Identifying Driving Factors of Basin Ecosystem Service Value Based on Local Bivariate Spatial Correlation Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
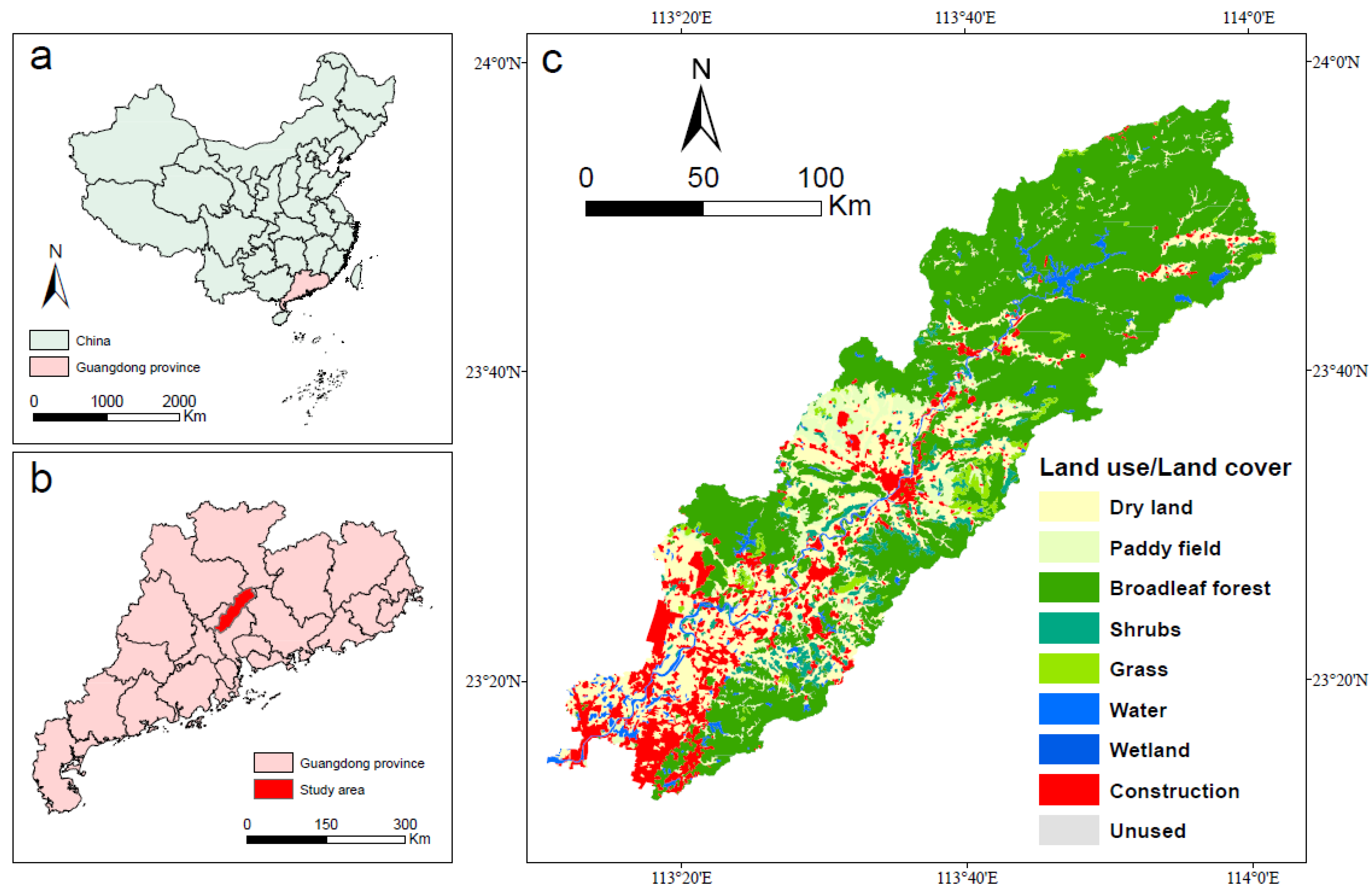
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
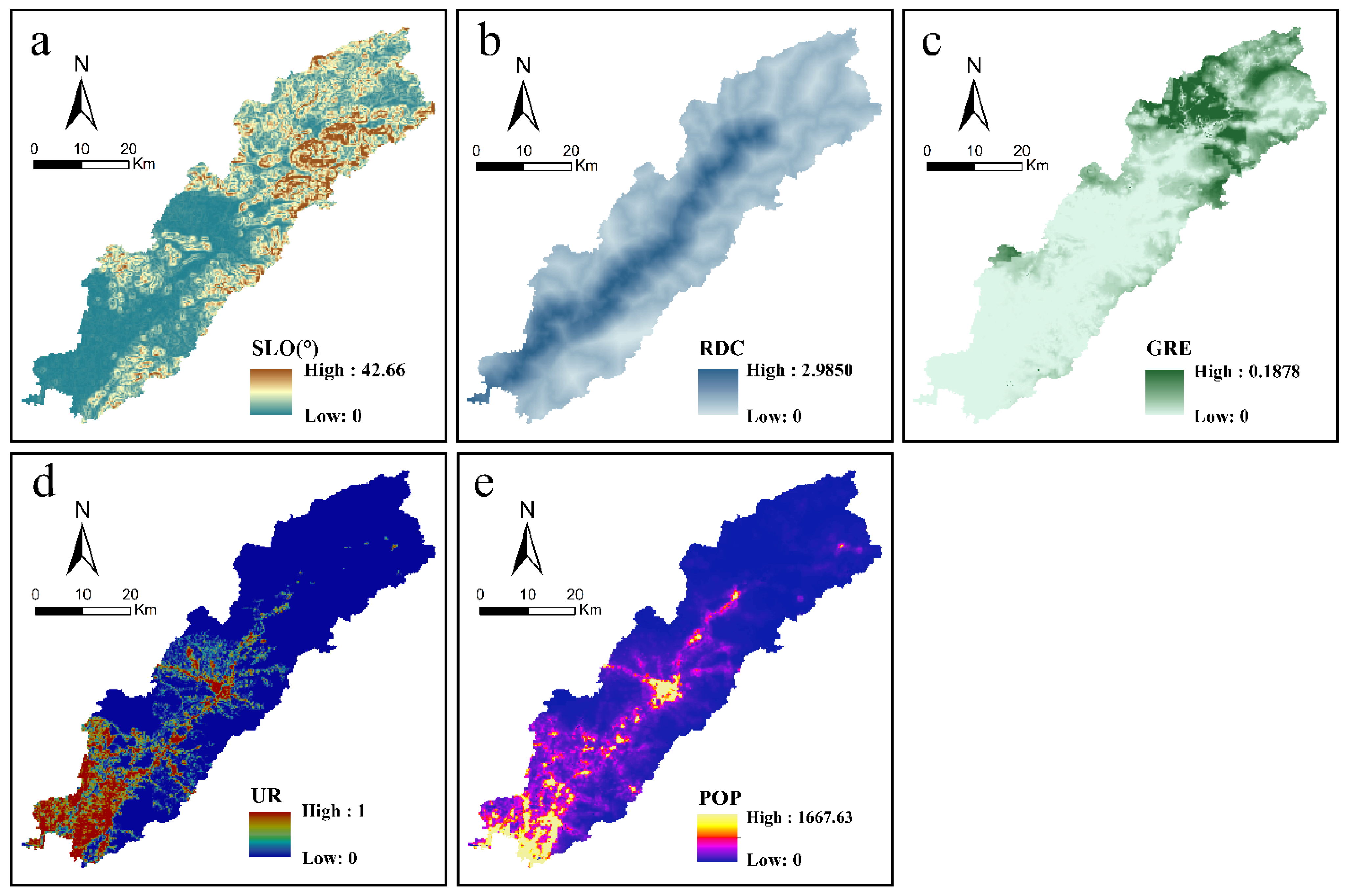
2.3. Driving Factors Selection and Data Processing
3. Methodology
3.1. Estimation of Ecosystem Service Value
3.1.1. Calculation of ESV
3.1.2. Correction of Equivalent Factor
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
3.2.1. Univariate Spatial Autocorrelation
3.2.2. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation
3.3. Spatial Heterogeneity
3.3.1. GDM Factor Detection
3.3.2. GDM Interaction Detection
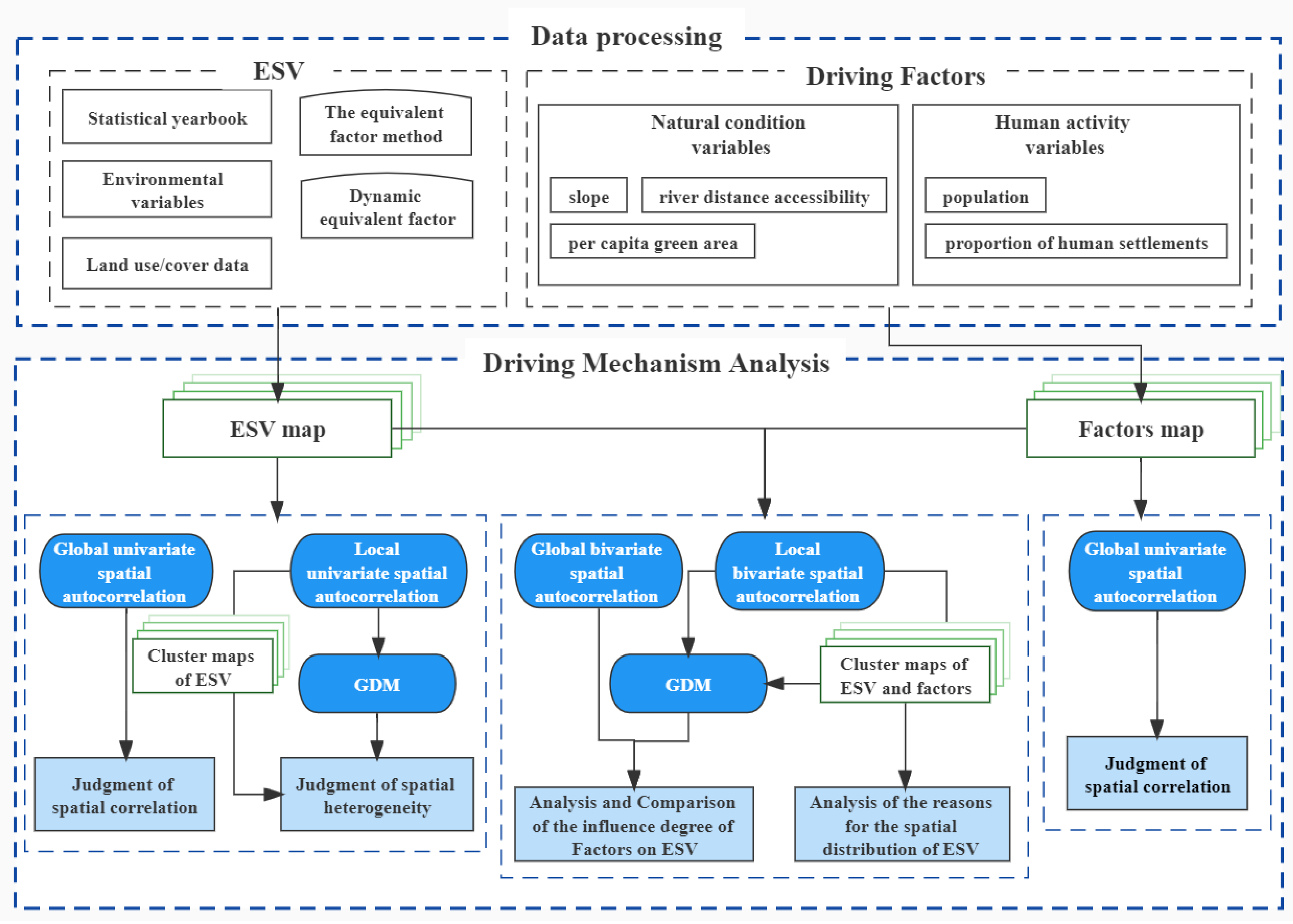
3.4. Research Framework
4. Results and Analysis
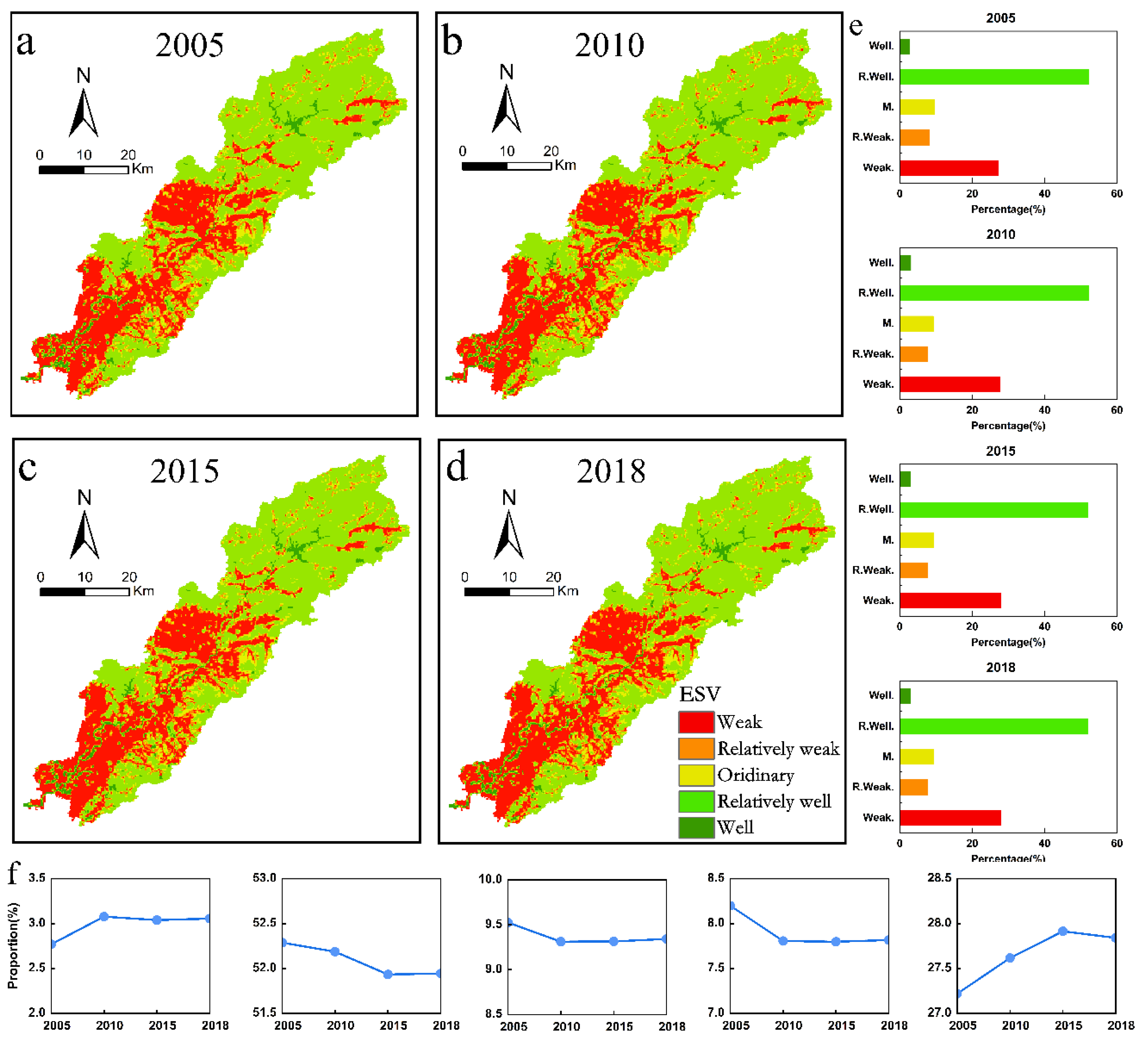
4.1. The Spatiotemporal Characteristics of ESV
4.2. Correlation Analysis Results of Spatial Factors
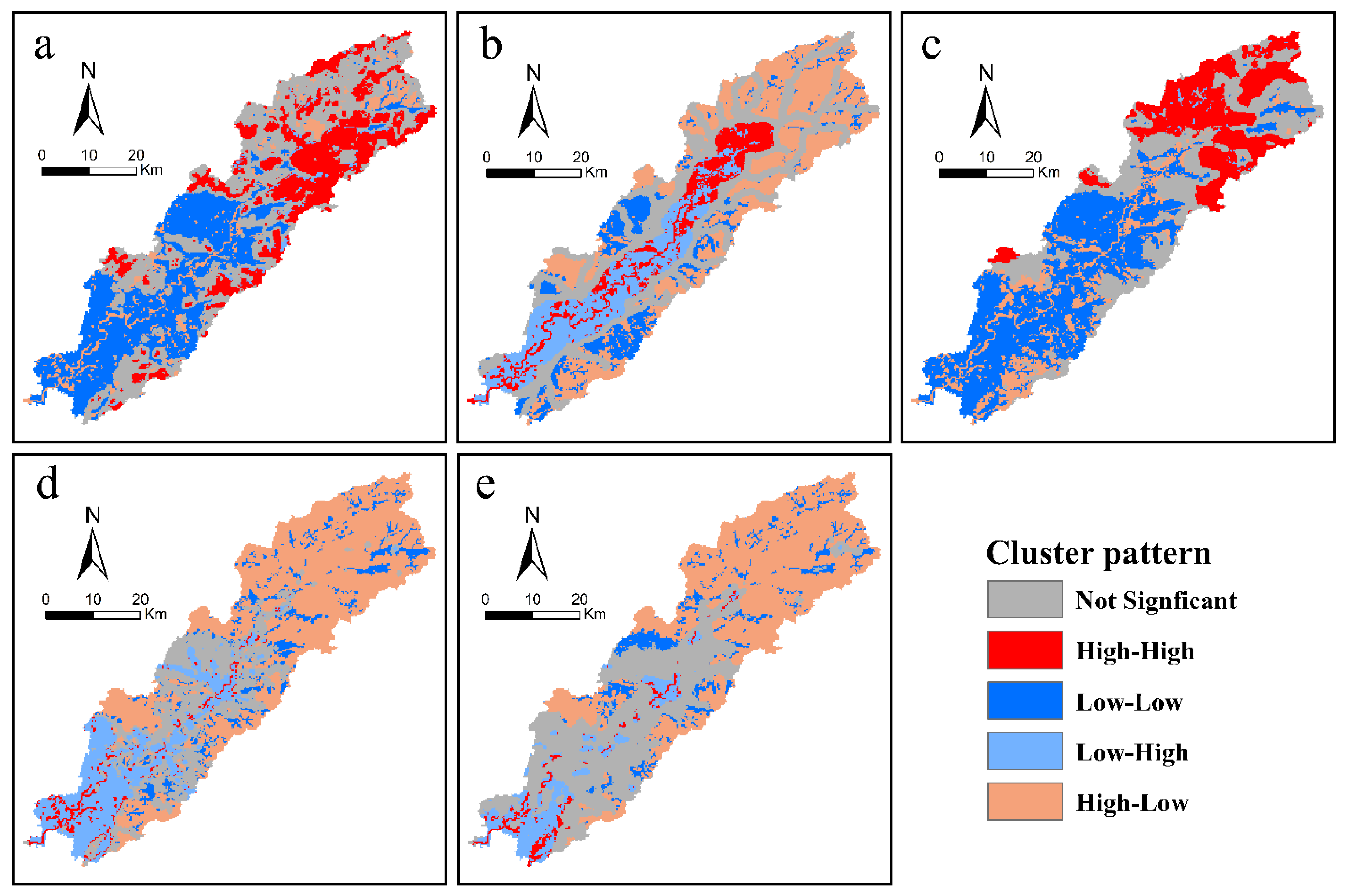
4.3. Moran Bivariate Analysis
4.4. GDM Factor Detection
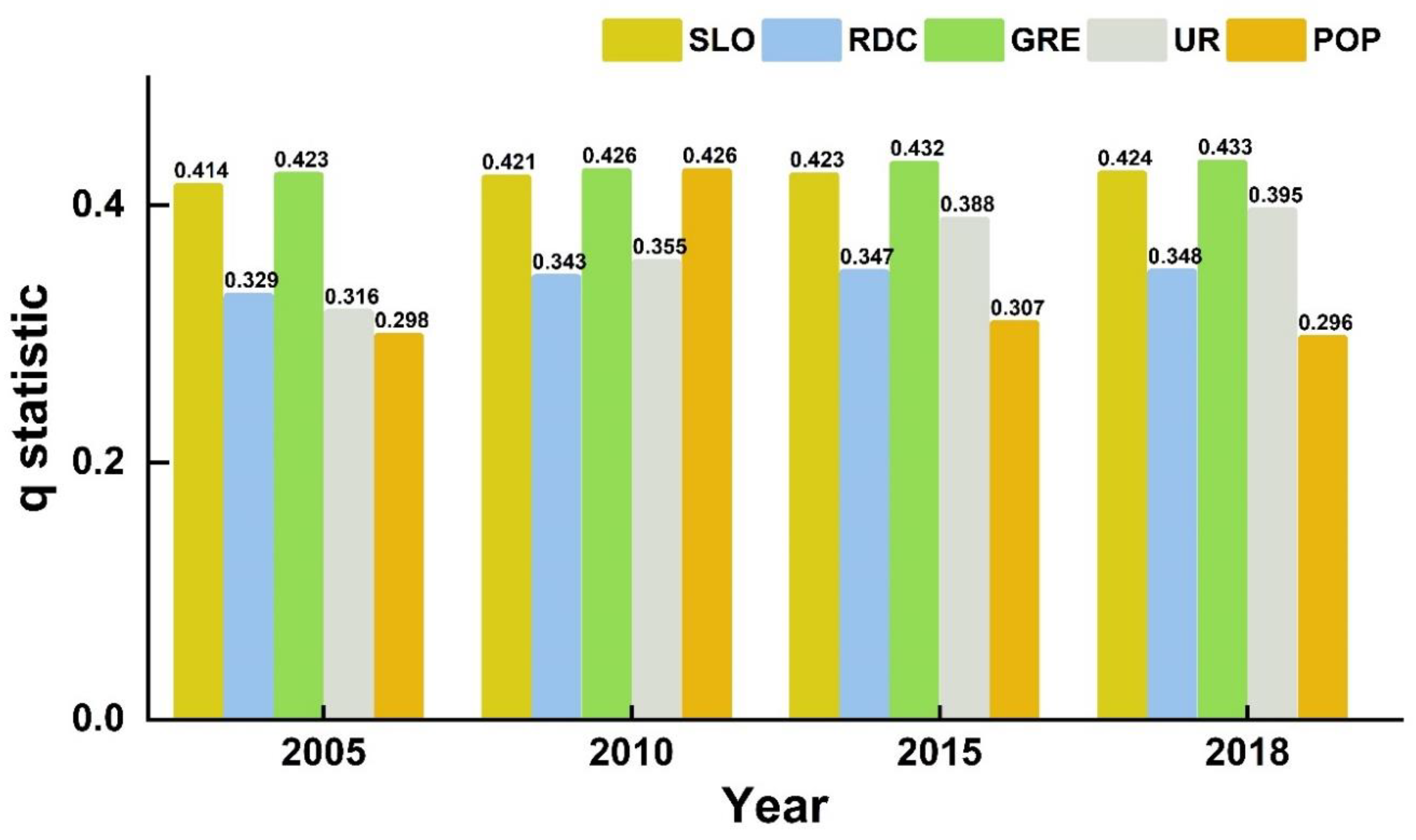
4.4.1. Single Factor Detection
4.4.2. Two-Factor Interaction Detection
5. Discussion
5.1. The Reason for the Formation of the Spatial Distribution of ESV
5.2. Driving Mechanism of ESV
5.3. Policy Recommendations for the Liuxi River Basin
5.4. Study Limitations and Prospects for Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.Y.; Zhou, D.Y.; Jiang, G.H. Conflict or Coordination? Multiscale assessment of the spatio-temporal coupling relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: The case of the Jingjinji Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, L.C.; de Groot, R. The ecosystem services agenda:bridging the worlds of natural science and economics, conservation and development, and public and private policy. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J.; Costanza, R.; McMichael, A.J. Assessing ecosystem health. