Effect of Membrane Type for the Treatment of Organized Industrial Zone (OIZ) Wastewater with a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Batch Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
2.2. Membranes
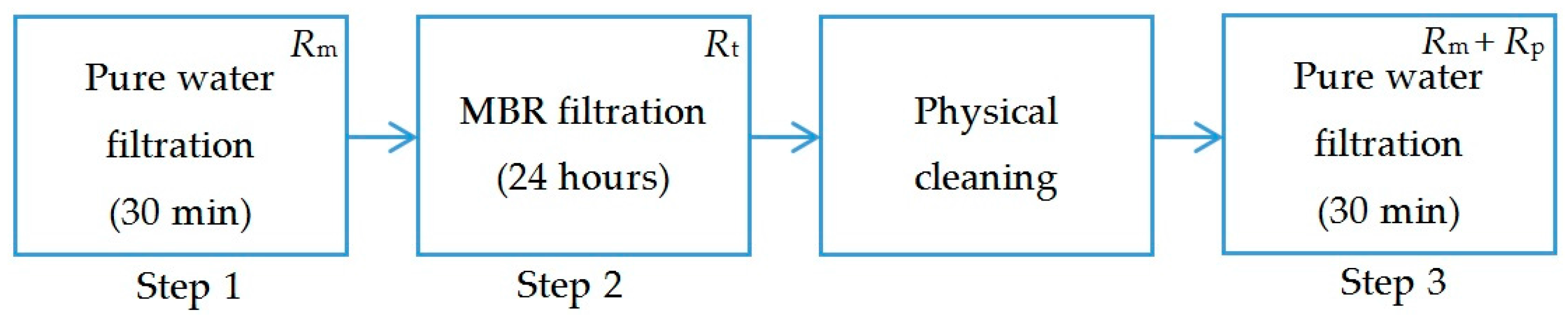
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
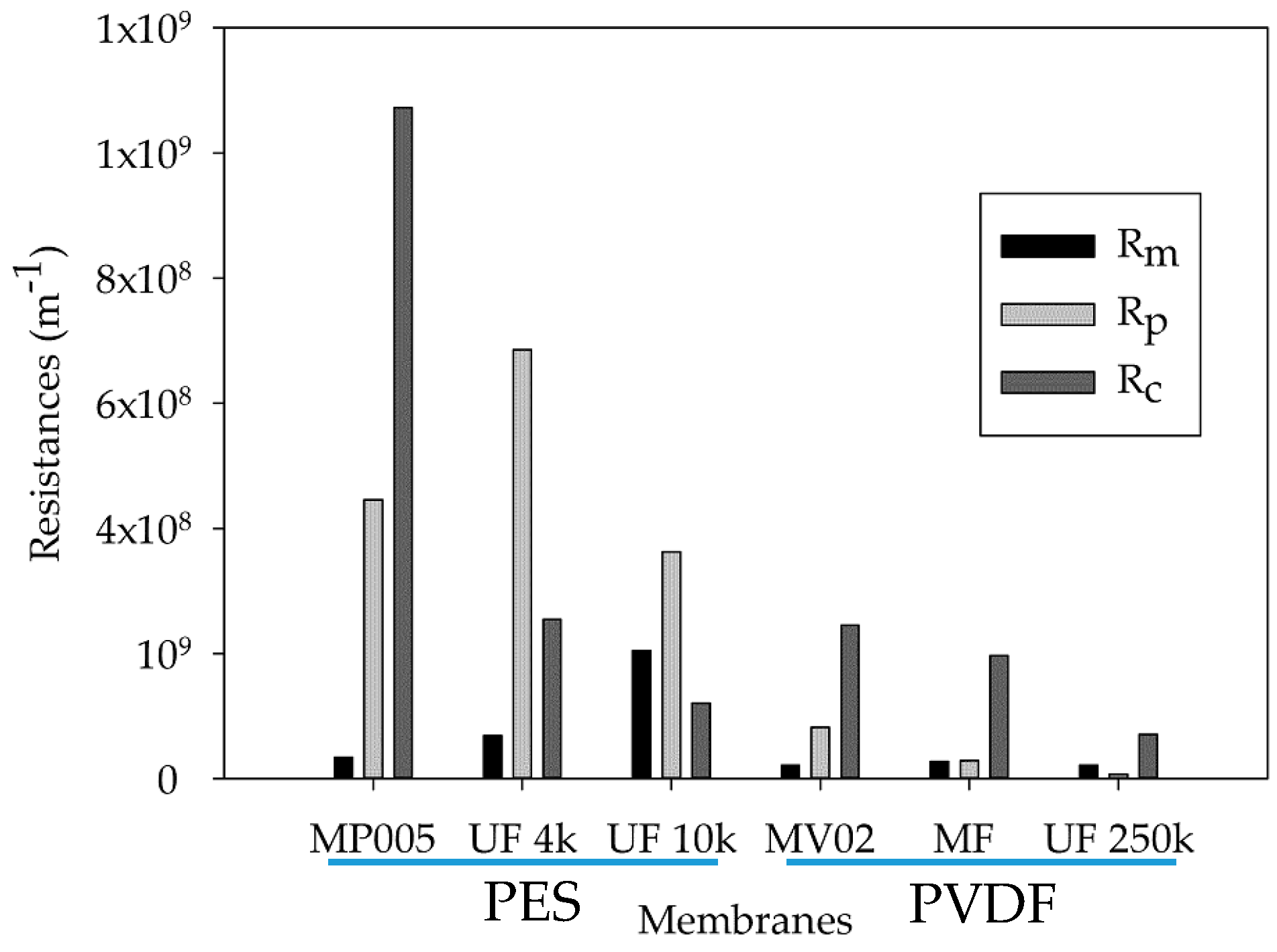
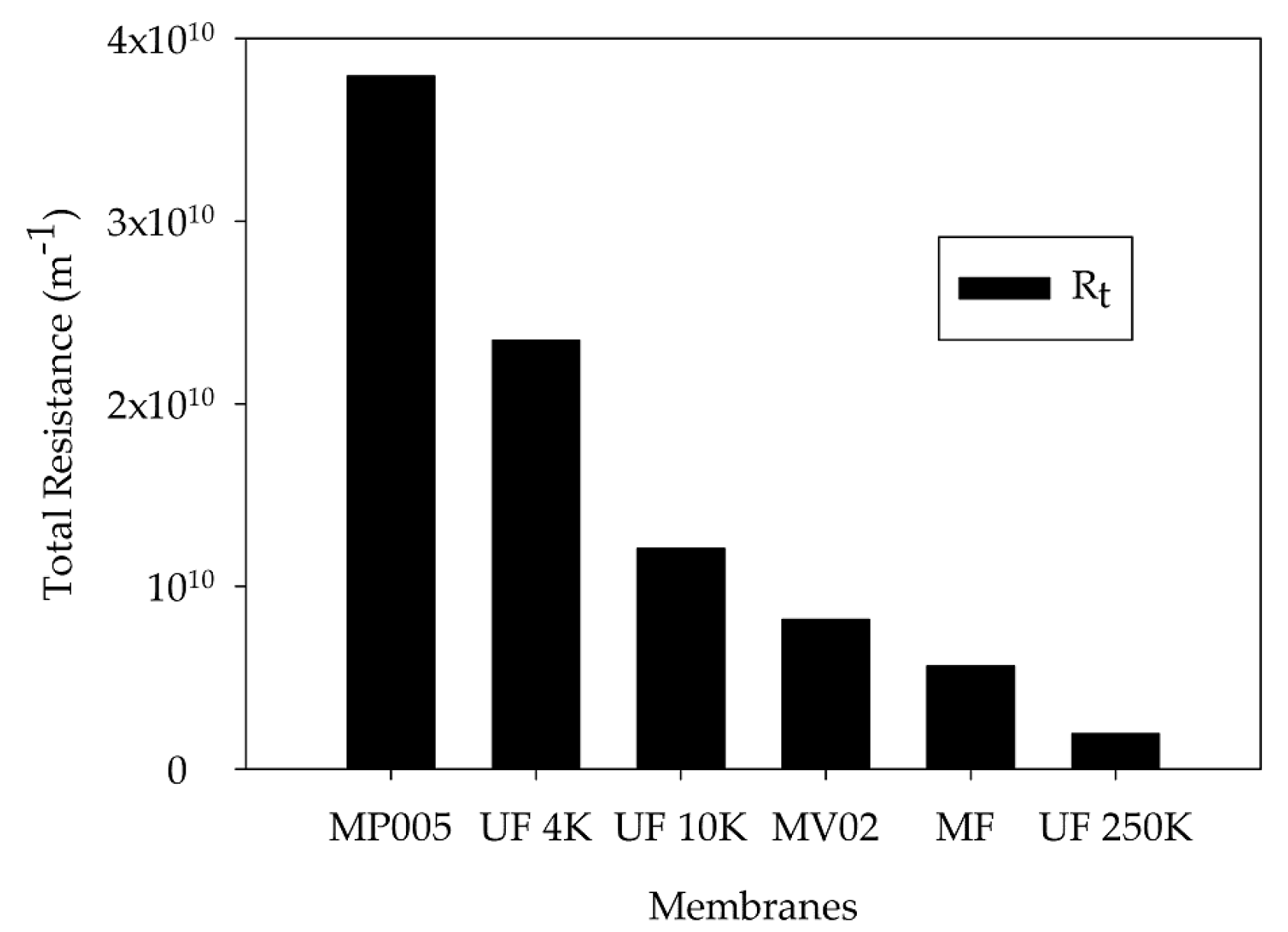
3.1. Resistances
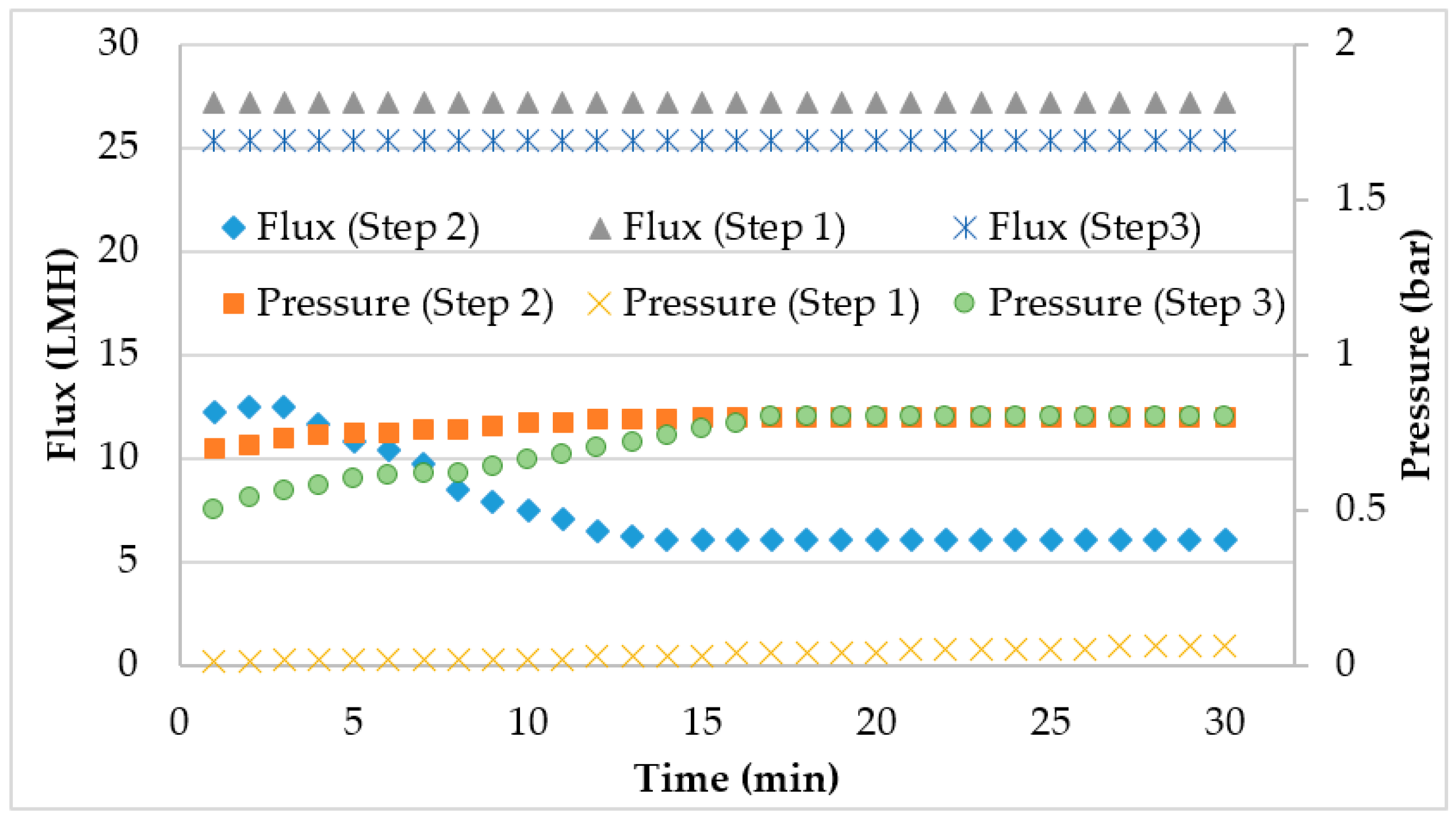
3.2. Flux Pressure Profiles
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaylali-Abanuz, G. Heavy metal contamination of surface soil around gebze industrial area, Turkey. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarovska, A.; Ustinovichius, L.; Shevchenko, G.; Nazarko, L. Multicriteria evaluation of commercial industrial zone development. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2015, 19, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Vankar, P.S.; Sahu, R.S. Geochemical trends of heavy metal in aquifer system of kanpur industrial zone, uttar pradesh (India): A case study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7287–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkish Republic Science, Industry, and Technology Ministry. Organized Industrial Zones. 2014. Available online: https://osbbs.sanayi.gov.tr/citylist.aspx (accessed on 1 May 2017).
- Rahman, M.A.; Rusteberg, B.; Uddin, M.S.; Saada, M.A.; Rabi, A.; Sauter, M. Impact assessment and multicriteria decision analysis of alternative managed aquifer recharge strategies based on treated wastewater in northern Gaza. Water 2014, 6, 3807–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-Y.; Baek, S.-R.; Kim, J.-I.; Choi, J.-W.; Hur, J.; Lee, T.-U.; Park, C.