Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
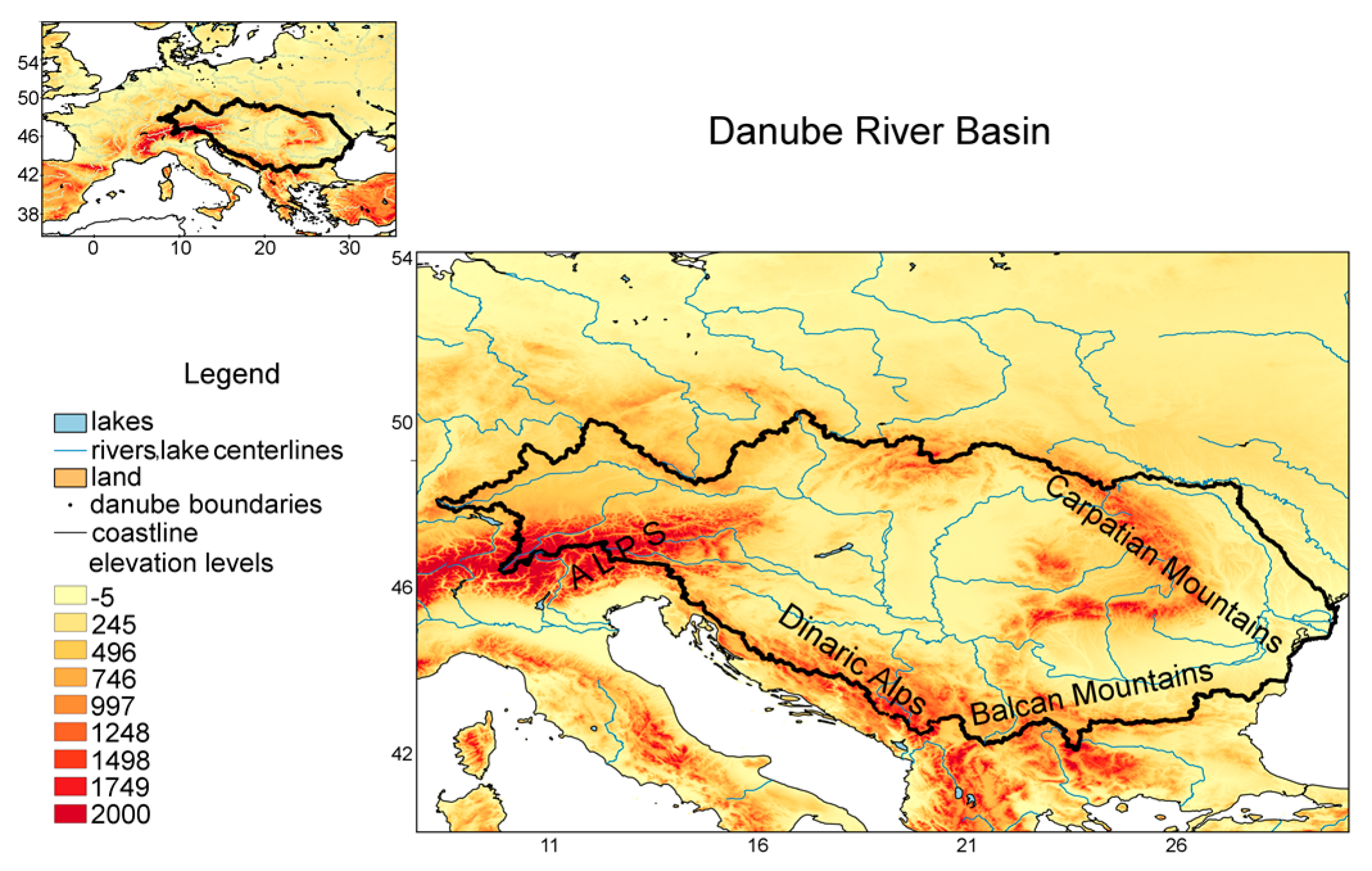
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Precipitation Dataset
2.2. Ranking of Wet Spell Extreme Precipitation Events
2.3. Moisture Sources Anomalies
3. Results
3.1. Detection of the Wet Spells
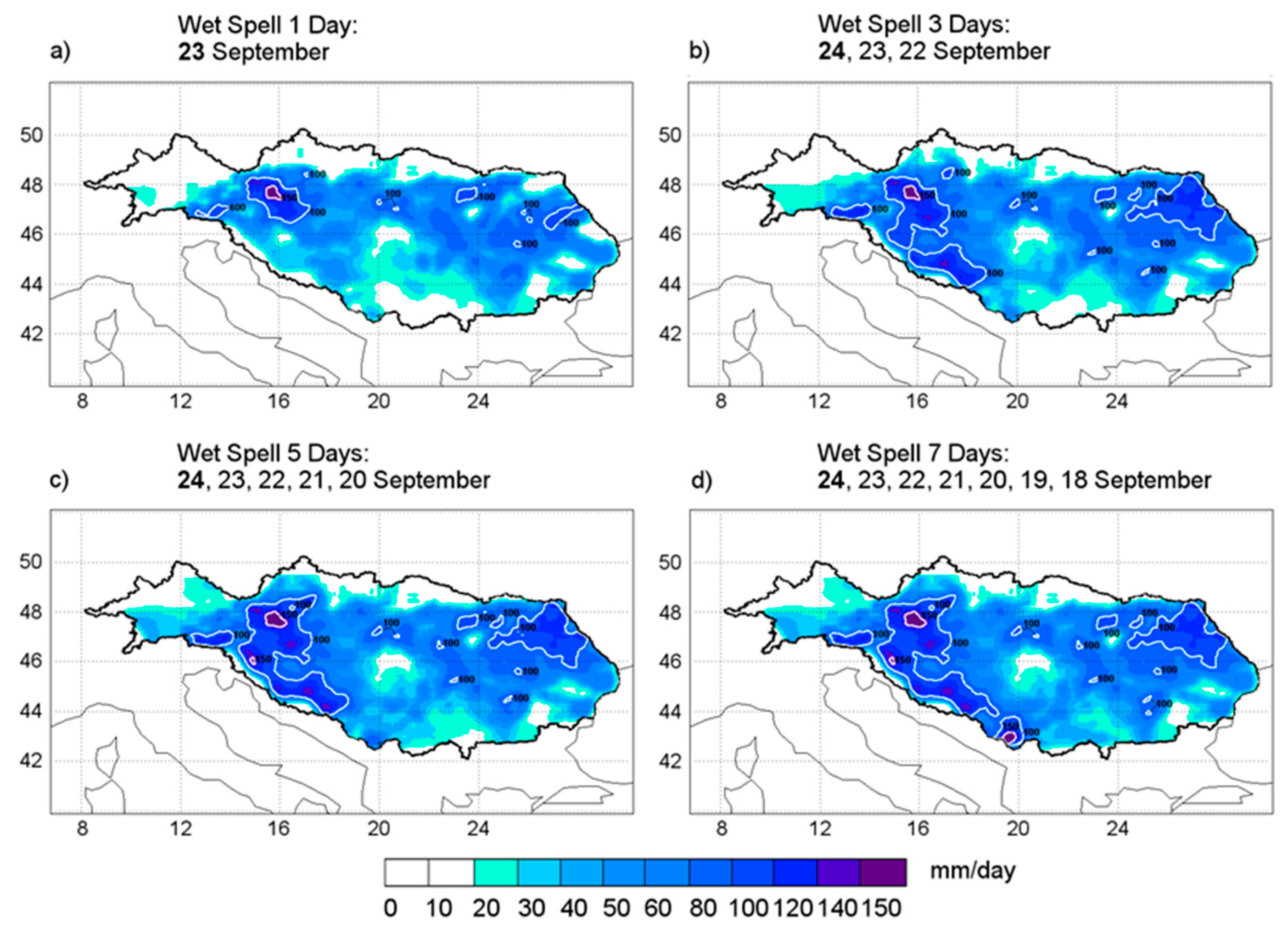
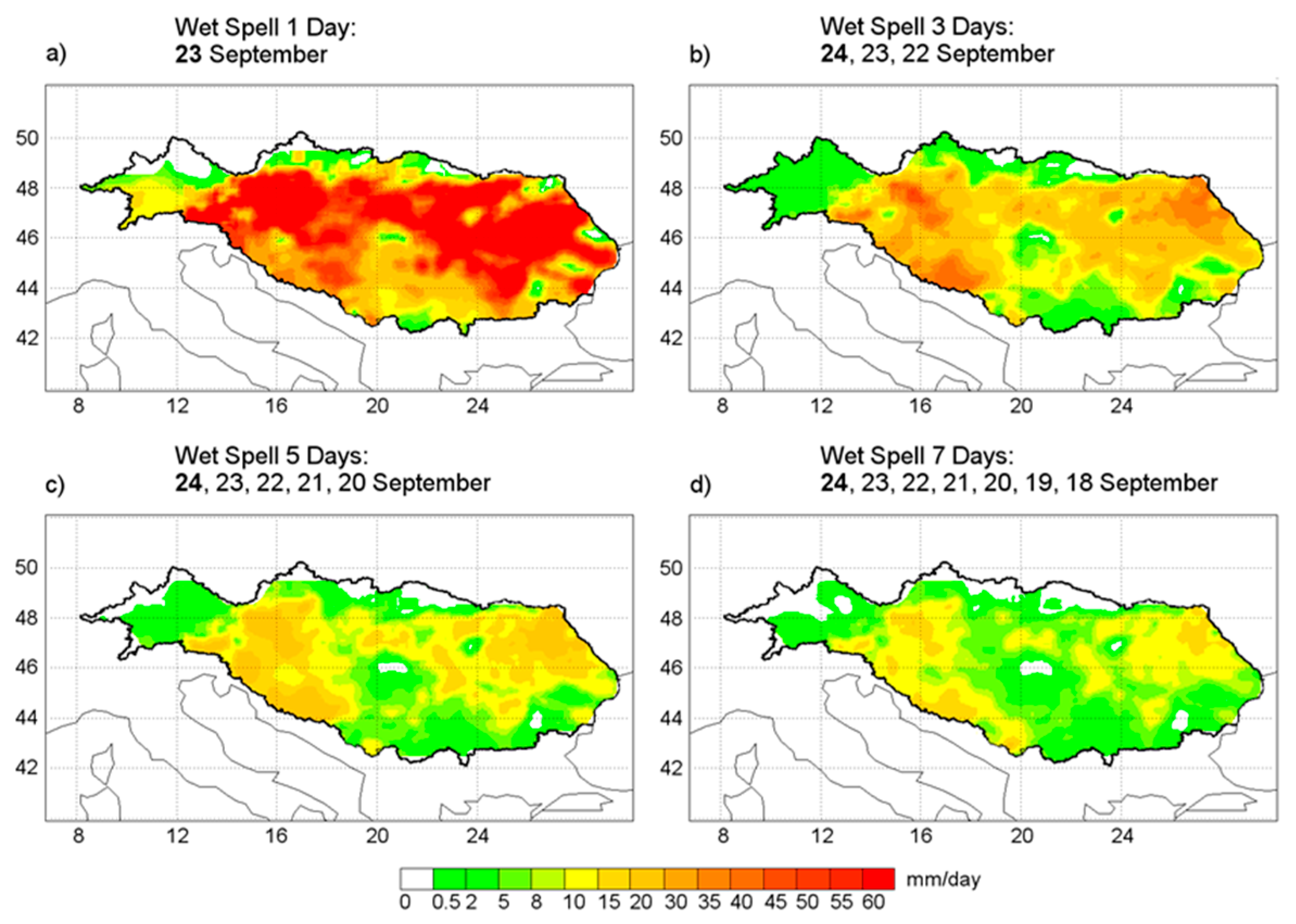
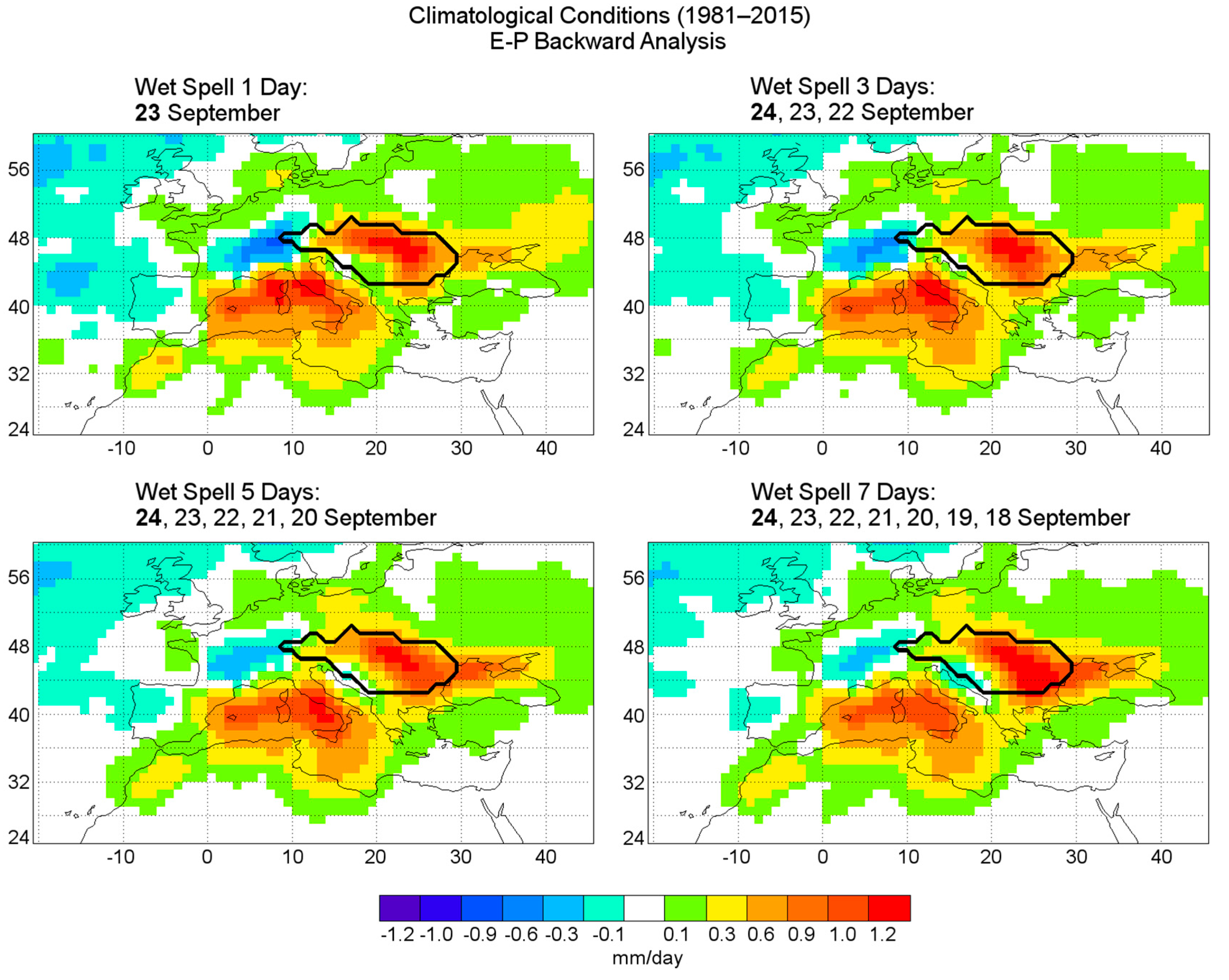
3.2. Wet Spell Event 23 September 1996
3.2.1. Precipitation
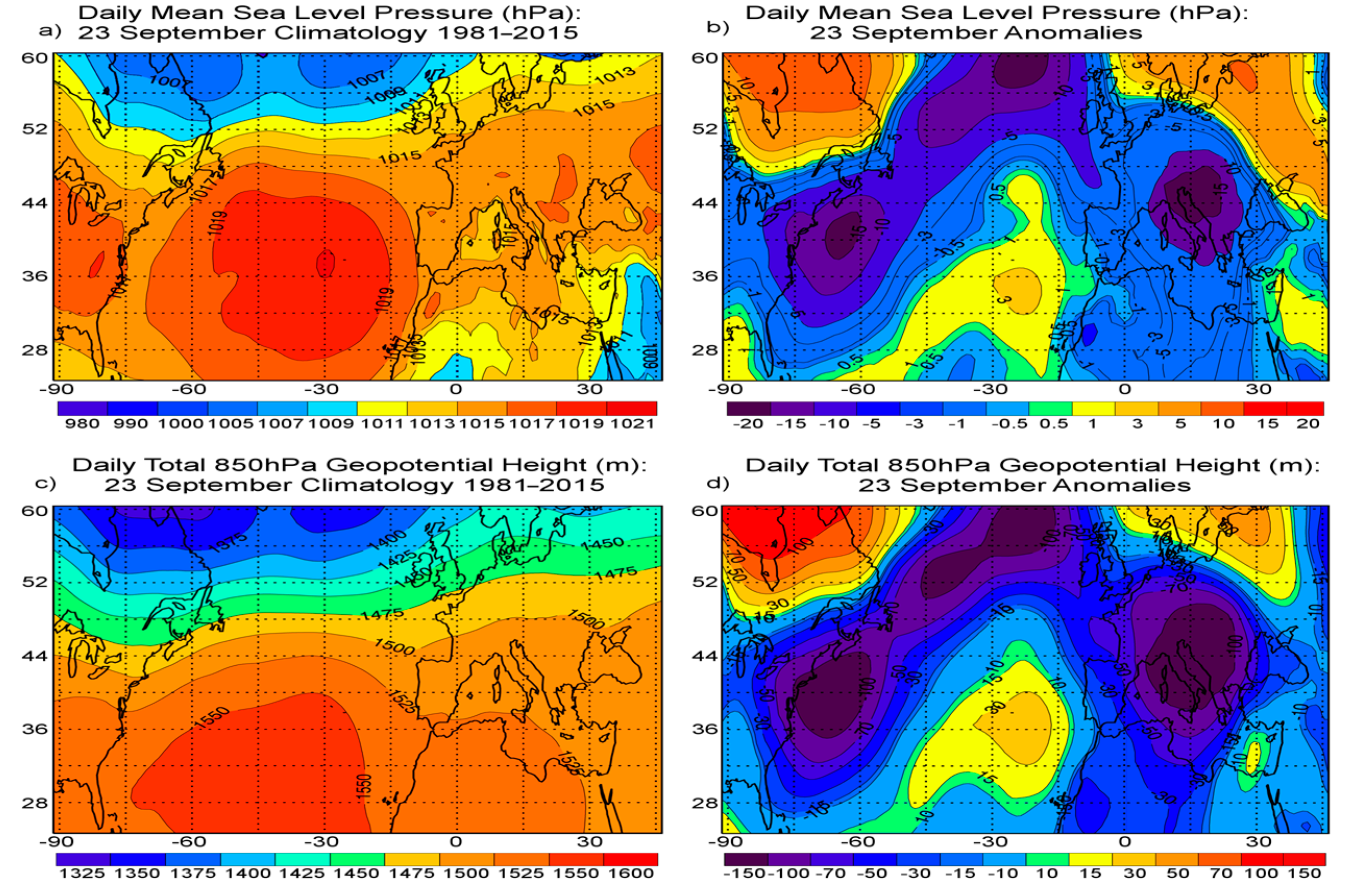
