Assessing the Impact of Government Behavior on Regional High-Quality Development: A Case of Fiscal Expenditures on People’s Livelihoods in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
3. Research Design
3.1. Regression Model
3.2. Variable Description
3.2.1. Indicators of the Regional High-Quality Development Level
3.2.2. The Level of Government Expenditure on People’s Livelihood
3.2.3. Indicators for Measuring Urbanization Level
3.2.4. Description of Control Variables
3.3. Data Sources
4. Regression Analysis
4.1. Evaluation of Indicator Measurements

4.2. Baseline Regression Analysis
4.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.4. Analysis of the Mediating Effect
4.5. Analysis of the Moderating Effect
5. Conclusions and Implications
6. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The specific method is given by the following formula: |
| 2 | http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/download.html?searchText=GS(2019)1822 (accessed on 1 September 2023). |
References
- Cheng, C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Ebrahimi, O.V. Adjustment to a “New Normal”: Coping Flexibility and Mental Health Issues during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Qiu, R.; Tu, Y. Pulling Off Stable Economic System Adhering Carbon Emissions, Urban Development and high-quality development Values. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 814656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, R.D.; Wu, J.J. The 2017 state new economy index. SSRN Electron. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolcárová, P.; Kološta, S. Assessment of sustainable development in the EU 27 using aggregated SD index. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, B.; Rodenhäuser, D.; Diefenbacher, H.; Zieschank, R. The national and regional welfare index (nwi/rwi): redefining progress in Germany. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 145, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, J. Study on the “High-Quality Development” Economics. China Ind. Econ. 2018, 4, 5–18. Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/CPE-10-2018-016/full/html?utm_source=TrendMD&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=China_Political_Economy_TrendMD_1 (accessed on 1 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Mlachila, M.; Tapsoba, R.; Tapsoba, S.J.A. A Quality of Growth Index for Developing Countries: A Proposal. Soc. Indic. Res. 2017, 134, 675–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, H.; Derbali, A. Quality of human capital accumulation, higher education graduates and economic growth: A comparative analysis between BRICS, Southeast Asian and MENA countries. Hum. Syst. Manag. 2020, 40, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J. Economic Growth Effect of Public Health Investment and Its Impact on Living Environment. J. Environ. Public Health 2022, 2022, 2192255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingkai, Z.; Xinlan, C.; Guangming, Y. Coupling coordination degree and influencing factors of green science and technology innovation efficiency and digital economy level: Evidence from provincial panel data in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wang, D.; Van Assche, A.; Du, J. Do capital goods imports improve the quality of regional development? Evidence from Chinese cities. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, C.; Feng, Y.; Hu, F. Impact of the digital economy on high-quality urban economic development: Evidence from Chinese cities. Econ. Model. 2023, 120, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Ding, L. Does marine financial policy affect total factor productivity of marine enterprises? An empirical evidence based on Chinese first guidance on strengthening finance for marine economy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xie, D.; Muhammad, A.; Isik, C. The construction of green finance and high-quality economic development under China’s SDGs target. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, E.; Liao, H. Does fiscal decentralization affect regional high-quality development by changing peoples’ livelihood expenditure preferences: Provincial evidence from China. Land 2022, 11, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y. Analysis of the synergistic impacts of public services expenditure on economic growth and social equity. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Management Science & Engineering 19th Annual Conference Proceedings, Dallas, TX, USA, 20–22 September 2012; pp. 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterly, W.; Rebelo, S. Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth: An Empirical Investigation. J. Monetary Econ. 1993, 32, 417–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C. IS There a Trade-Off between Employment and Growth? Oxf. Econ. Pap. 1997, 49, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellettini, G.; Ceroni, C.B. Social security expenditure and economic growth: An empirical assessment. Res. Econ. 2000, 54, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Roy, U. Fiscal policy, long-run growth, and welfare in a stock-flow model of public goods. Can. J. Econ./Rev. Can. Déconomique 2004, 37, 742–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosi, S.; Laurent, T. Health, growth and welfare: A theoretical appraisal of the long-run impact of medical R&D. Asia-Pacific J. Account. Econ. 2011, 18, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Railaite, R.; Čiutienė, R. The Impact of Public Health Expenditure on Health Component of Human Capital. Eng. Econ. 2020, 31, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. The Role of Public Services in China’s Economic Growth: Based on Population Structure and Population Aggregation. Popul. Res. 2020, 44, 92–107. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2020&filename=RKYZ202005007&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=5iSLgmb6sLgl6EkycTE5UZlYR2Gc-54CifEIFOxat3FEMEyAXvIBcOGpPTrj7nEX (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Musgrave, R.A. The Theory of Public Finance; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modigliani, F.; Cao, S.L. The Chinese Saving Puzzle and the Life-Cycle Hypothesis. J. Econ. Lit. 2004, 42, 145–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.