Land Use Function Transition and Associated Ecosystem Service Value Effects Based on Production–Living–Ecological Space: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
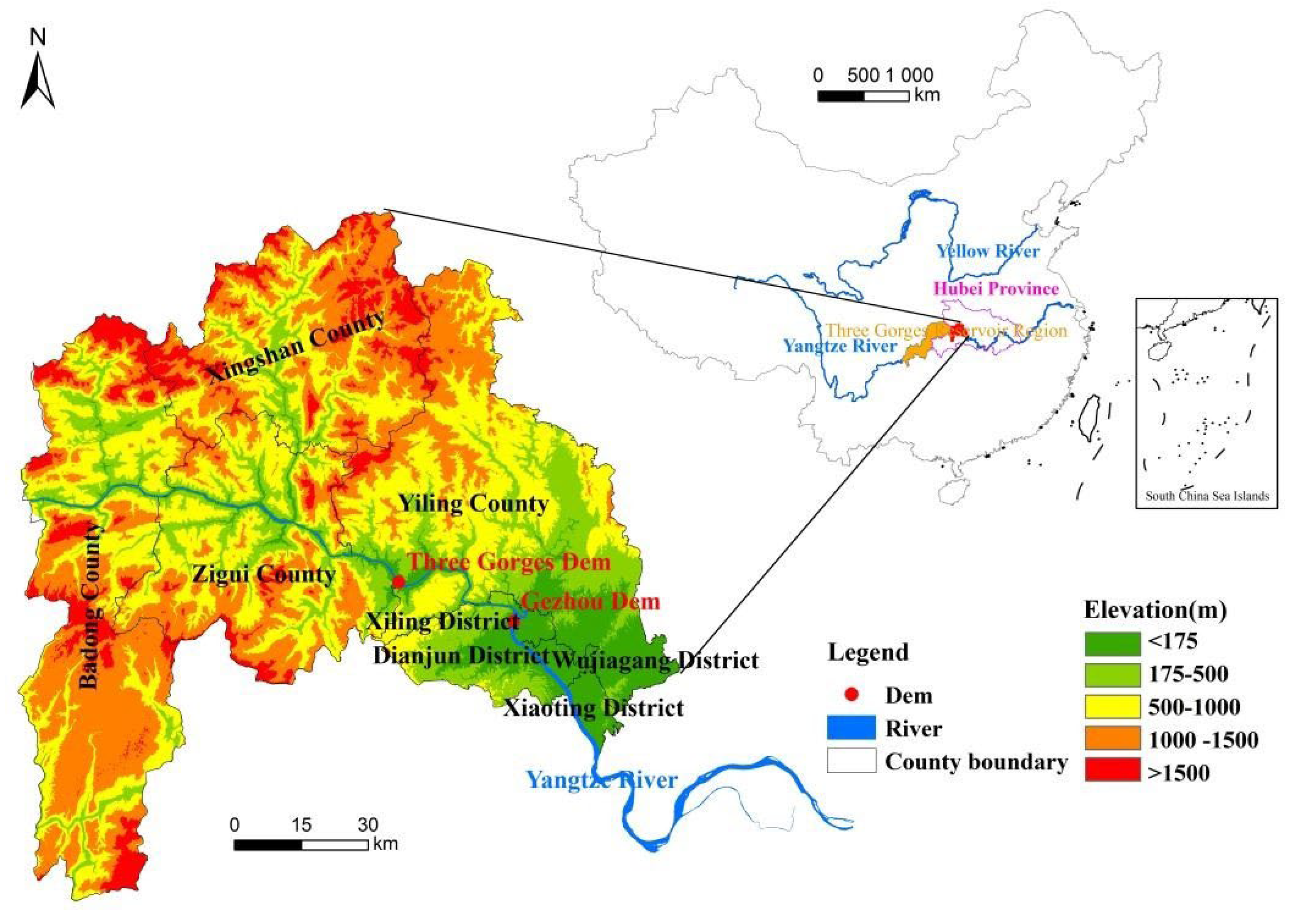
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
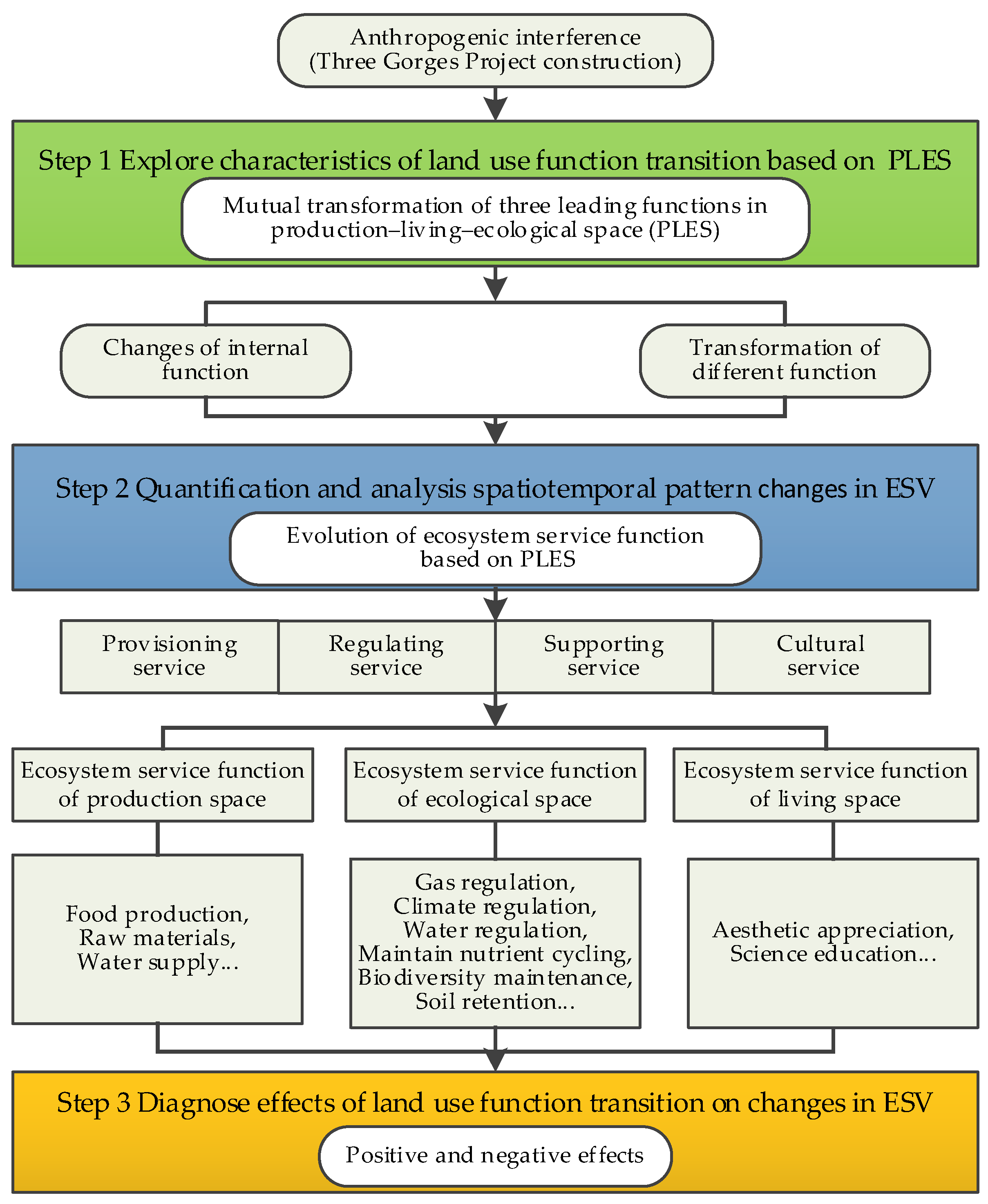
3.1. Research Framework
3.2. Analysis of LUFT
3.2.1. PLES Classification System
3.2.2. Methods of LUFT
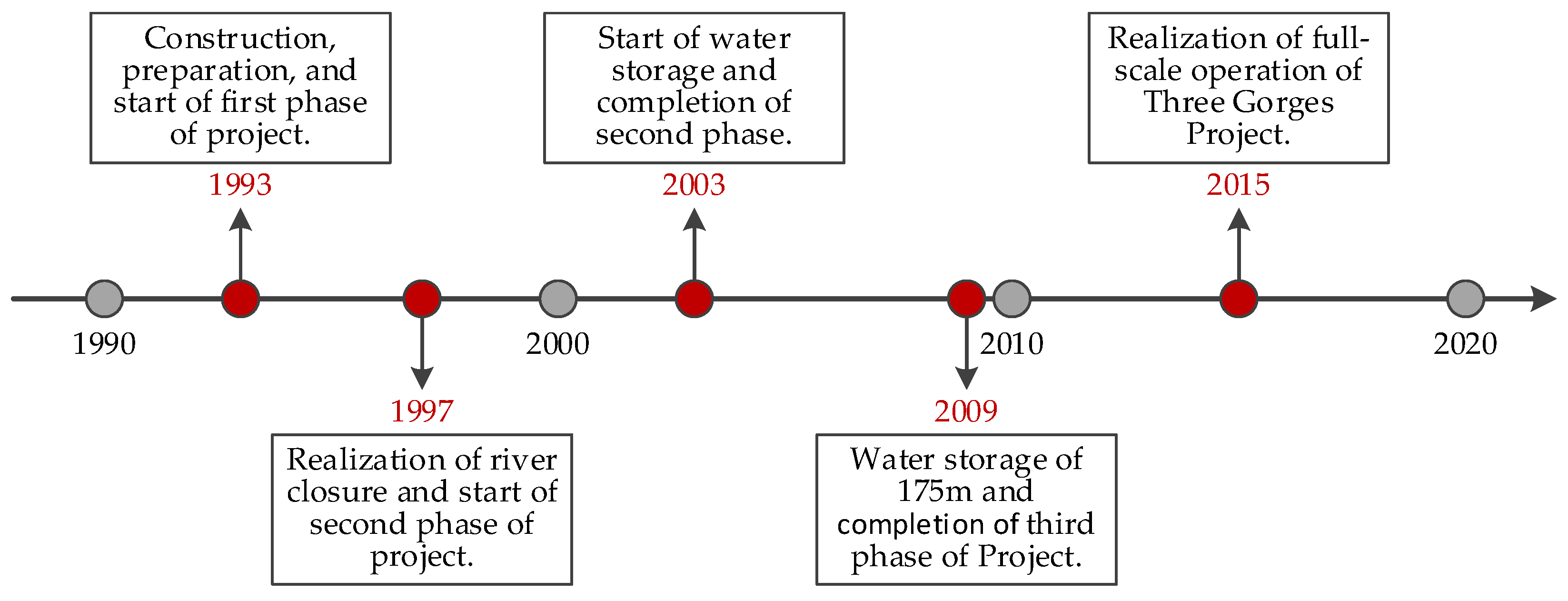
3.2.3. Time Node Division
3.3. Assessment of ESV from the Perspective of PLES
3.4. The Effects of LUFT on Changes of ESV
3.5. Data Sources
4. Results
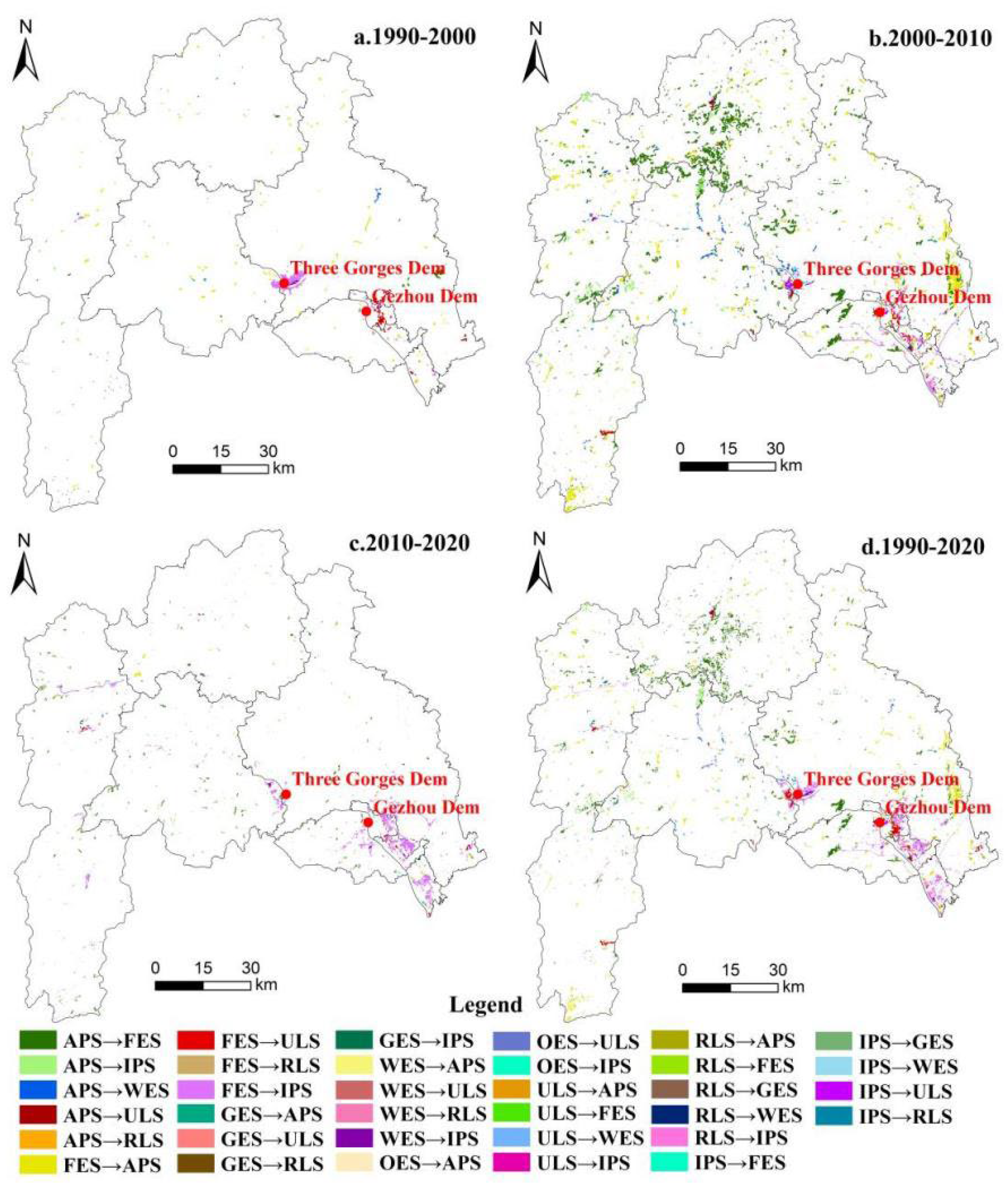
4.1. Characteristics of the Transition of Land Use Function
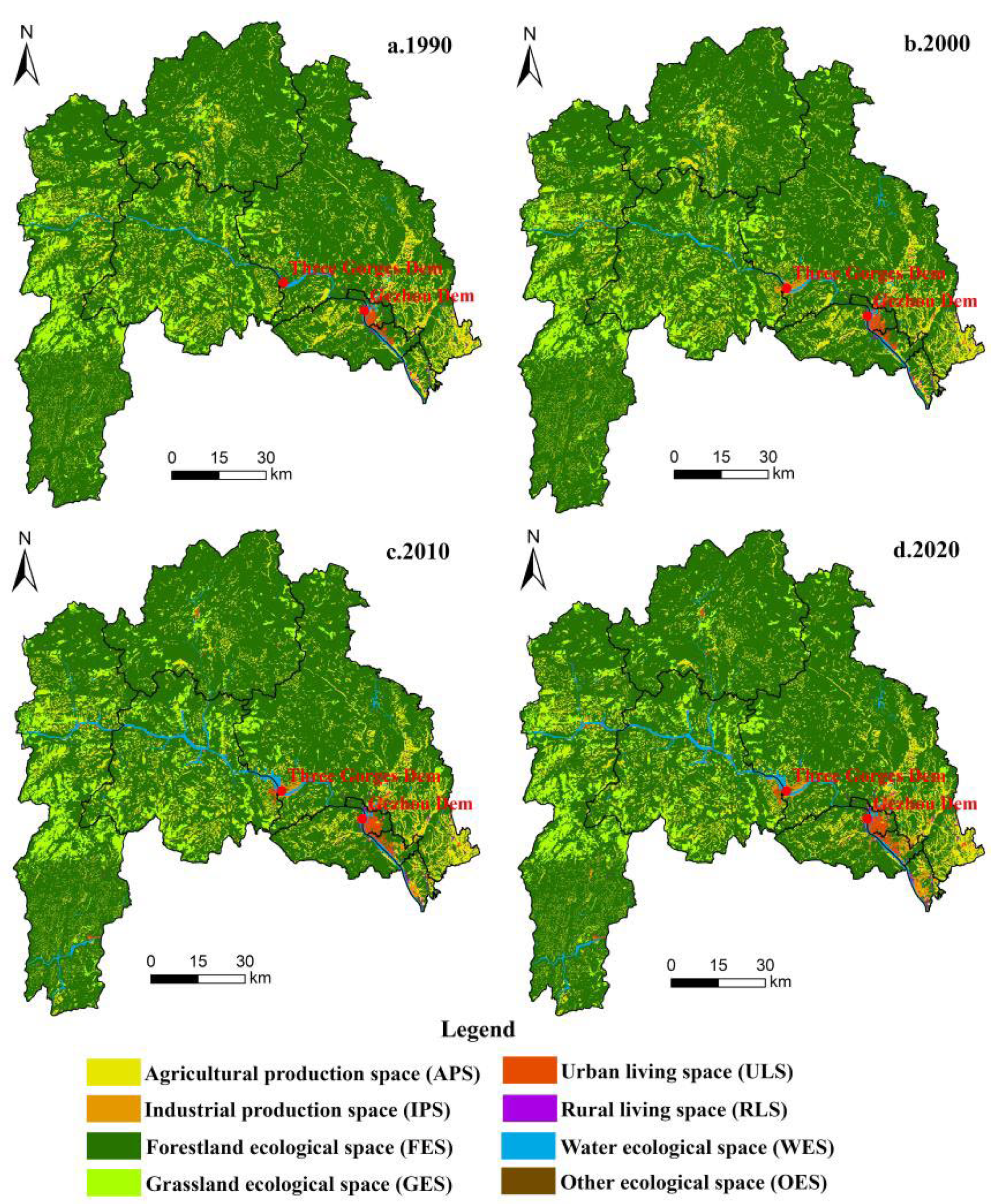
4.1.1. Evaluation of Land Use Function in the TGRA-HS from 1990 to 2020
4.1.2. Structural Transform of Land Use Function in the TGRA-HS from 1990 to 2020
4.2. Characteristics of ESV Change
4.2.1. Quantity Characteristics of ESV Change from the perspective of PLES
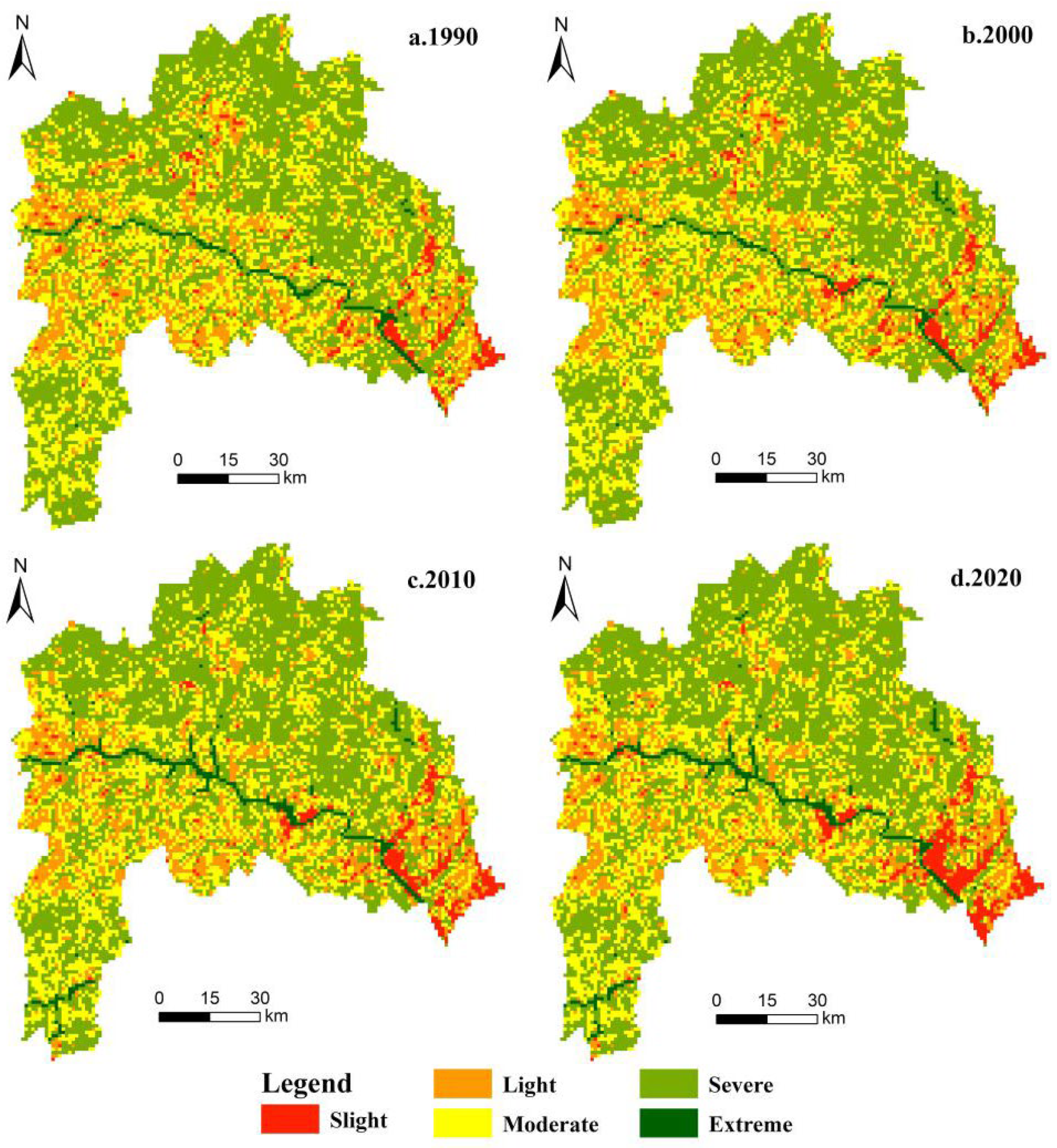
4.2.2. Spatial Characteristics of ESV Change
4.3. The Effects of LUFT on Changes of ESV
5. Discussion
5.1. Construction of the TGP and Stage Response
5.2. Implications for Theory and Practice
5.3. Limitations and Future Works
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perring, M.; De Frenne, P.; Baeten, L.; Maes, S.; Depauw, L.; Blondeel, H.; Caron, M.; Verheyen, K. Global environmental change effects on ecosystems: The importance of land-use legacies. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güneralp, B.; Seto, K.; Ramachandran, M. Evidence of urban land teleconnections and impacts on hinterland. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, L.; Kangas, M.; Ballut, N.; Doucet, A.; Schoenecker, K.; Johnson, P.; Gharehaghaji, M.; Minor, E. Changes in land use and land cover along an urban-rural gradient influence floral resource availability. Curr. Landsc. Ecol. Rep. 2021, 6, 46–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhong, T. Environmental effects of land-use/cover change caused by urbanization and policies in Southwest China Karst area: A case study of Guiyang. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; Grow, D.; Philyaw, L.S. Influence of historical land-use change on contemporary channel processes, form, and restoration. Geosciences 2021, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Land use and land cover change in Greater Dhaka, Bangladesh: Using remote sensing to promote sustainable urbanization. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Land use transition and its eco-environmental effects in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration: A production–living–ecological perspective. Land 2020, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allington, G.; Li, W.; Brown, D. Urbanization and environmental policy effects on the future availability of grazing re-sources on the Mongolian Plateau: Modeling socio-environmental system dynamics. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 68, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.; Jetz, W. Global habitat loss and extinction risk of terrestrial vertebrates under future land-use-change scenarios. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Angadi, D. Land use-land cover (LULC) transformation and its relation with land surface temperature changes: A case study of Barrackpore Subdivision, West Bengal, India. Remote Sens. Appl. 2020, 19, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R. Function-analysis and valuation as a tool to assess land use conficts in planning for sustainable, multi-functional landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 75, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.; Meyfroidt, P. Land use transitions: Socio-ecological feedback versus socio-economic change. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asabere, S.; Acheampong, R.; Ashiagbor, G.; Beckers, S.; Keck, M.; Erasmi, S.; Schanze, J.; Sauer, D. Urbanization, land use transformation and spatio-environmental impacts: Analyses of trends and implications in major metropolitan regions of Ghana. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, T. Farmland transition and its influences on grain production in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthgen, N.; Dormann, C.; Prati, D.; Klaus, V.; Kleinebecker, T.; Hölzel, N.; Alt, F.; Boch, S.; Gockel, S.; Hemp, A.; et al. A quantitative index of land-use intensity in grasslands: Integrating mowing, grazing and fertilization. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2012, 13, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.; Erb, K.; Mertz, O.; Espindola, G. Land system science: Between global challenges and local realities. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberté, E.; Wells, J.A.; Declerck, F.; Metcalfe, D.J.; Catterall, C.P.; Queiroz, C.; Aubin, I.; Bonser, S.P.; Ding, Y.; Fraterrigo, J.M.; et al. Land use intensification reduces functional redundancy and response diversity in plant communities. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, M.; Boelens, L.; Bijl, R. Bus rapid transit system: A study of sustainable land-use transformation, urban density and economic impacts. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, P.; Vinoj, V.; Swain, D.; Roberts, G.; Dash, J.; Tripathy, S. Land use and land cover change effect on surface temperature over Eastern India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, H.; Li, T.; Tu, S. Land use transitions and their effects on water environment in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Land Use Policy 2015, 47, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuissl, H.; Haase, D.; Lanzendorf, M.; Wittmer, H. Environmental impact assessment of urban land use transitions—A context-sensitive approach. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.; Murayama, Y. Landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes: Implications for environmental sustainability planning for the rapidly urbanizing summer capital of the Philippines. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 116, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.; Rounsevell, M.; Geist, H. Are agricultural land-use models able to predict changes in land-use intensity? Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Reddy, M.; Tiwari, S.; Umapathy, G. Land Use Change Increases Wildlife Parasite Diversity in Anamalai Hills, Western Ghats, India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, S.; Wright, C.; Costanza, P. Environmental change in the equatorial Andes: Linking climate, land use and land cover transformations. Remote Sens. Appl. 2016, 8, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, A.; Lu, L.; Ji, Z. Progress and prospects of “production-1iving-ecological” functions evaluation. J. China Agric. Univ. 2021, 26, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Lv, D.N.; Dong, J.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, B. Processes coupling and spatial integration: Characterizing ecological restoration of territorial space in view of landscape ecology. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, W.; Li, M.; Meng, L. Coupling Coordination Degree of Production, Living and Ecological Spaces and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neil, R.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Wilson, M.; Boumans, R. A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coatanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van Der Ploeget, S.; Anderson, S.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, H. Land use transitions and their dynamic mechanism: The case of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassl, M.; Löffler, J. Ecosystem services in coupled social–ecological systems: Closing the cycle of service provision and societal feedback. Ambio 2015, 44, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftcioglu, G. Assessment of the relationship between ecosystem services and human wellbeing in the social-ecological landscapes of Lefke Region in North Cyprus. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, G.; Otero, M.; Clerici, N.; Szantoi, Z.; González-González, A.; Escobedo, F. Interacting municipal-level anthropogenic and ecological disturbances drive changes in Neotropical forest carbon storage. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 937147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, M.; Orozco-Ramírez, Q.; Ramírez-Santiago, R.; Garza, G. Migration, socioeconomic transformation, and land-use change in Mexico’s Mixteca Alta: Lessons for forest transition theory. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, J. Land use transformation and eco-environmental effects based on production-living-ecological spatial synergy: Evidence from Shaanxi Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41492–41504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Li, T.; Li, Y. Effects of land use transitions due to rapid urbanization on ecosystem services: Implications for urban planning in the new developing area of China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Spatio-temporal evolution of land use transition and its eco-environmental effects: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Land 2020, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Deng, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, H. Evaluation of the production-living-ecology space function suitability of Pingshan County in the Taihang mountainous area, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 2562–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Amable, G.S.; Xu, B. Integrated analysis of urbanization-triggered land use change trajectory and implications for ecological land management: A case study in Fuyang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 660, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, M.; Li, L.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, N.; La, L.; Liu, C.; Xiao, W. Identifying and analyzing ecosystem service bundles and their socioecological drivers in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, X.; Paudel, B.; Xu, F.; Deng, Q. Stable sediment retention and rapid economic growth occurred together from the end of the 1970s to 2015 in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3653–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wu, B.; Lü, Y.; Xu, Z. Three Gorges Project: Efforts and challenges for the environment. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2010, 34, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.; Helmi, M. Impacts of land-use transformation on agriculture land in Afghanistan, Kabul city as case study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaarts, J. Summary for policymakers of the global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2019, 45, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Z. Habitat Quality Effect