Identification of Thermal Environment Networks in the Wanjiang Urban Agglomeration Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
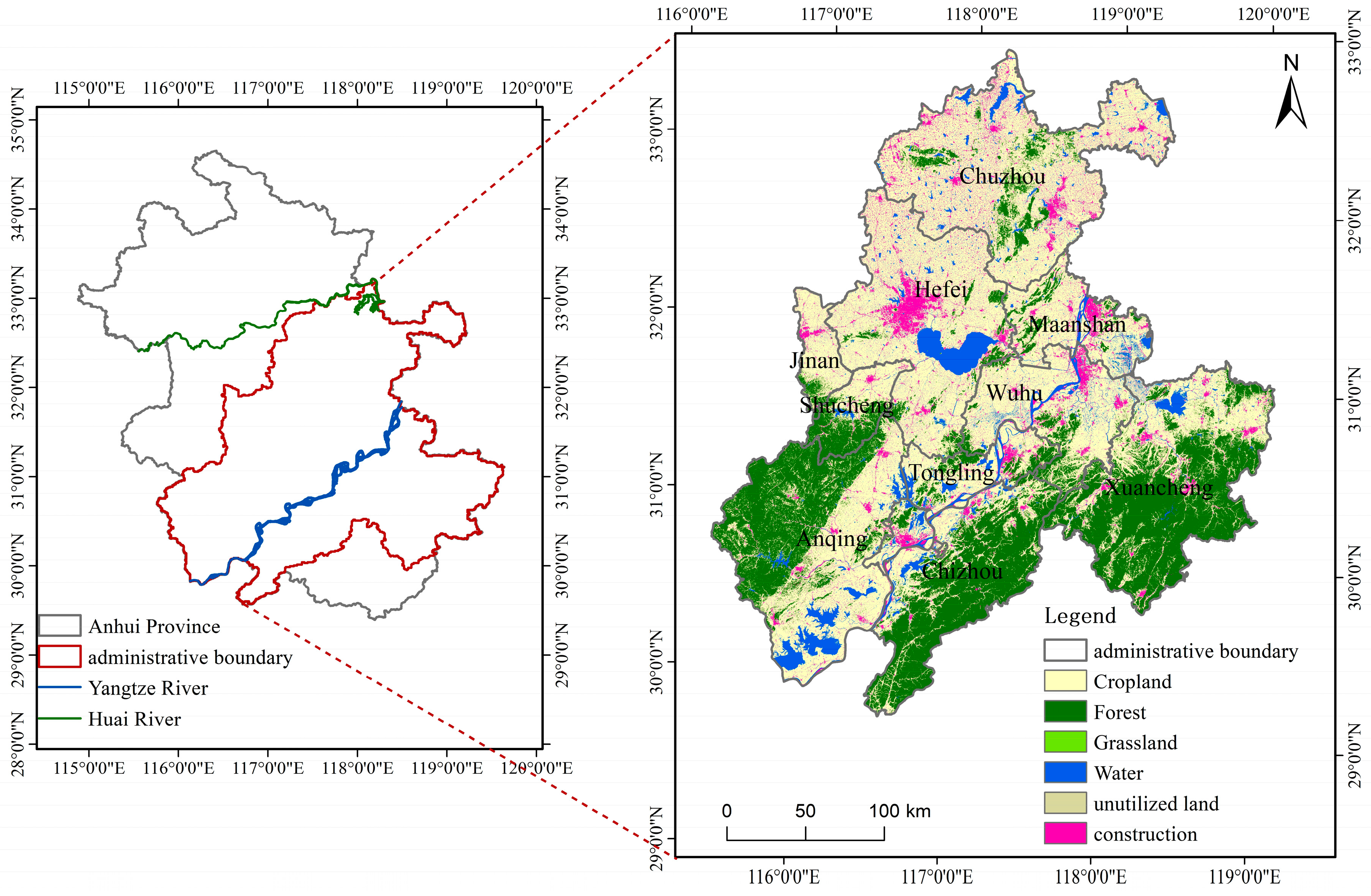
2.1. The General Situation of the Research Area
2.2. Data and Sources Required for the Study
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Urban Thermal Environment Source Extraction Based on the MSPA Model
2.3.2. Construction of the Resistance Surface of the Urban Thermal Environment
2.3.3. Linkage Mapper-Based Spatial Network Recognition in the Thermal Environment
Extraction of Urban Heat Island Corridors
Identification of Heat Island Network Pinch Point
Identification of Heat Island Network Barrier Point
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Urban Heat Island Patch Types
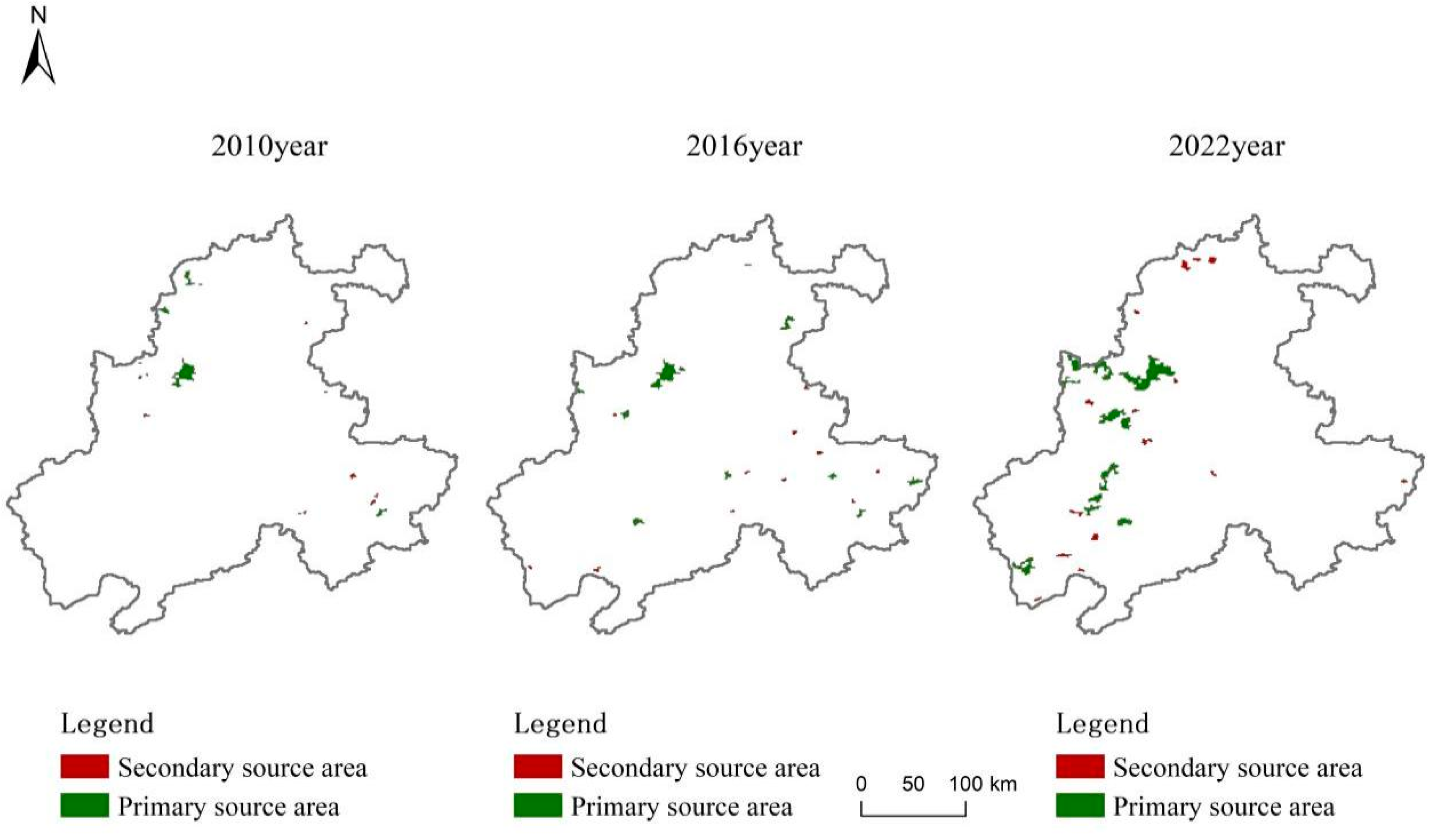
3.2. Urban Thermal Environment Source Extraction
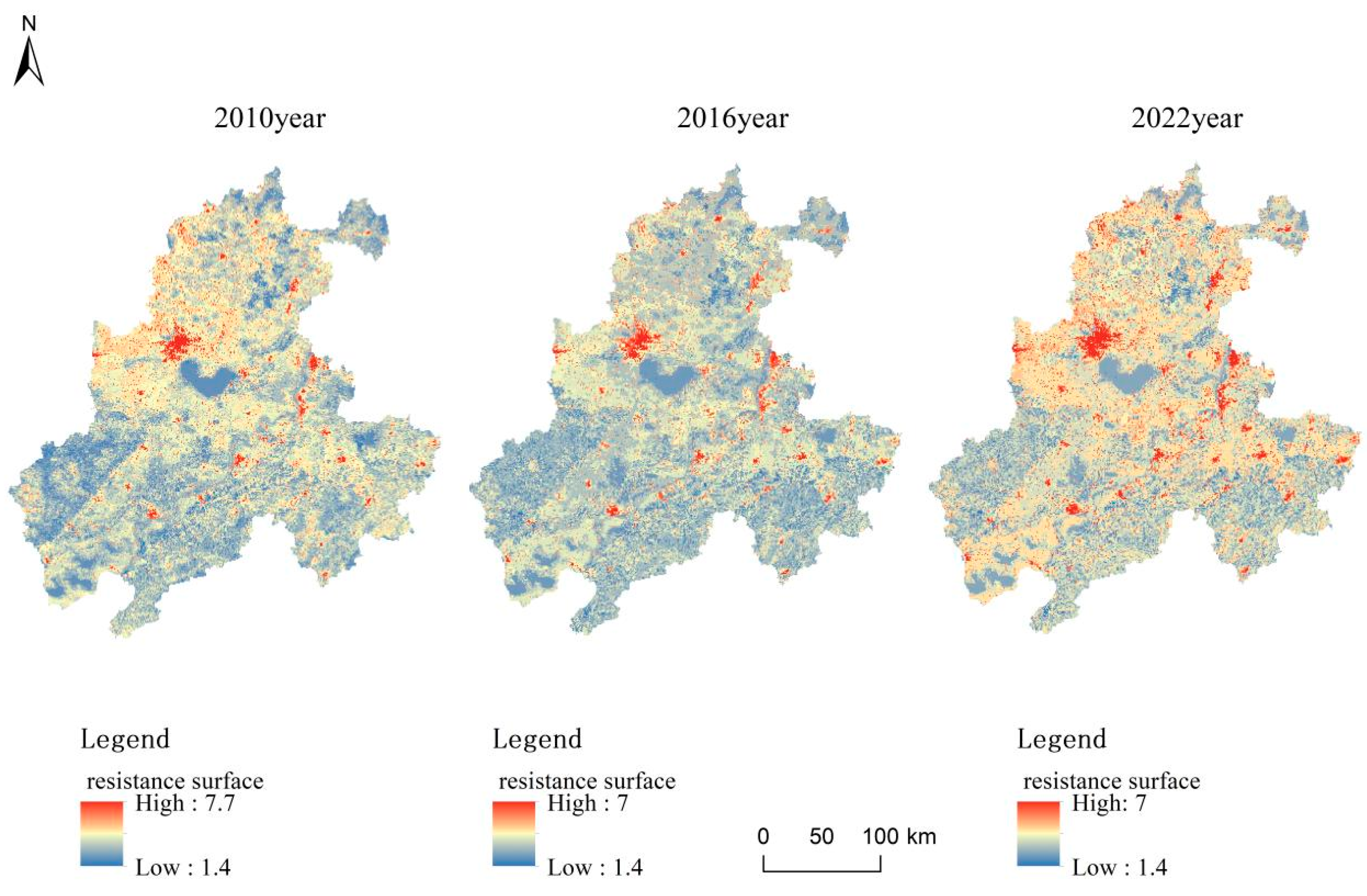
3.3. Construction Results of the Resistance Surface of the Urban Thermal Environment
3.4. Spatial Evolution of the Thermal Environment in the Urban Agglomeration
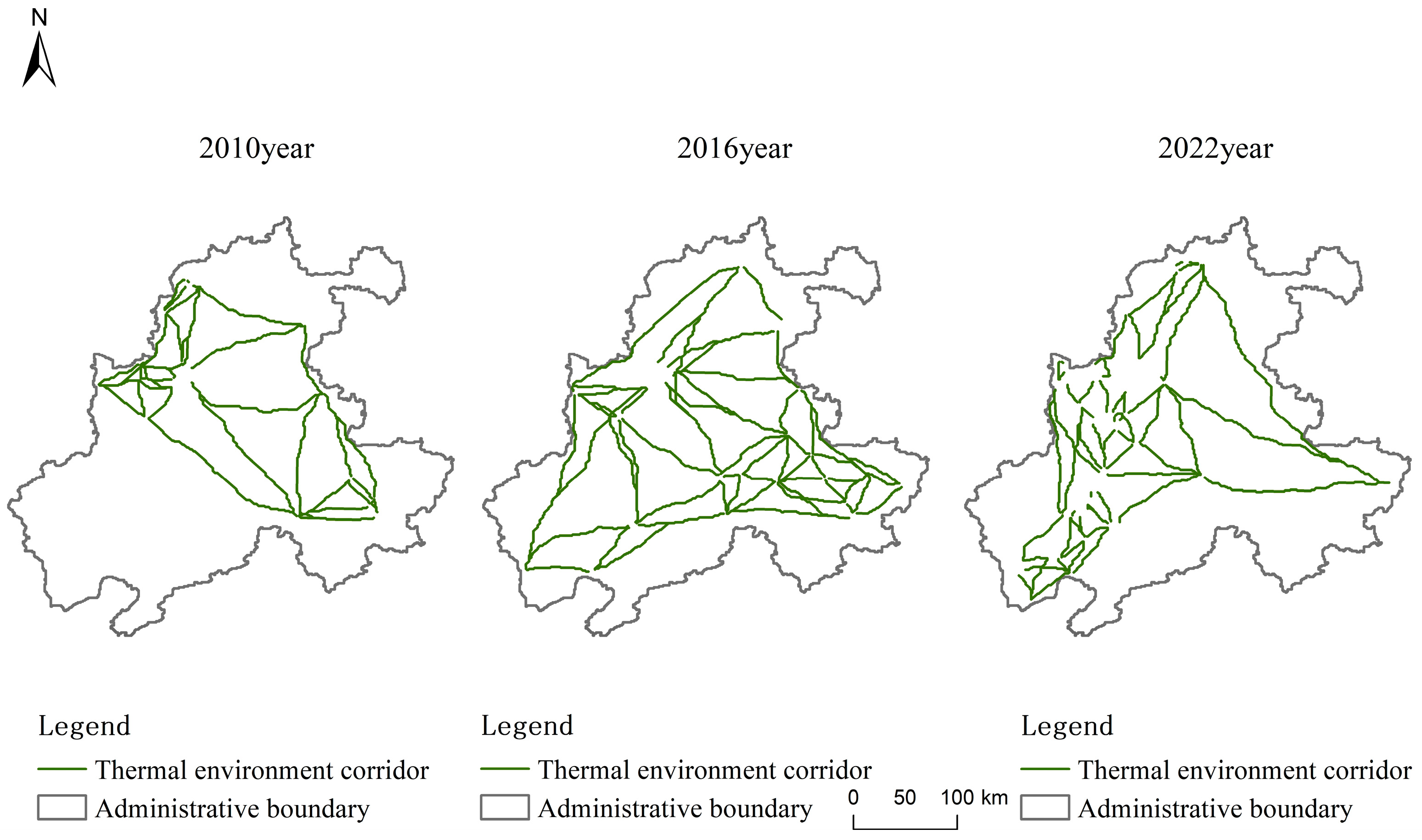
3.4.1. Identification of Heat Island Corridors
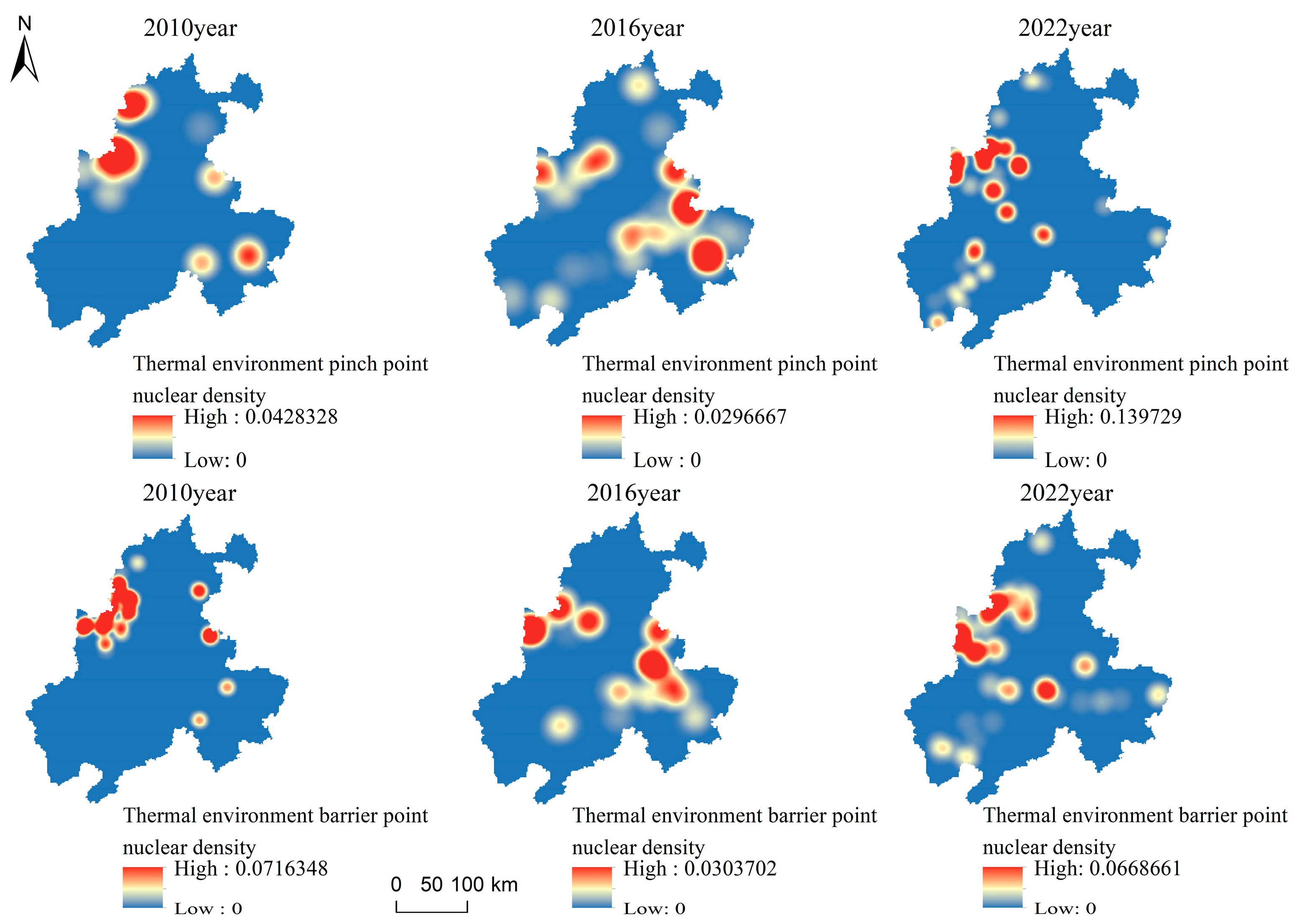
3.4.2. Extraction of Pinch Points in the Heat Island Network
3.4.3. Extraction of Heat Island Network Barrier Points
3.4.4. Nuclear Density Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the Overall Connectivity of Thermal Environment Networks
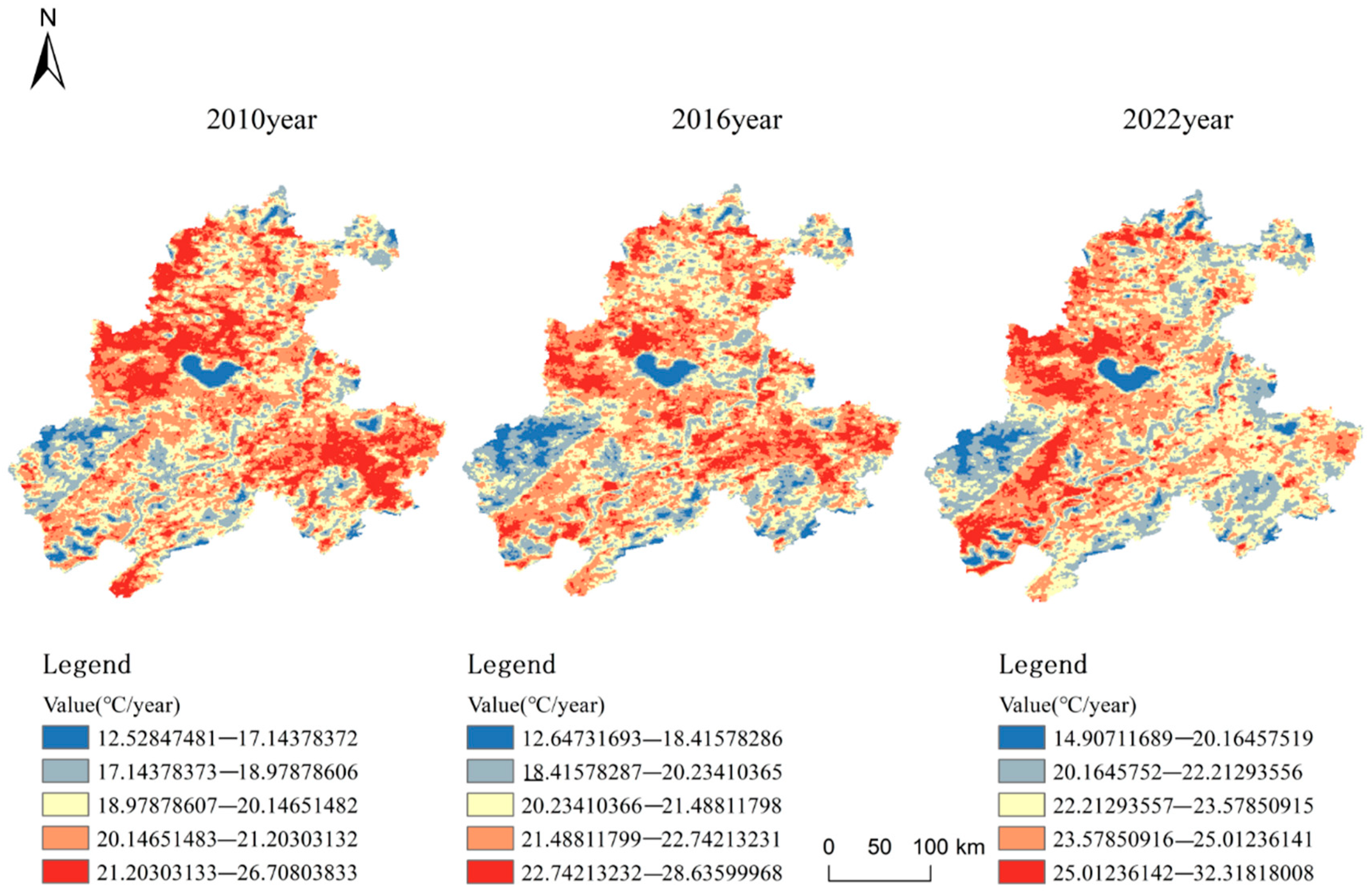
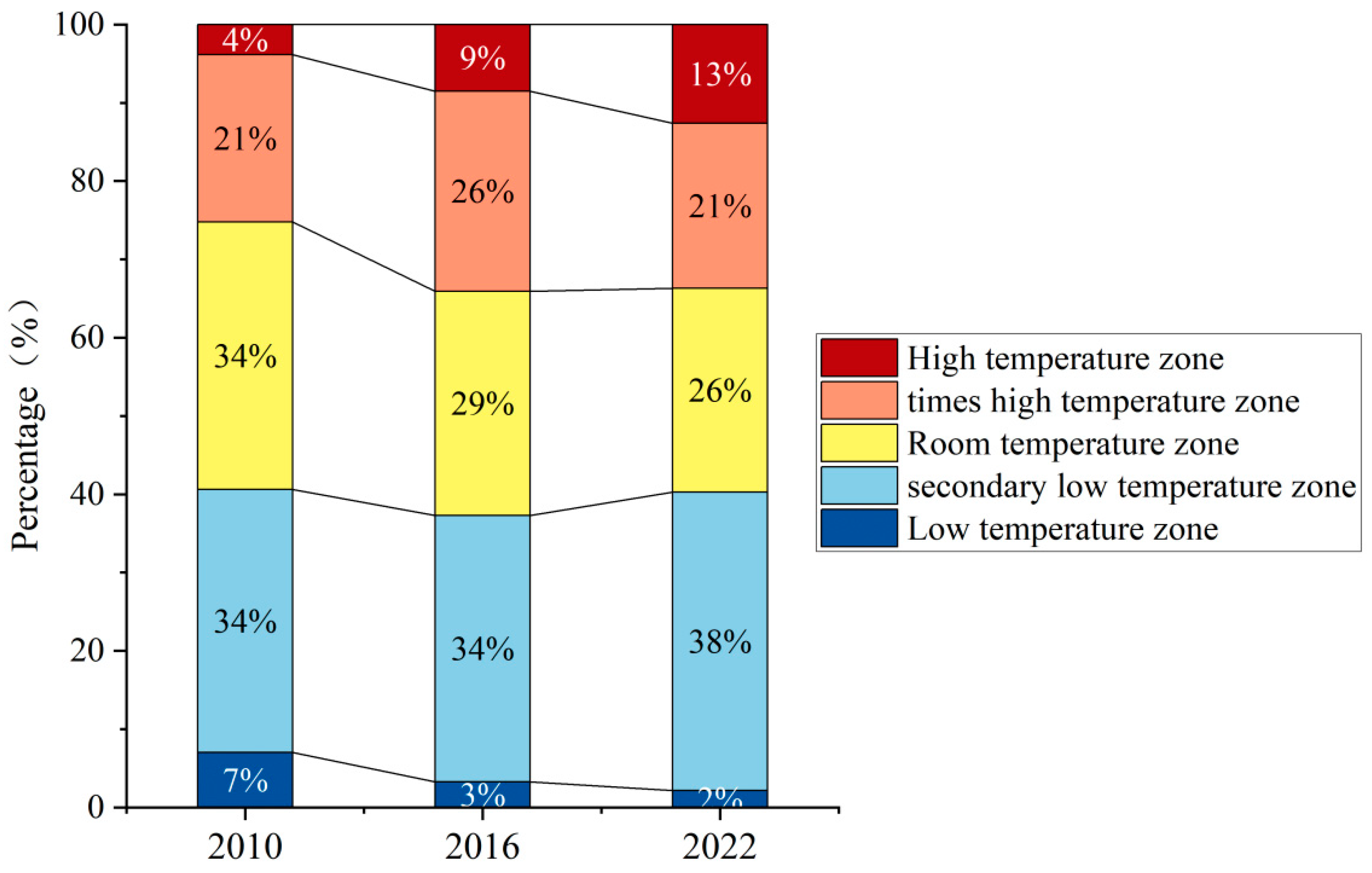
4.2. Spatial Evolution of the Land Surface Temperature and Heat Island Region in the Urban Agglomeration
4.3. The Application Practice of Coupling and Coordinating the Network Pattern of the Urban Agglomeration Thermal Environment
4.4. Current Research and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, C.; Zhou, L.G.; Yao, Y.R.; Ma, W.C.; Kinney Partric, L. Estimating spatial effects of anthropogenic heat emissions upon the urban thermal environment in an urban agglomeration area in East China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 57, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreevastava, A.; Rao, P.S.C.; McGrath, G.S. Emergent selfsimilarity and scaling properties of fractal intra-urban heat islets for diverse global cities. