Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Rural Settlements in Metropolitan Fringe Area: A Case Study of Nanjing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What are the distribution characteristics of rural settlements in the metropolitan fringe area? Using R statistic, kernel density analysis, hotspot detection analysis and semi-variogram, from three different dimensions: scale distribution, space distribution and morphological distribution, this paper analyzed the spatial distribution characteristics of rural settlements in the metropolitan fringe area.
- What are the factors affecting the distribution of rural settlements in the metropolitan fringe area? On the basis of theoretical analysis of influencing factors, terrain, river system, traffic, economic, social development, cultural and policy factors were adopted to analyze the internal relationship between them and the distribution of rural settlements, and revealed the influencing mechanism of the distribution pattern of rural settlements in the metropolitan fringe area.
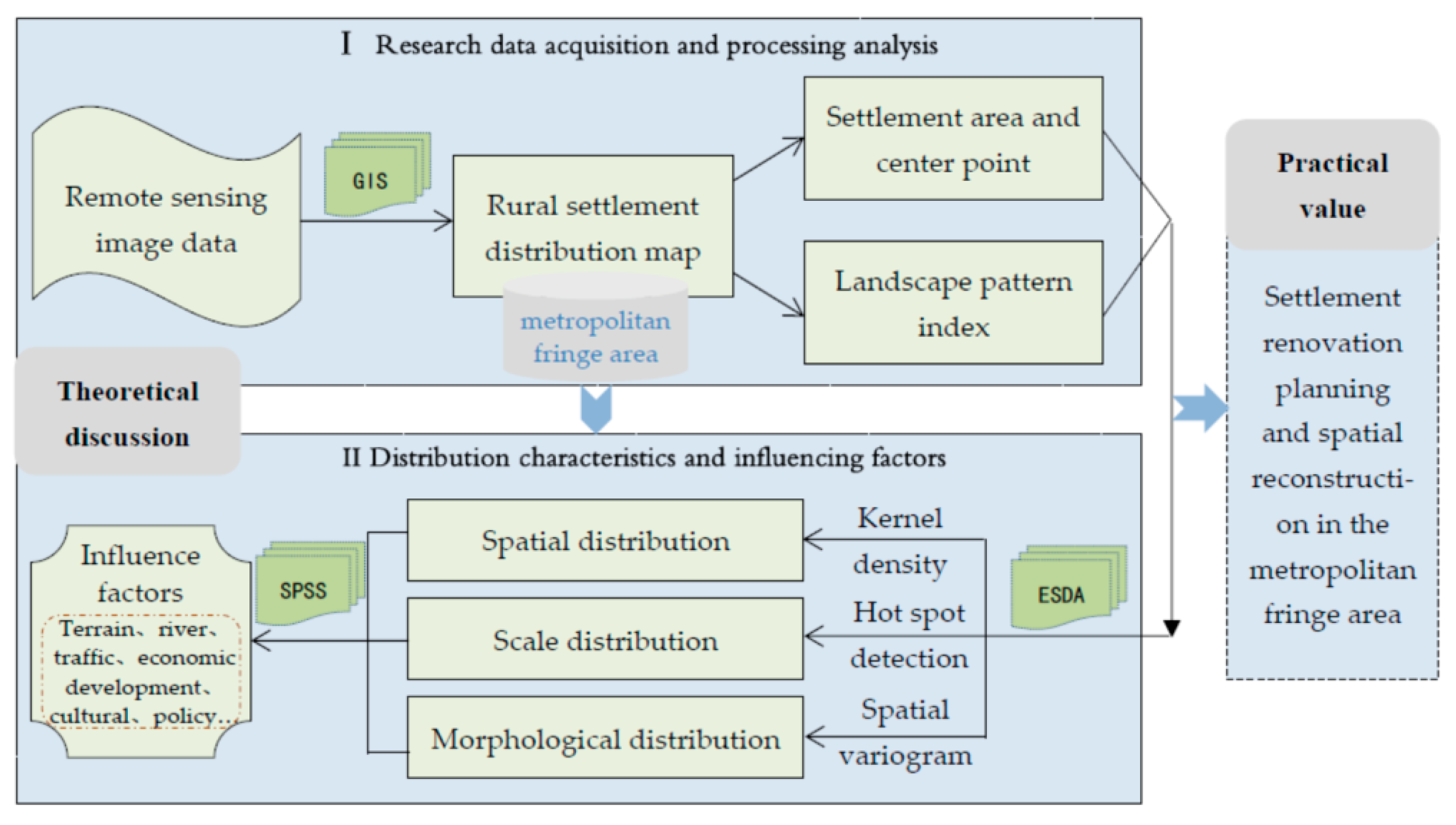
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. R Statistics
2.2.2. Kernel Density Analysis
2.2.3. Hot Spot Detection Analysis
2.2.4. Semi Variant Function
2.3. Data Collection
3. Results
3.1. Distribution Characteristics
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Rural Settlements
3.1.2. Scale Distribution Characteristics of Rural Settlements
3.1.3. Morphological Distribution Characteristics of Rural Settlements
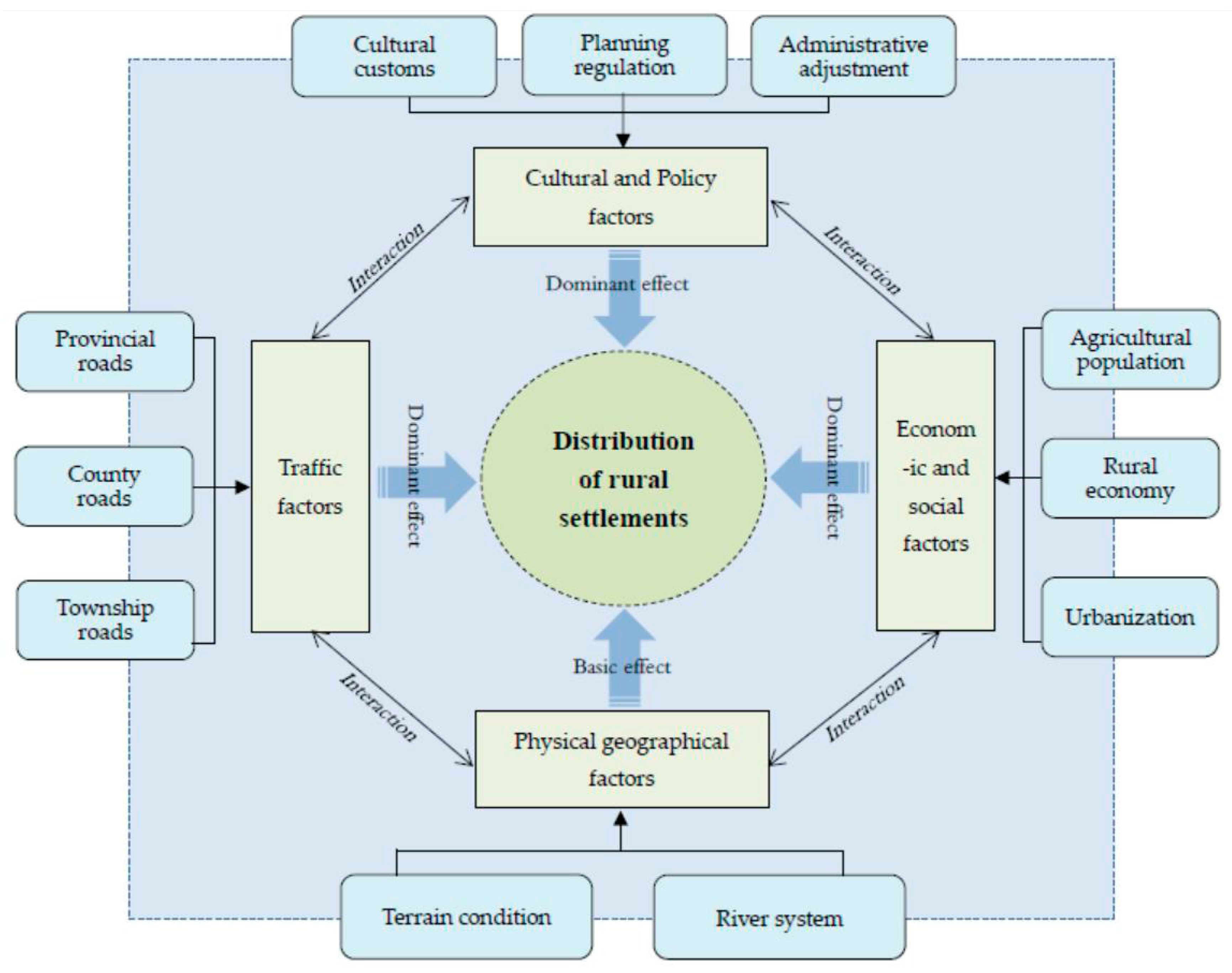
3.2. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.2.1. Rural Settlements Distribution and Terrain Factors
3.2.2. Rural Settlement Distribution and River System Factors
3.2.3. Rural Settlement Distribution and Traffic Factors
3.2.4. Rural Settlement Distribution and Economic Social Development Factors
3.2.5. Rural Settlement Distribution and Cultural Policy Factors
4. Discussion
- Urban transformation type. This type refers to the rural settlements distributed at the edge of the county seat and the central town and near the main traffic arteries. Suggestions for optimizing layout: bring rural residential areas close to built-up areas or central towns into the urban planning system, actively guide the transformation of rural residential areas into urban residential areas, increase the construction of transportation and other infrastructure, emphasize the functional zoning of internal land, and form an all-round and multi-level land use pattern.
- Key development type. This model mainly refers to the rural settlements which are far away from the urban center, large scale, transportation location and good level of economic development. Suggestions for optimizing layout: the rural residential areas with small scale and poor conditions in towns and townships should be relocated to the central village nearby, focusing on the construction of the central village within the city scope; and improve the basic and public service facilities of central village, based on the resource advantages of central village, develop and expand the characteristic industries, attract the surrounding small natural villages to gather in the central village.
- Limited development type. On the premise of the stability of the original spatial pattern of rural residential areas, this type of rural residential areas should be rebuilt and reasonably developed. Through promoting the renovation and construction of rural residential areas, the potential of the village’s internal land use should be fully exploited, and the village, especially the hollow village, should effectively “lose weight” to improve the intensive use of rural residential land in hilly areas.
