Abstract
Nested Delft 3D and Hydrus 1D models were applied to simulate variations in the hydrological process of tidal creeks, soil water, and salt transport in the soil profile of the reconstruction area in the Yellow River Delta under six gate dam scenarios. The results showed that the gate dam set up near the sea area was more conducive to reducing the variation range of water depth in the reconstruction area. The water depth changes in scenarios with 6 m gate valves were higher than those with 3 m sluice valves in the same gate dam location. The variations in surface water salinity, cumulative flooding time, flooding frequency, and cumulative infiltration in each scenario were similar to those for water depth. Rapid changes in soil water and salt content occurred in each scenario in periods without flooding. The fluctuation of soil salt content in different soil layers was contrary to the changes in soil water content. The overall difference in the soil salt contents and soil water content of the soil profile in scenarios with a gate dam near the sea was relatively larger than that of those with a gate dam near the shore. Obvious differences in both the soil water content and soil salt content between scenarios with 3 m and 6 m gate valves were not observed. Our results contribute to the understanding of the function of gate dams in controlling soil water and salt content in coastal wetlands.
1. Introduction
The Yellow River Delta wetland, a transit station, resting place, and breeding ground for migratory wader species along the West Pacific Flyway [], is one of the most important and representative estuarine wetlands in the world []. This wetland has great significance for protecting birds and maintaining biodiversity []. The essential nutrients for biological survival in the coastal intertidal zone are mainly provided through tidal processes []. Under the influence of human activities (such as the construction of dams, ditches, and roads), the hydrological status of estuarine wetlands has been changed [], resulting in a threat to the living environment of the original vegetation community. The population and distribution density of benthos were significantly reduced, resulting in a decrease in the food quality and quantity of birds and crustaceans. The disturbance and destruction of the hydrological environment in the wetlands of the Yellow River Delta from human-made construction increased in recent years, which further affects the environmental conditions of soil and water [,]. The number of artificial hydraulic constructions has rapidly increased in the wetlands of the Yellow River Mouth since 1985. Buildings such as dams, roads, and ditches weaken the hydrological connectivity of coastal wetlands []. To protect the ecological environment and improve the efficiency of water resources management while developing the economy, the construction proportion of gate dams has increased significantly since 2005 []. A gate dam has a significant impact on the water and salt regime of the estuary wetland []. It is well known that water and salt are the necessary internal conditions for forming estuarine wetlands. The ratio of water and salt determines the vegetation type and distribution pattern, the wetland evolution, and the ecological function of the wetland. However, few reports about soil water–salt infiltration under dam and gate valves in wetlands of the Yellow River Delta have been created.
Dams are water-retaining structures around rivers, lakes, oceans, and reservoirs. As an important part of hydraulic engineering construction, they play an important role in blocking flood overflow, resisting storm surge attacks, and weakening sea waves[]. However, the construction of dams has also brought many negative effects, such as dividing watersheds, reducing water connectivity, and hindering the exchange of material and energy, resulting in serious changes in the function of the ecosystem area of the nearby water body [,]. Dams can reduce the flow in the river’s lower reaches, make the landscape in the middle and lower reaches more complex and fragmented, and increase the difficulty of sustainably managing water resources []. The passage of fish can be hindered [], and the reduction in coastal wetland area and functional degradation can be aggravated by dam constructions []. In the 1990s, the dam of Scheldt estuary burst due to the destruction of a storm surge. Ten years later, the function of coastal wetland was restored in this area. The establishment of a gate in the area affected by the dam can also enhance water quality and flow []. Therefore, more and more scientific researchers have paid attention to the ecological restoration and hydrological environment of the coastal wetland by building gates in dams [].
Experiments to explore the effects of dams and gate valves on wetlands can only be carried out under specific conditions, but the hydrological model provides an efficient and economical method []. In this study, the nested Delft 3D model and Hydrus 1D model were applied to simulate the hydrological process of the reconstruction area in the Yellow River Delta under different scenarios and soil water and salt transportation processes. This study aims to (1) compare the impact of the location and gate width of a gate dam on the hydrological status of the reconstruction area and (2) reveal the law of variation of soil water and soil salt contents in different scenarios. We believe that our results could provide some schemes for restoring the Yellow River Delta wetland and could be an inspired practice for sustainability.
2. Study Area
The study area is located in the Yellow River Delta wetland, which is a typical siltation estuarine wetland (Figure 1). The distinctive hydrological environment of the study site was shaped by irregular semi-diurnal tide characteristics coupled with the Yellow River’s water–sediment regulation. The salinity of offshore surface seawater in this area is 14.9–26 g kg−1, the average high tide interval is 10–11 h, the average spring tide range is 1.06–1.78 m, and the neap tide range is about 0.46–0.78 m []. To improve the hydrological situation of the delta wetland, a series of gate dams were constructed in the study area. The soil is mainly fluvo-aquic soil and saline soil. The soil-salinization process precedes the soil-forming process. Evaporation is 2–3 times greater than precipitation, which provides favorable conditions for the upward migration of soil salt []. The terrain is flat, and the natural gradient ratio is 1/8000–1/12,000 []. The predominant natural vegetation is Tamarix chinensis, Suaeda salsa, and Phragmites australis. According to the USDA’s soil classification system [], the soil texture of the study site was classified as silty loam. The climate of the study area is characterized by a temperate monsoon climate. The average temperature is 11.7–12.6 °C. The average precipitation is 530–630 mm, 70% of which occurs in summer.
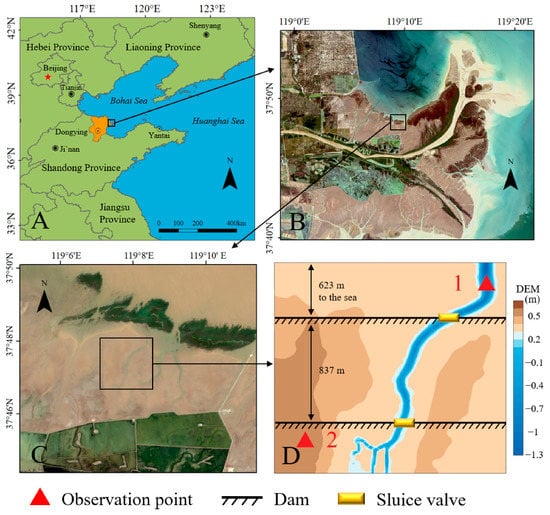
Figure 1.
