Abstract
Amid global environmental degradation, understanding the spatiotemporal dynamics and trade-offs of ecosystem services (ESs) under varying land-use scenarios is critical for advancing the sustainable development of social–ecological systems. This study analyzed the Chaohu Lake Basin (CLB), focusing on four scenarios: natural development (ND), economic priority (ED), ecological protection (EP), and sustainable development (SD). Using the PLUS model and multi-objective genetic algorithm (MOGA), land-use changes for 2030 were simulated, and their effects on ESs were assessed quantitatively and qualitatively. The ND scenario led to significant declines in cropland (3.73%) and forest areas (0.18%), primarily due to construction land expansion. The EP scenario curbed construction land growth, promoted ecosystem recovery, and slightly increased cropland by 0.05%. The SD scenario achieved a balance between ecological and economic goals, maintaining relative stability in ES provision. Between 2010 and 2020, construction land expansion, mainly concentrated in central Hefei City, led to a marked decline in habitat quality (HQ) and landscape aesthetics (LA), whereas water yield (WY) and soil retention (SR) improved. K-means clustering analysis identified seven ecosystem service bundles (ESBs), revealing significant spatial heterogeneity. Bundles 4 through 7, concentrated in mountainous and water regions, offered high biodiversity maintenance and ecological regulation. In contrast, critical ES areas in the ND and ED scenarios faced significant encroachment, resulting in diminished ecological functions. The SD scenario effectively mitigated these impacts, maintaining stable ES provision and ESB distribution. This study highlights the profound effects of different land-use scenarios on ESs, offering insights into sustainable planning and ecological restoration strategies in the CLB and comparable regions.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem services (ESs) refer to the various benefits that humans derive, either directly or indirectly, from ecosystems, forming the foundation for sustaining human survival and development [1]. However, with the rapid pace of economic development and continuous population growth in the 21st century, land-use and land-cover (LULC) patterns have changed significantly, leading to profound negative impacts on ESs [2,3]. This is particularly evident at the basin scale, where these changes have triggered a series of environmental challenges, such as habitat loss, diminished water purification capacity, increased soil erosion, and more frequent flooding [4,5]. In this context, ESs serve as a critical link between natural ecosystems and socio-economic systems. Not only do they meet the growing resource demands of humans, but they also play a vital role in maintaining the essential functions and resilience of ecosystems [6,7]. Therefore, a thorough study of ESs trends is not only crucial for understanding the impacts of human activities on ecological systems but is also essential for achieving the harmonious coexistence of humans and nature.
Current research on ESs focuses on various aspects, such as the quantification and valuation of services [8,9,10,11], the drivers influencing their quantification [12,13], and the spatial and temporal evolution of ESs [14,15,16]. While these studies have made significant progress in understanding the roles and changes of ESs, most existing analyses are static assessments at specific points in time, lacking in-depth exploration of ES changes under future scenarios. This limitation hinders the ability of regional ecological planning to fully consider the potential impacts of rapidly changing socio-economic environments on ESs. In recent years, with advances in land-use simulation technologies, some scholars have begun to explore ESs under future scenarios through various approaches [17,18,19]. For instance, Zhao et al. (2019) [20] simulated land-use changes in the Northwest Arid Zone using cellular automata (CA) and the Markov Chain model, predicting the impact of ecological engineering on carbon storage. Xu et al. (2024) [21] combined multi-objective prediction (MOP), the SD model, and the PLUS model to project ESs in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region under different climate scenarios, significantly improving simulation accuracy. Additionally, Wang et al. (2022) [22] applied a multi-objective genetic algorithm (MOGA) to compare and analyze various land-use change scenarios, proposing strategies for ES protection in the Bortala region. However, these studies primarily focus on individual ES changes, with less attention given to the spatial correlation patterns among multiple ESs, their interdependencies, and potential cumulative impacts. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the complex interactions and dynamics among multiple ESs, particularly under future scenarios, is crucial.
Relationships between ESs are often characterized by trade-offs and synergies [23,24]. A trade-off occurs when the enhancement of one ES comes at the expense of another, while synergies arise when multiple ESs improve simultaneously [25]. To better understand the spatial and temporal trade-offs and synergies among ESs, Kareiva et al. (2007) introduced the concept of “ecosystem service bundles” (ESBs), which refer to groups of recurring ESs that exhibit spatial and temporal regularity [26]. Various studies have identified and classified ESBs using methods such as principal component analysis (PCA) [27], self-organizing feature maps (SOM) [28], and K-means clustering [29], revealing their spatial and temporal distribution patterns [30] and examining the impacts of land-use and land-cover changes (LUCC) on ESBs [31]. While these studies provide valuable insights into the complex relationships among ESs, the integration of scenario-based prediction models with current research remains limited. Moreover, further investigation is urgently needed to explore the spatial and temporal dynamics of ESBs and their compositions.
In-depth research on ESBs under future scenarios can not only uncover the spatial and temporal dynamics of multiple ESs but also offer effective tools for the optimal management of complex ecosystems. Traditional ecological zoning methods are often based on the natural geographic characteristics of individual ecological elements [32,33], ecological risk assessments [34,35], or the construction of ecological security patterns [36]. However, these methods tend to focus on ecological optimization goals with limited consideration of socio-economic needs. In contrast, the ESB approach integrates multiple ESs, enabling a more balanced resolution of conflicts between ecological, economic, and social demands. As a result, it has emerged as an effective tool for managing multifunctional ecosystems and landscapes [25,26,37]. The ESB approach is particularly valuable in regions where both economic development and ecological protection are priorities. Its flexibility allows it to be applied across various scales of study, with research outcomes demonstrated at national, regional, and basin levels [30,38,39].
Current research on ES trade-offs based on land-use scenario simulations still faces several gaps, particularly regarding the dynamic relationships between ESs [5], the combined effects of multiple ESs [40], and the integration of scenario predictions with the spatiotemporal dynamics of ESBs [29]. To address these gaps, this study uses the CLB as a case study for in-depth analysis. The CLB is experiencing rapid socio-economic development alongside significant ecological challenges [41,42]. Investigating the changes in ESs and their interactions with land-use changes in this region is not only critical for the sustainable development of similar basins but also provides valuable insights into the global challenge of balancing ecological protection with economic growth.
Based on this context, the present study aims to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the spatial and temporal changes in ESs in the CLB under different scenarios for the years 2010, 2020, and 2030, as well as the complex relationships among various types of ESs. The specific objectives of this study are: (1) to simulate LUCC under different scenarios using the PLUS model; (2) to evaluate the spatial and temporal distribution of various types of ESs and analyze the trade-offs and synergistic relationships among them in the CLB using the InVEST model; (3) to identify the ESs in the CLB and explore their spatial differences under future scenarios; (4) to integrate historical changes with future trends and propose optimization recommendations for the ecological management and land-use planning of the CLB. Through these studies, we aim to provide a robust scientific basis for the sustainable development and optimal management of ESs in the CLB. Additionally, we hope to offer insights into the ecological management of other basins, facilitating a win-win scenario for both ecological health and economic development.
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
Chaohu Lake, the fifth largest freshwater lake in China, its basin is located in central Anhui Province (30°52′25′′~32°7′53′′ N, 116°23′59′′~118°22′5′′ E), encompassing a drainage area of approximately 13,780 km2 (Figure 1). The Chaohu Lake Basin (CLB) was selected as the study area due to its representativeness as a region experiencing rapid socio-economic development coupled with significant environmental pressures. The basin hosts a diverse range of ecosystems, including lakes, wetlands, forests, and farmlands, which provide essential ecosystem services (ESs) such as water resource protection, soil conservation, flood control, and ecological regulation [43]. As a critical component of the Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone, the CLB’s agriculture, industry, and tourism sectors have contributed substantially to regional economic growth [44,45]. However, the basin faces escalating ecological and environmental challenges, including poor water resource management [46], land-use conflicts [41], and localized degradation of ESs [47]. Additional pressures such as agricultural non-point source pollution [42], unstable hydro-ecological functions [48], and insufficient flood management [49] have further threatened the region’s ecological health and sustainable development. To address these issues, the “Mountain, Water, Forest, Farmland, Lake, Grassland, and Desert Integrated Protection and Restoration Project”, scheduled for completion in 2024, aims to enhance ESs as a core objective [50]. This initiative provides a unique opportunity to explore strategies for balancing ecological protection with economic development. In summary, the CLB serves as an ideal case study for investigating ES dynamics, trade-offs, and sustainable management approaches in rapidly developing regions.
