Research on the Coupling Co-ordination between Quality of County-Level New Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value in Shaanxi Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
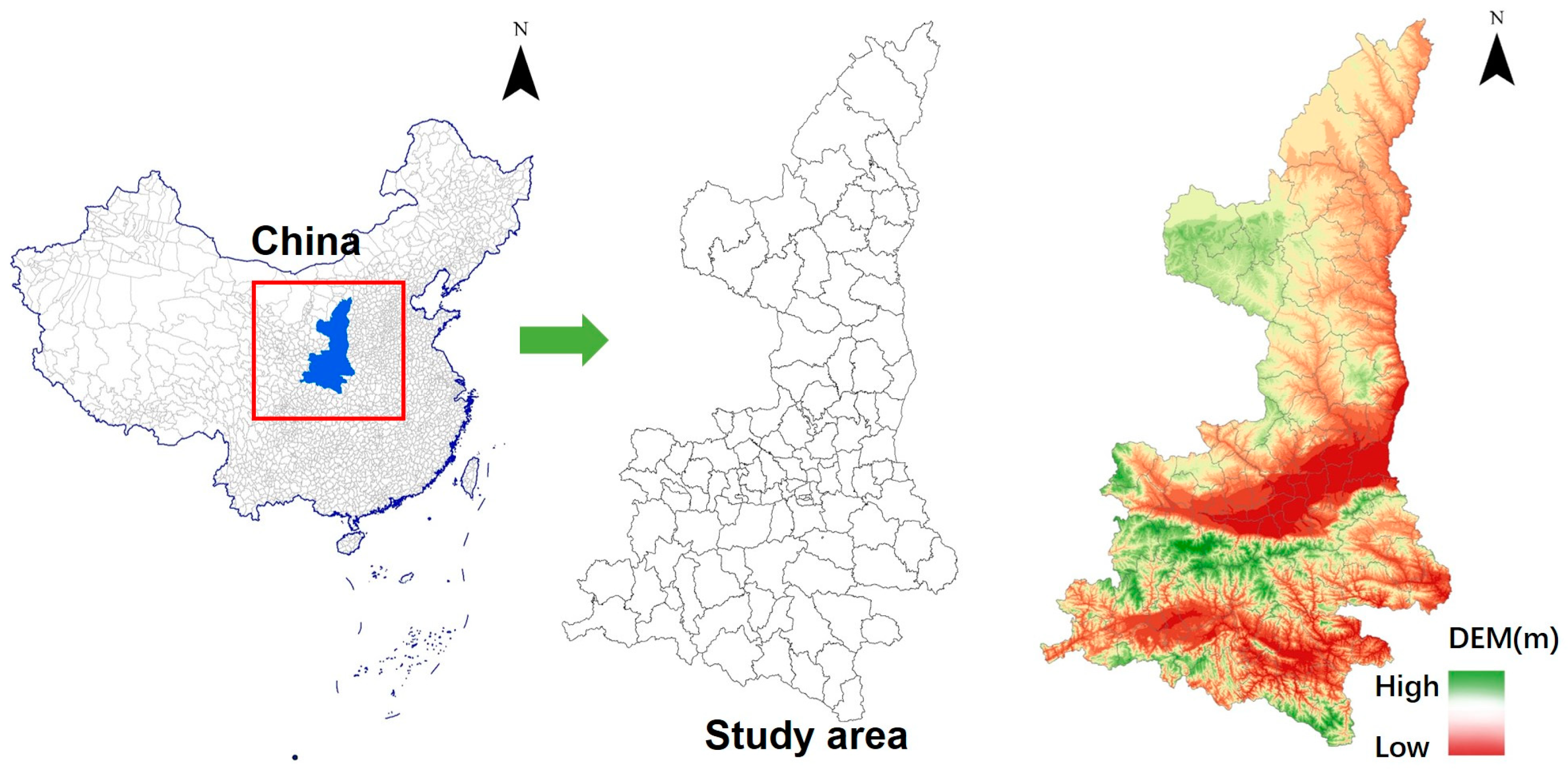
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Resource
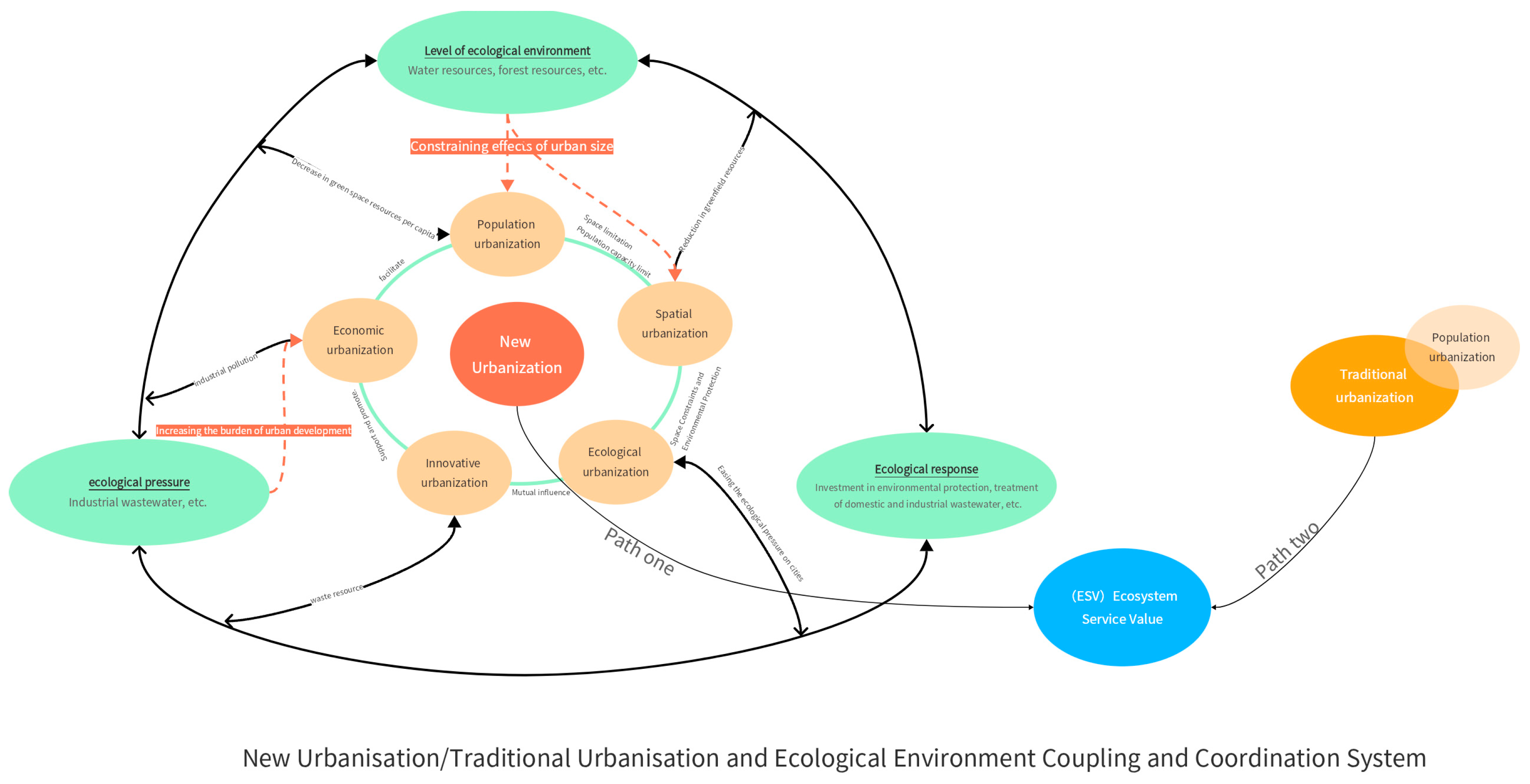
2.3. Research Framework
2.4. Evaluation of Traditional Urbanization and Construction of Evaluation Index System for New Urbanization Quality
2.5. Calculation of Value of Ecosystem Services
2.6. Evaluation of the Coupled Co-ordination between Urbanization Level and the Value of Ecosystem Services
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Ecosystem Service Valuation Results
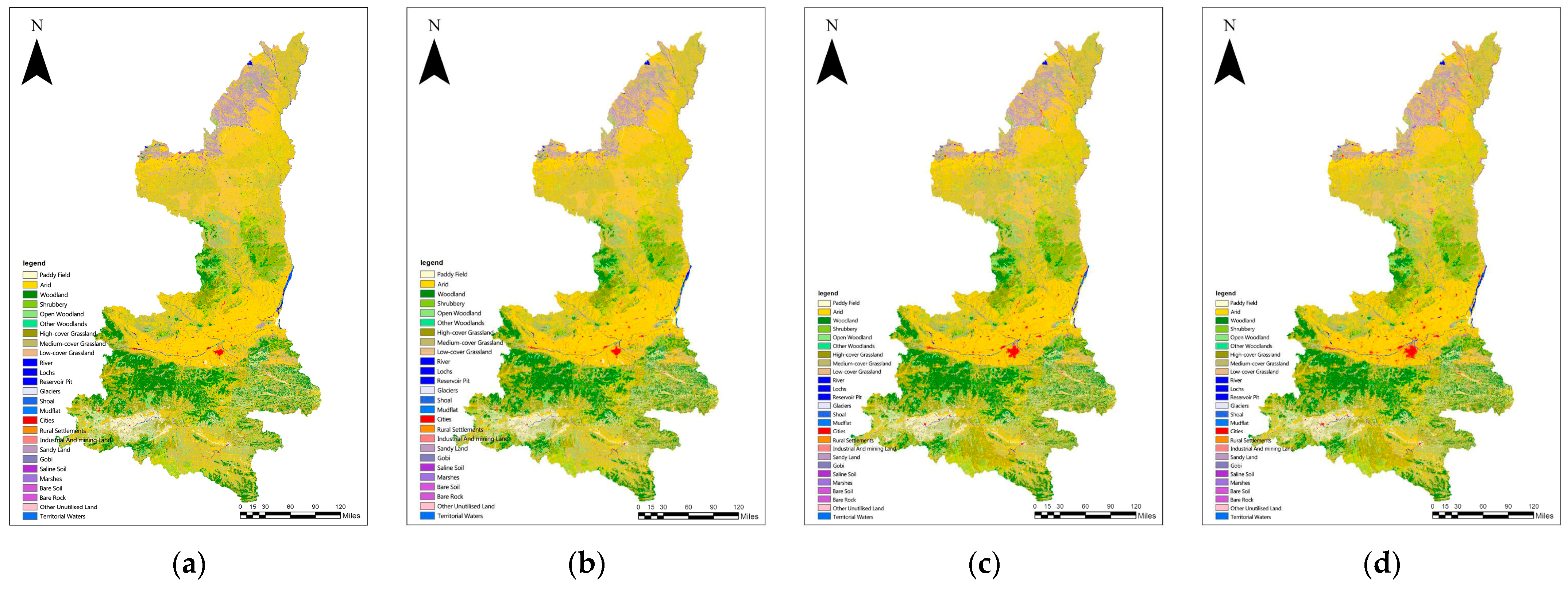
3.1.1. The Analysis of Land Use Change
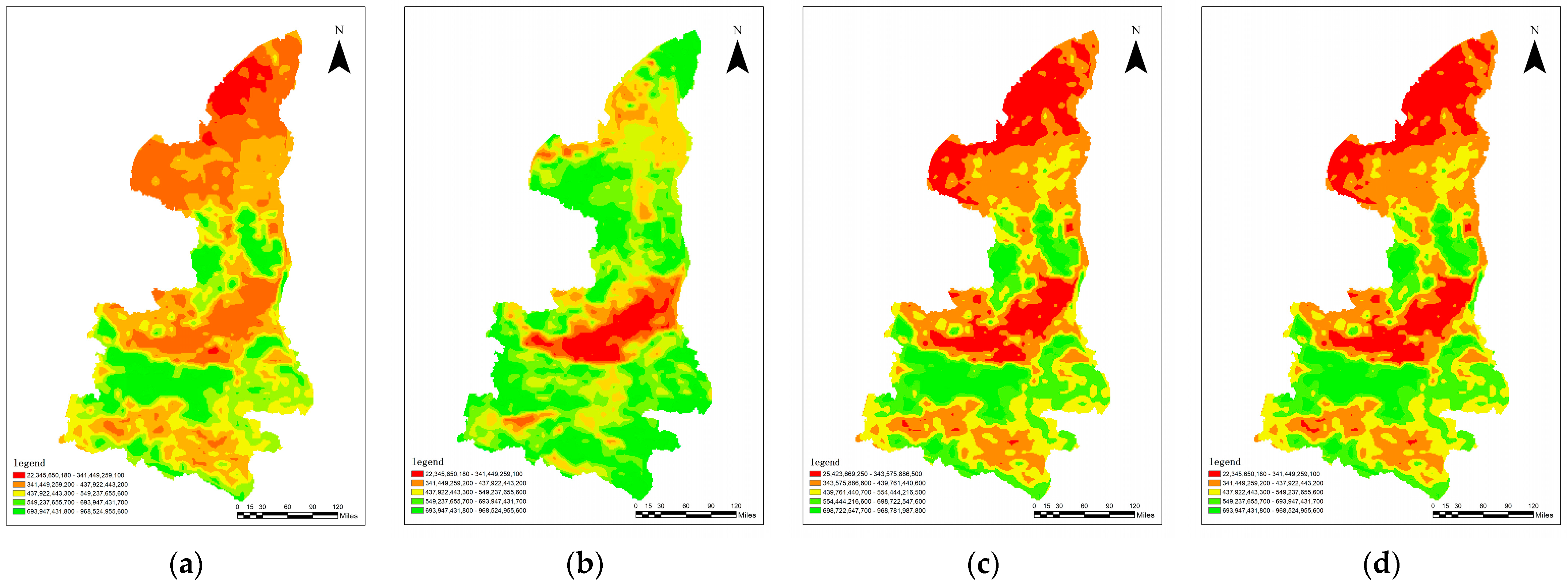
3.1.2. The Evaluation of Ecosystem Services Value
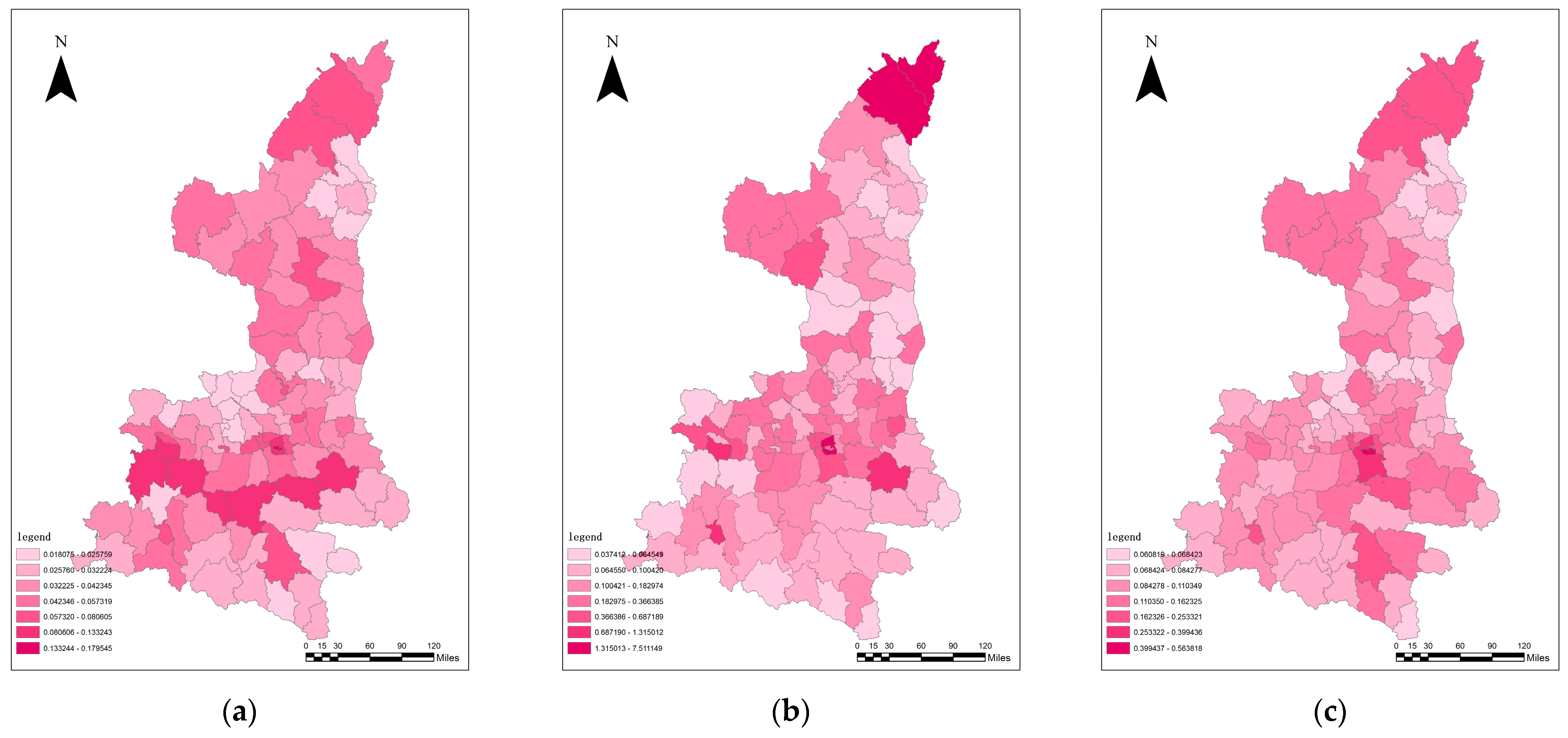
3.2. The Analysis of Traditional Urbanization
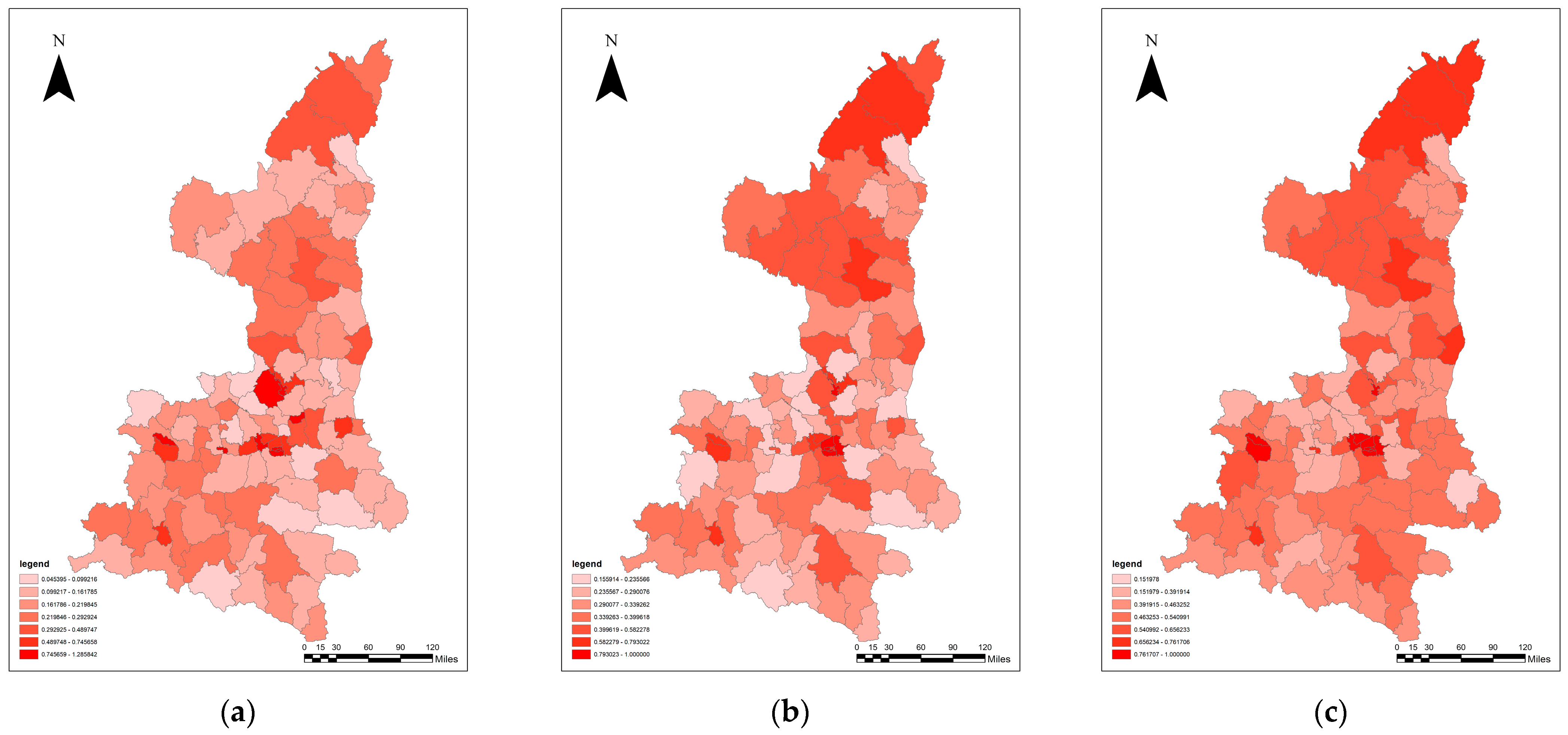
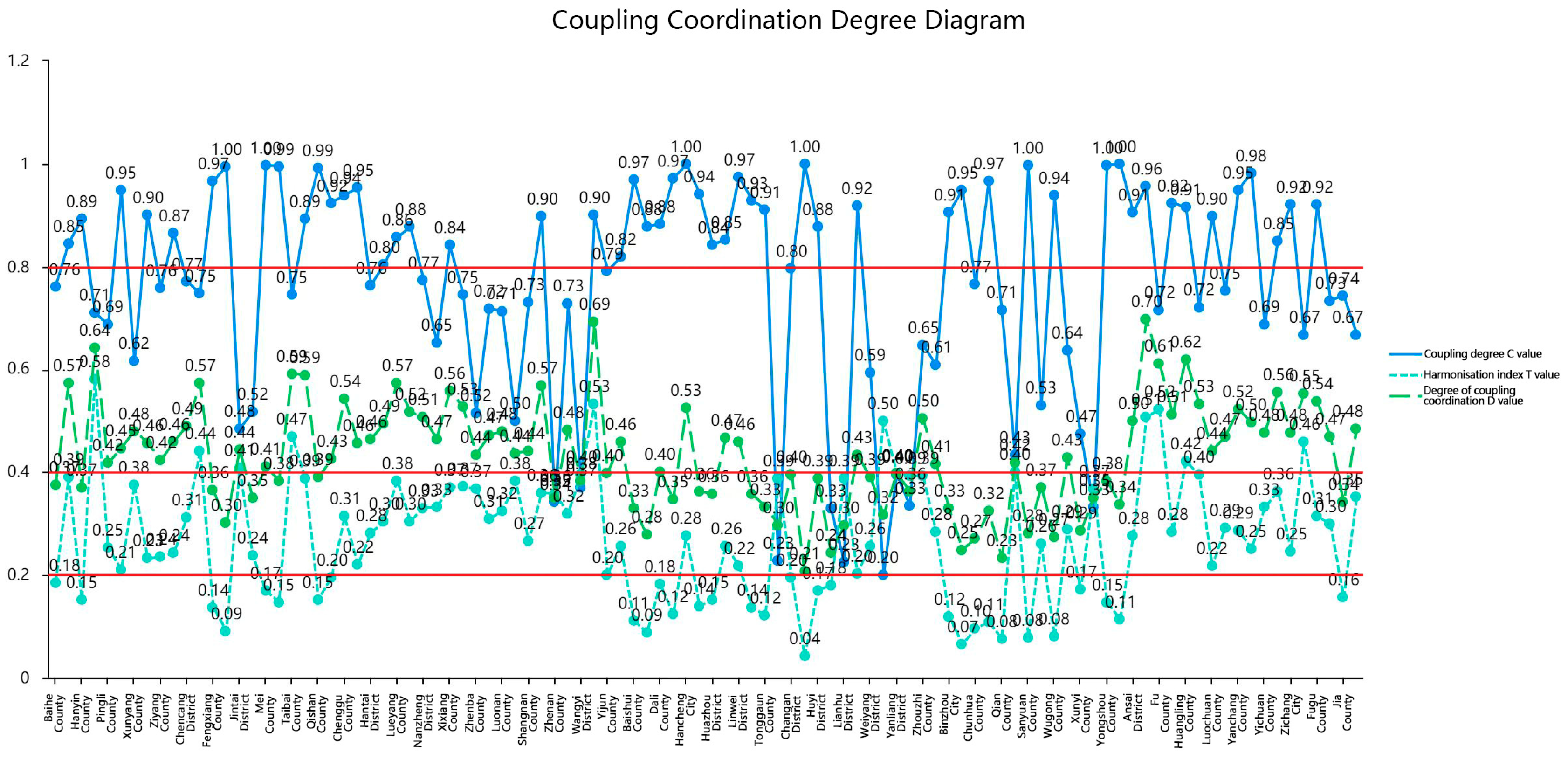
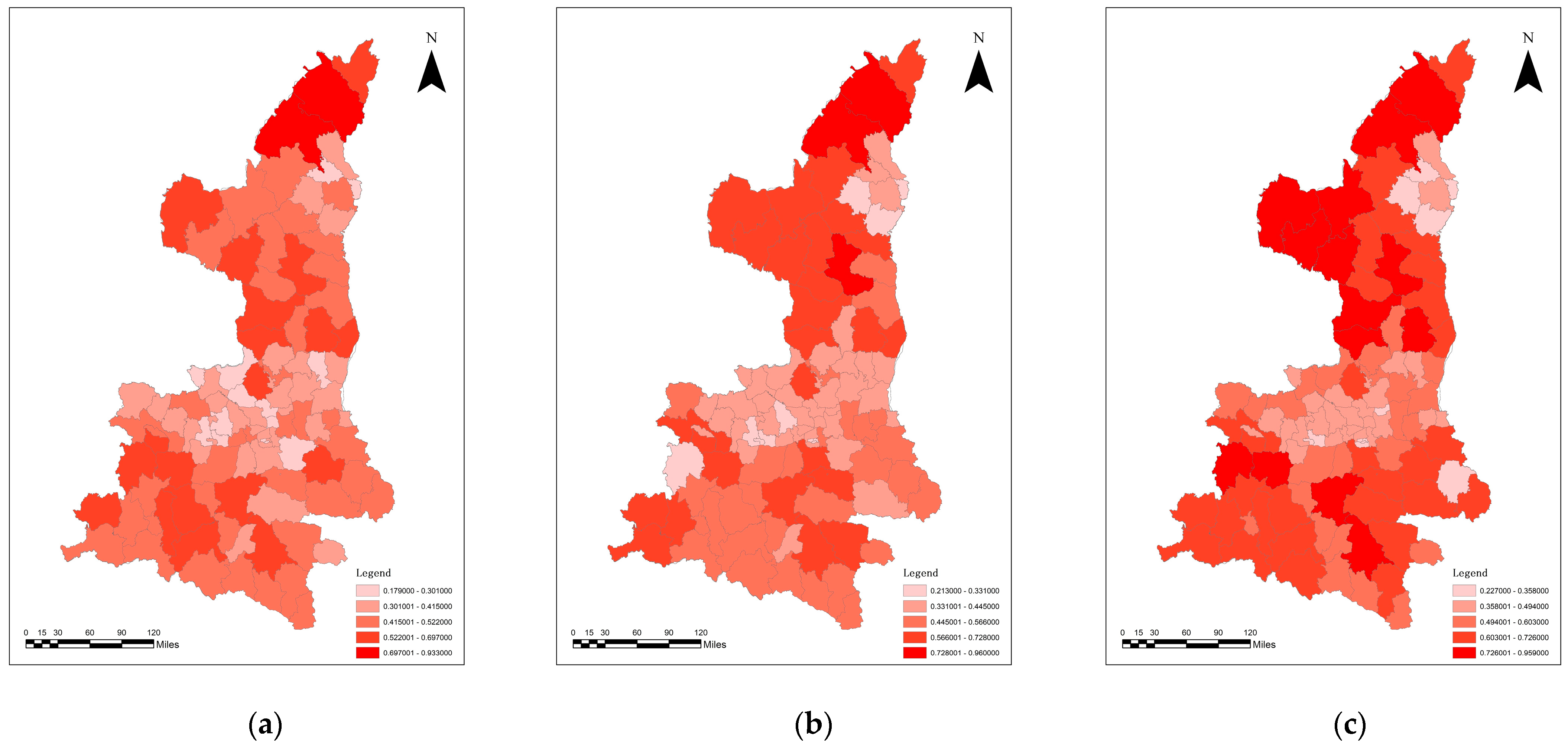
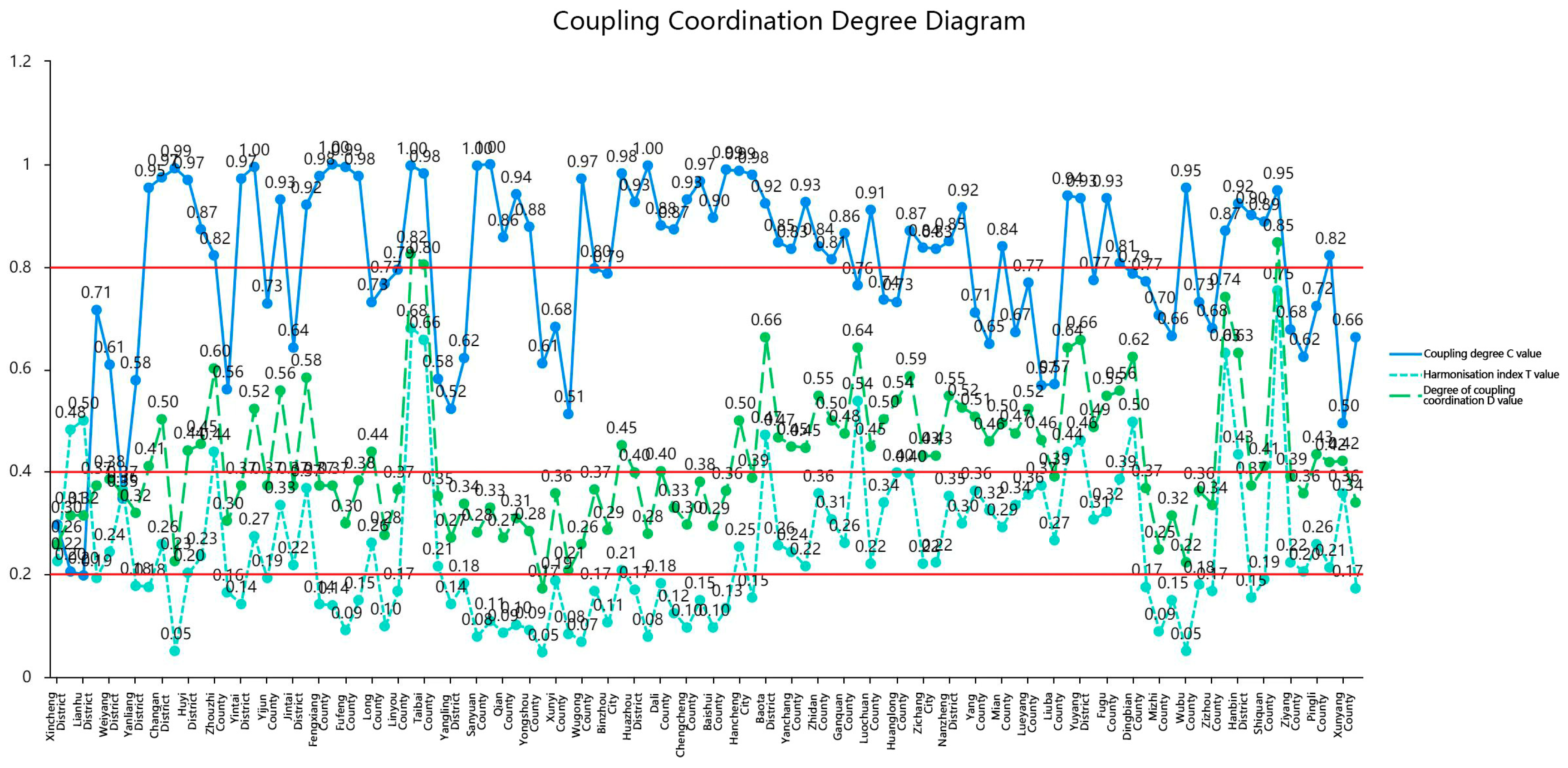
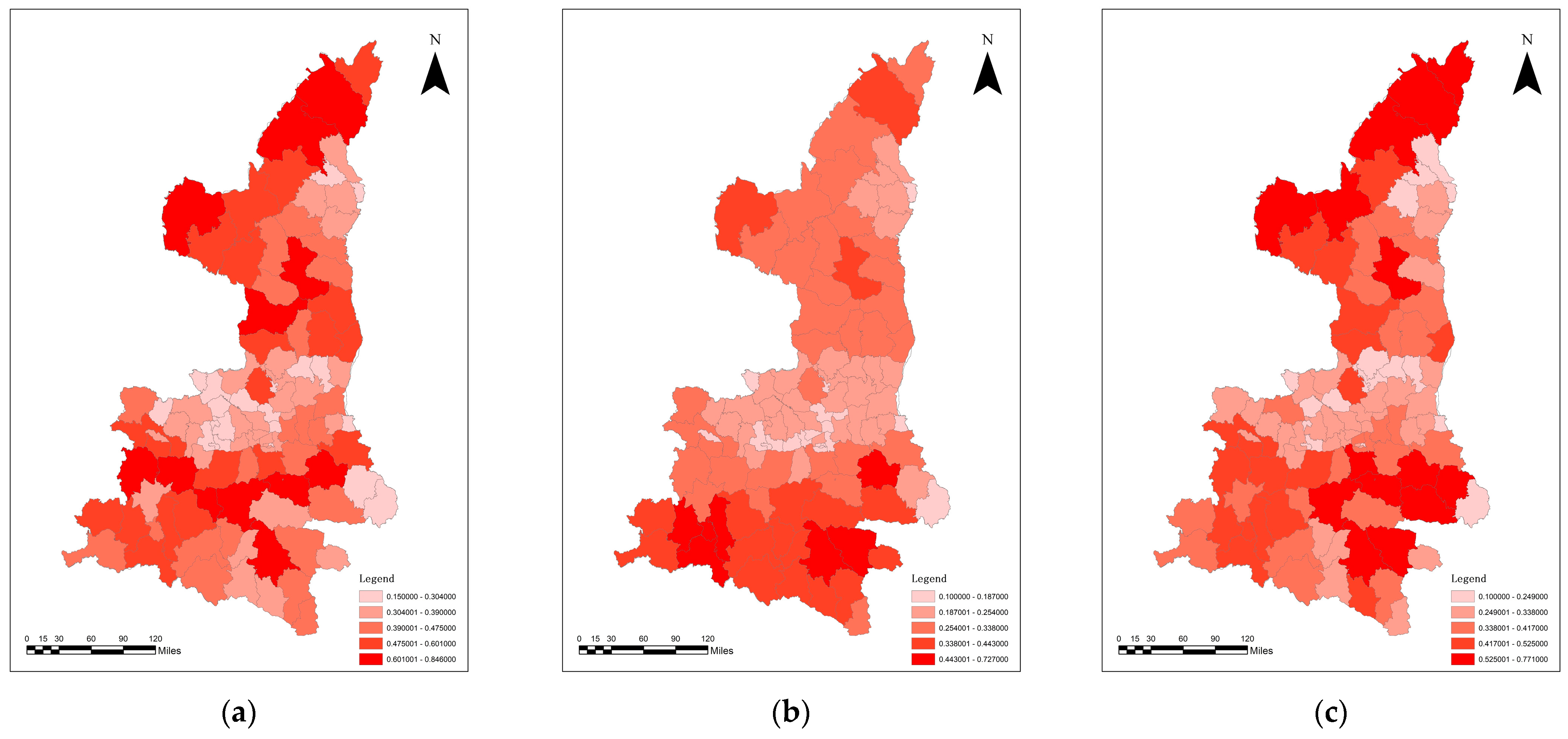
3.3. Analysis of the Coupling Co-ordination between Traditional Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value
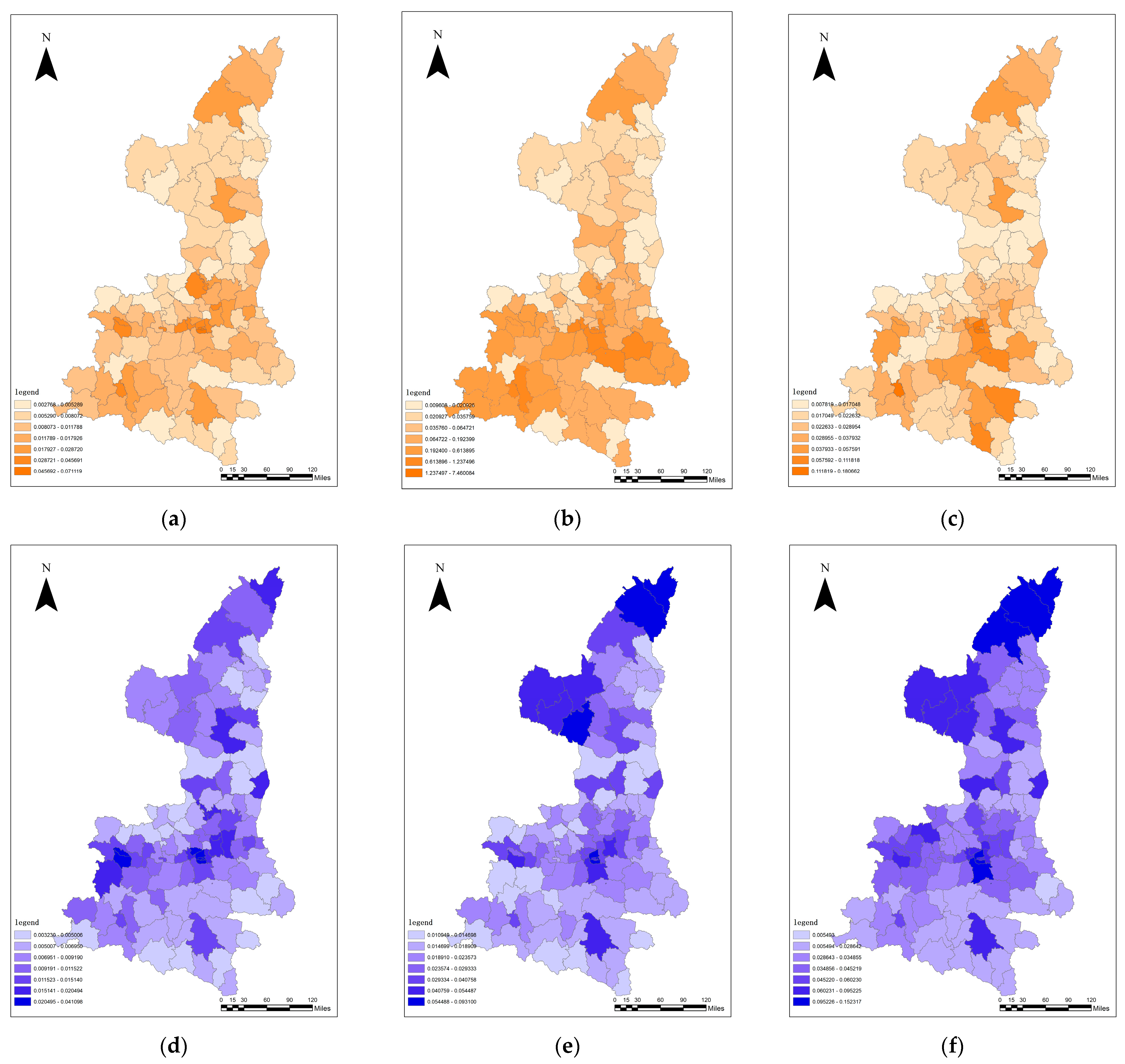
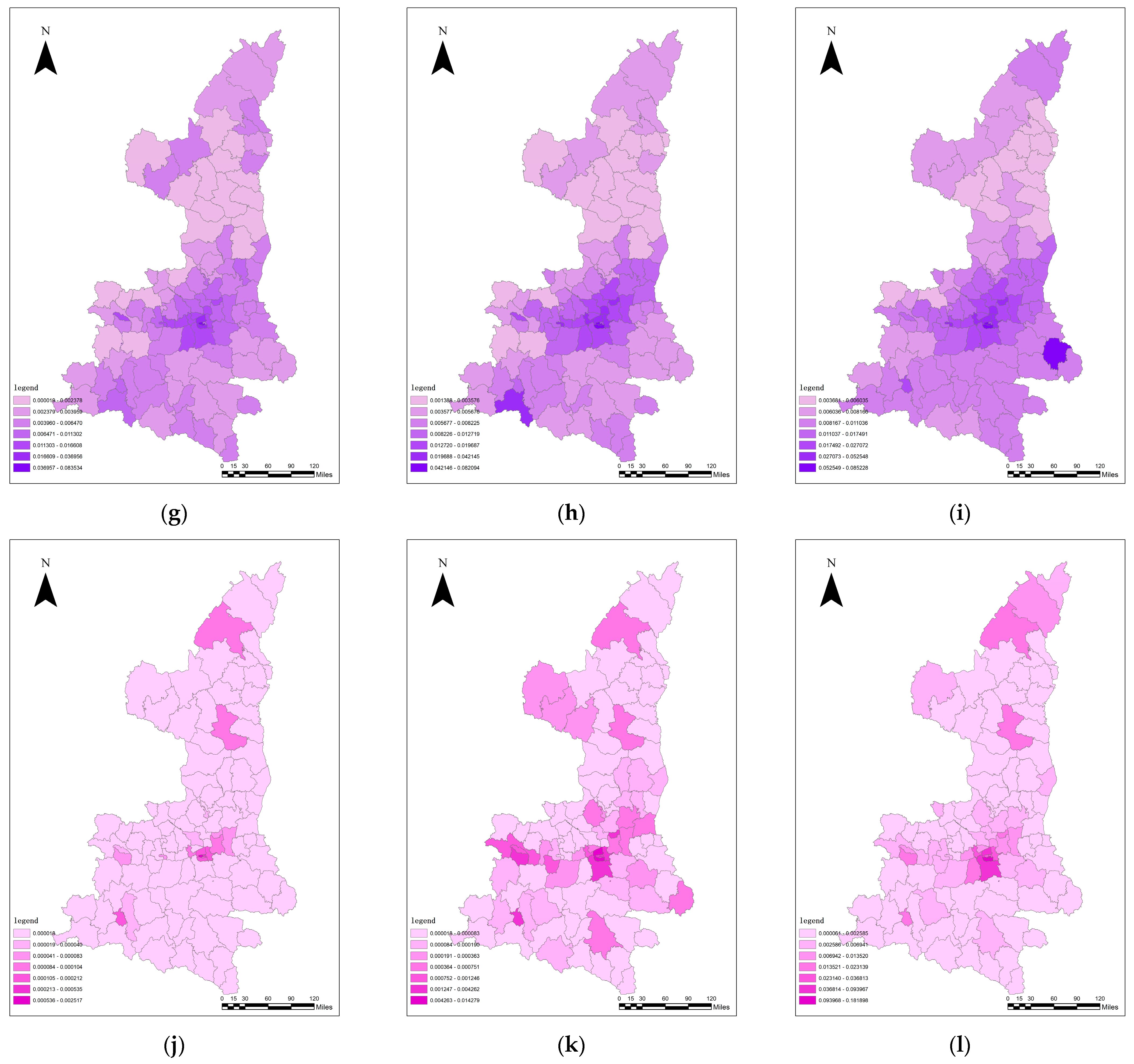
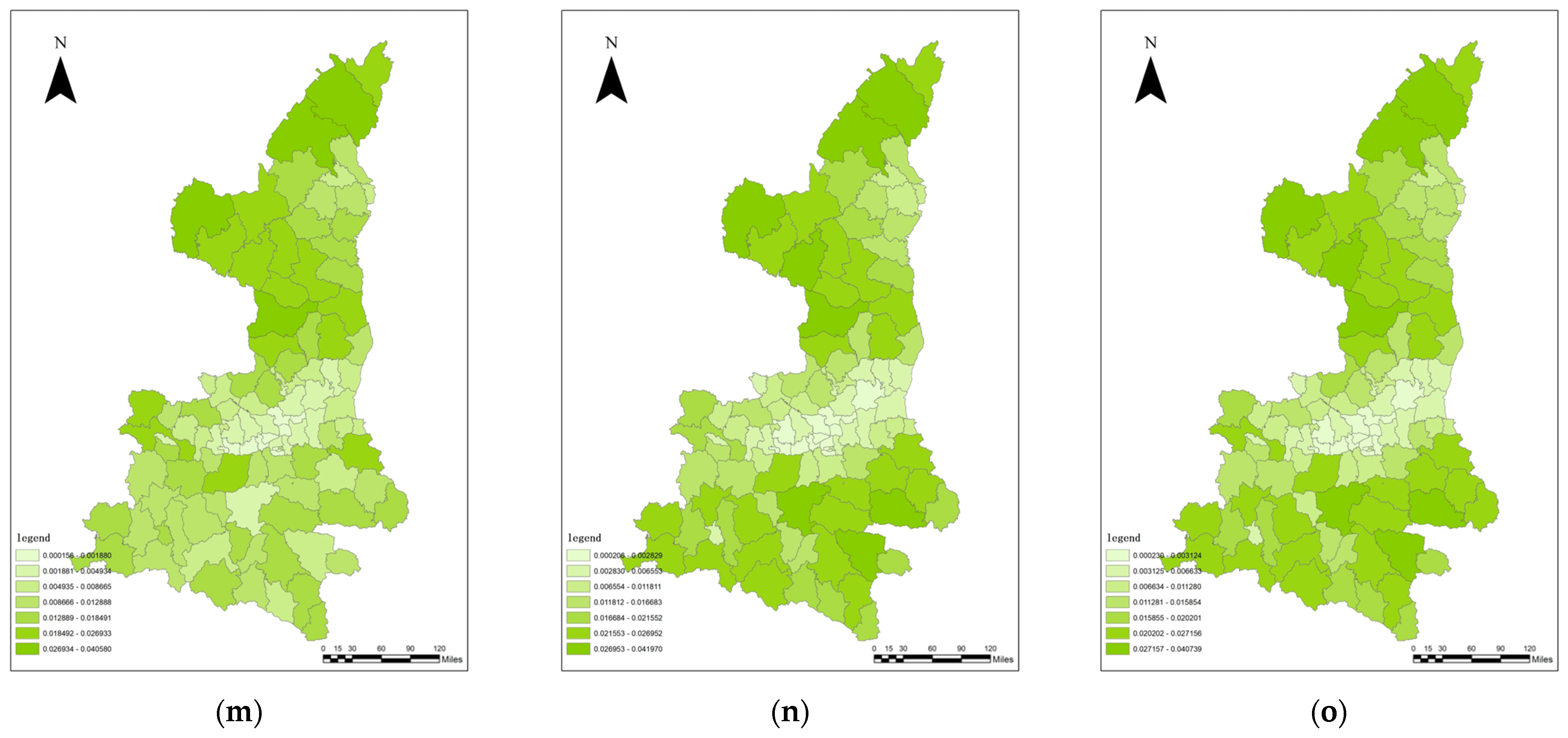
3.4. Analysis of the Effects of New Urbanization
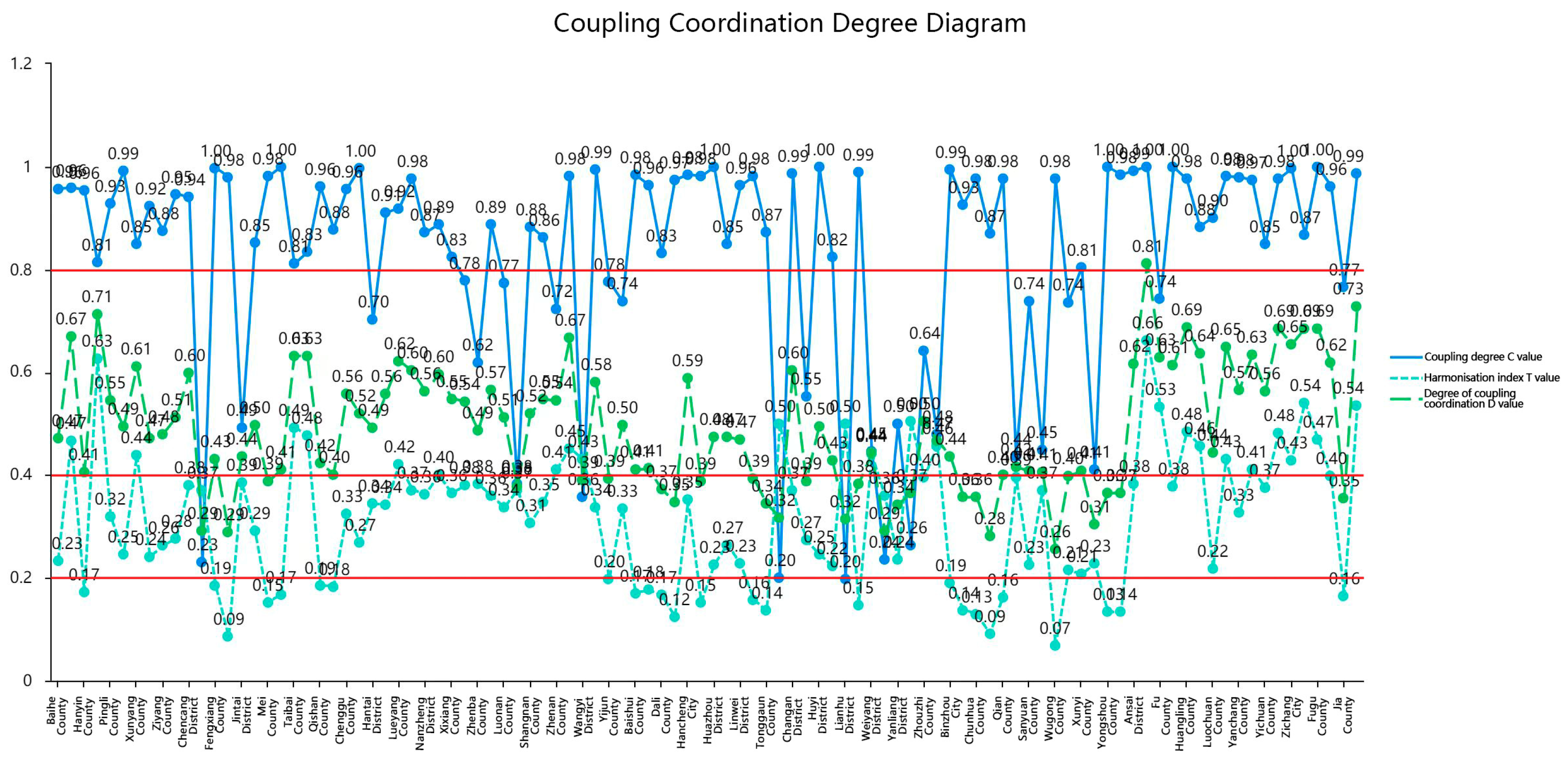
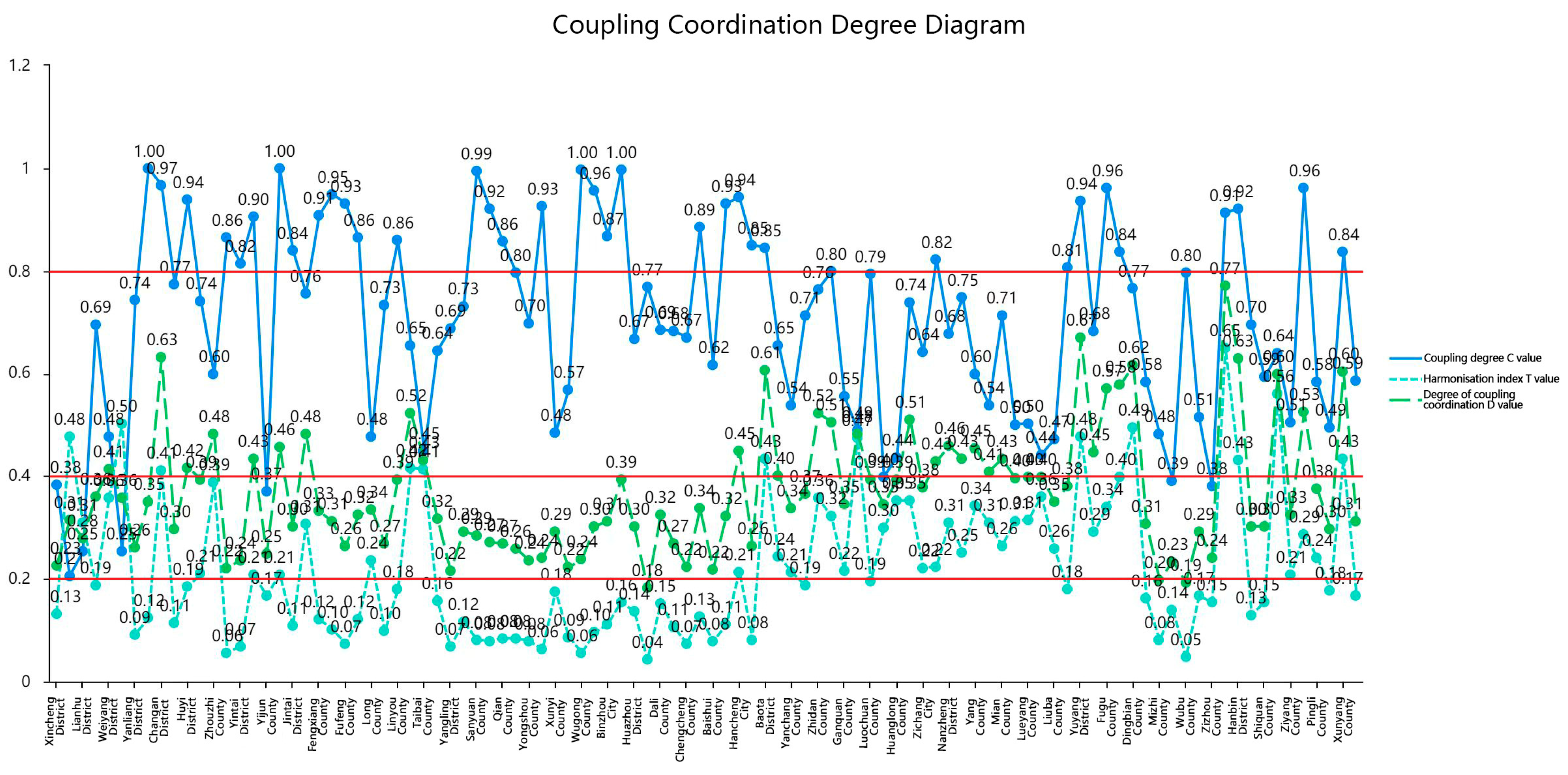
3.5. Analysis of the Coupling Co-ordination between the Quality of New Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, G.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Jia, K. Multi-Dimensional Feature Recognition and Policy Implications of Rural Human–Land Relationships in China. Land 2021, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Yin, J.; Niu, J. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Driving Mechanisms of Rural Residentials from the Perspective of the Human-Land Relationship: A Case Study from Luoyang, China. Land 2022, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ma, L.; Yao, Y.; Cui, X. Man-land relationship based on the spatial coupling of population and residential land—A case study of Yuzhong County in Longzhong Loess Hilly Region, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 116, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wan, Z.; Xu, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, J. Environmental Adaptation in the Process of Human-Land Relationship in Southeast China’s Ethnic Minority Areas and Its Significance on Sustainable Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2737. [Google Scholar]