- Relocation type. This type of rural residential area is mostly located in areas with poor suitability level of urban residential areas, with shortage of cultivated land resources, inconvenient transportation and more villagers going out to work. Suggestions for optimizing layout: gradually move to another place by taking multiple approaches such as urban resettlement, central village resettlement, small villages merging into large villages and building independent new villages.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.H. Revitalize the world’s countryside. Nature 2017, 548, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, A. Valuing the outputs of multifunctional agriculture. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2002, 29, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.S. Rural restructuring in China. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 47, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, X.L.; Chen, K.L.; Li, Z.G.; Lin, S.N. Characteristics and influencing factors of spatial restructuring of rural settlements in Wuhan City. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 180–189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J.; Hu, X.Y.; Shi, Y.W.; Yang, H.M. The role of rural settlements in rural revitalization: Perspective of economic geography. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, L. Progress in rural geography. Prof. Geogr. 1983, 36, 124–125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.X.; Chen, X.J. Geographical researches on rural settlements: Review and prospect. World Reg. Stud. 1994, 1, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, S.; Herlin, I.S. A sustainable development framework for a landscape of dispersed historic settlement. Landsc. Res. 2009, 34, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trukhachev, A. Methodology for evaluating the rural tourism potentials: A tool to ensure sustainable development of rural settlements. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3052–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, W.H. Transformation of rural settlement in Bulgaria. Geogr. Rev. 1964, 54, 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Brendan, M.G. The sustainability of a car dependent settlement pattern: An evaluation of new rural settlement in Ireland. Environmentalist 1998, 19, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Zhang, X.L. A review and trend on rural settlement geography abroad. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 27, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ruda, G. Rural buildings and environment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1998, 41, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigmore, P. Rural process-pattern relationships: Nomadization, sedentarization and settlement fixation. Geogr. J. 1994, 16, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M. Researching rural conflicts: Hunting, local politics and actor-networks. J. Rural Stud. 1997, 14, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, S. Sustainable rural geographies. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 1993, 17, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eva, K. Rural restructuring in hungary in the period of socio-economic transition. GeoJournal 2000, 51, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- David, L.B. Post-socialist restructuring and population redistribution in hungary. Rural Sociol. 2005, 70, 336–359. [Google Scholar]