-C.; Laffargue, J.-P.; Yu, E. The Chinese saving puzzle and the life-cycle hypothesis: A revaluation. China Econ. Rev. 2011, 22, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Cao, S. Marx’s theory of urban and rural development and its enlightenment to new urbanization strategy. Theor. Platf. Tibet. Dev. 2022, 3, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, E. The Complete Works of Marx and Engels, Volume 46; People’s Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 1979; p. 480. [Google Scholar]
- Kassiola, J.J. Coordinated Rural-Urban Development in China: A New Social Spatial Reorganization Plan for Urbanization, Migration, and Rural Development. J. Chin. Politics Sci. 2017, 22, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiuškaitė, D.; Pilinkienė, V.; Žvirdauskas, D. The Conceptualization of the Sharing Economy as a Business Model. Eng. Econ. 2019, 30, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Nguyen, L.D. The relationship between urbanization and economic growth. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 2018, 45, 316–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinelli, L.; Black, D. Urbanization and growth. J. Urban Econ. 2004, 56, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Energy and carbon intensity in China during the urbanization and industrialization process: A panel VAR approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirtas, T.; Akpolat, A.G. The relationship between energy consumption, urbanization, and economic growth in new emerging-market countries. Energy 2018, 147, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, T.-D. The impact of economic growth, industrial structure and urbanization on carbon emission intensity in China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.L.; Li, X.S. Tobit model estimation method and application. Econ. Perspect. 2012, 615, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The Moderator–mediator Variable Distinction in Social Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, and Statistical Considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Chang, L.; Hau, K.T.; Liu, H. Testing and application of the mediating effects. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2004, 5, 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, Y.; Liu, P.; He, J.; Zhuo, X. The Target Requirement and Strategic Path of High Quality Development. Manag. World 2019, 35, 1–7. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2019&filename=GLSJ201907003&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=tI3YudqOkuK3SuOTUvsMh1sPa8aTSsGIf1eIxkOC5L6Fgp0f3gytenlbQuF9okyZ (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Ding, L.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Wu, D. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Urban high quality Development in China Based on the Topsis-Entropy Method. Sustainability 2016, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Jia, S.; Liao, J.; Yang, X. Evaluation of Urban High-quality Development Level based on Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Two-step Method. J. Econ. Anal. 2022, 1, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