and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Transitions: A Case Study of Henan Water Source Area of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Land 2021, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, R. Influence mechanism of production-living-ecological space changes in the urbanization process of Guangdong province, China. Land 2021, 10, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Ma, J. Optimizing the Production-Living-Ecological Space for Reducing the Ecosystem Services Deficit. Land 2021, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.R.; Chan, K.M.A.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M.; et al. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.; Peterson, G.; Gordon, L. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Classification evaluation and spatial-temporal analysis of “production-living-ecological” spaces in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1290–1304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meehan, T.; Gratton, C.; Diehl, E.; Hunt, N.; Mooney, D.; Ventura, S.; Barham, B.; Jackson, R. Ecosystem-service tradeoffs associated with switching from annual to perennial energy crops in riparian zones of the US Midwest. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, J. Land use transitions and the associated impacts on ecosystem services in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China based on the geo-informatic Tupu method. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, M.; Li, M.; Xia, B. Spatio-temporal changes in ecosystem service value in response to land-use/cover changes in the Pearl River Delta. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Chuai, X.; Dai, C.; Lai, L.; Zhang, M. The impact of land use change on the temporospatial variations of ecosystems services value in China and an optimized land use solution. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Wei, D.; Lin, W. Evaluation of ecosystem services value and its implications for policy making in China: A case study of Fujian Province. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.; Webster, R. A tutorial guide to geostatistics: Computing and modelling variograms and kriging. Cetena 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubei Provincial Statistics Bureau; National Bureau of Statistics Hubei Investigation Team. Hubei Statistical Year Book; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hubei Provincial People’s Government. Hubei Province Main Functional Area Planning. 