How Has Land Restriction Policy Influenced Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence from Chinese Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Literature Review
2. Methodology
2.1. Theoretical Frameworks
2.1.1. Impact of the LRP on Land Transfer
2.1.2. Impacts of the LRP on GTFP
2.1.3. The LRP, Intermediary Variables, and GTFP
2.1.4. Direct, Indirect, and Total Impacts of the LRP on Urban GTFP
2.2. Data Sources and Variable Definitions
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Description of Variables
3. Results
3.1. Results of Benchmark Regressions
3.2. Impacts of the LRP and Intermediary Variables on Urban GTFP
3.2.1. Price Mechanism
3.2.2. Industrial Structural Change
3.2.3. Technological Innovation
3.3. Direct Impacts of the LRP on the Urban GTFP
3.4. Indirect Impacts of the LRP on the Urban GTFP
3.5. Total Impact of the LRP on GTFP
3.6. Robustness Tests
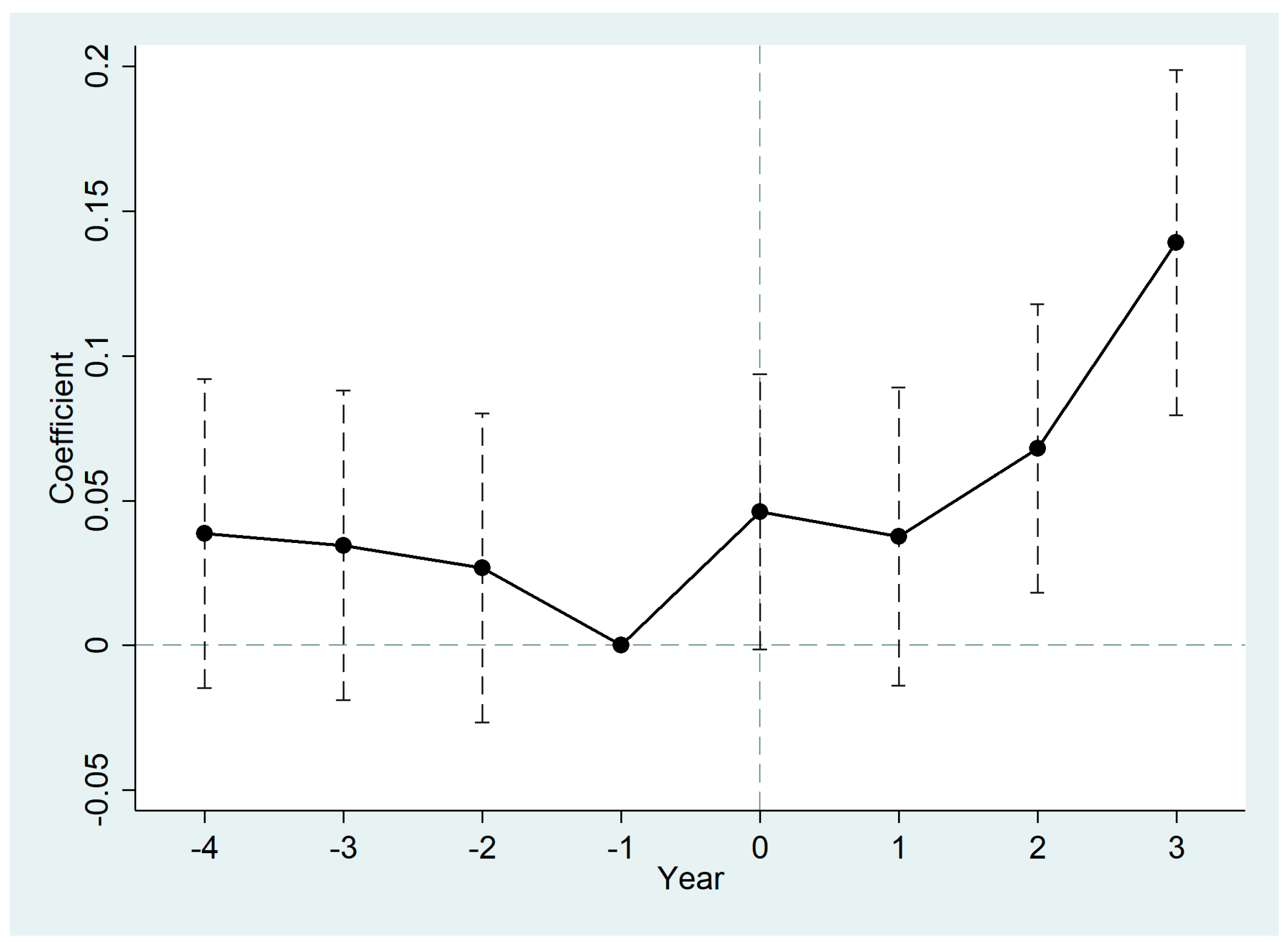
3.6.1. Parallel Trend Test
3.6.2. Placebo Testing
3.6.3. Exclusion of Interference from Other Policies
3.6.4. PSM-DID Model
3.7. Heterogeneity Analysis
3.7.1. Economic Regions
3.7.2. Levels of Cities
3.7.3. Resource Endowments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S. China’s Two-Stage Land Reform. Int. Econ. Rev. 2017, 131, 24+29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Kung, J.K.-S. Fiscal incentives and policy choices of local governments: Evidence from China. J. Dev. Econ. 2015, 116, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, X. The Exhaustion of China’s “Land-Driven Development” Mode: An Analysis Based on Threshold Regression. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 80–92+119+246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ling, Y. Structural Transformation, TFP and High-quality Development. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Analysis of industrial eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in China. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, H. Effects of land urbanization and land finance on carbon emissions: A panel data analysis for Chinese provinces. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Deng, X.; Cheshmehzangi, A.; Mangi, E. Structural succession of land resources under the influence of different policies: A case study for Shanxi Province, China. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Thill, J.-C.; Peiser, R.B. Land pricing and its impact on land use efficiency in post-land-reform China: A case study of Beijing. Cities 2016, 50, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Yuan, Y.; Goto, M. A literature study for DEA applied to energy and environment. Energy Econ. 2017, 62, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; An, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. Environmental efficiency evaluation based on data envelopment analysis: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4465–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, G. Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction and China’s Green Economic Growth—Based on a Total Factor Productivity Perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2015, 5, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lu, Z.; Salman, M.; Song, S. Impacts of heterogenous technological innovations on green productivity: An empirical study from 261 cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ren, S.; Yan, G.; Hao, Y. Does China’s outward direct investment improve green total factor productivity in the “Belt and Road” countries? Evidence from dynamic threshold panel model analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, J. Accounting and determinants analysis of China’s provincial total factor productivity considering carbon emissions. China Econ. Rev. 2021, 65, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumont Jeanneney, S.; Hua, P. How does real exchange rate influence labour productivity in China? China Econ. Rev. 2011, 22, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Xiong, Y.; Xiang, G. Environmental regulation benefits for whom? Heterogeneous effects of the intensity of the environmental regulation on employment in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Ramanathan, R. Exploring the relationships between different types of environmental regulations and environmental performance: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-ming, Y.; Ya-ling, D.; Sai-lian, X. Research on environmental regulatory behavior strategy of central government and local government under the perspective of competition. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Letta, M.; Tol, R.S.J. Weather, Climate and Total Factor Productivity. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 73, 283–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, T.J.; Rao, D.S.P. Total factor productivity growth in agriculture: A Malmquist index analysis of 93 countries, 1980–2000. Agric. Econ. 2005, 32, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-C.; Yu, M.-M.; Chang, C.-C.; Hsu, S.-H. Total factor productivity growth in China’s agricultural sector. China Econ. Rev. 2008, 19, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M. The effects of agglomeration externalities on urban green total-factor productivity in China. Econ. Syst. 2023, 47, 101025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, J.-B.; Wang, M. Analysis of green total-factor productivity in China’s regional metal industry: A meta-frontier approach. Resour. Policy 2018, 58, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.L.; Williams, A.P.; Styles, D. Key performance indicators to explain energy & economic efficiency across water utilities, and identifying suitable proxies. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Golley, J. ‘Green’ productivity growth in China’s industrial economy. Energy Econ. 2014, 44, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Chen, Z. Does factor market distortion inhibit the green total factor productivity in China? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, N. The drivers of China’s regional green productivity, 1999–2013. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 153, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and Undesirable Outputs: A Directional Distance Function Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Environmentally sensitive productivity growth: A global analysis using Malmquist–Luenberger index. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 56, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlberg, B.; Luptacik, M.; Sahoo, B.K. Examining the drivers of total factor productivity change with an illustrative example of 14 EU countries. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 72, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Measuring green productivity growth of Chinese industrial sectors during 1998–2011. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 36, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fan, M.; Shao, S.; Yang, L. Does carbon intensity constraint policy improve industrial green production performance in China? A quasi-DID analysis. Energy Econ. 2017, 68, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Lin, B. Promoting green productivity growth for China’s industrial exports: Evidence from a hybrid input-output model. Energy Policy 2017, 111, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Peng, D. Analysis of Environmental Production Efficiency and Environmental Total Factor Productivity in China. Econ. Res. J. 2012, 47, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, C. Sources of production inefficiency and productivity growth in China: A global data envelopment analysis. Energy Econ. 2015, 49, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Impact of energy conservation policies on the green productivity in China’s manufacturing sector: Evidence from a three-stage DEA model. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Bressers, H.T.A.; Buchanan, K.S. Productivity growth and environmental regulations-accounting for undesirable outputs: Analysis of China’s thirty provincial regions using the Malmquist–Luenberger index. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; An, Q. A Study of Environmental Regulatory Costs and Environmental Total Factor Productivity. J. World Econ. 2012, 35, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Xu, J. Green total factor productivity: A re-examination of quality of growth for provinces in China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 62, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Economic growth model, structural transformation, and green productivity in China. Appl. Energy 2017, 187, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cui, H.; Zhao, Q. Effect of green technology innovation on green total factor productivity in China: Evidence from spatial durbin model analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z. Green innovation and enterprise green total factor productivity at a micro level: A perspective of technical distance. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Cen, Y. How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ. 2020, 92, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-P. Environmental regulations, induced R&D, and productivity: Evidence from Taiwan’s manufacturing industries. Resour. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 514–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancevic, P.I. Environmental regulation and productivity: The case of electricity generation under the CAAA-1990. Energy Econ. 2016, 60, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, S. Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Share green growth: Regional evaluation of green output performance in China. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 219, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Su, X.; Ren, S.; Ran, Q.; Wang, J.; Cao, J. Analysis of the influence of land finance on haze pollution: An empirical study based on 269 prefecture-level cities in China. Growth Change 2023, 54, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L. Exploring regional land use dynamics under shared socioeconomic pathways: A case study in Inner Mongolia, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Yao, S.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q. Does misallocation of land resources reduce urban green total factor productivity? An analysis of city-level panel data in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 122, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhao, H.; Xie, B.; Li, Z.; Li, K. The impacts of land misallocation on urban industrial green total-factor productivity in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 1865–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, P.; Xu, P. The study on the evolution mechanism of urban green total factor productivity—From the perspective of urban energy and land factor constraints. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Wang, D. Optimization of County-Level Land Resource Allocation through the Improvement of Allocation Efficiency from the Perspective of Sustainable Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, D. Does the Upgrading of Development Zones Improve Land Use Efficiency under the Net-Zero Carbon City Goal? Prefectural-Level Evidence from Quasi-Natural Experiments in China. Land 2024, 13, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Xiao, T.; Geng, C.; Sheng, Y. Digital Transformation and Division of Labor between Enterprises: Vertical Specialization or Vertical Integration. China Ind. Econ. 2021, 9, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ji, S. Dynamic Impact of Environmental Regulation on Industrial Upgrading Path. Econ. Theory Bus. Manag. 2013, 33, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. The “Embarrassment”of Environmental Philosophy: A Paradox of Technology and Environment. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 46, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. How Does Industrial Restructuring Improve Regional Energy Efficiency? An Empirical Study Based on Two Dimensions of Magnitude and Quality. J. Financ. Econ. 2017, 43, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xie, R. FDI, Environmental Regulation and Green Total Factor Productivity Growth of China’s Industry: An Empirical Study Based on Luenberger Index. J. Int. Trade 2015, 8, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Luo, Y. Upgrading of Industrial Structure, Energy Efficiency, Green Total Factor Productivity. Theory Pract. Financ. Econ. 2018, 39, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, P. Appropriate Technology, Technological Selection, and Economic Growth in Developing Countries. China Econ. Q. 2006, 5, 985–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Mi, M.; Gao, T. The