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 032142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Ding, J.; Shen, J.; Wei, F.; Li, S. Changing effect of urban form on the seasonal and diurnal variations of surface urban heat island Intensities (SUHIIs) in more than 3000 cities in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.Q.; Wu, Z.F.; Tan, J.J. Spatio-temporal changes of urban thermal environment with thermal centroid in Guangzhou. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2010, 30, 620–623. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Xu, Z.; Dong, B.; Xu, H.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X. Habitat suitability evaluation and ecological corridor construction of wintering cranes in Poyang Lake. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 189, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G. China Blue Book on Climate Change (2021) was released. Environment 2021, 11, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.M.; Qin, M.Z.; Li, B.; Li, C.Y.; Song, L.L. Research on the green infrastructure network in the Zhengzhou-Kaifeng metropolitan area based on MSPA and circuit theory. J. Henan Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 48, 631–638. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Q.; Zhu, Z.M.; Qin, M.L.; Shi, Q.Q.; Song, Y.Z. Research on the optimization of territorial space ecological network of Nanning city based on MSPA and circuit theory. J. Guangxi Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 46, 306–318. [Google Scholar]
- Soille, P.; Vogt, P. Morphological segmentation of binary patterns. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2009, 30, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.G.; Xiao, R.B.; Cai, Y.N.; Wang, Y.W.; Wu, C.G. Research progress of quantitative evaluation techniques for urban thermal environment. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.A.; Meng, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Hu, D.; Yang, T.L. Haikou city based on CA-Markov model. Heat island simulation and prediction. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 39, 742–753. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, R.H.; Zeng, J.; Li, K.; Zhou, I.H.; Hu, J.Q.; Kong, J.G.; Wang, Q.W. Identification of key areas of imbalance between supply and demand of urban thermal environment regulation services. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 3124–3142. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Fu, B.; Zhao, W. The “source” and “hui” landscape theory and their ecological significance. J. Ecol. 2006, 26, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Gao, Z.J.; Sun, B.W. Identification of key areas for territorial ecological restoration based on ecological security pattern: A case study of Songyuan City, Jilin Province. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.W.; Lin, M.; Mo, H.; Huang, Y.B.; Hu, X.Y. Construction and optimization of ecological network in Foshan City. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 3288–3298. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, B.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y. Construction of ecological security pattern of plateau lake city: A case study of Dali City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 8153–8166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Tan, B.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.Q. Construction of ecological security pattern and identification of ecological restoration zones in Kaidu River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 10127–10137. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Qin, M.Z. Integrated circuit theory of ecological corridor and their importance identification. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3344–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Liu, C.X.; Yu, X.Y.; Jiao, S. Resilience evaluation and optimization of urban water ecological network: Take Changsha as an example. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, M.A.; Tapia, J.; Gallardo, C.; Núñez, P.; Varas-Belemmi, K. Loss of coastal ecosystem spatial connectivity and services by urbanization: Natural-to-urban integration for bay management. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kuang, D.; Wei, X. Developing ecological networks based on MSPA and MCR: A case study in Yujiang county. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 2017, 26, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Integrating the MCR and DOI models to construct an ecological security network for the urban agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Q.