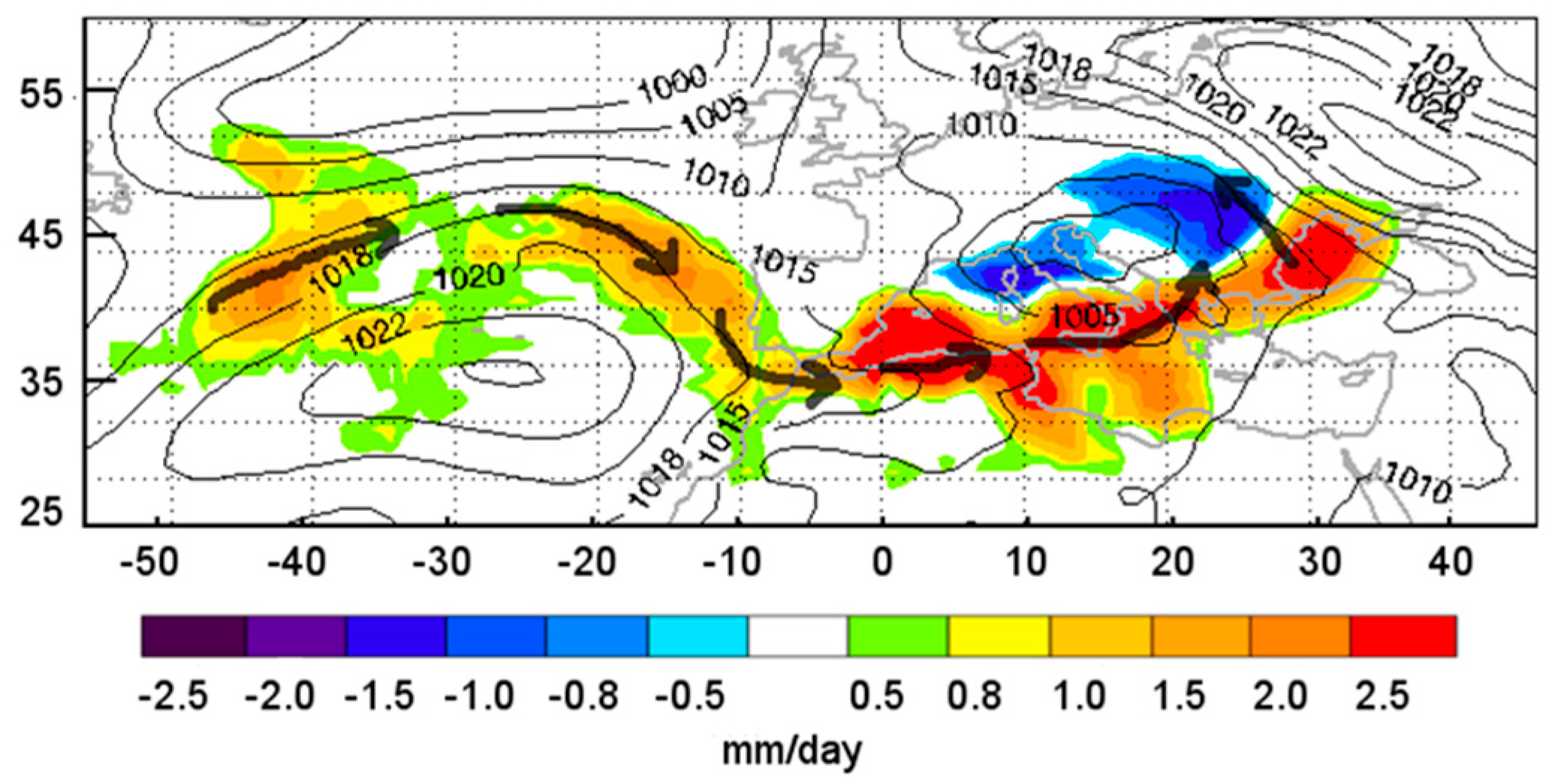
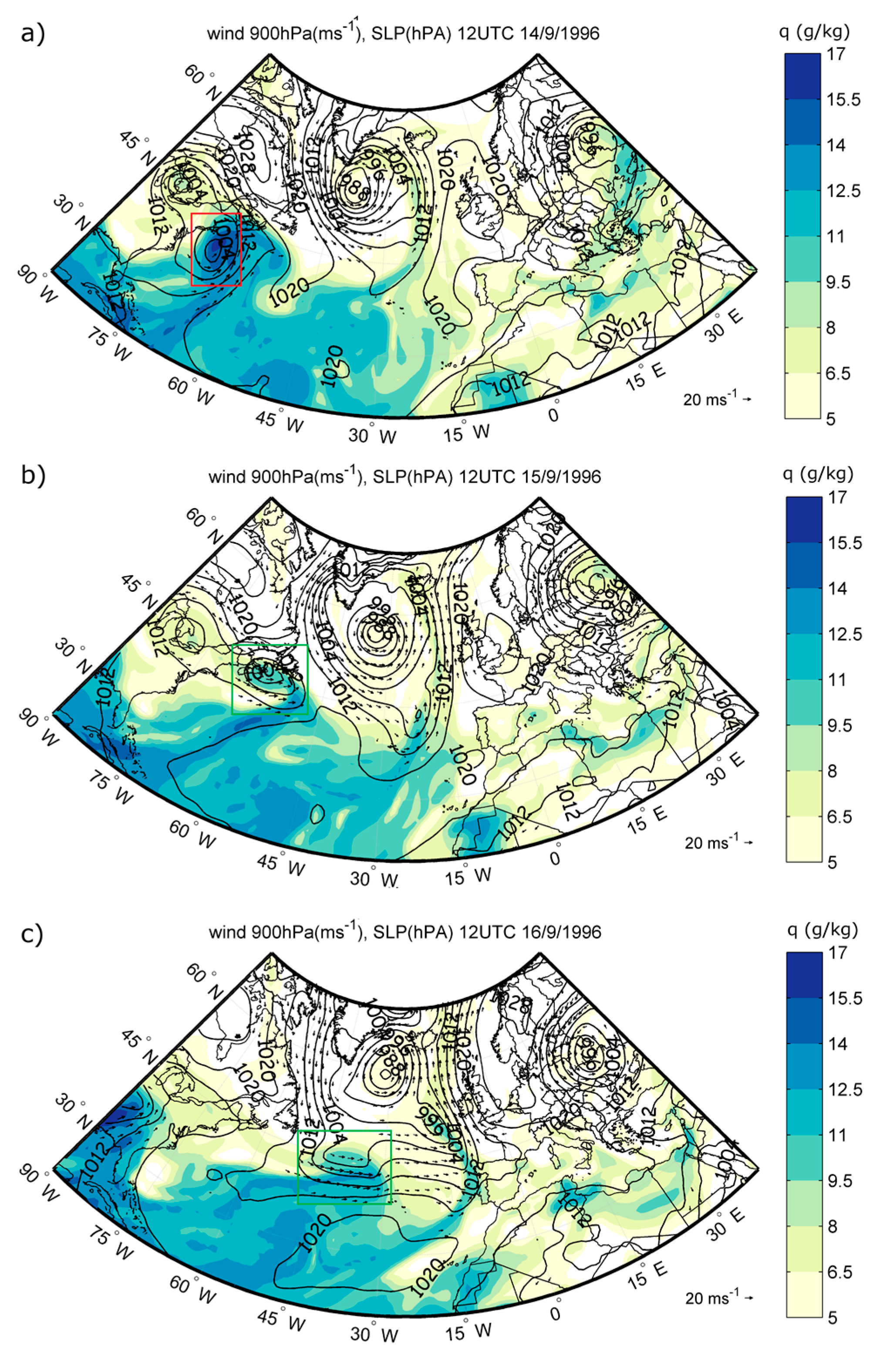
3.2.2. Meteorological Configuration
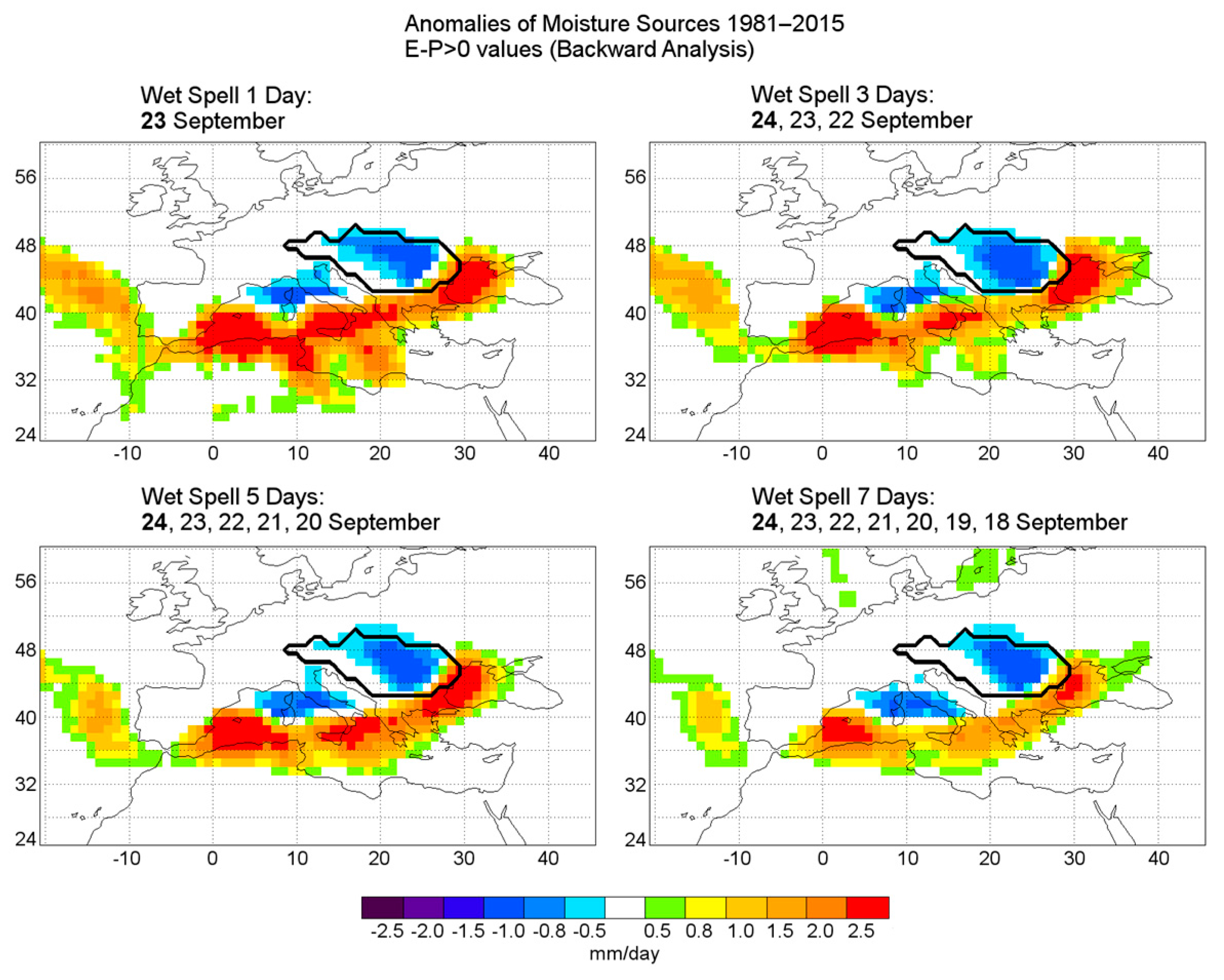
3.2.3. Anomalous Moisture Uptake during the 23 September 1996 Wet Spell Event
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P.; Alcamo, J.; Henrichs, T.; Kaspar, F. Estimating the Impact of Global Change on Flood and Drought Risks in Europe: A Continental, Integrated Analysis. Chlimatic. Chang. 