Delineation of Salt Water Intrusion through Use of Electromagnetic-Induction Logging: A Case Study in Southern Manhattan Island, New York
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Historical Background
3. Methods
3.1. Manhattan Island Well Network
3.2. Groundwater Levels and Hydraulic Testing
3.3. Chloride Concentrations
3.4. Borehole-Geophysical Logging
4. Hydrogeology of the Glacial Aquifer in Manhattan Island
4.1. Extent and Thickness of the Glacial Aquifer
4.2. Water-Table Map of the Glacial Aquifer
4.3. Hydraulic Properties of the Glacial Aquifer
5. Extent of Saltwater Intrusion of the Glacial Aquifer in Southern Manhattan Island
5.1. Chloride Concentrations in the Glacial Aquifer in 1940–1950
5.2. Present Chloride Concentrations in the Glacial Aquifer
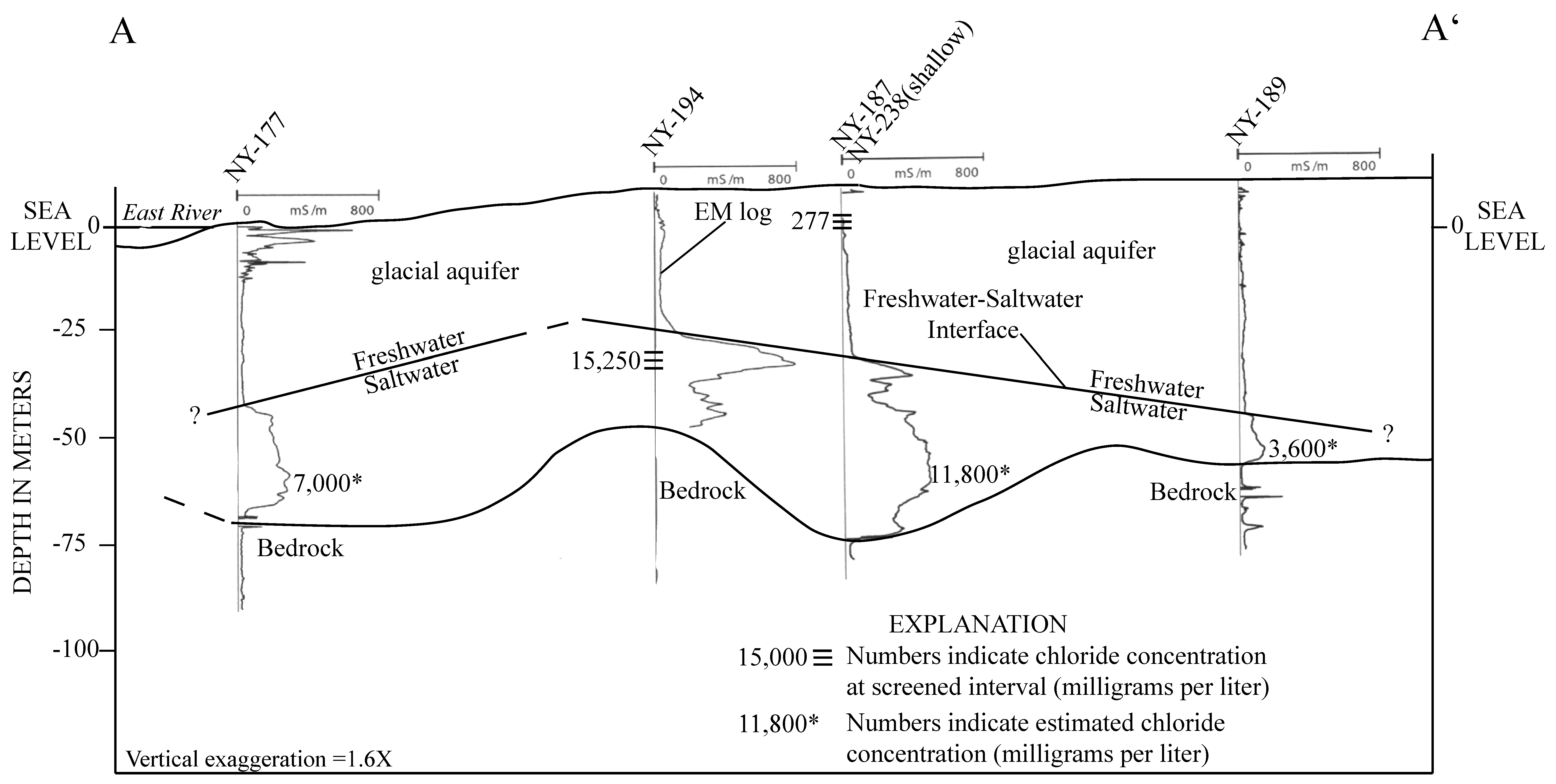
5.2.1. Saltwater Wedge A
5.2.2. Saltwater Wedges B, C, and D Under Current Conditions
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perlmutter, N.M.; Arnow, T. Ground Water in Bronx, New York, and Richmond Counties with Summary Data on Kings and Queens Counties, New York City, New York; Bulletin GW-32; New York State Water Power and Control Commission: Albany, NY, USA, 1953; 86p.
- Viele, E.L. Sanitary and Topographical Map of the City and Island of New York; NYC Council of Hygiene and Public Health, 1 Sheet, Scale 1:10,000; Ferd. Mayer & Co., Lithographers: New York, NY, USA, 1865. [Google Scholar]
- Graether, L.F. Geologic Map and Sections of Manhattan Island, New York; 2 Sheets, Scale 1:20,000; Leonard F. Graether: New York, NY, USA, 1898. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, W.H. The Configuration of the Rock Floor of Greater New York; U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 270; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1905; 96p.