The location of study area and experimental design. (A) means the location of Dongying City, Shandong Province. (B) means the location of Yellow River Delta. (C) means the location of study area. (D) means the experimental design.
The study sites are located in the Yellow River Delta Nature Reserve (37°35′–38°12′ N, 118°33′–119°20′ E) located in Dongying city, a Northeastern city of Shandong Province, China (Figure 1). The altitude of the experiment ranged from MSL −1.3 m to MSL + 0.7 m. Monitoring was conducted from 1 April 1 to 30 April, 2021. The total precipitation, total evaporation, and daily average temperature in April were 23.2 mm, 62.6 mm, and 14.15 ± 2.31 °C, respectively (Figure 2). The dam type is mainly an earth embankment with a height of 3–4 m. The sluice is constructed of reinforced concrete materials, and the width of the water passage of the sluice is 3 m or 6 m.
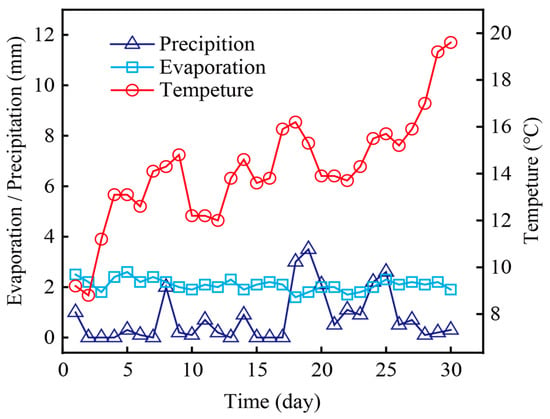
Figure 2.
Precipitation, evaporation, and temperature in April in study site.
3. Methodology
Our study used the method of nesting two models. We refer to the area between the gate dam and the nearshore side of the tidal creek as the reconstruction area. The flow module of Delft 3D and the 1-dimensional module of Hydrus 1D were used to simulate the hydrological condition in the reconstruction area after calibration with field data in the natural state. The module took the water depth and water salinity data in observation point 1 as the open boundary condition of Delft 3D to simulate the variation in the flooding depth and salt content of infiltration water in observation point 2 (Figure 1D). We took these two output results as the parameter settings of the Hydrus 1D model to simulate the effects of different gate dam scenarios on soil water and salt variation in the construction area. The simulation study focuses on the hydrological connectivity in the case of maximum flow (the gate is fully open), which depends on the tidal height.
3.1. Delft 3D Model
In this experiment, a complete and undisturbed tidal ditch system in the natural wetland of the Yellow River Delta was selected as the research site. Two sets of the water level meters (Diver DXT) were placed at the two observation points (1 and 2), respectively, to record the dynamic changes in water level (Figure 1). A portable conductivity instrument (DDBJ-350) was used to measure the water salinity. The monitoring data from observation point 1 were used as open boundary parameters of Delft 3D model. The monitoring data from observation point 2 were used for model validation (Figure 1D). The water level and water salinity changes of observation point 2 under different scenarios were simulated by Delft 3D.
The overall terrain of the tidal flat is relatively flat, and the elevation difference is small, while the terrain near the tidal creek changes sharply for tidal erosion and sedimentation, which means obtaining the elevation data is difficult. We used DJ UAV (Spirit 4 multispectral) to capture and generate high-resolution images of low-altitude and digital elevation models (DEM) in the study area. The flight parameters of the altitude and the resolution were set as 90 m and 4.8 cm/px, respectively. The water depth data of the tidal creek were measured by using a digital water level gauge. The digital water level gauge was used to measure the water depth values of scattered points and obtain the overall water depth of the tidal creek by using the triangular interpolation method in the QUICKIN program. The water depth topographic interpolation map was generated using monitoring data combined with DEM (Figure 1).
Figure 3 depicts the grid composition of the study area. The first step in building the Delft 3D hydrodynamic model is to devise the calculation grid of the research area. The quality of the grid not only determines the accuracy of hydrodynamic simulation results but also has a great impact on the computational efficiency and operation stability of the model in the calculation process []. To improve the simulation accuracy of the model, the tidal creek and its surrounding areas with large topographic relief were divided into high-resolution grids. To improve the operation efficiency of the model, the area with small topographic relief was divided into lower resolution grids []. The generated grid consisted of 7475 cells with M = 113 by N = 79 (where M is the water flow direction and N is perpendicular to M). The grid property was very fine because orthogonal values were 0–0.02, and the grid aspect ratio was 1–1.9 []. The average distance of the generated grid nodes was 10 m. Table 1 shows the main parameters of the Delft 3D model. The roughness coefficient adopted Manning coefficient, and its value was set to 0.013 []. The variation of tidal height at the closed boundary is quite small, and the flooding height in the area of observation point B is also small, which has little effect on the simulation results. Thus, there are two kinds of boundaries in the model: open boundary of water level and closed boundary.
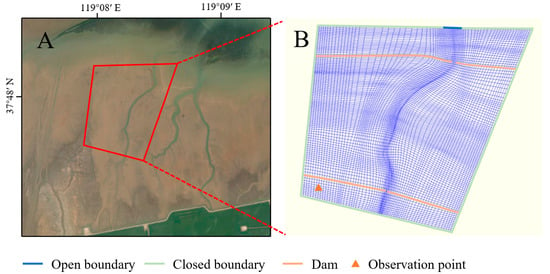
Figure 3.
Tidal creek grid element composition. (A) means the location of tidal creek. (B) means the grid element composition.

Table 1.
Delft 3D model main parameter settings.
The hydrological processes of the reconstruction area under six different scenarios were simulated and discussed by adding a dike and/or gate valve in the tidal creek using Delft 3D model (Table 2). Figure 4 (S1–S6) represents the gate and dam settings for scenarios S1–S6, respectively. Scenario S1 simulated a natural tidal creek without dams and gate valves. Scenarios S2 and S3 set a dam with a 3 and 6 m gate valve, which was similar to a local gate valve on the land side of the tidal creek, respectively. Scenarios S4 and S5 set up a dam with a 3 or 6 m gate valve near the ocean, respectively. Scenario S6 set up a dam without a gate valve near the ocean.

Table 2.
Dam and gate valve settings in different scenarios.