-J.; Lee, B.J. Characteristics and biodegradability of wastewater organic matter in municipal wastewater treatment plants collecting domestic wastewater and industrial discharge. Water 2017, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 2nd ed.; IWA Press: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, S. The status of industrial and municipal effluent treatment with membrane bioreactor technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 305, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Okamura, R.; Ishigami, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Kato, N.; Matsuyama, H. The effect of membrane material and surface pore size on the fouling properties of submerged membranes. Water 2016, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Cho, J.; Lim, B.R.; Song, K.G.; Ahn, K.H. Effects of sludge retention time on membrane fouling and microbial community structure in a membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Hori, T.; Navarro, R.R.; Habe, H.; Yanagishita, H.; Ogata, A. Fine-scale monitoring of shifts in microbial community composition after high organic loading in a pilot-scale membrane bioreactor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurtsever, A.; Sahinkaya, E.; Aktaş, Ö.; Uçar, D.; Çinar, Ö.; Wang, Z. Performances of anaerobic and aerobic membrane bioreactors for the treatment of synthetic textile wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanysacker, L.; Declerck, P.; Bilad, M.R.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Biofouling on microfiltration membranes in mbrs: Role of membrane type and microbial community. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Zabczynski, S.; Göbel, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Löffler, D.; McArdell, C.S.; Ternes, T.A.; Thomsen, A.; Siegrist, H. Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: Proposing a classification scheme. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjenović, J.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (cas) and advanced membrane bioreactor (mbr) treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.R.; Ritchie, C.B.; Tran, T.; Bolto, B.A. Effect of nom characteristics and membrane type on microfiltration performance. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-H.; Ng, H.Y. Effect of membrane type and material on performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodík, I.; Blšťáková, A.; Dančová, L.; Sedláček, S. Comparison of flat-sheet and hollow-fiber membrane modules in municipal wastewater treatment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 18, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-M.; Li, X.-Y.; Huang, X. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor (smbr): Characterisation of the sludge cake and its high filtration resistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 52, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Liang, H.; Zhou, J.; Nan, J.; Shao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Ultrafiltration membrane fouling caused by extracellular organic matter (eom) from microcystis aeruginosa: Effects of membrane pore size and surface hydrophobicity. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Kennedy, M.D.; van der Meer, W.G.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Schippers, J.C. The role of blocking and cake filtration in MBR fouling. Desalination 2003, 157, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.H.; Li, X. Membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor (MBR): Sludge cake formation and fouling characteristics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Trussell, R.R. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, E.L.; Howe, K.J.; Thomson, B.M. Effect of membrane bioreactor solids retention time on reverse osmosis membrane fouling for wastewater reuse. Water Res. 2014, 49, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffin, M.; Germain, E.; Judd, S. Wastewater polishing using membrane technology: A review of existing installations. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyanık, İ.; Özkan, O.; Koyuncu, İ. Nf-ro membrane performance for treating the effluent of an organized industrial zone wastewater treatment plant: Effect of different uf types. Water 2017, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.L.; Bai, R. Membrane fouling and cleaning in microfiltration of activated sludge wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 216, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liao, B.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. Effects of hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of membrane on membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | Influent | Effluent |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.1 ± 0.36 | 7.9 ± 0.4 |
| Electrical conductivity (EC) (ms/cm) | 4.8 ± 0.92 | 5.1 ± 1.1 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) (mg/L) | 471 ± 228 | 39.5 ± 22.3 |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) (mg/L) | 211 ± 75 | 0 |
| NO2-N (mg/L) | 0 | 0 |
| NO3-N (mg/L) | <0.01 | 3.5 ± 2.1 |
| Membrane Type | Brand | Pore Size (µm) | Membrane Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| MP005 | Microdyn-Nadir | 0.05 | PES |
| UF 4 kDa | Philos | 0.07 | PES |
| UF 10 kDa | Philos | 0.1 | PES |