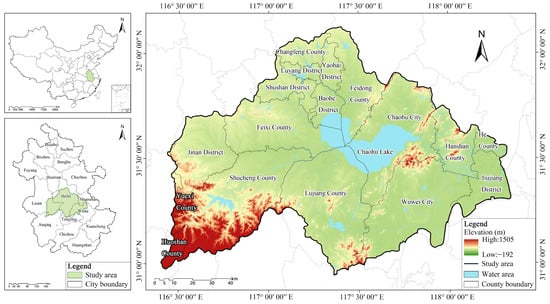
Figure 1.
Location of the research area.
2.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
The land-use data utilized in this study were obtained from the CNLUCC dataset released by the Resource and Environmental Science Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The primary land-use classification within this dataset comprises six categories: cropland, forestland, grassland, water area, construction land, and unused land, with an overall accuracy rate exceeding 90% [51]. Additionally, we incorporated topographic, meteorological, population, and GDP data to characterize the regional natural environment and socio-economic conditions. Annual average evaporation data were also used as indicators for ESs. The aforementioned data underwent pre-processing steps, including projection transformation, cropping, and resampling, with the resampling resolution standardized to 30 m accuracy, and the coordinate system was standardized to WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_50N. Detailed information regarding these datasets is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Details on research data.
3. Methods
We simulated the LULC of the CLB for 2030 by establishing various future development scenarios. Multi-objective genetic algorithms (MOGA) and the PLUS model were employed for optimizing and predicting land-use demand (Figure 2). Subsequently, we analyzed ESs under different scenarios and applied Pearson correlation analysis to explore the trade-offs and synergistic relationships among these services. Finally, we identified and mapped the ESBs using the K-means clustering algorithm, revealing the spatial distribution of ESs across the scenarios. This analysis provides a crucial foundation for future ecological management and planning.
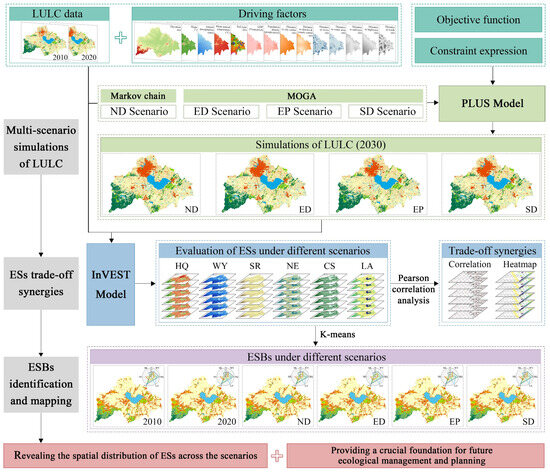
Figure 2.
Conceptual framework of the study.
3.1. Multi-Scenario Simulations of LULC
3.1.1. Multi-Scenario Settings
In this study, we established four development scenarios for the CLB based on current development trends and policies: natural development (ND), economic priority (ED), ecological protection (EP), and sustainable development (SD). The ND scenario reflects the natural evolution pattern predicted by the Markov Chain for each land-use type in the study area. The ED scenario aims to maximize economic benefits while adhering to the constraints outlined in the “Anhui Province Territorial Spatial Plan (2021–2035)” (hereinafter referred to as the “Plan”). Conversely, the EP scenario focuses on maximizing ecological benefits, while the SD scenario seeks to integrate optimization objectives for both economic and ecological benefits. Referring to the previous research [52,53], economic benefits are estimated based on the “Anhui Province Statistical Yearbook”, and the detailed calculation process is shown in the Supplementary Materials. Ecological benefits are derived from the calculation of the ecological service value equivalent factor (see Table 2). Consequently, evaluation formulas for economic and ecological benefits, along with the objective functions for land-use demand under the ED, EP, and SD scenarios, have been constructed (see Table 3). To ensure that future land-use changes across the multiple scenarios align with development patterns and planning expectations, this study utilizes the land-use change rates from 2010 to 2020, as well as the guidelines provided in the Plan, to establish the constraints (see Table 4).

Table 2.
Ecosystem service value coefficients per unit area (106 yuan/hm2).

Table 3.
Research data of this study.

Table 4.
Constraints of optimization objective simulations.
The MOGA algorithm was employed to calculate the optimal solutions for land-use demand across various ecological and economic benefit trade-off scenarios. The distribution of the Pareto frontier solutions in this study is illustrated in Figure 3. By comparing and analyzing the areas of land-use types corresponding to each optimal solution, we selected the scenarios yielding the highest economic and ecological benefits as the land-use data for the ED and EP scenarios, respectively. Furthermore, based on previous studies [22,57], we identified the land-use data for the SD scenario by selecting the configuration with the largest water area, the smallest areas of unused and construction land, and one that closely resembles the ND scenario. This approach not only ensures high ecological sustainability across the scenarios but also maintains economic benefits for the SD scenario that are approximately equivalent to those of the ND scenario.
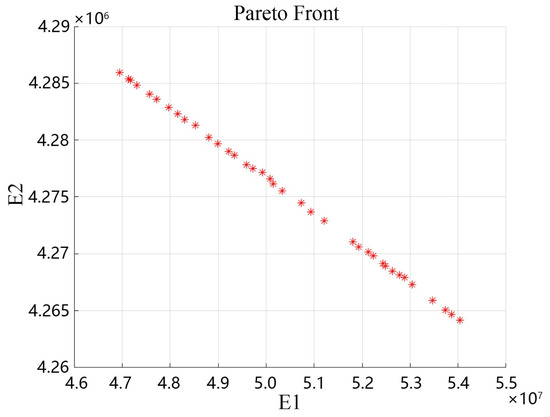
Figure 3.
Pareto front distribution based on the MOGA.
3.1.2. The PLUS Model
The simulation process of the PLUS model primarily involves land expansion analysis and land-use simulation [58]. During the land expansion analysis phase, the influence of each driving factor on the expansion of different land types was assessed to determine the expansion probability for each land type [54]. In the land-use simulation phase, a cellular automata model based on random seeds (CARS) was employed to simulate changes in land patches [59]. Previous studies by Liang et al. (2021) and Li et al. (2021) have demonstrated that incorporating drivers such as topography, climate, and proximity to infrastructure into the PLUS model enhances the accuracy of predictions and supports optimized land expansion strategies by capturing the complexities of LULC changes [19,58]. Based on these findings, this study identified 14 key drivers influencing land-use change in the CLB: elevation, slope, annual precipitation, mean annual temperature, soil type, GDP, population density, distance to the city, district, and county center, distance to rivers [59], distance to water area, distance to railways, distance to highways, and distance to roads [19] (Figure 4). The selection of these drivers reflects a comprehensive consideration of both natural and anthropogenic factors known to shape land-use dynamics. Additionally, the interconversion between land-use types was constrained based on the characteristics of the four development scenarios (Table 5). Following this, the prediction accuracy of the model was validated using data from 2020 as the baseline. After verifying accuracy using the kappa coefficient and the Figure of Merit (FoM) [58], the spatial distribution of land use across the four development scenarios was further predicted.
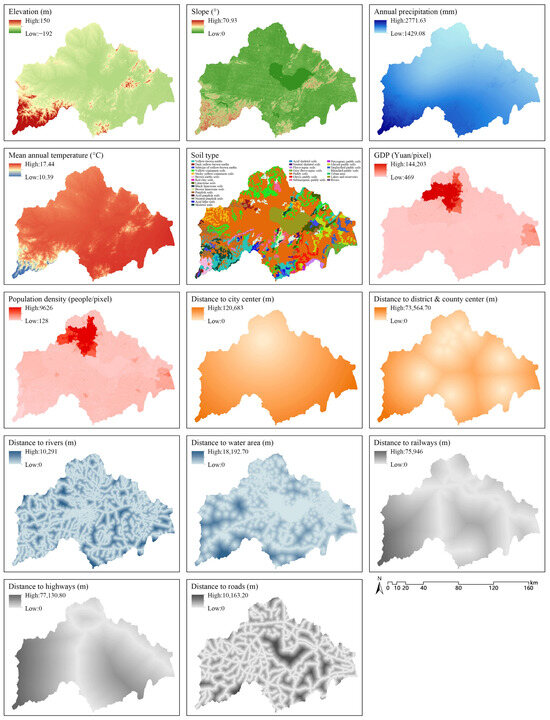
Figure 4.