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boithias, L.; Terrado, M.; Corominas, L.; Ziv, G.; Kumar, V.; Marques, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Acuna, V. Analysis of the uncertainty in the monetary valuation of ecosystem services--A case study at the river basin scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; Oneill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Lu, N.; Xu, Z.; Ren, J.; Xing, K. Linking land use change, ecosystem services and human well-being: A case study of the Manas River Basin of Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 27, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Zhong, M.; Pan, S. Coupling Analysis of Ecosystem Services Value and Economic Development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: A Case Study in Hunan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Regional ecosystem health response to rural land use change: A case study in Lijiang City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.P.; Xu, D.; Guo, P.P.; Wang, D.; Li, L.B.; Gao, J. Exploring variations of ecosystem service value in Hangzhou Bay Wetland, Eastern China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 37, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, Z.M.; Li, F.; Crittenden, J.C. Analyzing spatio-temporal changes and trade-offs to support the supply of multiple ecosystem services in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhou, W.Q.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Yu, W.J.; Li, W.F. A multiscale analysis of urbanization effects on ecosystem services supply in an urban megaregion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Lu, X.; Liu, B.Y.; Wu, D.T.; Fu, G.; Zhao, Y.T.; Sun, P.L. Spatial relationships between ecosystem services and socioecological drivers across a large-scale region: A case study in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lü, Y. A review on the progress of modeling techniques in ecosystem services. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5287–5296. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.U.; Li, S.C. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.Q.; Zhang, S.W. Ecosystem service decline in response to wetland loss in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Catena, M.R.; Ahmad, S.; Jia, H.; Guan, Y. Multifactor-based spatio-temporal analysis of effects of urbanization and policy interventions on ecosystem service capacity: A case study of Pingshan River Catchment in Shenzhen city, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Li, L.; Jia, M.; Dong, Z.; Miao, Z.; Ren, C.; Song, C. Quantifying changes in multiple ecosystem services during 1992-2012 in the Sanjiang Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Pan, Z.; Liu, D.; Guo, X. Exploring the regional differences of ecosystem health and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, B. Spatial differences of ecosystem services and their driving factors: A comparation analysis among three urban agglomerations in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Jia, X.; Li, J. Spatial correlations among ecosystem services and their socio-ecological driving factors: A case study in the city belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Jiang, J.; Chu, L.; Zhang, J.-C. Threshold effect of ecosystem services in response to climate change and vegetation coverage change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological shelter. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Xiang, A.; Qureshi, S.; Li, T.; Song, D.; Zhang, C. Quantifying the human disturbance intensity of ecosystems and its natural and socioeconomic driving factors in urban agglomeration in South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 11493–11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Nie, X.D.; Li, Z.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Xiao, H.B.; Hu, X.Q.; Wang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.T.; Zhang, G.Y.; et al. How trade-offs between ecological construction and urbanization expansion affect ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wang, L.C.; Huang, C.B.; Fang, L.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, L.Z. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem services in the urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Feng, C.C.E.; Xu, N.Y.; Guo, L. Spatial heterogeneous relationship between ecosystem services and human disturbances: A case study in Chuandong, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Ecosystem services response to urbanization in metropolitan areas: Thresholds identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. Spatial spillover effects of urbanization on ecosystem services value in Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fang, C. Factors influencing ecosystem services in the Pearl River Delta, China: Spatiotemporal differentiation and varying importance. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, Z. Spatial Correlation between Ecosystem Services and Human Disturbances: A Case Study of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Chen, Y.Y. On the spatial relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, C.-C.; Yu, Q.; Guo, L. Integrating supply and demand factors for estimating ecosystem services scarcity value and its response to urbanization in typical mountainous and hilly regions of south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Feng, C.C.; Han, R.; Guo, L. Impact of Urbanization on Ecosystem Health: A Case Study in Zhuhai, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Yan, J.; Xu, H.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Q. Estimates of shifts in ecosystem service values due to changes in key factors in the Manas River basin, northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutilleul, P. Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity: Concepts and Analyses; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Y.; Li, X. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Ecosystem Service Value and Its Coordinated Development with Economy: A Case Study in Hainan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Identifying the impacts of natural and human factors on ecosystem service in the Yangtze and Yellow River Basins. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Yan, F.Q.; Su, F.Z. Impacts of Urbanization on the Ecosystem Services in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenjie, Z.; Zibo, Y.; Bingjun, L. Analysis of Spatio-temporal Evolution of Land Use and Landscape Pattern in Liuxi River Basin Driven by Rapid Urbanization. Pearl River 2020, 41, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Gedo, H.W.; Morshed, M.M. Inadequate accessibility as a cause of water inadequacy: A case study of Mpeketoni, Lamu, Kenya. Water Policy 2013, 15, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Tourian, M.J.; Devaraju, B.; Sneeuw, N.; Kunstmann, H. Basin-scale runoff prediction: An Ensemble Kalman Filter framework based on global hydrometeorological data sets. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8450–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Zhang, D. Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin based on InVEST model and GeoDetector. J. Desert Res. 2021, 41, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, B.; Yang, Z.; Bi, X.; Fu, Q.; Li, B. Spatial-temporal correlation analysis of ecosystem services value and human activities-a case study of Huayang Lakes area in the middle reaches of Yangtze River. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 3531–3541. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) human settlement changes in China reflected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.N.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, W.M.; Ye, C.C.; Zhao, Y. Selected Environmental Assessment Model and Spatial Analysis Method to Explain Correlations in Environmental and Socio-Economic Data with Possible Application for Explaining the State of the Ecosystem. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. GeoDa 0.9 User’s Guide; Spatial Analysis Laboratory, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign: Urbana, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Rey, S.J. Modern Spatial Econometrics in Practice: A Guide to GeoDa, GeoDaSpace and PySAL; GeoDa Press LLC.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Thirty years of spatial econometrics. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2010, 89, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Deng, L.Y.; Zuo, S.D.; Song, X.D.; Liao, Y.L.; Xu, C.D.; Chen, Q.; Hua, L.Z.; Li, Z.W. Quantifying the influences of various ecological factors on land surface temperature of urban forests. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data Category | Type of Data | Resolution | Time (Year) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land use/cover Data | Raster data | 30 m | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2018 | Land cover remote sensing monitoring data set for multi-period land use in China (CNLUCC). Available online: http://www.resdc.cn (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Soil Erodibility | Raster data | 500 m | 2005, 2010, 2015 | Erosion Area of China in Five-year Increments. Available online: https://doi.org/10.3974/geodb.2021.05.03.V1 (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | Raster data | 250 m | 2000 | NASA dataset. Available online: https://earthdata.nasa.gov (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Average Monthly Precipitation | Raster data | 1000 m | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2018 | National Earth System Science Data Center. Available online: http://www.geodata.cn (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Population | Raster data | 100 m | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2018 | WordPress Project. Available online: https://www.worldpop.org/ (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Human Settlements (urban and rural) | Raster data | 30 m | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2017 | Impervious surface dataset. Available online: http://data.ess.tsinghua.edu.cn/ (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| 16-day Net Primary Productivity (NPP) | Raster data | 500 m | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2018 | MODIS/Terra Net Primary Production Gap-Filled Yearly L4 Global 500 m SIN Grid. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod17a3hgfv006/ (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Water System | Vector data | / | 2017 | National Geographic Information Resources 1:1,000,000 National Basic Geographic Database. Available online: https://www.webmap.cn/ (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Food Data | Statistical data | / | 2005, 2010, 2015, 2018 | Guangdong Statistical Yearbook. Available online: http://stats.gd.gov.cn/gdtjnj/ (assessed on 1 June 2022) |
