Local- and Plot-Scale Measurements of Soil Moisture: Time and Spatially Resolved Field Techniques in Plain, Hill and Mountain Sites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Soil Moisture and Soil–Water Relations
1.2. Soil Moisture and Field Measurement Techniques: A General Overview
2. Soil Moisture Field Measurement Methods: A Focus on the Techniques Used
2.1. Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR)
2.2. Soil Moisture Sensors Directly Connected to Data Loggers
2.3. Electromagnetic Induction (EMI)
2.4. Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
2.5. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
3. Results: Testing Sites Description
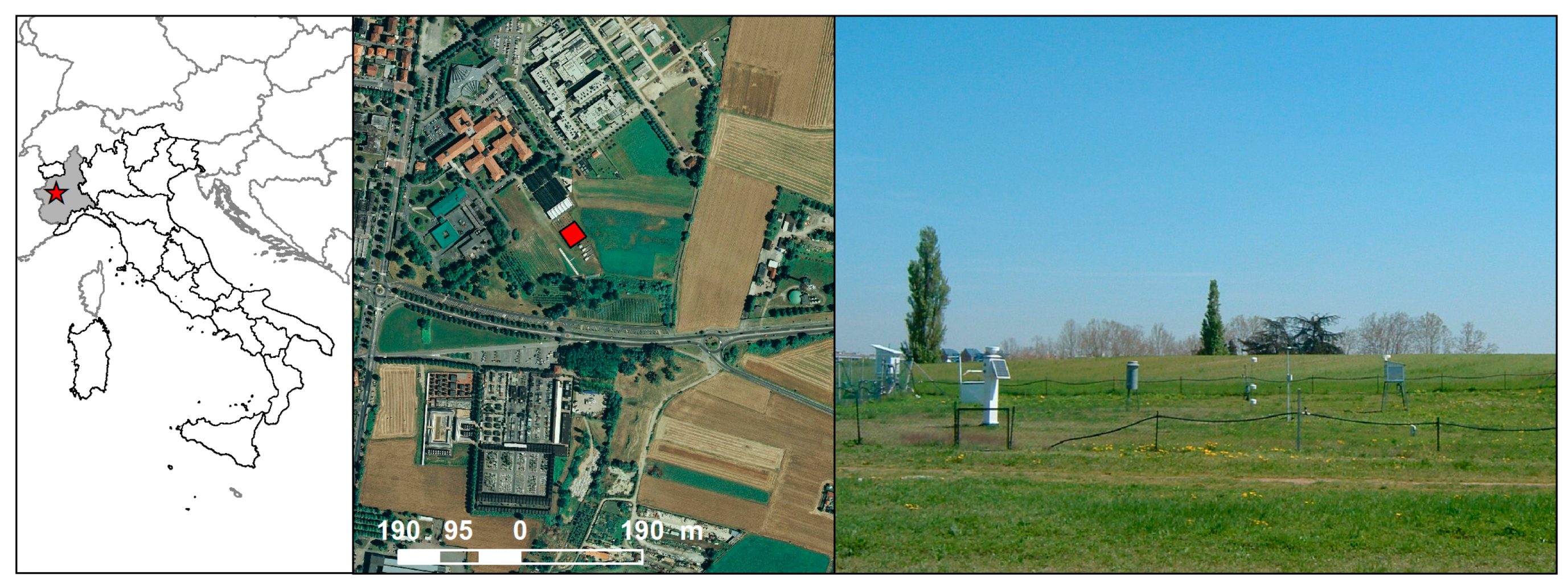
3.1. Plain Permanent Meadow
3.2. Mountain Permanent Meadow
3.3. Hilly Vineyard
4. Results: Measurement Campaigns and Surveys Outputs
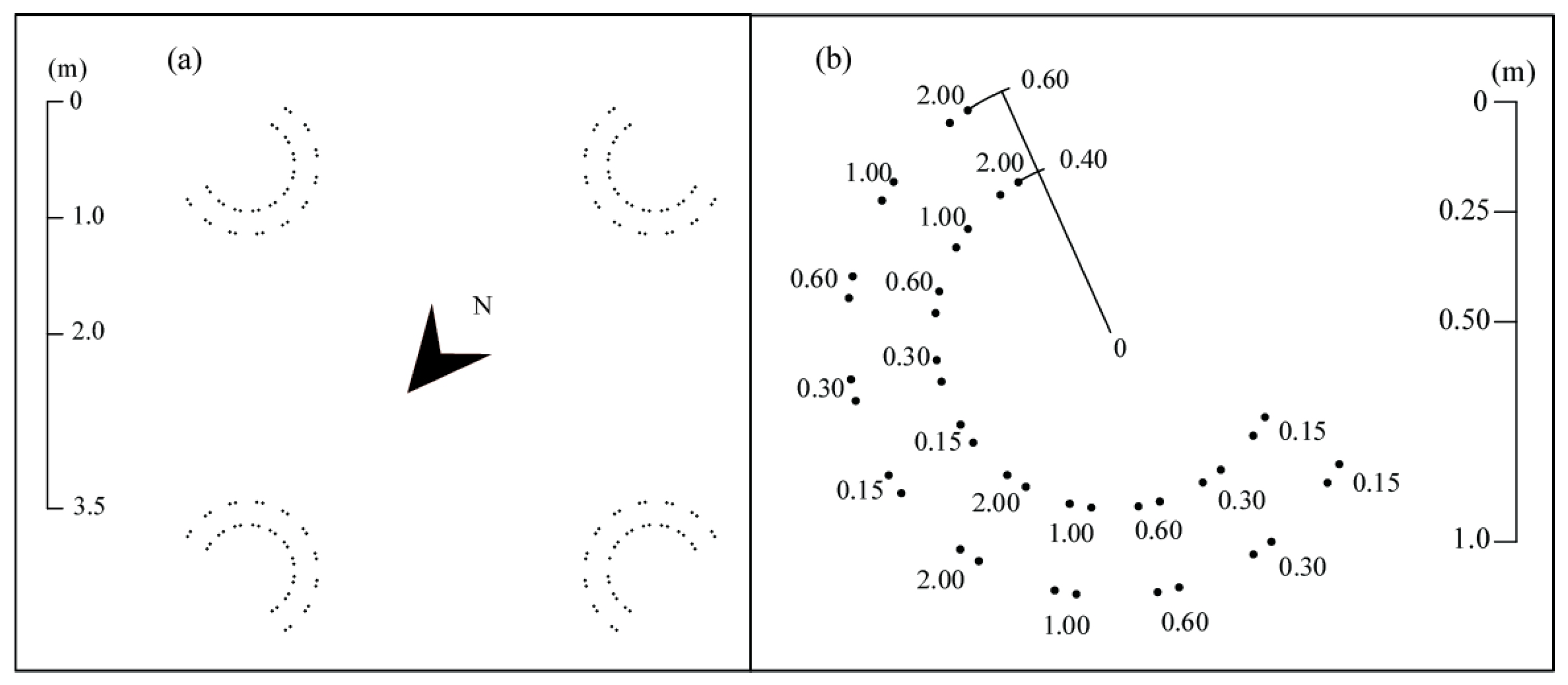
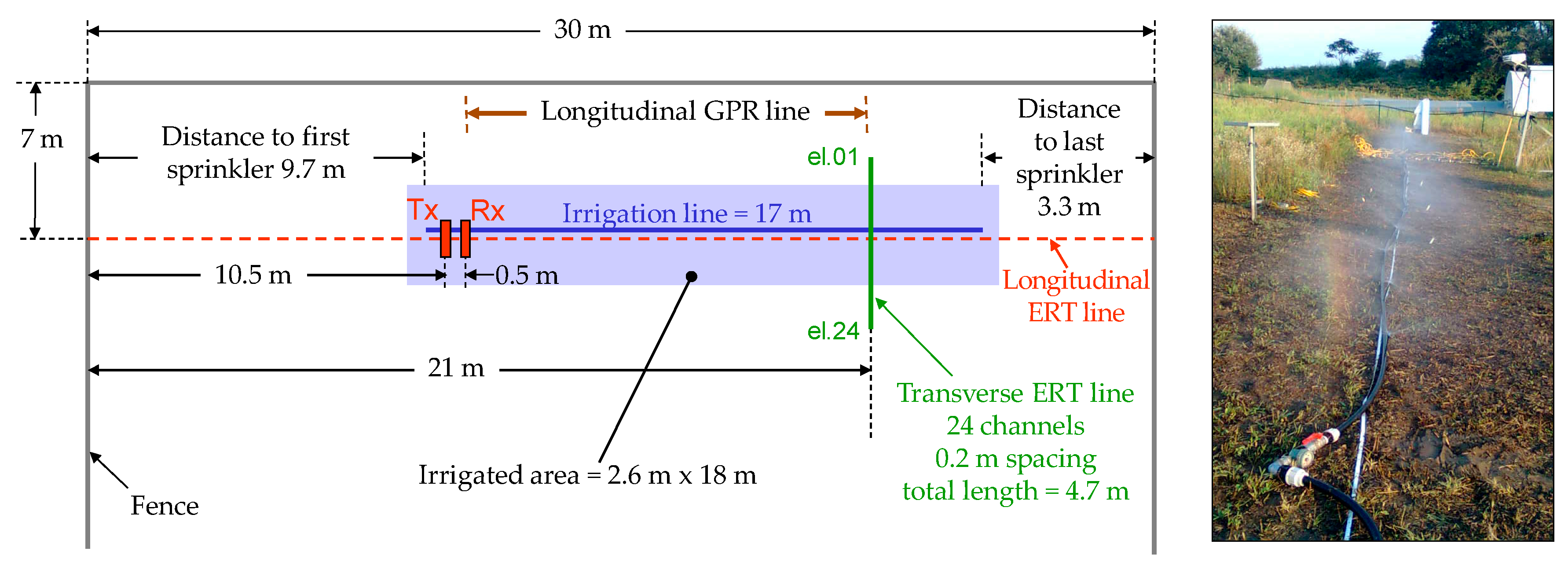
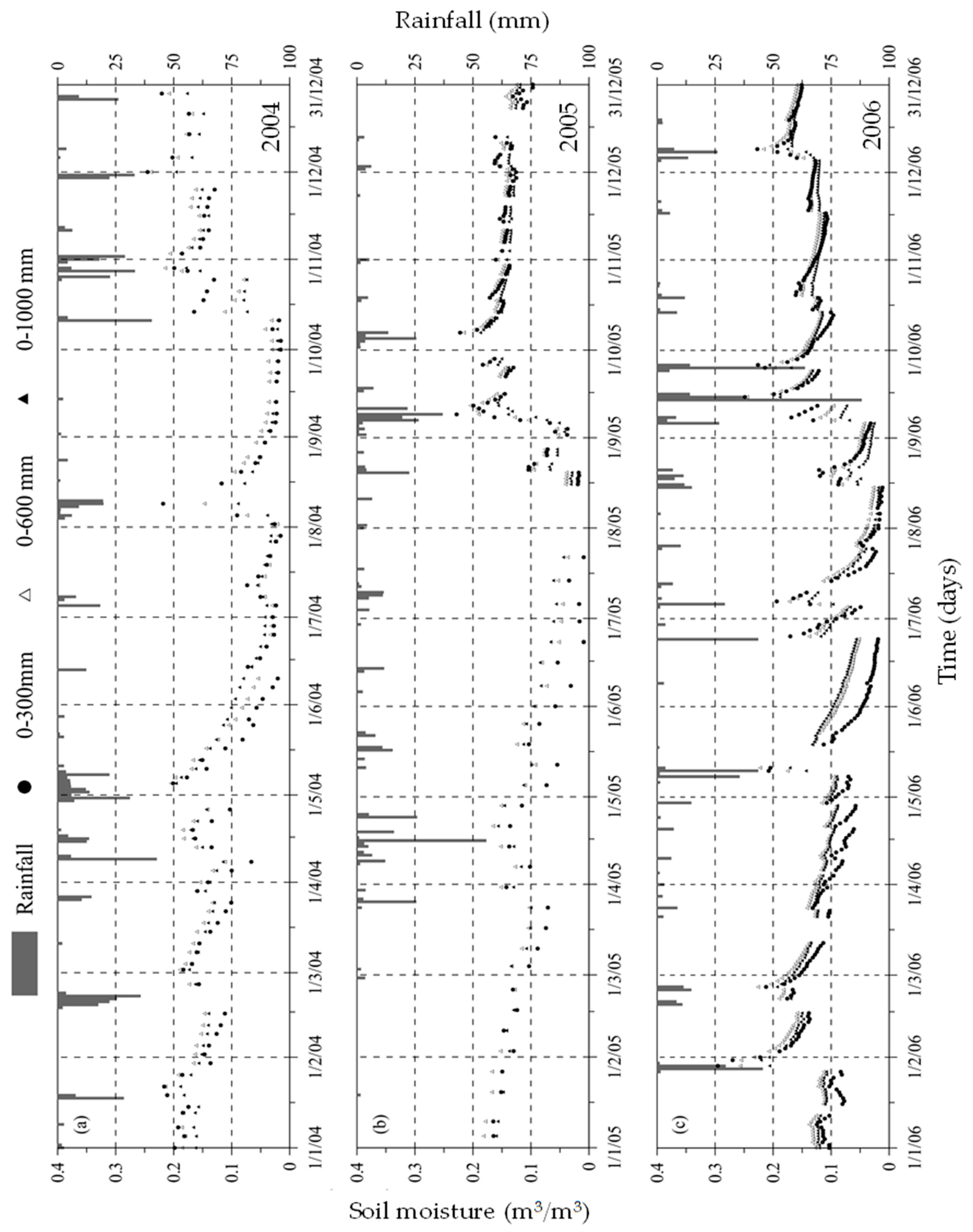
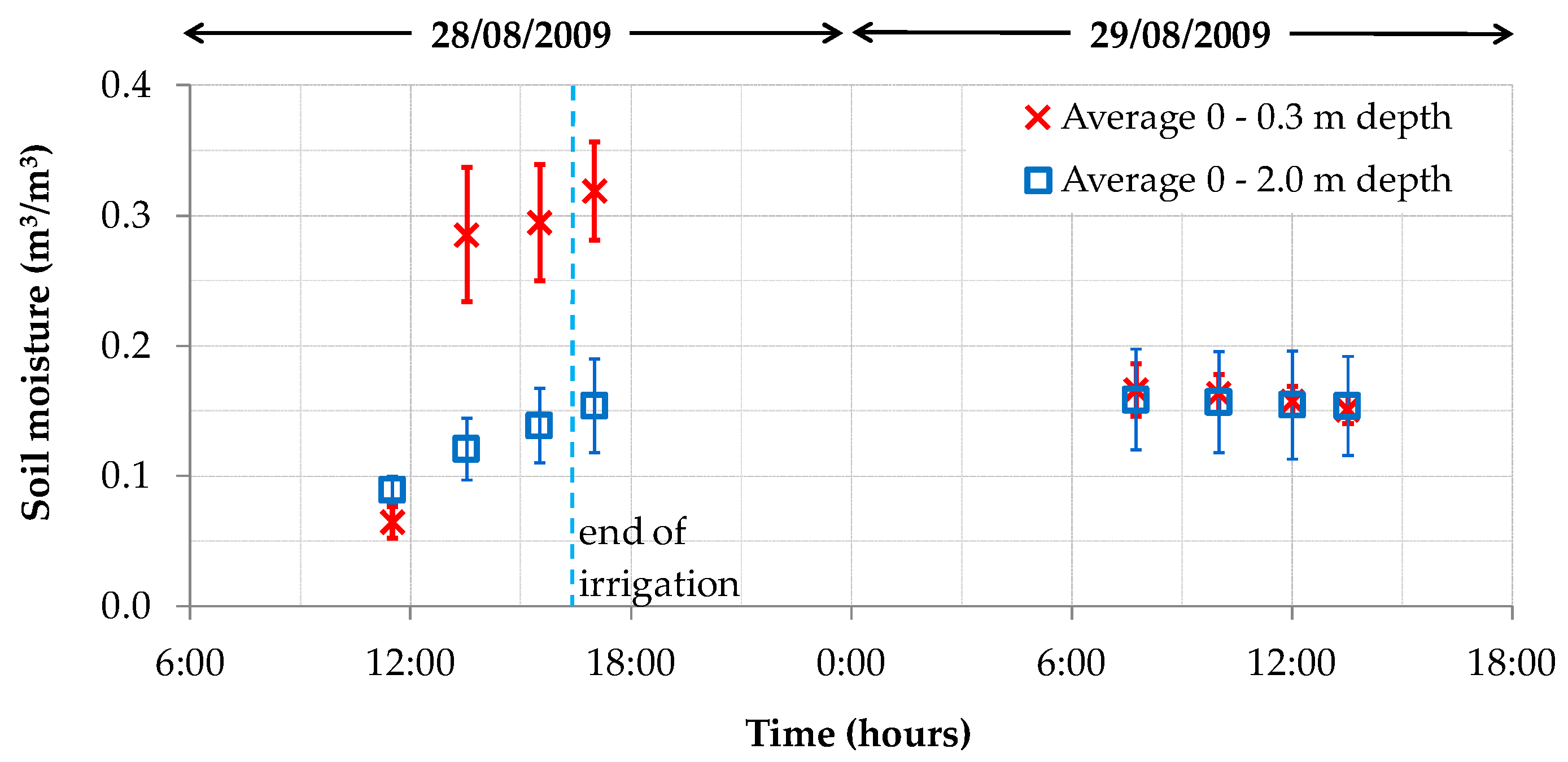
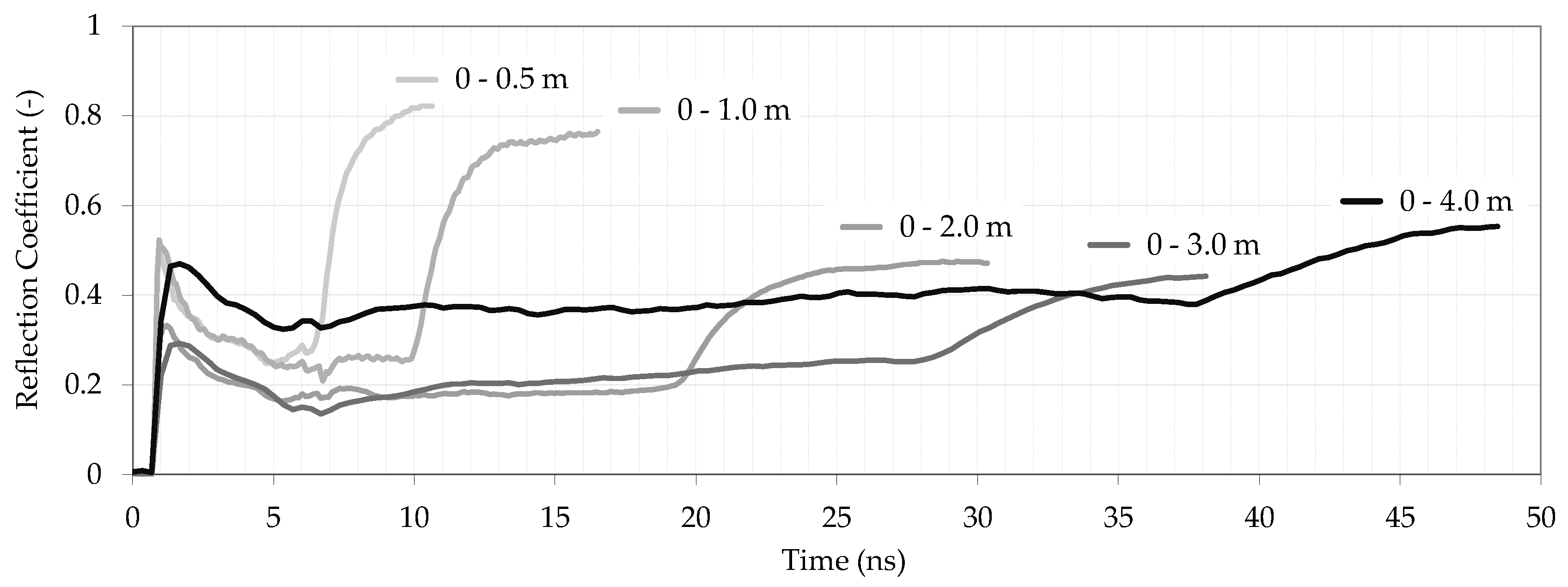
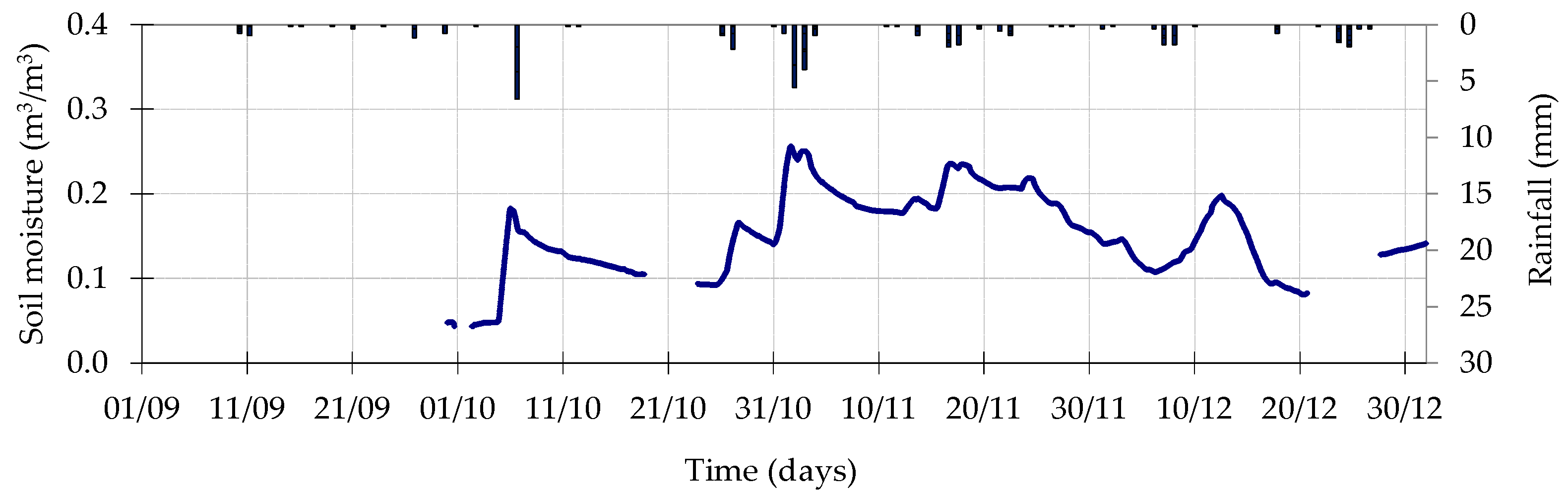
4.1. Plain Permanent Meadow
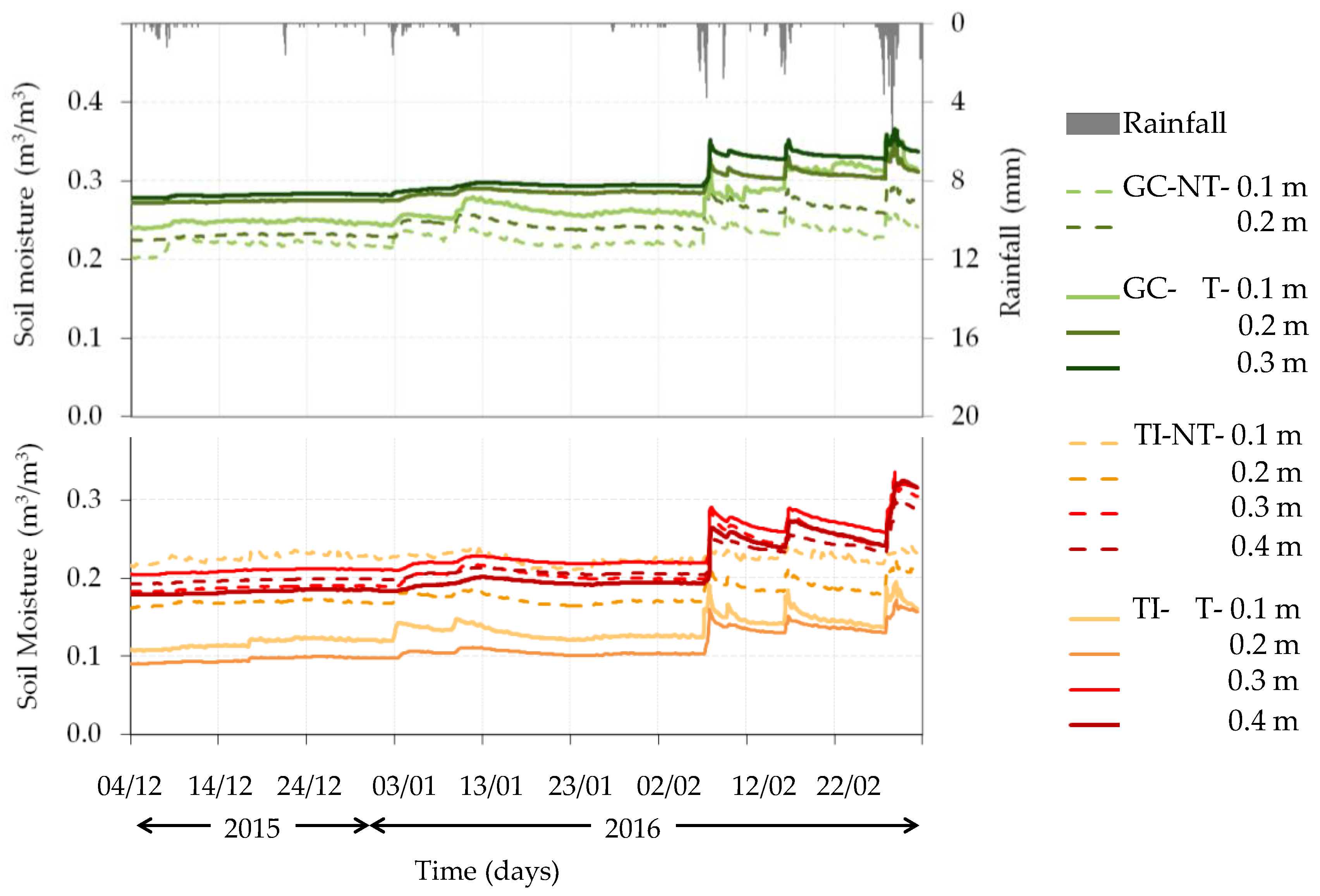
4.2. Mountain Permanent Meadow
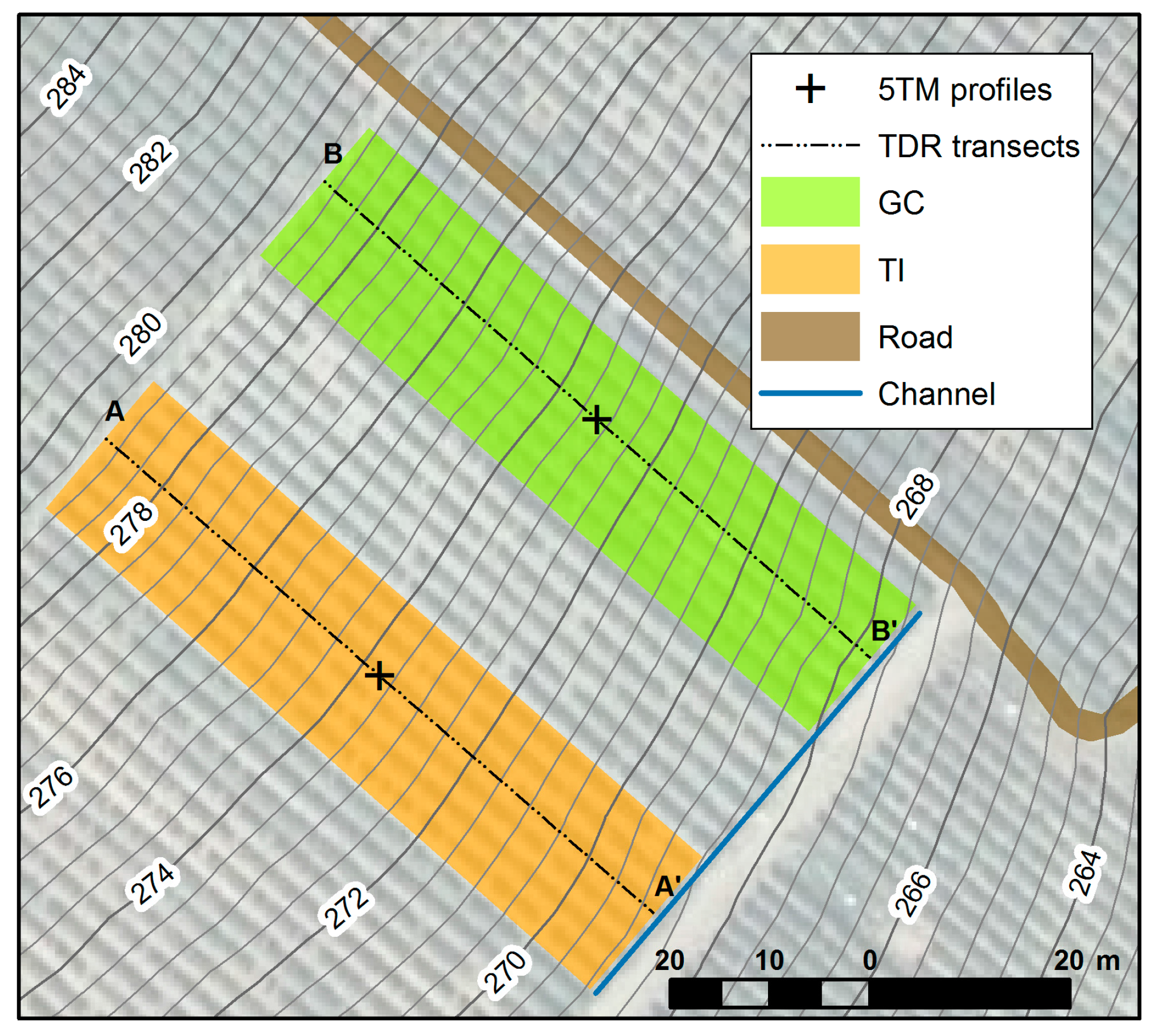
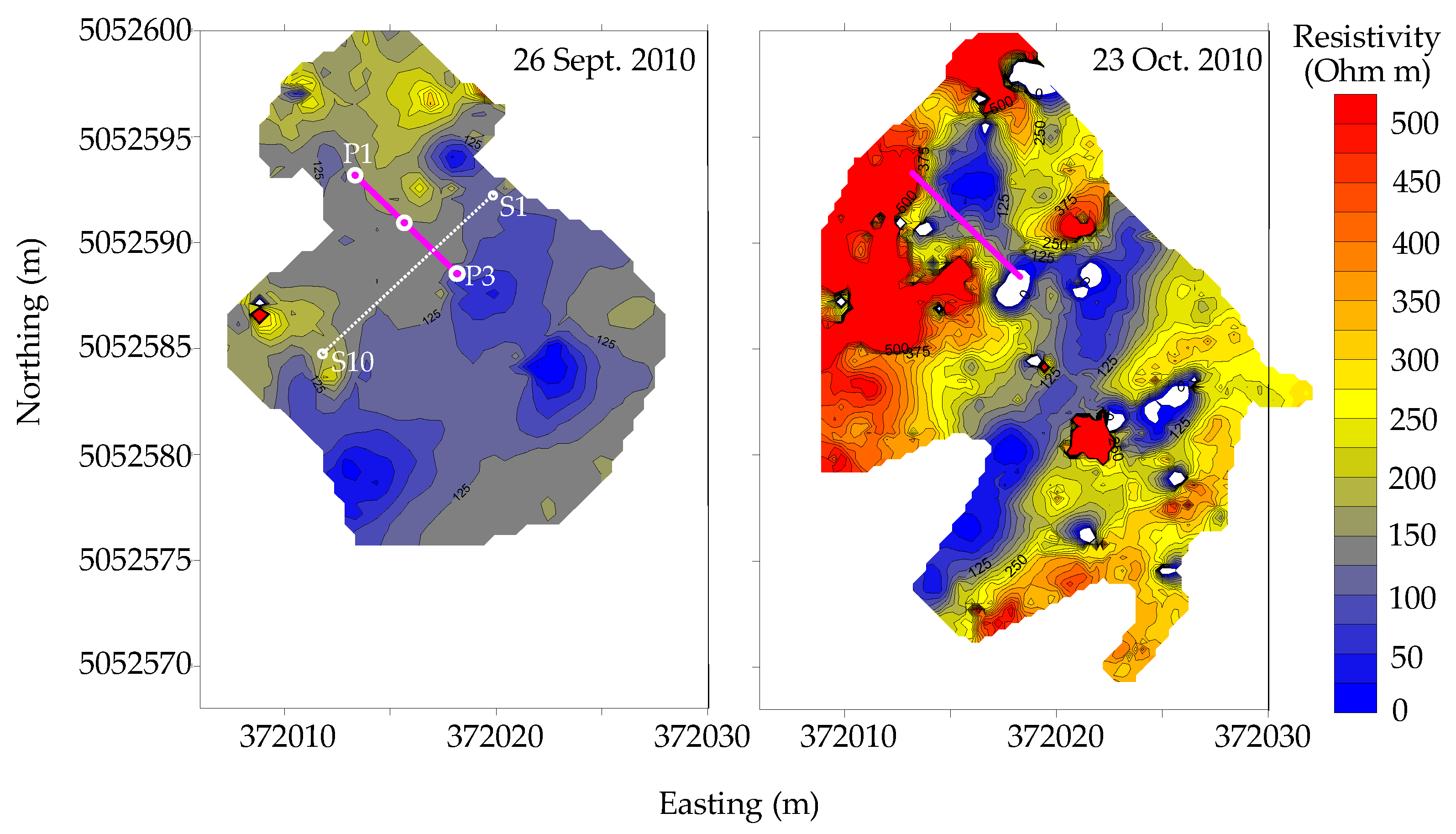
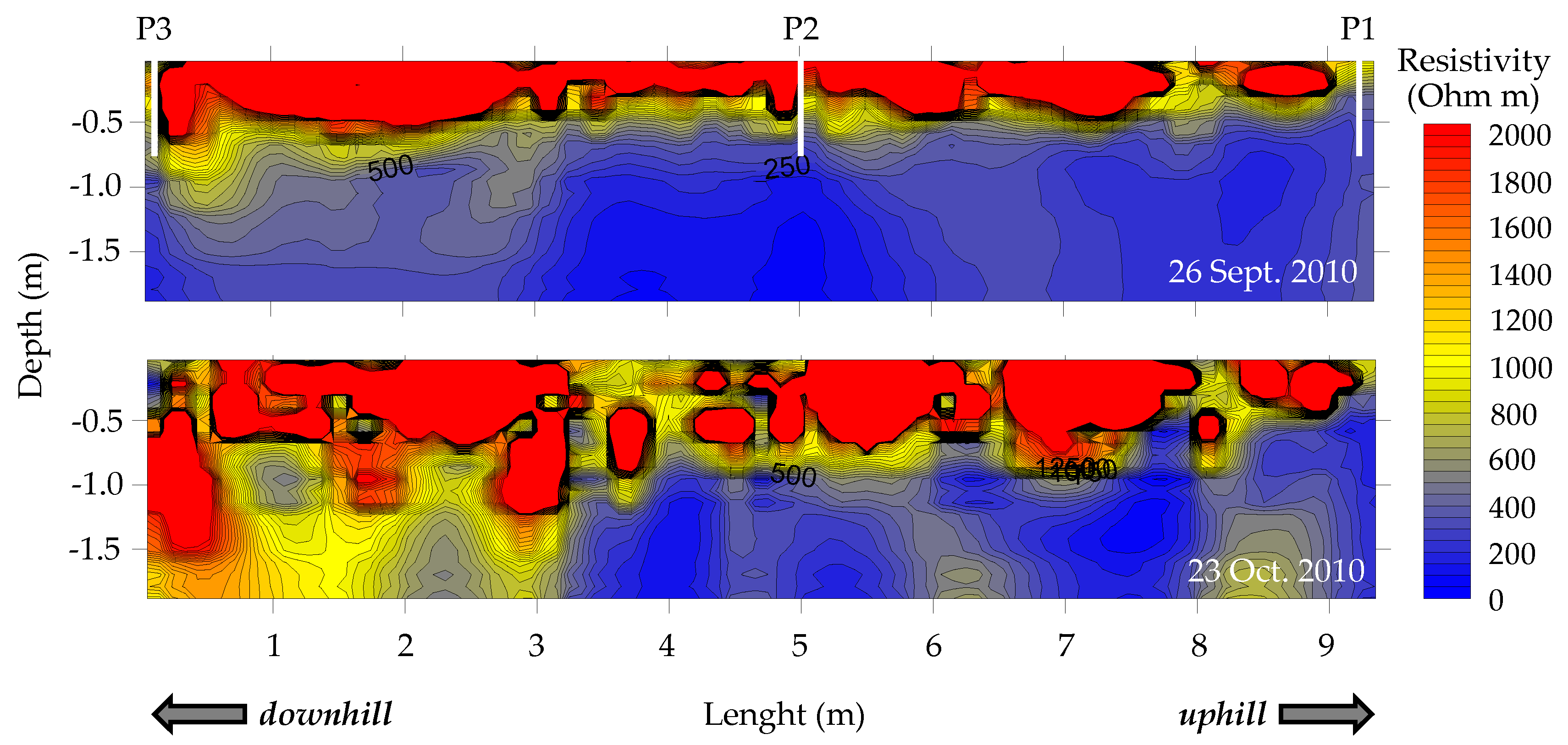
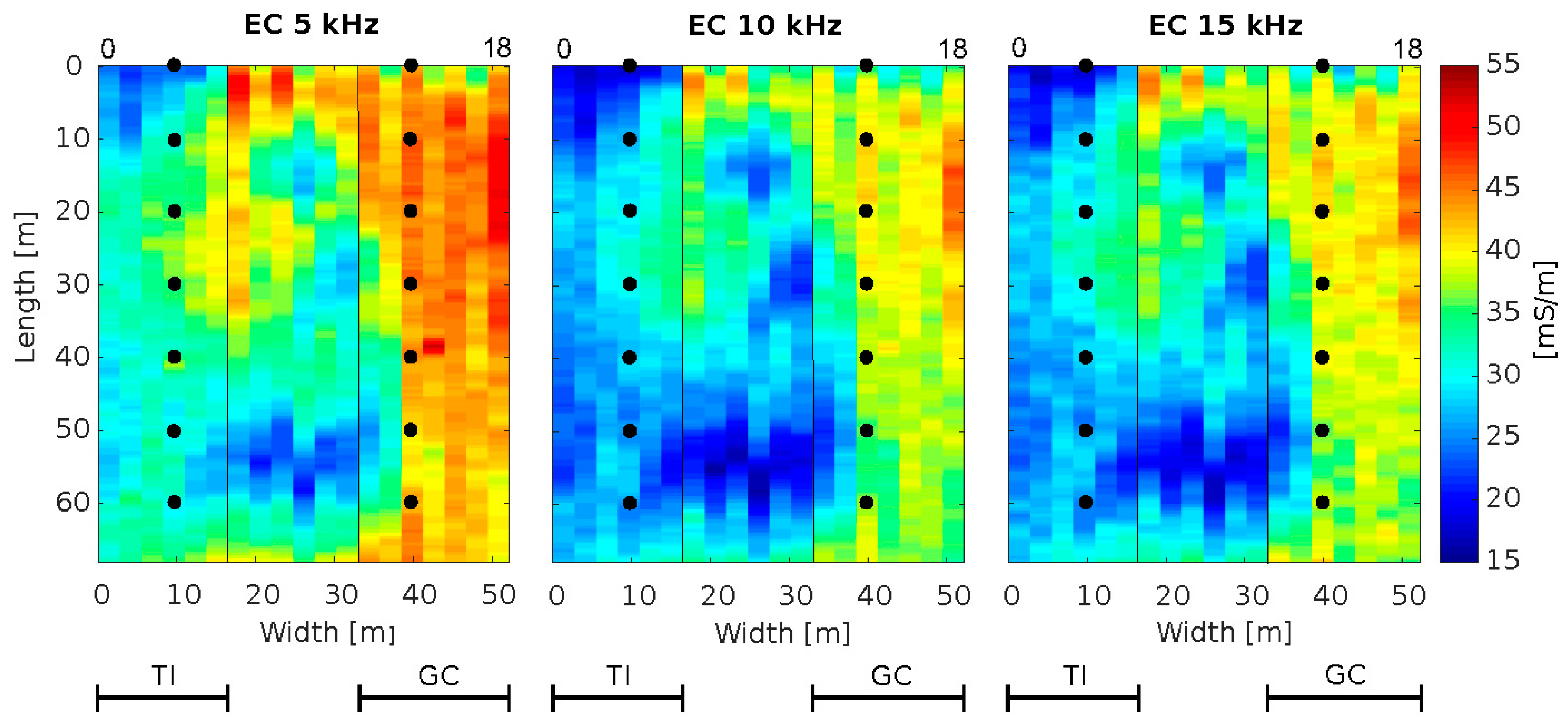
4.3. Hilly Vineyard
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, H. Temporal stability of soil moisture spatial pattern and subsurface preferential flow pathways in the shale hills catchment. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 317–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp-van Meerveld, H.J.; McDonnell, J.J. On the interrelations between topography, soil depth, soil moisture, transpiration rates and species distribution at the hillslope scale. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuling, A.J.; Hupet, F.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Troch, P.A. Climate variability effects on spatial soil moisture dynamics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Huisman, J.A.; Bogena, H.; Vanderborght, J.; Vrugt, J.A.; Hopmans, J.W. On the value of soil moisture measurements in vadose zone hydrology: A review. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Huisman, J.A.; Pachepsky, Y.; Montzka, C.; Van Der Kruk, J.; Bogena, H.; Vanderborght, J. On the spatio-temporal dynamics of soil moisture at the field scale. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 76–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceaglio, E.; Mitterer, C.; Maggioni, M.; Ferraris, S.; Segor, V.; Freppaz, M. The role of soil volumetric liquid water content during snow gliding processes. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 136, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomblies, A. Modeling the role of rainfall patterns in seasonal malaria transmission. Clim. Chang. 2012, 112, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previati, M.; Bevilacqua, I.; Canone, D.; Ferraris, S.; Haverkamp, R. Evaluation of soil water storage efficiency for rainfall harvesting on hillslope micro-basins built using time domain reflectometry measurements. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canone, D.; Previati, M.; Bevilacqua, I.; Salvai, L.; Ferraris, S. Field measurements based model for surface irrigation efficiency assessment. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 156, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canone, D.; Previati, M.; Ferraris, S. Evaluation of Stemflow Effects on the Spatial Distribution of Soil Moisture Using TDR Monitoring and an Infiltration Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 2017, 143, 04016075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Campbell, C.S.; Hopmans, J.W.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Jones, S.B.; Knight, R.; Ogden, F.; Selker, J.; Wendroth, O. Soil moisture measurement for ecological and hydrological watershed-scale observatories: A review. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, A.; Temimi, M.; Morgan, K.; Kelleners, T.J. In-situ and remote soil moisture sensing technologies for vadose zone hydrology. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Tarpanelli, A. Soil Moisture for Hydrological Applications: Open Questions and New Opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N. Soil moisture at local scale: Measurements and simulations. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C. State of the art of measuring soil water content. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 2993–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Jones, S.B.; Wraith, J.M.; Or, D.; Friedman, S.P. A review of advances in dielectric and electrical conductivity measurement in soils using time domain reflectometry. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 444–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Jones, S.B.; Blonquist, J.M.; Friedman, S.P. A physically derived water content/permittivity calibration model for coarse-textured, layered soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, F.; Campbell, C.S.; Campbell, G.S.; Cobos, D.R.; Teare, B.L.; Carter, B.; Hopmans, J.W. Frequency, electrical conductivity and temperature analysis of a low-cost capacitance soil moisture sensor. J. Hydrol. 2008, 352, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonquist, J.M.; Jones, S.B.; Robinson, D.A.; Rasmussen, V.P.; Or, D. Standardizing characterization of electromagnetic water content sensors. Vadose Zone J. 2005, 4, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogena, H.R.; Huisman, J.A.; Oberdorster, C.; Vereecken, H. Evaluation of a low-cost soil water content sensor for wireless network applications. J. Hydrol. 2007, 344, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, U.; Huisman, J.A.; Weuthen, A.; Vereecken, H.; Bogena, H.R. Sensor-to-sensor variability of the ECH2O EC-5, TE, and 5TE sensors in dielectric liquids. Vadose Zone J. 2010, 9, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.M.; Allmaras, R.R. System for automating and multiplexing soil moisture measurement by time-domain reflectometry. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimovaara, T.J.; Bouten, W. A computer-controlled 36-channel time domain reflectometry system for monitoring soil water contents. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Dobriyal, P.; Qureshi, A.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A. A review of the methods available for estimating soil moisture and its implications for water resource management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 458, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.A.; Hubbard, S.S.; Redman, J.D.; Annan, A.P. Measuring soil water content with ground penetrating radar. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbin, G.; Or, D. Ground-penetrating radar measurement of crop and surface water content dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Weihermüller, L.; Huisman, J.A.; Vereecken, H.; Vanclooster, M.; Slob, E.C. Analysis of air-launched ground-penetrating radar techniques to measure the soil surface water content. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Slob, E.; Chavarro, D.; Lubczynski, M.; Vereecken, H. Measuring soil surface water content in irrigated areas of southern Tunisia using full-waveform inversion of proximal GPR data. Near Sur. Geophys. 2008, 6, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.; Van der Kruk, J.; Bikowski, J.; Vereecken, H. Quantitative conductivity and permittivity estimation using full-waveform inversion of onground GPR data. Geophysics 2012, 77, H79–H91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzsche, A.; Van der Kruk, J.; Linde, N.; Doetsch, J.; Vereecken, H. 3-D characterization of high-permeability zones in a gravel aquifer using 2-D crosshole GPR full-waveform inversion and waveguide detection. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 195, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Manoli, G.; Pasetto, D.; Deiana, R.; Ferraris, S.; Strobbia, C.; Cassiani, G. Coupled inverse modeling of a controlled irrigation experiment using multiple hydro-geophysical data. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 82, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Lebron, I.; Kocar, B.; Phan, K.; Sampson, M.; Crook, N.; Fendorf, S. Time-lapse geophysical imaging of soil moisture dynamics in tropical deltaic soils: An aid to interpreting hydrological and geochemical processes. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Ursino, N.; Deiana, R.; Vignoli, G.; Boaga, J.; Rossi, M.; Ludwig, R. Non-invasive monitoring of soil static characteristics and dynamic states: A case study highlighting vegetation effects on agricultural land. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovelli, A.; Cassiani, G. Effective permittivity of porous media: A critical analysis of the complex refractive index model. Geophys. Prospect. 2008, 56, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brovelli, A.; Cassiani, G. Combined estimation of effective electrical conductivity and permittivity for soil monitoring. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Chambers, J.E.; Rucker, D.F.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P.B. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, J.; Huisman, J.A.; Van der Kruk, J.; Vereecken, H. Geophysical methods for field-scale imaging of root zone properties and processes. In Soil–Water–Root Processes: Advances in Tomography and Imaging; Anderson, S.H., Hopmans, J.W., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2013; pp. 247–281. [Google Scholar]
- Manoli, G.; Rossi, M.; Pasetto, D.; Deiana, R.; Ferraris, S.; Cassiani, G.; Putti, M. An iterative particle filter approach for coupled hydro-geophysical inversion of a controlled infiltration experiment. J. Comput. Phys. 2015, 283, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbuckle, B.K.; England, A.W.; De Roo, R.D.; Fischman, M.A.; Boprie, D.L. Vegetation canopy anisotropy at 1.4 GHz. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, K.; Wigneron, J.P.; Waldteufel, P.; De Rosnay, P.; Schwank, M.; Calvet, J.C.; Kerr, Y.H. Estimates of surface soil moisture under grass covers using L-band radiometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Shin, I. A physically-based inversion algorithm for retrieving soil moisture in passive microwave remote sensing. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, K.C.; Coulibaly, P. Advances in soil moisture retrieval from synthetic aperture radar and hydrological applications. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 460–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigber, A.; Scheiber, R.; Jager, M.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Hajnsek, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Horn, R. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreda, M.; Desilets, D.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Scott, R.L. Measuring soil moisture content non-invasively at intermediate spatial scale using cosmic-ray neutrons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreda, M.; Shuttleworth, W.J.; Zeng, X.; Zweck, C.; Desilets, D.; Franz, T.; Rosolem, R. COSMOS: The COsmic-ray soil moisture observing system. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 4079–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera Villarreyes, C.A.; Baroni, G.; Oswald, S.E. Integral quantification of seasonal soil moisture changes in farmland by cosmic-ray neutrons. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogena, H.R.; Huisman, J.A.; Baatz, R.; Hendricks Franssen, H.J.; Vereecken, H. Accuracy of the cosmic-ray soil water content probe in humid forest ecosystems: The worst case scenario. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5778–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Tan, L.; Gao, S.; Jiao, Q. Observation on soil moisture of irrigation cropland by cosmic-ray probe. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Mohanty, B.P. Development of a deterministic downscaling algorithm for remote sensing soil moisture footprint using soil and vegetation classifications. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6208–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, A.V.M.; Mohanty, B.P.; Shin, Y. An unmixing algorithm for remotely sensed soil moisture. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Niesel, J. Spatial downscaling of satellite soil moisture data using vegetation temperature condition index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Niesel, J.; Loew, A. Evaluation of soil moisture downscaling using a simple thermal-based proxy: The REMDHUS network (Spain) example. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4765–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, J.