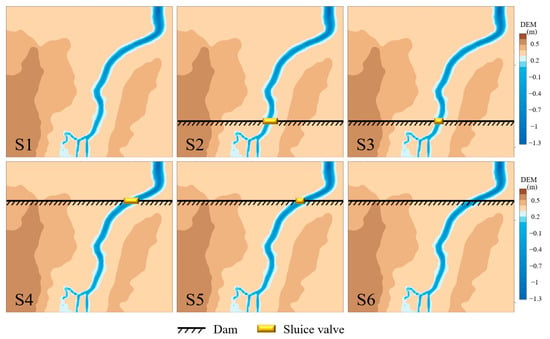
Figure 4.
Dam and gate valve settings in scenarios S1–S6.
3.2. Hydrus 1D Model
The stratified samples of 0–80 cm soils (10 cm interval) with three repetitions in the study area were collected using a stainless-steel ring knife. An oven-dried sample (dried at 105 °C for 48 h to a constant weight) was used to calculate the soil bulk density (Equation (1)) and the volumetric soil water content (Equation (2)).
where is the soil bulk density (g cm−3), and and denote the weight of the dry soil (g) and volume of the ring knife (cm3). is the volumetric soil water content (%), is the gravimetric soil water content (%), and is the original soil weight (g).
The volume water content of the soil is 26–38%. The saturated water content and saturated hydraulic conductivity of soil were measured by the constant head method [] and calculated by using Equation (3) and Equation (4), respectively.
where is the saturated water content (%), is the weight of the saturated soil (g), is the weight of the dry soil (g), and is the volume of the ring knife (cm3). Ks is the saturated hydraulic conductivity (cm min−1), is the infiltration water quantity (cm−3), is the depth of the soil (cm), is the water potential difference between the upper and lower soil samples (cm), is the cross-sectional area of soil mass (cm−2), and is time (min).
The residual water content of the soil was measured by the oven-drying method []. The soil particle size composition (Table 3) was measured with the laser particle sizer (Mastersizer 3000, Malvern Panalytical, Beijing, China) using air-dried soil samples after grinding and screening. The soil salt content was determined by the extraction method (soil–water ratio of 1:5). The initial salt content of each layer was measured as 15.13 ± 0.45, 15.89 ± 0.37, 16.22 ± 0.83, 16.74 ± 0.91, 18.99 ± 0.62, 19.36 ± 0.26, 18.23 ± 0.41, and 16.43 ± 0.62 g/kg, respectively. The saturated hydraulic conductivity (KS), reciprocal of inlet suction in the model (α), and pore volume size distribution index (n) were obtained by inversion and optimization in the neural network prediction module according to the particle size composition of the soil.

Table 3.
Soil particle size distribution and bulk density in the study.
The water contents in different scenarios were predicted based on neural networks. The soil hydraulic property parameters were obtained according to van Genuchten [], as in Equations (5)–(8).
where is the volumetric soil water content (%), is time (day), is the water pressure head (cm), and is the depth from the soil surface (cm). is the water retention curve, is the residual water content (%), is the saturated water content (%), (cm−1) and are the water content shape parameters, and is the empirical shape factor in the water retention function. is hydraulic conductivity curve. is hydraulic conductivity shape parameter and commonly set at 0.5 []; is the relative saturation.
The solute transportation process in a variably saturated soil was calculated by the advection–diffusion equation (Equation (9)). Additionally, the optimized parameters are listed in Table 4.
where is the salt concentration in the soil solution (g kg−1), is the volumetric soil water content (%), is time (day), is the effective dispersion coefficient (cm day−1), and is the water flux (cm2 day−1). The subscripts and denote x or z coordinates.

Table 4.
Optimized hydraulic parameters in the study.
4. Results
4.1. Variation of Surface Water and Salt in Different Scenarios
The simulation results of the variation of water depth and salinity over time under scenarios S1–S5 are shown in Figure 5. The result of scenario S6 is not shown because the tide could not reach the reconstruction area due to the complete blocking by the dam in this scenario. To validate the veracity of simulation results, the field monitoring data of water depth and salinity were used for the examination analysis. The validation results of water depth (R2 = 0.96, RMSE = 0.41) and salinity (R2 = 0.93, RMSE = 0.19) from scenario S1 indicated that the simulation of the Delft 3D model was accurate and reliable. The simulation water depth variation was basically consistent with the law of tidal fluctuations in this area. There were no water depth data for each scenario from 9 April to 17 April because the local tides were in a neap tidal cycle, and the tides could not reach the observation area.
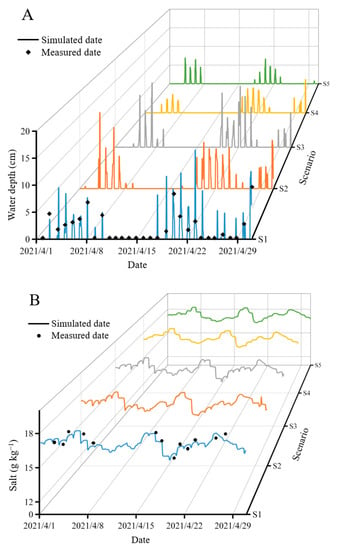
Figure 5.
Water depth (A) and water salt content (B) variations in the reconstruction area of each scenario.
The hydrological processes of the tidal creek were changed by the gate valve and dam. The maximum simulation flooding depth in the natural state where there was no block by the dam (scenario S1) was highest (16.57 cm), while the maximum simulation water depths of scenarios S2–S5 decreased to 15.7 cm, 14.6 cm, 8.3 cm, and 6.9 cm, respectively. Compared with the natural state of scenario S1, the changed maximum simulation flooding depths of scenarios S2–S5 were 0.87 cm, 1.97 cm, 8.27 cm, and 9.67 cm. The difference in the simulated water depth between scenario S1 and scenario S6 was the biggest (16.57 cm) because the tide was completely blocked by the dam in scenario S6. The simulation results indicated that the effects of the location of the gate dam set up for water depth were great. The water depth changes of scenarios S2 and S3 (gate dam set up near the shore) were 1.75 and 2.27 times greater than those of scenarios S4 and S5 (gate dam set up near the sea area), respectively. The gate dam set up near the sea area was more conducive to stabilizing the water depth fluctuation in the reconstruction area. The size of the sluice valve was also an important effect factor for water depth changes. The water depth changes in scenario S2 and scenario S4 with a 6 m sluice valve were higher than those in scenario S3 and scenario S5 with a 3 m sluice valve, respectively. The simulated water salinity difference was 1.9–2.6 g kg−1 (Figure 5B). The variations in simulated water salinity in each scenario were similar to the variations in the simulated water depth (Figure 5A), indicating the synchronous functions of the gate dam for both water depth and water salinity.
