Assessing and Predicting Spatiotemporal Alterations in Land-Use Carbon Emission and Its Implications to Carbon-Neutrality Target: A Case Study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
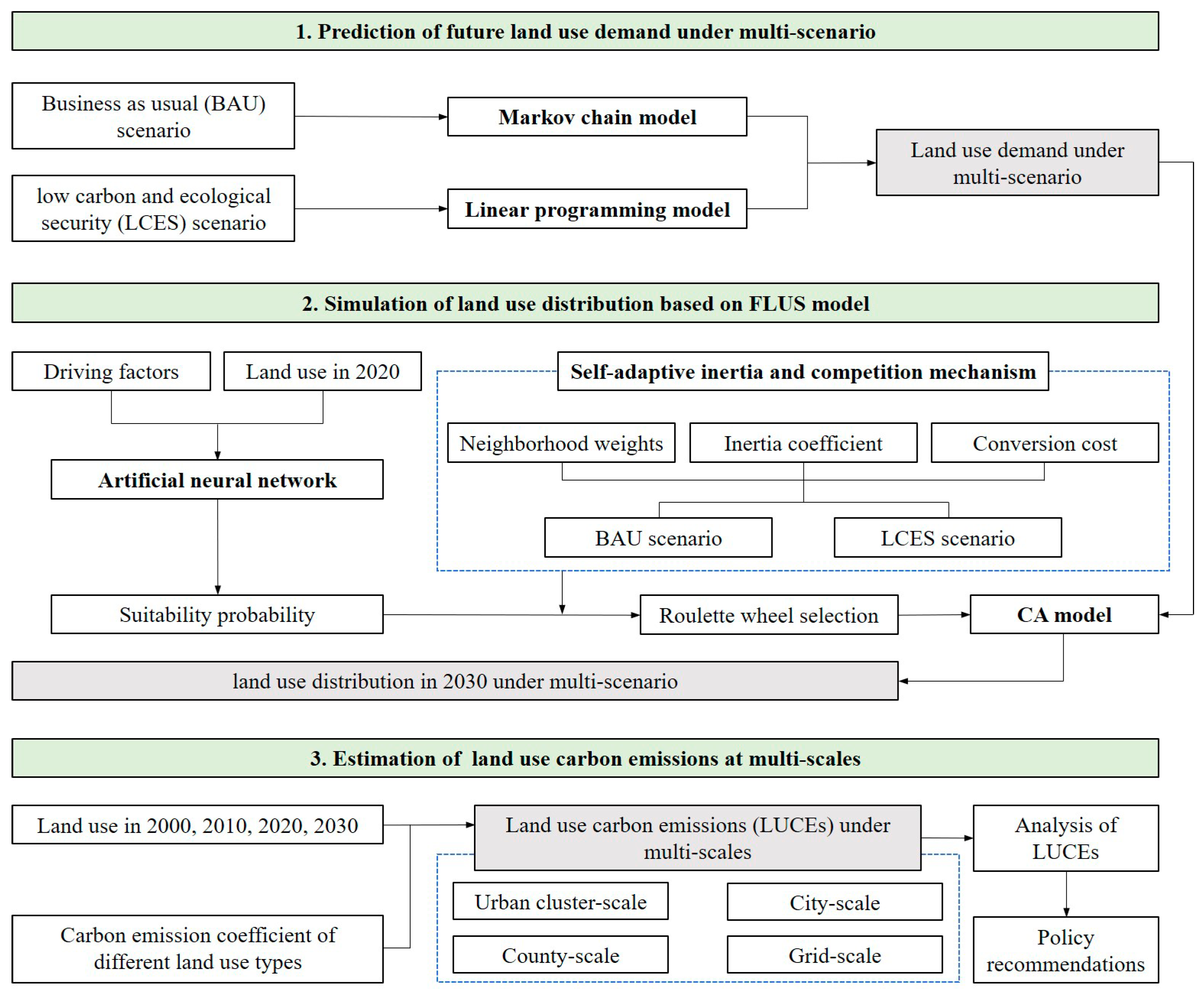
2.2. Research Framework
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Design of Different Scenarios
2.3.2. Markov Chain Model
2.3.3. Linear Programming Model
2.3.4. FLUS Model
2.3.5. Carbon Emission Coefficient
2.4. Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. Historical Land Use and Land-Use Carbon Emission Alterations
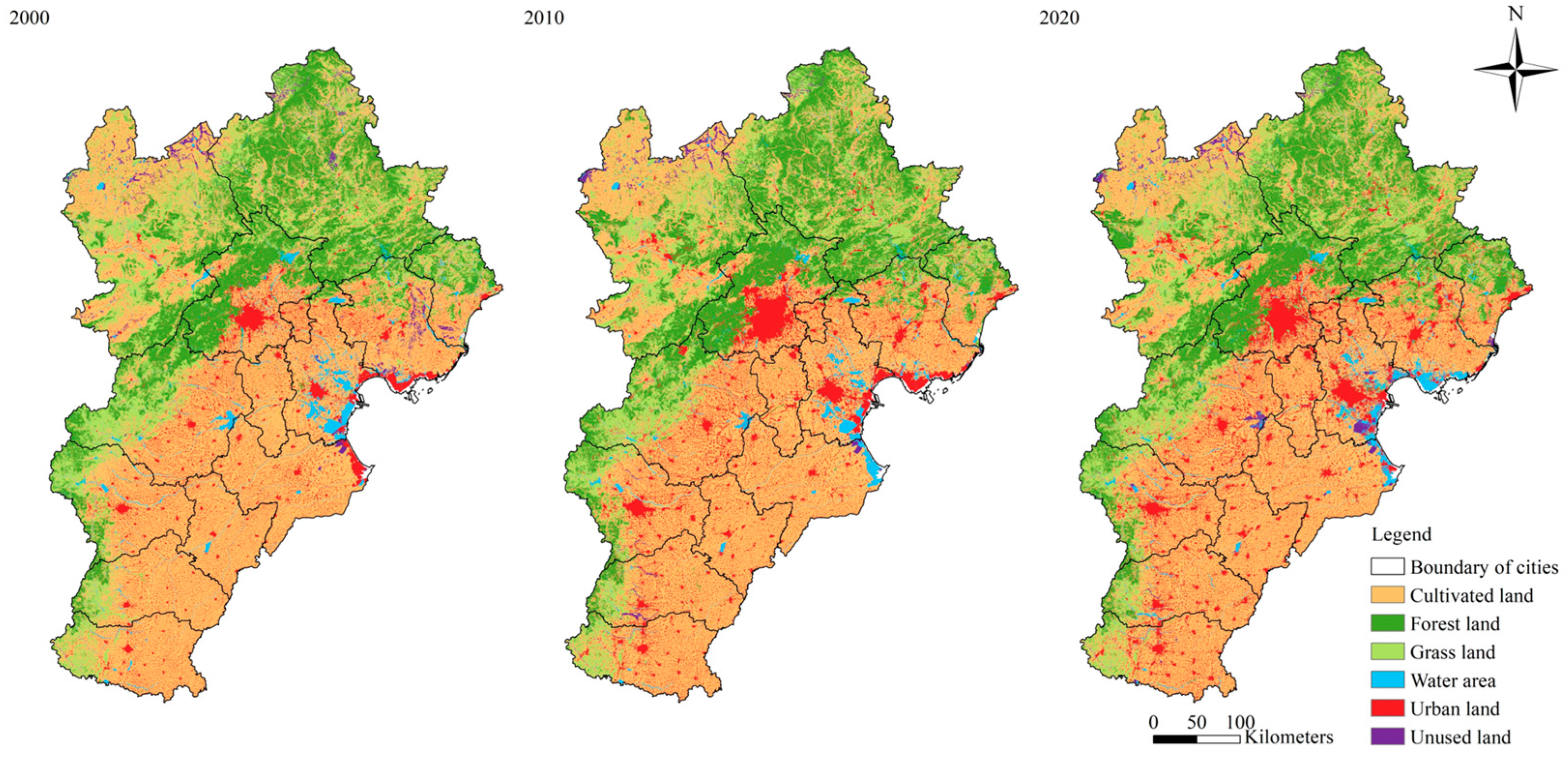
3.1.1. Land-Use Changes Between 2000 and 2020
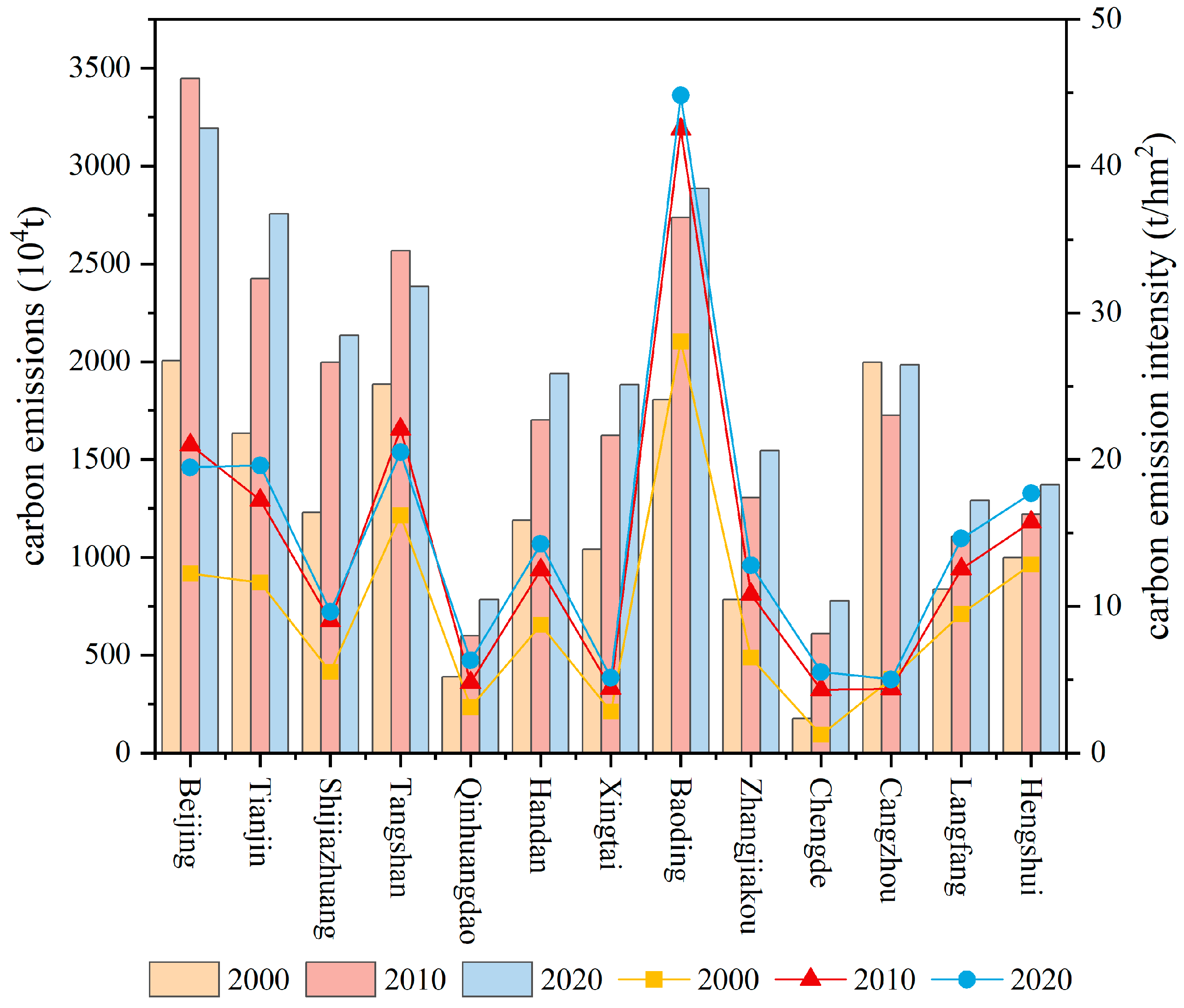
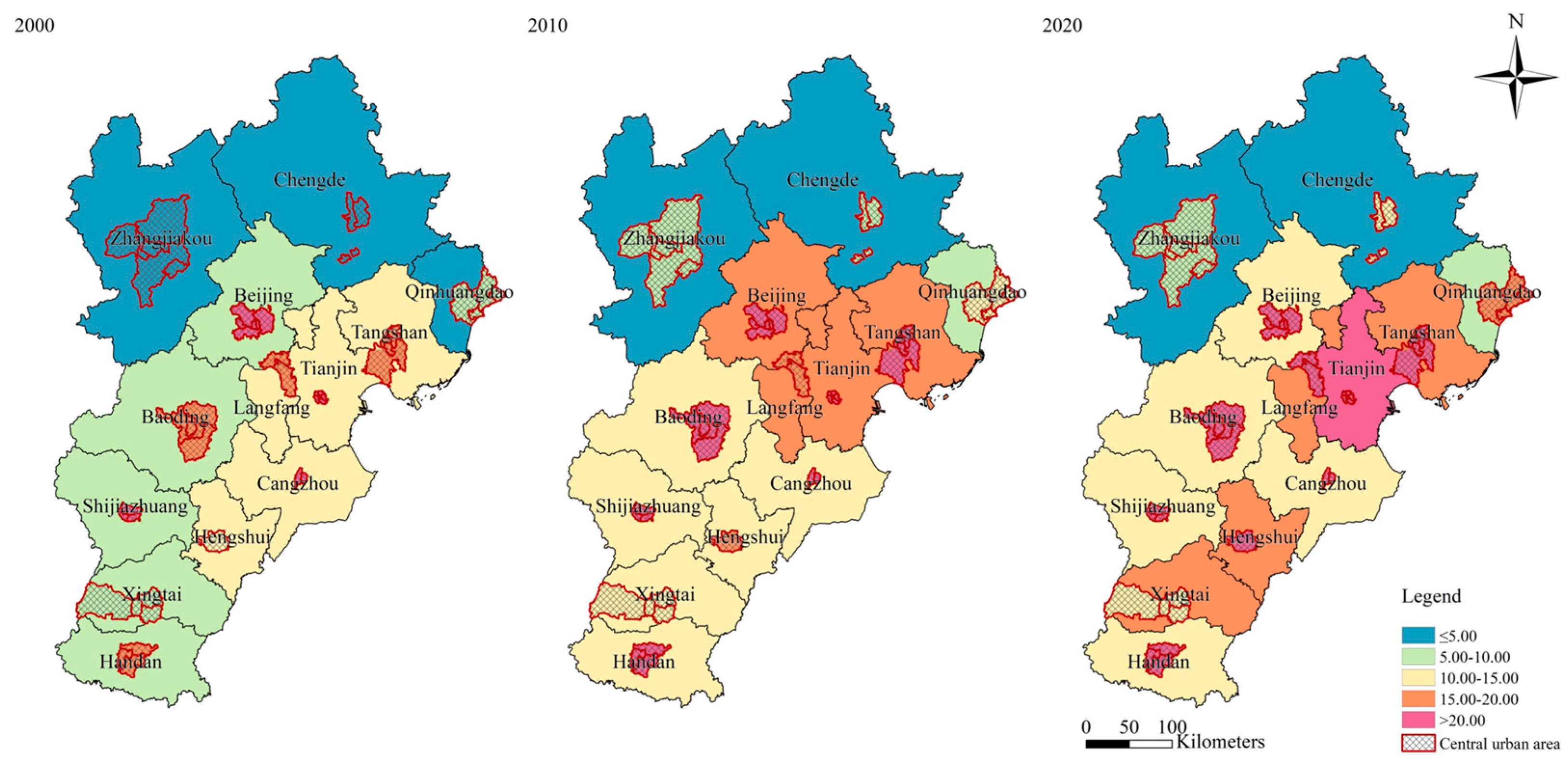
3.1.2. Land-Use Carbon Emission Changes Between 2000 and 2020
3.2. Future Land Use and Land-Use Carbon Emission Alterations in Various Scenarios
3.2.1. Future Land-Use Changes in Various Scenarios
3.2.2. Future Land-Use Carbon Emission Changes in Various Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing Land-Use Carbon Emissions
4.1.1. Impact of Urbanization on Carbon Emissions from Land Use
4.1.2. Impact of Development Policies and Spatial Planning on Carbon Emissions from Land Use
4.2. Recommendations for Low-Carbon Development at Various Scales
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- JingYun, F.; JiangLing, Z.; ShaoPeng, W.; Chao, Y.; HaiHua, S. Global Warming, Human-Induced Carbon Emissions, and Their Uncertainties. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, S.; Plattner, G.-K.; Knutti, R.; Friedlingstein, P. Irreversible Climate Change Due to Carbon Dioxide Emissions. Enrivon. Sci. 2009, 106, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S. Research Progress in Climate Change Impact, Risk, and Adaptation: An Interpretation of Part 2 of China’s Fourth National Assessment Report on Climate Change. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, W. Climate Change and Interconnected Risks to Sustainable Development in the Mediterranean. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.; Barros, V.R.; Dokken, D.J.; Mach, K.J.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Bilir, T.E.; Chatterjhee, M.; Ebi, K.L.; Estrada, Y.O.; Genova, R.C.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge Univeristy Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Guillén Bolaños, T.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.A.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.; et al. The Human Imperative of Stabilizing Global Climate Change at 1.5 °C. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleick, P.H.; Adams, R.M.; Amasino, R.M.; Anders, E.; Anderson, D.J.; Anderson, W.W.; Anselin, L.E.; Arroyo, M.K.; Asfaw, B.; Ayala, F.J.; et al. Climate Change and the Integrity of Science. Science 2010, 328, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, R.A.; House, J.I.; Pongratz, J.; Van Der Werf, G.R.; DeFries, R.S.; Hansen, M.C.; Le Quéré, C.; Ramankutty, N. Carbon Emissions from Land Use and Land-Cover Change. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 5125–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.B.; Powell, T.; Cox, P.M.; House, J.; Huntingford, C.; Lenton, T.M.; Sitch, S.; Burke, E.; Chadburn, S.E.; Collins, W.J.; et al. Land-Use Emissions Play a Critical Role in Land-Based Mitigation for Paris Climate Targets. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Qi, X.; Li, J.; Zuo, T.; Lu, Q.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Zhao, R. A Preliminary Study of the Carbon Emissions Reduction Effects of Land Use Control. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Mahmood, R.; Zheng, Z. Land Use/Land Cover Changes and Regional Climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001–2009. Part I: Observational Evidence. Clim. Chang. 2015, 129, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyssaert, S.; Jammet, M.; Stoy, P.C.; Estel, S.; Pongratz, J.; Ceschia, E.; Churkina, G.; Don, A.; Erb, K.; Ferlicoq, M.; et al. Land Management and Land-Cover Change Have Impacts of Similar Magnitude on Surface Temperature. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Huang, X.; Zhong, T.; Chuai, X. Carbon Effect Evaluation and Low-Carbon Optimization of Regional Land Use. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F. Effect of Carbon Tax Policy on Agricultural Land Use Change and Its Carbon Emission. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zheng, X. The Prospects of Development of the Three-North Afforestation Program (TNAP): On the Basis of the Results of the 40-Year Construction General Assessment of the TNAP. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, M. Evolution and Assessment of Forest Carbon Sink Policy over the Past 20 Years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 3430–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Huang, S.; Liu, R. Progress and Review of the Research of Farmland Requisition-Compensation Balance in China. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 2342–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, L.; Cheng, T.; Chen, D.; Zhou, G.; Liu, C.; Kou, S.; Chen, Z.; Guan, Q. CarbonVCA: A Cadastral Parcel-Scale Carbon Emission Forecasting Framework for Peak Carbon Emissions. Cities 2023, 138, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C. Effects of Land-Use Change on Carbon Emission and Its Driving Factors in Shaanxi