- Barosova, I.; Santruckova, M.; Matiska, P.; Baros, A. Ornamental perennials in small rural settlements: A case study from the Czech Republic. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 47, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J. Impulses towards a multifunctional transition in rural Australia: Gaps in the research agenda. J. Rural Stud. 2006, 22, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.C. A location theory for rural settlement. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1969, 59, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisler, M.I.; Kirch, P.V. The structure of settlement space in a Polynesian chiefdom: Kawela, Molokai, Hawaiian Islands. N. Z. J. Archaeol. 1985, 7, 129–158. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, C.; Rudloff, M.; Abdullaev, I.; Thiel, M.; Low, F. Measuring rural settlement expansion in Uzbekistan using remote sensing to support spatial planning. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 62, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallarati, M. Built landscape typological components. In INTBAU International Annual Event; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1045–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Prus, B.; Wilkosz-Mamcarczyk, M.; Salata, T. Landmarks as cultural heritage assets affecting the distribution of settlements in rural areas-An analysis based on LIDAR DTM, digital photographs, and historical maps. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, C.; Sofer, M. Land use changes in the rural-urban fringe: An Israeli case study. Land Use Policy 2013, 33, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibilev, A.A.; Akhmetov, R.S. Cluster differentiation of municipal districts of Orenburg oblast by features of rural settlement pattern. Reg. Res. Russ. 2015, 5, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulent, Y.; Dasdemir, I.; Atmis, E. Factors affecting rural development in turkey: Bartin case study. For. Policy Econ. 2010, 12, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Argen, N.M.; Smailes, P.J.; Griffin, T. Tracing the density impulse in rural settlement systems: A quantitative analysis of the factors underlying rural population density across South-Eastern Australia. Popul. Environ. 2005, 27, 151–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, A.; Wesolowska, M. Deagrarianisation of the economic structure and the evolution of rural settlement patterns in Poland. Land 2021, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarini, L. The role of planning in shaping better urban-rural relationships in Bristol city region. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.M. The history and current trends of research on rural settlement geography in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1988, 55, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, B.L.; Gao, J.B.; Gao, Y.; Cai, W.M.; Zhang, F.R. Land use transition of mountainous rural areas in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 503–517. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Wu, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.H. Characteristics and mechanism of rural settlements spatial reconstruction in developed areas—A case study of Southern Jiangsu. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 591–603. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Zhu, J.G.; Qiao, J.J. Research progress and prospect on Chinese rural settlement. Hum. Geogr. 2016, 31, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Liu, Y.S.; Long, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.J. Spatial distribution characteristics and optimized reconstructing analysis of rural settlement in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.S.; Wu, X.Q.; Dong, G.H. Spatio-temporal dynamic patterns of farmland and rural settlements in Su-Xi-Chang region: Implications for building a new countryside in coastal China. Land Use Policy 2008, 26, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.H.; He, Y.H.; Tang, C.L.; Yu, T.; Xiao, G.Y. Dynamic mechanism and present situation of rural settlements evolution in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Liu, S.Q.; Huang, M.; Cao, S.; Yu, H. Driving