| Land Use Type | Dry Land | Paddy Field | Broadleaf Forest | Shrubs | Grass | Wetland | Water | Construction | Unused | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem Classification | ||||||||||
| Natural environment comprehensive service functions | food production | 0.85 | 1.36 | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.51 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 |
| raw materials | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.66 | 0.43 | 0.56 | 0.5 | 0.23 | 0 | 0 | |
| gas regulation | 0.67 | 1.11 | 2.17 | 1.41 | 1.97 | 1.9 | 0.77 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| climate regulation | 0.36 | 0.57 | 6.5 | 4.23 | 5.21 | 3.6 | 2.29 | 0 | 0 | |
| environmental purification | 0.1 | 0.17 | 1.93 | 1.28 | 1.72 | 3.6 | 5.55 | 0 | 0.1 | |
| nutrient cycle maintenance | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.2 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | |
| biodiversity maintenance | 0.13 | 0.21 | 2.41 | 1.67 | 2.18 | 7.87 | 2.55 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| aesthetic landscape | 0.06 | 0.09 | 1.06 | 0.69 | 0.96 | 4.73 | 1.89 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| Water source conditions comprehensive service functions | water supply | 0.02 | −2.63 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 2.59 | 8.29 | 0 | 0 |
| water regulation | 0.27 | 2.72 | 4.74 | 3.35 | 3.82 | 24.23 | 102.24 | 0 | 0.03 | |
| Soil conservation service function | soil conservation | 1.03 | 0.01 | 2.65 | 1.72 | 2.4 | 2.31 | 0.93 | 0 | 0.02 |
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | TOL | VIF | p | TOL | VIF | p | TOL | VIF | p | TOL | VIF | |
| SLO | 0 | 0.824099 | 1.213447 | 0 | 0.777684 | 1.285870 | 0 | 0.755122 | 1.324289 | 0 | 0.749637 | 1.333978 |
