Dependence of Sediment Suspension Viscosity on Solid Concentration: A Simple General Equation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simple Newly-Proposed Equation
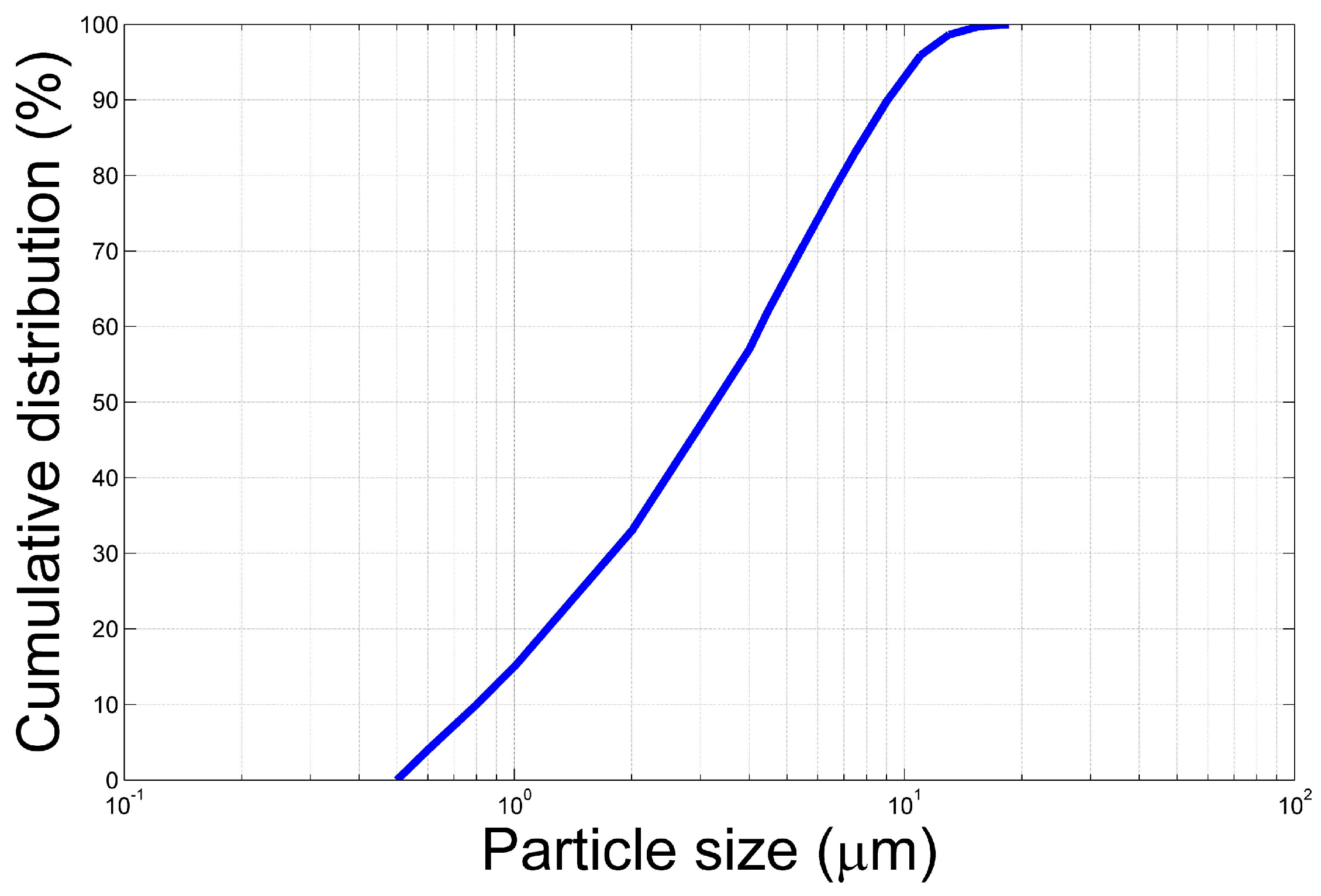
3. Experiment Introduction
4. Comparison with Experimental Results and Published Observational Data