| MV02 | Microdyn-Nadir | 0.2 | PVDF |
| MF | Philos | 0.24 | PVDF |
| UF 250 kDa | Philos | 0.44 | PVDF |
| Membrane | Effluent pH | EC (ms/cm) | COD (mg/L) | Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP005 | 8.10 ± 0.12 | 4.06 ± 0.08 | 19 ± 7 | 0.42 ± 0.25 |
| UF 4 k | 8.19 ± 0.24 | 4.23 ± 0.06 | 32 ± 11 | 0.36 ± 0.18 |
| UF 10 k | 8.10 ± 0.09 | 4.62 ± 0.11 | 38 ± 4 | 0.72 ± 0.09 |
| MV02 | 8.16 ± 0.17 | 4.41 ± 0.10 | 66 ± 14 | 0.88 ± 0.13 |
| MF | 8.01 ± 0.05 | 5.02 ± 0.27 | 67 ± 9 | 0.96 ± 0.07 |
| UF 250 k | 8.41 ± 0.10 | 4.65 ± 0.18 | 21 ± 16 | 0.21 ± 0.16 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özkan, O.; Uyanık, İ. Effect of Membrane Type for the Treatment of Organized Industrial Zone (OIZ) Wastewater with a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Batch Experiments. Water 2017, 9, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080582
Özkan O, Uyanık İ. Effect of Membrane Type for the Treatment of Organized Industrial Zone (OIZ) Wastewater with a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Batch Experiments. Water. 2017; 9(8):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080582
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzkan, Oktay, and İbrahim Uyanık. 2017. "Effect of Membrane Type for the Treatment of Organized Industrial Zone (OIZ) Wastewater with a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Batch Experiments" Water 9, no. 8: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080582
APA StyleÖzkan, O., & Uyanık, İ. (2017). Effect of Membrane Type for the Treatment of Organized Industrial Zone (OIZ) Wastewater with a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Batch Experiments. Water, 9(8), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080582