2006, 75, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, D.; Stojanovic, M.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Tracking the Origin of Moisture over the Danube River Basin Using a Lagrangian Approach. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancik, A.; Jovanovic, S. Hidrology of the River Danube; Priroda: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1988; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Brilly, M. Hydrological Processes of the Danube River Basin: Perspective from the Danubian Countries; Springer Science & Business Media: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2010; Volume 1, p. 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolina, O. Multidecadal trends in the duration of wet spells and associated intensity of precipitation as revealed by a very dense observational German network. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, M.; Müller, M. Selection of historic heavy large-scale rainfall events in the Czech Republic. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 1359–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, M.; Babić-Mladenović, M.; Danko, B.; Pavel, B.; Razvan, B.; Lenka, C. Flood Risk Management Plan for the Danube River Basin District; International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Blöschl, G.; Nester, T.; Komma, J.; Parajka, J.; Perdigão, R.A.P. The June 2013 flood in the Upper Danube Basin, and comparisons with the 2002, 1954 and 1899 floods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 5197–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtherr, L.; Coumou, D.; Petoukhov, V.; Petri, S.; Rahmstorf, S. Record Balkan floods of 2014 linked to planetary wave resonance. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EASAC. Trends in Extreme Weather Events in Europe: Implications for National and European Union Adaptation Strategies; EASAC Policy Report 22; European Academies Science Advisory Council: Halle, Germany, 2013; Available online: www.easac.eu (accessed on 24 April 2017).