Driving factors of LULC change.

Table 5.
Land-use conversion matrix.
3.2. ES Trade-Off Synergies
3.2.1. Evaluation of ESs
In assessing ESs in the CLB, we selected water yield (WY), nitrogen export (NE), soil retention (SR), carbon storage (CS), habitat quality (HQ), and landscape aesthetics (LA) as key indicators. This selection was guided by the region’s specific characteristics, policy directives, and international assessment frameworks. Policy documents such as the “Red Line of Ecological Protection in Anhui Province” emphasize priorities like water resource management, water quality protection, soil erosion control, and biodiversity conservation, directly supporting the inclusion of WY, NE, SR, and CS in the assessment [62,63]. Additionally, the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA, 2005) framework underscores the need to address provision, regulation, and support services [6], while LA, as a crucial cultural service, highlights the unique natural and cultural values of the CLB. This indicator is particularly relevant for its significant role in promoting regional economic development, enhancing residents’ well-being, and advancing environmental education [64]. The calculation methodology for each indicator is detailed in the Supplementary Materials [6,9,10,52,53,63,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85].
3.2.2. Correlation Analysis of ESs
Analyzing the trade-offs and synergies among various ESs is essential for achieving a balanced output of these services and promoting sustainable development within the region. Pearson correlation analysis is an effective method for assessing the relationships between different factors in spatial contexts, and it is widely utilized for identifying trade-offs and synergistic relationships among ESs [21]. To explore the relational characteristics of ESs under various future scenarios, we first extracted the mean value of each type of ES within a 1 km × 1 km grid, resulting in a total of 13,354 sample cells. Subsequently, we employed linear regression and Pearson correlation analysis through the Python platform to analyze the ESs across different scenarios. A Pearson’s correlation coefficient greater than 0 indicated a synergistic relationship, while a coefficient less than 0 indicated a trade-off relationship.
3.3. ESBs Identification and Mapping
ESBs illustrate the spatial patterns of aggregation and distribution of various types of ESs. To elucidate these patterns, this study employed the K-means clustering algorithm, which effectively divides the dataset into distinct bundles while calculating the mean values of different features within each bundle [38]. This methodology enables the identification of the primary characteristics of each bundle and highlights their differences, therefore laying a foundation for spatial analysis of ES aggregation patterns. In implementing the algorithm, the selection of the number of bundles significantly influences the interpretability and validity of the clustering results. To scientifically and rationally determine the optimal number of bundles, we utilized the Calinski–Harabasz (CH) criterion [86]. This criterion provides a comprehensive evaluation of bundle quality by simultaneously assessing inter-bundle variation and intra-bundle cohesion [87,88]. Ultimately, we mapped the identified optimal results to spatial locations, allowing for the visualization of ESB distribution under various scenarios. This analysis not only reveals the dynamic changes in ESs over time and space but also provides a critical scientific basis for future ES management and planning.
4. Results
4.1. Multi-Scenario Simulation of LULC
4.1.1. Multi-Scenario LULC Area Projections
Through accuracy verification, the overall accuracy of the predictions in the study area was found to be 0.96, with a kappa coefficient of 0.94 and a FoM coefficient of 0.26. These results indicate a high level of simulation accuracy, enabling a robust projection of future land-use changes in the CLB under multiple scenarios [58]. The study reveals significant differences in the proportional area of each land type within the CLB. Cropland occupies the largest area, followed by forestland, construction land, water area, and grassland, with unused land comprising the smallest proportion, significantly lower than the other land types (Table 6). From 2010 to 2020, the areas of cropland and forestland exhibited a continuous decline, while grassland, water area, construction land, and unused land showed an increasing trend. Notably, the encroachment of construction land onto cropland was most pronounced, and the increases in grassland and water area were also significant.

Table 6.
Land-use type area and changes under different scenarios (unit: km2).
The trends of land-use change vary across different scenarios. In the ND scenario, the trends observed from 2010 to 2020 persist, with cropland and forestland continuing to decline. Construction land expands, albeit at a slower rate, while grassland, water area, and unused land increase to their maximum extents. In the ED scenario, policy guidance supports the orderly expansion of construction land, resulting in a significant reduction in unused land by 29.99%. Conversely, the EP scenario imposes restrictions on construction land expansion, maximizing ecological benefits, resulting in a slight increase in cropland (0.05%) and a minor decrease in forestland (0.18%), while the areas of other land types remain unchanged. In the SD scenario, the land-use strategy seeks to balance ecological preservation and economic benefits. Among the four future scenarios, the SD scenario exhibits the largest area of forestland, while the cropland area approaches that observed in the EP scenario. Grassland and water areas align more closely with those in the ND scenario, while unused land declines. This overall distribution results in a more stable and sustainable land-use pattern.
4.1.2. Spatial Dynamics of Land Use Under Multi-Scenario Projections
In terms of spatial distribution, the changes in construction land, cropland, and unused land between 2010 and 2020 exhibit significant differences when compared to the four projected scenarios (Figure 5). From 2010 to 2020, the expansion of construction land into cropland was particularly pronounced, primarily concentrated in the downtown areas of Hefei City, Chaohu City, Lujiang County, and Shucheng County. Additionally, some forestland, such as the Yinping Mountain area, was also encroached upon by construction activities. Simultaneously, adjustments in land-use types were observed in parts of Hefei’s city center, where cropland and construction land were converted into unused land, grassland, or water areas. This transformation is exemplified by the development of the Hefei West Expansion Park, Emerald Park, and Dafang Ying Reservoir. Furthermore, there were instances of water areas being converted into cropland in the southeastern part of Huangpi Lake.
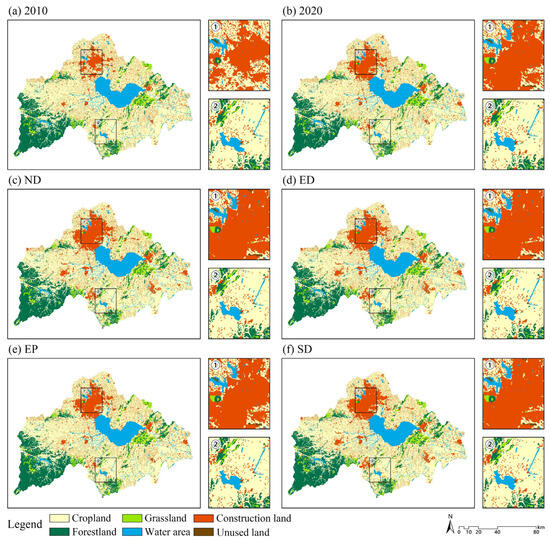
Figure 5.
Different scenarios of spatial distribution of land-use types in the CLB.
Specifically, under the ND scenario, the expansion of construction land into cropland is the most pronounced, accompanied by an increase in the encroachment of mountainous forest land by grassland. In the ED scenario, unused land is primarily converted into construction land, particularly concentrated in the center of Hefei City, with some mountainous forest land also being transformed into cropland or construction land. Under the EP scenario, the expansion of construction land is restricted, leading to a stable spatial pattern that maximizes ecological benefits. Conversely, the SD scenario exhibits a more balanced approach to changes in various land-use types, featuring orderly expansion of construction land while curbing encroachment on cropland, forestland, and grassland. Additionally, some cropland is sporadically converted into water area.
4.2. Trade-Offs and Synergies in ESs
4.2.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of ESs Under Historical and Scenario-Based LULC Simulations
In terms of spatial distribution characteristics, habitat quality (HQ), water yield (WY), carbon storage (CS), and landscape aesthetics (LA) exhibit a pattern characterized by scarce high values, rare low values, and widely distributed intermediate values (Figure 6). Specifically, high values of HQ and LA, alongside low values of WY, are primarily located in hilly regions such as Dabie Mountain, Taihu Mountain, Yinping Mountain, Zipeng Mountain, and around water areas like Chaohu Lake, Wanfo Lake, and Fengle River. Conversely, low values of HQ and LA and high values of WY are predominantly found in densely developed areas such as Hefei City, Chaohu City, and Lujiang County, while intermediate values are broadly distributed across cultivated and unused land. For carbon storage, high values are concentrated in mountainous regions; intermediate values are found in cropland and unused land, whereas low values are present in water areas and construction land.