- Evers, A.M.; Lindén, L.; Rappe, E. A Review of Human Issues in Horticulture in Finland: Urbanization Motivates a Renewed Appreciation for Plants and Nature. Horttechnology 2000, 10, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narain, V. Periurban Water Security in a Context of Urbanization and Climate Change: A Review of Concepts and Relationships. 2010. Available online: https://www.eldis.org/document/A100890 (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Seto, K.C.; Giineralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.L.; Lambin, E.F.; Reenberg, A. The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20666–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Tang, H.; Liang, H. A theoretical framework for researching cultural ecosystem service flows in urban agglomerations. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Nijkamp, P.; Xu, J. Space–time indicators in interdependent urban–environmental systems: A study on the Huai River Basin in China. Habitat Int. 2015, 45, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.F. Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems: Edited by Lance H. Gunderson and C.S. Holling. Island Press, 2002. xxiv+507 pages. ISBN 1-55963-857-5 (paper), $35. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 114, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Ting, L. Analysis of Coordinated Development of Urbanization and Ecological Environment in Inner Mongolia. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2014, 30, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L. Low carbon eco-city: New approach for Chinese urbanisation. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, D. Can New Urbanization Construction Improve Ecological Welfare Performance in the Yangtze River Economic Belt? Sustainability 2023, 15, 8758. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Fang, C.; Liao, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X. Revealing the heterogeneous effects of new urbanization on urban-rural inequality using geographically weighted quantile regression. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 159, 103082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Feng, C.; Guo, L. Exploring coordinated development between urbanization and ecosystem services value of sustainable demonstration area in China- take Guizhou Province as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Jiao, F.; Zheng, X.; Pang, J. Analysis of the Influence Mechanism of New Urbanization on High-Quality Economic Development in Northeast China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7992. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Du, J. The Impact of New Urbanization Construction on Sustainable Economic Growth of Resource-Based Cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 96860–96874. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z. Research Regarding the Coupling and Coordination Relationship between New Urbanization and Ecosystem Services in Nanchang. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, J. Climate change and urbanization in the Yangtze River Delta. Habitat Int. 2011, 35, 544–552. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Jiao, H. Coupling and coordination between urbanization and ecological environment in China. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2015, 29, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y. Regional coupling coordination degree between new urbanization and water ecological civilization in China, 2009–2018. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 16, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, A.R.; Hodge, R.A. Natural Change in the Environment: A Challenge to the Pressure-State-Response Concept. Soc. Indic. Res. 1998, 44, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia-Harris, J.L.; Chambers, D.; Kahn, J.R. Taking the “U” out of Kuznets: A comprehensive analysis of the EKC and environmental degradation. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Indicators to Measure Decoupling of Environmental Pressure from Economic Growth. 2002. Available online: http://www.olis.oecd.org/olis/2002doc.nsf/LinkTo/Sg-Sd (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Jiang, G. Socio-Economic-Natural Complex Ecosystem. Green China 2018, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, W.; Peng, C. A Social-Economic-Natural Compound Ecosystem Constructed for Urban Rivers— Planning and Design for the remediation and Ecological Restoration of the Guitang River Watershed in Changsha City, China. Landsc. Archit. Front. 2019, 7, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, X.; Xiao, W.; Tang, Y. A quantitative assessment of vulnerability using social-economic-natural compound ecosystem framework in coal mining cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, D.; Feng, H.; Zhang, N. The influencing factors and mechanisms for urban flood resilience in China: From the perspective of social-economic-natural complex ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, M. Advances in Urban Ecology : Integrating Humans and Ecological Processes in Urban Ecosystems. In Advances in Urban Ecology: Integrating Humans and Ecological Processes in Urban Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A.; Boone, C.G.; Fragkias, M.; Haase, D.; Langanke, T.; Marcotullio, P.; Munroe, D.K.; Olah, B.; Simon, D. Urban land teleconnections and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Urban ecology and sustainability: The state-of-the-science and future directions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, N.B.; Niemela, J.