forces for the spatial reconstruction of rural settlements in mountainous areas based on structural equation models: A case study in Western China. Land 2021, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis on the evolution of rural settlement pattern and its influencing factors in China from 1995 to 2015. Land 2021, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.B.; Guo, X.D.; Zhang, Q.Y. Spatio-temporal distribution and optimization of rural settlements in Gangu county of loess hilly area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.X. The rural settlement morphological types and spatial system characteristics in the Jianghan Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, S.S.; Long, H.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhou, X.Y. Process and driving factors of rural restructuring in typical villages. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 323–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Li, S.Y.; Zhen, J. The evolution and mechanism of Guangdong Zengcheng Hakka settlements. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.D.; Li, Q.L.; Shen, Y. Morphological difference and regional types of rural settlements in Jiangsu Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 516–525. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.R.; Li, J.T. Conversion from rural settlements and arable land under rapid urbanization in Beijing during 1985–2010. J. Rural. Stud. 2017, 51, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Ma, L.B.; Zhang, W.B.; Gong, M. Differentiation and correlation of spatial pattern and multifunction in rural settlements considering topographic gradients: Evidence from Loess Hilly Region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.D.; Niu, S.W.; Wu, W.H.; Ma, L.B. Characters of rural settlement spatial distribution and its influence factors in Loess hilly area of Gansu Province. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2010, 24, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.P.; Liu, L.M.; Fu, Y.H.; Yuan, C.C.; Song, Z.J. Analysis of characteristic and influencing factors of rural settlement landscape pattern in metropolitan suburbs. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.K.; Luo, J.; Luo, M.H.; Tian, L.L.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.Y. Analysis of spatial pattern of rural settlements in metropolitan areas: A case study of Wuhan. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Cai, J.M. The evolution and reconstruction of peri-urban rural habitat in China. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 1272–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Linacre, J.M. R Statistics: Survey and review of packages for the estimation of Rasch models. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2022, 13, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.T.; Wu, F.N.; Ren, P. Study on spatial pattern evolvement and features of rural settlement based on GIS. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 20, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.W.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.J.; Fu, T.L.; Yang, Y.X. Analysis of the characteristics and spatial pattern of the catering industry in the four central cities of the Yangtze River Delta. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, E.; Forget, T.; Barbaresco, F.; Angulo, J. Kernel density estimation on the siegel space with an application to radar processing. Entropy 2017, 18, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartone, A.; Casolani, N.; Liberatore, L.; Postiglione, P. Spatial analysis of grey water in Italian cereal crops production. Land Use Policy 2017, 68, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Fennell, S.; Luan, B.; Wang, F.; Meng, D.