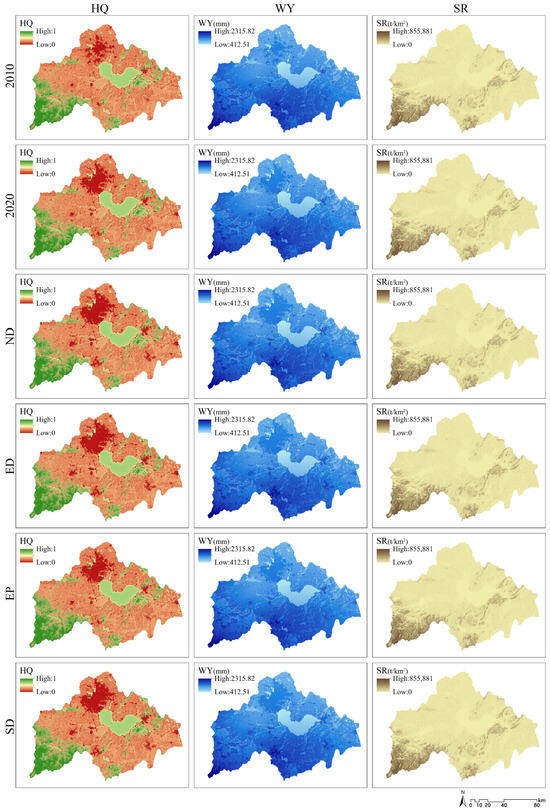
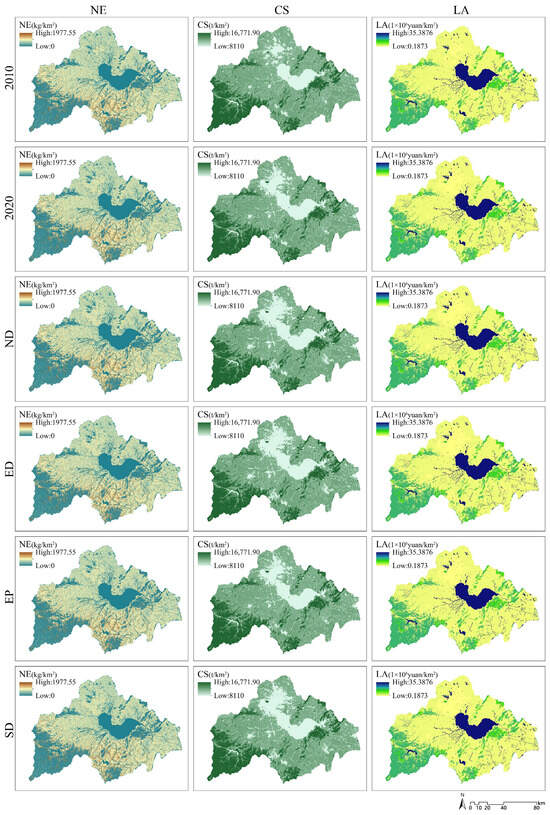
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of ESs under different scenarios.
Nitrogen export (NE) is inversely proportional to water purification capacity and similar to soil retention (SR), exhibits a distribution pattern characterized by a scarcity of high values and a wide spread of intermediate and low values. High NE values are predominantly concentrated around surface runoff areas, displaying a radial distribution. Notably, these high values are particularly significant in the paddy fields located in the southern part of Chaohu Lake and at the junction of Dabie Mountain with other land-use areas, with NE values decreasing in correlation with the distance from the runoff source. Intermediate and low values of NE are primarily found in construction land and cropland, while mountainous and water areas exhibit values of zero. Conversely, high SR values are concentrated in mountainous and hilly areas, whereas low values are observed in plains and water areas, which also show values of zero.
Between 2010 and 2030, the spatial distribution of each ES exhibited distinct patterns in response to changes in land use. In terms of overall service provision, HQ, CS, and LA demonstrated a declining trend from 2010 to 2020, while WY, SR, and NE showed an increasing trend. Between 2020 and 2030, the total volume of each ES remains constant in the EP scenario. In contrast, the other scenarios exhibit a shift in NE services from a growth phase to a decline, while other services continue their 2010–2020 trends. Specifically, in the ED scenario, WY and SR show the highest service volumes, whereas HQ, CS, and LA are at their lowest. In the EP scenario, HQ, NE, CS, and LA services reach the highest volumes, while WY and SR services remain the lowest. The SD scenario demonstrates higher volumes for HQ, SR, and CS, positioning it as the second highest among the four future scenarios, with other ESs occupying moderate levels within the range.
4.2.2. Patterns of Trade-Offs and Synergies in ESs
In this study, Pearson correlation analysis was performed on ESs within the study area, examining a total of 90 pairs of ES combinations. The analysis revealed that 83 of these pairs exhibited significant correlations (p < 0.05, −1 < r < 1). Specifically, 52 pairs demonstrated positive correlations, while 31 pairs showed negative correlations (Figure 7 and Figure 8). In the 2010 scenario analysis, six significant trade-off relationships were identified, four of which involved the ES of NE in relation to other ESs. These trade-off relationships were categorized into three classes based on the absolute value of the correlation coefficient (r). The most significant trade-off relationship was observed between NE and LA, with a correlation coefficient of r = −0.83; this was followed by the relationship between NE and HQ, with r = −0.78, both classified as the first class. The second class included the trade-off relationships between SR and NE and between WY and LA, with correlation coefficients of −0.40 and −0.33, respectively. Finally, the relationship between NE and CS had an r-value of −0.23, categorizing it as the third class.
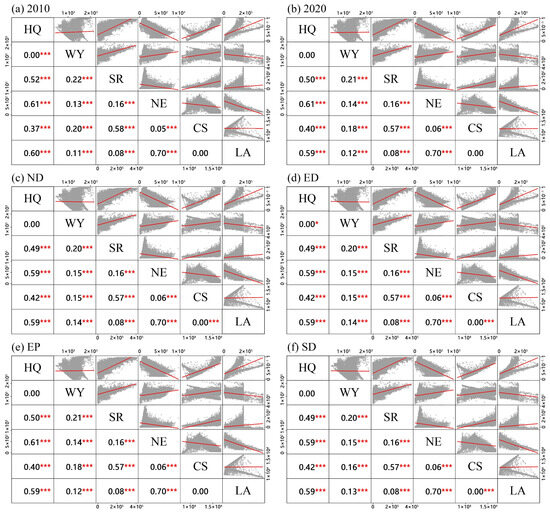
Figure 7.
Correlation between ESs in different scenarios. The red line represents the linear regression curve, showing the trend between independent and dependent variables. The gray area indicates data scatter distribution, reflecting observed value dispersion relative to the regression curve. Asterisks (*) denote correlation levels: * for p < 0.05, and *** for p < 0.001.
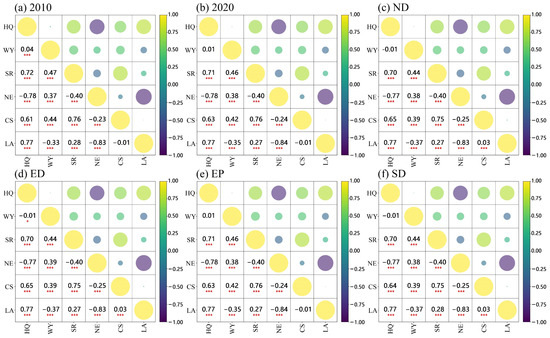
Figure 8.
Heatmap of the association between ESs in different scenarios. Asterisks (*) denote correlation levels: * for p < 0.05, and *** for p < 0.001.
In terms of synergistic relationships, a total of nine significant synergistic relationships were identified, encompassing six types of ESs. These relationships were classified into four categories based on the absolute value of the correlation coefficient (r). The most prominent synergistic relationship was observed between HQ and LA, with a correlation coefficient of r = 0.77. This was followed by the relationships between SR and CS, SR and HQ, HQ and CS, with correlation coefficients of 0.76, 0.72, and 0.61, respectively, all categorized as the first class. The second category included the relationships between WY and SR, WY and CS, WY, and NE, with correlation coefficients of 0.47, 0.44, and 0.37, respectively. The third category included the relationship between SR and LA, with a correlation coefficient of 0.28. Finally, the relationship between HQ and WY, with a correlation coefficient of 0.04, indicated a weak synergistic relationship and was categorized as the fourth class. No significant correlation was found between CS and LA.