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Mcphearson, T.; Qureshi, S.; Breuste, J.; Haase, D.; Weber, C.; Elmqvist, T.; Alberti, M. Advancing Urban Ecology toward a Science of Cities. BioScience 2016, 66, 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Li, C.; Hu, J.; Yang, B.; Pan, K. Study on the Coupling Development between Urbanization and Ecosystem—The Comparative Analysis Based on Guizhou, Yunnan, Hunan and Zhejiang Province. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 100, 05030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Gao, P.; Wang, S.; Ma, Z. Coupling Fuzzy Bi-Level Chance Constraint Programming and Spatial Analysis for Urban Ecological Management. Land 2023, 12, 901. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Pan, S.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, T. Spatial relationship between land urbanization and ecosystem health in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Multiscale Integrated Model of Ecosystem Services (MIMES): Simulating the interactions of coupled human and natural systems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 30–41. [CrossRef]
- Alberti, M. The Effects of Urban Patterns on Ecosystem Function. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2014, 28, 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.; Cadenasso, M.; Grove, M.; Warren, P. Urban ecological systems: Scientific foundations and a decade of progress. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 331–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William. Global Change, Urban Sustainability and the Vulnerability of Cities: An Ecological Footprint Perspective. Seek. Truth. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhouse, R.E.; Medema, S.G. Retrospectives: On the Definition of Economics. J. Econ. Perspect. 2009, 23, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A.; Dobriyal, P.; Barthwal, S. Ecosystem Services and Human Wellbeing. In Ecosystem Services and its Mainstreaming in Development Planning Process; M/s Bishen Singh Mahendra Pal Singh: Dehradun, Indian, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; Groot, R.D.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Grove, J.M.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Redman, C.L. Integrated Approaches to Long-TermStudies of Urban Ecological Systems. BioScience 2009, 50, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, B.; Guo, C.; Ouyang, X.; Gao, J. Non-linear effects of multi-dimensional urbanization on ecosystem services in mega-urban agglomerations and its threshold identification. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110846. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Hu, L.; Cook, I.G. China’s urbanization in 1949–2015: Processes and driving forces. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Feng, L.; Meng, L. Study on comprehensive measurement of urbanization level in Changzhou. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering (ICSEEE), Shenzhen, China, 20–21 December 2016; pp. 928–932. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Yang, X.; Wan, L.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J. Study of coordination of population urbanization with land urbanization in Harbin, a cold northern city. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2017, 39, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z. The study on comprehensive evaluation and urbanization division at county level in China. Geogr. Res. 2012, 31, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Miao, C. Urbanization Level in Chinese Counties: Imbalance Pattern and Driving Force. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Impact of China’s new-type urbanization on energy intensity: A city-level analysis. Energy Econ. 2021, 99, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Research on Shandong Provincial New-type Urbanization Driving-force Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT), Tianjin, China, 13–14 June 2015; pp. 557–561. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B. Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, W.; Lu, D. Challenges and the way forward in China’s new-type urbanization. Land Use Policy 2016, 55, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Bo, Z.; Ling, M. A Review of Chinese Internal Migration Research Under the Background of New-type Urbanization:Topics and Prospects. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. The New Stage of China’s Rural Development: Urbanization in Village-Based Regions. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2015, 10, 4–14. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; Stern, D.; Fisher, B.; He, L.; Ma, C. Influential publications in ecological economics: A citation analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2004, 50, 261–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yan, Y. Ecosystem service value assessment in downtown for implementing the “Mountain-River-Forest-Cropland-Lake-Grassland system project”. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110751. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Liu, G. Temporal and spatial heterogeneity of land use, urbanization, and ecosystem service value in China: A national-scale analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 137911. [Google Scholar]
- Tirthankar, B.; Arijit, D.; Ketan, D.; Paulo, P. Urban expansion induced loss of natural vegetation cover and ecosystem service values: A scenario-based study in the siliguri municipal corporation (Gateway of North-East India). Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106838. [Google Scholar]