-C.; Noilhan, J. From near-surface to root-zone soil moisture using year-round data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2000, 1, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, J.M.; Jarlan, L.; Calvet, J.C.; Bouyssel, F.; De Rosnay, P. From near-surface to root-zone soil moisture using different assimilation techniques. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Rudiger, C.; Pellarin, T.; Calvet, J.-C.; Fritz, N.; Froissard, F.; Suquia, D.; Petitpa, A.; Piguet, B.; Martin, E. From near-surface to root-zone soil moisture using an exponential filter: An assessment of the method based on in-situ observations and model simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfreda, S.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Sheffield, J. A physically based approach for the estimation of root-zone soil moisture from surface measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbs, E.; Gerard, F.; Petrie, A.; DeWitte, E. Emerging and Potential Future Applications of satellite-Based Soil Moisture products. In Satellite Soil Moisture Retrievals: Techniques and Applications; Petropoulos, G.P., Srivastava, P., Kerr, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 19, pp. 379–400. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Merlin, O.; Verhoest, N.E.C. A review of spatial downscaling of satellite remotely sensed soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.P.; Cosh, M.H.; Lakshmi, V.; Montzka, C. Soil moisture remote sensing: State-of-the-science. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desilets, D.; Zreda, M. Footprint diameter for a cosmic-ray soil moisture probe: Theory and Monte Carlo simulations. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, T.E.; Zreda, M.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Rosolem, R.; Zweck, C.; Stillman, S.; Zeng, X.; Shuttleworth, W.J. Measurement depth of the cosmic ray soil moisture probe affected by hydrogen from various sources. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W08515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhli, M.; Schrön, M.; Zreda, M.; Schmidt, U.; Dietrich, P.; Zacharias, S. Footprint characteristics revised for field-scale soil moisture monitoring with cosmic-ray neutrons. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 5772–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, M.T.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C.; El-Rayes, M.A.; Wu, L.K. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil-part 1: Empirical models and experimental observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R. Soil water measurement by time domain reflectometry. In Encyclopedia of Water Science; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Bushland, TX, USA, 2003; pp. 894–898. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, G.C.; Ferré, T.P.A. Methods for measurement of soil water content: Time domain reflectometry. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 434–446. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, K.; Schulin, R.; Flühler, H.; Attinger, W. Calibration of time domain reflectometry for water content measurement using a composite dielectric approach. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkelrath, W.N.; Hamburg, S.P.; Murphy, F. Automatic, real-time monitoring of soil moisture in a remote field area with time domain reflectometry. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content using TDR: I. Applications to wetting fronts and steep gradients. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content using TDR: II. Evaluation of installation and configuration of parallel transmission lines. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegelin, S.J.; White, I.; Jenkins, D.R. Improved field probes for soil water content and electrical conductivity measurement using time domain reflectometry. Water Resour. Res. 1989, 25, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimovaara, T.J. Design of triple-wire time domain reflectometry probes in practice and theory. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, P.A.; Rudolph, D.L.; Kachanoski, R.G. Spatial averaging of water content by time domain reflectometry: Implications for twin rod probes with and without dielectric coatings. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, P.A.; Knight, J.H.; Rudolph, D.L.; Kachanoski, R.G. The sample areas of conventional and alternative time domain reflectometry probes. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canone, D.; Previati, M.; Ferraris, S.; Haverkamp, R. A new coaxial time domain reflectometry probe for water content measurement in forest floor litter. Vadose Zone J. 2009, 8, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelakun, I.A.; Ranjan, R.S. Design of a Multilevel TDR Probe for Measuring Soil Water Content at Different Depths. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, H.H.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Moldrup, P. Sample area of two- and three-rod time domain reflectometry probes. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, C.M.; Jones, S.; Meding, M.; Tuller, M. Evaluation of standard calibration functions for eight electromagnetic soil moisture sensors. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.S.; Campbell, G.S.; Cobos, D.R.; Bissey, L.L. Calibration and Evaluation of an Improved Low-Cost Soil Moisture Sensor. 2009. Available online: http://www.decagon.com (accessed on 12 September 2017).
- Logsdon, S.D.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Hatfield, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Prueger, J.H.; Schilling, K.E. Soil water and shallow groundwater relations in an agricultural hillslope. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.R.; Bandaranayake, W.M. Performance of a new capacitance soil moisture probe in a sandy soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evett, S.R.; Schwartz, R.C. Discussion of “Soil Moisture Measurements: Comparison of Instrumentation Performances” by Ventura Francesca, Facini Osvaldo, Piana Stefano, and Rossi Pisa Paola. J. Irrig. Drain. Res. 2011, 137, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, T.; Limsuwat, A.; Illangasekare, T.H. A simple method for calibrating dielectric soil moisture sensors: Laboratory validation in sands. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.P. Soil properties influencing apparent electrical conductivity: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, G.E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Boaga, J.; Rossi, M.; Fadda, G.; Putti, M.; Majone, B.; Bellin, A. Soil-plant interaction monitoring: Small scale example of an apple orchard in Trentino, North-Eastern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortuani, B.; Chiaradia, E.A.; Priori, S.; L’Abate, G.; Canone, D.; Comunian, A.; Giudici, M.; Mele, M.; Facchi, A. Mapping soil water capacity through EMI survey to delineate site specific management units within an irrigated field. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, G.P.; Fenu, C.; Rodriguez, G. Regularized solution of a nonlinear problem in electromagnetic sounding. Inverse Probl. 2014, 30, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz De Alba, P.; Rodriguez, G. Regularized inversion of multi-frequency EM data in geophysical applications. In Trends in Differential Equations and Applications; Ortegón, F., Gallego, M.V., Redondo, N., Rodríguez Galván, J.R., Eds.; SEMA SIMAI Springer Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 8, pp. 357–369. [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan, P.W.; Binley, A.; Whalley, W.R.; Watts, C.W. The Use of Electromagnetic Induction to Monitor Changes in Soil Moisture Profiles beneath Different Wheat Genotypes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaga, J. The use of FDEM in hydrogeophysics: A review. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 139, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, M.E.; Meju, M.A. Near-surface controlled-source electromagnetic induction: Background and recent advances. In Hydrogeophysics; Rubin, Y., Hubbard, S.S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 157–183. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, A.; Kemna, A. DC resistivity and induced polarization methods. In Hydrogeophysics; Rubin, Y., Hubbard, S.S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 129–156. [Google Scholar]