2012. Available online: https://www.hubei.gov.cn/zfwj/ezf/201303/t20130307_1711739.shtml (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Pan, F.; Song, M.; Wan, Q.; Yuan, L. A conservation planning framework for China’s national key ecological function area based on ecological risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäler, K.; Aniyar, S.; Jansson, A. Accounting for the value of ecosystem assets and their services. Implement. Environ. Acc. 2013, 28, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Connor, J. Land-use change impacts on ecosystem services value: Incorporating the scarcity effects of supply and demand dynamics. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 32, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Type | Secondary Type | Land Use Interpretation and Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Production space (P-space ) | Agricultural production space (APS) | Paddy field, dry land |
| Industrial production space (IPS) | Industrial and mining land, transportation construction land | |
| Living space (L-space) | Urban Living space (ULS) | Urban land |
| Rural Living space (RLS) | Rural residential land | |
| Ecological space (E-space) | Forestland Ecological space (FES) | Forestland, shrub land, sparse forestland, other forestland |
| Grassland Ecological space (GES) | High-coverage grassland, medium-coverage grassland, low-coverage grassland | |
| Water Ecological space (WES) | Canals, lakes, permanent glaciers, snowfields, tidal flats, beaches, reservoirs and pond | |
| Other Ecological space (OES) | Sandy land, Gobi, saline–alkali land, marshland, bare land, bare rock texture, other land |
| Category | Provision Service | Regulating Service | Supporting Service | Cultural Service |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS | 145.73 | 8743.63 | 2477.35 | 233.17 |
| IPS | −29,145.40 | −32,059.95 | 408.04 | 29.15 |
| ULS | −21,859.05 | −14,222.96 | 1253.26 | 32.15 |
| RLS | −8306.44 | 1165.81 | 1748.74 | 174.87 |
| FES | 3293.43 | 37,976.45 | 13,465.18 | 2710.53 |
| GES | 2215.05 | 22,704.27 | 8510.46 | 1719.58 |
| WES | 27,163.51 | 150,910.91 | 10,346.62 | 5508.48 |
| OES | 0.00 | 437.19 | 116.58 | 35.45 |
| Data | Sources |
|---|---|
| Land use data | Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn, accessed on 17 January 2023) |
| Digital elevation model data | |
| Administrative map | Department of Natural Resources of Hubei Province (https://zrzyt.hubei.gov.cn/, accessed on 17 January 2023) |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) data | Resource and Environment Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 17 January 2023) |
| Economic and social development data | Hubei Statistical Yearbook |
| Years/Period | P-space | L-space | E-space | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS | IPS | ULS | RLS | FES | GES | WES | OES | |
| 1990 | 12.86 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 78.80 | 6.70 | 1.10 | 0.00 |