- Wolde, M.; Merga, D.; Anna, T.; Amare, H. Effects of Long-Term Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Ecosystem Service Values: An Example from the Central Rift Valley, Ethiopia. Land 2021, 10, 1373. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.; Liu, D. Province based on GWR Spatiotemporal evolution of land ecosystem service value and its influencing factors in Shaanxi. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Assessment and spatiotemporal difference of ecosystem services value in Shaanxi Province. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, M. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between ecosystem services and new-type urbanization: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, P. Coupling coordination analysis of urbanization and energy eco-efficiency: A case study on the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 63975–63990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y. Coupling coordination analysis of ecosystem services and urban development of resource-based cities: A case study of Tangshan city. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ren, C.; Zhang, S.; Yin, A.; Yue, W. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Urban Development and Ecological Environment in Urban Area of Guilin Based on Multi-Source Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, G. Coupling Mechanism and Space-time Coordination of New-approach Urbanization, New-approach Industrialization and Service lndustry Modernization in Megacity Behemoths: A Case Study of Ten Citiesin China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.D.; Montrosse, B.E.; Sullins, C.D.; Russell, J.C.; Wise, A.; Dinsmore, C.S.; Spears, L.I.; Phillips, R.V.; Handy, S.L.; Boarnet, M.G. Complexity of Coupled Human and Natural Systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Cugurullo, F. Urban eco-modernisation and the policy context of new eco-city projects: Where Masdar City fails and why. Urban Stud. 2016, 53, 2417–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, R.; Lee, J.M. Coordinating and competing in ecosystems: How organizational forms shape new technology investments. Strateg. Manag. J. 2013, 34, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melliger, R.L.; Rusterholz, H.P.; Baur, B. Ecosystem functioning in cities: Combined effects of urbanisation and forest size on early-stage leaf litter decomposition of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.). Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 28, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, D. Urban data and definitions in sub-Saharan Africa: Mismatches between the pace of urbanisation and employment and livelihood change. Urban Stud. 2018, 55, 965–986. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Fu, M.; Huang, N.; Duan, W.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Song, W. Spatio-temporal variation and coupling coordination relationship between urbanisation and habitat quality in the Grand Canal, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiran, G.A.B.; DziwornuAsem, A.; Elikplim, F. Urbanisation and domestic energy trends: Analysis of household energy consumption patterns in relation to land-use change in peri-urban Accra, Ghana. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105047. [Google Scholar]



| Data | Type | Source | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land use map | Raster | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center (https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 10 August 2023). (30-m resolution) | resolution is 30 × 30 |
| Population and GDP | Number | Shaanxi Statistical Yearbook (2000–2020); Seventh National Population Census | - |
| Population density and GDP spatial distribution datasets | Raster | resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform (http://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 10 August 2023); | resolution is 30 × 30 |
| Shaanxi Province PM2.5 dataset | Shape file | Shaanxi Province Department of Ecology and Environment (http://sthjt.shaanxi.gov.cn/, accessed on 10 August 2023); https://sites.wustl.edu/acag/datasets/surface-pm2–5/#V5.GL.02, accessed on 10 August 2023 | resolution is 30 × 30 |
| Nighttime Lighting Dataset for Districts and Counties in Shaanxi Province | Raster | NOAA website (www.ngdc.naoo.gov, accessed on 15 August 2023); Geographic Data Sharing Infrastructure, global resources data cloud (www.gis5g.com, accessed on 15 August 2023) | resolution is 30 × 30 |
| Target Layers | Dimension | Indicator Layer | Indicator Attributes | Weights (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of the quality of new urbanization | population urbanization | Total population at the end of the year | + | 1.593 |
| population of cities and towns | + | 4.497 | ||
| densitization of the population | + | 11.193 | ||
| Number of people with high school education and above | + | 3.801 | ||
| Percentage of urban population | + | 2.726 | ||
| Urban population density | + | 9.737 | ||
| Economic urbanization | Total social consumption | + | 2.869 | |
| Share of value added in secondary and tertiary industries | + | 1.314 | ||
| Secondary and tertiary value added | + | 4.671 | ||
| GDP per capita | + | 5.119 | ||
| GDP | + | 6.092 | ||
| Percentage of population in secondary and tertiary sectors | + | 1.397 | ||
| Night time light index | + | 3.702 | ||
| spatial urbanization | Percentage of built-up land | + | 7.845 | |