- Binley, A.M.; Cassiani, G.; Deiana, R. Hydrogeophysics—Opportunities and Challenges. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2010, 51, 267–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cassiani, G.; Bruno, V.; Villa, A.; Fusi, N.; Binley, A.M. A saline trace test monitored via time-lapse surface electrical resistivity tomography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2006, 59, 244–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.C.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C.G. Occam’s Inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from EM sounding data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Brecque, D.J.; Heath, G.; Sharpe, R.; Versteeg, R. Autonomous monitoring of fluid movement using 3-D electrical resistivity tomography. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2004, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Godio, A.; Stocco, S.; Villa, A.; Deiana, R.; Frattini, P.; Rossi, M. Monitoring the hydrologic behaviour of a mountain slope via time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography. Near Sur. Geophys. 2009, 7, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinnell, A.C.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Vrugt, J.A.; Huisman, J.A.; Moysey, S.; Rings, J.; Kowalsky, M.B. Improved extraction of hydrologic information from geophysical data through coupled hydrogeophysical inversion. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beff, L.; Günther, T.; Vandoorne, B.; Couvreur, V.; Javaux, M. Three-dimensional monitoring of soil water content in a maize field using Electrical Resistivity Tomography. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garré, S.; Coteur, I.; Wongleecharoen, C.; Kongkaew, T.; Diels, J.; Vanderborght, J. Non-invasive monitoring of soil water dynamics in mixed cropping systems: A case study in Ratchaburi Province, Thailand. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L.; Binley, A.M.; Daily, W.; Johnson, R. Cross-hole electrical imaging of a controlled saline tracer injection. J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 44, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Binley, A. Modeling unsaturated flow in a layered formation under quasi-steady state conditions using geophysical data constraints. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, N.; Binley, A.; Tryggvason, A.; Pedersen, L.B.; Revil, A. Improved hydrogeophysical characterization using joint inversion of cross-hole electrical resistance and ground-penetrating radar traveltime data. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binley, A.; Cassiani, G.; Middleton, R.; Winship, P. Vadose zone flow model parameterisation using cross-borehole radar and resistivity imaging. J. Hydrol. 2002, 267, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuecco, G.; Borga, M.; Penna, D.; Canone, D.; Previati, M.; Ferraris, S. Towards improved understanding of land use effect on soil moisture variability: Analysis and modeling at the plot scale. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudena, M.; Bevilacqua, I.; Canone, D.; Ferraris, S.; Previati, M.; Provenzale, A. Soil water dynamics at a midlatitude test site: Field measurements and box modeling approaches. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.B.; Wraith, J.M.; Or, D. Time domain reflectometry measurement principles and applications. Hydrol. Processes 2002, 16, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, J.A.; Minzenmayer, F.E.; Waltman, S.W.; Benham, E.C.; Tuttle, J.W.; Peaslee, S.D. Ground-penetrating radar soil suitability map of the conterminous United States. Geoderma 2007, 141, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniconi, C.; Ferraris, S.; Putti, M.; Pini, G.; Gambolati, G. Three-dimensional numerical codes for simulating groundwater contamination: FLOW3D, flow in saturated and unsaturated porous media. In Pollution Modeling; CMP: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Or, D.; Jones, S.B.; VanSchaar, J.R.; Humphries, S.D.; Koberstein, R.L. WinTDR v.6.1: A Windows-based Time Domain Reflectometry Program for Measurement of Soil Water Content and Electrical Conductivity—User Manual. Utah State Univ. Soil Physics Group, Logan. 2004. Available online: https://psc.usu.edu/ou-files/wintdr/Introduction.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2017).
