Land-Greening Hotspot Changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt during the Last Four Decades and Their Connections to Human Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
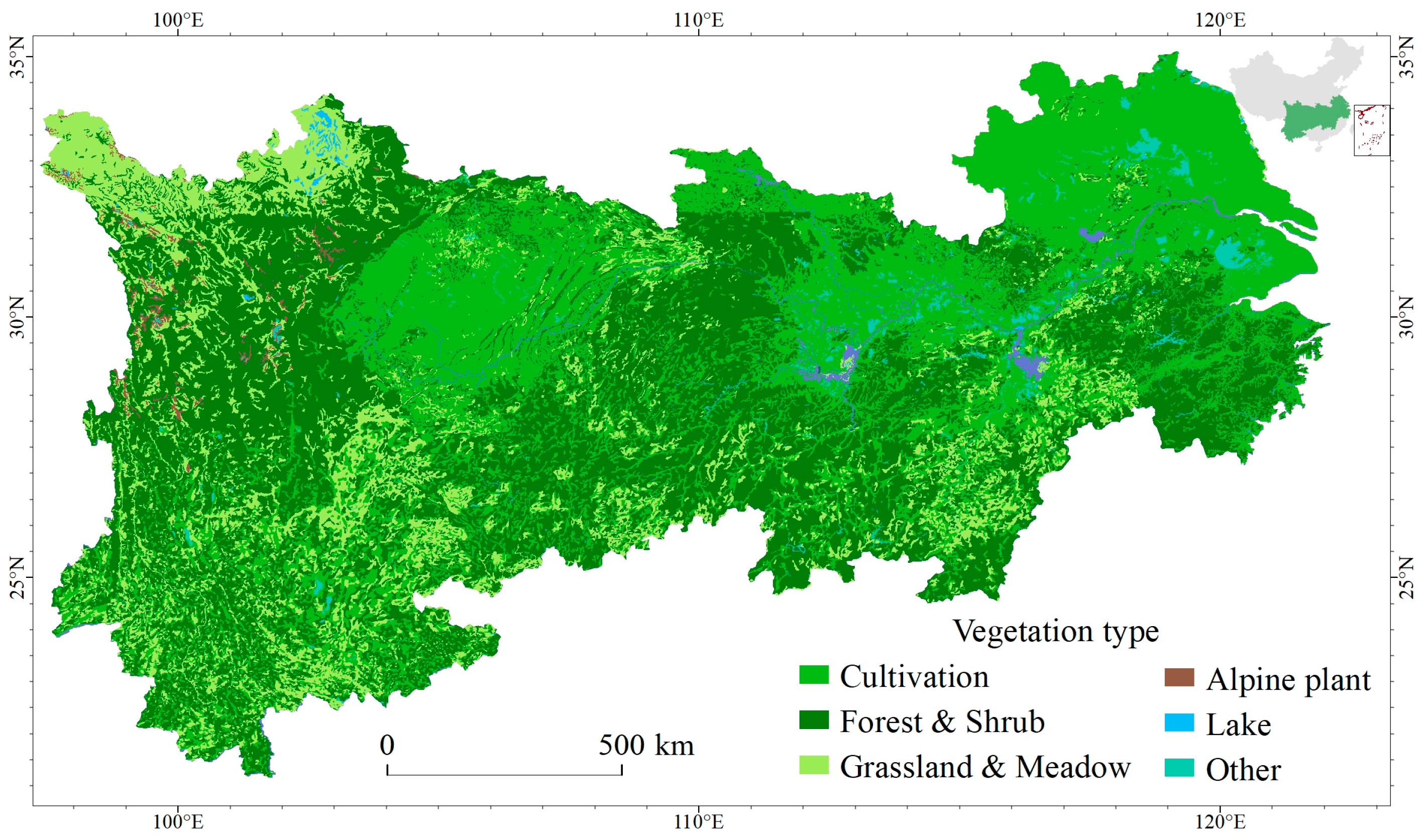
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. NDVI Dataset
2.2.2. Meteorology Data
2.2.3. Social and Economic Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. NDVI Prediction in the Growing Season with Temperature and Precipitation
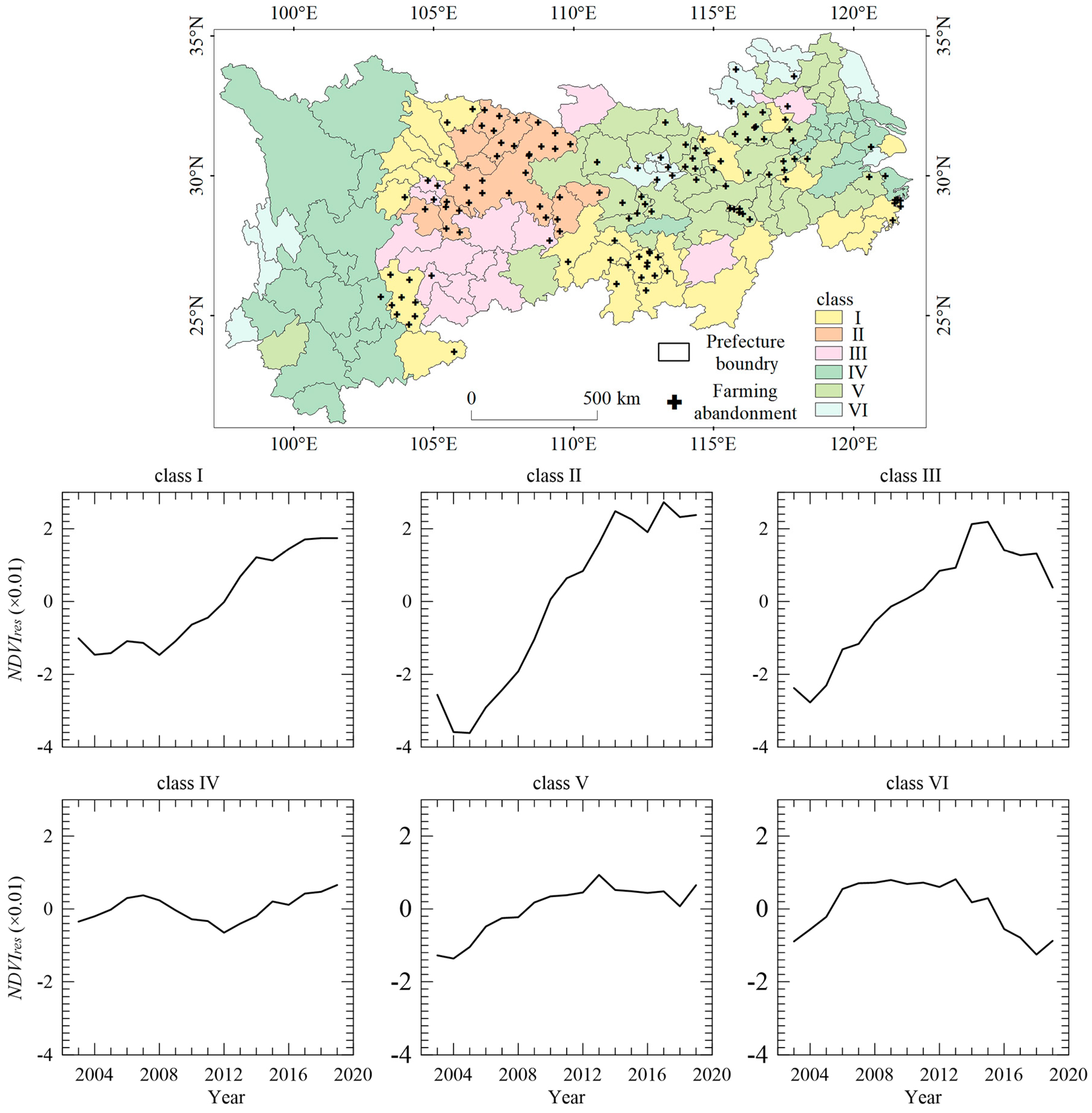
2.3.2. Cluster Analysis of the NDVIres TIME Serials
3. Results
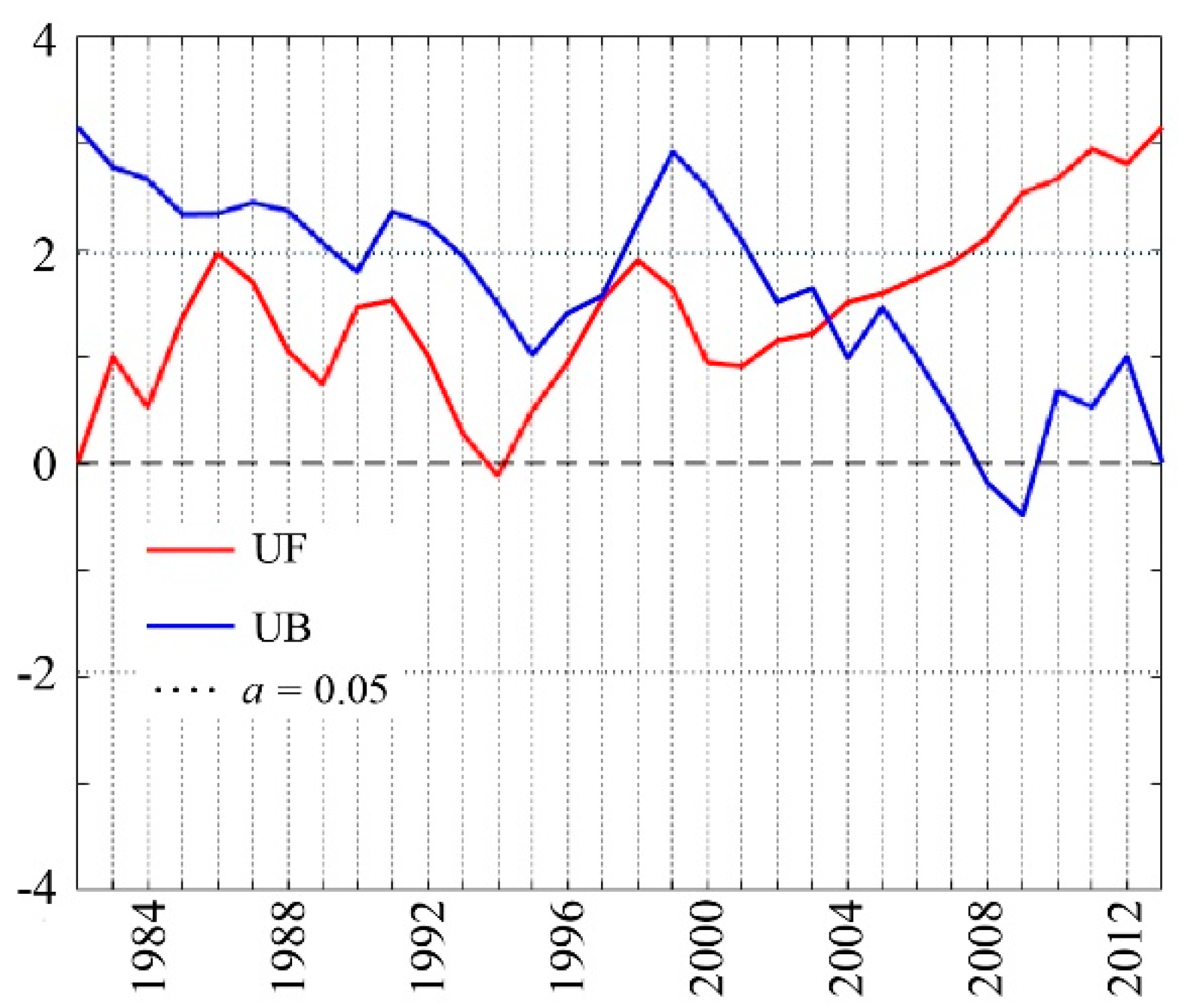
3.1. Temporal Variations in NDVI and the Spatial Pattern
3.1.1. Temporal Variations of the Regional Mean NDVI Values
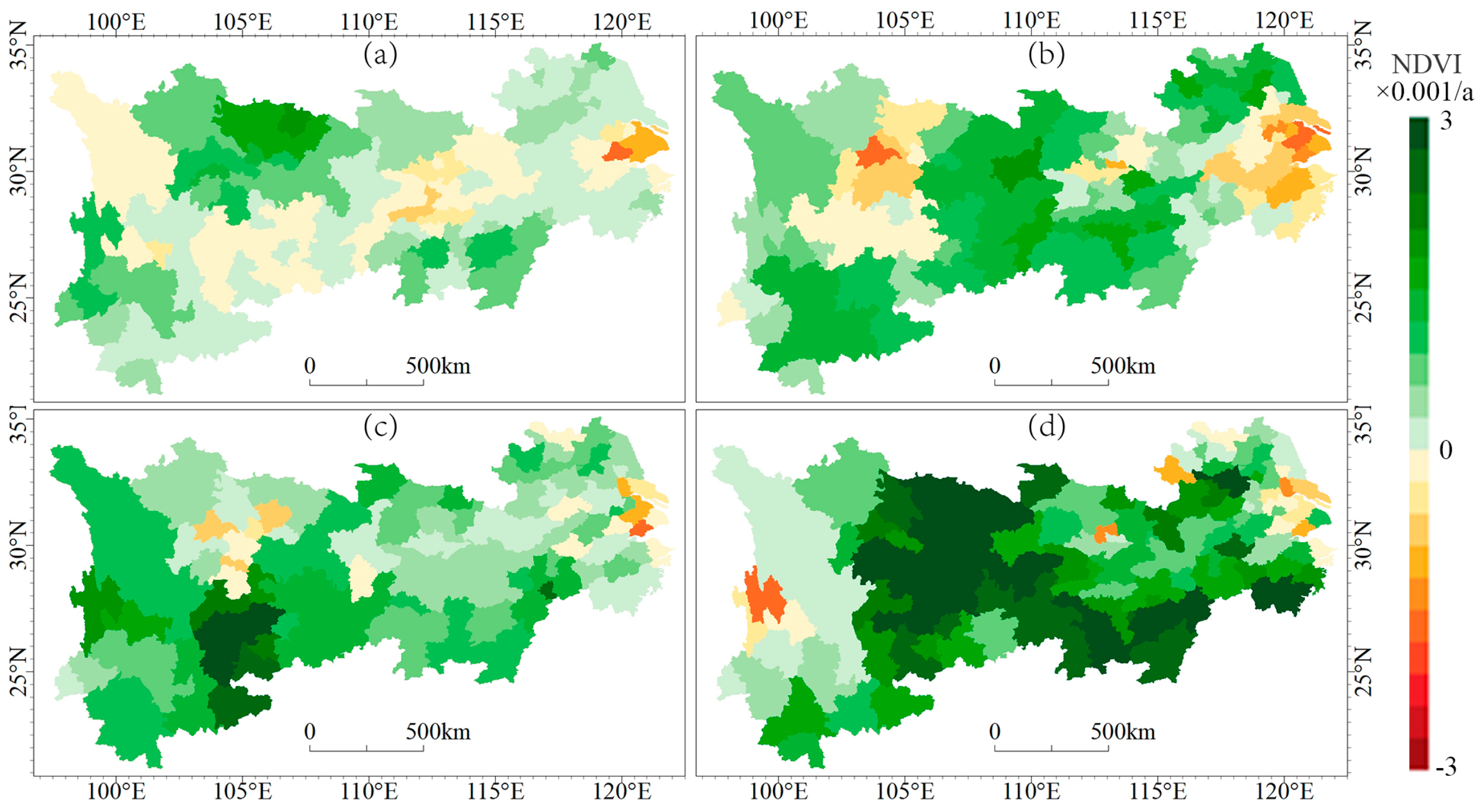
3.1.2. Spatial Variations of NDVI Trends during the Warm Season
3.2. Variations of NDVI with Climate Factors
3.3. The Modes of the Changes in the NDVIres
3.4. The Agriculture Status behind the NDVIres Uptrend from 2003 to 2019
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Ding, G. Response of soil respiration and Q10 to temperature and moisture in naturally regenerated and bare lands based on an 11-year observation period. CATENA 2022, 208, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, Z.; Shen, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Yan, R.; Yan, Y.; Xin, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, M.; et al. Spatial patterns and driving factors of aboveground and belowground biomass over the eastern Eurasian steppe. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, R.; Smettem, K. Runoff change induced by vegetation recovery and climate change over carbonate and non-carbonate areas in the karst region of South-west China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Adiku, S.; Tenhunen, J.; Granier, A. On the relationship of NDVI with leaf area index in a deciduous forest site. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.; Li, J.; Chen, Y. An Analysis of Angle-Based With Ratio-Based Vegetation Indices. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, L.; Bégué, A.; Seen, D.L.; Jolivot, A.; Kayitakire, F. Driving forces of recent vegetation changes in the Sahel: Lessons learned from regional and local level analyses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Yi, F.; Zhou, C. Quantifying influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on vegetation changes using structural equation modeling: A case study in Jiangsu Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, F.; Hu, H.C.; Sivapalan, M. Soil moisture controls on patterns of grass green-up in Inner Mongolia: An index based approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Daun, C.; Yuan, L.; Rao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, W. Assessment of the restoration of a degraded semi-humid evergreen broadleaf forest ecosystem by combined single-indicator and comprehensive model method. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Innes, J.L.; Wang, G.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Myneni, R.B. Changes in Vegetation Growth Dynamics and Relations with Climate over China’s Landmass from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3263–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wen, Z. The impacts of land conversion and management measures on the grassland net primary productivity over the Loess Plateau, Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Wei, J.-Z.; Pei, J.-Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.-L.; Huang, F.-Q.; Li, F.-M.; Ye, J.-S. Impacts of climate change and human activities on grassland vegetation variation in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y. Changes in Growing Season Vegetation and Their Associated Driving Forces in China during 2001–2012. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15517–15535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, S.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, M. What drives the vegetation restoration in Yangtze River basin, China: Climate change or anthropogenic factors? Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gang, C.; An, R.; Li, J. Vegetation dynamics and its driving forces from climate change and human activities in the Three-River Source Region, China from 1982 to 2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Anyamba, A.; Tucker, C.J. Recent trends in vegetation dynamics in the African Sahel and their relationship to climate. Glob. Environ. Change 2005, 15, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, S.; Xu, M.; Qin, Y.; Chen, S.; Ye, B. Effects of permafrost degradation on alpine grassland in a semi-arid basin on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 045403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X. Characterization of elevation and land cover dependent trends of NDVI variations in the Hexi region, northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Xiang, F.; Qin, W.; Jiang, W. Vegetation dynamics and the relations with climate change at multiple time scales in the Yangtze River and Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Guli·jiapaer, G.; Bao, A.; Guo, H.; Ndayisaba, F. Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Dai, E.; Zheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Tong, M. What drives the vegetation dynamics in the Hengduan Mountain region, southwest China: Climate change or human activity? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wu, J.; Huang, J. Distinguishing between human-induced and climate-driven vegetation changes: A critical application of RESTREND in inner Mongolia. Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Li, J. Impacts of Precipitation and Temperature on Changes in the Terrestrial Ecosystem Pattern in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, G.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, Q.; Hao, F. Contributions of climate change to eco-compensation identification in the Yangtze River economic Belt, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Li, B.-L.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. The development of China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: How to make it in a green way? Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Q.; Song, Y. Does China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt policy impact on local ecosystem services? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Total-factor ecological efficiency and productivity in Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: A non-parametric distance function approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; He, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Urban Land-Use Expansion: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Cai, Z.; Fu, Z. Does the new-type urbanization construction improve the efficiency of agricultural green water utilization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64103–64112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Venevsky, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, M. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and its response to climate changes at Amur-Heilongjiang River Basin from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Mbow, C. Evaluation of earth observation based long term vegetation trends—Intercomparing NDVI time series trend analysis consistency of Sahel from AVHRR GIMMS, Terra MODIS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Fensholt, R.; Verbesselt, J.; Grogan, K.; Horion, S.; Wang, Y.J. Evaluating temporal consistency of long-term global NDVI datasets for trend analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, A.; Eklundh, L.; Hellström, M.; Bärring, L.; Jönsson, P. Annual changes in MODIS vegetation indices of Swedish coniferous forests in relation to snow dynamics and tree phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, T.; Mount, D.M.; Netanyahu, N.S.; Piatko, C.D.; Silverman, R.; Wu, A.Y. An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yao, R.; Gui, X.; Xiang, F.; Ji, Y. Impacts of Drought and Climatic Factors on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yellow River Basin and Yangtze River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, K.; Yue, Y.; Brandt, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, C.; Liao, C.; Fensholt, R. Quantifying the effectiveness of ecological restoration projects on long-term vegetation dynamics in the karst regions of Southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, H. Responses of Natural Vegetation Dynamics to Climate Drivers in China from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10243–10268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.