Assessing Urban Resilience from the Perspective of Scaling Law: Evidence from Chinese Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Urban Resilience
2.2. Urban Scaling Laws
3. Methodology
3.1. Resilience Index
3.2. Scaling Exponent and Allometric Growth Exponent Calculation
3.3. Scale-Adjusted Metropolitan Indicator (SAMI)
3.4. Case Study and Data Source
4. Scaling Laws of Resilience Indicators in China
4.1. Scaling Exponents of Resilience Indicators
4.2. Temporal Variations of Scaling Exponents
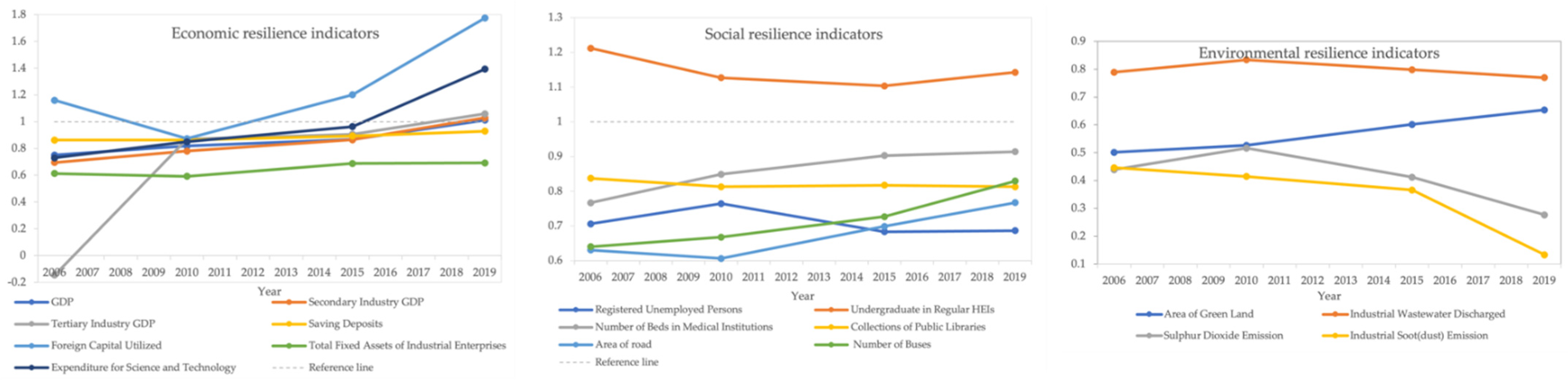
4.3. Allometric Growth of Resilience Indicators in China
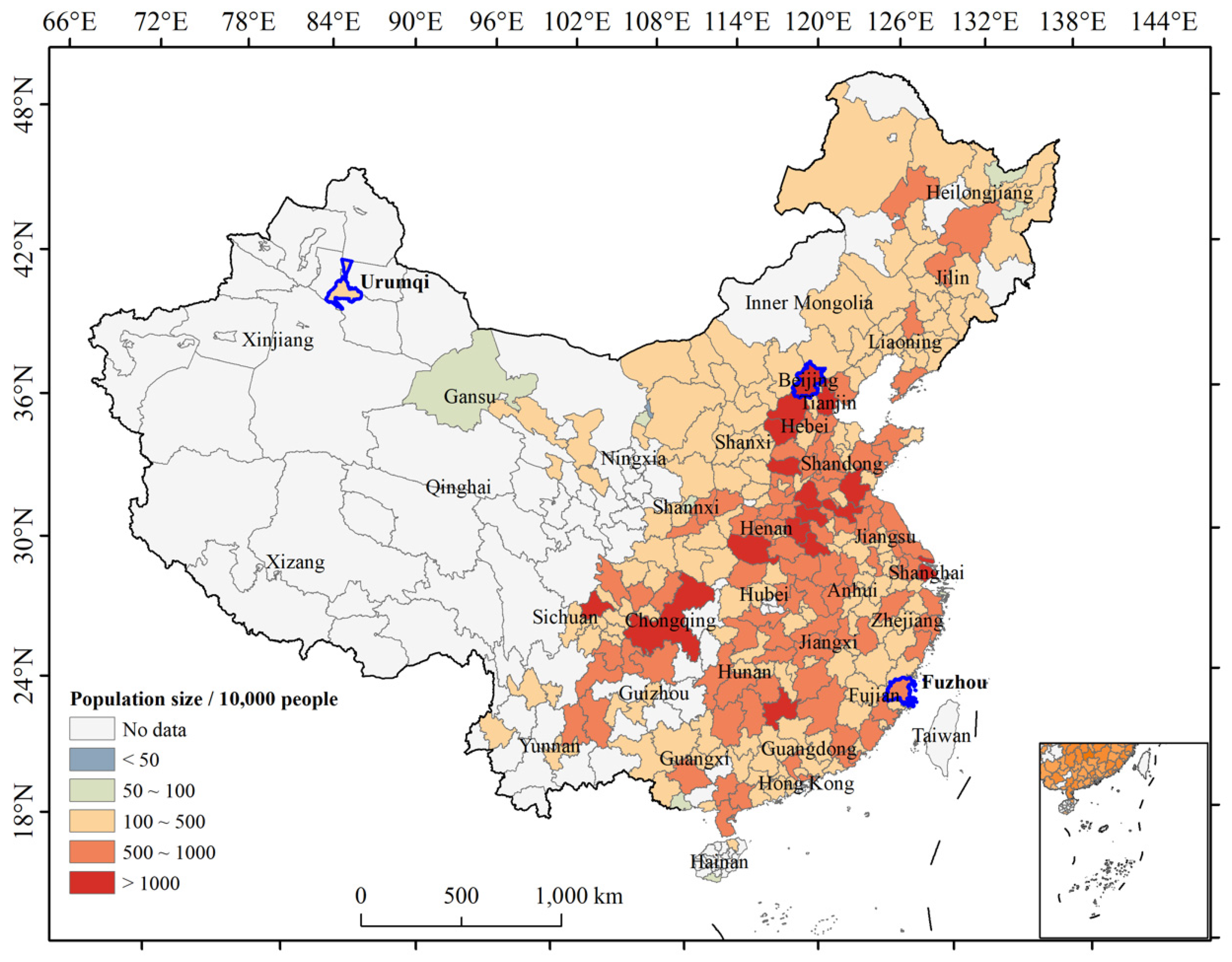
4.4. Spatial Pattern of Urban Resilience SAMI and Comparison with per Capita Indicators
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Webber, S.; Leitner, H.; Sheppard, E. Wheeling Out Urban Resilience: Philanthrocapitalism, Marketization, and Local Practice. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2021, 111, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyüközkan, G.; Ilıcak, Ö.; Feyzioğlu, O. A Review of Urban Resilience Literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, E.P. Chapter 27—Smart City Technologies plus Nature-Based Solutions: Viable and Valuable Resources for Urban Resilience. In Smart Cities Policies and Financing; Vacca, R.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 377–398. ISBN 978-0-12-819130-9. [Google Scholar]
- West, G.B.; Brown, J.H.; Enquist, B.J. A General Model for the Origin of Allometric Scaling Laws in Biology. Science 1997, 276, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabaix, X. Zipf’s Law and the Growth of Cities. Am. Econ. Rev. 1999, 89, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C. Resilience: The Emergence of a Perspective for Social–Ecological Systems Analyses. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2006, 16, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerow, S.; Newell, J.P.; Stults, M. Defining Urban Resilience: A Review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 147, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldunce, P.; Beilin, R.; Howden, M.; Handmer, J. Resilience for Disaster Risk Management in a Changing Climate: Practitioners’ Frames and Practices. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, S. Resilience Resistance: The Challenges and Implications of Urban Resilience Implementation. Cities 2020, 103, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat, H.; Wilkinson, S.; Williams, P.; Khatibi, H. Choosing a Holistic Urban Resilience Assessment Tool. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 71, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhai, G.; Xu, L.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, W. Assessment Methods of Urban System Resilience: From the Perspective of Complex Adaptive System Theory. Cities 2021, 112, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, H.; Kopainsky, B. Using System Dynamics to Support a Participatory Assessment of Resilience. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2020, 40, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.; Doyon, A. Building Urban Resilience with Nature-Based Solutions: How Can Urban Planning Contribute? Cities 2019, 95, 102483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, P.R.; Foley, K.; Collier, M.J. Operationalizing Urban Resilience through a Framework for Adaptive Co-Management and Design: Five Experiments in Urban Planning Practice and Policy. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 62, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A. Of Resilient Places: Planning for Urban Resilience. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2015, 24, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duit, A.; Galaz, V.; Eckerberg, K.; Ebbesson, J. Governance, Complexity, and Resilience. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, L.; Anderies, J.M.; Campbell, B.; Folke, C.; Hatfield-Dodds, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Wilson, J. Governance and the Capacity to Manage Resilience in Regional Social-Ecological Systems. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.; Juhola, S. Adaptive Climate Change Governance for Urban Resilience. Urban Stud. 2015, 52, 1234–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockefeller Foundation. Arup City Resilience Index. In City Resilience Framework; Rockefeller Foundation: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.; Morley, P. The Australian Natural Disaster Resilience Index. Aust. J. Emerg. Manag. 2017, 32, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, S.L.; Burton, C.G.; Emrich, C.T. Disaster Resilience Indicators for Benchmarking Baseline Conditions. J. Homel. Secur. Emerg. Manag. 2010, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastiggi, M.; Meerow, S.; Miller, T.R. Governing Urban Resilience: Organisational Structures and Coordination Strategies in 20 North American City Governments. Urban Stud. 2021, 58, 1262–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, Z. Assessment of Urban Ecological Resilience and Its Influencing Factors: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration of China. Land 2022, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Li, D.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J. Influencing Factors and Their Influencing Mechanisms on Urban Resilience in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Guo, N.; Gao, X.; Wu, F. How Carbon Emission Reduction Is Going to Affect Urban Resilience. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Dueñas-Osorio, L.; Min, X. A Three-Stage Resilience Analysis Framework for Urban Infrastructure Systems. Struct. Saf. 2012, 36–37, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S. Economic Resilience: Definition and Measurement; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Simmie, J.; Martin, R. The Economic Resilience of Regions: Towards an Evolutionary Approach. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2010, 3, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Westley, F.; Turner, M.G. Surrogates for Resilience of Social–Ecological Systems. Ecosystems 2005, 8, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, S.L. The Landscape of Disaster Resilience Indicators in the USA. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.; Bekera, B. A Metric and Frameworks for Resilience Analysis of Engineered and Infrastructure Systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 121, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Holling, C.S.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kinzig, A. Resilience, Adaptability and Transformability in Social–Ecological Systems. Ecol. Soc. 2004, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xie, X.-L.; Lin, C.-Z.; Wang, M.; He, X.-J. Development as Adaptation: Framing and Measuring Urban Resilience in Beijing. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2018, 9, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Miner, T.W.; Stanton-Geddes, Z. Directions in development. In Building Urban Resilience: Principles, Tools, and Practice; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Guo, N.; Zeng, L.; Wu, F. How Climate Change Is Going to Affect Urban Livability in China. Clim. Serv. 2022, 26, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lu, X.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluating Urban Agglomeration Resilience to Disaster in the Yangtze Delta City Group in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Wu, D. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Urban Sustainable Development in China Based on the TOPSIS-Entropy Method. Sustainability 2016, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. Regional Economic Resilience, Hysteresis and Recessionary Shocks. J. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 12, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybski, D.; Arcaute, E.; Batty, M. Urban Scaling Laws. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A. The Origins of Scaling in Cities. Science 2013, 340, 1438–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.; West, G. A Unified Theory of Urban Living. Nature 2010, 467, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Lobo, J.; Helbing, D.; Kühnert, C.; West, G.B. Growth, Innovation, Scaling, and the Pace of Life in Cities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7301–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.G.A.; Mendes, R.S.; Lenzi, E.K.; Ribeiro, H.V. Scale-Adjusted Metrics for Predicting the Evolution of Urban Indicators and Quantifying the Performance of Cities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Lobo, J.; Strumsky, D.; West, G.B. Urban Scaling and Its Deviations: Revealing the Structure of Wealth, Innovation and Crime across Cities. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcaute, E.; Hatna, E.; Ferguson, P.; Youn, H.; Johansson, A.; Batty, M. Constructing Cities, Deconstructing Scaling Laws. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20140745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Jiao, L.; Xu, G.; Zhou, Z. Urban Scaling in Rapidly Urbanising China. Urban Stud. 2022, 59, 1889–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Gong, P. Removing Spatial Autocorrelation in Urban Scaling Analysis. Cities 2022, 124, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.-X.; Di, Z.; Stanley, H.E. Simple Spatial Scaling Rules behind Complex Cities. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.; Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Strumsky, D.; West, G.B. Urban Scaling and the Production Function for Cities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, E.; Sood, V. Rich and Poor Cities in Europe. An Urban Scaling Approach to Mapping the European Economic Transition. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.V.; Hanley, Q.S.; Lewis, D. Unveiling Relationships between Crime and Property in England and Wales via Density Scale-Adjusted Metrics and Network Tools. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.G.A.; Ribeiro, H.V.; Lenzi, E.K.; Mendes, R.S. Distance to the Scaling Law: A Useful Approach for Unveiling Relationships between Crime and Urban Metrics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, N.Z.; Jha, A. Does Environmental Policy Affect Scaling Laws between Population and Pollution? Evidence from American Metropolitan Areas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Xu, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhao, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. Assessment of Urban Land Use Efficiency in China: A Perspective of Scaling Law. Habitat Int. 2020, 99, 102172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gong, M.; Xu, Z.; Qu, S. Urban Scaling Patterns for Sustainable Development Goals Related to Water, Energy, Infrastructure, and Society in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordbeck, S. Urban Allometric Growth. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 1971, 53, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Yang, V.C.; Lobo, J.; Kempes, C.P.; Rybski, D.; Hamilton, M.J. The Interpretation of Urban Scaling Analysis in Time. J. R. Soc. Interface 2020, 17, 20190846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.L.; Meirelles, J.; Netto, V.M.; Neto, C.R.; Baronchelli, A. On the Relation between Transversal and Longitudinal Scaling in Cities. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depersin, J.; Barthelemy, M. From Global Scaling to the Dynamics of Individual Cities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban Agglomeration: An Evolving Concept of an Emerging Phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, D. The Magnitude and Causes of Agglomeration Economies. J. Reg. Sci. 2010, 50, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
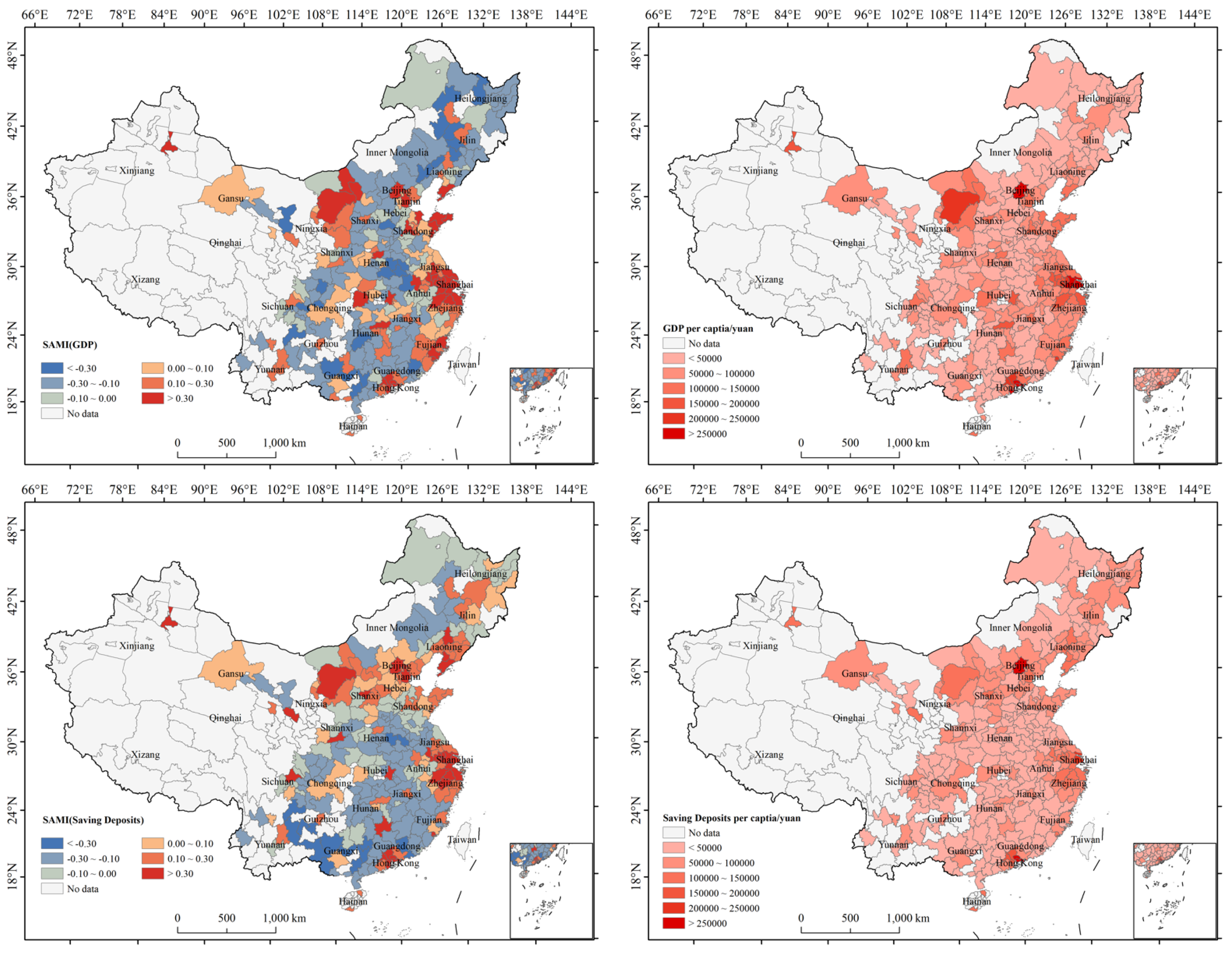
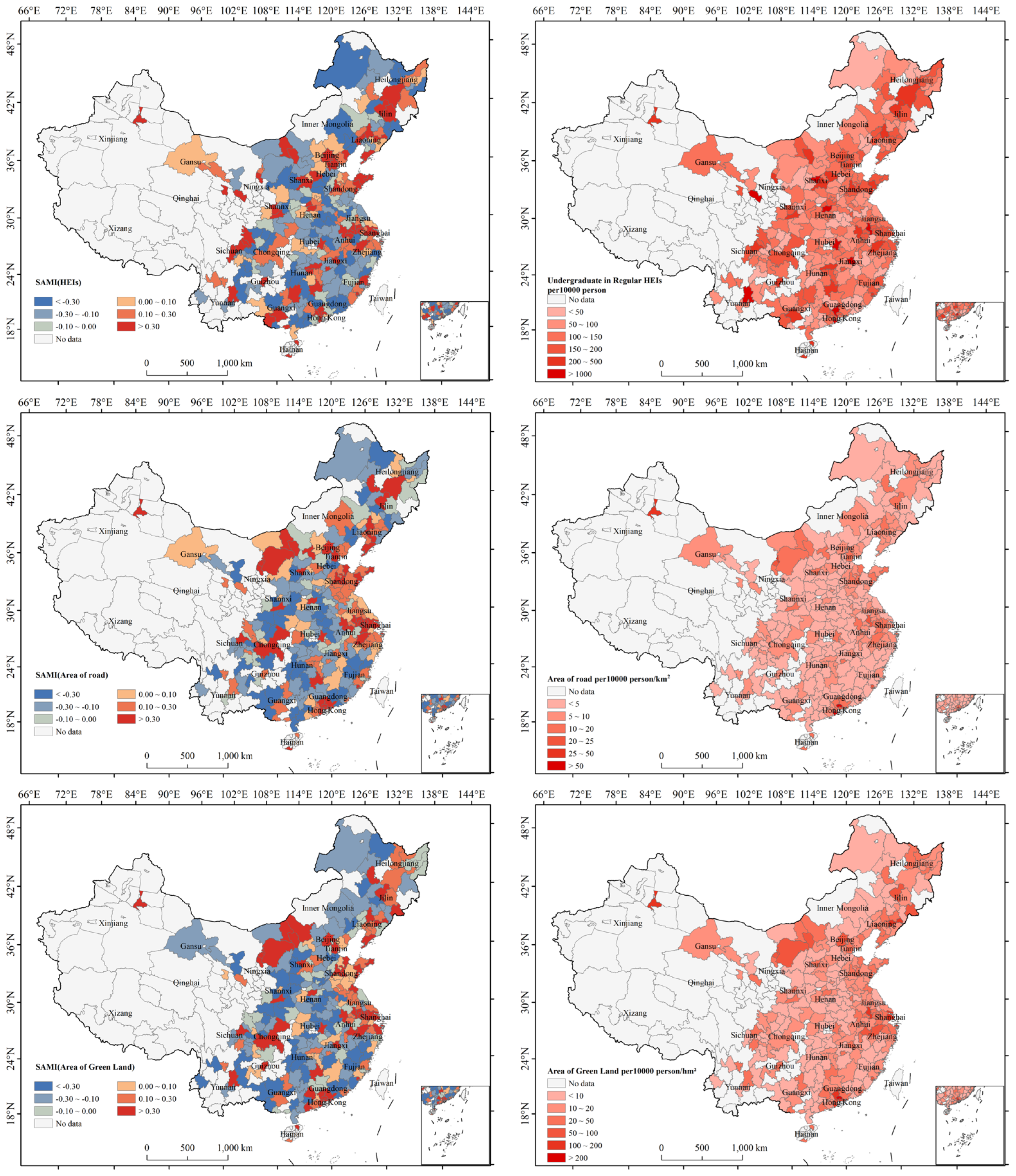
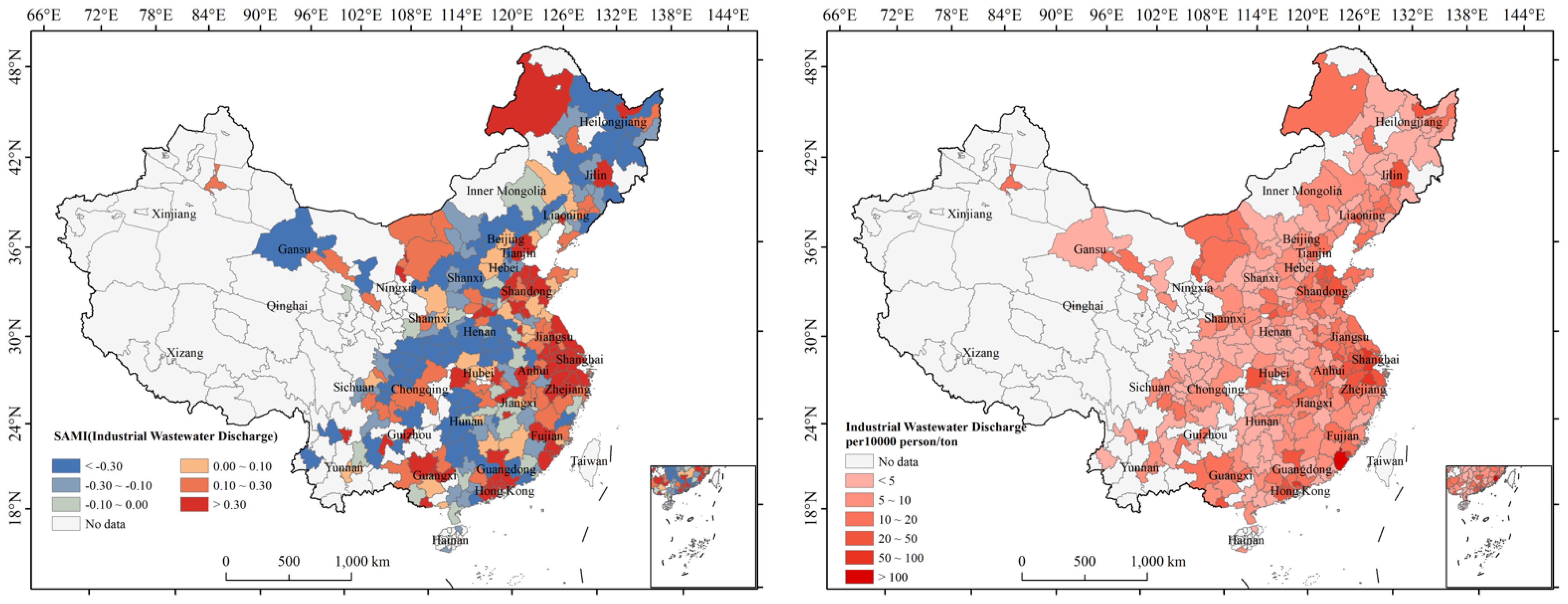
| Dimension | Variable |
|---|---|
| Economy | GDP (10,000 yuan) |
| Secondary Industry GDP (10,000 yuan) | |
| Tertiary Industry GDP (10,000 yuan) | |
| Saving Deposits (10,000 yuan) | |
| Amount of Foreign Capital Actually Utilized (USD 10,000) | |
| Total Fixed Assets of Industrial Enterprises above Designated Size (10,000 yuan) | |
| Expenditure for Science and Technology (10,000 yuan) | |