| 2000 | 12.85 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 78.44 | 6.70 | 1.11 | 0.00 |
| 2010 | 11.81 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.24 | 78.11 | 6.82 | 1.94 | 0.00 |
| 2020 | 11.59 | 1.12 | 0.57 | 0.24 | 77.71 | 6.80 | 1.96 | 0.00 |
| 1990–2000 | –0.02 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 0.01 | –0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2000–2010 | –1.04 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.04 | –0.33 | 0.12 | 0.83 | 0.00 |
| 2010–2020 | –0.22 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.01 | –0.40 | –0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 1990–2020 | –1.28 | 1.08 | 0.26 | 0.06 | –1.09 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 0.00 |
| Period | Number | Transition Types | Area (hm2) | Change Rates (%) | Accumulative Change Rates (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–2000 | 1 | FES → IPS | 2507.81 | 37.55 | 37.55 |
| 2 | FES → APS | 1602.92 | 24.00 | 61.55 | |
| 3 | APS → FES | 620.96 | 9.30 | 70.85 | |
| 4 | APS → ULS | 548.97 | 8.22 | 79.07 | |
| 5 | FES → ULS | 352.47 | 5.28 | 84.34 | |
| 6 | WES → IPS | 287.52 | 4.30 | 88.65 | |
| 7 | WES → APS | 172.02 | 2.58 | 91.22 | |
| 8 | APS → GES | 134.79 | 2.02 | 93.24 | |
| 9 | APS → WES | 124.72 | 1.87 | 95.11 | |
| 10 | FES → RLS | 86.41 | 1.29 | 96.40 | |
| 2000–2010 | 1 | APS → FES | 16,149.51 | 43.09 | 43.09 |
| 2 | FES → APS | 8917.54 | 23.79 | 66.88 | |
| 3 | FES → IPS | 2452.59 | 6.54 | 73.43 | |
| 4 | APS → GES | 2415.21 | 6.44 | 79.87 | |
| 5 | APS → WES | 1544.04 | 4.12 | 83.99 | |
| 6 | FES → ULS | 907.02 | 2.42 | 86.41 | |
| 7 | IPS → ULS | 778.33 | 2.08 | 88.49 | |
| 8 | APS → ULS | 699.77 | 1.87 | 90.35 | |
| 9 | IPS → WES | 532.49 | 1.42 | 91.77 | |
| 10 | FES → RLS | 498.83 | 1.33 | 93.11 | |
| 2010–2020 | 1 | FES → IPS | 4618.55 | 78.06 | 78.06 |
| 2 | APS → FES | 219.98 | 3.72 | 81.78 | |
| 3 | FES → APS | 182.07 | 3.08 | 84.86 | |
| 4 | FES → ULS | 136.73 | 2.31 | 87.17 | |
| 5 | WES → IPS | 132.18 | 2.23 | 89.40 | |
| 6 | APS → RLS | 115.94 | 1.96 | 91.36 | |
| 7 | IPS → FES | 85.78 | 1.45 | 92.81 | |
| 8 | APS → ULS | 71.00 | 1.20 | 94.01 | |
| 9 | FES → RLS | 58.15 | 0.98 | 94.99 | |
| 10 | RLS → APS | 54.83 | 0.93 | 95.92 |
| Years/Period | P-space | L-space | E-space | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS | IPS | ULS | RLS | FES | GES | WES | OES | |
| 1990 | 1807.98 | −29.96 | −130.27 | −11.71 | 54842.66 | 2852.42 | 2590.48 | 0.03 |
| 2000 | 1805.77 | −232.62 | −164.14 | −12.54 | 54597.45 | 2852.05 | 2596.65 | 0.02 |
| 2010 | 1660.12 | −384.79 | −236.39 | −14.91 | 54366.90 | 2902.79 | 4556.84 | 0.00 |
| 2020 | 1628.64 | −823.90 | −241.98 | −15.41 | 54086.03 | 2897.82 | 4607.67 | 0.00 |