Province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 68313–68326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, C. Carbon Emission and Economic Development Trade-Offs for Optimizing Land-Use Allocation in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A Future Land Use Simulation Model (FLUS) for Simulating Multiple Land Use Scenarios by Coupling Human and Natural Effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Spatial Correlation Evolution and Prediction Scenario of Land Use Carbon Emissions in China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Fang, R.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Carbon Emissions from Land Use Change in Yellow River Delta Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, Z.A.; Kafy, A.-A.; Saha, M.; Rahim, A.A.; Almulhim, A.I.; Rahaman, S.N.; Fattah, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Kalaivani, S.; Faisal, A.-A.; et al. Assessing the Impacts of Vegetation Cover Loss on Surface Temperature, Urban Heat Island and Carbon Emission in Penang City, Malaysia. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kafy, A.-A.; Xiao, P.; Han, S.; Zou, S.; Saha, M.; Zhang, C.; Tan, S. Impact of Urban Expansion on Land Surface Temperature and Carbon Emissions Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Wuhan, China. Urban Clim. 2023, 47, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.D.; Rigby, M.; Lunt, M.F.; Smallman, T.L.; Comyn-Platt, E.; Manning, A.J.; Ganesan, A.L.; O’Doherty, S.; Stavert, A.R.; Stanley, K.; et al. Quantifying the UK’s Carbon Dioxide Flux: An Atmospheric Inverse Modelling Approach Using a Regional Measurement Network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4345–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Guo, Z.; Piao, S.; Chen, A. Estimation of Carbon Sinks of Terrestrial Vegetation in China from 1981 to 2000. Sci. Sin. (Terrae) 2007, 37, 804–812. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Ciais, P.; Peylin, P.; Huang, Y.; Sitch, S.; Wang, T. The Carbon Balance of Terrestrial Ecosystems in China. Nature 2009, 458, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.A.; Nassikas, A.A. Global and Regional Fluxes of Carbon from Land Use and Land Cover Change 1850–2015. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Schwingshackl, C.; Gasser, T.; Houghton, R.A.; Sitch, S.; Canadell, J.G.; Cescatti, A.; Ciais, P.; Federici, S.; Friedlingstein, P.; et al. Harmonising the Land-Use Flux Estimates of Global Models and National Inventories for 2000–2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 1093–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C. Land Use, Total Carbon Emissions Change and Low Carbon Land Management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.R.; Middleton, J. A Markov Model of Land-Use Change Dynamics in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. Landsc. Ecol. 1994, 9, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bretz, M.