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Qiu, S.J.; Han, Y.N. Integrating spatial continuous wavelet transform and kernel density estimation to identify ecological corridors in megacities. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2020, 199, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Zhao, W.; Cherubini, F.; Hu, X.P.; Pereira, P. Sensitivity and future exposure of ecosystem service functions to climate change on the Tibetan Plateau of China. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 3451–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H. Spatiotemporal changes in ecological network resilience in the Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Peng, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y. Incorporating circuit theory, complex networks, and carbon offsets into the multi-objective optimization of ecological networks: A case study on karst regions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Xu, Z.H.; Dan, Z.Y.; Ye, Y.Y. Construction of ecological security pattern integrating multiple ecological protection objectives in Guangdong Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; He, G. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Regional Water Resources Carrying Capacity and Influencing Factors—Anhui Province as an Example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Li, K. Land use and habitat quality change in the Yellow River Basin: A perspective with different CMIP6-based scenarios and multiple scales. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Wu, D.; Yan, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, K. Interpreting regional ecological security from perspective of ecological networks: A case study in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 65412–65426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Construction and evaluation of traditional village cultural landscape safety corridor: A case study of Anyi ancient village in Nanchang. J. Nanchang Inst. Technol. 2019, 38, 5059. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, J. Linking the minimum spanning tree and edge betweenness to understand arterial corridors in an ecological network. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Guo, C.-X.; Zhao, M.-Y.; Yang, Z.-G.; Guo, M.-Y.; Wu, B.-Y.; Chen, Q.