Towards Sustainable Development Goals: Coupling Coordination Analysis and Spatial Heterogeneity between Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security in China
Abstract
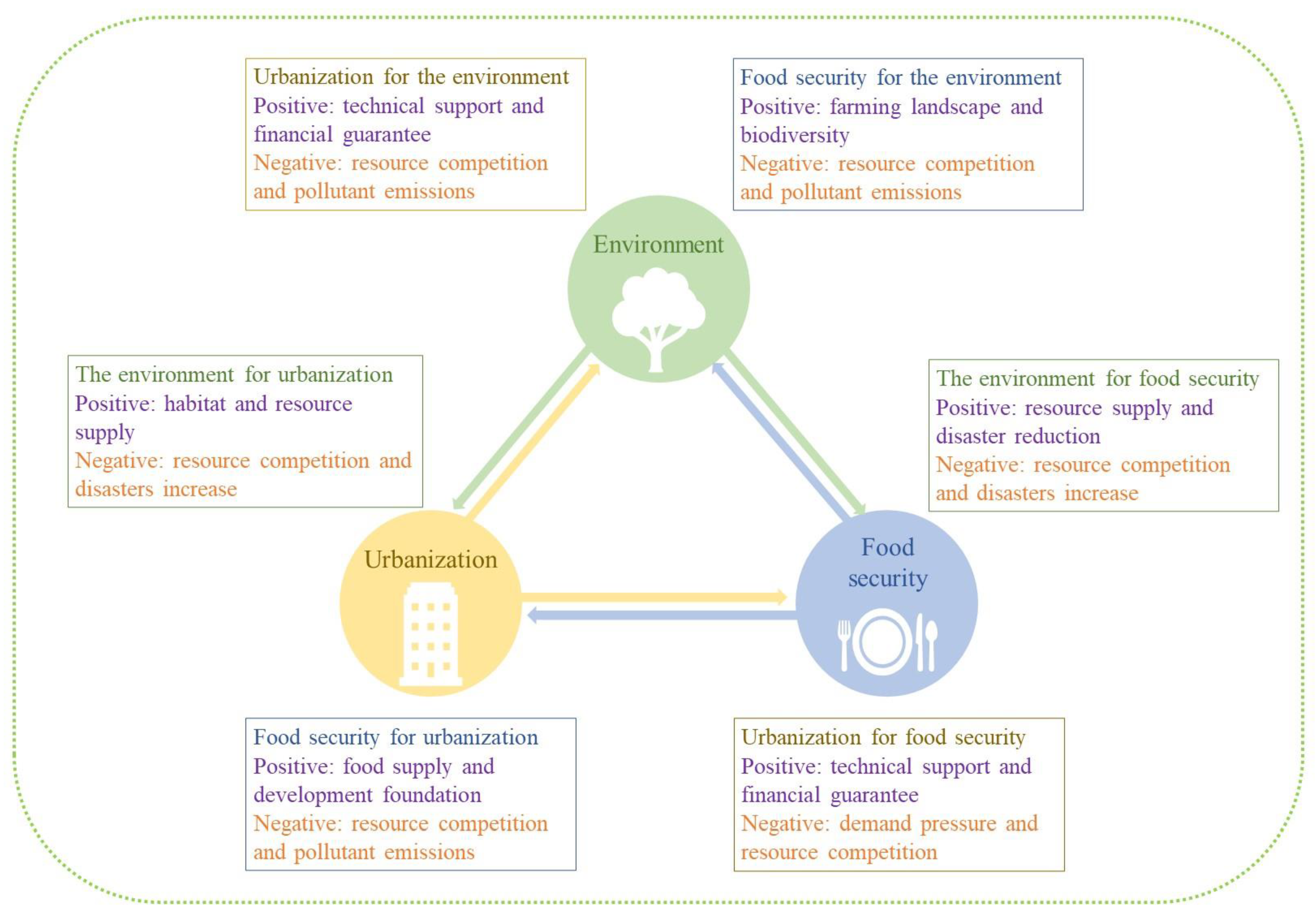
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
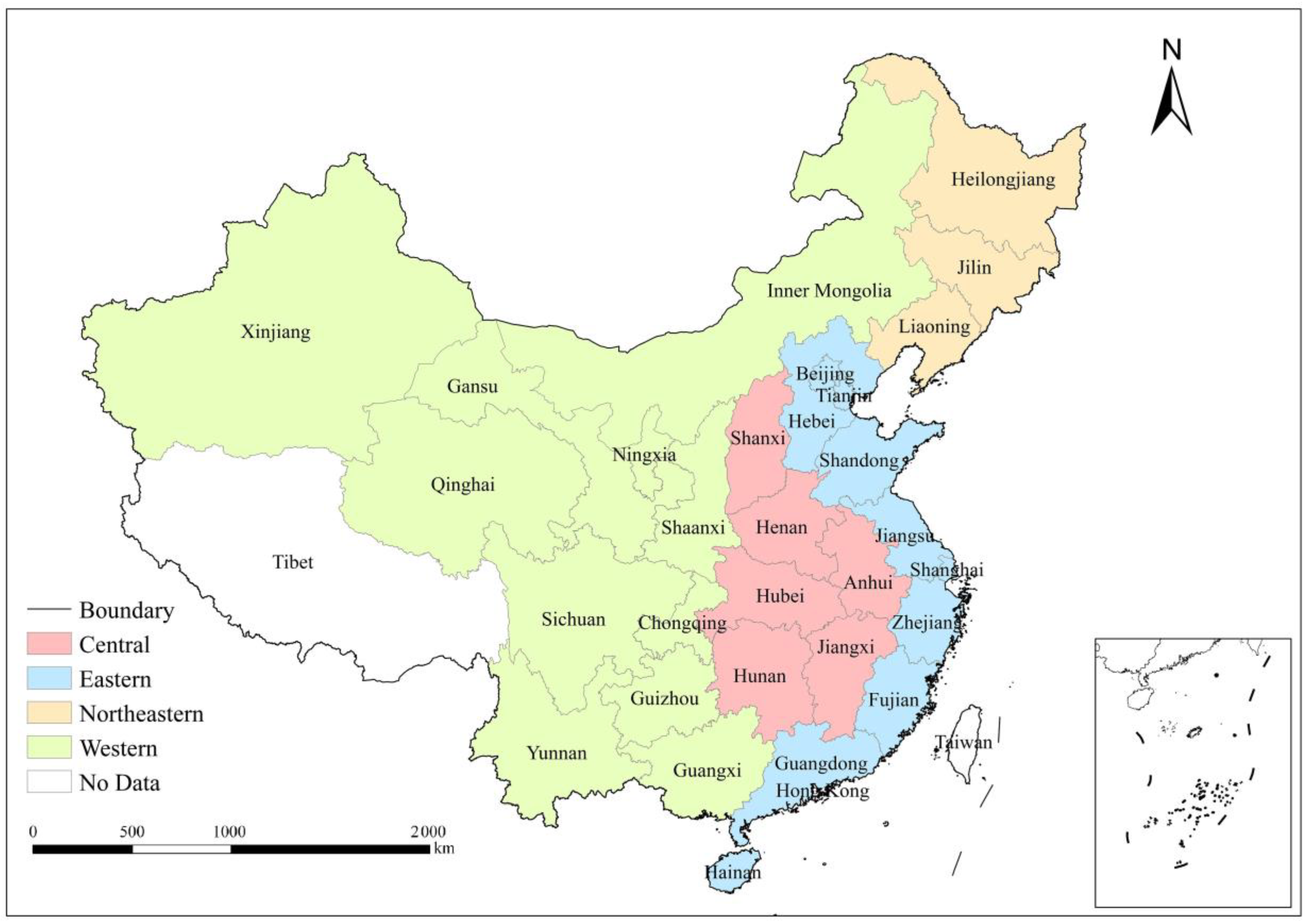
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Evaluation Index System
2.2.1. Evaluation Index System for Urbanization
2.2.2. Evaluation Index System for the Environment
2.2.3. Evaluation Index System for Food Security
2.2.4. Weight Determination and Calculation of Comprehensive Development Index
2.3. Coupling Coordination Degree Model (CCDM)
2.4. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
2.5. Dagum Gini Coefficient
2.6. Obstacle Diagnosis Model
3. Results
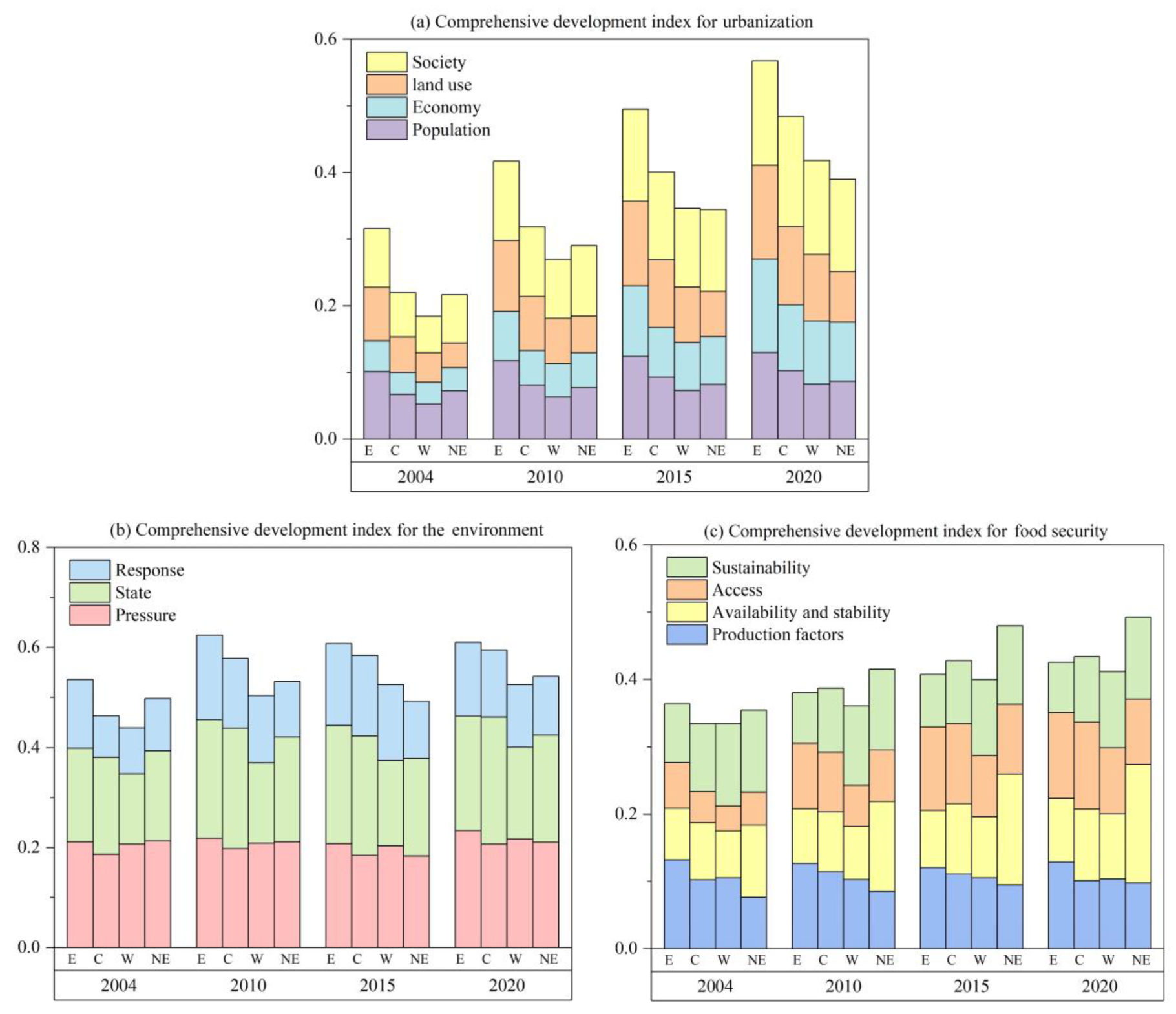
3.1. Analysis of Comprehensive Development Index (CDI) for Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security
3.1.1. Evolution Characteristics of the CDI for Urbanization
3.1.2. Evolution Characteristics of the CDI for the Environment
3.1.3. Evolution Characteristics of the CDI for Food Security
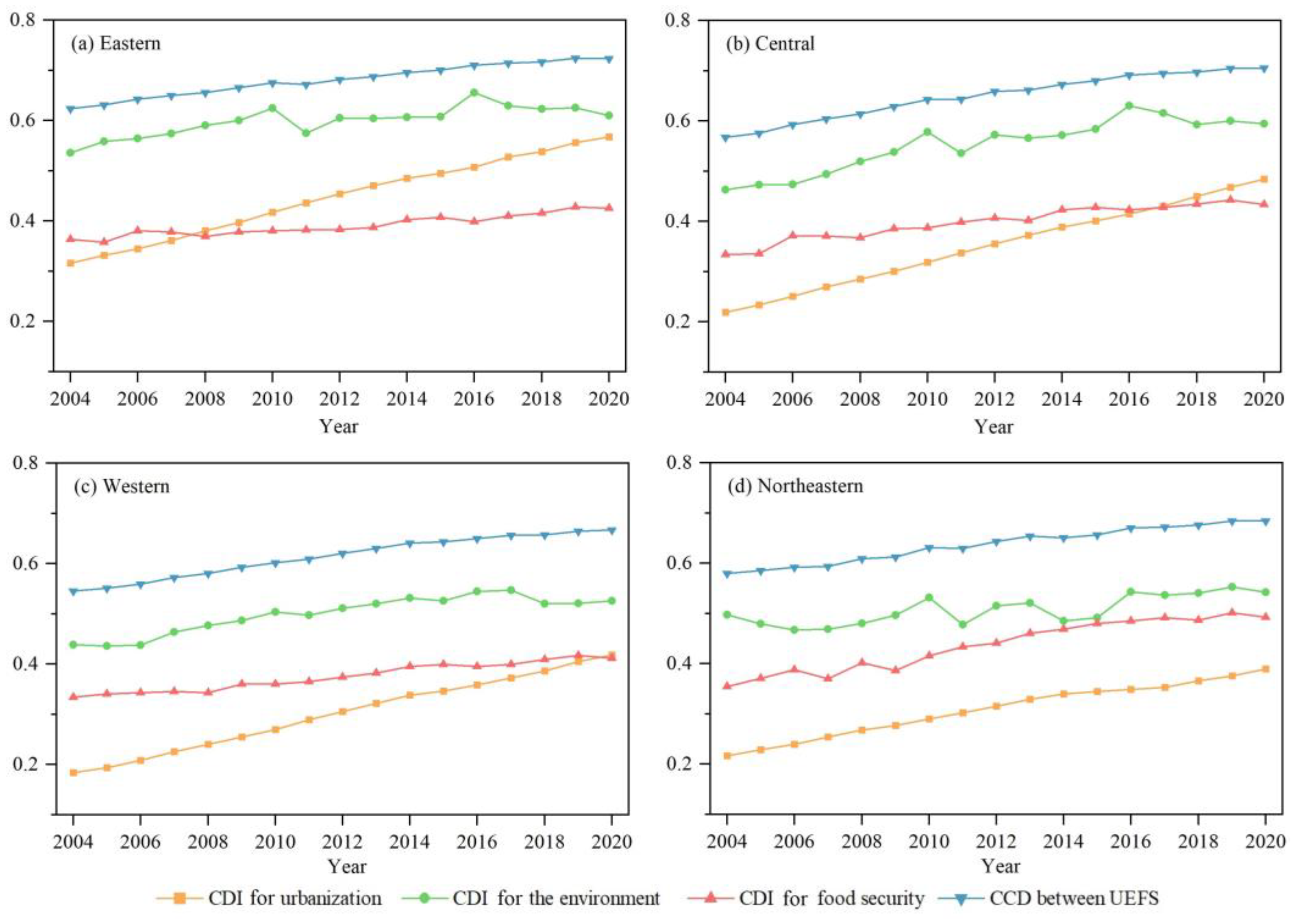
3.2. Analysis of the Coupling Coordination between Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security
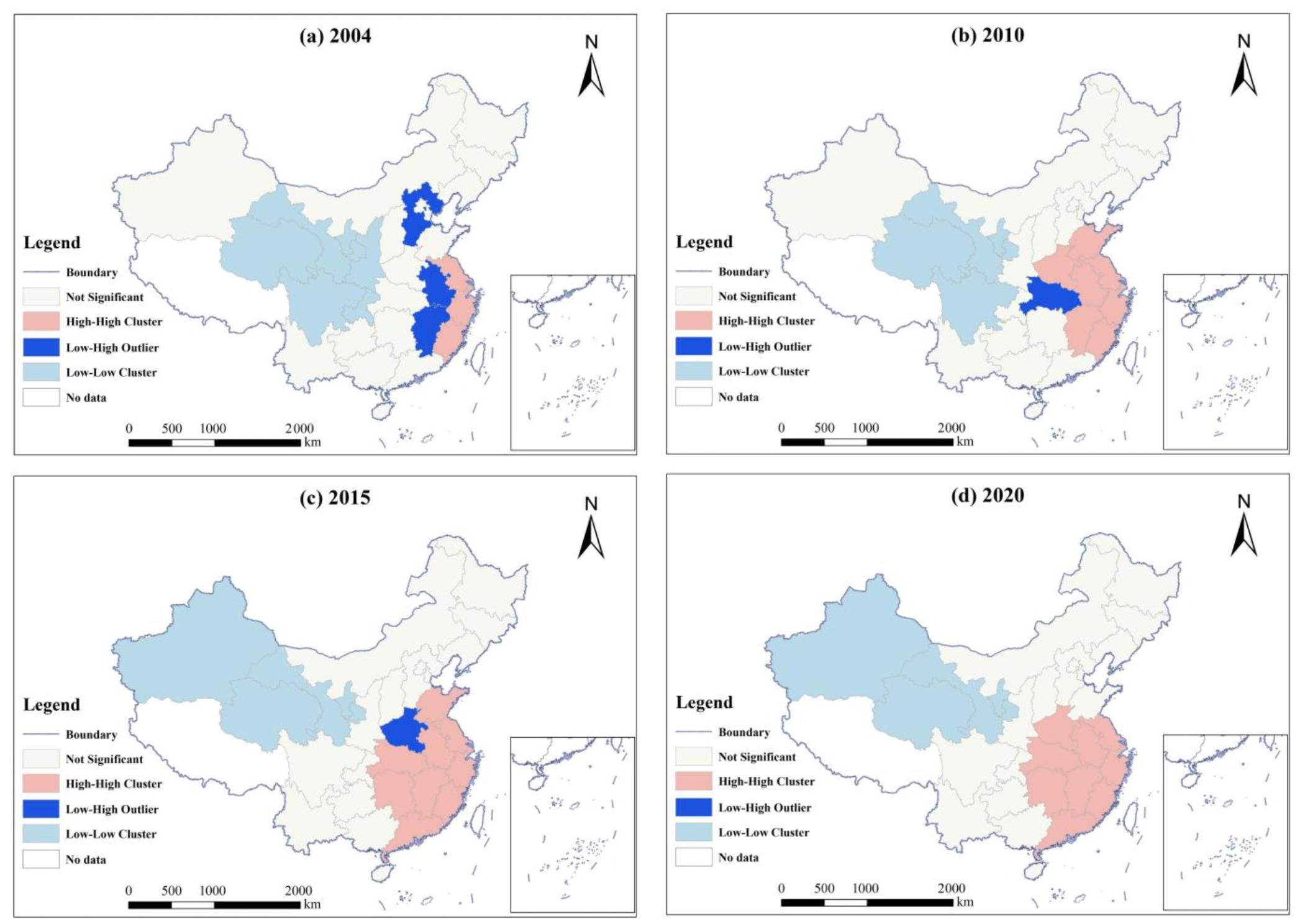
3.3. Spatial Correlation of Coordinated Development between UEFS
3.4. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Coordinated Development between UEFS
3.5. Diagnosis of Factors Influencing the Coordinated Development between UEFS
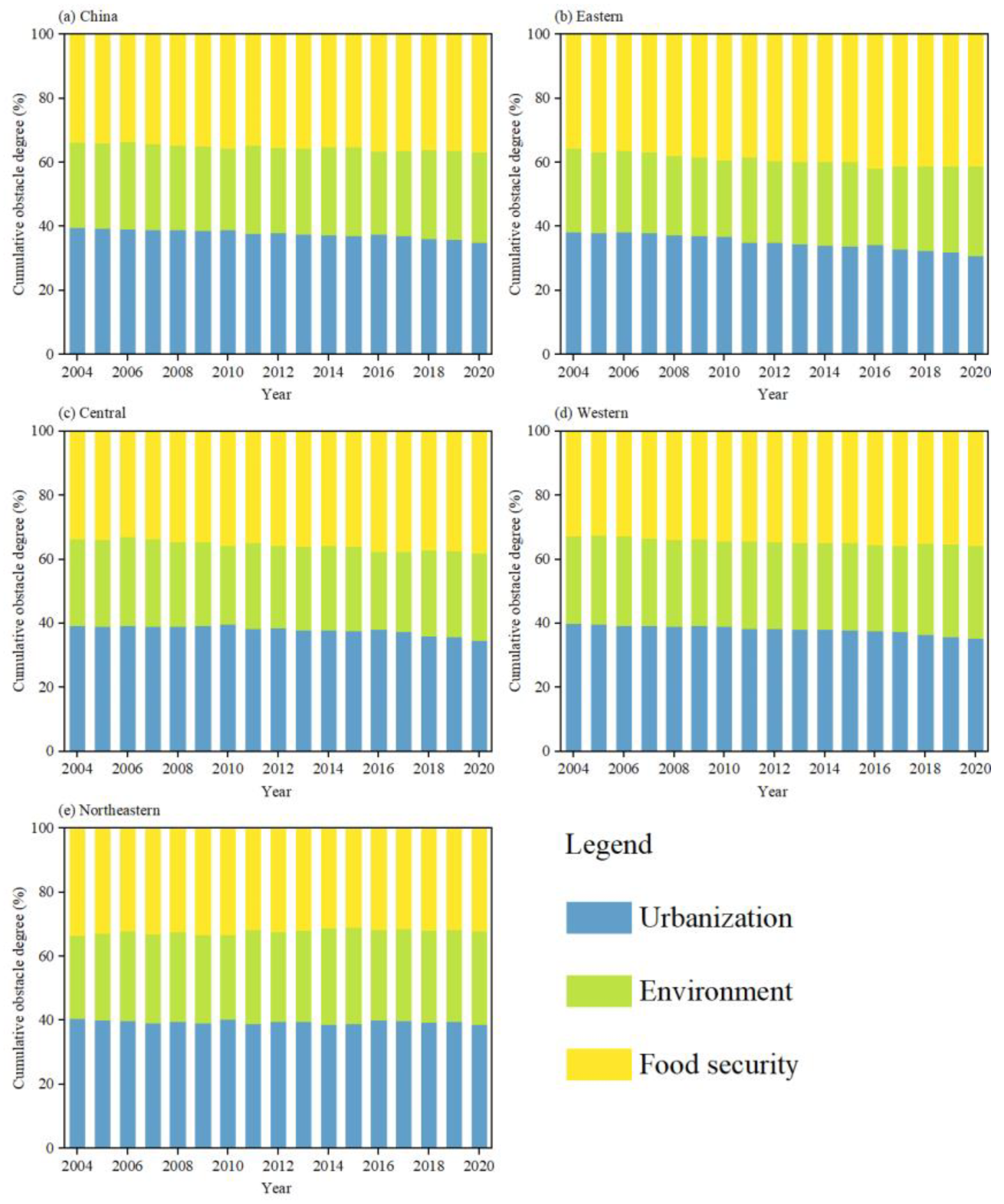
3.5.1. Obstacle Degree in System Layer
3.5.2. Obstacle Degree in Subsystem Layer
3.5.3. Obstacle Degree in Indicator Layer
4. Discussion
4.1. Coordinated Development between UEFS in Different Regions
4.2. Key Factors Influencing the Coordinated Development between UEFS
4.3. Policy Implications
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, X.; Wei, H.; Lu, S.; Dai, Q.; Su, H. Assessment on the urbanization strategy in China: Achievements, challenges and reflections. Habitat Int. 2018, 71, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, Q.; Cao, S. Real estate supports rapid development of China’s urbanization. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Pisani, J.A. Sustainable development–historical roots of the concept. Environ. Sci. 2006, 3, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Pickett, S.T.; Yu, W.; Li, W. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Song, M.; Zhang, A. Dynamics of the eco-environmental quality in response to land use changes in rapidly urbanizing areas: A case study of Wuhan, China from 2000 to 2018. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliot, S.; Sumner, D.A. Traceability, liability, and incentives for food safety and quality. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 90, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Cobbinah, P.B. Can rapid urbanization be sustainable? The case of Saudi Arabian cities. Habitat Int. 2023, 139, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Urbanization can benefit agricultural production with large-scale farming in China. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, B. Conserving habitat and ecosystem in protected areas amid increasing intensive human modification: A case study of China’s Pan-Pearl River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Si, J.; Deng, Y.; Jia, B.; Li, X.; He, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Qin, J.; et al. Assessment of Land Desertification and Its Drivers in Semi-Arid Alpine Mountains: A Case Study of the Qilian Mountains Region, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, G.; LaFleur, W. Ways of (un) knowing landscapes: Tracing more-than-human relations in regenerative agriculture. J. Rural. Stud. 2023, 101, 103059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.; Huusela, E.; Hyvönen, T.; Marjamäki, P.; Järvinen, A.; Kuussaari, M. Effects of crop type and production method on arable biodiversity in boreal farmland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerer, K.S.; Olivencia, Y.J.; Rodríguez, L.P.; López-Estébanez, N.; Álvarez, F.A.; Olmo, R.M.; Ochoa, C.Y.; Pulpón, Á.R.R.; García, Ó.J. Assessing