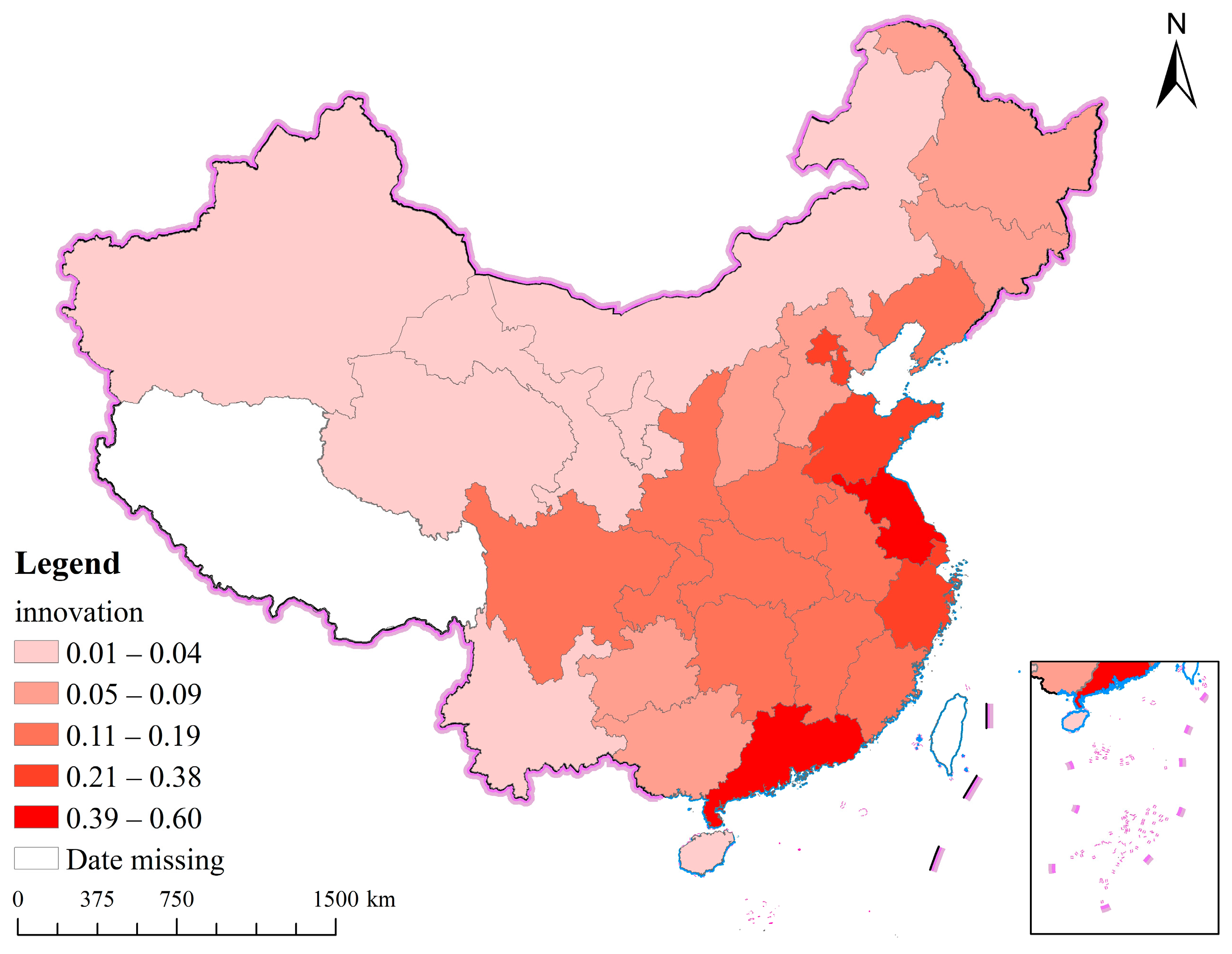
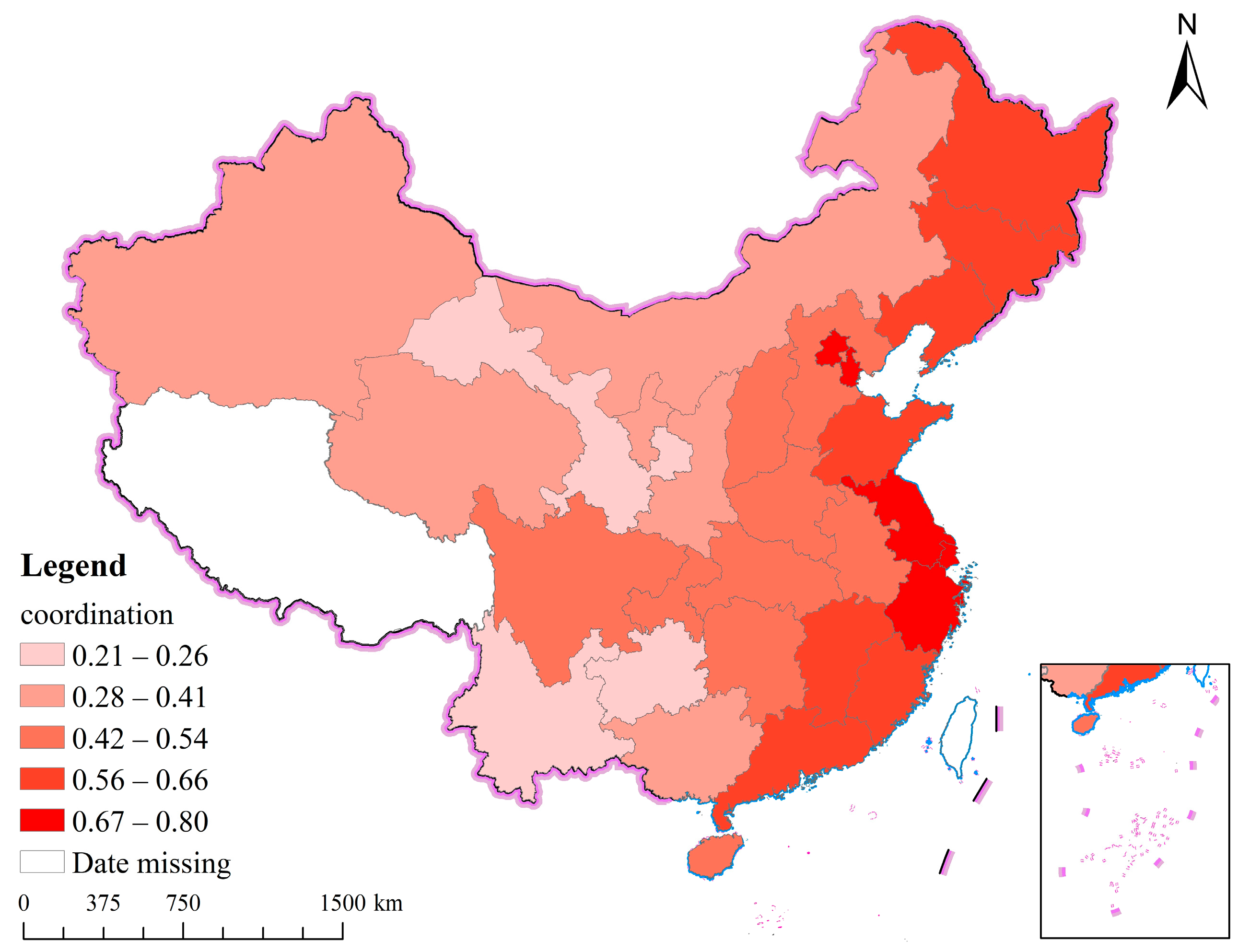



| First Level Indicators | Second Level Indicators | Third Level Indicators | Specific Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-quality development level (hqd) | Innovation (Z1) | The vitality of technological innovation (Z11) | Total number of full-time R&D employees, Z11 |
| Technology research and development capability (Z12) | Number of invention patents authorized, Z12 | ||
| Technology transformation capability (Z13) | High-tech industry’s development degree (Main business income/GDP), Z13 | ||
| Coordination (Z2) | The coordination of regional industrial structure (Z21) | Industrial structure rationalization index, Z21 | |
| The coordination between urban and rural areas (Z22) | The ratio of rural income to urban income, Z22 | ||
| Greenness (Z3) | Basic environmental change degree (Z31–34) | Population-weighted concentrations of PM2.5 Z31; The average value of GDP per unit of energy consumption, Z32; Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste, Z33; Regional sewage recycling rate, Z34 | |
| The level of green technology development (Z35) | The regional granted number of green invention patents, Z35 | ||
| Openness (Z4) | External attractiveness (Z41) | The actual regional scale of foreign capital utilized, Z41 | |
| Degree of marketization (Z42) | Marketization index by region, Z42 | ||
| The development of ICT(Z43) | Regional internet penetration rate, Z43 | ||
| Sharing (Z5) | People’s quality of life (Z51) | Consumption level of regional residents, Z51 | |
| Social civilization level (Z52) | Number of college students per unit of population in the region, Z52 | ||
| Life and health security (Z53–54) | Number of hospital beds per ten thousand people in the region, Z53; Number of practicing (assistant) physicians per ten thousand people in the region, Z54 | ||
| Basic social security (Z55–57) | Utilization rate of labor resources, Z55; Percentage of medical insurance cover, Z56; Percentage of unemployment insurance cover, Z57 |
| VarName | Obs | Mean | Median | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hqd | 390 | 0.379 | 0.372 | 0.108 | 0.166 | 0.706 |
| Innovation | 390 | 0.162 | 0.108 | 0.159 | 0.005 | 0.958 |
| Coordination | 390 | 0.519 | 0.520 | 0.166 | 0.000 | 0.911 |
| Greenness | 390 | 0.449 | 0.448 | 0.092 | 0.249 | 0.815 |
| Openness | 390 | 0.385 | 0.356 | 0.159 | 0.106 | 0.805 |
| Sharing | 390 | 0.339 | 0.330 | 0.133 | 0.088 | 0.845 |
| ms | 390 | 6.667 | 6.787 | 0.774 | 4.098 | 8.351 |
| com | 390 | 1.207 | 1.023 | 0.708 | 0.380 | 4.250 |
| urb | 390 | 0.541 | 0.524 | 0.136 | 0.275 | 0.896 |