| 1990−2000 | −2.21 | −202.66 | −33.87 | −0.83 | −245.21 | −0.37 | 6.17 | −0.01 |
| 2000−2010 | −145.64 | −152.17 | −72.25 | −2.37 | −230.55 | 50.75 | 1960.20 | −0.02 |
| 2010−2020 | −31.49 | −439.11 | −5.59 | −0.50 | −280.87 | −4.98 | 50.83 | 0.00 |
| 1990−2020 | −179.34 | −793.94 | −111.71 | −3.70 | −756.62 | 45.40 | 2017.20 | −0.03 |
| Effect Type | Transition Type | Difference of ESV (CNY 106) | Contribution Rates (%) | Proportion of Contribution Rates (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive effects of ESV | APS → FES | 747.41 | 0.358317 | 64.33 |
| APS → WES | 290.21 | 0.139130 | 24.98 | |
| APS → GES | 59.70 | 0.028619 | 5.14 | |
| ULS → WES | 29.70 | 0.014240 | 2.56 | |
| RLS → WES | 14.25 | 0.006832 | 1.23 | |
| ULS → FES | 4.35 | 0.002085 | 0.37 | |
| IPS → ULS | 3.91 | 0.001875 | 0.34 | |
| RLS → APS | 3.78 | 0.001812 | 0.33 | |
| RLS → FES | 3.62 | 0.001738 | 0.31 | |
| IPS → FES | 3.03 | 0.001454 | 0.26 | |
| Negative effects of ESV | FES → IPS | −1016.67 | −0.487402 | 52.37 |
| FES → APS | −455.63 | −0.218434 | 23.47 | |
| FES → ULS | −160.92 | −0.077147 | 8.29 | |
| WES → IPS | −69.08 | −0.033119 | 3.56 | |
| APS → ULS | −61.52 | −0.029492 | 3.17 | |
| WES → APS | −46.73 | −0.022405 | 2.41 | |
| WES → ULS | −40.87 | −0.019594 | 2.11 | |
| FES → RLS | −39.45 | −0.018914 | 2.03 | |
| RLS → IPS | −15.30 | −0.007337 | 0.79 | |
| GES → APS | −11.94 | −0.005724 | 0.61 | |
| APS → RLS | −10.64 | −0.005100 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, F.; Shu, N.; Wan, Q.; Huang, Q. Land Use Function Transition and Associated Ecosystem Service Value Effects Based on Production–Living–Ecological Space: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Land 2023, 12, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020391
Pan F, Shu N, Wan Q, Huang Q. Land Use Function Transition and Associated Ecosystem Service Value Effects Based on Production–Living–Ecological Space: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Land. 2023; 12(2):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020391
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Fangjie, Nannan Shu, Qing Wan, and Qi Huang. 2023. "Land Use Function Transition and Associated Ecosystem Service Value Effects Based on Production–Living–Ecological Space: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area" Land 12, no. 2: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020391
APA StylePan, F., Shu, N., Wan, Q., & Huang, Q. (2023). Land Use Function Transition and Associated Ecosystem Service Value Effects Based on Production–Living–Ecological Space: A Case Study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Land, 12(2), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020391