| Society | Registered Unemployed Persons |
| Undergraduate in Regular HEIs 1 | |
| Number of Beds in Medical Institutions | |
| Collections of Public Libraries | |
| Area of road (km2) | |
| Number of Buses and Trolley Buses under Operation | |
| Environment | Area of Green Land (hectare) |
| Volume of Industrial Wastewater Discharged (10,000 ton) | |
| Volume of Sulphur Dioxide Emission (ton) | |
| Volume of Industrial Soot(dust) Emission (ton) |
| Resilience Indicator | Resilience Dimension | Scaling Law | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
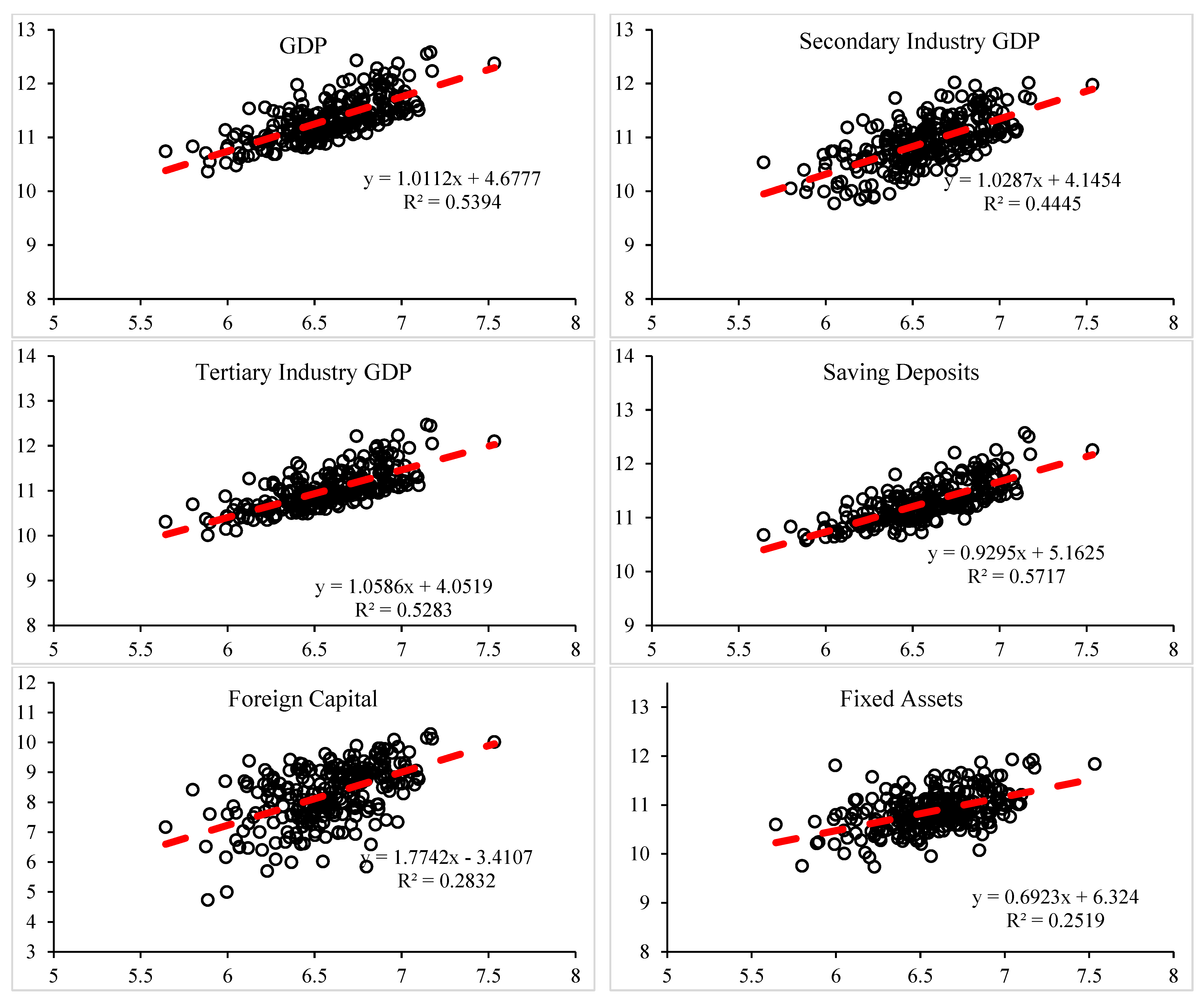
| GDP | Economy | superlinear | 1.0112 | 0.5394 |
| Secondary Industry GDP | Economy | superlinear | 1.0287 | 0.4445 |
| Tertiary Industry GDP | Economy | superlinear | 1.0586 | 0.5283 |
| Saving Deposits | Economy | sublinear | 0.9295 | 0.5717 |
| Foreign Capital | Economy | superlinear | 1.7742 | 0.2832 |
| Fixed Assets | Economy | sublinear | 0.6923 | 0.2519 |
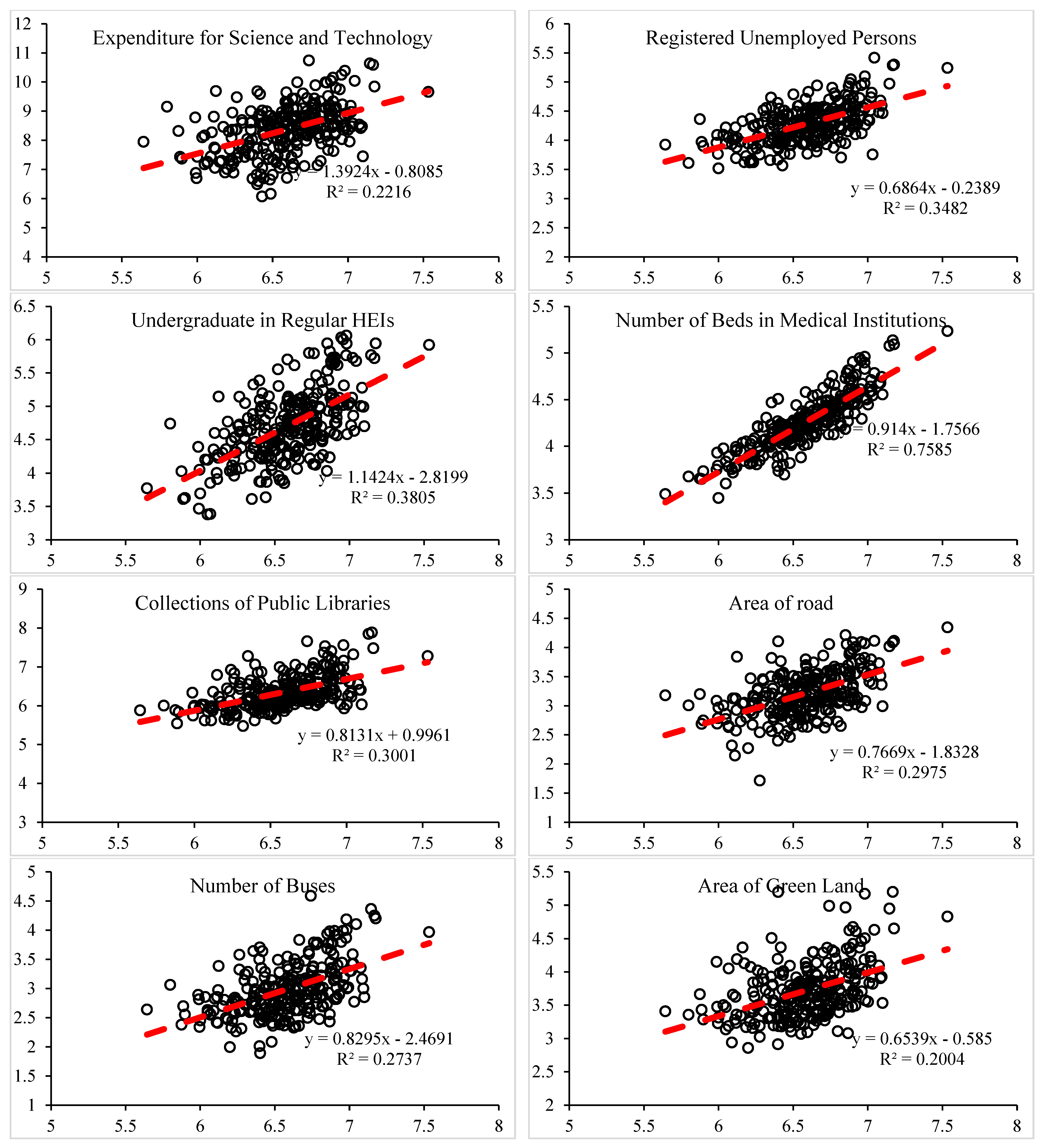
| Expenditure for Science and Technology | Economy | superlinear | 1.3924 | 0.2216 |
| Registered Unemployed Persons | Society | sublinear | 0.6864 | 0.3482 |
| Undergraduate in Regular HEIs | Society | superlinear | 1.1424 | 0.3805 |
| Number of Beds in Medical Institutions | Society | sublinear | 0.914 | 0.7585 |
| Collections of Public Libraries | Society | sublinear | 0.8131 | 0.3001 |
| Area of road | Society | sublinear | 0.7669 | 0.2975 |
| Number of Buses | Society | sublinear | 0.8295 | 0.2737 |
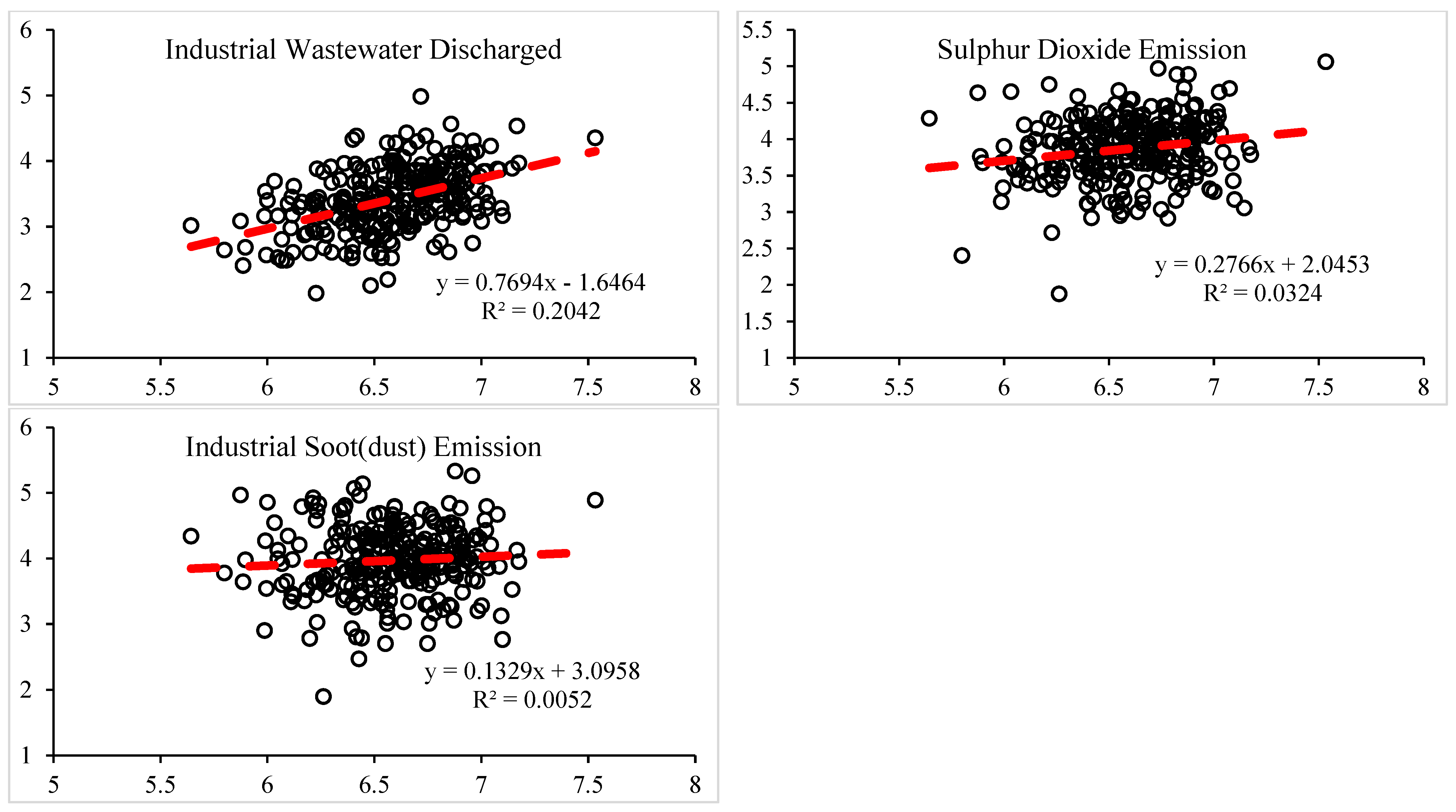
| Area of Green Land | Environment | sublinear | 0.6539 | 0.2004 |
| Industrial Wastewater Discharged | Environment | sublinear | 0.7694 | 0.2042 |
| Sulphur Dioxide Emission | Environment | sublinear | 0.2766 | 0.0324 |
| Industrial Soot(dust) Emission | Environment | sublinear | 0.1329 | 0.0052 |
| Resilience Indicator | Resilience Dimension | Beijing | Fuzhou | Urumqi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
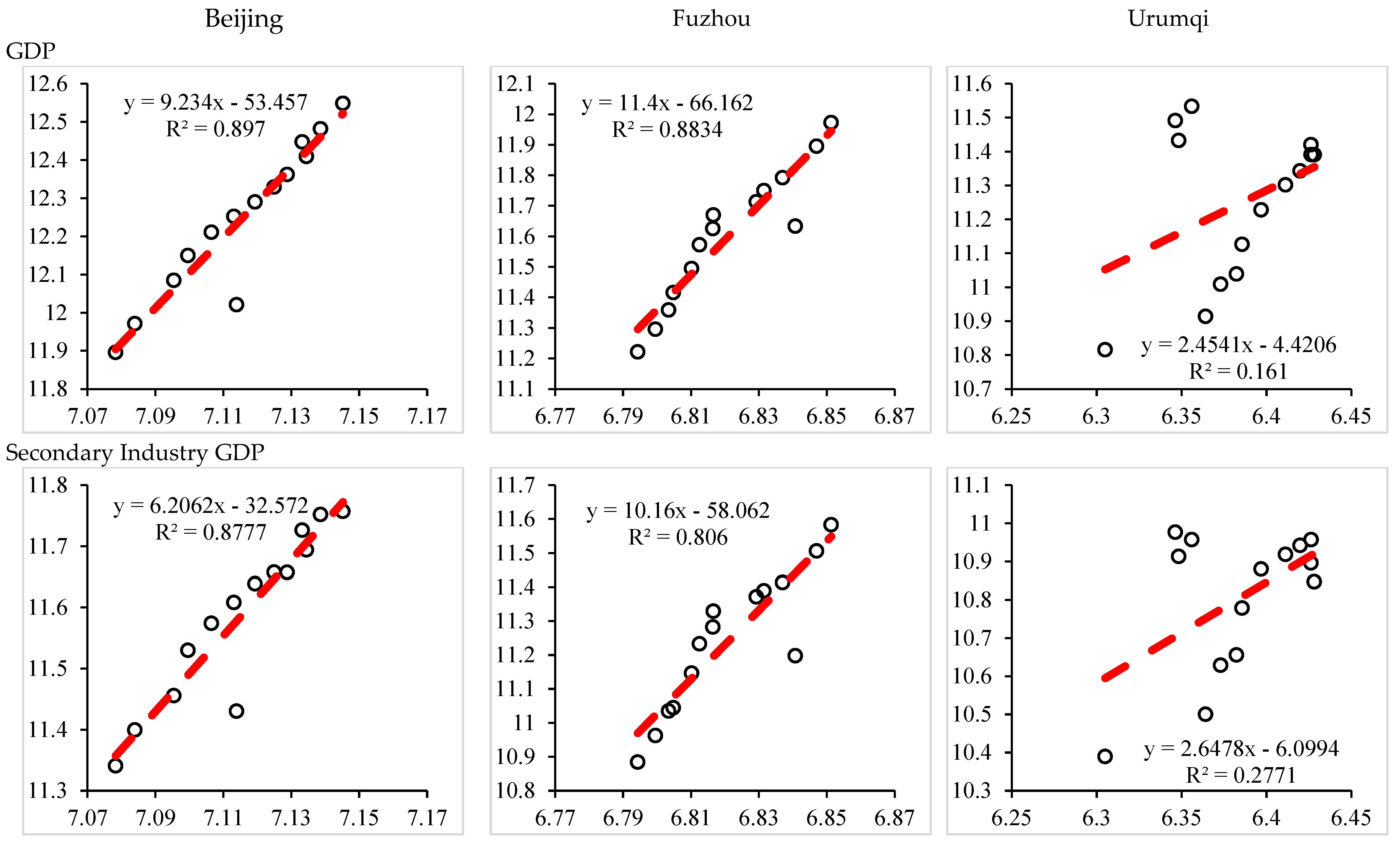
| GDP | Economy | 9.23 | 11.40 | 2.45 |