In the other five scenarios, the trade-off and synergistic relationships among the ES combinations remained consistent, except for changes in the relationships between two service groups, HQ and WY, as well as CS and LA. These changes were characterized by only slight variations in the correlation coefficient (r) values (Figure 7). No significant correlation was found between these two service groups in the 2020 and EP scenarios. In the ND, ED, and SD scenarios, the correlation coefficient between CS and LA was 0.03, indicating a weak trade-off relationship, while the correlation coefficient between HQ and WY was −0.01, suggesting no significant correlation between these two ESs.
4.3. ESBs Characteristics and Changes
Through the application of the CH criterion, we determined that seven bundles were most appropriate for categorizing the ES functions across different scenarios (Figure 9). We named and classified these seven bundles based on their distinct performances in ES functions. Bundle 1 is termed the “Inefficient Purification Bundle”, characterized by poor water purification capacity and relatively weak performance in other functions, such as water production and carbon storage. Bundle 2 is referred to as the “Water Regulating Bundle”, which excels primarily in water production and associated water resource functions. Despite its limited water purification capacity, it plays a significant role in water resource management. Bundle 3 is designated the “Integrated Median Bundle”, where all ESs are more balanced, but no single function stands out. Bundle 4 is named the “Efficient Habitat Bundle”, distinguished by its strong habitat quality and carbon storage capabilities while also scoring highly in water production and soil conservation. Bundle 5 is identified as the “Strong Carbon Storage Bundle”, showcasing excellent carbon storage and habitat quality with balanced functionality and strong overall performance. Bundle 6 is called the “Carbon and Water Balance Bundle”, characterized by a balanced approach to carbon storage and water production, exhibiting moderate performance in other functionalities. Bundle 7 is labeled the “Landscape Aesthetics Bundle”, which is primarily focused on landscape aesthetics but demonstrates weak performance in other ESs.
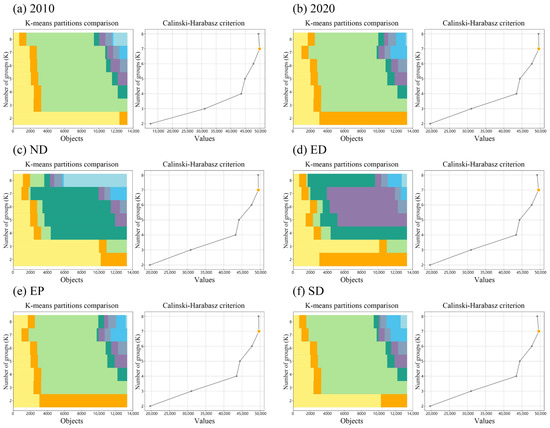
Figure 9.
K-means clustering results for different scenarios. In each set of figures, the left panel shows the horizontal axis as the number of objects and the vertical axis as the number of groups in each partition. Each colored area in the left panel represents the data assigned to different clusters for a specific K value. The orange point in the right panel indicates the corresponding maximum value, representing the optimal number of clusters.
4.3.1. Characterization and Spatial Distribution of ESBs
In terms of spatial distribution, these ESBs exhibit significant differences. Bundle 1 is numerically dominant, primarily concentrated in cropland and construction land within flat areas. Bundles 2 and 3 are more widely distributed around water areas and in valleys, encompassing a diverse range of land-use types. Bundles 4 through 7 are in specific terrains such as mountainous regions and around lakes. Bundle 4 is predominantly characterized by forestland, while Bundles 5 and 6 consist mainly of forestland and grassland. In contrast, Bundle 7 is primarily found in areas with water areas. The spatial distribution characteristics of these bundles illuminate the impacts of various land-use types on the provision of ESs, as well as the potential and limitations of different regions in supplying these ESs. For instance, Bundle 1, despite its high water-supply capacity, scores low on other ESs due to degradation. Conversely, Bundles 4 and 5, although lower in overall volume, are highly valued for their provision of key ESs and thus require special protection and management.
The ES scores for Bundle 1 to Bundle 3 and Bundle 6 remained relatively stable across scenarios but exhibited notable variability at the local level. Specifically, in the 2010 scenario, Bundle 1 showed significantly lower habitat quality (HQ) scores and relatively landscape aesthetics (LA) scores compared to other scenarios. In the ED scenario, Bundle 2 demonstrated significantly lower water yield (WY) and nitrogen export (NE) scores. For Bundle 3, higher HQ and LA scores and lower NE and carbon storage (CS) scores were observed in both the 2010 and ED scenarios. In contrast, Bundle 6 in the 2020 and EP scenarios recorded lower HQ, WY, soil retention (SR), and CS scores than in other scenarios. Bundle 4, Bundle 5, and Bundle 7, however, displayed marked stability with similar scores across all scenarios, underscoring strong consistency. The stability and variability in these scores highlight the adaptability and susceptibility of various ESBs under different land-use scenarios. The relative stability of Bundle 1 to Bundle 3 and Bundle 6 may indicate adaptability to current land-use patterns, while the variability signals significant shifts in land-use practices in specific regions. Conversely, the stability observed in Bundle 4, Bundle 5, and Bundle 7 likely reflects the inherent value and resilience of these areas in delivering essential ESs. This information is critical for developing effective land management and conservation strategies, enabling decision-makers to understand and anticipate potential shifts in ESs under various land-use scenarios.
4.3.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in ESBs Under Multi-Scenario
Under various scenarios, the population share and spatial distribution of the seven ESBs in the study area remained largely consistent, with only localized areas exhibiting significant differences (Table 7, Figure 10). Between 2010 and 2020, Bundles 1, 3, 5, and 6 demonstrated a declining trend, whereas Bundles 2, 4, and 7 experienced growth. Spatially, the transitions between Bundles 1, 2, and 3 were the most significant, particularly in and around the downtown area of Hefei City. Additionally, the transitions between Bundles 1 and 7 were more pronounced at the Dafang Ying Reservoir and Huangpi Lake.

Table 7.
ESB type area and changes under different scenarios (unit: km2).
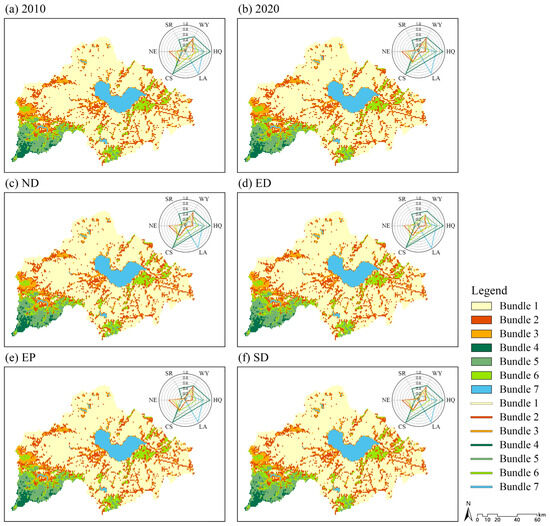
Figure 10.
Spatial distribution of ESBs in different scenarios and normalized scores of ESs in each bundle.
In the ND scenario, Bundle 1 and Bundle 3 continue to decline, while Bundle 2 reverses its growth trend and decreases. In contrast, Bundle 4 shows a significant increase, reaching its maximum value. A slight increase is observed in Bundle 6, while the values for Bundles 5 and 7 remain constant. Spatially, the transitions from Bundles 2 and 3 to Bundle 6 are significant and concentrated at the interface between the mountainous hills and plains. Additionally, the transitions from Bundle 5 to Bundle 4 and from Bundle 6 to Bundle 5 are more pronounced, primarily located in the mountainous regions of the southwestern and southern parts of the study area.
In the ED scenario, Bundles 1 and 6 exhibit growth, while Bundles 2, 3, 4, and 5 decline, and Bundle 7 remains unchanged. Notably, Bundle 1 is the only bundle that experiences growth across all scenarios. Spatially, the overall pattern remains stable, with a significant shift observed from Bundle 2 to Bundle 1, which is evenly distributed across major cities and counties. In the EP scenario, the numerical structure and spatial distribution of ESBs remain consistent with those of 2020. In the SD scenario, Bundles 3, 4, and 5 decrease, while Bundle 6 grows, and Bundles 1, 2, and 7 maintain their levels from 2020. Overall, the spatial distribution remains stable, with conversions among ESBs occurring sporadically across the study area, primarily involving a small number of conversions between Bundles 1, 2, 3, and 6.