- Martín, M.L.; Santos-Muñoz, D.; Morata, A.; Luna, M.Y.; Valero, F. An objectively selected case study of a heavy rain event in the Mediterranean Basin: A diagnosis using numerical simulation. Atmos. Res. 2006, 81, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansa, A.; Genoves, A. Western Mediterranean cyclones and heavy rain. Part 1: Numerical experiment concerning the Piedmont flood case. Meteorol. Appl. 2000, 7, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberato, M.L.R.; Pinto, J.G.; Trigo, I.F.; Trigo, R.M. Klaus, an exceptional winter storm over Northern Iberia and Southern France—A comparison between storm diagnostics. Weather 2011, 66, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. First results from Version 7 TRMM 3B43 precipitation product in combination with a new downscaling—Calibration procedure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, R.; Venugopal, V. Wet and dry spell characteristics of global tropical rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3830–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Tsiang, M.; Rajaratnam, B.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Observed changes in extreme wet and dry spells during the South Asian summer monsoon season. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Dominguez, F.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Drumond, A.; Reason, C.; Taschetto, A.S.; Ramos, A.M.; Kumar, R.; Marengo, J. Major Mechanisms of Atmospheric Moisture Transport and Their Role in Extreme Precipitation Events. Annu. Rev. Environ. Res. 2016, 41, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Stohl, A. On the origin of continental precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 3, L13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Stohl, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Domínguez, F.; Yoshimura, K.; Yu, L.; Drumond, A.; Durán-Quesada, A.M.; Nieto, R. Oceanic and Terrestrial Sources of Continental Precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Liberato, M.L.R. A ranking of high-resolution daily precipitation extreme events for the Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2014, 15, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Liberato, M.L.R. Ranking of multi-day extreme precipitation events over the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Trejoa, F.J.; Barbosa, H.A.; Lakshmi Kumar, T.V. Validating CHIRPS-based satellite precipitation estimates in Northeast Brazil. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 139, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tuo, Y.; Chiogna, G.; Disse, M. Evaluation of eight high spatial resolution gridded precipitation products in Adige Basin (Italy) at multiple temporal and spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1536–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuo, Y.; Duan, Z.; Disse, M.; Chiogna, G. Evaluation of precipitation input for SWAT modeling in Alpine catchment: A case study in the Adige river basin (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanos, D.; Retalis, A.; Tymvios, F.; Michaelides, S. Analysis of precipitation extremes based on satellite (CHIRPS) and in situ dataset over Cyprus. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandu; Awange, J.L.; Forootan, E. An evaluation of high-resolution gridded precipitation products over Bhutan (1998–2012). Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 36, 1067–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.E.; Grumm, R.H. Using normalised climatological anomalies to rank synoptic-scale events objectively. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 2426–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle. Part I: Method description, validation, and demonstration for the August 2002 flooding in central Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 656–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohl, A.; James, P. A Lagrangian analysis of the atmospheric branch of the global water cycle: Part II: Moisture transports between Earth’s ocean basins and river catchments. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numaguti, A. Origin and recycling processes of precipitating water over the Eurasian continent: Experiments using an atmospheric general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Hernandez, E.; Gimeno, L. A Lagrangian analysis of the variation in moisture sources related to drier and wetter conditions in regions around the Mediterranean Basin. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2307–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Quesada, A.M.; Gimeno, L.; Amador, J.A.; Nieto, R. Moisture sources for Central America: Identification of moisture sources using a Lagrangian analysis technique. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D05103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. Where Does the Iberian Peninsula Moisture Come from? An Answer Based on a Lagrangian Approach. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L.; Gallego, D.; Trigo, R.M. Contributions to the moisture budget of airmasses over Iceland. Meteorol. Z. 2007, 16, 037–044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodemann, H.; Schwierz, C.; Wernli, H. Interannual variability of Greenland winter precipitation sources: Lagrangian moisture diagnostic and North Atlantic Oscillation influence. J Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D03107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond, A.