The cumulative flooding time, flooding frequency, cumulative depth of flooding, and cumulative infiltration, which were the key parameters for water and salt infiltration in soils, were selected to characterize the hydrodynamic processes under different scenarios in the restructured area. The simulation results showed that the dams and gate valves’ setup greatly weakened the hydrodynamic process (Figure 6). The cumulative flooding times in scenarios S1–S5 were 104 h, 102 h, 93 h, 78 h, and 56 h in 30 days. Scenario S1, the natural state, was affected by the tide for the longest time. Compared to scenario S1, the cumulative flooding times of scenarios S2–S5 with gate dams were reduced by 2%, 11%, 25%, and 46%, respectively. The flooding frequency in scenarios S1–S5 was 25, 23, 19, 16, and 11, respectively, in the study period. Compared with the cumulative depth of flooding of scenario S1 (491 cm), scenarios S2–S5 decreased by 3%, 13%, 53%, and 65%, respectively. Our results showed that the gate dam with a 6 m gate valve near the shore (scenario S2) was closest to the natural state. The functions for the hydrodynamic process weakness of scenarios with narrow dam gate valves were greater than those of scenarios with wide dam gate valves, and the scenarios of a gate dam near the sea were much stronger than those near the shore for weakening the hydrodynamic process. Certainly, the hydrodynamic process was weakened the most in scenario S6, for the tide was completely blocked by a dam without a gate valve.
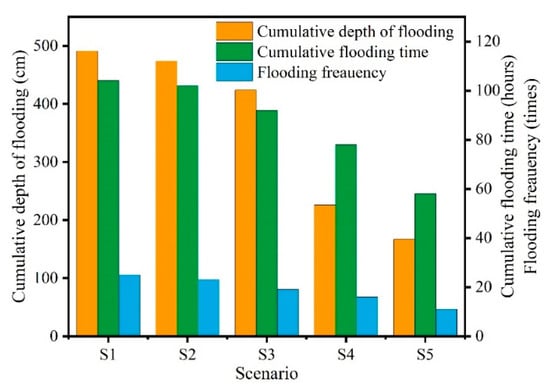
Figure 6.
Cumulative flooding time, flooding frequency, and cumulative flooding depth of each scenario.
Because the movement process of salt followed with water, the cumulative water infiltration was discussed emphatically in different scenarios. The cumulative infiltration of scenarios S1–S6 was 553.14 cm, 534.97 cm, 493.85 cm, 397.27 cm, 312.4 cm, and 2.32 cm in 30 days, respectively (Figure 7). Our results indicated that the cumulative water infiltration increased with water exchange enhancement, and thus the cumulative water infiltration of scenario S1 was highest, and that of scenario S6 was lowest. The change patterns of scenarios S1–S3 are closely related, as are scenarios S4 and S5, but the latter appear significantly different from the former. The small differences in cumulative water infiltration occurred within 150 h.
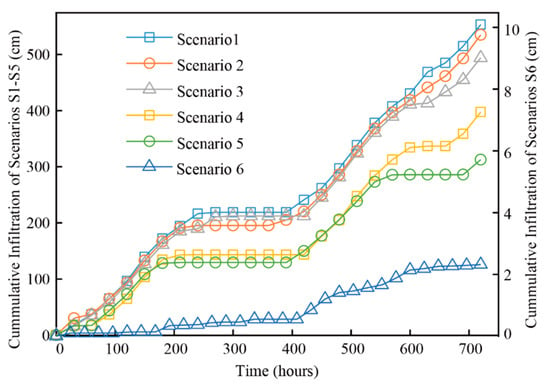
Figure 7.
Water cumulative infiltration in each scenario.
4.2. Variation of Soil Water Content in the Soil Profile
The variation trends of the soil water content at depths of 0–10 cm, 30–40 cm, and 60–70 cm under different scenarios were stimulated by the Hydrus 1D model using the simulated results of water depth and salt from Delft 3D. The validation results for scenario S1 (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 0.02) using field measurement data indicated that the simulation effect of the Hydrus 1D model was accurate (Figure 8, S1).
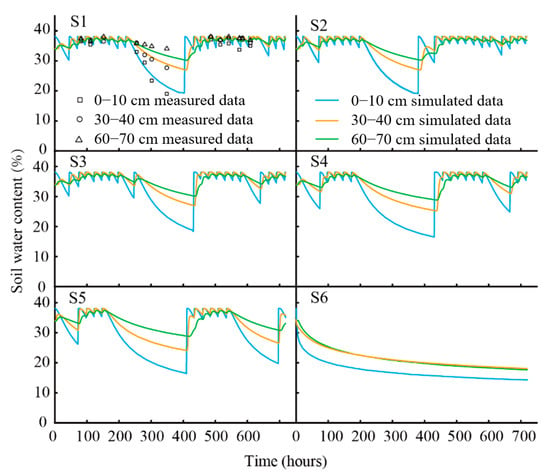
Figure 8.
The variation of soil water contents in each scenario S1–S6.
In scenarios S1–S5, the fluctuation amplitude of soil water content in each layer decreased with depth (Figure 8, S1–S5). The range of soil water content at depths of 0–10 cm, 30–40 cm, and 60–70 cm were 16.3–38.1%, 24.0–38.1%, and 29.4–36.8%, respectively. The two valleys of soil water content were observed in different soil layers of scenarios S1–S5. The deep and shallow valleys occurred at about 380–430 h and 650–700 h, respectively. The values of water content in the soil profiles of scenarios S1–S5 in the deep valley were 11.60%, 11.8%, 12.4%, 13.0%, and 13.2%, respectively. The soil water contents in different soil layers decreased gradually with time in scenario S6, which was quite different from scenarios S1–S5 (Figure 8, S6). The rapid soil water content decrease of 15.90% in the 0–10 cm soil layer, 6.00% in the 30–40 cm soil layer, and 6.90% in the 60–70 cm soil layer occurred within 0–50 h, while no more than 10% water content in each soil layer was lost from 50 h to 720 h.