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatial Heterogeneity and Land-Use Impact on ESs
In our study of ESs in the CLB, we observed significant spatial heterogeneity among these services, which aligns with findings from other regions worldwide. Specifically, the distribution of cropland, forestland, and unused land varies considerably across different areas, profoundly influencing the capacity of ESs and highlighting the complex interactions between human activities and ecosystems [89,90]. Notably, the continuous reduction in cultivated land is closely associated with the expansion of construction land, particularly in the central and surrounding areas of Hefei City. This phenomenon mirrors the observations made by Shen et al. (2020), who noted that urbanization poses a threat to the supply of ESs in nearby regions [91]. Urban expansion not only encroaches upon agricultural land but also contributes to habitat fragmentation and a decline in biodiversity, therefore weakening the ecosystem’s regulatory functions and its capacity to provide services [92,93].
Meanwhile, while certain areas—such as those around mountains and water areas—continue to maintain some ES functions (e.g., water quality purification), a significant supply–demand imbalance remains evident [39,89]. Xu et al. (2020) emphasized that, amid rapid urbanization, rational land planning is essential to ensure the supply of ESs [90]. Consequently, this study not only systematically assessed the current land-use patterns but also underscored the need to address the ES supply gap through effective land management strategies. Furthermore, the negative impacts of increased construction land use on habitat quality have directly contributed to a decline in water regulation capacity [89]. This undersupply phenomenon necessitates urgent attention from policymakers to develop more effective land-use planning aimed at ensuring ecosystem sustainability and service provision. Gou et al. (2021) also demonstrated that land-use changes directly or indirectly affect ESs, particularly in areas experiencing rapid agricultural intensification and urbanization [92]. These findings provide a scientific foundation for land-use planning and ecosystem management, highlighting the urgency and importance of protecting and restoring ESs in the context of urbanization and land-use change.
5.2. Trade-Offs and Synergies Among ESs Under Future Land-Use Scenarios
Our study revealed complex interactions among ES functions under different future land-use scenarios. Notably, a significant negative correlation (r = −0.83) was identified between nitrogen export (NE) and habitat quality (HQ). This finding aligns with the conclusions of Sun et al. (2020), who indicated that urban expansion significantly impacts ecological services, particularly regarding water quality and habitat quality [94]. This suggests that as urbanization progresses, land-use changes may adversely affect certain ESs, resulting in a decline in their functional capacity. Conversely, there are also synergistic effects among various ESs, particularly under effective land management scenarios. The positive correlation (r = 0.76) between HQ and soil retention (SR) indicates that appropriate land management not only prevents ecosystem degradation but also fosters the synergistic enhancement of multiple ESs. This finding is consistent with Geng et al. (2019), who underscored the importance of the synergistic effects of ESs for sustainable regional development [95].
Through further analysis, we found that different future land-use scenarios significantly impact the trade-off and synergy of ESs. In the ED scenario, although the orderly expansion of construction land promotes the development of some previously unused land, it concurrently leads to a decline in the supply capacity of ESs. This phenomenon underscores the necessity for rational planning and management to prevent the overconsumption of ESs. In contrast, the stringent restrictions on construction land in the EP scenario effectively maintain ecosystem stability, highlighting the potential of land-use policies to optimize ES provision. The findings of this study resonate with the spatial heterogeneity of ESs observed at various scales, as noted by Xia et al. (2023), who found significant spatial differences in the decline of food production and an increase in water supply [96]. Similarly, Feng et al. (2020) investigated the Loess Plateau of China, where they identified positive effects of ecological restoration measures on soil erosion control and carbon sequestration while also noting potential negative impacts on water resource production [97]. Furthermore, Geng et al. (2022) emphasized the spatial heterogeneity of the impacts of land-use types and topographic conditions on ES provision in the Yellow River Basin [95]. Additionally, Deng et al. (2021) pointed out regional disparities in trade-off coefficients between ecological construction and urbanization expansion in the Xiangjiang River Basin, suggesting that land-use planning must balance ESs with urbanization demands to maintain ecosystem health in rapidly urbanizing areas [98]. Building on previous studies, such as those by Liang et al. (2024), who assessed the dynamic trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services (ESs) in the Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration [99], and Luo et al. (2022), who explored the spatiotemporal interactions between urbanization and ESs in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, this study also contributes to understanding the complex relationships between ESs [100]. Shao et al. (2022) further evaluated the spatiotemporal variations of ES value in southern China and proposed future land-use planning strategies [101]. These studies, along with the findings from the CLB, offer important insights into land-use and ecosystem management in similar regions, facilitating the dual benefits of economic development and ecological conservation.
5.3. Ecological Conservation and Sustainable Development of ESs in the CLB
As a critical freshwater lake in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, the coordinated development of ecological protection and ES functions in CLB is pivotal to regional ecological management. Despite recent efforts, including the “Shan-shui Initiative in China” and the “Construction of the Top Ten Wetlands around Chaohu Lake”, research indicates a significant degradation of the lake’s ESs. The compounded effects of land-use change, climate change, and human activities have rendered the lake ecosystem increasingly fragile. In particular, an agricultural-dominated land-use pattern exacerbates human–land conflicts, constraining the effectiveness of current policy measures [29,102]. Current policies have largely failed to mitigate the decline in key ESs, such as habitat quality (HQ) and carbon storage (CS). This is particularly evident in plain areas, where construction land expansion has intensified ecological degradation. Furthermore, ES distribution remains uneven, with the ecological potential of high-altitude regions underutilized, exposing deficiencies in regional coordinated development strategies. Simulation results under EP and SD scenarios demonstrate that stringent controls on construction land and cross-regional policy coordination can enhance the stability and balance of key ESs. These findings underscore the potential of eco-friendly land-use patterns to restore ecological functions and offer a scientific foundation for policy optimization.
To achieve sustainable development in the CLB basin, policy design should focus on several key aspects. First, dynamic assessments of climate change impacts on lake ESs must be strengthened. The integration of remote sensing technologies with ecological models will enable timely adjustments to protection strategies in response to climate variability [103]. Second, cross-departmental and cross-regional cooperation mechanisms should be established to enhance policy coordination through unified lake protection and land-use planning, ensuring a balanced spatial distribution of ESs [104]. Public participation is also critical for improving policy implementation. Awareness campaigns and community engagement can foster societal recognition of and commitment to ecological protection efforts [105]. Optimizing land-use structures should prioritize ecological restoration, promote ecological agriculture in plain regions, and enhance service supply through land reclamation and fallow practices [106]. Moreover, establishing an ecological compensation mechanism is essential. Financial subsidies can offset economic losses incurred by farmers due to ecological conservation, incentivizing the adoption of environmentally friendly land-use practices. This approach facilitates the coordinated development of ecological, social, and economic systems [29].
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
In this study, ESBs were constructed through future multi-scenario LULC projections to facilitate prospective planning for basin ecology. However, several limitations must be acknowledged. First, the study selected only representative types of ESs, highlighting the need for future research to develop a more comprehensive framework for ES assessment. This framework should improve both the diversity of ES types considered and the accuracy of the assessment models used. Second, the InVEST model exhibits a degree of subjectivity in parameter settings and limitations in localization. For instance, when estimating future water yield, this study does not account for future climate conditions and simplifies complex ecological processes. Future research should address these limitations through field validation and model refinement. Third, the choice of clustering analysis methods may influence the performance characteristics of ESBs, potentially leading to variations in classification outcomes. While Pearson correlation is a widely used method for analyzing trade-offs and synergies among ESs, it does not account for possible nonlinear interactions. Future studies should consider employing more sophisticated nonlinear analysis methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complex dynamic relationships among ESs. Additionally, due to spatial constraints, environmental scale factors were not fully incorporated into the analytical framework of this study, which limits a thorough understanding of ESB characteristics. Future research should enhance the analysis of multi-scale environmental characteristics to assess the impacts of these factors more accurately on ESs. Finally, it is essential for future studies to delve deeper into the driving mechanisms underlying the complex relationships between ESs from both socio-economic and ecological perspectives. Such an approach will improve our understanding of their interactions and provide a more robust scientific basis for effective basin management.
