Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
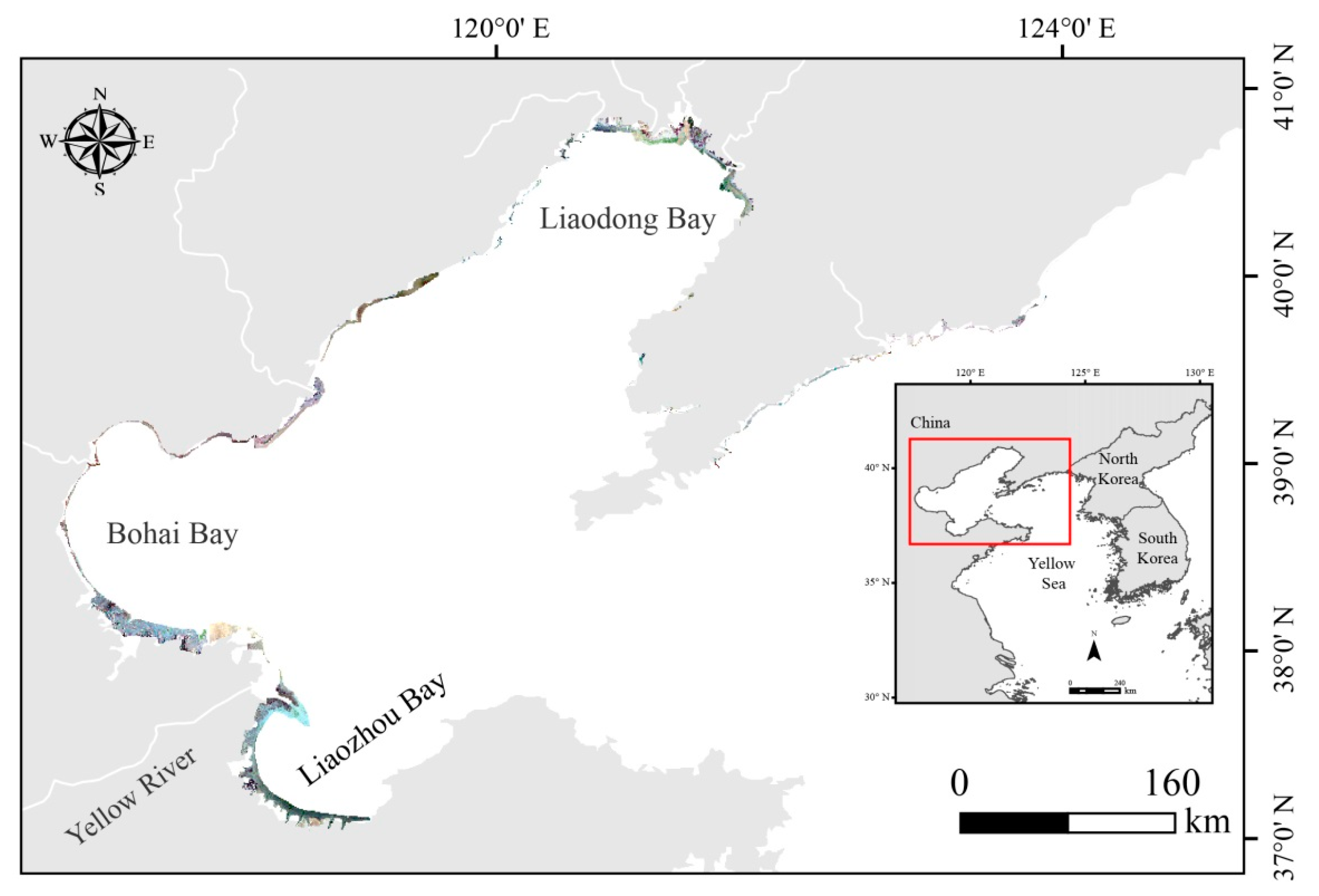
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Landsat Images and Pre-Processing to Analyze Land Cover Changes in NYSC
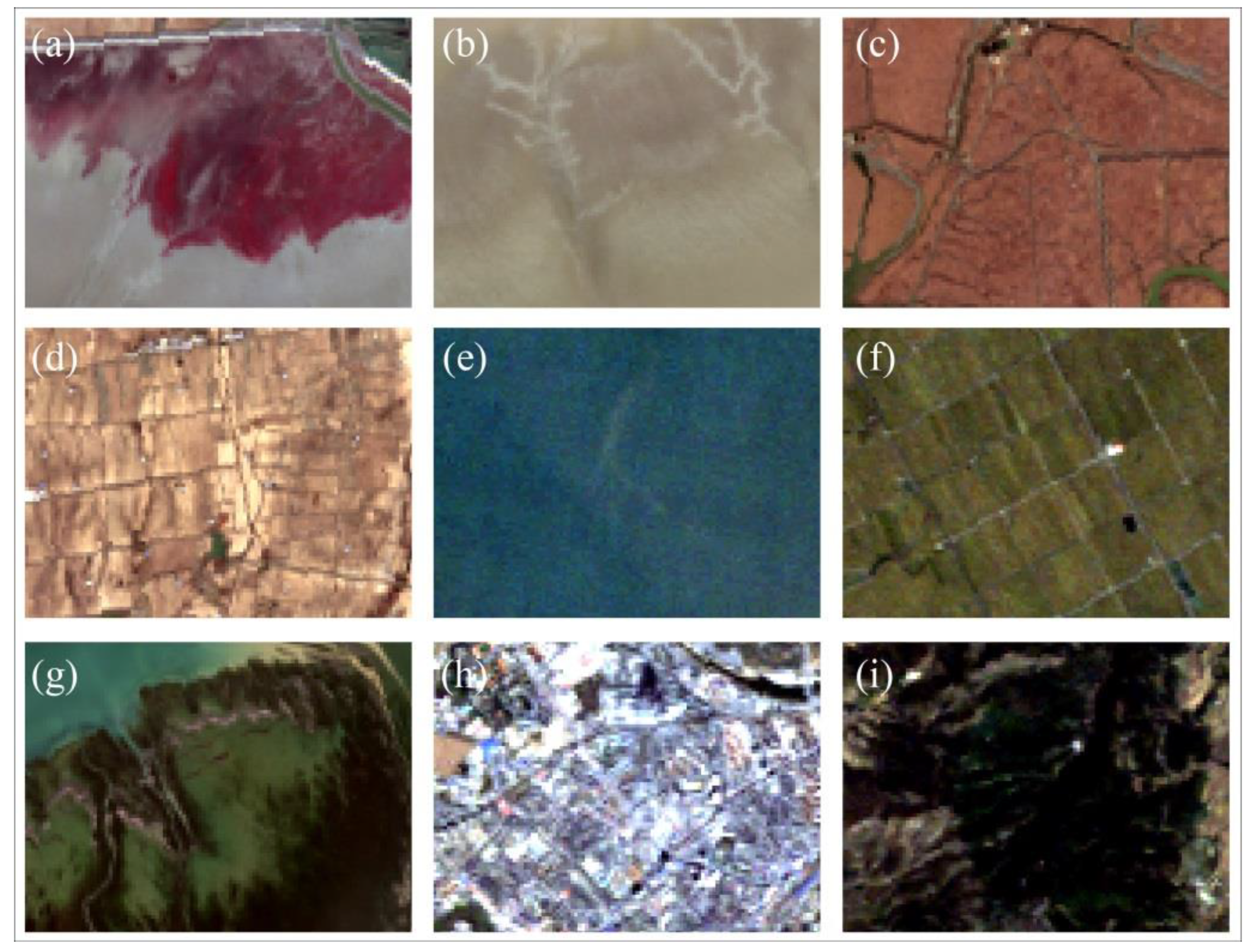
2.3. Extracting S. salsa Saltmarsh Distribution Data
2.4. Accuracy Assessment
2.5. Land Cover Change of S. salsa Saltmarsh
3. Results
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of S. salsa Saltmarsh
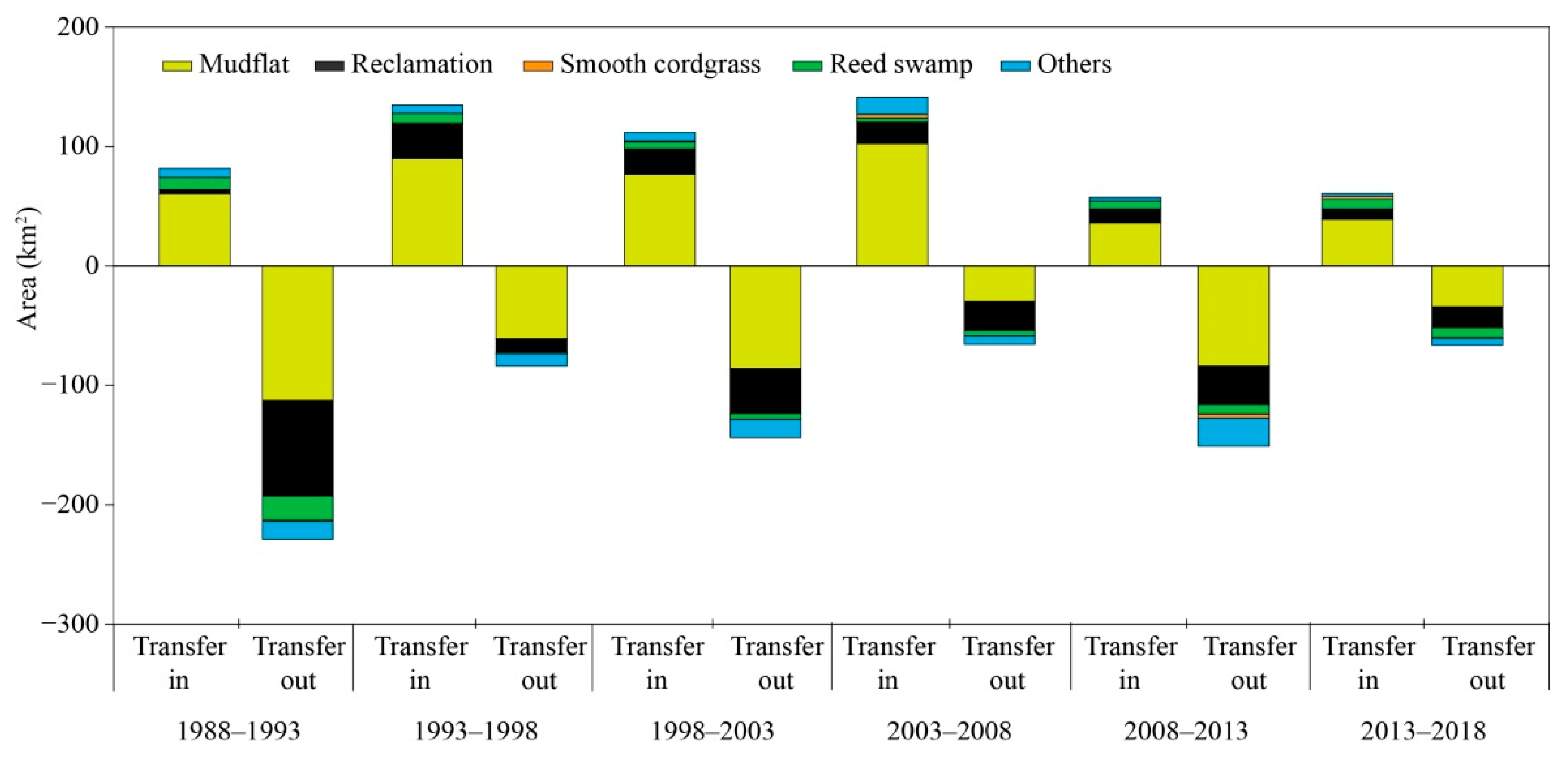
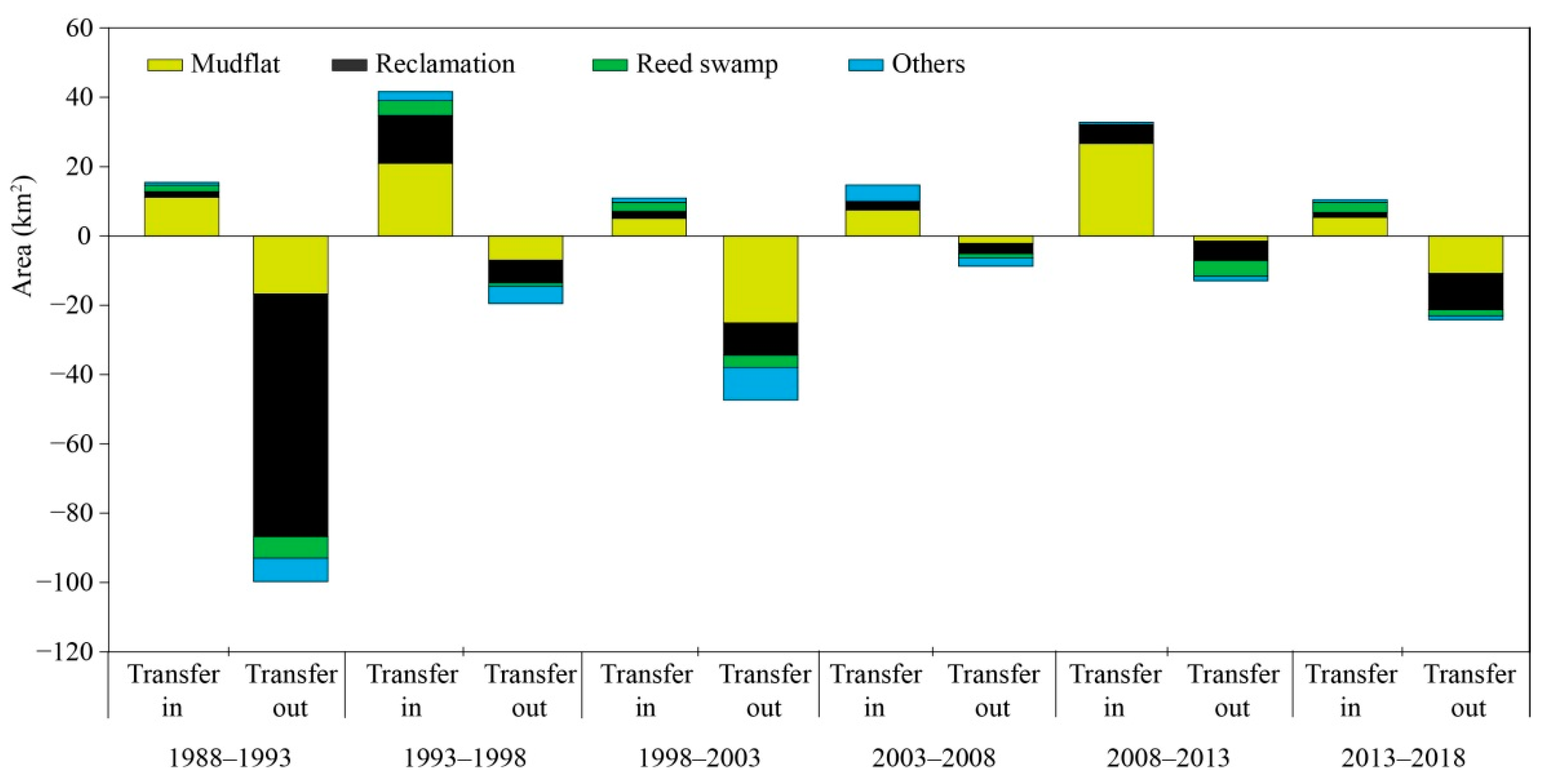
3.2. Effects of Reclamation and Natural Succession on S. salsa Saltmarsh Dynamics
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arkema, K.K.; Guannel, G.; Verutes, G.; Wood, S.A.; Guerry, A.D.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Kareiva, P.; Lacayo-Emery, M.; Silver, J.M. Coastal habitats shield people and property from sea-level rise and storms. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Melville, D.S.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Piersma, T.; Li, B. Rethinking China’s new great wall. Science 2014, 346, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.; Silliman, B. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Ma, Z.; Tan, K.; Melville, D.; Li, B.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, F. Effects of reclamation and natural changes on coastal wetlands bordering China’s Yellow Sea from 1984 to 2015. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.; Phinn, S.R.; DeWitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, M.