social-ecological connectivity of agricultural landscapes in Spain: Resilience implications amid agricultural intensification trends and urbanization. Agric. Syst. 2022, 203, 103525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Y. Influence of urban scale and urban expansion on the urban heat island effect in metropolitan areas: Case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Fang, C.L. Water resources flows related to urbanization in China: Challenges and perspectives for water management and urban development. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Hanjra, M.A.; Mu, J. Water management and crop production for food security in China: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemessa, F.; Simane, B.; Seyoum, A.; Gebresenbet, G. Assessment of the Impact of Industrial Wastewater on the Water Quality of Rivers around the Bole Lemi Industrial Park (BLIP), Ethiopia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grennfelt, P.; Engleryd, A.; Forsius, M.; Hov, Ø.; Rodhe, H.; Cowling, E. Acid rain and air pollution: 50 years of progress in environmental science and policy. Ambio 2020, 49, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zheng, X.; Hou, L.; Xiao, N.; Deng, X. Changes in China’s food security driven by nutrition security and resource constraints. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Griggs, D.; Visbeck, M. Policy: Map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature 2016, 534, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, C.; Wu, F. Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of sustainable land use in China: Based on sustainable development goals framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Wen, Z.G. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, H.M.; Remais, J.; Fung, M.C.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.S.M. Food supply and food safety issues in China. Lancet 2013, 381, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K.; Isik, C. Determinants of the load capacity factor in China: A novel dynamic ARDL approach for ecological footprint accounting. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Hu, R.; Vatn, A. What does sustainability demand? An institutionalist analysis with applications to China. J. Chin. Gov. 2021, 6, 486–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.L.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.H.; Peng, S.S.; Li, J.S.; Zhou, L.P.; Liu, H.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Ding, Y.H.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J. Coupling Coordination between Marine S&T Innovation and the High-Quality Development of the Marine Economy: A Case Study of China’s Coastal Provinces. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7373. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y. The coordinated relationship among industrialization, environmental carrying capacity and green infrastructure: A comparative research of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Environ. Dev. 2022, 44, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Da, B. Examining the coordination between urbanization and eco-environment using coupling and spatial analyses: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, S. Coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and agro-ecological environment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Assessment of coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment: Case study of resource-based cities in Northeastern China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Reflections on China’s food security and land use policy under rapid urbanization. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Wu, S.; He, C.; Yan, D. Study on the coordinated development of economy, environment and resource in coal-based areas in Shanxi Province in China: Based on the multi-objective optimization model. Resour. Policy 2018, 55, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.; Hu, M. Dynamic simulation and assessment of the coupling coordination degree of the economy–resource–environment system: Case of Wuhan City in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, P. Assessment of city sustainability—Coupling coordinated development between economy, society and environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hu, W.Q. A research on coordination between economy, society and environment in China: A case study of Jiangsu. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, K.; Yi, T. Spatial-temporal differentiation of the coupling coordinated development of regional energy-economy-ecology system: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, E.M.; Bruce, E.; Boruff, B.; Duncan, J.M.; Horsley, J.; Pauli, N.; McNeill, K.; Neef, A.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Curnow, J.; et al. Sustainable development and the water–energy–food nexus: A perspective on livelihoods. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.Y.; Liang, Q.M. Sustainability evaluation of the provincial water-energy-food nexus in China: Evolutions, obstacles, and response strategies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahtebay, J.; Zhang, F.; Ariken, M.; Chan, N.W.; Tan, M.L. Evaluation of the coordinated development of urbanization-resources-environment from the incremental perspective of Xinjiang, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 325, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Assessing sustainability of urbanization by a coordinated development index for an Urbanization-Resources-Environment complex system: A case study of Jing-Jin-Ji region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Xu, W.; Gu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ren, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y. A new framework of land use efficiency for the coordination among food, economy and ecology in regional development. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Longwu, L.; Zhenbo, W.; Liangkan, C.; Faming, Z. Exploration of coupling effects in the Economy–Society–Environment system in urban areas: Case study of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Sarker MN, I.; Lv, Y. Coupling coordination of the regional economy, tourism industry, and the ecological environment: Evidence from western China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lu, D.; Zhang, H. Comprehensive evaluation and the driving factors of China’s urbanization. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Lu, D.; Zha, L. The comprehensive evaluation of China’s urbanization and effects on resources and environment. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatio-temporal investigation of the interactive relationship between urbanization and eco-system services: Case study of the Jingjinji urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Examining the influences of urbanization on carbon dioxide emissions in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Kuznets curve relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Wei, X.; Zhang, F. Exploring the coupling relationship between urbanization and energy eco-efficiency: A case study of 281 prefecture-level cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal variation of the coupling relationship between urbanization and air quality: A case study of Shandong Province. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Li, R.D.; Song, X.F. Analysis of coupling degrees of urbanization and ecological environment in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 20, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini, F.; Massetti, L.; Pearlmutter, D.; Sanesi, G. Usage of urban green space and related feelings of deprivation during the COVID-19 lockdown: Lessons learned from an Italian case study. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Guo, P.; Zeng, Y. Wetland ecosystem health assessment through integrating remote sensing and inventory data with an assessment model for the Hangzhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, L.