Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP) in the Soil of Teff-Acacia decurrens-Charcoal Production System in Northern Ethiopia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. The TM and TACP Systems
2.3. Soil Sampling
2.4. Analysis of Soil Properties
2.5. Analysis of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates
2.6. Calculation of BaP-Equivalent Concentrations
2.7. Statatistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Level of PAHs
3.2. Toxic Assessment
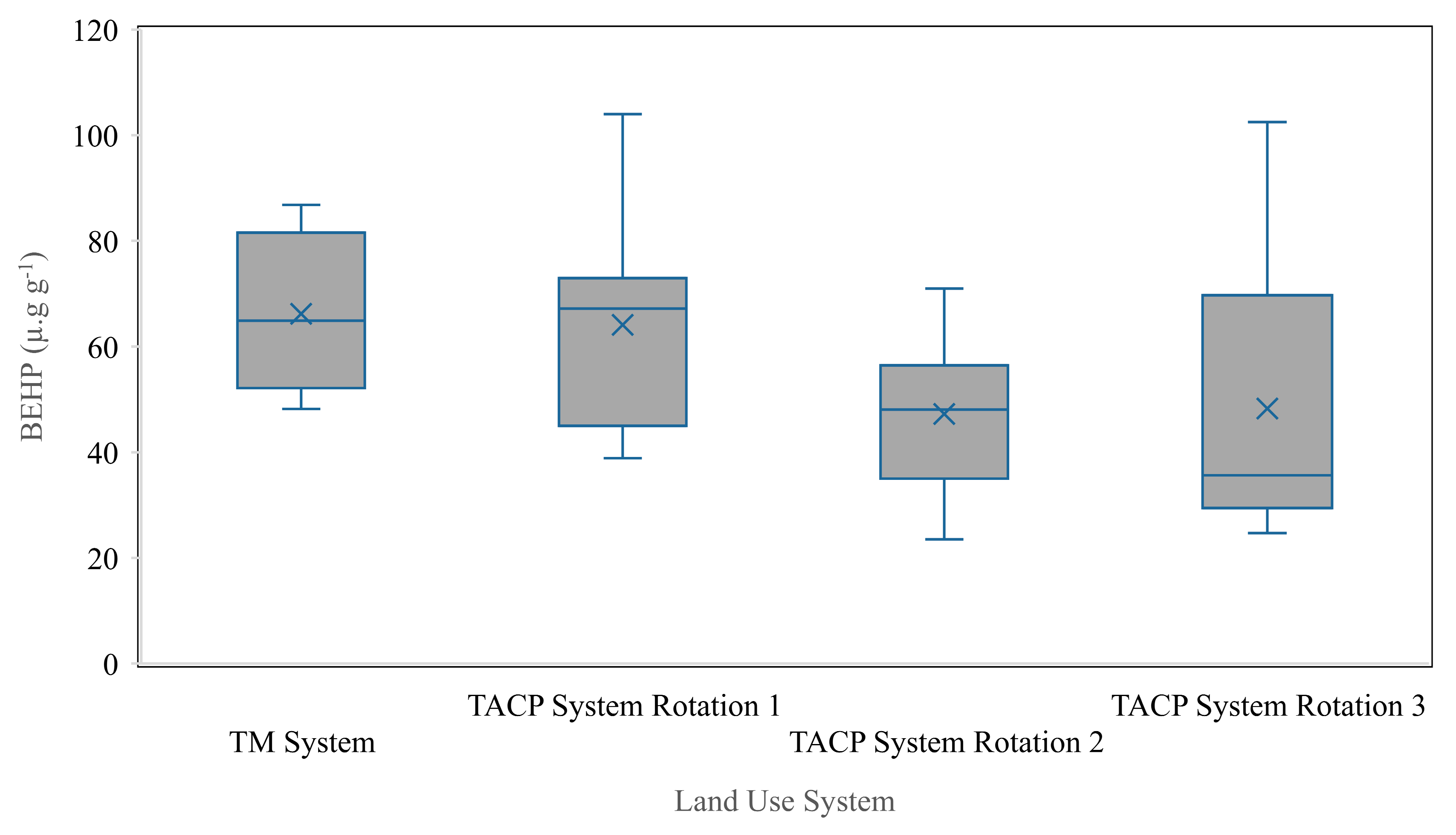
3.3. Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP)
4. Discussions
4.1. Level of PAHs
4.2. Toxic Assessment
4.3. Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Sequestering Carbon in Soils of Agro-Ecosystems. Food Policy 2011, 36, S33–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Gaunt, J.; Rondon, M. Bio-Char Sequestration in Terrestrial Ecosystems—A Review. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2006, 11, 403–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, X.; Harris, W. Phosphorus Release from Dairy Manure, the Manure-Derived Biochar, and Their Amended Soil: Effects of Phosphorus Nature and Soil Property. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, F.P.; Baronti, S.; Lugato, E.; Genesio, L.; Castaldi, S.; Fornasier, F.; Miglietta, F. Biochar as a Strategy to Sequester Carbon and Increase Yield in Durum Wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, L.A.; Harpole, W.S. Biochar and Its Effects on Plant Productivity and Nutrient Cycling: A Meta-Analysis. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.D.; Crandell, D.W.; Singleton, D.R.; Aitken, M.D. Stable-Isotope Probing of the Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacterial Guild in a Contaminated Soil: Identification of PAH-Degrading Bacteria by SIP. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A Quantitative Review of the Effects of Biochar Application to Soils on Crop Productivity Using Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, B.; Reddy, P.V.L.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.S.; Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.-H. Benefits and Limitations of Biochar Amendment in Agricultural Soils: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A.; Cox, L.; Spokas, K.A.; Celis, R.; Hermosín, M.C.; Cornejo, J.; Koskinen, W.C. Comparative Sorption and Leaching Study of the Herbicides Fluometuron and 4-Chloro-2-Methylphenoxyacetic Acid (MCPA) in a Soil Amended with Biochars and Other Sorbents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12550–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Fan, S.; Müller, K.; Hu, G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Che, L.; Wang, H. Biochar Reduces the Bioavailability of Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Soil. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, S.E.; Lehmann, J.; Rutherford, D.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Bachmann, R.T.; Shitumbanuma, V.; O’Toole, A.; Sundqvist, K.L.; Arp, H.P.H.; Cornelissen, G. Quantifying the Total and Bioavailable Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Dioxins in Biochars. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilber, I.; Blum, F.; Leifeld, J.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Bucheli, T.D. Quantitative Determination of PAHs in Biochar: A Prerequisite To Ensure Its Quality and Safe Application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3042–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Jośko, I.; Kuśmierz, M. Biochar Properties Regarding to Contaminants Content and Ecotoxicological Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Sun, K.; Jin, J.; Gao, B.; Yan, Y.; Han, L.; Wu, F.; Xing, B. Properties of the Plant- and Manure-Derived Biochars and Their Sorption of Dibutyl Phthalate and Phenanthrene. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, A.; Ivanova, R. Determination of Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sludge from Wastewater Treatment Basins. J. Environ. Monitor. 2003, 5, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds in Nature. Sci. Am. 1976, 234, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.L.; Lafleur, A.L.; Busby, W.F.; Donhoffner, L.L.; Penman, B.W.; Crespi, C.L. Mutagenicity of C24H14 PAH in Human Cells Expressing CYP1A1. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 1999, 446, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEFs) for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.C.S.; Santos, L.G.G.V.; Sant’Anna, M.V.S.; Souza, M.R.R.; Damasceno, F.C.; Alexandre, M.R. Seasonal Distribution of Aliphatic Hydrocarbons in the Vaza Barris Estuarine System, Sergipe, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Thavamani, P.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Lee, Y.B.