| cu | 390 | 0.365 | 0.365 | 0.062 | 0.218 | 0.542 |
| gdp | 390 | 0.133 | 0.121 | 0.063 | −0.040 | 0.298 |
| fdi | 390 | 0.109 | 0.072 | 0.132 | 0.000 | 0.851 |
| energy | 390 | 1.060 | 0.904 | 0.613 | 0.224 | 4.142 |
| rd | 390 | 2.164 | −0.192 | 7.604 | −0.946 | 66.562 |
| patent | 390 | 1.223 | 0.449 | 2.459 | 0.036 | 21.810 |
| upd | 390 | 0.280 | 0.258 | 0.122 | 0.060 | 0.631 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hqd | hqd | hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.102 *** | 0.095 *** | 0.067 *** | 0.107 *** | 0.089 *** |
| (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.011) | |
| gdp | −0.073 *** | −0.089 *** | −0.017 | −0.066 *** | −0.012 |
| (0.024) | (0.026) | (0.036) | (0.024) | (0.034) | |
| energy | −0.016 ** | −0.023 *** | −0.011 * | −0.012 | −0.002 |
| (0.007) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.008) | (0.006) | |
| rd | 0.002 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.002 *** | 0.000 |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.000) | |
| patent | 0.010 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.006 *** | 0.010 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | |
| fdi | −0.008 | 0.020 | 0.050 ** | −0.023 | 0.022 |
| (0.023) | (0.024) | (0.019) | (0.023) | (0.019) | |
| upd | 0.034 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.040 * | 0.019 |
| (0.023) | (0.024) | (0.019) | (0.024) | (0.019) | |
| constant | −0.303 *** | −0.242 *** | −0.093 * | −0.337 *** | −0.234 *** |
| (0.044) | (0.043) | (0.053) | (0.044) | (0.063) | |
| Individual fixed | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| 0.067 *** | |||||
| (0.009) | |||||
| 0.022 *** | |||||
| (0.001) | |||||
| R2 | 0.946 | 0.911 | 0.948 | ||
| Wald Test | 3684.90 *** | 3141.59 *** | |||
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Innovation | Coordination | Greenness | Openness | Sharing | hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.142 *** | 0.091 *** | 0.087 *** | 0.020 | 0.102 *** | 0.031 *** | 0.036 *** | 0.089 *** |
| (0.025) | (0.021) | (0.017) | (0.014) | (0.016) | (0.005) | (0.005) | (0.011) | |
| constant | −0.789 *** | −0.131 | −0.127 | 0.090 | −0.328 *** | 0.258 *** | 0.218 *** | −0.227 *** |
| (0.147) | (0.122) | (0.100) | (0.084) | (0.094) | (0.041) | (0.042) | (0.065) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 360 | 360 | 360 |
| R2 | 0.561 | 0.809 | 0.845 | 0.938 | 0.939 | 0.807 | 0.806 | 0.945 |
| 2006–2012 | 2013–2018 | |
|---|---|---|
| hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.019 * | 0.133 *** |
| (0.010) | (0.024) | |
| constant | 0.153 ** | −0.477 *** |
| (0.060) | (0.165) | |
| Control | YES | YES |
| Individually fixed | YES | YES |
| Time-fixed | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.936 | 0.908 |
| Observations | 210 | 180 |
| (Eastern) | (Central) | (Western) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.093 *** | 0.070 ** | 0.061 *** |
| (0.023) | (0.027) | (0.014) | |
| constant | −0.257 * | −0.134 | −0.044 |