6. Conclusions
This study systematically analyzed land-use and land-cover changes (LUCC) in the Chaohu Lake Basin (CLB) under various scenarios and their effects on ecosystem services (ESs), revealing the spatial distribution characteristics of these services. The results indicated that cropland predominated; however, the continuous expansion of construction land led to a significant reduction in both cropland and forest areas, particularly in the natural development (ND) and economic priority (ED) scenarios. The ecological protection (EP) scenario effectively curtailed the expansion of construction land and facilitated the recovery of cropland and ecosystems, while the sustainable development (SD) scenario achieved a relative balance between ecological efficiency and economic growth. Furthermore, the study conducted an in-depth analysis of the spatial distribution and trends of ESs, finding that the expansion of construction land between 2010 and 2020 was primarily concentrated in the central and surrounding areas of Hefei City. This expansion resulted in a marked decline in habitat quality (HQ) and landscape aesthetics (LA), whereas water yield (WY) and soil retention (SR) improved due to construction land expansion. This suggests that the transformation of different land types has a complex impact on ESs. Under various scenarios, the trend of ES provision generally aligned with adjustments in land-use patterns, with the SD scenario demonstrating relative stability in service provision. Finally, through K-means clustering analysis, this study identified and mapped the spatial distribution characteristics of seven types of ecosystem service bundles (ESBs). Bundle 1 is primarily concentrated in cropland and construction land in plains, offering substantial water-supply services. Conversely, Bundles 4 through 7 are concentrated in mountainous regions and around water areas, offering higher biodiversity maintenance and ecological regulation functions. The adaptability and vulnerability of various ESBs under different scenarios revealed the impact of land-use changes on ESs, particularly in the ND and ED scenarios, where critical service areas were encroached upon, resulting in diminished ecological functions. In contrast, the SD scenario more effectively balances the adaptability and vulnerability of ESBs, maintaining a stable ESB distribution pattern while supporting steady economic growth. In summary, this study underscores the profound impacts of differing land-use scenarios on the supply and spatial distribution of ESs. It provides a scientific basis for sustainable planning and ecological restoration strategies in the CLB and analogous basins.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land13122210/s1. Table S1: Economic value coefficients for each LULC; Table S2: Biophysical parameters for each LULC class in the water yield evaluation; Table S3: Biophysical parameters for each LULC class in the carbon sequestration evaluation; Table S4: Biophysical parameters for each LULC class in the soil conservation evaluation; Table S5: Biophysical parameters for each LULC class in the water purification evaluation; Table S6: Landscape Aesthetic value coefficients; Table S7: Threats and their maximum distance of influence and weights; Table S8: The sensitivity of habitat types to each threat. References [6,9,10,52,53,63,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.J. and G.Z.; methodology, A.J.; software, A.J. and G.Z.; validation, A.J.; formal analysis, A.J.; investigation, P.M. and G.Z.; resources, A.J. and P.M.; data curation, G.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, A.J. and G.Z.; writing—review and editing, G.Z., P.M. and A.J.; visualization, G.Z.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China “Urban Ecological Space Control and Layout Optimization Technology” (2022YFC3800203).
Data Availability Statement
Data and materials are available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F. Evolving landscape-urbanization relationships in contemporary China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 171, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C.; Lin, G. Quantitative assessment of the relative impacts of climate change and human activity on flood susceptibility based on a cloud model. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Ou, W.X.; Guo, J. A land-cover-based approach to assessing ecosystem services supply and demand dynamics in the rapidly urbanizing Yangtze River Delta region. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEA (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment). Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards systematic analyses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: Main concepts, methods and the road ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Rao, E. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, W.; Tang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Xu, X. Estimation of water provision service for monsoon catchments of South China: Applicability of the InVEST model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 182, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, G. How Perceived Sensory Dimensions of Urban Green Spaces Affect Cultural Ecosystem Benefits: A Study on Haizhu Wetland Park, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 86, 127983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Identifying the Impacts of Natural and Human Factors on Ecosystem Service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, E.D.; Evans, D.M.; Atkins, J.P. Investigating the impacts of climate change on ecosystem services in UK agro-ecosystems: An application of the DPSIR framework. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, Z. The balance between economic development and ecosystem service value in the process of land urbanization: A case study of China’s land urbanization from 2000 to 2015. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Jiao, H.; He, Q. Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Impacts of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Value: A Case from Guiyang, China. Land 2024, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Gao, B. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier. China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.H. Land space optimization of urban-agriculture-ecological functions in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan Urban Agglomeration, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Ran, Q.; Gao, X.; Ding, X.; Ge, D. Spatial-temporal evolution and prediction of carbon storage: An integrated framework based on the MOP–PLUS–InVEST model and an applied case study in Hangzhou, East China. Land 2022, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; He, Z.B.; Du, J.; Chen, L.F.; Lin, P.F.; Fang, S. Assessing the effects of ecological engineering on carbon storage by linking the CA-Markov and InVEST models. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Qiu, H.; Wang, Z. Ecosystem services response to future land use/cover change (LUCC) under multiple scenarios: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 205, 123525. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q.; Li, L. A new approach to land use optimization and simulation considering urban development sustainability: A case study of Bortala, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.P.; Beard, T.D.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S.; Cork, S.; Agard, J.; Dobson, A.P.; Peterson, G.D. Trade-offs across space, time, and ecosystem services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Balvanera, P. The future of production systems in a globalized world. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Bennett, E.M. Ecosystem service bundles for analyzing tradeoffs in diverse landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5242–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareiva, P.; Watts, S.; McDonald, R.; Boucher, T. Domesticated nature: Shaping landscapes and ecosystems for human welfare. Science 2007, 316, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsboom, C.; Vrebos, D.; Staes, J.; Meire, P. Using dimension reduction PCA to identify ecosystem service bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 209–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wu, H.Q.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.F.; Wan, W. Exploring the interrelations and driving factors among typical ecosystem services in the Yangtze river economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.J.; Zhang, S.P.; Cao, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, Y.L. The spatiotemporal dynamics of ecosystem services bundles and the social-economic-ecological drivers in the Yellow River Delta region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.G.; Odgaard, M.V.; Bocher, P.K.; Dalgaard, T.; Svenning, J.C. Bundling ecosystem services in Denmark: Trade-offs and synergies in a cultural landscape. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.M.; Feng, J.L.; Jia, X.H.; Li, J.J. Spatial correlations among ecosystem services and their socio-ecological driving factors: A case study in the city belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogaris, S.; Economou, A.N.; Dimopoulos, P. Ecoregions in the Southern Balkans: Should Their Boundaries Be Revised? Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Ai, D.; Chen, G.; Lin, Y. Integrating risk zoning and multifactor analysis: A strategic approach to ecological carbon sink management. Eco. Inform. 2024, 82, 102671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Sha, Y.; Chen, Y. The coupling coordination and influencing factors of urbanization and ecological resilience in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Land 2024, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Liu, W.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, F.; Lu, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, K. Construction and optimization strategy of ecological security pattern in a rapidly urbanizing region: A case study in central-south China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meacham, M.; Norström, A.V.; Peterson, G.D.; Andersson, E.; Bennett, E.M.; Crouzat, E.; Cord, A.F.; Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Fischer, J.; Hamann, M.; et al. Advancing Research on Ecosystem Service Bundles for Comparative Assessments and Synthesis. Ecosyst. People 2022, 18, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, R.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Qu, W. Identification of bundles and driving factors of ecosystem services at multiple scales in the eastern China region. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, S. Uncovering the Relationships between Ecosystem Services and Social-Ecological Drivers at Different Spatial Scales in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkelboom, F.; Leone, M.; Jacobs, S.; Kelemen, E.; García-Llorente, M.; Baró, F.; Termansen, M.; Barton, D.N.; Berry, P.; Stange, E.; et al. When we cannot have it all: Ecosystem services trade-offs in the context of spatial planning. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Gao, Y. The influences of land use changes on the value of ecosystem services in Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Miao, C. Will agricultural land scale management aggravate non-point source pollution?—Chaohu Lake Basin, China as a case study. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 158, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, G.; Zhou, C.; Chou, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J. Spatial distribution and multiple sources of heavy metals in the water of Chaohu Lake, Anhui, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2763–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, M.; Miao, C.; Duan, X.; Yan, W. Formation mechanisms and general characteristics of cultivated land use patterns in the Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Deng, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, B.; Yang, J. Spatiotemporal Patterns in Urbanization Efficiency within the Yangtze River Economic Belt between 2005 and 2014. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, J. Ecological security assessment of Chaohu Lake Basin of China in the context of River Chief System reform. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2773–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.R.; Meng, W.; Jin, X.C.; Zheng, B.H.; Zhang, L.; Xi, H.Y. Ecological security problems of the major key lakes in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3825–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lu, W.; Cui, K.; Li, J.; Yang, K.