| Secondary Industry GDP | Economy | 6.21 | 10.16 | 2.65 |
| Tertiary Industry GDP | Economy | 10.17 | 13.42 | 2.33 |
| Saving Deposits | Economy | 9.04 | 10.81 | 1.88 |
| Foreign Capital | Economy | 9.32 | 3.47 | 13.85 |
| Fixed Assets | Economy | 5.25 | 9.21 | 3.45 |
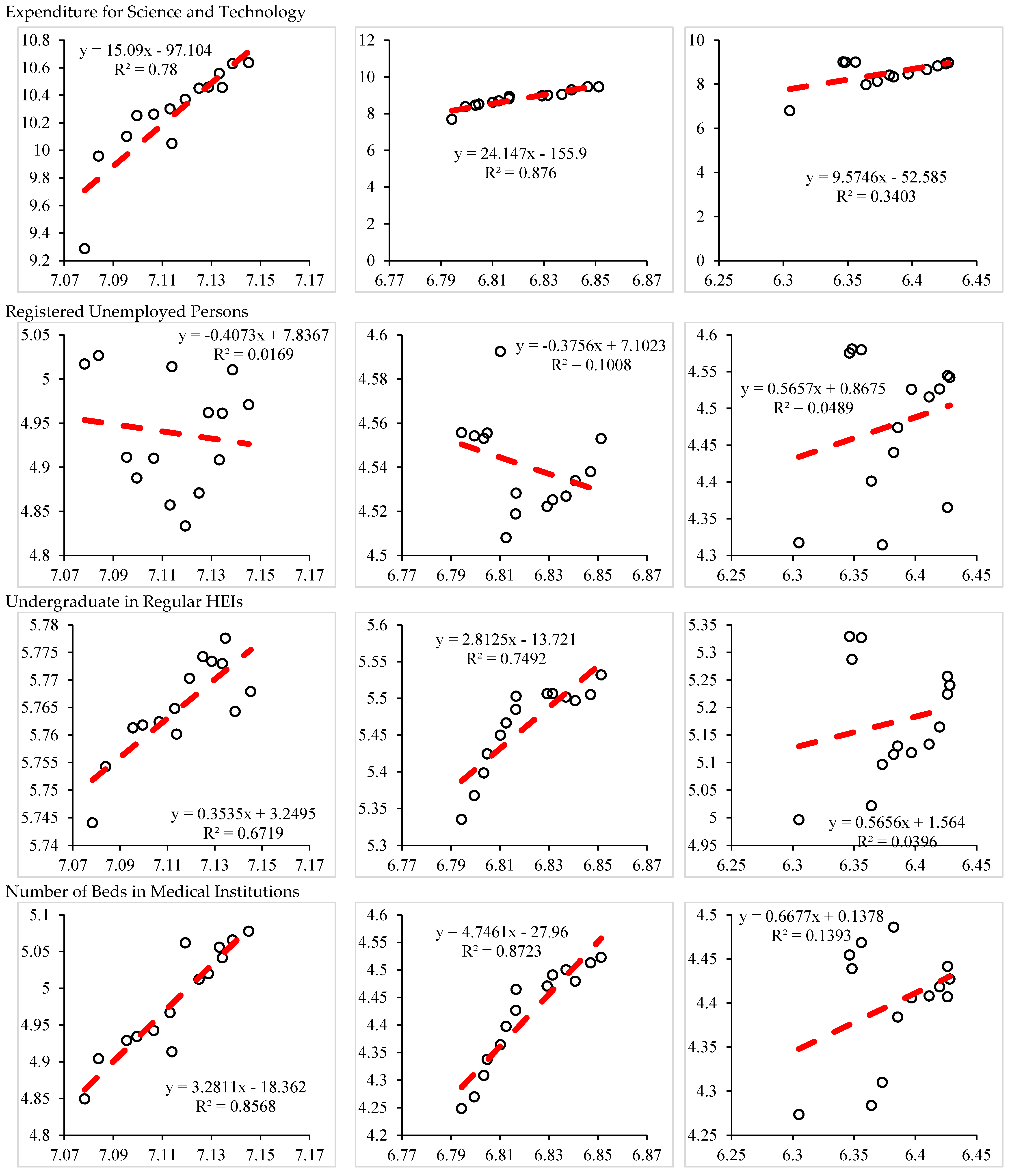
| Expenditure for Science and Technology | Economy | 15.09 | 24.15 | 9.57 |
| Registered Unemployed Persons | Society | −0.41 | −0.38 | 0.57 |
| Undergraduate in Regular HEIs | Society | 0.35 | 2.81 | 0.57 |
| Number of Beds in Medical Institutions | Society | 3.28 | 4.75 | 0.67 |
| Collections of Public Libraries | Society | 4.14 | 5.67 | 1.14 |
| Area of road | Society | 2.79 | 6.48 | 0.98 |
| Number of Buses | Society | 1.25 | 6.54 | 0.04 |
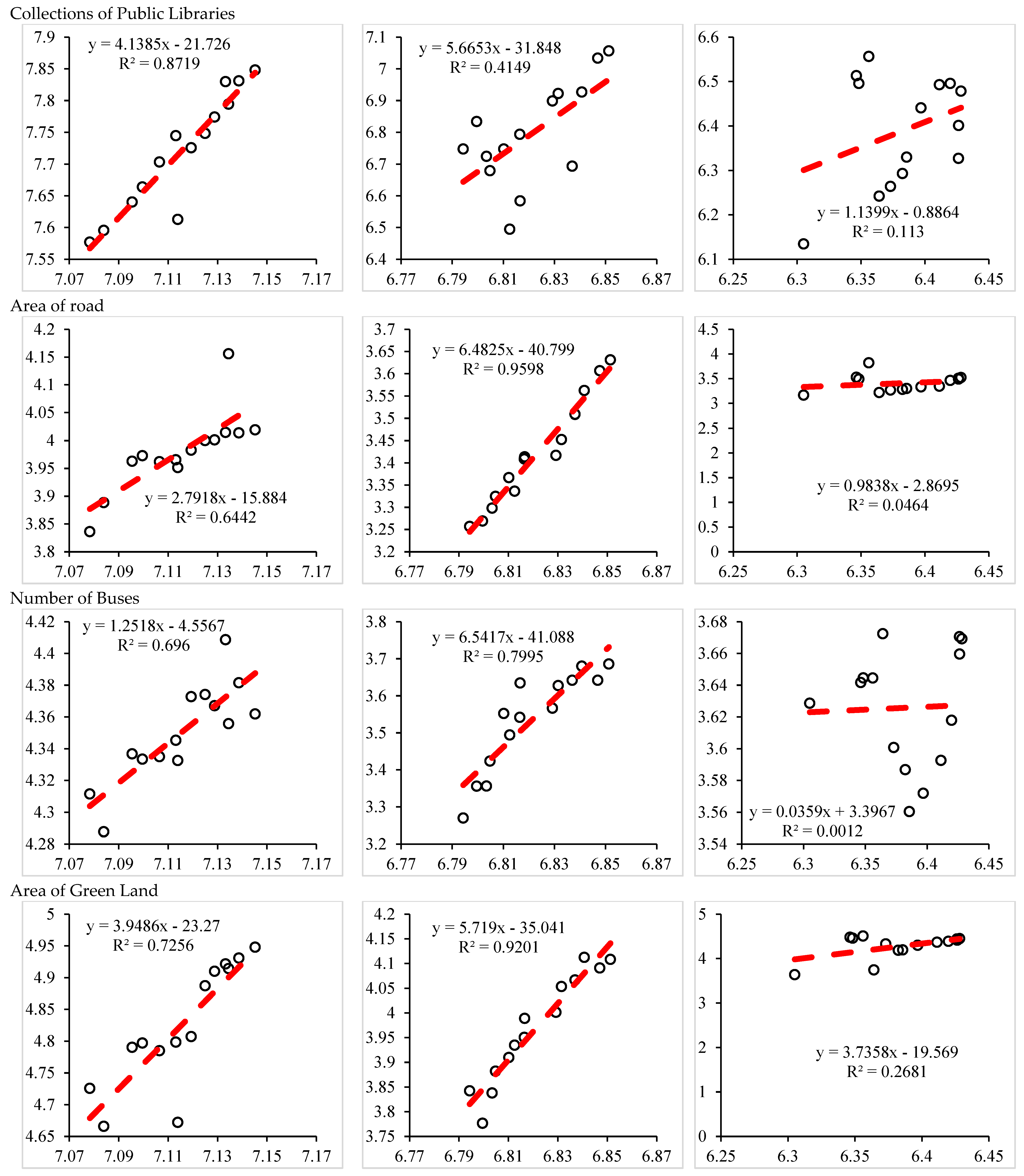
| Area of Green Land | Environment | 3.95 | 5.72 | 3.74 |
| Industrial Wastewater Discharged | Environment | −0.81 | −1.17 | 0.70 |
| Sulphur Dioxide Emission | Environment | −26.08 | −10.05 | 1.19 |
| Industrial Soot(dust) Emission | Environment | −8.05 | 17.66 | 1.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, C.; Guo, N.; Zhu, X.; Wu, F. Assessing Urban Resilience from the Perspective of Scaling Law: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Land 2022, 11, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101803
Shi C, Guo N, Zhu X, Wu F. Assessing Urban Resilience from the Perspective of Scaling Law: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Land. 2022; 11(10):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101803
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Chenchen, Naliang Guo, Xiaoping Zhu, and Feng Wu. 2022. "Assessing Urban Resilience from the Perspective of Scaling Law: Evidence from Chinese Cities" Land 11, no. 10: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101803
APA StyleShi, C., Guo, N., Zhu, X., & Wu, F. (2022). Assessing Urban Resilience from the Perspective of Scaling Law: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Land, 11(10), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11101803