| GRE | 0 | 0.888490 | 1.125505 | 0 | 0.827045 | 1.209124 | 0 | 0.814747 | 1.227374 | 0 | 0.809450 | 1.235407 |
| UR | 0 | 0.640032 | 1.562421 | 0 | 0.559448 | 1.787476 | 0 | 0.562794 | 1.776848 | 0 | 0.551702 | 1.812574 |
| POP | 0 | 0.662943 | 1.508425 | 0 | 0.611686 | 1.634826 | 0 | 0.660070 | 1.514992 | 0 | 0.664477 | 1.504943 |
| RDC | 0 | 0.845667 | 1.182499 | 0 | 0.838894 | 1.192046 | 0 | 0.827211 | 1.208882 | 0 | 0.823948 | 1.213669 |
| SLO | RDC | GRE | UR | POP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0.760 | 0.993 | 0.923 | 0.666 | 0.857 |
| 2010 | 0.760 | 0.993 | 0.924 | 0.751 | 0.865 |
| 2015 | 0.760 | 0.993 | 0.929 | 0.805 | 0.858 |
| 2018 | 0.760 | 0.993 | 0.938 | 0.815 | 0.857 |
| Dominant Interaction | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SLO∩POP | 0.48914 | SLO∩RDC | 0.50597 | SLO∩RDC | 0.51013 | SLO∩RDC | 0.51112 |
| 2 | SLO∩RDC | 0.49076 | SLO∩POP | 0.49619 | SLO∩UR | 0.50460 | SLO∩UR | 0.50825 |
| 3 | SLO∩GRE | 0.48693 | SLO∩GRE | 0.49619 | RDC∩UR | 0.50105 | RDC∩UR | 0.50501 |
| 4 | SLO∩UR | 0.47996 | SLO∩UR | 0.49606 | SLO∩POP | 0.50009 | SLO∩GRE | 0.50279 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, X.; Shu, Y.; Tang, X.; Ma, J. Identifying Driving Factors of Basin Ecosystem Service Value Based on Local Bivariate Spatial Correlation Patterns. Land 2022, 11, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101852
Ding X, Shu Y, Tang X, Ma J. Identifying Driving Factors of Basin Ecosystem Service Value Based on Local Bivariate Spatial Correlation Patterns. Land. 2022; 11(10):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101852
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Xue, Yuqin Shu, Xianzhe Tang, and Jingwen Ma. 2022. "Identifying Driving Factors of Basin Ecosystem Service Value Based on Local Bivariate Spatial Correlation Patterns" Land 11, no. 10: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101852
APA StyleDing, X., Shu, Y., Tang, X., & Ma, J. (2022). Identifying Driving Factors of Basin Ecosystem Service Value Based on Local Bivariate Spatial Correlation Patterns. Land, 11(10), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101852