4.3. Variation of Salt Content in the Soil Profile
The validated results of the soil salt content for scenario S1 (R2 = 0.82, RMSE = 0.28) indicated that the simulation effect of the Hydrus 1D model was credible. The fluctuation of salt content in the 0–10 cm soil layer in all the scenarios of S1–S5 was the largest (Figure 9, S1–S5). The fluctuation amplitude of salt content became mild with the increase in soil depth under the same scenario, which better reflected the migration law of salt followed by water. A peak of salt content in each soil layer appeared at 380–430 h, and a second small peak was observed at 650–700 h in scenarios S1–S5. The maximum difference of soil salt content appeared at the upper soil layer (0–10 cm depth) and decreased with the soil depth increase in scenarios S1–S5. The maximum values in the soil profiles ranged 3.0–5.1 g kg−1, 3.1–5.2 g kg−1, 2.9–6.3 g kg−1, 4.0–9.3 g kg−1, 4.4–9.7 g kg−1, and 0.3–11.1 g kg−1 in scenarios S1, S2, S3, S4, and S5. The simulated salt content of the 0–10 cm soil layer in scenario S6 increased with time in the study period, while the salt content variations in the 30–40 cm soil layer and 60–70 cm soil layer were relatively stable (Figure 9, S6). The slight increase in the 60–70 cm soil layer and a small decline in the 30–40 cm soil layer occurred within 100 h.
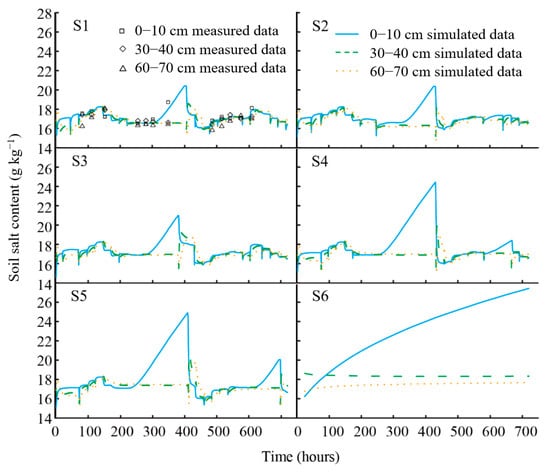
Figure 9.
The variation of soil salt content in each scenario.
The maximum salt content of soil profile in each scenario occurred at t 0–10 cm soil layer. The salt content peak values of the soil profile in scenarios S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 were 20.3 g kg−1, 20.3 g kg−1, 20.9 g kg−1, 24.4 g kg−1, 24.9 g kg−1, and 27.4 g kg−1, respectively. The highest peak value of salt content appeared in scenario S6. The difference in salt contents in the soil profile at the high peaks of scenarios S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 was 3.7 g kg−1, 4.0 g kg−1, 4.1 g kg−1, 7.4 g kg−1, 7.5 g kg−1, and 10.0 g kg−1, respectively. The overall salinity difference of the soil profile was small and close between scenarios S1, S2, and S3. The overall difference in the salt contents of the soil profile in scenarios S4 and S5 were close and higher than those in scenarios S1–S3. In scenario S6, the soil salt content in the 0–10 cm-deep layer increased from 16.2 to 27.4 g kg−1 during the study period, while the soil salt content in the 30–40 cm and 60–70 cm soil layers changed slowly with time.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Simulation of the Delft 3D and Hydrus 1D Models
A gate dam is not only an important driving factor of a natural wetland but also one of the most common ways for human beings to change tidal hydrology. This paper analyzed the influence of gate dams on water and salt transport in the Yellow River Delta wetlands.
The application of the model not only captured the hydrological characteristics of the tidal creeks but also depicted the changes in soil water content and salinity under different hydraulic building scenarios, which overcame the limitations of labor and time in the traditional experimental methods. Researchers in [,] compared publicly available numerical software used to simulate estuarine and coastal hydrodynamic forces. They found that the Delft 3D model has the smallest difference in the simulation of the water level and flow field. Noshadi et al. [] used the SALTMED and Hydrus 1D models to simulate the soil water content, salt content, and wheat production value with irrigation water of different salinities, respectively. The results show that the latter models are more accurate than the former in simulating the soil water and salt content. By filling layered soil in soil columns and designing water infiltration experiments with different depths, Ma et al. [] found that water depth mainly modified the water transport process by affecting the pressure potential at the infiltration interface. With the augmentation of the increase in water depth, the infiltration rate increased. It was proved that Hydrus 1D could accurately predict the variation tendency of the water and salt cumulative infiltration process. Werner et al. [] used Hydrus 1D to simulate changes in soil salt content in the Queensland coastal zone and concluded that surface salinization was greatly affected by the tide. Hydrus 1D is appropriate for the simulation of water and salt transport because it can capture water flow under flooding. This paper creatively nested Hydrus 1D and Delft 3D models, which provides a flexible and comprehensive method for researchers to study the change of the estuarine hydrological environment. Previous studies proved that the Delft 3D model could accurately simulate the water depth and velocity changes [,] and the spatiotemporal changes in the tide level, temperature, and salinity [,], while the Hydrus 1D model could accurately predict the variation tendency of the water and salt cumulative infiltration process [,]. Due to the limitation of observation points, we did not study the downstream water body of the tidal creek but focused on water and salt transport in the reconstruction area (non-tidal channel). In our study, the Delft 3D and Hydrus 1D models were nested to stimulate the changes in the hydrological process of the tidal creeks and the variations in soil water and salt transport in the soil profile under six scenarios. The validation results of the surface water depth (R2 = 0.96, RMSE = 0.41) and salt content (R2 = 0.93, RMSE = 0.19) (Figure 5), soil water content (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 0.02) (Figure 8, S1), and soil salt content (R2 = 0.82, RMSE = 0.28) (Figure 9, S1) showed that the nested models could accurately predict the water and salt migration processes in scenarios with different barriers from dam and gate valves.
The simulation results of surface water depth are quite accurate. This is probably because the water depth verification data (0 cm) in the no-flooding period of the dry period was included in the verification process, resulting in high verification results. In fact, there is still a degree of deviation between the calculated water level and the measured water level. There were two main reasons that caused a little deviation in the study’s simulation results of water and salt. One was that the model assumed that soil water could infiltrate freely without the action of capillary suction in the process of infiltration, without considering the lag effect during migration []. The other was that the model defaulted to the complete dissolution of salt in soil water in the simulation process, even though there might be salt retention in the infiltration process [].