Suitable Degree of Technology Progress and Innovation Driven Industrial Structure Adjustment—An Empirical Analysis Based on Biased Technology Progress. China Ind. Econ. 2015, 11, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, N. A coin has two sides: Which one is driving China’s green TFP growth? Econ. Syst. 2016, 40, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z. Policy Conditions for Compatibility between Economic Growth and Environmental Quality: A Test of Policy Bias Effects from the Perspective of the Direction of Environmental Technological Progress. J. Manag. World 2020, 36, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Jia, S.; Meng, H. Fiscal policy choices of local governments in China: Land finance or local government debt? Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2022, 80, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gong, B. New Growth Accounting Framework, TFP Measurement and Drivers for High-quality Development. China Econ. Q. 2022, 22, 613–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gatto, M.; Di Liberto, A.; Petraglia, C. Measuring Productivity. J. Econ. Surv. 2011, 25, 952–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoie, P.; Laurent-Lucchetti, J.; Johnstone, N.; Ambec, S. Environmental policy, innovation and performance: New insights on the porter hypothesis. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2011, 20, 803–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Chen, K.; Wang, P.; Guo, B.; Dong, Y.; Yang, J. Trade-offs in land-use competition and sustainable land development in the North China Plain. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 141, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
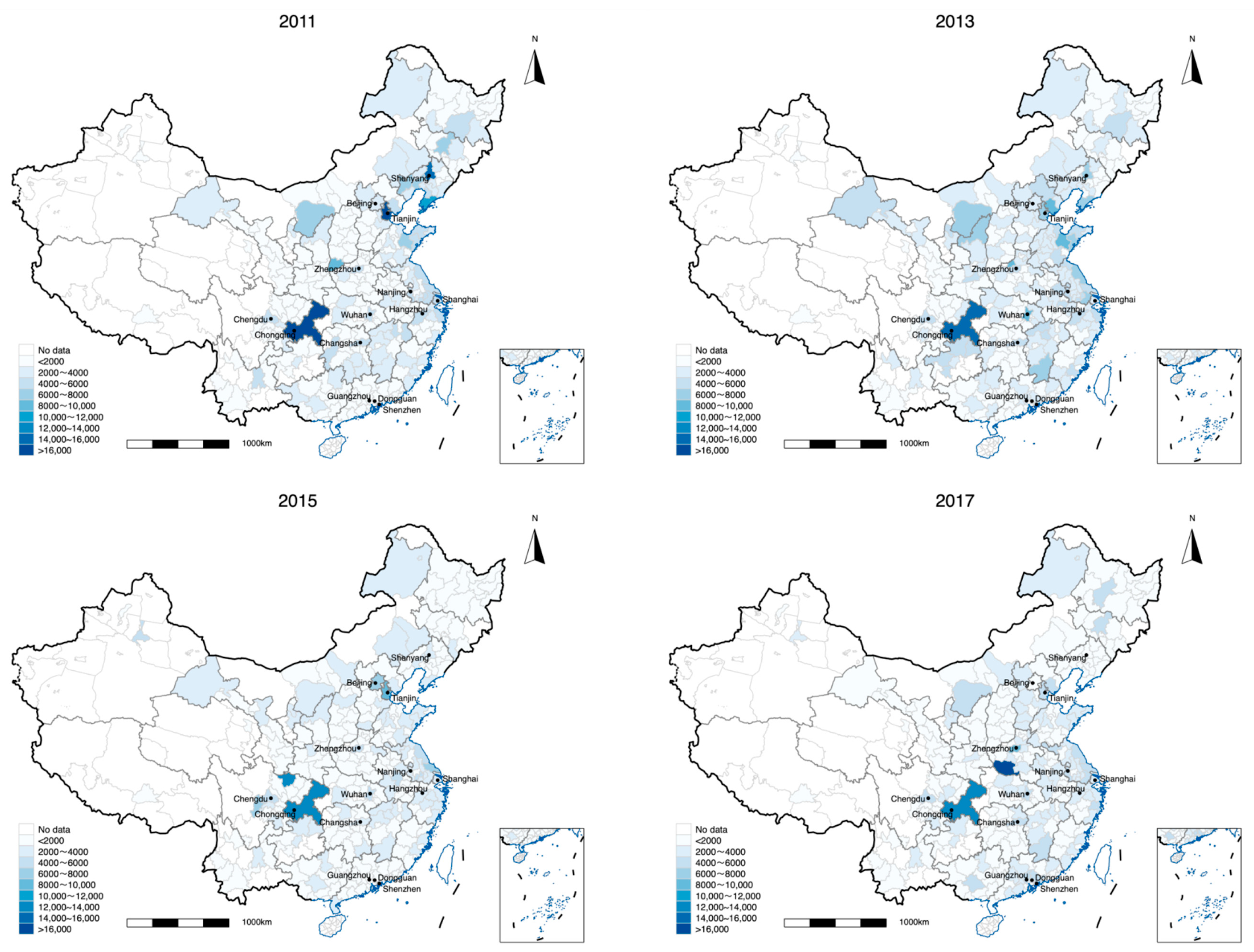
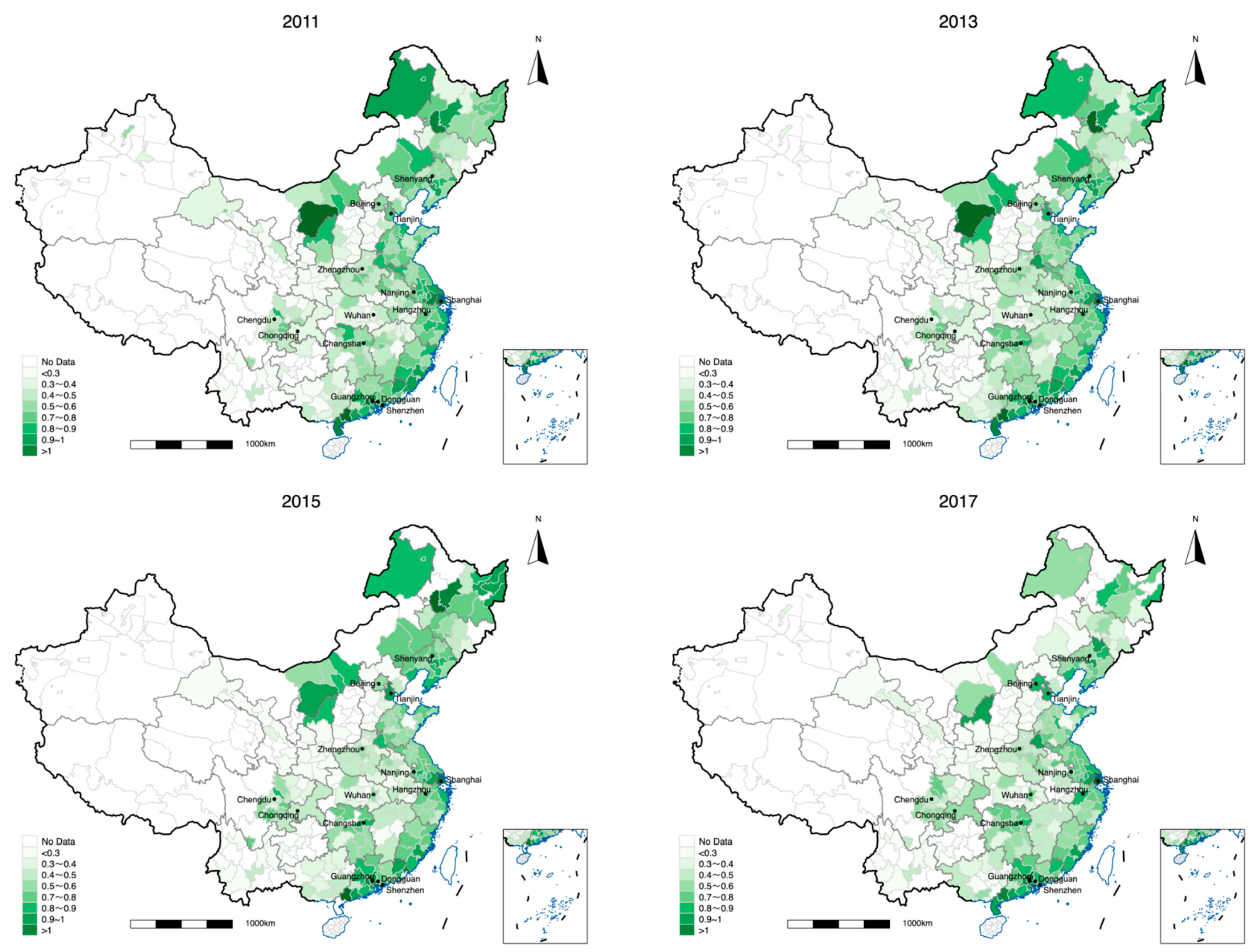
| Direct impacts | Via land transfer management and allocation efficiency | ||
| Indirect effects via intermediary transmission channels | Impacts of LRP on intermediary variables (a) | Impacts of intermediary variables on GTFP (b) | Impact of LRP on GTFP (c) = a × b |
| Total effects | |||
| Variables | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTFP | 5231 | 0.422 | 0.270 | −1.083 | 1.286 |
| LRP | 5390 | 0.010 | 0.098 | 0.000 | 1.000 |
| PGDP | 4799 | 24,106.165 | 63,295.245 | 77.276 | 4,163,697.000 |
| Road | 4735 | 1397.110 | 2022.854 | 1.000 | 21,490.000 |
| Edu | 5177 | 0.014 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.131 |
| Rr_RGDP | 4812 | 622.783 | 401.849 | 8.564 | 16,907.125 |
| FDIK | 5099 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 0.328 |
| KL | 5259 | 30.809 | 22.795 | 0.317 | 197.786 |
| Land | 6284 | 626.079 | 850.367 | 0.010 | 9086.840 |
| Addland | 4663 | 432.265 | 530.524 | 0.030 | 5788.560 |
| Price | 6282 | 563,327.710 | 1,541,074.100 | 1.000 | 27,182,414.000 |
| Industry | 5297 | 0.873 | 0.454 | 0.094 | 9.482 |
| Firm | 6145 | 55.759 | 25.013 | 0.269 | 99.981 |
| Investment | 6145 | 57.672 | 22.835 | 6.356 | 99.981 |
| Invent | 6145 | 63.237 | 18.835 | 40.140 | 99.962 |
| IRIEC | 6145 | 57.405 | 24.262 | 0.240 | 99.942 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| lnLand | lnAddland | |
| LRP | −0.415 *** | −0.477 *** |
| (−4.721) | (−3.172) | |