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Remediation Approaches for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Contaminated Soils: Technological Constraints, Emerging Trends and Future Directions. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 944–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berset, J.D.; Holzer, R. Organic Micropollutants in Swiss Agriculture: Distribution of Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB) in Soil, Liquid Manure, Sewage Sludge and Compost Samples; a Comparative Study. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1995, 59, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCME [Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment]. Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for Carcinogenic and Other Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Environmental and Human Health Effects); Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Brome-Missisquoi, QC, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Global Warming of 1.5 °C: Summary for Policymakers; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira Netto, A.D.; Cunha, I.F.; Krauss, T.M. Persistence of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Soil of a Burned Area for Agricultural Purposes in Brazil. Bull Environ. Contam Toxicol. 2004, 73, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, W.; Graham, M.C.; MacKinnon, G.; Mašek, O. Strategies for Producing Biochars with Minimum PAH Contamination. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 119, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, D.; Rombolà, A.G.; Torri, C.; Spokas, K.A. Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Biochar and Biochar Amended Soil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 103, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, K.; Kassomenos, P. Aerosol Contributions at an Urban Background Site in Eastern Mediterranean—Potential Source Regions of PAHs in PM10 Mass. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, W.; Liao, X.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, Z.; Jiao, W.; Bai, Y. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Soils of Beijing: Status, Sources, Distribution and Potential Risk. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, M.; Kang, Y.; Wang, H.; Leung, A.O.W.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Urban Surface Dust of Guangzhou, China: Status, Sources and Human Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4519–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.R.; Jones, K.C. Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the United Kingdom Environment: A Preliminary Source Inventory and Budget. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 88, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddo, A.; Cai, C.; Reid, B.J. Environmental Contextualisation of Potential Toxic Elements and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 171, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagernäs, L.; Kuoppala, E.; Simell, P. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Birch Wood Slow Pyrolysis Products. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6960–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Biochar Foundation (EBC). European Biochar Certificate Version 6.0: Guidelines for a Sustainable Production of Biochar; European Biochar Foundation: Arbaz, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- de Resende, M.F.; Brasil, T.F.; Madari, B.E.; Pereira Netto, A.D.; Novotny, E.H. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Biochar Amended Soils: Long-Term Experiments in Brazilian Tropical Areas. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Mirza, M.; Fahlman, B.; Rybchuk, R.; Yang, J.; Harfield, D.; Anyia, A.O. Mapping Thermomechanical Pulp Sludge (TMPS) Biochar Characteristics for Greenhouse Produce Safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, J.; Khan, M.Y.; Matsui, M.; Côcco, L.C.; Yamamoto, C.I.; Lopes, W.A.; de Andrade, J.B.; Pillon, C.N.; Arizaga, G.G.C.; Mangrich, A.S. Evaluation of PAH Contamination in Soil Treated with Solid By-Products from Shale Pyrolysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R. Phthalates and Human Health. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 62, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshir, M.; Tadesse, M.; Yimer, F.; Brüggemann, N. Factors Affecting Adoption and Intensity of Use of Tef-Acacia Decurrens-Charcoal Production Agroforestry System in Northwestern Ethiopia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshir, M.; Yimer, F.; Brüggemann, N.; Tadesse, M. Soil Properties of a Tef-Acacia Decurrens-Charcoal Production Rotation System in Northwestern Ethiopia. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, T.; Mekonnen, M.; Yitaferu, B.; Cerdà, A. Conversion of Crop Land Use to Plantation Land Use, Northwest Ethiopia. Trees For. People 2021, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NWEMA. Northwest Ethiopia Meteorological Agency; NWEMA: Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Assistance to Land Use Planning Ethiopia Geomorphology and Soils; FAO: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yihenew, G. Selected Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Soils of Adet Research Center and Its Testing Sites in Northwestern Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Nat. Resour. 2002, 4, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Eyasu, E. Farmers’ Perceptions of Soil Fertility Changes and Managment; Institute for Sustainable Development: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tegegn, Z.; Abebe, A.; Agide, Z. Understanding Catchments’ Hydrologic Response Similarity of Upper Blue Nile (Abay) Basin through Catchment Classification. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 8, 3305–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Peters, A.; Trinks, S.; Schonsky, H.; Facklam, M.; Wessolek, G. Impact of Biochar and Hydrochar Addition on Water Retention and Water Repellency of Sandy Soil. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Encyclopedia of Soil Science, 3rd ed.; Taylor and Francis: Columbus, OH, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Black, C.A.; Evans, D.D.; Esingoger, L.E.; White, J.L.; Clark, F.E. Physical Properties. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part I and II; American Society of Agronomy Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer, M.; Schulten, H.R. The Analysis of Soil Organic Matter by Pyrolysis-Field Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Rombolà, A.G.; Meredith, W.; Snape, C.E.; Baronti, S.; Genesio, L.; Vaccari, F.P.; Miglietta, F.; Fabbri, D. Fate of Soil Organic Carbon and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a Vineyard Soil Treated with Biochar. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11037–11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a Sorbent for Contaminant Management in Soil and Water: A Review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyika, C.; Majid, Z.A.; Rashid, M.; Isa, A.B.; Ismail, N.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yahya, A. Toxic and Nontoxic Elemental Enrichment in Biochar at Different Production Temperatures. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśmierz, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Kraska, P.; Pałys, E.; Andruszczak, S. Persistence of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Biochar-Amended Soil. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Pignatello, J.J. Time-Dependent Isotherm Shape of Organic Compounds in Soil Organic Matter: Implications for Sorption Mechanism. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa, J.M.; Paneque, M.; Hilber, I.; Blum, F.; Knicker, H.E.; Bucheli, T.D. Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Biochar and Biochar-Amended Agricultural Soil from Southern Spain. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Toxicity and Sorption Behaviour of Biochars Prepared by Pyrolysis of Paper Mill Effluent Treatment Plant Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.G.I.D.; Moldrup, P.; Paradelo, M.; Elsgaard, L.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; de Jonge, L.W. Effects of Biochar on Air and Water Permeability and Colloid and Phosphorus Leaching in Soils from a Natural Calcium Carbonate Gradient. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska-Kordybach, B. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Agricultural Soils in Poland: Preliminary Proposals for Criteria to Evaluate the Level of Soil Contamination. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.C.; Overcash, M.R. Fate of Polynuclear Aromatic Compounds (PNAs) in Soil-Plant Systems. In Residue Reviews; Gunther, F.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 1–68. ISBN 978-1-4612-5571-0. [Google Scholar]