- Baskerville, C.A. Bedrock and Engineering Geologic Maps of New York County and Parts of Kings and Queens Counties, New York; U.S. Geological Survey Miscellaneous Investigations Series, Map I-2306, 2 Sheets, Scale 1:24,000; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1994.
- Suter, R.; de Laguna, W.; Perlmutter, N.M. Mapping of Geologic Formations and Aquifers of Long Island, New York; Groundwater Bulletin 18; New York State Water Power and Control Commission: Albany, NY, USA, 1949; 212p.
- Stumm, F.; Chu, A.; Monti, J., Jr. Delineation of Faults, Fractures, Foliation, and Ground-Water-Flow Zones in Fractured-Rock, on the Southern part of Manhattan, New York, through Use of Advanced Borehole Geophysical Techniques; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 04-1232; USGS New York Water Science Center: Reston, VA, USA, 2004; 212p.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Monthly and Annual Precipitation at Central Park, Manhattan, New York. 2010. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/IPS/lcd/lcd.html?_page=1&state=NY&stationID=94728&_target2=Next+%3E (accessed on 23 August 2017).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Tides and Water Levels at the Battery, Manhattan, New York. 2017. Available online: https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/waterlevels.html?id=8518750 (accessed on 21 August 2017).
- Duffield, G.M. AQTESOLV for Windows Version 4.5 User's Guide; HydroSOLVE, Inc.: Reston, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, S.P. Effect of partial penetration on flow in unconfined aquifers considering delayed gravity response. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a borehole using groundwater storage. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moench, A.F. Flow to a borehole of finite diameter in a homogeneous, anisotropic water-table aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusczynski, N.J. Filter-Press Method of Extracting Water Samples for Chloride Analysis; Water-Supply Paper 1544-A; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; 13p.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. User Guide—Chloride Ion Selective Electrode; Thermo FisherS cientific Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2008; 39p. [Google Scholar]
- Koterba, M.T.; Wide, F.D.; Lapham, W.W. Groundwater Data-Collection Protocols and Procedures for the National Water-Quality Assessment Program—Collection and Documentation of Water-Quality Samples and Related Data; Open-File Report 95-399; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1995; 113p.
- Fishman, M.L. Methods of Analysis by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory—Determination of Inorganic and Organic Constituents in Water and Fluvial Sediments; Open File Report 93-125; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1993; 217p.
- Archie, G.E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans. AIME 1942, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, W.S.; MacCary, L.M. Application of borehole geophysics to water-resources investigations. In U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1971; 126p. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, O. Fundamentals of Well-Log Interpretation; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1984; 423p. [Google Scholar]
- Keys, W.S. Borehole geophysics applied to water-resources investigations. In U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1990; 150p. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, J.D.; Hunter, J.A.; Bosner, M. Application of a borehole induction magnetic susceptibility logger to shallow lithological mapping. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 1996, 1, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Lane, J.W. Advances in Borehole Geophysics for Ground-Water Investigations; Fact Sheet 002-98; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1998; 4p.
- Buxton, H.T.; Soren, J.; Posner, A.; Shernoff, P.K. Reconnaissance of the Ground-Water Resources of Kings and Queens Counties, New York; Open-File Report 81-1186; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1981; 64p.
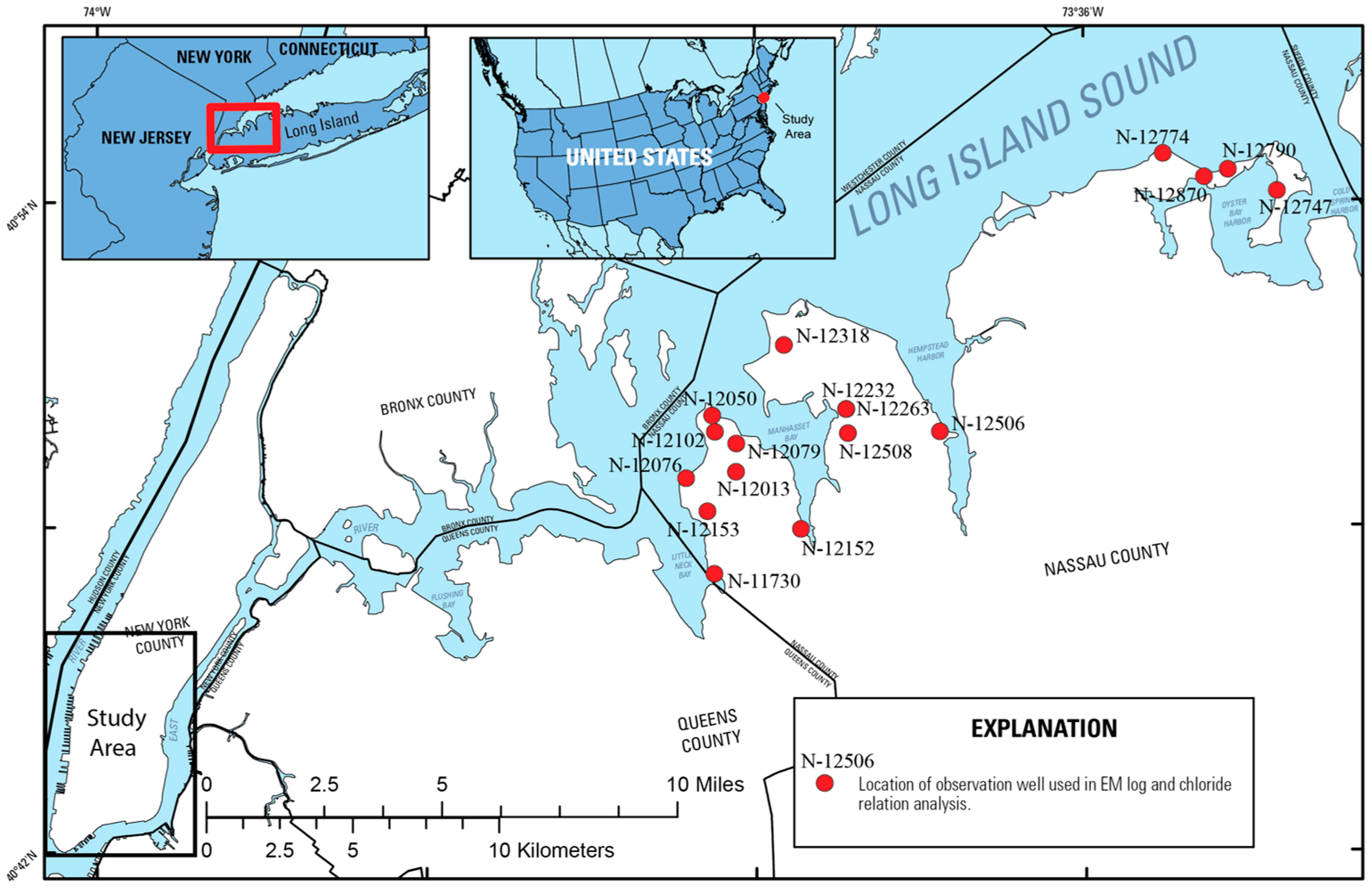
- Metzger, L.F.; Izbicki, J.A. Electromagnetic-induction logging to monitor changing chloride concentrations. Ground Water 2013, 51, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumm, F. Hydrogeology and Extent of Saltwater Intrusion of the Great Neck Peninsula, Great Neck, Long Island, New York; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4280; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2001; 41p.