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal differentiation and the factors influencing urbanization and ecological environment synergistic effects within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Gajanan, S.; Sanyal, P. Food Security, Poverty and Nutrition Policy Analysis: Statistical Methods and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, C.; Teng, Y.; Huang, L. Evaluation index system construction and empirical analysis on food security in China. Trans-Actions Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Clapp, J.; Moseley, W.G.; Burlingame, B.; Termine, P. The case for a six-dimensional food security framework. Food Policy 2021, 106, 102164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Yu, Z.; Zou, N. The empirical study on the spatial coupling of ecology and food security in major grain-producing areas in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2020, 41, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, C.B. Measuring food insecurity. Science 2010, 327, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongley, E.D.; Xiaolan, Z.; Tao, Y. Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source pollution assessment in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wei, Z. Selection of Agricultural Machinery Based on Improved CRITIC-Entropy Weight and GRA-TOPSIS Method. Processes 2022, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Lu, D. Evaluation of Urban Resilience Based on Trio Spaces: An Empirical Study in Northeast China. Buildings 2023, 13, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, J.; Li, Z.; Ming, L.; Li, C.; Li, C. Coupling Coordination and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Urban Compactness and Land-Use Efficiency in Resource-Based Areas: A Case Study of Shanxi Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Liang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, C. A systematic method for assessing progress of achieving sustainable development goals: A case study of 15 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, L. Spatial Agglomeration and Coupling Coordination of Population, Economics, and Construction Land in Chinese Prefecture-Level Cities from 2010 to 2020. Land 2023, 12, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Jin, J.; Zhou, R.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y. Coordination evaluation and obstacle factors recognition analysis of water resource spatial equilibrium system. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, L.; Chang, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, C. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Ecosystem Services Supply-Demand and Influencing Factors: A Case Study of Resource-Based Cities in the Yellow River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagum, C. A new approach to the decomposition of the Gini income inequality ratio. In Income Inequality, Poverty, and Economic Welfare; Physica-Verlag HD: Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Li, C.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y. Fuzzy Assessment of Ecological Security on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Based on Pressure–State–Response Framework. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Chi, W.; Zhang, C. The rapid and massive urban and industrial land expansions in China be-tween 1990 and 2010: A CLUD-based analysis of their trajectories, patterns, and drivers. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 145, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.Q.; Mongol, N.; Zhang, F.S. The transformation of agriculture in China: Looking back and looking forward. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Afshan, S.; Irfan, M. Can renewable energy technology innovation promote mineral resources’ green utilization efficiency? Novel insights from regional development inequality. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, W.U.H.; Lu, Y.; Hao, G.; Yan, H.; Yasmeen, R. Impact of “Three Red Lines” Water Policy (2011) on Water Usage Efficiency, Production Technology Heterogeneity, and Determinant of Water Productivity Change in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Wei, X.; Gong, X.; Zhang, S. Internet use and the satisfaction with governmental environmental protection: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yin, S. Quantitative Assessment of Climate Change Impact and Anthropogenic Influence on Crop Production and Food Security in Shandong, Eastern China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Song, G.; Wang, Q.; Sui, H. Impact of “Non-Grain” in Cultivated Land on Agricultural Development Resilience: A Case Study from the Major Grain-Producing Area of Northeast China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, T.; Long, F. High-speed rail, new town development, and the spatial mismatch of land leases in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Long, Y.; Sun, W.; Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, J. Evaluating cities’ vitality and identifying ghost cities in China with emerging geographical data. Cities 2017, 63, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xin, Y. Exploring the characteristics and driving factors of coupling coordination of regional sustainable development: Evidence from China’s 31 provinces. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71075–71099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Lai, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X. A study on the path of improving the performance of China’s provincial circular economy—An empirical study based on the fsQCA method. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wan, X.; Jahanger, A.; Li, M.; Murshed, M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Does the digital economy reduce air pollution in China? A perspective from industrial agglomeration. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 3625–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Hu, S.; Tong, L.; Xia, C.; Ran, P. Dynamics and Determinants of the Grain Yield Gap in Major Grain-Producing Areas: A Case Study in Hunan Province, China. Foods 2022, 11, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, R.; Singh, V.P.; Xu, C.-Y.; Fan, K.; Shen, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J. Dynamic vulnerability of ecological systems to climate changes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, Q.; Lan, X.; Fang, L.; Wen, C. Assessing China’s development zones and carbon emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 99298–99309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Y. Experiences and lessons from Agri-Food system transformation for sustainable food security: A review of China’s practices. Foods 2022, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fang, C.; Zhang, L. Analysis of the coupling coordinated development of the Population–Water–Ecology–Economy system in urban agglomerations and obstacle factors discrimination: A case study of the Tianshan North Slope Urban Ag-glomeration, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 90, 104359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, C.; Luo, M.; Zhou, S.; Liu, C. An investigation of the coupling coordination of a regional agricultural eco-nomics-ecology-society composite based on a data-driven approach. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, Q.; Khan, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Urban water resource management for sustainable environment planning using artificial intelligence techniques. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cao, X.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Li, T.; Shang, R. Sustainable management of agricultural water and land resources under changing climate and socio-economic conditions: A multi-dimensional optimization approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Miao, X.; Afshan, S. Dynamic effects of natural resource abundance, green financing, and government environmental concerns toward the sustainable environment in China. Resour. Policy 2022, 79, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zheng, C. The distribution characteristics and driving mechanism of vacant land in Chengdu, China: A perspective of urban shrinkage and expansion. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Meng, F.; Prishchepov, A.V. How is urbanization shaping agricultural land-use? Unraveling the nexus between farmland abandonment and urbanization in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 214, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Long, H.; Tang, L.; Tu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y. Analysis of the spatial variations of determinants of agricultural production efficiency in China. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ren, Z.; Qiao, G. How Does Agricultural Trade Liberalization Have Environmental Impacts? Evidence from a Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, R. Does urbanization redefine the environmental Kuznets curve? An empirical analysis of 134 Countries. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| System | Subsystem | Indicator | Entropy | CRITIC | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization | Demographic | U1: Proportion of urban population (%) | 0.0552 | 0.0654 | 0.0603 |
| U2: Urban population density (person/km2) | 0.1588 | 0.092 | 0.1254 | ||
| U3: Proportion of employees in the secondary and tertiary industries (%) | 0.0322 | 0.063 | 0.0476 | ||
| Economic | U4: GDP per capita (CNY 10,000) | 0.1128 | 0.0622 | 0.0875 | |
| U5: Proportion of the output value from the secondary and tertiary industries to GDP (%) | 0.0159 | 0.0287 | 0.0223 | ||
| U6: Per capita disposable income of urban residents (CNY 10,000) | 0.12 | 0.0677 | 0.0939 | ||
| Land use | U7: Output value per unit of built-up area (CNY 100 million/km2) | 0.1427 | 0.1522 | 0.1475 | |
| U8: Per capita urban road (m2) | 0.0527 | 0.0615 | 0.0571 | ||
| U9: Proportion of built-up area to urban area (%) | 0.0754 | 0.0758 | 0.0756 | ||
| Social | U10: Number of beds in medical institutions per 10,000 people | 0.1169 | 0.075 | 0.096 | |
| U11: Number of students in institutions of higher learning per 10,000 people | 0.071 | 0.1048 | 0.0879 | ||
| U12: Per capita park area (m2) | 0.0465 | 0.1516 | 0.0991 | ||
| Environment | Pressure | E1: Total sulfur dioxide emissions (10,000 tons) | 0.0458 | 0.0826 | 0.0642 |
| E2: Total emissions of solid particulate matter (10,000 tons) | 0.0315 | 0.0675 | 0.0495 | ||
| E3: Industrial solid waste generation (10,000 tons) | 0.0213 | 0.0702 | 0.0457 | ||
| E4: Total chemical oxygen demand (10,000 tons) | 0.0369 | 0.0962 | 0.0665 | ||
| E5: Electricity consumption per unit of GDP (CNY 10,000/kwh) | 0.0261 | 0.0712 | 0.0487 | ||
| State | E6: Forest coverage (%) | 0.1822 | 0.1056 | 0.1439 | |
| E7: Proportion of desertification land area (%) | 0.0469 | 0.0892 | 0.068 | ||
| E8: Water resources endowment (10,000 m3/km2) | 0.3022 | 0.0745 | 0.1883 | ||
| E9: Green coverage in built-up area (%) | 0.0313 | 0.0623 | 0.0468 | ||
| Response | E10: Ratio of investment in environmental pollution control to GDP (%) | 0.1446 | 0.0894 | 0.117 | |
| E11: Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste (%) | 0.0796 | 0.0945 | 0.087 | ||
| E12: Proportion of household garbage harmless treatment (%) | 0.0516 | 0.0969 | 0.0743 | ||
| Food security | Factors of production | F1: Per capita cultivated area (hectare) | 0.1477 | 0.0606 | 0.1042 |
| F2: Labor input in agricultural production (person/hectare) | 0.072 | 0.094 | 0.083 | ||
| F3: Agricultural machinery input (kw/hectare) | 0.0954 | 0.0921 | 0.0938 | ||
| F4: Water consumption per unit area (m3/hectare) | 0.1365 | 0.0805 | 0.1085 | ||
| Availability and stability | F5: Per capita sown area of grain crops (hectare) | 0.1276 | 0.051 | 0.0893 | |
| F6: Proportion of the area of crops affected by disasters (%) | 0.0136 | 0.0644 | 0.039 | ||
| F7: Per unit area yield of grain (kg) | 0.0591 | 0.0741 | 0.0666 | ||
| F8: Per capita grain output (kg) | 0.1283 | 0.0478 | 0.0881 | ||
| Access | F9: Density of regional road network (km/km2) | 0.0946 | 0.0928 | 0.0937 | |
| F10: Engel coefficient of urban resident | 0.0349 | 0.0603 | 0.0476 | ||
| F11: Engel coefficient of rural resident | 0.0338 | 0.0698 | 0.0518 | ||
| Sustainability | F12: Intensity of fertilizer application (kg/hectare) | 0.0242 | 0.0762 | 0.0502 | |
| F13: Intensity of pesticide used (kg/hectare) | 0.0193 | 0.0727 | 0.046 | ||
| F14: Intensity of agricultural plastic film used (kg/hectare) | 0.013 | 0.0637 | 0.0384 |