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Delavar, M.A. Machine Learning in Modelling Land-Use and Land Cover-Change (LULCC): Current Status, Challenges and Prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, H.; Yao, Y. Delineating Multi-Scenario Urban Growth Boundaries with a CA-Based FLUS Model and Morphological Method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 177, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Deng, S.; Wu, D.; Liu, W.; Bai, Z. Research on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Use Landscape Pattern in a County Area Based on CA-Markov Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tang, B.; Yeung, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheung, G. A System Dynamics Model for the Sustainable Land Use Planning and Development. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, K.; Zuo, C.; Li, Q. Spatiotemporal Variation of Land-Use Carbon Emissions and Its Implications for Low Carbon and Ecological Civilization Strategies: Evidence from Xiamen-Zhangzhou-Quanzhou Metropolitan Circle, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 86, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Xu, N.; Ye, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, X. Estimating Chinese Energy-Related CO2 Emissions by Employing a Novel Discrete Grey Prediction Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.J.; Wu, W.B.; Yang, P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Verburg, P.H. Recent Progresses of Land Use and Land Cover Change (LUCC) Models. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 456–468. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; He, J. Concepts, Methodologies, and Tools of an Integrated Geographical Simulation and Optimization System. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 633–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Tang, W.; Liu, D. An Adaptive Agent-Based Optimization Model for Spatial Planning: A Case Study of Anyue County, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 51, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Q. Characteristics and Progress of Land Use/Cover Change Research during 1990–2018. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Jiang, W.; Ling, Z.; Hou, P.; Deng, Y. Evaluating the Potential Impacts of Land Use Changes on Ecosystem Service Value under Multiple Scenarios in Support of SDG Reporting: A Case Study of the Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, S.; Yu, M. Projections of Land Use Change and Habitat Quality Assessment by Coupling Climate Change and Development Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z. Modelling the Potential Impacts of Urban Ecosystem Changes on Carbon Storage under Different Scenarios by Linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST Models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, P.; Feng, K.; Hubacek, K.; Li, X.; Sun, L. Impacts of Urban Expansion on Terrestrial Carbon Storage in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6834–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, B.; Wei, H. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of Land-Use Carbon Emissions in Nine Provinces of the Yellow River Basin Based on the LMDI Model. Land 2023, 12, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X. Urban Growth Simulation by Incorporating Planning Policies into a CA-Based Future Land-Use Simulation Model. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Sun, S.; Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Zeng, L. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Its Impact on Ecosystem Services in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on the FLUS-InVEST Model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 4473–4487. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Fan, B. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation of Carbon Emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Land Use and Night Time Light Data. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 38, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Tang, Z.; Mei, Z. Urbanization, Land Use Change, and Carbon Emissions: Quantitative Assessments for City-Level Carbon Emissions in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, J.; Yang, X.; Peng, Q. Zoning and Governance of County Ecological Space for the Increase of Carbon Sinks: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Planners 2022, 38, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, H. Optimizing Land Use Patterns to Improve the Contribution of Land Use Planning to Carbon Neutrality Target. Land Use Policy 2023, 135, 106959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.J.; Hinojosa, R. Markov Analysis of Land Use Change: Continuous Time and Stationary Processes. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 1977, 11, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsanjani, J.J.; Helbich, M.; Kainz, W.; Boloorani, A.D. Integration of Logistic Regression, Markov Chain and Cellular Automata Models to Simulate Urban Expansion. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Lan, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, P. Optimization of Low-Carbon Land Use in Chengdu Based on Multi-Objective Linear Programming and the Future Land Use Simulation Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 989747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Xue, F.; Li, Q.; Fang, K.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, J. Exploring Potential of Urban Land-Use Management on Carbon Emissions—A Case of Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Sun, Y.; Nijhuis, S.; Wang, Z. Scenario-Based Flood Risk Assessment for Urbanizing Deltas Using Future Land-Use Simulation (FLUS): Guangzhou Metropolitan Area as a Case Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Huanhuan Song Pattern of Spatial Evolution of Rural Settlements in the Jizhou District of China during 1962–2030. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 122, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Hu, Y. Assessing Temporal-Spatial Land Use Simulation Effects with CLUE-S and Markov-CA Models in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32231–32245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Pu, L.; Wen, J.; Xu, Y. Hypothesis and Validation on the Kuznets Curve of Construction Land Expansion and Carbon Emission Effect. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 723–733. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, F.; Ouyang, Z. Carbon Sequestration and Its Potential by Wetland Ecosystems in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhou, J.; Hao, R.; Chen, D. Changes in Land Use Carbon Emissions and Coordinated Zoning in China. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Chang, X.; Cui, Q.; Tao, Y. Land Use Patterns on Carbon Emission and Spatial Association in China. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Urbanization Impact on Regional Sustainable Development: Through the Lens of Urban-Rural Resilience. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Z. Farmers’ Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Rural Industrial Land Changes and Their Influencing Factors: Evidences from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 86, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kuang, W. Spatio-Temporal Trajectories of Urban Land Use Change During 1980–2015 and Future Scenario Simulation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 187–194+200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, W. Using the InVEST-PLUS Model to Predict and Analyze the Pattern of Ecosystem Carbon Storage in Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Response and Multi-Scenario Prediction of Carbon Storage to Land Use/Cover Change in the Main Urban Area of Chongqing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Chi, W.; Zhang, C. The Rapid and Massive Urban and Industrial Land Expansions in China between 1990 and 2010: A CLUD-Based Analysis of Their Trajectories, Patterns, and Drivers. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 145, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Effects and Driving Factors of Land Use Carbon Emissions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Pratacult. Sci. 2022, 39, 2539–2553. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, K.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Y. Study of Integrated Land Consolidation Strategy: A Case Study of Cangzhou City, Hebei Province. Sci. Technol. Manag. Land Resour. 2013, 30, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Tian, H.; Wu, A.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal Changes and the Drivers of Coastal Land Use in Hebei and Tianjin in Recent 40 Years. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Duan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, P.; Tong, X.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, T. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use/Cover Change and Carbon Storage Assessment in Hainan Coastal Zone from Perspective of Free Trade Port Construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gen-Suo, J. New Understanding of Land-Climate Interactions from IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Land. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2020, 16, 9. [Google Scholar]



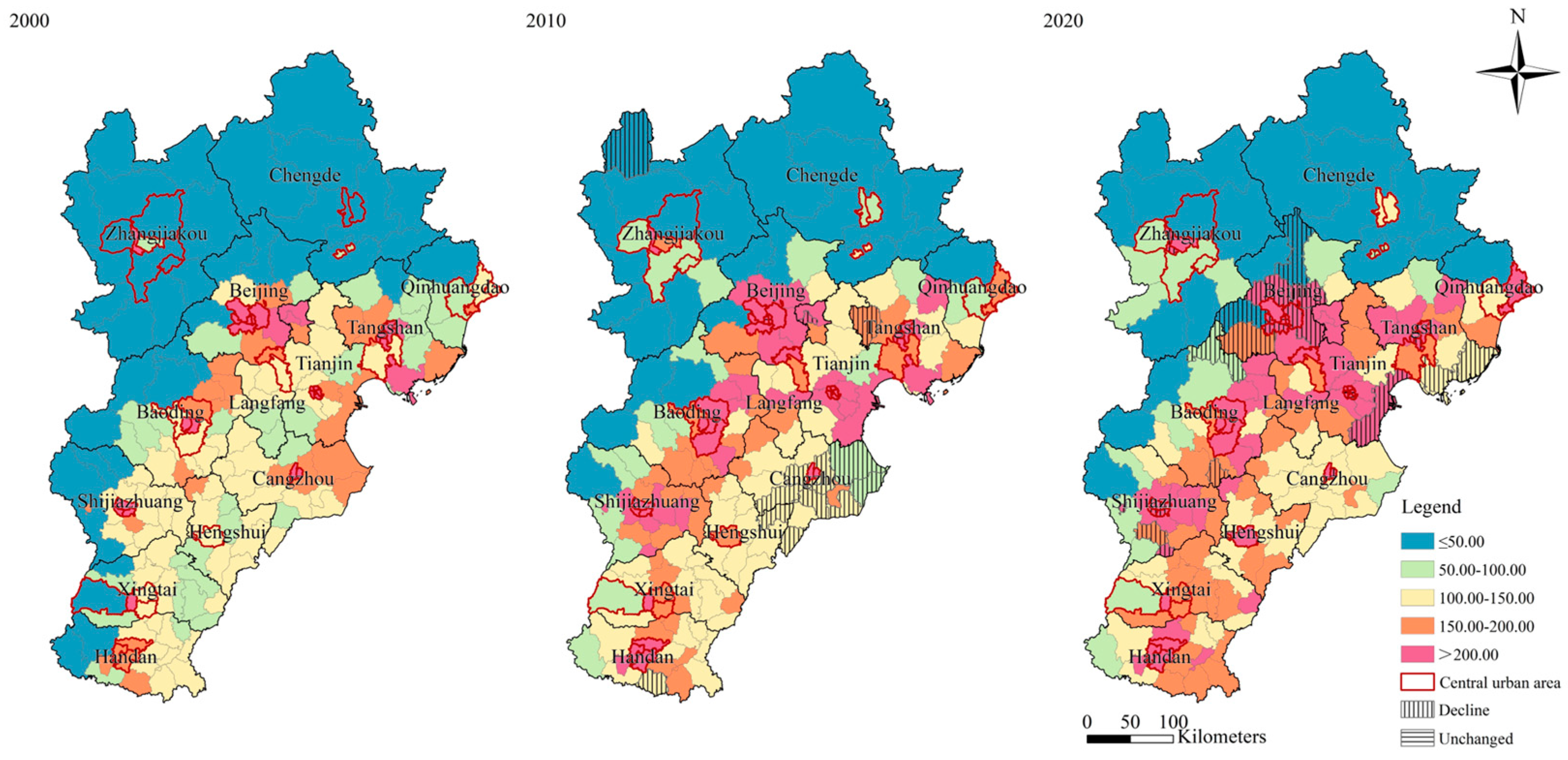

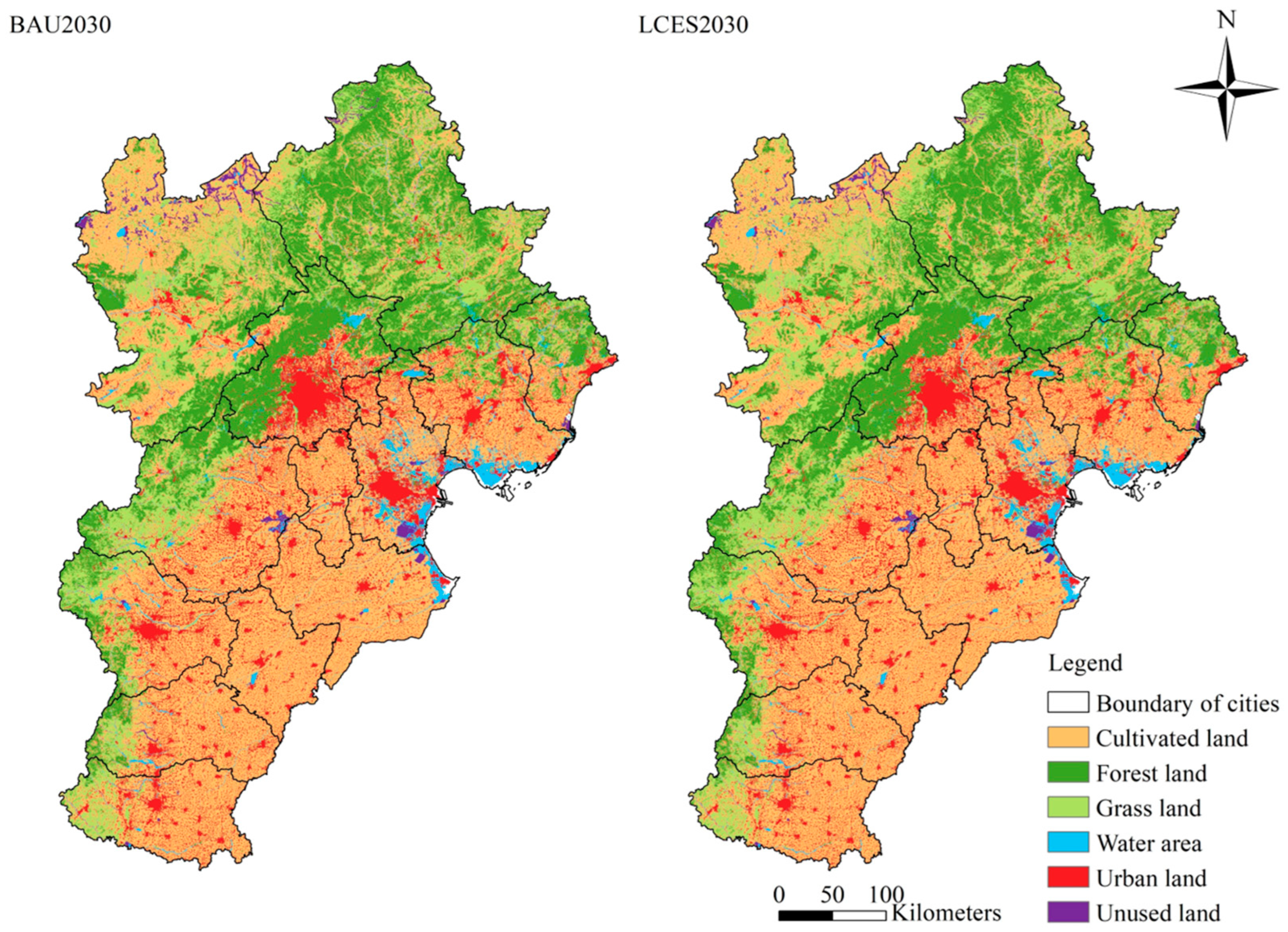
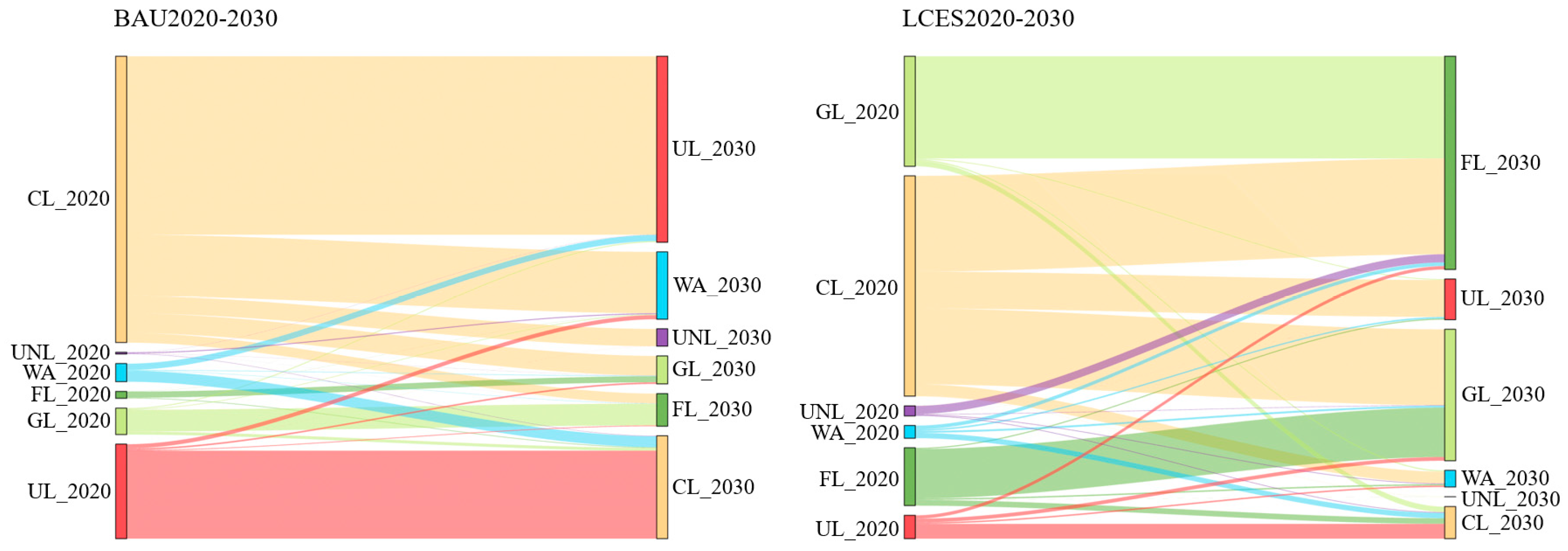

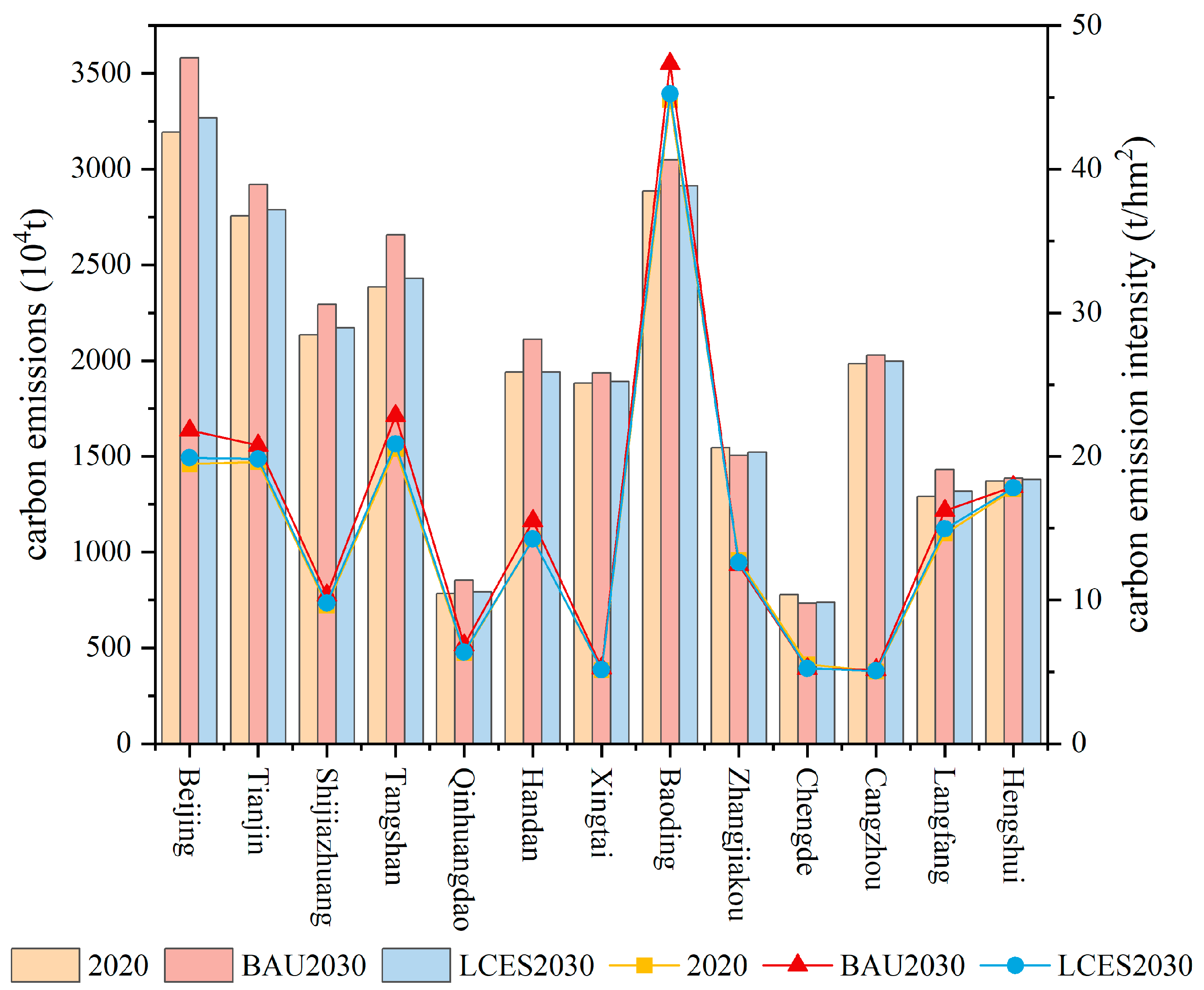
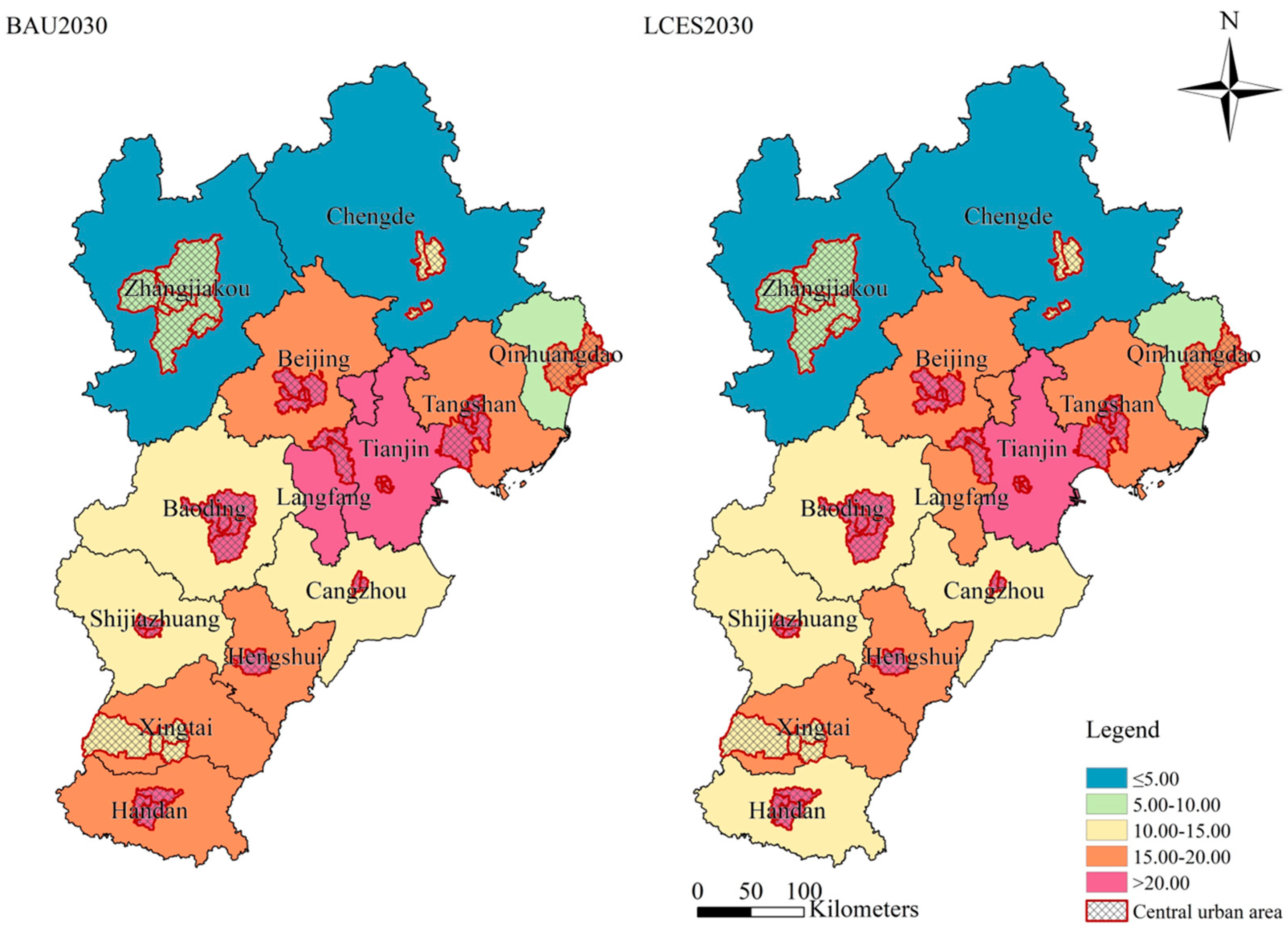

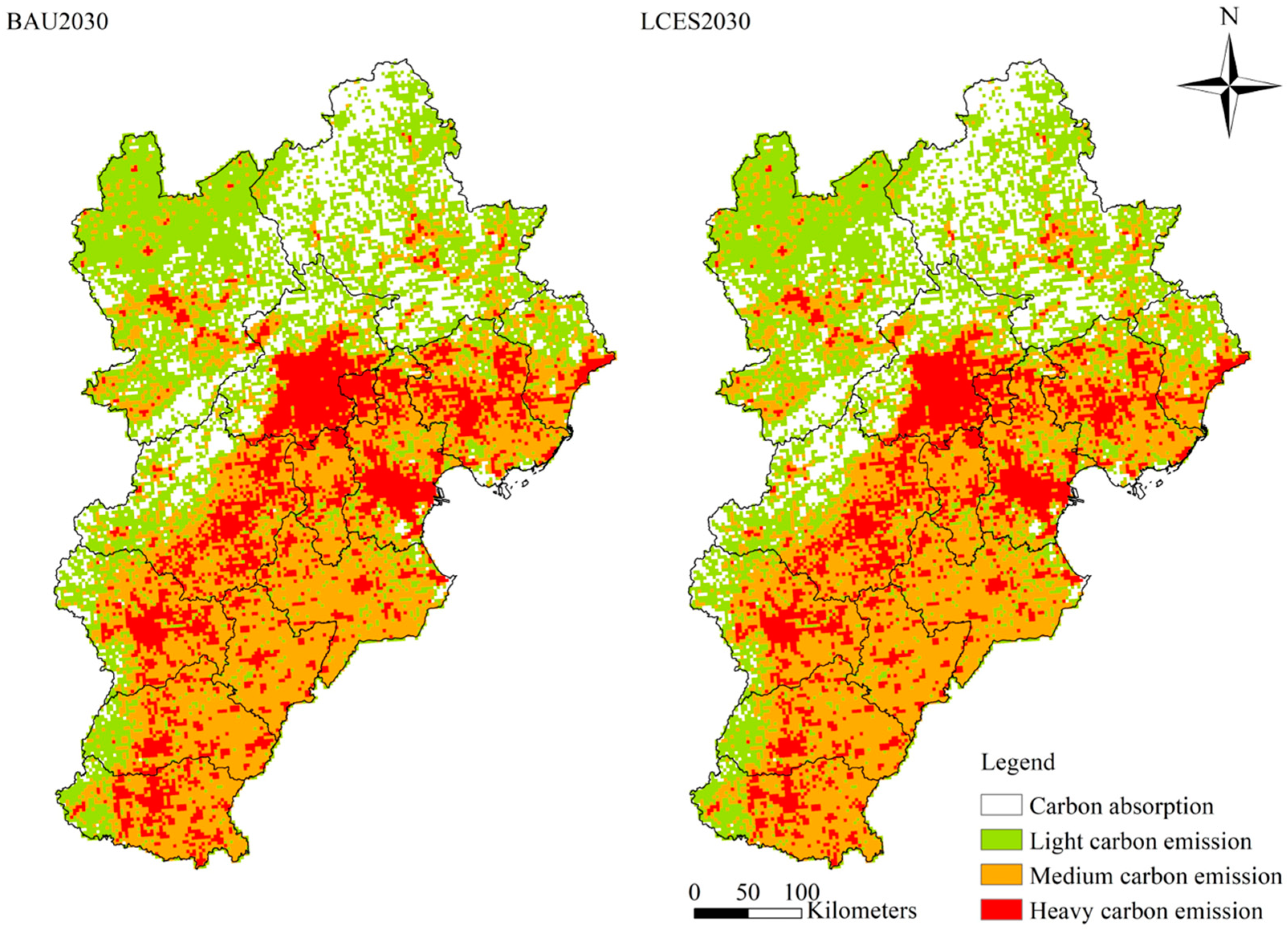

| Land-Use Categories | Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grassland | Water Area | Urban Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAU | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.01 |
| LCES | 0.3 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.01 |
| Land-Use Category | Carbon Emission Coefficient | References |
|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 0.422 | [23,61] |
| Forest land | −0.581 | [27] |
| Grassland | −0.021 | [27] |
| Water area | −0.253 | [62] |
| Urban land | 90.558 | According to the total energy consumption and urban land area of BTH from 2000 to 2020 |
| Unused land | −0.050 | [63,64] |
| 2020 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grassland | Water Area | Urban Land | Unused Land | Total | Losses | ||
| 2000 | Cultivated land | 43.42 | 0.64 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 5.30 | 0.05 | 50.82 | 7.40 |