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, L.; et al. Spatial-temporal dynamics of grain yield and the potential driving factors at the county level in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, F.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Z.P.; Xiong, H.G.; Han, F.; Wang, Z.G. Temporal-spatial variability of tourism festivals and its mechanism in Shandong Province during 1990–2011. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 940–949. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero, A.; Unowicz, B.; Lipiec, J. Effects of tractor traffic on spatial variability of soil strength and water content in grass covered and cultivated sloping vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 84, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscha, M.S.; Ferreirab, M.E. The role of the rural settlements in the Brazilian savanna deforesting process. J. Land Use Sci. 2017, 12, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.B.; Li, H.; Wang, D.Y.; Liu, S.H. Optimization of rural settlement distributions based on the ecological security pattern: A case study of Da’an City in Jilin Province of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R. An analysis of rural settlement patterns and their effect mechanisms based on road traffic accessibility of Guangdong. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.Y. The suitability evaluation of social and economic factors on the location of rural settlement—Take Erhai Rim Region of Yunnan for example. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Li, H.B.; Hu, Z.Y.; Wen, Y.L.; Che, J.L. An evaluation and optimization of the spatial pattern of county rural settlements: A case study of Changshu City in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land 2022, 11, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I.A.; Sofer, M. Integrated rural heritage landscapes: The case of agricultural cooperative settlements and open space in Israel. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 54, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Yang, H.M. The Change of rural settlements and their future development patterns. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.A.; Zhao, M.D. A GIS based research on the distribution of rural settlements-Taking Yulin area as an example. Econ. Geogr. 2000, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.D.; Ma, L.B.; Zhang, Q.Y. The spatial distribution characteristics and the basic types of rural settlement in Loess Hilly Area: Taking Qin’an County of Gansu Province as a case. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.B.; Tian, Y.Y.; Xie, Z.L.; Guo, X.D.; Gu, Y. Evaluation of quality and spatial reconstruction of oasis rural settlements based on micro-scale. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, X.J.; Kong, X.S.; Liu, G.G. Restructuring rural settlements based on subjective well-being (SWB): A case study in Hubei province, central China. Land Use Policy 2017, 63, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.X.; Xu, Y.Q.; Lu, L.H.; Duan, Y.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, A. Research progress and prospects for spatial optimization of rural settlements. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; He, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zeng, S.; Xiao, L. Optimizing the spatial organization of rural settlements based on life quality. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Indicators | a | C + C0 | C0 | Fitting Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter value | 797,024 | 0.0402 | 0.0378 | Gaussian | 0.895 |