| Constant | 0.561 | −3.865 *** |
| (1.053) | (−3.647) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4240 | 3830 |
| R-squared | 0.796 | 0.687 |
| r2_a | 0.780 | 0.660 |
| F | 50.32 | 25.50 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRP | 0.173 *** | 0.168 *** |
| (8.096) | (9.930) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.129 *** | |
| (13.920) | ||
| lnRoad | −0.029 *** | |
| (−4.941) | ||
| Edu | 1.256 *** | |
| (4.912) | ||
| lnRr_RGDP | −0.080 *** | |
| (−11.957) | ||
| lnFDIK | 0.007 *** | |
| (3.303) | ||
| lnKL | 0.034 *** | |
| (5.764) | ||
| Constant | 0.204 *** | −0.415 *** |
| (6.336) | (−3.934) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 5201 | 4103 |
| R-squared | 0.767 | 0.846 |
| r2_a | 0.752 | 0.834 |
| F | 52.91 | 68.69 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRP | 0.166 *** | 0.162 *** | 0.140 *** | 0.144 *** | 0.137 *** | 0.144 *** |
| (9.786) | (9.599) | (8.052) | (8.395) | (8.056) | (8.396) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.127 *** | 0.141 *** | 0.138 *** | 0.134 *** | 0.127 *** | 0.135 *** |
| (13.631) | (14.875) | (14.786) | (14.487) | (13.903) | (14.582) | |
| lnRoad | −0.030 *** | −0.027 *** | −0.028 *** | −0.028 *** | −0.024 *** | −0.028 *** |
| (−5.040) | (−4.508) | (−4.692) | (−4.791) | (−4.033) | (−4.771) | |
| Edu | 1.249 *** | 0.990 *** | 0.982 *** | 0.973 *** | 1.093 *** | 1.009 *** |
| (4.885) | (3.818) | (3.801) | (3.765) | (4.312) | (3.925) | |
| lnRr_RGDP | −0.082 *** | −0.080 *** | −0.077 *** | −0.077 *** | −0.081 *** | −0.077 *** |
| (−12.090) | (−11.966) | (−11.327) | (−11.324) | (−12.074) | (−11.372) | |
| lnFDIK | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.008 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.008 *** |
| (3.227) | (3.263) | (3.684) | (4.192) | (2.917) | (3.761) | |
| lnKL | 0.033 *** | 0.037 *** | 0.040 *** | 0.041 *** | 0.035 *** | 0.040 *** |
| (5.651) | (6.314) | (6.766) | (6.823) | (6.018) | (6.705) | |
| lnPrice | 0.005* | |||||
| (1.808) | ||||||
| Industry | 0.044 *** | |||||
| (5.496) | ||||||
| Firm | −0.002 *** | |||||
| (−6.553) | ||||||
| Investment | −0.002 *** | |||||
| (−6.673) | ||||||
| Invention | −0.003 *** | |||||
| (−10.383) | ||||||
| IRIEC | −0.002 *** | |||||
| (−7.217) | ||||||
| Constant | −0.453 *** | −0.671 *** | −0.364 *** | −0.346 *** | −0.192 * | −0.358 *** |
| (−4.214) | (−5.837) | (−3.443) | (−3.267) | (−1.805) | (−3.392) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4103 | 4101 | 4079 | 4079 | 4079 | 4079 |
| R-squared | 0.846 | 0.847 | 0.848 | 0.848 | 0.850 | 0.848 |
| r2_a | 0.834 | 0.835 | 0.836 | 0.836 | 0.838 | 0.836 |
| F | 68.52 | 69.04 | 69.48 | 69.51 | 70.87 | 69.67 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnPrice | Industry | Firm | Investment | Invention | IRIEC | |
| LRP | 0.416 *** | 0.170 *** | −0.257 *** | −0.243 *** | −0.187 *** | −0.245 *** |
| (4.258) | (4.851) | (−11.311) | (−9.347) | (−10.096) | (−9.073) | |
| Control variable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4200 | 4198 | 4176 | 4176 | 4176 | 4176 |
| R-squared | 0.900 | 0.796 | 0.895 | 0.848 | 0.866 | 0.847 |
| r2_a | 0.892 | 0.780 | 0.887 | 0.836 | 0.856 | 0.835 |