- Oleszczuk, P.; Kuśmierz, M.; Godlewska, P.; Kraska, P.; Pałys, E. The Concentration and Changes in Freely Dissolved Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Biochar-Amended Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.J.; Thomas, G.O.; Jaward, F.M.; Steinnes, E.; Gustafsson, O.; Jones, K.C. PAHs in Background Soils from Western Europe: Influence of Atmospheric Deposition and Soil Organic Matter. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-O.; Choi, S.-D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Soils from a Multi-Industrial City, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, T.; Khillare, P.S.; Shridhar, V.; Ray, S. Pattern, Sources and Toxic Potential of PAHs in the Agricultural Soils of Delhi, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orecchio, S. Contamination from Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Soil of a Botanic Garden Localized next to a Former Manufacturing Gas Plant in Palermo (Italy). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Levels of Metals, PCBs, PCNs and PAHs in Soils of a Highly Industrialized Chemical/Petrochemical Area: Temporal Trend. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyakora, C.; Ogbeche, A.; Palmer, P.; Coker, H. Determination of Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Marine Samples of Siokolo Fishing Settlement. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1073, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogribny, I.P. Environmental Exposures and Epigenetic Perturbations. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-801238-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L. Pollution Characteristics, Spatial Distributions, and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Cultivated Soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lena, Q. Compasrsion of Three Aqua Regia Digestin Methods for Twenty Florida Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 2001, 65, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, C.D.; Thompson, I.P.; Burns, R.G. Degradation and Impact of Phthalate Plasticizers on Soil Microbial Communities. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D.; Rodricks, J.V. Assessment of Possible Carcinogenic Risk to Humans Resulting from Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl)Phthalate (DEHP). J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1985, 4, 111–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in Freshwater and Terrestrial Environments: Evaluating the Current Understanding to Identify the Knowledge Gaps and Future Research Priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S. Occurrence, Health Risks and Soil-Air Exchange of Phthalate Acid Esters: A Case Study in Plastic Film Greenhouses of Chongqing, China. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Soil Properties | Land-Use Types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TACP System | ||||
| TM System | Rotation 1 | Rotation 2 | Rotation 3 | |
| Sand | 29.67 | 29.21 | 29.25 | 26.75 |
| Silt | 29.42 | 29.20 | 29.25 | 30.30 |
| Clay | 40.92 | 41.78 | 41.20 | 42.87 |
| pH | 5.06 | 4.48 | 4.65 | 5.02 |
| SOC | 2.34 | 4.19 | 4.10 | 1.87 |
| Bd | 0.76 | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.81 |
| TN | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.19 |
| PAHs [ng g−1] | Land-Use Types | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TACP System | ||||
| TM System | Rotation 1 | Rotation 2 | Rotation 3 | |
| Flu | ND | 22.84 | 24.69 | ND |
| Ace | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Phe | 42.42 | 66.34 | 61.42 | 58.10 |
| Ant | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Pyr | ND | ND | ND | 21.99 |
| BaA | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Chr | ND | ND | ND | 21.79 |
| BkF | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| BbF | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| BaP | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| IcdP | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| BghiP | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| DBahA | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Total | 42.42 | 89.18 | 86.11 | 101.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beshir, M.; Brüggemann, N.; Yimer, F.; Tadesse, M.; Thiele, B.; Hofmann, D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP) in the Soil of Teff-Acacia decurrens-Charcoal Production System in Northern Ethiopia. Land 2023, 12, 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122117
Beshir M, Brüggemann N, Yimer F, Tadesse M, Thiele B, Hofmann D. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP) in the Soil of Teff-Acacia decurrens-Charcoal Production System in Northern Ethiopia. Land. 2023; 12(12):2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122117
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeshir, Miftha, Nicolas Brüggemann, Fantaw Yimer, Menfese Tadesse, Björn Thiele, and Diana Hofmann. 2023. "Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP) in the Soil of Teff-Acacia decurrens-Charcoal Production System in Northern Ethiopia" Land 12, no. 12: 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122117
APA StyleBeshir, M., Brüggemann, N., Yimer, F., Tadesse, M., Thiele, B., & Hofmann, D. (2023). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (BEHP) in the Soil of Teff-Acacia decurrens-Charcoal Production System in Northern Ethiopia. Land, 12(12), 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122117