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature 2018, 565, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wu, G. Analysis of Suaeda heteroptera cover change and its hydrology driving factors in the Liao River Estuary wetlands, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 467, 012150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passeri, D.L.; Hagen, S.C.; Medeiros, S.C.; Bilskie, M.V.; Alizad, K.; Wang, D. The dynamic effects of sea level rise on low-gradient coastal landscapes: A review. Earth’s Futur. 2015, 3, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xiao, J.; Lei, W.; Du, J.; Li, Z.; Cong, P.; Hou, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Human activities accelerated the degradation of saline seepweed red beaches by amplifying top-down and bottom-up forces. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Studds, C.E.; Kendall, B.E.; Murray, N.; Wilson, H.B.; Rogers, D.I.; Clemens, R.S.; Gosbell, K.; Hassell, C.J.; Jessop, R.; Melville, D.S.; et al. Rapid population decline in migratory shorebirds relying on Yellow Sea tidal mudflats as stopover sites. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, M. Shorebirds of the Yellow Sea: Importance, Threats and Conservation Status; Wetlands International Global Series 9; International Wader Studies 12; Wetlands International: Canberra, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon, J.; Verkuil, Y.I.; Murray, N. IUCN Situation Analysis on East and Southeast Asian Intertidal Habitats, with Particular Reference to the Yellow Sea (Including the Bohai Sea); Occasional Paper of the IUCN Species Survival Commission No. 47; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bamford, M.; Watkins, D.; Bancroft, W.; Tishchler, G.; Wahl, J. Migratory Shorebirds of the East Asian—Australasian Flyway; Wetland