| Housing area per capita | + | 8.206 | ||
| Built-up area | + | 2.446 | ||
| Innovative urbanization | Number of national patent applications | + | 18.188 | |
| ecological urbanization | Ecological land area | + | 3.211 | |
| Percentage of ecological land | + | 1.079 | ||
| PM2.5 | - | 0.336 |
| Classification | Gas Regulation | Climate Regulation | Water Conservation | Soil Formation and Conservation | Waste Disposal | Biodiversity Conservation | Food Production | Value of Raw Materials | Entertainment and Cultural Value | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arable land | 225.6 | 401.6 | 270.8 | 658.9 | 740.1 | 320.4 | 451.3 | 45.1 | 4.5 | 3118.3 |
| forest land | 1579.5 | 1218.4 | 1444.1 | 1760.0 | 591.21 | 1471.1 | 45.1 | 1173.3 | 577.6 | 9860.3 |
| Grassland | 361.0 | 406.2 | 361.0 | 880.0 | 591.2 | 491.9 | 135.4 | 22.5 | 18.1 | 3267.3 |
| Water | 0 | 207.6 | 9196.9 | 4.5 | 8204.2 | 1123.7 | 45.1 | 4.5 | 1958.5 | 20,745 |
| Urban and rural industrial, mining, and residential land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused land | 0 | 0 | 13.5 | 9 | 4.5 | 153.4 | 4.5 | 0 | 4.5 | 189.4 |
| Ocean | 0 | 207.6 | 9196.9 | 4.5 | 8204.2 | 1123.7 | 45.1 | 4.5 | 1958.5 | 20,745 |
| 0 ≤ D ≤ 0.2 | 0.2 ≤ D ≤ 0.3 | 0.3 ≤ D ≤ 0.4 | 0.4 ≤ D ≤ 0.5 | 0 ≤ D ≤ 0.2 | 0.5 ≤ D ≤ 0.6 | 0.6 ≤ D ≤ 0.7 | 0.7 ≤ D ≤ 0.8 | 0.8 ≤ D ≤ 0.9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| degree of co-ordination | severe disorder | Moderate disorder | Mild disorder | On the verge of becoming dysfunctional | Barely co-ordinated | Elementary co-ordination | Intermediate co-ordination | Good co-ordination | Quality co-ordination |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, Q.; Ma, X.; Duan, R.; Liang, Y.; Cui, P. Research on the Coupling Co-ordination between Quality of County-Level New Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value in Shaanxi Province. Land 2024, 13, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010105
Ni Q, Ma X, Duan R, Liang Y, Cui P. Research on the Coupling Co-ordination between Quality of County-Level New Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value in Shaanxi Province. Land. 2024; 13(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Qingsong, Xue Ma, Ruiming Duan, Yan Liang, and Peng Cui. 2024. "Research on the Coupling Co-ordination between Quality of County-Level New Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value in Shaanxi Province" Land 13, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010105
APA StyleNi, Q., Ma, X., Duan, R., Liang, Y., & Cui, P. (2024). Research on the Coupling Co-ordination between Quality of County-Level New Urbanization and Ecosystem Service Value in Shaanxi Province. Land, 13(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13010105