| Type | Distribution | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Strip type | It is mainly distributed in Qixia District, such as Liudong Village, Shuangqiao Village, Wangpeng Village. | The river network is dense, and the agricultural production mode is mainly traditional paddy field planting. The cultivation radius is small, and the distribution along the riverbank highland is in the form of strip extension. |
| Arcbelt type | It is mainly distributed in Gaochun District, such as Shangshang Village, Laozhuang Village, Xinyang Village. | The settlements are built along the river, affected by the trend of the river, the rural settlements are arc-shaped. The farming radius is large and the village scale is small, but tspatial layout is compact. |
| Cluster type | It is mainly distributed in Lishui District and Jiangning District, such as Qingwei Village, Jiufangdian Village. | The cultivated land is rich and has a large farming radius, which is easy to form large-scale settlements. The rural settlements have a regular shape, a large distribution density and a cluster distribution rural settlement pattern. |
| Scatter type | It is mainly distributed in Luhe District and Pukou District, such as Hewang Village, Xialiang Village. | The cultivated land resources are relatively rich, and the river system is relatively developed. However, affected by the hilly terrain, the distribution pattern of small and medium density scattered rural settlements has been formed. |
| Altitude | Area (km2) | Density (Units/km2) | Distance Index (Units/km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤100 m | 20,345 | 0.56 | 0.32 |
| 100~200 m | 18,973 | 0.52 | 0.35 |
| 200~300 m | 10,294 | 0.43 | 0.44 |
| 300~400 m | 5903 | 0.33 | 0.47 |
| ≥400 m | 1003 | 0.15 | 0.55 |
| Minimum Distance | Number of Plaques (Units) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| ≤500 m | 8786 | 48.78 |
| 500 m < D ≤ 1000 m | 5893 | 32.71 |
| 1000 m < D ≤ 1500 m | 2134 | 11.84 |
| 1500 m < D ≤ 2000 m | 876 | 4.86 |
| 2000 m < D ≤ 2500 m | 239 | 1.32 |
| 2500 m < D ≤ 3000 m | 86 | 0.48 |
| Common Factor | Characteristic Value | Contribution Rate | Cumulative Contribution Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.52 | 58.76 | 58.76 |
| 2 | 4.88 | 27.93 | 86.69 |
| Variable | Amount of Load | |
|---|---|---|
| The Common Factor 1 | The Common Factor 2 | |
| Total agricultural population X1 | 0.983 | −0.343 |
| Total grain output X2 | 0.563 | −0.422 |
| Agricultural income X3 | 0.523 | 0.936 |
| Rural labor force X4 | 0.974 | 0.378 |
| Per capita net income of farmers and herdsmen X5 | 0.632 | 0.902 |
| Total output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery X6 | −0.453 | 0.927 |
| Primary industry income X7 | 0.378 | 0.785 |
| Secondary industry income X8 | 0.403 | 0.893 |
| Urbanization rate X9 | 0.945 | 0.342 |
| Population density X10 | 0.967 | −0.203 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhang, X. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Rural Settlements in Metropolitan Fringe Area: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Land 2022, 11, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11111989
Zhang R, Zhang X. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Rural Settlements in Metropolitan Fringe Area: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Land. 2022; 11(11):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11111989
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rongtian, and Xiaolin Zhang. 2022. "Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Rural Settlements in Metropolitan Fringe Area: A Case Study of Nanjing, China" Land 11, no. 11: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11111989
APA StyleZhang, R., & Zhang, X. (2022). Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Rural Settlements in Metropolitan Fringe Area: A Case Study of Nanjing, China. Land, 11(11), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11111989