| (0.132) | (0.150) | (0.075) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES |
| Individually fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Time-fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.937 | 0.978 | 0.974 |
| Observations | 143 | 104 | 143 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| com | hqd | Innovation | Coordination | Greenness | Openness | Sharing | |
| ms | 0.472 *** | 0.081 *** | 0.088 *** | 0.075 *** | 0.094 *** | 0.066 *** | 0.098 *** |
| (0.034) | (0.006) | (0.013) | (0.013) | (0.009) | (0.010) | (0.010) | |
| com | 0.055 *** | 0.007 | 0.067 *** | −0.010 | 0.107 *** | 0.101 *** | |
| (0.008) | (0.017) | (0.016) | (0.011) | (0.012) | (0.013) | ||
| constant | −2.163 *** | −0.219 *** | −0.524 *** | −0.056 | −0.177 *** | −0.206 *** | −0.375 *** |
| (0.275) | (0.044) | (0.093) | (0.088) | (0.060) | (0.067) | (0.070) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.897 | 0.922 | 0.529 | 0.713 | 0.841 | 0.886 | 0.901 |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
| Sobel test | 0.026 *** | 0.003 | 0.031 *** | −0.005 | 0.050 *** | 0.048 *** | |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.008) | (0.005) | (0.007) | (0.007) | ||
| Bootstrap test | 0.026 *** | 0.003 | 0.031 *** | −0.005 | 0.050 *** | 0.048 *** | |
| (0.004) | (0.011) | (0.007) | (0.006) | (0.009) | (0.005) |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hqd | hqd | hqd | hqd | |
| ms | 0.089 *** | 0.046 *** | 0.016 | 0.056 *** |
| (0.011) | (0.011) | (0.013) | (0.011) | |
| urb | 0.540 *** | 0.102 | 0.102 | |
| (0.063) | (0.118) | (0.118) | ||
| urb×ms | 0.074 *** | |||
| (0.017) | ||||
| c_urb×ms | 0.074 *** | |||
| (0.017) | ||||
| constant | −0.234 *** | −0.268 *** | −0.069 | −0.069 |
| (0.063) | (0.057) | (0.072) | (0.072) | |
| control | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.948 | 0.957 | 0.960 | 0.960 |
| Observations | 390 | 390 | 390 | 390 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L. Assessing the Impact of Government Behavior on Regional High-Quality Development: A Case of Fiscal Expenditures on People’s Livelihoods in China. Land 2023, 12, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12101924
Wang G, Wang D, Zhang L. Assessing the Impact of Government Behavior on Regional High-Quality Development: A Case of Fiscal Expenditures on People’s Livelihoods in China. Land. 2023; 12(10):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12101924
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guowei, Dingqing Wang, and Liang Zhang. 2023. "Assessing the Impact of Government Behavior on Regional High-Quality Development: A Case of Fiscal Expenditures on People’s Livelihoods in China" Land 12, no. 10: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12101924
APA StyleWang, G., Wang, D., & Zhang, L. (2023). Assessing the Impact of Government Behavior on Regional High-Quality Development: A Case of Fiscal Expenditures on People’s Livelihoods in China. Land, 12(10), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12101924