International: Canberra, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- China Coastal Waterbird Census Group; Bai, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Dong, G.; Dong, J.; Dong, W.; Fu, V.W.K.; Han, Y.; Lu, G.; et al. Identification of coastal wetlands of international importance for waterbirds: A review of China Coastal Waterbird Surveys 2005–2013. Avian Res. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, Y.; Melville, D.S.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Tan, K.; Cheng, X.; Fuller, R.A.; Xiao, X.; et al. Changes in area and number of nature reserves in China. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the Coast of Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China (Phase I). Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1606/ (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Murray, N.; Clemens, R.S.; Phinn, S.R.; Possingham, H.; Fuller, R. Tracking the rapid loss of tidal wetlands in the Yellow Sea. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moores, N.; Rogers, D.I.; Rogers, K.; Hansbro, P. Reclamation of tidal flats and shorebird declines in Saemangeum and elsewhere in the Republic of Korea. Emu 2016, 116, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A. Muddy coasts of the world: Processes, deposits and functions. J. Coast. Conserv. 2002, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.-B.; Anderson, G.Q.A.; Chang, Q.; Choi, C.-Y.; Chowdhury, S.U.; Clark, N.A.; Gan, X.; Hearn, R.D.; Li, J.; Lappo, E.G.; et al. The intertidal wetlands of southern Jiangsu Province, China—globally important for Spoon-billed Sandpipers and other threatened waterbirds, but facing multiple serious threats. Bird Conserv. Int. 2017, 27, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, C.