-L. Integrating morphological spatial pattern analysis and the minimal cumulative resistance model to optimize urban ecological networks: A case study in Shenzhen city, China. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yang, W.; Yu, K.; Geng, J.; Liu, J. Identification and Construction of Ecological Nodes in the Fuzhou Ecological Corridors. Forests 2022, 13, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, Y.; Duanmu, Z.; Li, M. Exploring habitat patch clusters based on network community detection to identify restored priority areas of ecological networks in urban areas. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 78, 127771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-G.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Guo, C.-X.; Yang, X.-J.; Xu, X.-J. Based on morphological spatial pattern analysis Construction of ecological network in Guangzhou with minimum cumulative resistance model. Appl. Stud. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 29, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. City based on functional network evaluation Urban ecological security pattern: A case study of Changzhou City. Peking Univ. J. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 45, 728–736. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Gong, Y.; Ge, J.; Ai, Z.; Xie, S. Urban landscape based on circuit theory Construction of ecological security pattern: A case study of Hengyang City, Hunan Province. Appl. Ecol. Chin. J. Sci. 2018, 32, 2555–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. A dynamic evaluation method of urban ecological networks combining Graphab and the FLUS Model. Land 2022, 11, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S. Bibliometric analysis of global research on ecological networks in nature conservation from 1990 to 2020. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.S. The role of land use change in affecting ecosystem service functions and the ecological security pattern of the Hexi Regions, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, L.; Liu, Y. Robustness test of multiple protection strategies for ecological networks from the perspective of complex networks: Evidence from Wuhan Metropolitan Area, China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumia, G.; Praticò, S.; Di Fazio, S.; Cushman, S.; Modica, G. Combined use of urban Atlas and Corine land cover datasets for the implementation of an ecological network using graph theory within a multi-species approach. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.J.; Biondi, D.; Corte, A.P.; Reis, A.R.; Oliveira, T.G. A methodological framework to create an urban greenway network promoting avian connectivity: A case study of Curitiba City. Urban. For. Urban. Gree. 2023, 87, 128050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, H.L.; Liu, Y.X.; Hu, Y.N.; Yang, Y. Identification and optimization of ecological security pattern in Xiong’an New Area. Acta Geograph. Sin. 2018, 73, 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.; Pen, Y. Development and optimization of ecological network of Shunyi District of Beijing based on RS and GIS. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2016, 22, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.Q.; Li, X.Y. A cold island connectivity and network perspective to mitigate the urban heat island effect. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 94, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Wright, T.M.; Cardille, J.; Pearsall, H.; Ogneva-Himmelberger, Y.; Riemann, R.; Riitters, K.; Partington, K. Forest fragmentation in Massachusetts, USA: A town-level assessment using morphological spatial pattern analysis and affinity propagation. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2016, 53, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Liu, M.; Gao, C.C.; Sun, Y.W.; Cai, C.L.; Su, L. Construction of ecological source identification system in metropolitan areas and diagnosis of key areas for territorial ecological restoration. J. Ecol. 2022, 42, 7056–7067. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Long, Y.D.; Chen, Y.F.; Gao, F. Biodiversity conservation in Chenggong New District of Kunming based on habitat network. Chin. Urban. For. 2022, 20, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, C. Construction of urban ecological network based on natural protected areas in Guangzhou. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ye, X.; Zhao, X.; Nie, B.; Rao, J. Research on ecological corridor construction and optimization based on MSPA and MCR: A case study of Xinjian District in Nanchang City. Reg. Res. Dev. 2023, 42, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Li, S.; Tang, J.; Su, J. Construction of urban wetland ecological landscape planning model based on MSPA analysis method. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. 2022, 30, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.X.; Ren, J.; Zhai, J.; Li, W.C. Just green enough’in urban renewal: A multifunctional and pragmatic approach in realizing multiscale urban green space optimization in built-up residential areas. Urban. For. Urban. Gree. 2023, 82, 127891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Ke, Y.Y.; Zhou, Q.X.; Tao, R.Q.; Wang, Y.B. Derived regional soil-environmental quality criteria of metals based on Anhui soil-crop systems at the regulated level. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Pan, J.; Liu, X. Landscape ecological safety assessment and landscape pattern optimization in arid inland river basin: Take Ganzhou district as an example. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 782–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Fan, C.; Wang, T. Promoting landscape connectivity of highly urbanized area: An ecological network approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. The complex ecological network’s resilience of the Wuhan metropolitan area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Rong, W.Z. Construction of ecological network in Suzhou based on the PLUS and MSPA models. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110740. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, M. Comprehensive Evaluation of Agricultural Water Resources’ Carrying Capacity in Anhui Province Based on an Improved TOPSIS Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, R.; Chu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wei, J. Construction of ecological security pattern and identification of key regions based on ecological assessment and circuit theory: A case study of Anhui Province. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 209–216 + 226. [Google Scholar]
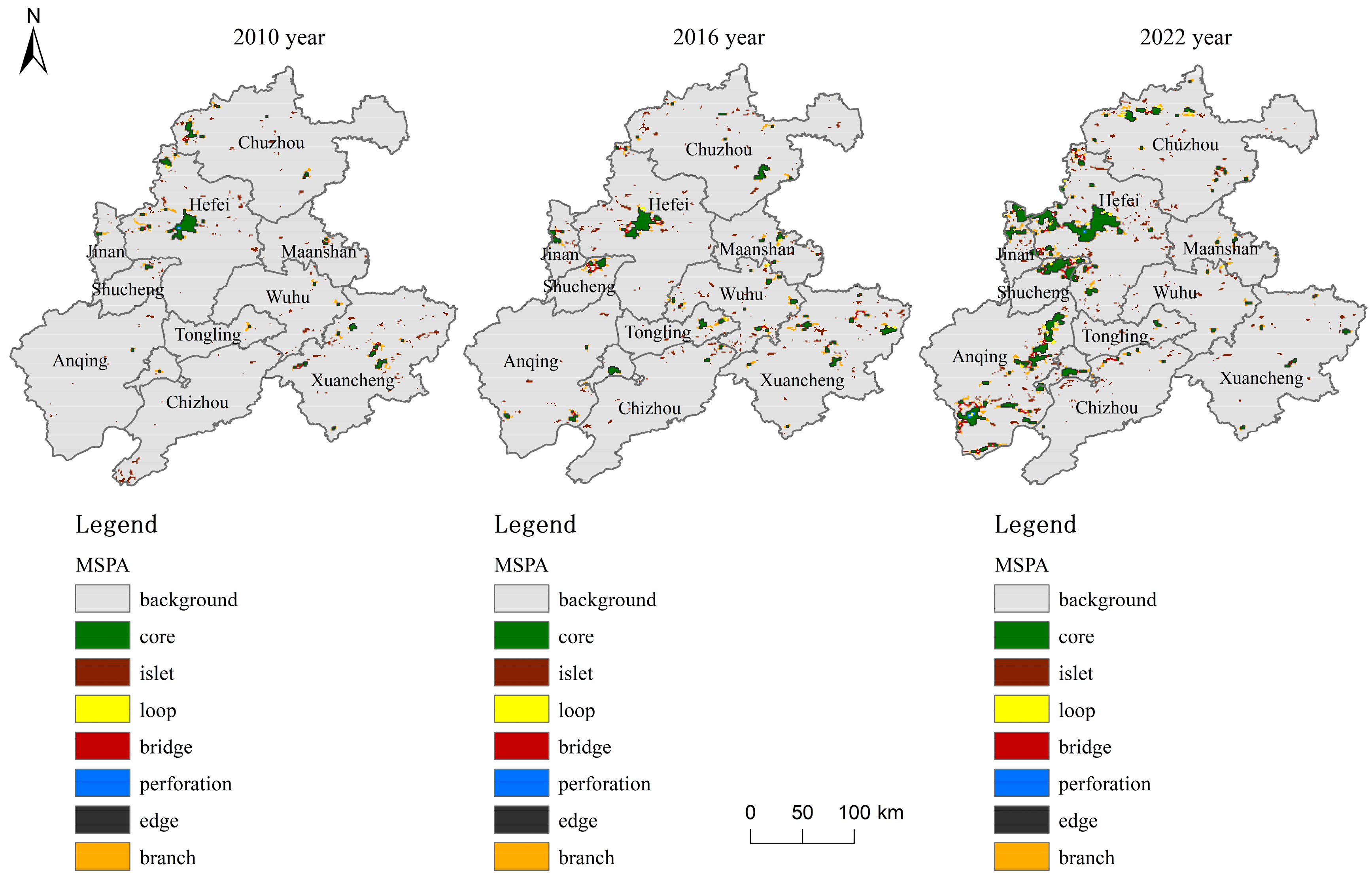



| Heat Island Patch Type | Spatial Morphological Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Core | Large, continuous, and does not contain its edges |
| Island | Scattered, isolated urban heat island patches with an area smaller than the minimum threshold of the core area |
| Perforation | The boundary between the urban heat island core area and the inner non-heat island patch |
