (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Feng, J.; Hong, G.; Qian, W.; Hu, R.; Shi, G. Aging in China: An International and Domestic Comparative Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council of the PRC. National Planning for the Development of the Aging Career and the Elderly Service System during the 14th Five-Year Plan Period (2021–2025). Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2022-02/21/content_5674844.htm (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Hung, Q.F. Research on the Development of China’s Pension Service Industry; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.P.; Gorr, W.L.; Roehrig, S. Location of Service Facilities for the Elderly. Ann. Oper. Res. 2005, 136, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.-Y. A Study of Social Program Space Layout in the Elderly Welfare Facility-Case Study of 22 Elderly Welfare Facilities in the Honam Province. Arch. Des. Res. 2007, 20, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Faraji Sabokbar, H.; Mohammadi, H.; Tahmasbi, S.; Rafii, Y.; Hosseini, A. Measuring Spatial Accessibility and Equity to Healthcare Services Using Fuzzy Inference System. Appl. Geogr. 2021, 136, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millas, A.J. Planning for the Elderly within the Context of a Neighborhood. Ekistics 1980, 47, 264–273. [Google Scholar]
- Carstens, D.Y. Site Planning and Design for the Elderly: Issues, Guidelines, and Alternatives; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, X.; Luo, J.; Zhao, G. Research on the Needs and Influencing Factors of Embedded Elderly Care Services in the Elderly Community. J. Nurs. 2022, 37, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Xin, L.; Yang, H. Research on Planning and Layout of Elderly Service Facilities Based on Supply and Demand Matching. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 24, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ma, S. Efficient Methods for a Bi-Objective Nursing Home Location and Allocation Problem: A Case Study. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 65, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, L.; Antwi, H.A.; Chen, X. Evaluation of Health Resource Utilization Efficiency in Community Health Centers of Jiangsu Province, China. Hum. Resour. Health 2018, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Rosenberg, M.W. Aging and the Changing Urban Environment: The Relationship between Older People and the Living Environment in Post-Reform Beijing, China. Urban Geogr. 2020, 41, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davern, M.; Winterton, R.; Brasher, K.; Woolcock, G. How Can the Lived Environment Support Healthy Ageing? A Spatial Indicators Framework for the Assessment of Age-Friendly Communities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Gong, P.; White, M. Study on Spatial Distribution Equilibrium of Elderly Care Facilities in Downtown Shanghai. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Wei, W.; Yin, L. Spatial Distribution Pattern and Evolution Characteristics of Elderly Population in Wuhan Based on Census Data. Land 2023, 12, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Wang, L.; Dai, X.; Yang, L. Assessing the Accessibility of Home-Based Healthcare Services for the Elderly: A Case from Shaanxi Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrail, M.R. Spatial Accessibility of Primary Health Care Utilising the Two Step Floating Catchment Area Method: An Assessment of Recent Improvements. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2012, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garavaglia, G.; Lettieri, E.; Agasisti, T.; Lopez, S. Efficiency and Quality of Care in Nursing Homes: An Italian Case Study. Health Care Manag. Sc. 2011, 14, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Fang, Y. Evaluating the Technical Efficiency of Care among Long-Term Care Facilities in Xiamen, China: Based on Data Envelopment Analysis and Tobit Model. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.G.; McGrail, K.M.; Morgan, S.G.; Barer, M.L.; Hertzman, C. APOCALYPSE NO: Population Aging and the Future of Health Care Systems. Can. J. Aging/Rev. Can. Du Vieil. 2001, 20, 160–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Tang, J.; Lu, X.; Cheng, C.; Jin, Y.; Bai, J. Current State of Care for the Elderly in China in the Context of an Aging Population. Biosci. Trends 2022, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Lu, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Liu, H.-L. Spatial Layout Monitoring and Optimization of Elderly Care Facilities. Sens. Mater. 2023, 35, 2681–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Miao, J. Study on the Spatial Distribution of Pension Facilities in Guangzhou. South Archit. 2022, 5, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y. Study on the Equity Performance and Spatial Optimization of Elderly Service Facility Allocation in Haizhu District of Guangzhou. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T. Research on the Allocation of Elderly Service Facilities Based on the Prediction of the Spatial Distribution of Guangzhou’s Old Population by 2030. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong Academy of Social Sciences, Guangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Evaluation and layout optimization of park green space in central urban area of Hefei City based on POI data. J. China Agric. Univ. 2023, 10, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.H.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.L.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y. Study on Evaluation and Planning of Urban Parks Based on Baidu POI Data. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2018, 3, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, D.; Miao, C.; Li, G.; Feng, Y.; Bie, Q. The Location Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Cultural Facilities in Zhengzhou Based on POI Data. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumetio Tekouabou, S.C.; Diop, E.B.; Azmi, R.; Jaligot, R.; Chenal, J. Reviewing the Application of Machine Learning Methods to Model Urban Form Indicators in Planning Decision Support Systems: Potential, Issues and Challenges. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 5943–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.; de Vries, W.T. Machine Learning Algorithms for Urban Land Use Planning: A Review. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Feng, Z.; Guangliang, X. Review on Urban AI Hotspots in 2023. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2024, 42, 306–313. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, A.M. Land Cover and Land Use Classification Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms in a Boreal Landscape Using Sentinel-2 Data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. An Approach to Data Acquisition for Urban Building Energy Modeling Using a Gaussian Mixture Model and Expectation-Maximization Algorithm. Buildings 2021, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas-Bel, D.; Garcia-López, M.-À.; Viladecans-Marsal, E. Building(s and) Cities: Delineating Urban Areas with a Machine Learning Algorithm. J. Urban Econ. 2021, 125, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lou, Z.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y. Multi-Source Data-Based Evaluation of Suitability of Land for Elderly Care and Layout Optimization: A Case Study of Changsha, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Li, S. More Urban Elderly Care Facilities Should Be Placed in Densely Populated Areas for an Aging Wuhan of China. Land 2023, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Jiang, F.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J. Analyzing Driving Factors of Land Values in Urban Scale Based on Big Data and Non-Linear Machine Learning Techniques. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, A.; Xing, X.; Song, D.; Li, Y. Identifying Core Driving Factors of Urban Land Use Change from Global Land Cover Products and POI Data Using the Random Forest Method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhou, J.; Luo, X. Mapping Spatial Variation of Population Aging in China’s Mega Cities. J. Maps 2016, 12, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.N.; Marselle, M.R.; Melrose, A.; Warber, S.L. Group Outdoor Health Walks Using Activity Trackers: Measurement and Implementation Insight from a Mixed Methods Feasibility Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, X.; Xia, C.; Kang, X.; Zhou, Y. Examining the Spatial Coordination between Metrorail Accessibility and Urban Spatial Form in the Context of Big Data. Land 2021, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, F. A Paradigm Shift for a Transition to Sustainable Urban Transport. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.; Alves, A.; Bento, C. POI Mining for Land Use Classification: A Case Study. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.; Reeve, N. Survey and Census Methods: Population Distribution and Density. Field Lab. Methods Primatol. 2003, 6, 90–109. [Google Scholar]
- Guangzhou Statistics Bureau Guangzhou Census Yearbook. 2020. Available online: http://tjj.gz.gov.cn/stats_newtjyw/tjsj/pcsj/d7crkpc/content/post_8706327.html (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Slocum, M. Decision Making Using Id3 Algorithm. Insight River Acad. J. 2012, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Vatta, S. Implementation of ID3 Algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 2013, 3, 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F. POI Mining and Generation. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X. Planning Situation and Its Countermeasures of Aged Care Facilities in Indemnificatory Community in Guangzhou. Ind. Constr. 2015, 45, 54–57+121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, B. Spatiotemporal Evolution of the Matching Relationship between the Elderly Population and Facilities for the Elderly: A Case Study of Guangzhou. Trop. Geogr. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning: Trends, Perspectives, and Prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla-Muñoz, V.; Agulló-Tomás, M.S.; Rodríguez-Blázquez, C.; Ayala, A.; Fernandez-Mayoralas, G.; Forjaz, M.J. Ageing Perception as a Key Predictor of Self-Rated Health by Rural Older People—A Study with Gender and Inclusive Perspectives. Land 2022, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Source | Category | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| POI data | Accommodation | 21,287 |
| Attractions | 6891 | |
| Catering facilities | 72,961 | |
| Corporations | 126,000 | |
| Governmental facilities | 29,750 | |
| Financial facilities | 12,572 | |
| Life services | 101,446 | |
| Medical services | 17,493 | |
| Real estate | 11,676 | |
| Scientific, educational, and cultural facilities | 31,167 | |
| Sports and leisure facilities | 3521 | |
| Shopping facilities | 225,541 | |
| Transportation | 2357 | |
| Service facilities for older people | 1369 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, H.; Tang, X.; Zou, C. Optimizing the Layout of Service Facilities for Older People Based on POI Data and Machine Learning: Guangzhou City as an Example. Land 2024, 13, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050700
Feng H, Tang X, Zou C. Optimizing the Layout of Service Facilities for Older People Based on POI Data and Machine Learning: Guangzhou City as an Example. Land. 2024; 13(5):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050700
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Huicheng, Xiaoxiang Tang, and Cheng Zou. 2024. "Optimizing the Layout of Service Facilities for Older People Based on POI Data and Machine Learning: Guangzhou City as an Example" Land 13, no. 5: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050700
APA StyleFeng, H., Tang, X., & Zou, C. (2024). Optimizing the Layout of Service Facilities for Older People Based on POI Data and Machine Learning: Guangzhou City as an Example. Land, 13(5), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13050700