| Stages | CCD Range | Coupling Coordination Types |
|---|---|---|
| Uncoordinated stage | (0.00, 0.10) | C1, extreme incoordination |
| (0.10, 0.20) | C2, severe incoordination | |
| (0.20, 0.30) | C3, moderate incoordination | |
| (0.30, 0.40) | C4, slight incoordination | |
| Transitional stage | (0.40, 0.50) | C5, approaching incoordination |
| (0.50, 0.60) | C6, slight coordination | |
| Highly coordinated stage | (0.60, 0.70) | C7, primary coupling coordination |
| (0.70, 0.80) | C8, moderate coupling coordination | |
| (0.80, 0.90) | C9, good coupling coordination | |
| (0.90, 1.00) | C10, superior coupling coordination |
| Year | Moran’s I | p-Value | Z-Score | Year | Moran’s I | p-Value | Z-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 0.2364 | 0.001 | 3.2729 | 2013 | 0.4094 | 0.001 | 5.3681 |
| 2005 | 0.2614 | 0.001 | 3.5709 | 2014 | 0.3999 | 0.001 | 5.2642 |
| 2006 | 0.3165 | 0.001 | 4.2401 | 2015 | 0.4483 | 0.001 | 5.8619 |
| 2007 | 0.324 | 0.001 | 4.3317 | 2016 | 0.4737 | 0.001 | 6.1753 |
| 2008 | 0.3706 | 0.001 | 4.8964 | 2017 | 0.462 | 0.001 | 6.0112 |
| 2009 | 0.376 | 0.001 | 4.9582 | 2018 | 0.4598 | 0.001 | 5.9689 |
| 2010 | 0.4213 | 0.001 | 5.5103 | 2019 | 0.4492 | 0.001 | 5.831 |
| 2011 | 0.3737 | 0.001 | 4.9279 | 2020 | 0.4595 | 0.001 | 5.9714 |
| 2012 | 0.4279 | 0.001 | 5.571 |
| Year | G | Intra-Regional Gini Coefficient | Inter-Regional Gini Coefficient | Contribution Rate (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Central | West | Northeast | East-Central | East-West | East-Northeast | Central-West | Central-Northeast | West-Northeast | Gw | Gnb | Gt | ||
| 2004 | 0.040 | 0.029 | 0.017 | 0.021 | 0.004 | 0.050 | 0.068 | 0.041 | 0.026 | 0.014 | 0.030 | 17.1 | 77.9 | 5.0 |
| 2005 | 0.041 | 0.030 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.003 | 0.049 | 0.069 | 0.041 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.030 | 17.5 | 76.8 | 5.7 |
| 2006 | 0.041 | 0.028 | 0.019 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.044 | 0.070 | 0.044 | 0.034 | 0.015 | 0.028 | 17.4 | 77.5 | 5.1 |
| 2007 | 0.039 | 0.025 | 0.017 | 0.026 | 0.003 | 0.040 | 0.064 | 0.046 | 0.033 | 0.019 | 0.022 | 18.2 | 75.7 | 6.1 |
| 2008 | 0.037 | 0.024 | 0.017 | 0.028 | 0.004 | 0.037 | 0.062 | 0.038 | 0.034 | 0.015 | 0.028 | 19.1 | 74.6 | 6.3 |
| 2009 | 0.037 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.033 | 0.058 | 0.043 | 0.035 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 19.6 | 72.8 | 7.6 |
| 2010 | 0.036 | 0.022 | 0.018 | 0.029 | 0.008 | 0.031 | 0.058 | 0.035 | 0.037 | 0.017 | 0.028 | 19.7 | 73.8 | 6.4 |
| 2011 | 0.033 | 0.020 | 0.018 | 0.03 | 0.005 | 0.028 | 0.051 | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.018 | 0.025 | 21.0 | 68.8 | 10.2 |
| 2012 | 0.032 | 0.022 | 0.020 | 0.027 | 0.005 | 0.027 | 0.050 | 0.033 | 0.034 | 0.018 | 0.024 | 21.2 | 68.2 | 10.6 |
| 2013 | 0.029 | 0.021 | 0.014 | 0.025 | 0.007 | 0.026 | 0.046 | 0.030 | 0.029 | 0.013 | 0.023 | 21.4 | 67.7 | 10.9 |
| 2014 | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.016 | 0.025 | 0.013 | 0.027 | 0.045 | 0.038 | 0.030 | 0.022 | 0.021 | 22.4 | 62.5 | 15.1 |
| 2015 | 0.032 | 0.026 | 0.020 | 0.026 | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.046 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.024 | 0.022 | 22.9 | 62.3 | 14.8 |
| 2016 | 0.031 | 0.024 | 0.016 | 0.025 | 0.007 | 0.025 | 0.046 | 0.031 | 0.034 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 21.9 | 67.1 | 10.9 |
| 2017 | 0.030 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.025 | 0.006 | 0.024 | 0.044 | 0.032 | 0.035 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 21.5 | 66.2 | 12.3 |
| 2018 | 0.031 | 0.022 | 0.019 | 0.027 | 0.008 | 0.025 | 0.045 | 0.031 | 0.037 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 21.8 | 65.1 | 13.1 |
| 2019 | 0.032 | 0.024 | 0.022 | 0.026 | 0.009 | 0.027 | 0.046 | 0.031 | 0.037 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 22.2 | 63.4 | 14.3 |
| 2020 | 0.031 | 0.023 | 0.020 | 0.027 | 0.009 | 0.025 | 0.043 | 0.031 | 0.036 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 22.8 | 61.6 | 15.6 |