- Ursino, N.; Cassiani, G.; Deiana, R.; Vignoli, G.; Boaga, J. Measuring and Modelling water related soil—Vegetation feedbacks in a fallow plot. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A. Resistivity Inversion Software. 2013. Available online: http://www.es.lancs.ac.uk/people/amb/Freeware/freeware.htm (accessed on 12 September 2017).
- Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Opsi, F.; Cavallo, E. Long-term monitoring of soil management effects on runoff and soil erosion in sloping vineyards in Alto Monferrato (North-West Italy). Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Pitacco, A.; Cavallo, E. Temporal variability of soil management effects on soil hydrological properties, runoff and erosion at the field scale in a hillslope vineyard, North-West Italy. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, J.L.; Paltineanu, I.C. Methods for Measurement of Soil Water Content: Capacitance Devices. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 463–474. [Google Scholar]
- Bittelli, M.; Flury, M.; Roth, K. Use of dielectric spectroscopy to estimate ice content in frozen porous media. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W04212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Dyck, M. Application of multiphase dielectric mixing models for understanding the effective dielectric permittivity of frozen soils. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Ramirez, A.; Daily, W. Regularised image reconstruction of noisy electrical resistance tomography data. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop of the European Concerted Action on Process Tomography, Bergen, Norway, 6–8 April 1995; pp. 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Monego, M.; Cassiani, G.; Deiana, R.; Putti, M.; Passadore, G.; Altissimo, L. Tracer test in a shallow heterogeneous aquifer monitored via time-lapse surface ERT. Geophysics 2010, 75, WA61–WA73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, W.; Ramirez, A.; LaBrecque, D.; Nitao, J. Electrical resistivity tomography of vadose water movement. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Andrieux, P. Infiltration characteristics of soils in Mediterranean vineyards in Southern France. Catena 1998, 32, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, A.; Usowicz, B.; Lipiec, J. Effects of tractor traffic on spatial variability of soil strength and water content in grass covered and cultivated sloping vineyard. Soil Till. Res. 2005, 84, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Binley, A.; Crook, N.; Day-Lewis, F.D.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Grauch, V.J.S.; Knight, R.; Knoll, M.; Lakshmi, V.; Miller, R.; et al. Advancing process-based watershed hydrological research using near-surface geophysics: A vision for, and review of, electrical and magnetic geophysical methods. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3604–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