- Taylor, K.C.; Hess, J.W.; Mazzela, A. Field evaluation of a slim-hole borehole induction tool. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 1989, 9, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. Technical Note 20 Geonics EM39 Borehole Conductivity Meter Theory of Operation; Geonics Limited: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1986; 18p. [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, F. Use of focused electromagnetic induction borehole geophysics to delineate the saltwater-freshwater interface in Great Neck, Long Island, New York. In Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems; Bell, R.S., Lepper, C.M., Eds.; Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 513–525. [Google Scholar]
- Paillet, F.; Hite, L.; Carlson, M. Integrating surface and borehole geophysics in ground water studies—An example using electromagnetic soundings in South Florida. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 1999, 4, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.T. Geohydrologic Framework of Recharge and Seawater Intrusion in the Pajaro Valley, Santa Cruz and Monterey Counties, California; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 03-4096. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/wri034096 (accessed on 21 August 2017).
- Land, M.; Reichard, E.G.; Crawford, S.M.; Everett, R.R.; Newhouse, M.W.; Williams, C.F. Ground-Water Quality of Coastal Aquifer Systems in the West Coast Basin, Los Angeles County, California, 1999–2002. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2004-5067. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2004/5067 (accessed on 21 August 2017).
- Fitterman, D.V.; Deszcz-Pan, M. Geophysical mapping of saltwater intrusion in Everglades National Park. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Ecohydraulics, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 12–16 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zuwaylif, F.H. General Applied Statistics; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1979; 434p. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, J.F. The geology of Manhattan Island [N.Y.]. N. Y. Acad. Sci. Trans. 1887, 7, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J.J.; Fluhr, T.W. The Subsoil and Bedrock of the Borough of Manhattan as Related to Foundations; Fourth Issue, Paper 212; Municipal Engineers Journal: New York City, NY, USA, 1944; pp. 119–157. [Google Scholar]
- Merguerian, C.; Baskerville, C.A. The geology of Manhattan Island and the Bronx, New York City, New York. In Northeastern Section of the Geological Society of America, Centennial Fieldguide; Roy, D.C., Ed.; The Geological Society of America, Inc.: Boulder, CO, USA, 1987; Volume 5, 481p. [Google Scholar]
- Lusczynski, N.J.; Swarzenski, W.V. Salt-Water Encroachment in Southern Nassau and Southeastern Queens Counties, Long Island, New York; Water-Supply Paper 1613-F; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1966; 76p.