| Region | Year | Obstacle Factors and the Order of Obstacle Degree | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization | Environment | Food security | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| China | 2004 | U7(14.67%) | U2(12.59%) | U12(9.77%) | E8(30.42%) | E10(17.52%) | E6(14.92%) | F1(12.49%) | F4(12.38%) | F9(11.91%) |
| 2020 | U7(14.53%) | U2(12.8%) | U12(9.64%) | E8(31.69%) | E10(24.98%) | E6(15.43%) | F4(16.49%) | F1(13.30%) | F5(11.51%) | |
| Eastern | 2004 | U7(14.62%) | U2(12.51%) | U12(9.76%) | E8(33.09%) | E10(20.48%) | E6(16.60%) | F1(14.93%) | F5(12.79%) | F8(12.65%) |
| 2020 | U7(14.36%) | U2(12.7%) | U12(9.75%) | E8(33.9%) | E10(28.89%) | E6(16.98%) | F1(17.17%) | F4(15.10%) | F5(14.44%) | |
| Central | 2004 | U7(14.65%) | U2(12.55%) | U12(9.79%) | E8(26.62%) | E10(19.00%) | E6(14.17%) | F4(14.06%) | F1(13.36%) | F9(11.38%) |
| 2020 | U7(14.5%) | U2(12.77%) | U12(9.67%) | E8(27.28%) | E10(25.59%) | E6(15.76%) | F4(17.11%) | F1(15.91%) | F5(12.68%) | |
| Western | 2004 | U7(14.63%) | U2(12.63%) | U12(9.77%) | E8(27.83%) | E6(16.15%) | E10(15.14%) | F9(12.97%) | F3(12.65%) | F1(11.57%) |
| 2020 | U7(14.56%) | U2(12.87%) | U10(9.61%) | E8(31.05%) | E10(21.81%) | E6(16.26%) | F4(14.41%) | F1(12.66%) | F5(12.00%) | |
| Northeastern | 2004 | U7(14.77%) | U2(12.65%) | U12(9.76%) | E8(34.13%) | E10(15.47%) | E6(12.74%) | F3(13.71%) | F4(13.67%) | F9(13.03%) |
| 2020 | U7(14.72%) | U2(12.87%) | U12(9.61%) | E8(34.51%) | E10(23.63%) | E6(12.71%) | F4(19.34%) | F2(15.67%) | F3(15.56%) | |
| Region | Year | Obstacle Factors and the Order of Obstacle Degree | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| China | 2004 | E8(8.11%) | U7(5.78%) | U2(4.96%) | E10(4.67%) | F1(4.24%) | F4(4.21%) | F9(4.05%) | E6(3.98%) | U12(3.85%) |
| 2020 | E8(8.88%) | E10(7.01%) | F4(6.25%) | F1(5.04%) | U7(4.95%) | F5(4.36%) | U2(4.36%) | E6(4.33%) | F3(4.29%) | |
| Eastern | 2004 | E8(8.56%) | U7(5.60%) | F1(5.35%) | E10(5.30%) | U2(4.80%) | F5(4.58%) | F8(4.53%) | E6(4.30%) | F4(4.00%) |
| 2020 | E8(9.43%) | E10(8.04%) | F1(7.13%) | F4(6.27%) | F5(6.00%) | F8(5.80%) | E6(4.73%) | U7(4.39%) | U2(3.89%) | |
| Central | 2004 | E8(7.18%) | U7(5.78%) | E10(5.12%) | U2(4.95%) | F4(4.73%) | F1(4.49%) | U12(3.86%) | F9(3.82%) | E6(3.82%) |
| 2020 | E8(7.37%) | E10(6.91%) | F4(6.53%) | F1(6.07%) | U7(5.04%) | F5(4.84%) | F8(4.64%) | U2(4.44%) | E6(4.26%) | |
| Western | 2004 | E8(7.61%) | U7(5.85%) | U2(5.05%) | E6(4.42%) | F9(4.23%) | E10(4.14%) | F3(4.13%) | U12(3.91%) | U10(3.85%) |
| 2020 | E8(8.86%) | E10(6.22%) | F4(5.20%) | U7(5.16%) | E6(4.64%) | U2(4.56%) | F1(4.56%) | F5(4.32%) | F8(4.27%) | |
| Northeastern | 2004 | E8(8.88%) | U7(5.99%) | U2(5.13%) | F3(4.58%) | F4(4.56%) | F9(4.35%) | E10(4.02%) | U12(3.96%) | U10(3.89%) |
| 2020 | E8(10.03%) | U10(6.87%) | F4(6.21%) | U7(5.72%) | F3(5.03%) | U2(5.00%) | F2(4.99%) | F9(4.48%) | U12(3.73%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Dai, X.; Sun, W.; Tang, H. Towards Sustainable Development Goals: Coupling Coordination Analysis and Spatial Heterogeneity between Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security in China. Land 2023, 12, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112002
Yin Q, Chen L, Li J, Wang Q, Dai X, Sun W, Tang H. Towards Sustainable Development Goals: Coupling Coordination Analysis and Spatial Heterogeneity between Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security in China. Land. 2023; 12(11):2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112002
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Qi, Liangzhao Chen, Jinhua Li, Qilong Wang, Xiaowen Dai, Wei Sun, and Hong Tang. 2023. "Towards Sustainable Development Goals: Coupling Coordination Analysis and Spatial Heterogeneity between Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security in China" Land 12, no. 11: 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112002
APA StyleYin, Q., Chen, L., Li, J., Wang, Q., Dai, X., Sun, W., & Tang, H. (2023). Towards Sustainable Development Goals: Coupling Coordination Analysis and Spatial Heterogeneity between Urbanization, the Environment, and Food Security in China. Land, 12(11), 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12112002