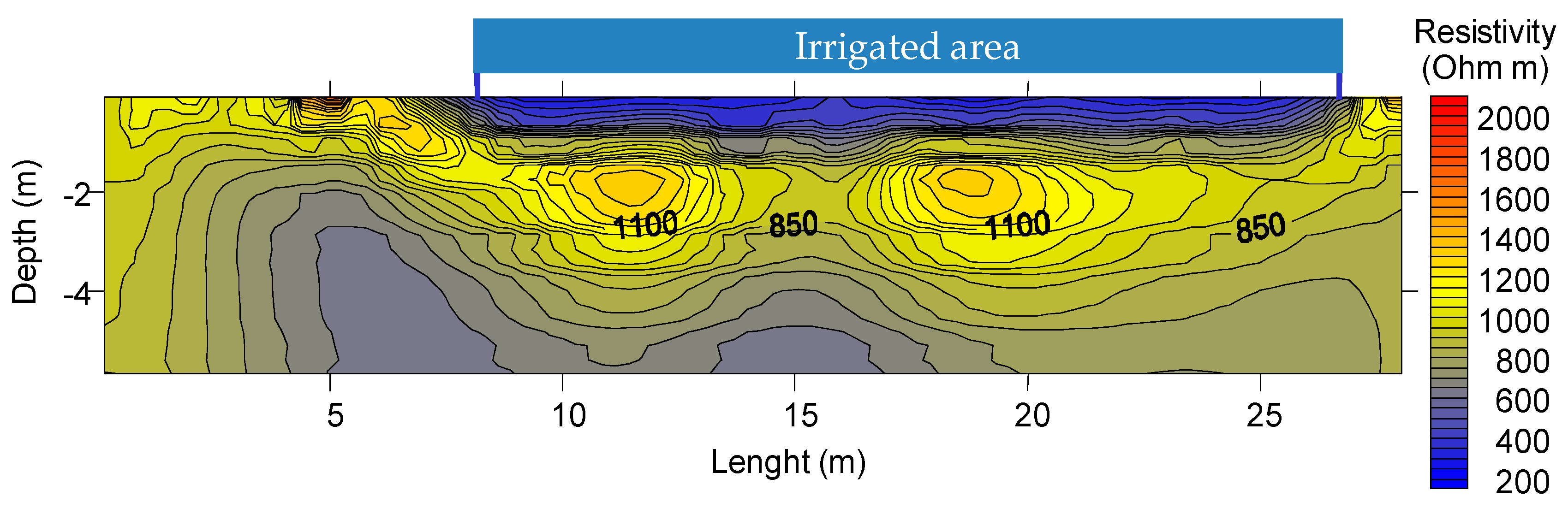
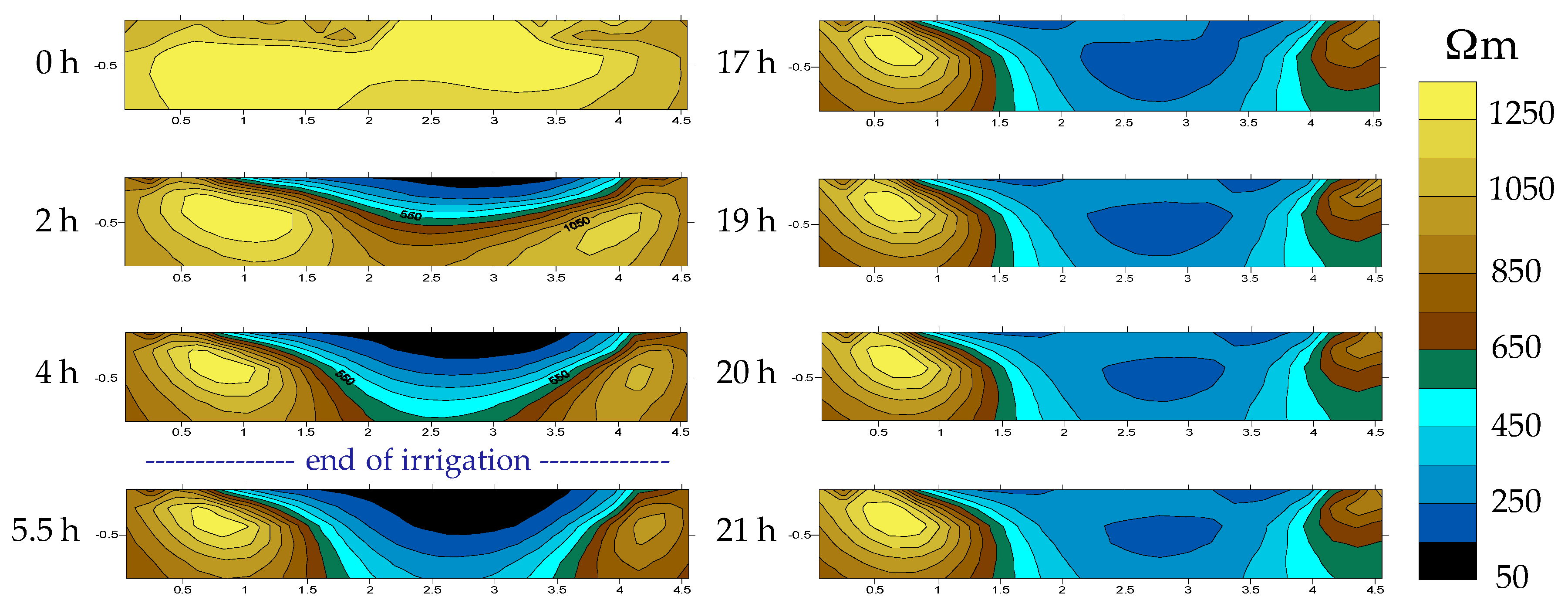
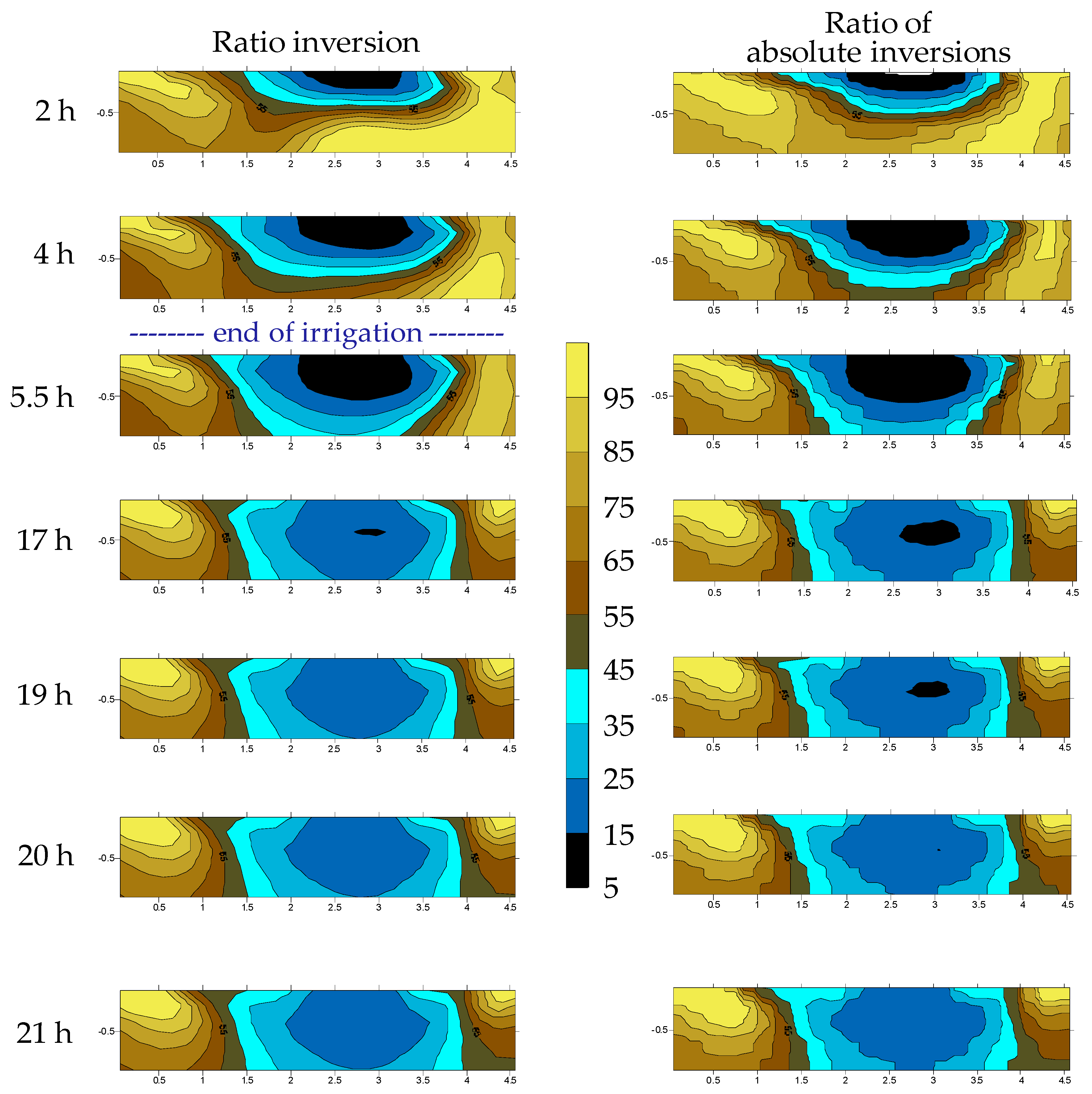
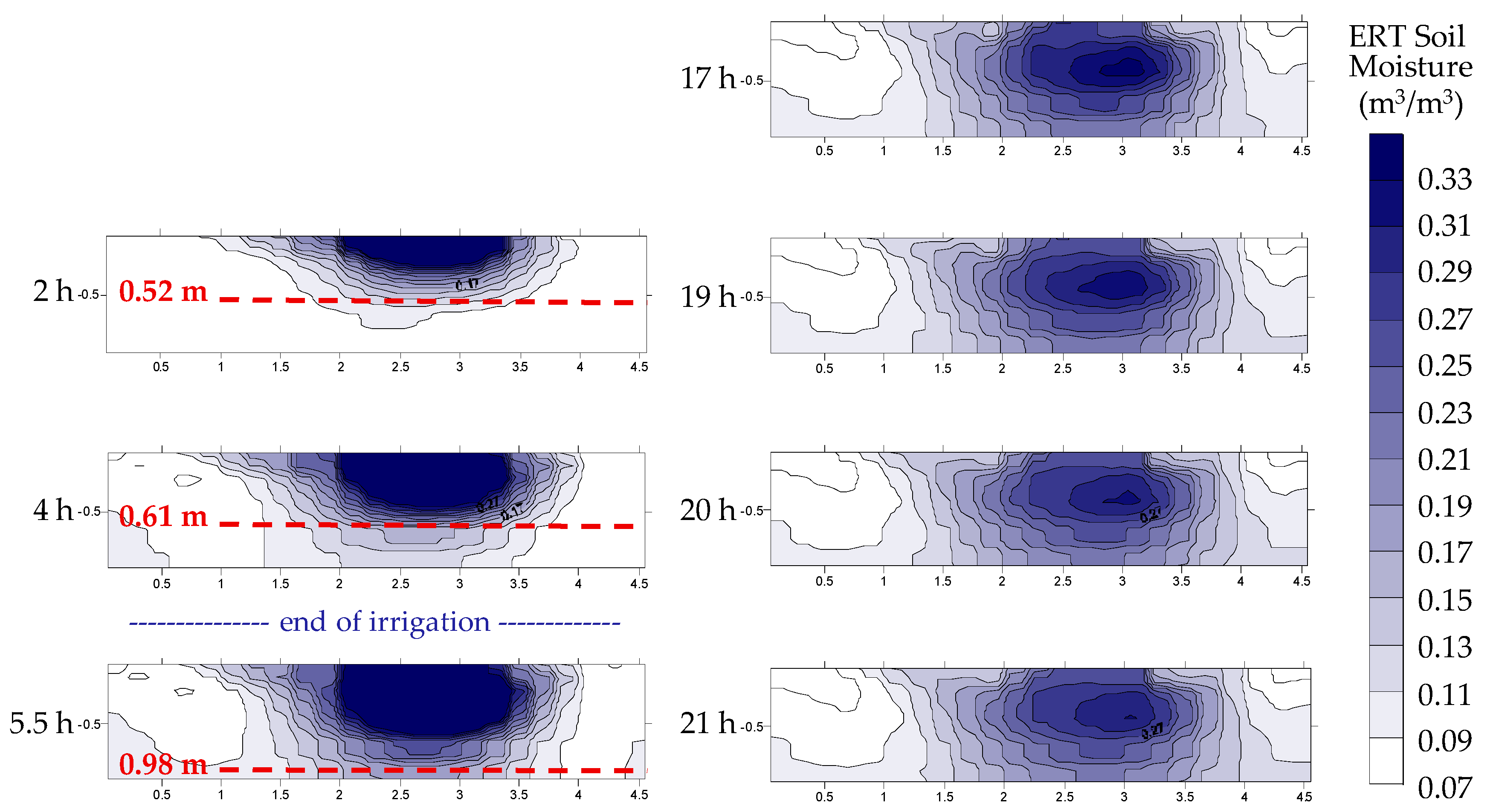


| Plain [Permanent Meadow] | Mountain [Permanent Meadow] | Hill [Vineyard] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long Time Surveys | Single Campaigns | Long Time Surveys | Single Campaigns | Long Time Surveys | Single Campaigns | |
| Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Soil moisture sensors directly connected to data loggers | √ | √ | ||||
| Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) | √ | √ | ||||
| Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) | √ | √ | ||||
| Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) | √ | |||||
| Probe Code | Transect “P” | Transect “S” | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | ||||||
| Depth from surface (m) | 0.75 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.30 | ||
| Soil moisture (m3/m3) | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.31 | - | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.27 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raffelli, G.; Previati, M.; Canone, D.; Gisolo, D.; Bevilacqua, I.; Capello, G.; Biddoccu, M.; Cavallo, E.; Deiana, R.; Cassiani, G.; et al. Local- and Plot-Scale Measurements of Soil Moisture: Time and Spatially Resolved Field Techniques in Plain, Hill and Mountain Sites. Water 2017, 9, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090706
Raffelli G, Previati M, Canone D, Gisolo D, Bevilacqua I, Capello G, Biddoccu M, Cavallo E, Deiana R, Cassiani G, et al. Local- and Plot-Scale Measurements of Soil Moisture: Time and Spatially Resolved Field Techniques in Plain, Hill and Mountain Sites. Water. 2017; 9(9):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090706
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaffelli, Giulia, Maurizio Previati, Davide Canone, Davide Gisolo, Ivan Bevilacqua, Giorgio Capello, Marcella Biddoccu, Eugenio Cavallo, Rita Deiana, Giorgio Cassiani, and et al. 2017. "Local- and Plot-Scale Measurements of Soil Moisture: Time and Spatially Resolved Field Techniques in Plain, Hill and Mountain Sites" Water 9, no. 9: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090706
APA StyleRaffelli, G., Previati, M., Canone, D., Gisolo, D., Bevilacqua, I., Capello, G., Biddoccu, M., Cavallo, E., Deiana, R., Cassiani, G., & Ferraris, S. (2017). Local- and Plot-Scale Measurements of Soil Moisture: Time and Spatially Resolved Field Techniques in Plain, Hill and Mountain Sites. Water, 9(9), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090706