| F | 114.9 | 49.62 | 108.7 | 70.86 | 82.38 | 70.59 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRP | 0.166 *** | 0.160 *** | 0.101 *** | 0.135 *** |
| (9.786) | (9.440) | (5.756) | (7.883) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.127 *** | 0.139 *** | 0.143 *** | 0.144 *** |
| (13.631) | (14.597) | (15.179) | (15.162) | |
| lnRoad | −0.030 *** | −0.027 *** | −0.022 *** | −0.026 *** |
| (−5.040) | (−4.614) | (−3.689) | (−4.484) | |
| Edu | 1.249 *** | 0.980 *** | 0.552** | 0.742 *** |
| (4.885) | (3.779) | (2.127) | (2.851) | |
| lnRr_RGDP | −0.082 *** | −0.082 *** | −0.077 *** | −0.078 *** |
| (−12.090) | (−12.120) | (−11.572) | (−11.596) | |
| lnFDIK | 0.006 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** |
| (3.227) | (3.180) | (3.659) | (3.621) | |
| lnKL | 0.033 *** | 0.036 *** | 0.045 *** | 0.042 *** |
| (5.651) | (6.198) | (7.611) | (7.085) | |
| lnPrice | 0.005 * | 0.006** | 0.008 *** | 0.007 ** |
| (1.808) | (1.976) | (2.959) | (2.465) | |
| Industry | 0.044 *** | 0.034 *** | 0.042 *** | |
| (5.552) | (4.316) | (5.339) | ||
| Firm | −0.001 *** | |||
| (−3.548) | ||||
| Investment | −0.001 *** | |||
| (−4.172) | ||||
| Invention | −0.002 *** | |||
| (−8.939) | ||||
| IRIEC | −0.002 *** | |||
| (−7.237) | ||||
| Constant | −0.453 *** | −0.715 *** | −0.415 *** | −0.658 *** |
| (−4.214) | (−6.110) | (−3.504) | (−5.625) | |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4103 | 4101 | 4077 | 4077 |
| R-squared | 0.846 | 0.847 | 0.853 | 0.850 |
| r2_a | 0.834 | 0.835 | 0.841 | 0.837 |
| F | 68.52 | 68.88 | 71.41 | 69.87 |
| Effect Categories | Coefficients According to Equations | Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Direct impacts: | ||
| - Firms, investment, and invention | j1 | 0.101 |
| - IRIEC | k1 | 0.135 |
| Indirect effects: | ||
| - Via price | j3l1 | 0.008 × 0.416 = 0.003 |
| - Via industry | j4m1 | 0.034 × 0.17 = 0.006 |
| - Via firms | j5n1 | −0.001 × (−0.257) = 0.0003 |
| - Via investment | j6o1 | −0.001 × (−0.243) = 0.0002 |
| - Via invention | j7p1 | −0.002 × (−0.187) = 0.0004 |
| or | ||
| - Via price | k3l1 | 0.007 × 0.416 = 0.003 |
| - Via industry | k4m1 | 0.042 × 0.17 = 0.007 |
| - Via IRIEC | k5q1 | −0.002 × (−0.245) = 0.0005 |
| Total effects: | ||
| - Firms, investment, and invention | j1 + j3l1 + j4m1 + j5n1 + j6o1 + j7p1 | 0.11 |
| - IRIEC | k1 +k3l1 + k4m1 + k5q1 | 0.15 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 years in advance | 4 years in advance | 3 years in advance | 2 years in advance | |
| GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRPfalse1 | 0.015 | |||
| (1.016) | ||||
| LRPfalse2 | −0.012 | |||
| (−0.838) | ||||
| LRPfalse3 | −0.010 | |||
| (−0.705) | ||||
| LRPfalse4 | −0.010 | |||
| (−0.684) | ||||
| Constant | −0.059 | −0.061 | −0.060 | −0.061 |
| (−0.299) | (−0.309) | (−0.303) | (−0.305) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4275 | 4275 | 4275 | 4275 |
| R-squared | 0.898 | 0.898 | 0.898 | 0.898 |
| r2_a | 0.891 | 0.891 | 0.891 | 0.891 |
| F | 113.2 | 113.2 | 113.2 | 113.2 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-control zone policy | Pilot innovative cities | Air pollution control zone | Low-carbon city pilot | |
| GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRP | 0.168 *** | 0.158 *** | 0.170 *** | 0.157 *** |