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Sources of moisture for China and their variations during drier and wetter conditions in 2000–2004: A Lagrangian approach. Clim. Res. 2011, 50, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorí, R.; Nieto, R.; Drumond, R.; Gimeno, L. The Niger River Basin Moisture Sources: A Lagrangian Analysis. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, K.R.; Connolly-Johnston, C. The Impact of Hurricane Debbie (1961) and Hurricane Charley (1986) on Ireland. In Advances in Hurricane Research—Modelling, Meteorology, Preparedness and Impacts; Hickey, K., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 9; Volume 1, pp. 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantillon, F.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Richard, E. Remote impact of North Atlantic hurricanes on the Mediterranean during episodes of intense rainfall in autumn 2012. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichak, S.O.; Feldstein, S.B.; Alpert, P.; Gualdi, S.; Scoccimarro, E.; Yano, J.I. Discussing the role of tropical and subtropical moisture sources in cold season extreme precipitation events in the Mediterranean region from a climate change perspective. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Dettinger, M.D. Storms, floods, and the science of atmospheric rivers. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2011, 92, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Vázquez, M.; Lavers, D.A. Atmospheric rivers: A mini-review. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Liberato, M.L.R.; Tome, R. Daily precipitation extreme events in the Iberian Peninsula and its association with Atmospheric Rivers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Waliser, D.E. Detection of atmospheric rivers: Evaluation and application of an algorithm for global studies. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12514–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| A(%) = Area | M = Mean Magnitude | R = index of Ranking | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) 1 day duration–Wet Spell Events | ||||
| 1 | 23 September 1996 | 44.87 | 4.43 | 198.65 |
| 2 | 28 December 2014 | 50.92 | 3.32 | 168.81 |
| 3 | 6 November 1985 | 40.26 | 3.89 | 156.70 |
| 4 | 1 March 2008 | 40.48 | 3.84 | 155.58 |
| 5 | 18 February 1994 | 44.66 | 3.19 | 142.60 |
| 6 | 27 November 1983 | 40.79 | 3.44 | 140.42 |
| 7 | 6 May 1987 | 36.20 | 3.81 | 138.02 |
| 8 | 14 March 2013 | 43.32 | 3.18 | 137.91 |
| 9 | 2 March 2014 | 31.11 | 4.38 | 136.17 |
| 10 | 27 March 1993 | 38.96 | 3.38 | 131.77 |
| (b) 3 day duration–Wet Spell Events | ||||
| 1 | 24 September 1996 | 53.11 | 4.71 | 249.95 |
| 2 | 23 September 1996 | 51.06 | 4.47 | 228.27 |
| 3 | 25 September 1996 | 47.25 | 4.75 | 224.59 |
| 4 | 11 February 1984 | 44.50 | 4.63 | 206.04 |
| 5 | 6 November 1985 | 51.45 | 3.97 | 204.39 |
| 6 | 8 January 2010 | 47.44 | 4.18 | 198.54 |
| 7 | 6 May 1987 | 49.73 | 3.99 | 198.36 |
| 8 | 10 February 1984 | 43.52 | 4.50 | 195.88 |
| 9 | 29 October 1990 | 48.53 | 4.02 | 195.15 |
| 10 | 31 October 1994 | 51.43 | 3.76 | 193.43 |
| (c) 5 day duration–Wet Spell Events | ||||
| 1 | 24 September 1996 | 53.66 | 4.75 | 254.85 |
| 2 | 25 September 1996 | 53.45 | 4.76 | 254.22 |
| 3 | 26 September 1996 | 53.67 | 4.69 | 251.71 |
| 4 | 14 December 1990 | 55.32 | 4.29 | 237.58 |
| 5 | 13 January 1998 | 51.67 | 4.55 | 234.92 |
| 6 | 27 September 1996 | 48.54 | 4.77 | 231.42 |
| 7 | 23 September 1996 | 51.73 | 4.46 | 230.92 |
| 8 | 22 January 1998 | 53.15 | 4.29 | 227.95 |
| 9 | 30 October 1990 | 53.80 | 4.13 | 222.08 |
| 10 | 31 October 1990 | 53.84 | 4.12 | 221.67 |
| (d) 7 day duration–Wet Spell Events | ||||
| 1 | 1 January 1996 | 70.41 | 4.24 | 298.19 |
| 2 | 15 December 1990 | 64.51 | 4.51 | 290.71 |
| 3 | 2 January 1996 | 69.34 | 4.00 | 277.60 |
| 4 | 14 December 1990 | 61.43 | 4.46 | 273.79 |
| 5 | 7 May 1987 | 61.21 | 4.26 | 260.72 |
| 6 | 27 September 1996 | 54.59 | 4.78 | 260.69 |
| 7 | 24 September 1996 | 54.73 | 4.72 | 258.47 |
| 8 | 16 December 1990 | 59.21 | 4.35 | 257.33 |
| 9 | 28 September 1996 | 54.33 | 4.73 | 256.91 |
| 10 | 25 September 1996 | 54.11 | 4.75 | 256.87 |
| (e) 10 days duration–Wet Spell Events | ||||
| 1 | 23 August 2005 | 68.21 | 4.78 | 325.98 |
| 2 | 18 December 1990 | 66.39 | 4.78 | 317.66 |
| 3 | 24 August 2005 | 66.78 | 4.73 | 315.91 |
| 4 | 4 January 1996 | 72.31 | 4.34 | 313.98 |
| 5 | 15 December 1990 | 65.40 | 4.79 | 313.50 |
| 6 | 17 December 1990 | 65.41 | 4.61 | 301.29 |
| 7 | 16 December 1990 | 65.68 | 4.58 | 300.85 |
| 8 | 14 December 1990 | 62.07 | 4.81 | 298.32 |
| 9 | 22 August 2005 | 64.18 | 4.65 | 298.17 |
| 10 | 12 May 1991 | 60.77 | 4.79 | 290.89 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciric, D.; Nieto, R.; Ramos, A.M.; Drumond, A.; Gimeno, L. Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin. Water 2017, 9, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080615
Ciric D, Nieto R, Ramos AM, Drumond A, Gimeno L. Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin. Water. 2017; 9(8):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080615
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiric, Danica, Raquel Nieto, Alexandre M. Ramos, Anita Drumond, and Luis Gimeno. 2017. "Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin" Water 9, no. 8: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080615
APA StyleCiric, D., Nieto, R., Ramos, A. M., Drumond, A., & Gimeno, L. (2017). Wet Spells and Associated Moisture Sources Anomalies across Danube River Basin. Water, 9(8), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080615