5.2. The Effects of Dam and Gate Valves on Surface Water and Salt
Even though the sea dams play an important role in weakening sea waves, resisting storm surges, etc., the construction of sea dams has brought many negative effects, such as reducing water connectivity, resulting in serious changes to the ecological functions of the coastal wetlands [,]. Our results of surface water depth, salt content (Figure 5), and cumulative water infiltration (Figure 7) variations in scenario S1 were synchronous with the tide level (Figure 10). However, there was no water entering the reconstruction area in scenario S6, in which the tide was blocked completely by the dam, indicating that the dam had a huge effect on the hydrological process in coastal wetlands, which agreed with previous studies. Dams hinder the flow of tidal creek water, resulting in a loss of water resources in coastal wetlands. Gate valves set up on the dam were an efficient approach for the hydrological management and restoration of coastal wetlands []. Therefore, the relations of location and width of the gate valve and its regulation capacity for the surface water and salt in the reconstruction area were focused on in the study. The maximum simulation water depths of scenarios S2 and S4 with a 6 m gate valve were higher than that of scenarios S3 and S5 with a 3 m gate valve, respectively, while the changed maximum simulation flooding depths compared with scenario S1 in scenarios with a wide gate valve were smaller than those in scenarios with a narrow gate valve at same gate valve location (Figure 5), indicating that the water depth in scenarios with a wide gate valve was much closer to the natural state. The variations in the simulated water salinity in each scenario were similar to the variations in the simulated water depth (Figure 5). The main reason for this was that the water and salt were brought by tidal creek flow [], while the tidal creek flow was controlled by the width of the gate valve in the simulated study. These conclusions were also supported by the other hydrological parameters in the study. The cumulative flooding times, flooding frequency, cumulative flooding depth (Figure 6), and the cumulative water infiltration (Figure 7) of scenario S1 were higher than those of scenarios S2–S5 with a dam gate, and the scenarios with a 6 m dam gate valve near the shore (scenario S2) were much closer to the natural state (Figure 6).
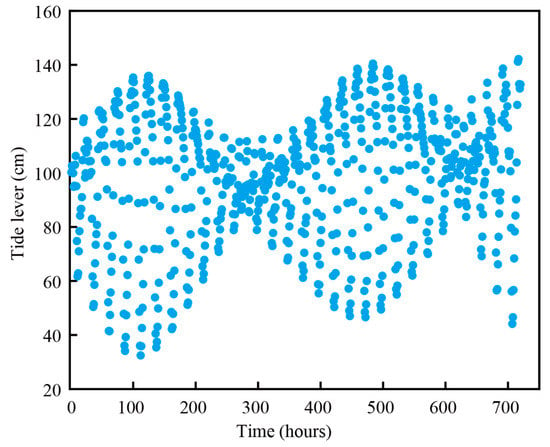
Figure 10.
The variation of tide level in April in study area.
Further analysis showed that the location of the dam gate valve was another important factor for water and salt changes in the reconstruction area. The water depth changes of scenarios with a gate dam set up near the shore (S2 and S3) were much higher than that of scenarios with a gate dam set up near the sea area (S4 and S5) (Figure 5). The hydrological parameters of the cumulative flooding time, flooding frequency, cumulative depth of flooding (Figure 6), and cumulative infiltration (Figure 7) in scenarios with a gate dam near the shore were much higher than those near the sea. The results indicated that the restriction for the hydrological process in the reconstruction area was strong when the gate dam was set up near the sea. To support our opinions, Zhao et al. [] found that the impacts of dam construction were larger in upstream locations than in downstream ones.
5.3. The Soil Water and Soil Salt Changes in Different Scenarios
With the increase in the soil depth of profiles, the fluctuations of soil water content decreased in scenarios S1–S5 (Figure 8). The soil water in different soil layers came from surface water infiltration. The deep-layer soils with a relatively large bulk density (Table 3) were relatively compact and had less porosity. The migration speed of soil water in the deep soil layer was reduced because of the small movement space in the process of surface water infiltration []. At the beginning of the ponding stage, the soil water content of each layer increased rapidly. The soil water at a depth of 0–10 cm reached the saturation state first. As soon as surface water disappeared, the soil water content of 0–10 cm decreased relatively rapidly. For the tide variation during the study period (Figure 10), the two valley values of soil water content in different soil layers were observed in different soil layers of scenarios S1–S5 (Figure 8, S1–S5). The occurrence periods of the valley values of soil water content were in the neap tide stage. In scenario S6, the tide could not enter the reconstruction area due to the interception of the dam. The soil water was mainly affected by evaporation and precipitation. The soil water content in different soil layers continually declined during the study period (Figure 8, S6) because the evaporation in the study area was higher than the precipitation (Figure 1). Previous studies found that the cumulative infiltration volume has a power function relationship with the water accumulation time []. The depth of stagnant water affects the pressure potential at the infiltration interface and has a direct effect on the infiltration flux found []. In agreement with the above concepts, we found that the soil water content decreases in different soil layers in scenarios S1–S6 mainly occurred in the periods of no surface flooding (Figure 8, S1–S6, Figure 5). As soon as the surface water disappears, the soil water of the middle and deep soil layers also can be supplemented by the infiltration of the upper soil water during the process of water loss [], leading to water loss of 0–10 cm soil layers that were much higher than those of 30–40 cm and 60–70 cm soil layers (Figure 8, S1–S6).
The obvious difference in soil water content variations between scenarios with a 3 m gate valve and a 6 m gate valve was not observed in the study. The water content variations between scenarios S1 (natural state), scenarios S2 and S3 (gate dam near the shore), and scenarios S4 and S5 (gate dam near the sea) were similar (Figure 8, S1–S5). The maximum water content variation of the 10 cm soil layer in scenario S1 was about 2.00% and 5.00% higher than that in scenarios with a gate dam near the sea and scenario with a dam (scenario S6), which is also supported by the study results of Zhao et al. [].