- Ghyben, B.W. Nota in verband met de voorgenomen putboring nabij Amsterdam. Tijdschr. Kon. Inst. Ing. 1888, 9, 8–22. [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg, A. Die Wasserversorgung Einiger Nordseebäder; J. Gasbeleucht. Wasserversorg: München, Germany, 1901; Volume 44, pp. 815–819, 842–844. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, A.; Stumm, F. Delineation of the saltwater-freshwater interface at selected locations in Kings and Queens Counties, Long Island, New York, through use of borehole geophysical techniques. In Proceedings of the 2nd Geology of Long Island and Metropolitan New York Conference, Stony Brook, NY, USA, 15 April 1995. [Google Scholar]
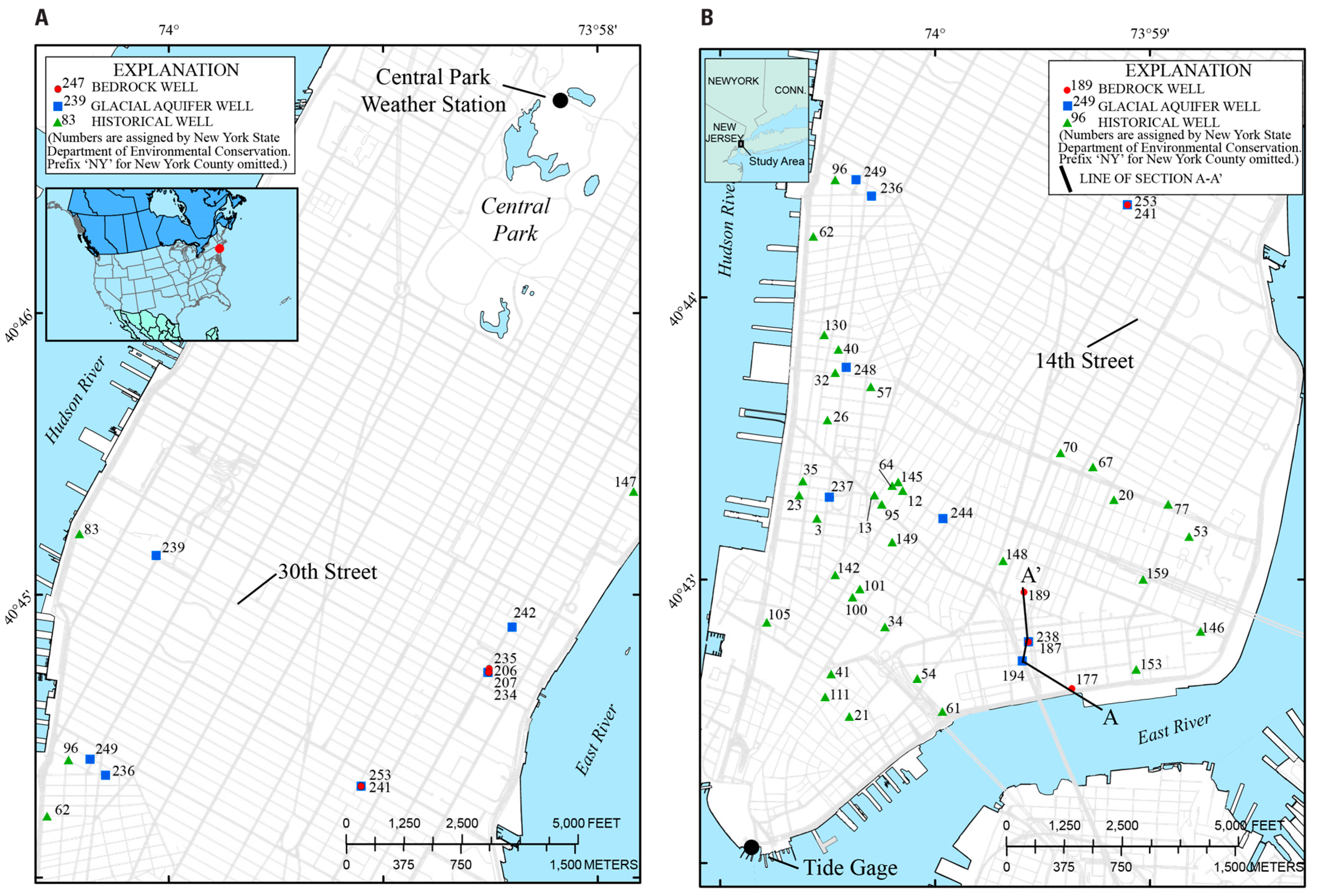