| Forest land | 0.42 | 19.36 | 0.70 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 20.80 | 1.44 | |
| Grassland | 0.70 | 1.09 | 13.99 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 0.08 | 16.44 | 2.44 | |
| Water area | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 1.74 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 2.85 | 1.12 | |
| Urban land | 1.17 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 6.39 | 0.02 | 8.12 | 1.73 | |
| Unused land | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 0.96 | 0.59 | |
| Total | 46.44 | 21.20 | 15.85 | 2.98 | 12.75 | 0.77 | 100.00 | ||
| Gains | 3.02 | 1.85 | 1.85 | 1.24 | 6.36 | 0.40 | |||
| Gains | Losses | Total Change | Swap Change | Net Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 3.02 | 7.40 | 10.42 | 6.04 | 4.38 |
| Forest land | 1.85 | 1.44 | 3.29 | 2.88 | 0.40 |
| Grassland | 1.85 | 2.44 | 4.30 | 3.70 | 0.59 |
| Water area | 1.24 | 1.12 | 2.36 | 2.23 | 0.13 |
| Urban land | 6.36 | 1.73 | 8.09 | 3.46 | 4.63 |
| Unused land | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0.19 |
| Total | 14.72 | 14.72 | 14.72 | 4.40 | 10.32 |
| Types Scenarios | Cultivated Land | Forest Land | Grassland | Water Area | Urban Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 9,975,226 | 4,554,327 | 3,403,514 | 640,302 | 2,738,883 | 165,952 |
| BAU2030 | 9,625,256 | 4,603,168 | 3,406,428 | 734,306 | 2,913,388 | 195,658 |
| LCES2030 | 9,675,938 | 4,801,338 | 3,437,635 | 646,706 | 2,766,297 | 150,290 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, W.; Xie, Y.; Zeng, P. Assessing and Predicting Spatiotemporal Alterations in Land-Use Carbon Emission and Its Implications to Carbon-Neutrality Target: A Case Study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Land 2024, 13, 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122066
Lv W, Xie Y, Zeng P. Assessing and Predicting Spatiotemporal Alterations in Land-Use Carbon Emission and Its Implications to Carbon-Neutrality Target: A Case Study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Land. 2024; 13(12):2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Weitong, Yongqing Xie, and Peng Zeng. 2024. "Assessing and Predicting Spatiotemporal Alterations in Land-Use Carbon Emission and Its Implications to Carbon-Neutrality Target: A Case Study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region" Land 13, no. 12: 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122066
APA StyleLv, W., Xie, Y., & Zeng, P. (2024). Assessing and Predicting Spatiotemporal Alterations in Land-Use Carbon Emission and Its Implications to Carbon-Neutrality Target: A Case Study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Land, 13(12), 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13122066