In the flooding stage, the soil salt contents of different soil layers in each scenario were similar (Figure 9, S1–S5) and closer to the salt content of tide water (16.00–18.00 g kg−1). The main reason for this was that the salt in water and soil continuously could move to the deep soil through convection and dispersion under the infiltration of tidal water []. The high flooding frequency could reduce the salt accumulation on the soil surface and balance the salinity difference between the different soil layers []. The fluctuation of soil salt content in different layers occurred during the no-flooding stage (Figure 9, S1–S6) and was contrary to the changes in soil water content (Figure 8, S1–S6). The soil salt content continued rising during the no-flooding stage, and the differences between each soil layer increased. As soon as the flooding stage began, the soil salt content in the 0–10 cm soil layer dropped immediately from its peak value; a little lag appeared in 30–40 cm and 60–70 cm soil layers. The largest fluctuation of salt content appeared in the 0–10 cm soil layer in the soil profile in all the scenarios of S1–S6. This phenomenon can be explained by the dynamic movement process of soil water and soil salt under evaporation and capillary action. As soon as flooding water is lost, the salt in the soil moves upwards by capillary action with the water. The salt accumulates in the upper soil layer after water evaporation, resulting in a relatively high salt content appearing in the upper soil layer []. Furthermore, the establishment of dam gate valves had also hindered the soil water–salt exchange and aggravated surface salt accumulation []. The overall difference in the salt contents of the soil profiles in scenarios S4 and S5 was close and higher than that in scenarios S1–S3 because the dam gate valve was set on the offshore side in scenarios S4 and S5. The tidal power in scenarios S4 and S5 were greatly weakened, causing surface flooding periods to be relatively short and the exposure times of soil surface to be relatively long (Figure 6).
6. Conclusions
Dam and gate valve constructions greatly impact the hydrological status of coastal wetlands. The six scenarios of dam and gate valve setup based on the actual local situations were selected to simulate water and salt transportation in the reconstruction area of the Yellow River Delta. The validation results showed that the nested Delft 3D and Hydrus 1D models applied in the study could accurately simulate the hydrological process of surface water and salt and the transportations of soil water and salt in the soil profile. When the surface water was cut off by a dam without a gate valve, the soil water content decreased, and soil salt content increased greatly and quickly in the upper soil layer. The effect of the location of a gate dam setup was great for hydrological processes of surface water. The surface water depth, cumulative flooding time, flooding frequency, and cumulative water infiltration, as well surface water salt in scenarios with a gate dam set up near the shore, were much closer to the natural state than those in scenarios with a gate dam setup near the sea. Little restriction of a dam gate valve setup near the shore for soil water and soil salt was found, while the scenarios of a dam gate valve setup near the sea caused the overall difference of both soil water contents and soil salt contents to increase in soil profiles. Even though the narrow gate valve was stronger than the wide gate valve for the surface water and salt exchange restriction, obvious differences in both soil water content and soil salt content between scenarios with 3 m and 6 m gate valves were not observed. Our results suggested that the location of the gate dam and the size of the gate valve should be paid attention to in coastal wetland management and restoration. To reduce the disturbance of the hydrological process of surface water and soil salt in coastal wetlands, a dam with a wide gate valve far away from the sea is recommended.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Writing—original draft and editing Z.Q. and Y.L. (Yunzhao Li); methodology, J.Y. (Junbao Yu); software, M.Y.; validation, J.Y. (Jisong Yang), D.Z. and X.W.; investigation, Z.W.; data curation, Y.Y., Y.Z. and Y.L. (Yue Ling); visualization, Y.M.; supervision, Review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Programme of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1806218, U2006215, U2106214), the National Science Foundation of China (41871087, 42171111), and the Project of the Cultivation Plan of Superior Discipline Talent Teams of Universities in Shandong Province: “the Coastal Resources and Environment team for the Blue–Yellow Area”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for support from the Key Program from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1806218, U2006215, U2106214), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41871087, 42171111) and the Project of the Cultivation Plan of Superior Discipline Talent Teams of Universities in Shandong Province: ‘the Coastal Resources and Environment team for Blue-Yellow Area’. Furthermore, the authors are grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for providing suggestions and advice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, J.; Hughes, A.C.; Dudgeon, D. Mapping wader biodiversity along the East Asian-Australasian flyway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210552. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.W.; Ma, T.T.; Li, X.W.; Cui, B.S. The simulation and assessment of the ecosystem services in the coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta based on InVEST model. Wetl. Sci. 2015, 13, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Xiao, N.; Wang, B.; Li, J. The effects of petroleum exploitation on water quality bio-assessment and benthic macro-invertebrate communities in the Yellow River Delta wetland, Dongying. Shengtai Xuebao Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Pezeshki, S.; DeLaune, R. The effects of salinity and soil drying on nutrient uptake and growth of Spartina alterniflora in a simulated tidal system. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2006, 58, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donders, T.H.; Gorissen, P.M.; Sangiorgi, F.; Cremer, H.; Wagner-Cremer, F.; McGee, V. Three-hundred-year hydrological changes in a subtropical estuary, Rookery Bay (Florida): Human impact versus natural variability. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008, 9, Q07V06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ke, Y.H.; Wang, D.W.; Ji, H.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Chen, M.M.; Lyu, M.Y.; Zhou, D.M. Human impact on suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary, China: Evidence from remote sensing data fusion using an improved spatiotemporal fusion method. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Sun, J.K.; Sun, Y.G.; Liu, S.J.; Fu, Z.Y. Multi-temporal characterization of land surface temperature and its relationships with normalized difference vegetation index and soil moisture content in the Yellow River Delta, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Pal, S. Impact of dam on inundation regime of flood plain wetland of punarbhaba river basin of barind tract of Indo-Bangladesh. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Xie, T.; Ma, X.; Cui, B.S.; Wu, X.; Che, C.G.; Zhang, X.T. Temporal and spatial pattern evolution of hydrological connectivity of the old track of Yellow River in Diaokouhe from 1985 to 2015. Environ. Ecol. 2020, 2, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alcérreca-Huerta, J.; Callejas-Jiménez, M.; Carrillo, L.; Castillo, M. Dam implications on salt-water intrusion and land use within a tropical estuarine environment of the Gulf of Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Talukdar, S.; Ghosh, R. Damming effect on habitat quality of riparian corridor. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maavara, T.; Chen, Q.W.; Van Meter, K.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, J.H.; Ni, J.R.; Zarfl, C. River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.H.; Cai, Y.P.; Yang, W.; Yang, Z.F. The effects of cascade dam construction and operation on riparian vegetation. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 131, 103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Liu, S.L.; Deng, L.; Dong, S.K.; Cong; Wang; Yang, Z.F.; Yang, J.J. Landscape change and hydrologic alteration associated with dam construction. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 16, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivari, D.; Pagliani, B.; Lemos, L.; Lima, D.; Gravena, W. Monitoring a critical population of the Bolivian river dolphin, Inia boliviensis, before and after closing the floodgates of a hydroelectric dam in the Amazon Basin, Brazil: A quantitative analysis. J. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 64, 126082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.P.; Guo, Q.Z.; Santasieri, C. Protecting People and Property While Restoring Coastal Wetland Habitats. Estuaries Coasts 2021, 44, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boys, C.A.; Pease, B. Opening the floodgates to the recovery of nektonic assemblages in a temperate coastal wetland. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 68, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eertman, R.H.; Kornman, B.A.; Stikvoort, E.; Verbeek, H. Restoration of the Sieperda tidal marsh in the Scheldt estuary, the Netherlands. Restor. Ecol. 2002, 10, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, Y.; Ai, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, F. Identifying changes in irrigation return flow with gradually intensified water-saving technology using HYDRUS for regional water resources management. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, D.D.; Shi, W.; Ning, Z.H.; Cai, Y.Z.; Song, Z.F.; Cui, B.S. Hydrological connectivity characteristics and ecological effects of a typical tidal channel system in the Yellow River Delta. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2018, 54, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Bai, J.H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Zhang, S. Changes of Biogenic Elements in Phragmites australis and Suaeda salsa from Salt Marshes in Yellow River Delta, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.G.; Li, Q.W.; Liang, C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yue, Y.; Gao, J.Q. Landscape index analysis of hydrological connectivity dynamics in the Yellow River Delta. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 57, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Horstman, E.; Dohmen-Janssen, M.; Hulscher, S. Modeling tidal dynamics in a mangrove creek catchment in Delft3D. Coast. Dyn. 2013, 2013, 833–844. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, V.; Carballo, R.; Ringwood, J.V. Application of the actuator disc theory of Delft3D-FLOW to model far-field hydrodynamic impacts of tidal turbines. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 1320–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, M.; Navera, U.K. Hydrodynamic and morphological analysis of Gorai River using delft 3d mathematical model. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), Khulna, Bangladesh, 12–14 February 2016; pp. 647–658. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Zhan, C.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Numerical study on the difference of geomorphic dynamics between the current and abandoned estuary coasts of the Yellow River. Mar. Geol. Front. 2019, 35, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, W.; Elrick, D.; Topp, G. A reexamination of the constant head well permeameter method for measuring saturated hydraulic conductivity above the water table1. Soil Sci. 1983, 136, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kelly, B.C. Accurate determination of moisture content of organic soils using the oven drying method. Dry. Technol. 2004, 22, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, A.M.; Vijverberg, T.; Post, S.; Van Der Spek, B.-J.; Henrotte, J.; Sokolewicz, M. Comparison between Mike 21 FM, Delft3D and Delft3D FM flow models of western port bay, Australia. Coast. Eng. 2016, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, S.; Baston, S.; Nemalidinne, R.; Chatzirodou, A.; Venugopal, V.; Side, J. Implementation of tidal turbines in MIKE 3 and Delft3D models of Pentland Firth & Orkney Waters. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 147, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Noshadi, M.; Fahandej-Saadi, S.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Application of SALTMED and HDRUS-1D models for simulations of soil water content and soil salinity in controlled groundwater depth. J. Arid Land 2020, 12, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.M.; Lin, Q.; Xu, S.H. Water Infiltration Characteristics of Layered Soil under Influences of Different Factors and Estimation of Hydraulic Parameters. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, A.D.; Lockington, D.A. The potential for soil salinization above aquifers influenced by seawater intrusion. In Proceedings of the 13th International Soil Conservation Organisation Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 4–8 July 2004; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bricker, J.D.; Schwanghart, W.; Adhikari, B.R.; Moriguchi, S.; Roeber, V.; Giri, S. Performance of models for flash flood warning and hazard assessment: The 2015 Kali Gandaki landslide dam breach in Nepal. Mt. Res. Dev. 2017, 37, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Mahani, F.F. DEM Uncertainty Based Coastal Flood Inundation Modeling Considering Water Quality Impacts. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 3083–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.J.; Wu, G.F.; Dong, P.; Zhang, K.F. An investigation of the pollutants discharge control strategies in Xiangshan bay based on 3D hydrodynamic and water quality numerical modelling. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2021, 40, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Des, M.; Fernandez-Novoa, D.; deCastro, M.; Gomez-Gesteira, J.L.; Sousa, M.C.; Gomez-Gesteira, M. Modeling salinity drop in estuarine areas under extreme precipitation events within a context of climate change: Effect on bivalve mortality in Galician Rias Baixas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djabelkhir, K.; Lauvernet, C.; Kraft, P.; Carluer, N. Development of a dual permeability model within a hydrological catchment modeling framework: 1D application. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.K.; Hasenmueller, E.A.; Chambers, L.G. Soil as a reservoir for road salt retention leading to its gradual release to groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 83, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Alinaghian, S.; Joksimovic, D.; Chen, L.H. An Integrated Hydraulic and Hydrologic Modeling Approach for Roadside Bio-Retention Facilities. Water 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, P.A.; Hodges, M. Modified tide gate management for enhancing instream habitat for native fish upstream of the saline limit. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, K.B.; Gorelick, S.M. Relating salt marsh pore water geochemistry patterns to vegetation zones and hydrologic influences. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 1729–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Liu, S.L.; Deng, L.; Dong, S.K.; Yang, Z.F.; Liu, Q. Determining the influencing distance of dam construction and reservoir impoundment on land use: A case study of Manwan Dam, Lancang River. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, T.W.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, C.P.; Fan, Y.T.; Qu, L.Q. Effects of rainfall intensity and antecedent soil water content on soil infiltrability under rainfall conditions using the run off-on-out method. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.L.; Wang, X.N.; Ge, M.; Li, C.Y.; Tan, J.L. Characteristics of Vertical Water Infiltration in A Sierozem Soil Soil Moisture of Farmland Gravel-Sand Mulching Condition. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.N.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Li, L.; Jiao, M.Y.; Chen, M.M.; Hou, W.T.; Fu, J.X. Simulation on water infiltration and redistribution of sandy soil improved by sludge. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Han, J.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, W.H. Move characteristics of soil salinity in Saline-Alkali land under impounding and draining conditions. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.H.; Wang, X.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S. Denitrification of soil nitrogen in coastal and inland salt marshes with different flooding frequencies. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 97, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Zhou, T.Z.; Lu, C.H.; Shen, C.J.; Zhang, C.M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Li, L. Combined effects of tides, evaporation and rainfall on the soil conditions in an intertidal creek-marsh system. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.W.; Bai, J.H.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Lu, Q.Q.; Zhang, S.Y. Profile differentiation of soil salinity for natural and anthropogenic disturbance wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 438–448. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).