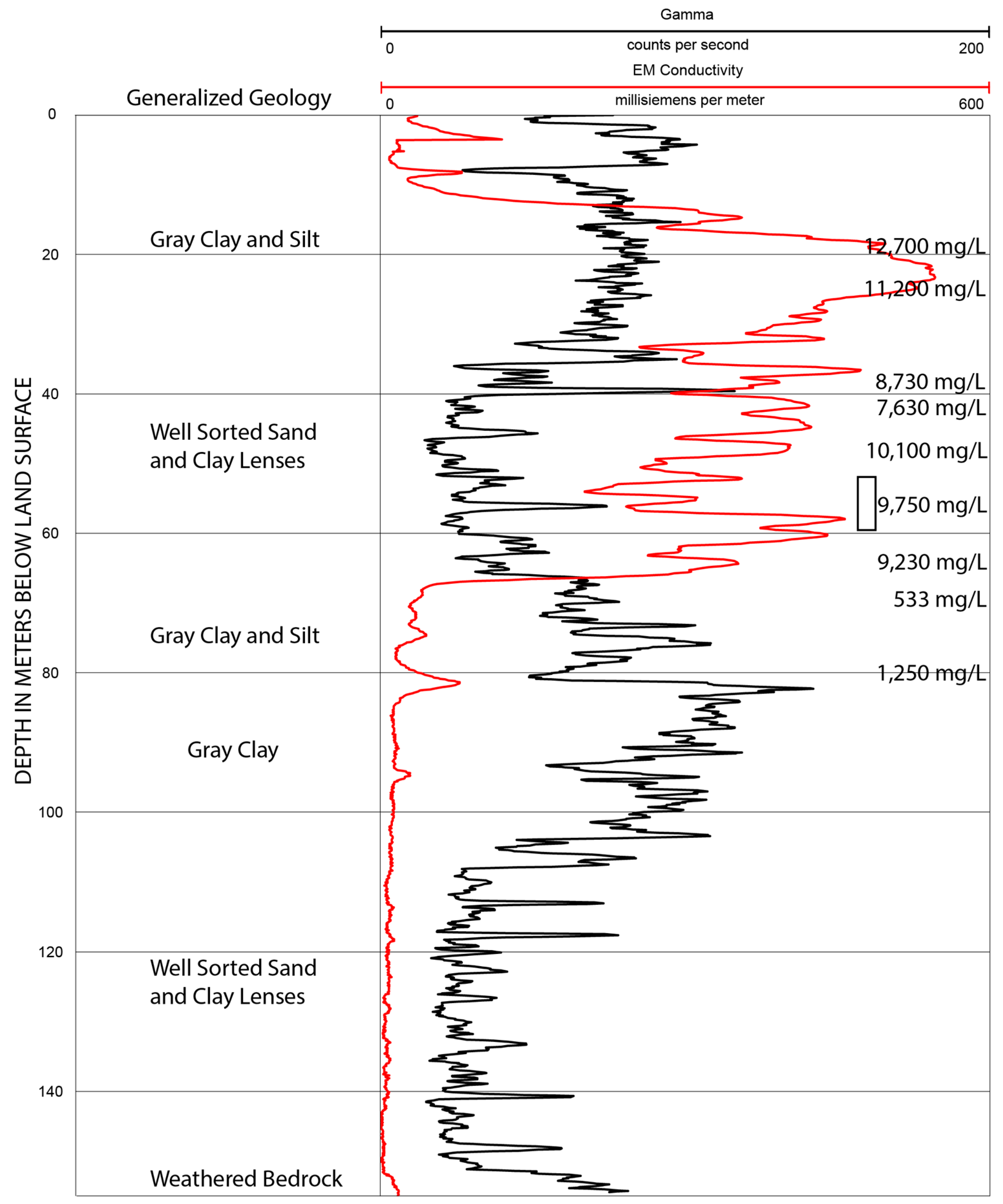
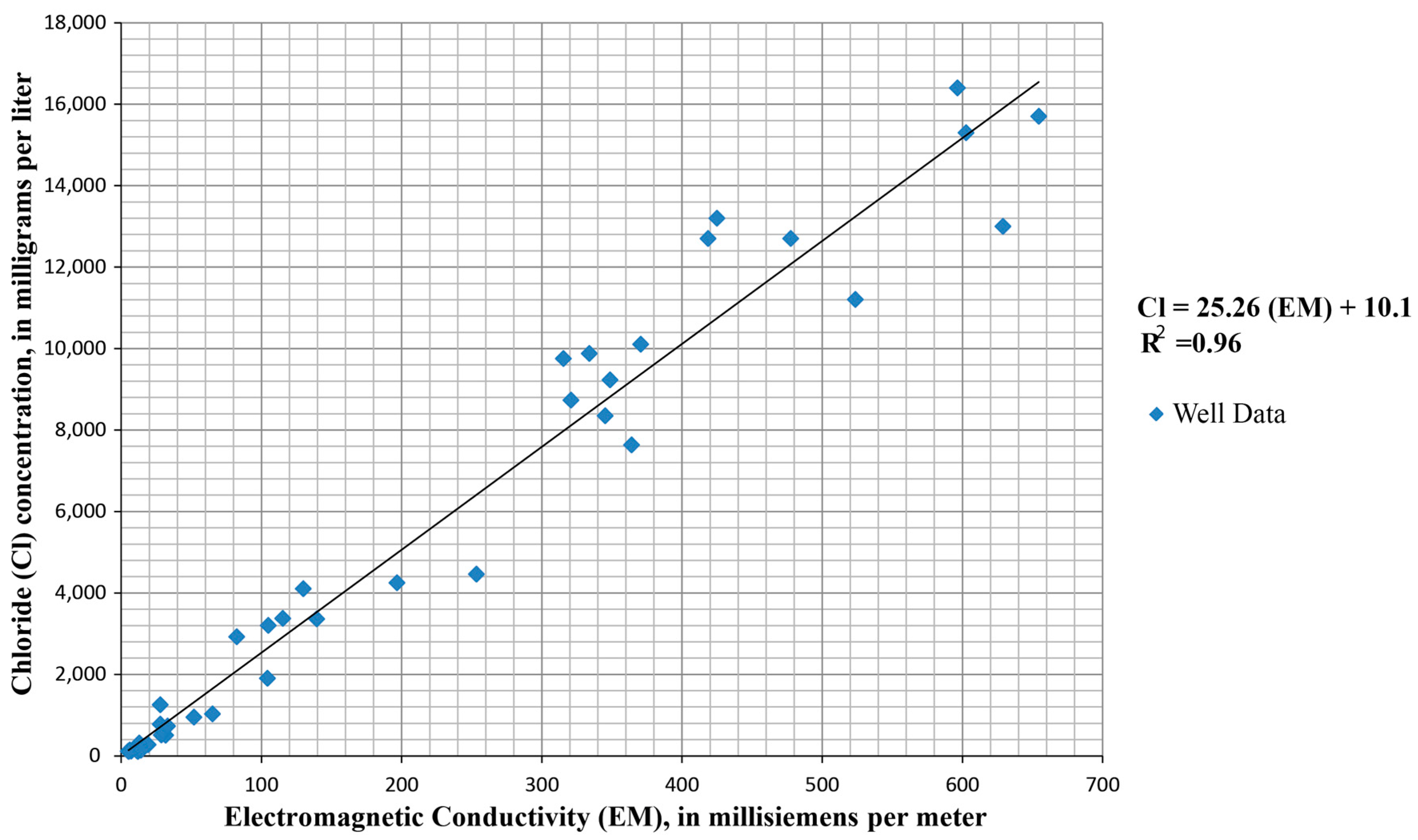
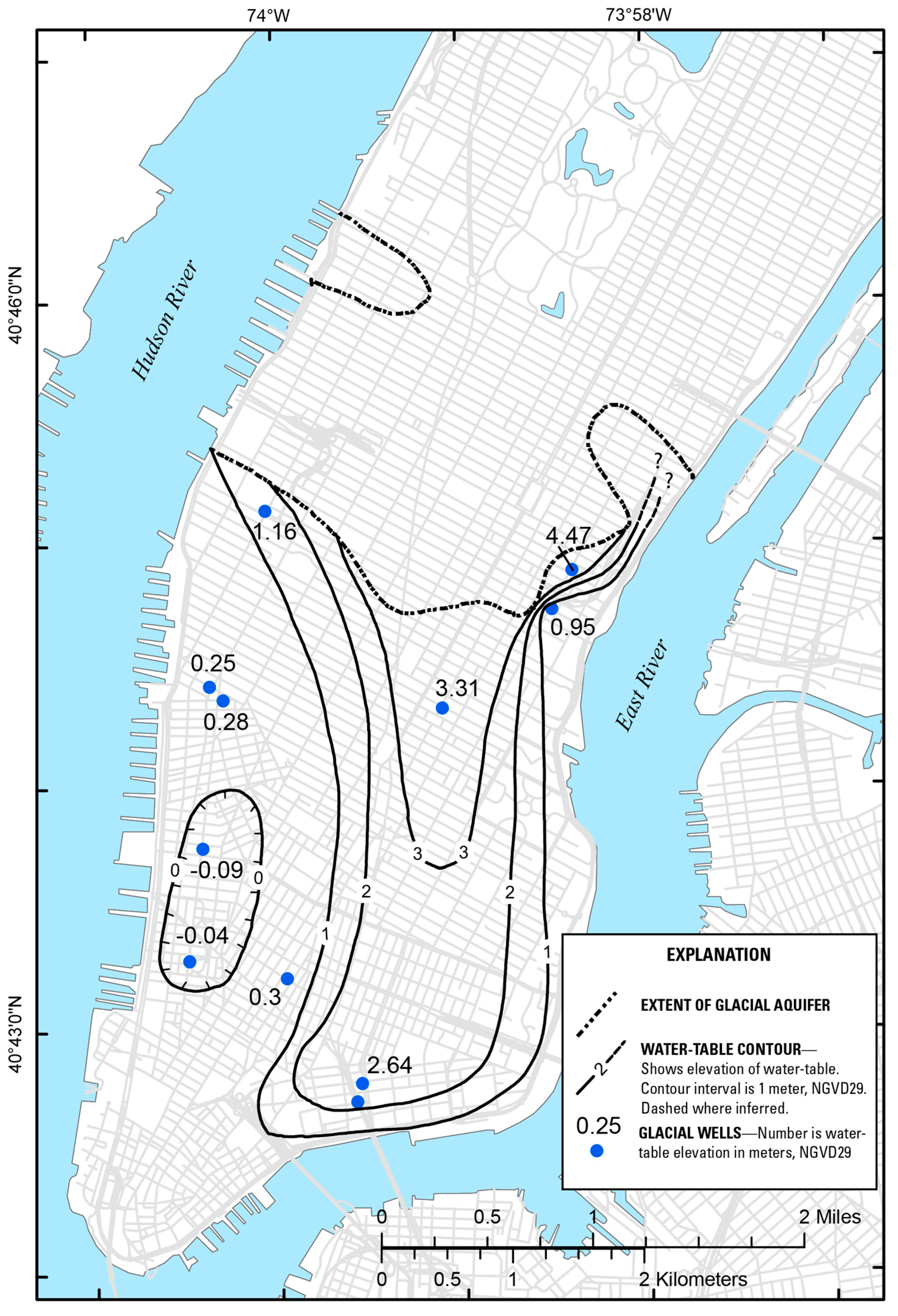
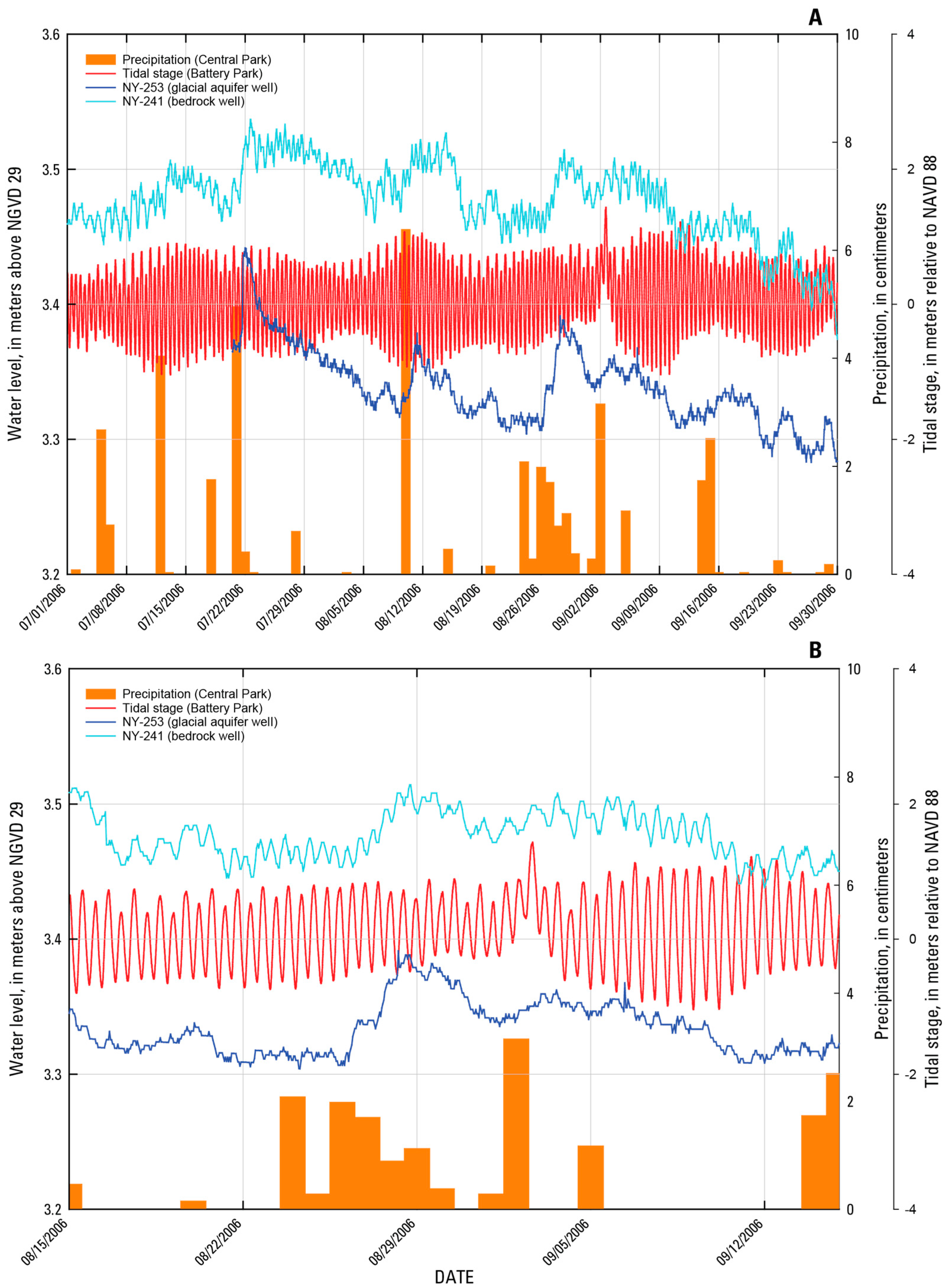
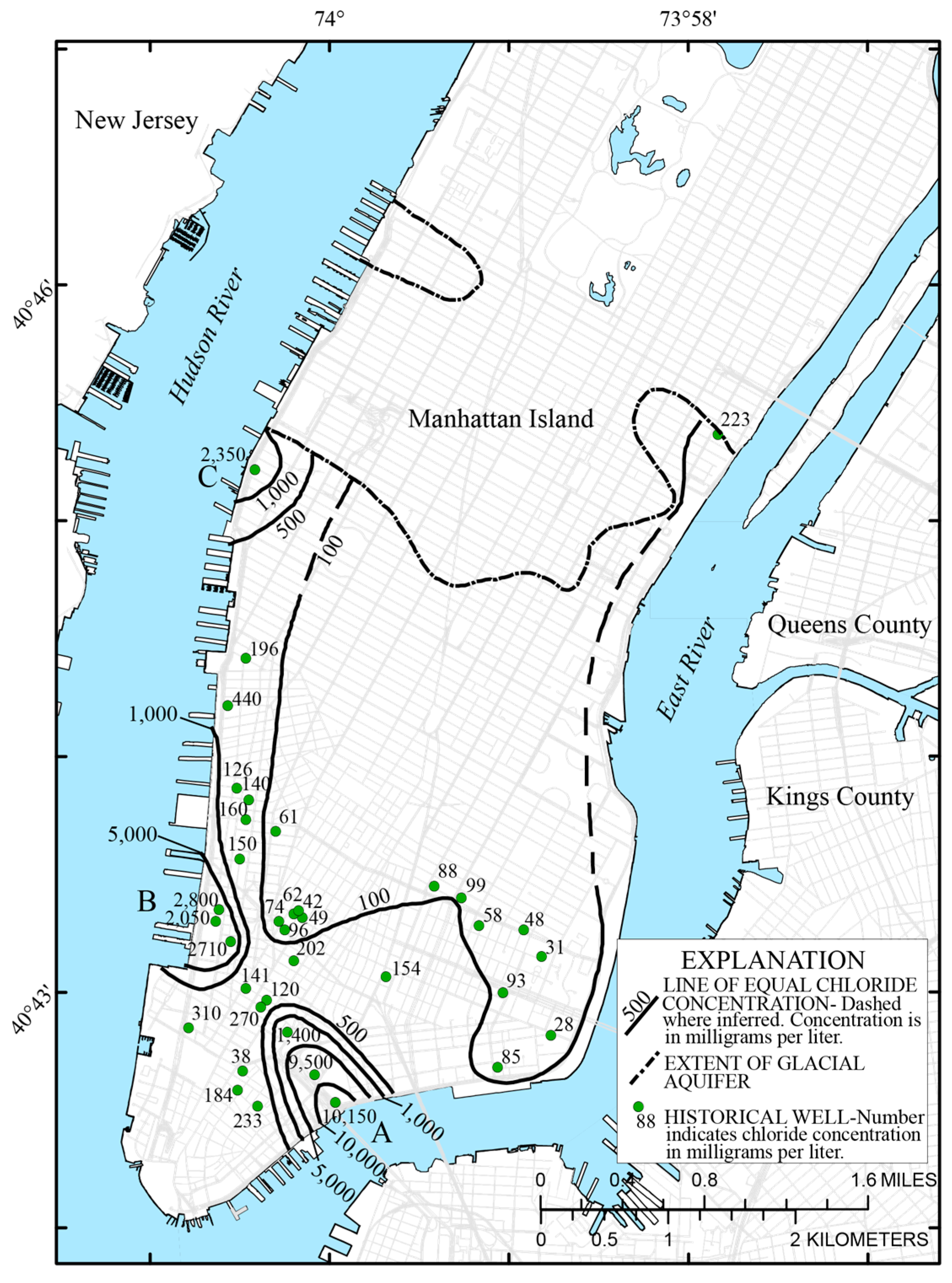
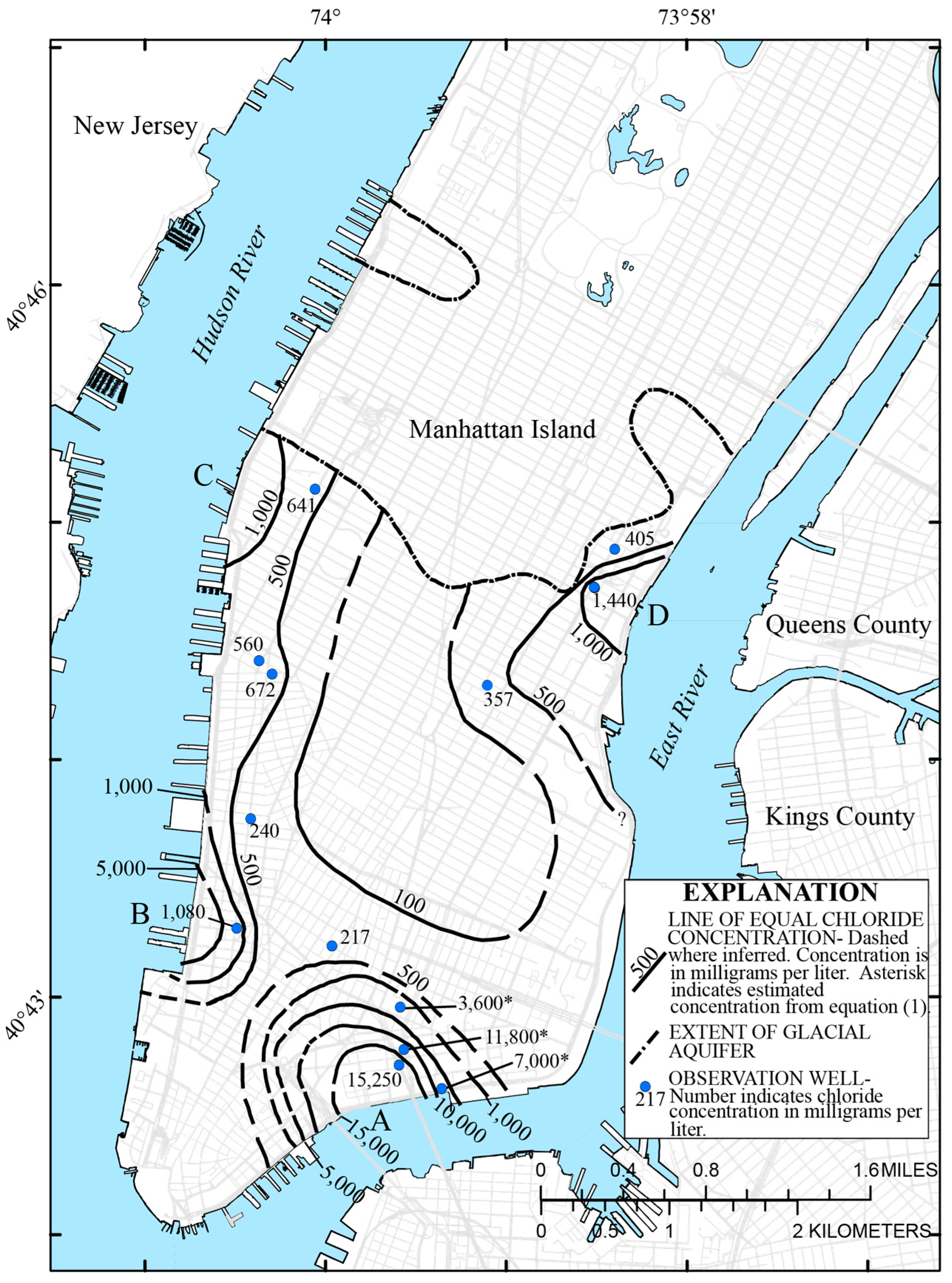
| Hydrogeologic Unit | New York State ID Number | Land Surface Elevation (m) | Bottom Depth of Well (m) | Casing Length (m) | Water Level (m) above Mean Sea Level | Chloride in Glacial Aquifer (mg/L) | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/Day) | Transmissivity (m2/Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bedrock | NY 241 | 8 | 183 | 15 | 3.41 | NA | NA | NA |