| Edge | The boundary between the urban heat island core area and the outer non-heat island patch |
| Loop | Urban heat island corridors connecting the same urban heat island core area |
| Bridge | Urban heat island corridors connecting different urban heat island core areas |
| Branch | An urban heat island patch connected only to one end of an urban heat island core, a bridge area, or a ring road area |
| Background | Non-urban heat island area |
| Resistance Factor | Grading Index | Resistance Value | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude | >800 m | 1 | 0.1 |
| 500–800 m | 3 | ||
| 200–500 m | 5 | ||
| <200 m | 7 | ||
| Slope | <3° | 1 | 0.15 |
| 3–5° | 3 | ||
| 5–10° | 5 | ||
| 10–15° | 7 | ||
| >15° | 9 | ||
| NDVI | >0.8 | 1 | 0.2 |
| 0.6–0.8 | 3 | ||
| 0.4–0.6 | 5 | ||
| 0.2–0.4 | 7 | ||
| <0.2 | 9 | ||
| Land use | Forest | 1 | 0.3 |
| Grassland | 1 | ||
| Water | 1 | ||
| Cropland | 4 | ||
| Unutilized land | 6 | ||
| Construction | 9 | ||
| LST | <20 °C | 1 | 0.25 |
| 20–22 °C | 3 | ||
| 22–24 °C | 5 | ||
| 24–26 °C | 7 | ||
| 26–28 °C | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Dong, B.; Xu, Z.; Qu, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, L. Identification of Thermal Environment Networks in the Wanjiang Urban Agglomeration Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory. Land 2024, 13, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101695
Han Y, Dong B, Xu Z, Qu J, Wang H, Xu L. Identification of Thermal Environment Networks in the Wanjiang Urban Agglomeration Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory. Land. 2024; 13(10):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101695
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yuexia, Bin Dong, Zhili Xu, Jianshen Qu, Hao Wang, and Liwen Xu. 2024. "Identification of Thermal Environment Networks in the Wanjiang Urban Agglomeration Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory" Land 13, no. 10: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101695
APA StyleHan, Y., Dong, B., Xu, Z., Qu, J., Wang, H., & Xu, L. (2024). Identification of Thermal Environment Networks in the Wanjiang Urban Agglomeration Based on MSPA and Circuit Theory. Land, 13(10), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13101695