-m.; Wen, Z.-g. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Dong, J.; Ge, Q. Spatio-Temporal pattern of cropland abandonment in China from 1992 to 2017: A Meta analysis. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Ge, J. Assessing Vegetation Cover Dynamics Induced by Policy-Driven Ecological Restoration and Implication to Soil Erosion in Southern China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Smettem, K.; Wang, T. Climate and land use influences on changing spatiotemporal patterns of mountain vegetation cover in southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, X. Effective Monitoring and Evaluation of Grain for Green Project in the Upper and Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R.; Fleming, C.S.; Pavuluri, K.; Alley, M.M.; Reiter, M.S.; Thomason, W.E. Influence of soil, crop residue, and sensor orientations on NDVI readings. Precis. Agric. 2015, 16, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, A.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Bernacchi, C.; Rogers, A.; Long, S.; Ort, D.R. Elevated CO2 effects on plant carbon, nitrogen, and water relations: Six important lessons from FACE. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2859–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Van Dijk, A.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Canadell, J.; McCabe, M.; Evans, J.; Wang, G. Recent reversal in loss of global terrestrial biomass. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Rogers, A. The response of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance to rising [CO2]: Mechanisms and environmental interactions. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Roderick, M.L.; Zhang, S.; McVicar, T.; Donohue, R.J. Hydrologic implications of vegetation response to elevated CO2 in climate projections. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Chen, S.; Su, H. Climate Dynamics of the Spatiotemporal Changes of Vegetation NDVI in Northern China from 1982 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B.; Doney, S.C. Climate, ecosystems, and planetary futures: The challenge to predict life in Earth system models. Science 2018, 359, eaam8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, J.; Konings, A.G.