| (9.930) | (9.222) | (9.264) | (9.280) | |
| ShuangKong | 0.111 * | |||
| (1.779) | ||||
| Innov_Pilot | 0.028 *** | |||
| (3.373) | ||||
| Atmos | −0.004 | |||
| (−0.342) | ||||
| Lowcarb_Pilot | 0.037 *** | |||
| (5.552) | ||||
| Constant | −0.526 *** | −0.436 *** | −0.412 *** | −0.418 *** |
| (−4.566) | (−4.129) | (−3.899) | (−3.981) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 4103 | 4103 | 4103 | 4103 |
| R-squared | 0.846 | 0.847 | 0.846 | 0.847 |
| r2_a | 0.834 | 0.834 | 0.834 | 0.835 |
| F | 68.69 | 68.69 | 68.45 | 69.10 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest neighbor matching | Radius matching | Kernel matching | Mahalanobis matching | |
| GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRP | 0.167 *** | 0.170 *** | 0.167 *** | 0.168 *** |
| (10.471) | (10.595) | (10.471) | (9.930) | |
| Constant | −0.162 | −0.167 | −0.162 | −0.415 *** |
| (−1.326) | (−1.368) | (−1.326) | (−3.934) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 3162 | 3158 | 3162 | 4103 |
| R-squared | 0.864 | 0.864 | 0.864 | 0.846 |
| r2_a | 0.851 | 0.850 | 0.851 | 0.834 |
| F | 62.59 | 62.36 | 62.59 | 68.69 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | Central | Western | Municipalities | Provincial capitals | Prefecture-level cities | Resource cities | Non-resource cities | |
| GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | GTFP | |
| LRP | 0.167 *** | 0.150 *** | 0.089 * | 0.809 *** | 0.084 *** | 0.183 *** | 0.145 *** | 0.101 *** |
| (8.645) | (3.997) | (1.720) | (10.210) | (3.981) | (4.129) | (3.306) | (9.648) | |
| Constant | 0.576 *** | −1.394 *** | −1.012 *** | 5.712 *** | −1.391 *** | −0.499 *** | 0.421 | 0.057 |
| (3.324) | (−7.295) | (−5.375) | (6.014) | (−4.138) | (−4.833) | (1.534) | (0.315) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Urban fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 1560 | 1513 | 1030 | 63 | 400 | 3640 | 1634 | 2489 |
| R-squared | 0.826 | 0.793 | 0.819 | 0.981 | 0.937 | 0.828 | 0.921 | 0.950 |
| r2_a | 0.811 | 0.775 | 0.799 | 0.969 | 0.929 | 0.814 | 0.913 | 0.946 |
| F | 55.98 | 43.75 | 41.09 | 82.53 | 111.4 | 59.24 | 121.2 | 221.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Liu, M.; Hua, P.; Chen, Y. How Has Land Restriction Policy Influenced Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence from Chinese Cities. Land 2024, 13, 2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122249
Xu S, Liu M, Hua P, Chen Y. How Has Land Restriction Policy Influenced Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence from Chinese Cities. Land. 2024; 13(12):2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122249
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shengyan, Miao Liu, Ping Hua, and Yibo Chen. 2024. "How Has Land Restriction Policy Influenced Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence from Chinese Cities" Land 13, no. 12: 2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122249
APA StyleXu, S., Liu, M., Hua, P., & Chen, Y. (2024). How Has Land Restriction Policy Influenced Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence from Chinese Cities. Land, 13(12), 2249. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122249