-Y.; Battley, P.; Potter, M.; Rogers, K.G.; Ma, Z. The importance of Yalu Jiang coastal wetland in the north Yellow Sea to Bar-tailed Godwits Limosa lapponica and Great Knots Calidris tenuirostris during northward migration. Bird Conserv. Int. 2014, 25, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Xia, S.; Jackson, M.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Teng, J.; Meng, Z.; Yu, X.; Shi, J. Identifying new sites of significance to waterbirds conservation and their habitat modification in the Yellow and Bohai Seas in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D. Community composition and behavioral differences of migrating shorebirds between two habitats within a Suaeda salsa saltmarsh-mudflat wetland mosaics. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Yu, J.; Lu, Z.; Xie, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. The ecological effects of Suaeda salsa on repairing heavily degraded coastal saline-alkaline wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 4835–4840. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Luo, L.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Liang, J. Using Landsat images to quantify different human threats to the Shuangtai Estuary Ramsar site, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 135, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Lloyd, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, S.; Wan, D.; Zhang, Z. Habitat-dependent changes in vigilance behaviour of Red-crowned Crane influenced by wildlife tourism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Lloyd, H.; Zhang, Z. Burrow ambient temperature influences Helice crab activity and availability for migratory Red-crowned cranes Grus japonensis. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11523–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, S.; Guan, L.; Lloyd, H.; Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Z. Patterns of waterbird community composition across a natural and restored wetland landscape mosaic, Yellow River Delta, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, Y.; Hong, J.; Zeng, D.; Yang, L. Spatial and temporal variations in wetland landscape patterns in the Yellow River Delta based on Landsat images. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 4314–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. Study on Migratory Waterbirds and Wetlands in the Yellow Sea; China Forestry Publish Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Xing, J. Some taxonomy errors in studies on China Suaeda. Mar. Sci. 2019, 43, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Shen, Y. Effects of Coast Beach Reclamation on the Change of Landscape Pattern and Its Spatial Centroids: A Case Study in Coastal Wetland of Part of Yancheng National Natural Reserve. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Y. Rapid Invasion of Spartina alterniflora in the Coastal Zone of Mainland China: New Observations from Landsat OLI Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, R.; Martínez, M.; Van Tussenbroek, B.; Guzmán-Rodríguez, L.; Mendoza, E.; López-Portillo, J. A Framework to Manage Coastal Squeeze. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Saito, Y.; Liu, P.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950–2005): Impacts of climate change and human activities. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.-S.; He, Q.; An, Y. Spartina alterniflora invasions and effects on crab communities in a western Pacific estuary. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1920–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, L.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Wen, Z. Habitat Changes for Breeding Waterbirds in Yancheng National Nature Reserve, China: A Remote Sensing Study. Wetlands 2010, 30, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Choi, C.-Y.; Jia, M.; Jackson, M.V.; Fuller, R.A. Remote Observations in China’s Ramsar Sites: Wetland Dynamics, Anthropogenic Threats, and Implications for Sustainable Development Goals. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lloyd, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D. Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea. Land 2021, 10, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080835
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Lloyd H, Zhang Z, Li D. Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea. Land. 2021; 10(8):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080835
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Yan Zhang, Huw Lloyd, Zhengwang Zhang, and Donglai Li. 2021. "Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea" Land 10, no. 8: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080835
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, Y., Lloyd, H., Zhang, Z., & Li, D. (2021). Rapid Reclamation and Degradation of Suaeda salsa Saltmarsh along Coastal China’s Northern Yellow Sea. Land, 10(8), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080835