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, H. Distribution, bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of trace metals in the food web of Chaohu Lake, Anhui, China. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Cheng, X.; Dai, M. Regional Flood Disaster Resilience Evaluation Based on Analytic Network Process: A Case Study of the Chaohu Lake Basin, Anhui Province, China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Dong, B.; Qu, J.; Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Gao, X. Optimization of composite ecological network patterns in Anhui Province based on multi-functional coupling of ecology-climate-economy. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, G. Exploring the Optimization of Spatial Patterns for Carbon Sequestration Services Based on Multi-Scenario Land Use/Cover Changes in the Changchun-Jilin-Tumen Region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 438, 140788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Projections of future land use changes: Multiple scenarios-based impacts analysis on ecosystem services for Wuhan city, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Tao, F.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Leng, H.; Zhou, T. Multi-scenario simulation and ecological risk analysis of land use based on the PLUS model: A case study of Nanjing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, P.; Yan, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T. Spatio-temporal evolution and optimization analysis of ecosystem service value-A case study of coal resource-based city group in Shandong, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xue, M. Optimization and Simulation of Mountain City Land Use Based on MOP-PLUS Model: A Case Study of Caijia Cluster, Chongqing. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2023, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jian, X.; Wang, D. Optimal vegetation coverage from the perspective of ecosystem services in the Qilian Mountains. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 115023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Su, F.; Yan, F.; Lyne, V.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L. Optimization of Multi-Objective Multi-Functional Landuse Zoning Using a Vector-Based Genetic Algorithm. Cities 2023, 137, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Lyu, X.; Tian, H.; Qu, T. How will ecosystem carbon sequestration contribute to the reduction of regional carbon emissions in the future? analysis based on the MOP-PLUS model framework. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Peng, S. Comparison of multimodel simulations of land use and land cover change considering integrated constraints—A case study of the Fuxian Lake basin. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, X.; Wu, M.; Wen, J.; Zou, J. Assessing the Water Conservation Function Based on the InVEST Model: Taking Poyang Lake Region as an Example. Land 2022, 11, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, X.; Xu, G.; Chi, J. Spatial-Temporal Variations and Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services in Anhui Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Shen, A.; Liu, C.; Wen, B. Impacts of ecological land fragmentation on habitat quality in the Taihu Lake basin in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, L. Identification of Ecological Sources Using Ecosystem Service Value and Vegetation Productivity Indicators: A Case Study of the Three-River Headwaters Region, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, T.; Wen, Q.; Yin, C.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Water Yield Services and Responses to Future Land Use Scenarios in Henan Province, China. Water 2024, 16, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Peng, S.; Huang, B. The impact of multi-scenario land use change on the water conservation in central Yunnan urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Pan, J.; Feng, X. Distribution of available soil water capacity in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wei, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, B. Depth-to-bedrock map of China at a spatial resolution of 100 meters. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Chen, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J. Assessment of coordinative relationship between comprehensive ecosystem service and urbanization: A case study of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomerations, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, N.; Cote-Navarro, F.; Escobedo, F.J.; Rubiano, K.; Villegas, J.C. Spatio-temporal and cumulative effects of land use-land cover and climate change on two ecosystem services in the Colombian Andes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; He, N.; Yu, G. A dataset of carbon density in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems (2010s). China Sci. Data 2019, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, T.; Chen, H. Spatial-temporal evolution and prediction of carbon storage in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration based on PLUS-InVEST model. Environ. Sci. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, L.; Sun, R. A Chinese soil conservation dataset preventing soil water erosion from 1992 to 2019. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Yu, F. Spatial distribution of soil erosion and its relationship to environment factors in Anhui Province. Geogr. Res. 2010, 29, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Zheng, H.; Rao, E.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, C. Evaluating indirect and direct effects of Eco-Restoration policy on soil conservation service in Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 887–894. [Google Scholar]
- Pärn, J.; Pinay, G.; Mander, Ü. Indicators of nutrients transport from agricultural catchments under temperate climate: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 22, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Dong, L.; He, W.; Wang, Q.; Mooij, W.M.; Xu, F. Estimation of the long-term nutrient budget and thresholds of regime shift for a large shallow lake in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dai, Z.; Jiang, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, C.; Chen, S. Simulation of nitrogen export scenarios in Chaohu Basin Based on land use patterns. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, T.; Xie, H.; Wan, N.; Xiong, Z.; Hu, Z.; Lai, X. Simulation and source analysis of nonpoint source nitrogen and phosphorus pollution export in a typical agricultural catchment draining to Chaohu Lake. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 2428–2438. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Lin, H.; Qureshi, S.; Cao, A.; Ma, Y. Understanding the dynamics and factors affecting cultural ecosystem services during urbanization through spatial pattern analysis and a mixed-methods approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C.; Muhar, A.; Arnberger, A.; Aznar, O.; Boyd, J.W.; Chan, K.M.A.; Costanza, R.; Elmqvist, T.; Flint, C.G.; Gobster, P.H.; et al. Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8812–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Hu, F.; Yuan, B.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, L. Impacts and predictions of urban expansion on habitat quality in the densely populated areas: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Quantifying the spatial impact of landscape fragmentation on habitat quality: A multi-temporal dimensional comparison between the Yangtze River Economic Belt and Yellow River Basin of China. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Su, Y.; Duan, H.; Wu, X.; Lu, R.; Su, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chu, Z. Study on spatiotemporal evolution and driving forces of habitat quality in the basin along the Yangtze River in Anhui Province based on InVEST model. Land 2023, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Cheng, S.; Huang, L.; Jiao, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H. Temporal and spatial variations in landscape habitat quality under multiple Land-Use/Land-Cover scenarios based on the PLUS-InVEST model in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Land 2023, 12, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, T.; Mount, D.M.; Netanyahu, N.S.; Piatko, C.D.; Silverman, R.; Wu, A.Y. An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliñski, T.; Harabasz, J. A Dendrite Method Foe Cluster Analysis. Commun. Stat. 1974, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- El Khattabi, M.Z.; El Jai, M.; Lahmadi, Y.; Oughdir, L.; Rahhali, M. Understanding the Interplay Between Metrics, Normalization Forms, and Data Distribution in K-Means Clustering: A Comparative Simulation Study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 2987–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K. Identification of Ecosystem Service Bundles and Driving Factors in Beijing and Its Surrounding Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, G.D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, P.; Lei, G.C. Mapping the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service relationships and bundles in Ningxia, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.S.; Li, S.C.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.B.; Li, D.L.; Wu, S.Y. Exploring the heterogeneity and nonlinearity of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services bundles in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.M.; Li, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, N.; La, L.M.; Liu, C.F.; Xiao, W.F. Identifying and analyzing ecosystem service bundles and their socioecological drivers in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, E. Spatial-temporal changes in ecosystem services and the trade-off relationship in mountain regions: A case study of Hengduan Mountain region in Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shan, R.; Liu, F. Spatio-temporal quantification of patterns, trade-offs and synergies among multiple hydrological ecosystem services in different topographic basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yang, D.; Jing, W.; Rong, T. Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs/synergies among ecosystem services in the Yellow river basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-Temporal Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Service Interactions and Their Social-Ecological Drivers: Implications for Spatial Planning and Management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.W.; Hu, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Daryanto, S.; Cherubini, F. Trading-off ecosystem services for better ecological restoration: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, J.; Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. How trade-offs between ecological construction and urbanization expansion affect ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, S.; Xu, Z. Assessment and Management Zoning of Ecosystem Service Trade-Off/Synergy Based on the Social–Ecological Balance: A Case of the Chang-Zhu-Tan Metropolitan Area. Land 2024, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhu, Z. What Is the Spatiotemporal Relationship between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services? A Case from 110 Cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Sang, W. Land use trade-offs and synergies based on temporal and spatial patterns of ecosystem services in South China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Investigating the trade-offs between the supply and demand for ecosystem services for regional spatial management. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325 Pt A, 116591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.Y.; Liu, D.R. Exploring the ecosystem services bundles and influencing drivers at different scales in southern Jiangxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Hou, Y.; Andersen, P.S.; Xin, R.; Rong, Y.; Skov-Petersen, H. An ecological perspective for understanding regional integration based on ecosystem service budgets, bundles, and flows: A case study of the Jinan metropolitan area in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hao, R.; Qiao, J.; Xue, H. Function zoning and spatial management of small basins based on ecosystem disservice bundles. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zuo, L.; Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Du, F.; Zhang, Y. Exploring the driving factors of trade-offs and synergies among ecological functional zones based on ecosystem service bundles. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).