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Berry, J.; Entekhabi, D.; Kolassa, J.; Lee, J.-E.; Gentine, P. Regionally strong feedbacks between the atmosphere and terrestrial biosphere. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Province | SC | CQ | GZ | HB | HN | JX | AH | ZJ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | |||||||||
| 2002–2006 | 8.02 | 10.84 | 4.59 | 10.13 | 9.24 | 8.23 | 7.68 | 23.82 | |
| 2007–2011 | 18.62 | 24.43 | 11.66 | 24.2 | 21.61 | 18.79 | 17.89 | 46.61 | |
| 2012–2016 | 33.53 | 48.04 | 26.55 | 46.85 | 38.42 | 33.04 | 34.06 | 73.58 | |
| Province | SC | CQ | GZ | HB | HN | JX | AH | ZJ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | |||||||||
| 2000 | 77.6 | 72.8 | 81.8 | 66.4 | 75 | 68.4 | 75 | 33.7 | |
| 2010 | 60.2 | 50.3 | 68.9 | 53.1 | 55.9 | 44.4 | 54.2 | 14.7 | |
| 2016 | 38.6 | 28.9 | 57.3 | 36.8 | 40.7 | 30 | 31.7 | 12.4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X. Land-Greening Hotspot Changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt during the Last Four Decades and Their Connections to Human Activities. Land 2022, 11, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050605
Zhang L, Luo H, Zhang X. Land-Greening Hotspot Changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt during the Last Four Decades and Their Connections to Human Activities. Land. 2022; 11(5):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050605
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liangsheng, Haijiang Luo, and Xuezhen Zhang. 2022. "Land-Greening Hotspot Changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt during the Last Four Decades and Their Connections to Human Activities" Land 11, no. 5: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050605
APA StyleZhang, L., Luo, H., & Zhang, X. (2022). Land-Greening Hotspot Changes in the Yangtze River Economic Belt during the Last Four Decades and Their Connections to Human Activities. Land, 11(5), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11050605