| NY 206 | 6 | 155 | 7 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| NY 207 | 6 | 183 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| NY 234 | 6 | 162 | 9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| NY 189 | 13 | 183 | 71 | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
| NY 187 | 11 | 171 | 88 | NA | 11,800 ** | NA | NA | |
| NY 177 | 2 | 182 | 69 | NA | 7000 ** | NA | NA | |
| glacial aquifer | NY 239 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 1.16 | 641 | 6 | 48 |
| NY 248 | 5 | 12 | 11 | −0.09 | 240 | 550 | 13,470 | |
| NY 237 | 5 | 12 | 11 | −0.04 | 1080 * | 12 | 297 | |
| NY 253 | 8 | 18 | 14 | 3.31 | 357 | NA | NA | |
| NY 235 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 0.95 | 1440 * | 0.05 | 0.10 | |
| NY 242 | 11 | 20 | 18 | 4.47 | 405 | 0.04 | 0.20 | |
| NY 236 | 6 | 25 | 24 | 0.28 | 672 * | 39 | 660 | |
| NY 244 | 8 | 20 | 19 | 0.30 | 217 | 52 | 670 | |
| NY 194 | 9 | 65 | 62 | NA | 15,250 * | 0.9 | 53 | |
| NY 238 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 2.64 | 277 | 22 | 1660 | |
| NY 249 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 0.25 | 560 | 92 | 409 |
This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stumm, F.; Como, M.D. Delineation of Salt Water Intrusion through Use of Electromagnetic-Induction Logging: A Case Study in Southern Manhattan Island, New York. Water 2017, 9, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090631
Stumm F, Como MD. Delineation of Salt Water Intrusion through Use of Electromagnetic-Induction Logging: A Case Study in Southern Manhattan Island, New York. Water. 2017; 9(9):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090631
Chicago/Turabian StyleStumm, Frederick, and Michael D. Como. 2017. "Delineation of Salt Water Intrusion through Use of Electromagnetic-Induction Logging: A Case Study in Southern Manhattan Island, New York" Water 9, no. 9: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090631
APA StyleStumm, F., & Como, M. D. (2017). Delineation of Salt Water Intrusion through Use of Electromagnetic-Induction Logging: A Case Study in Southern Manhattan Island, New York. Water, 9(9), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090631