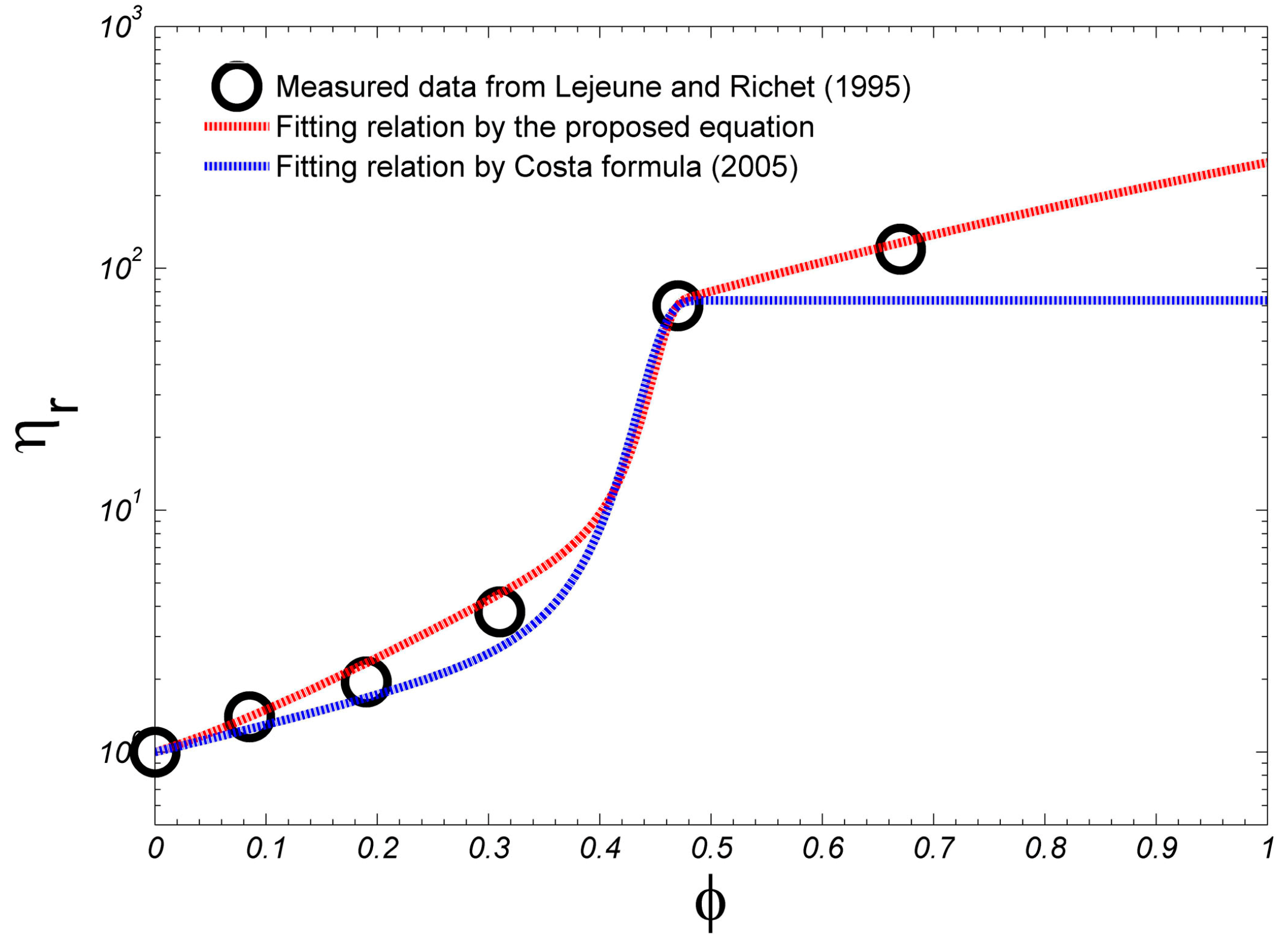
4.1. Comparison with Experimental Results
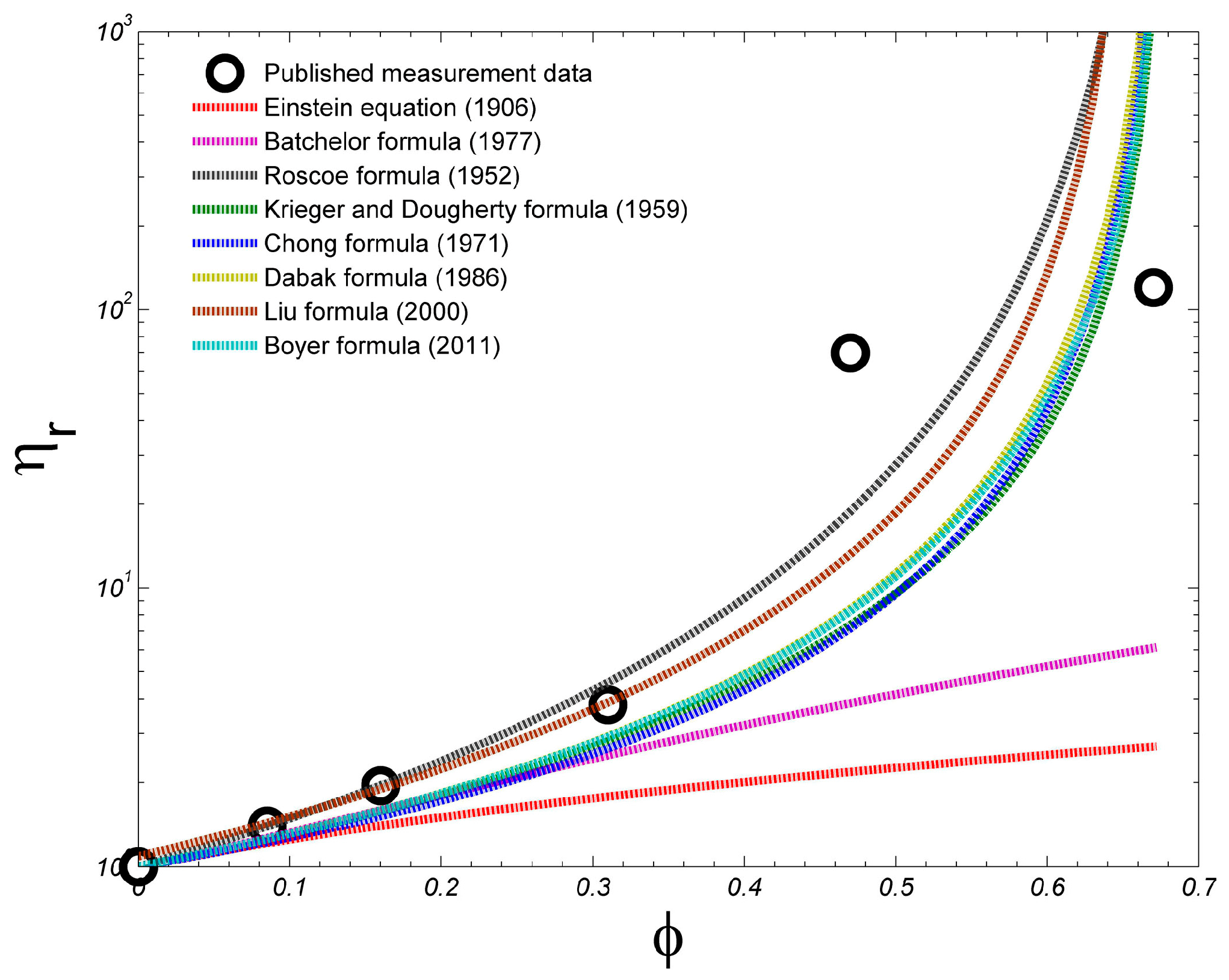
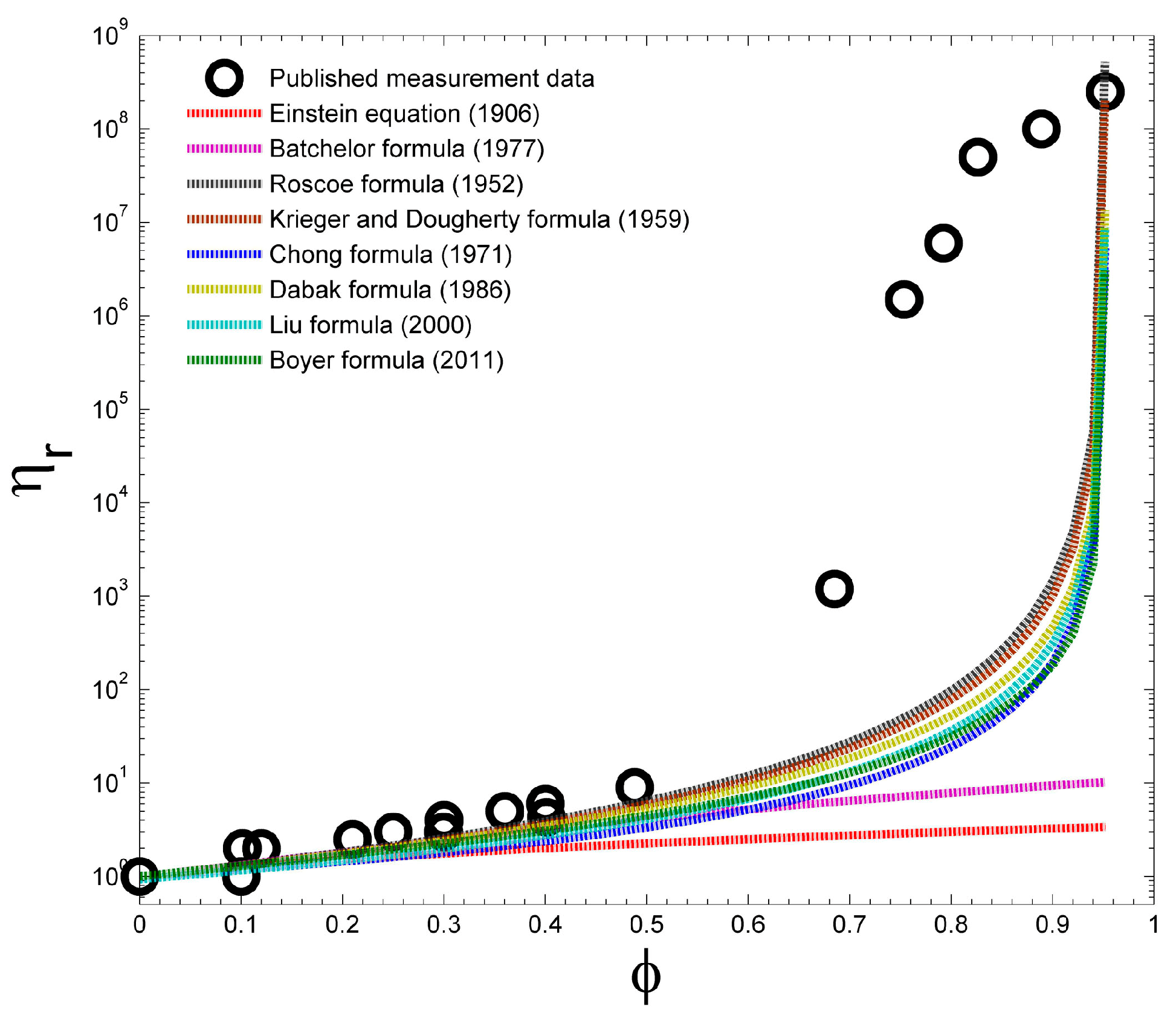
4.2. Comparison with Published Observational Data
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dean, R.G.; Dalrymple, R.A. Coastal Processes with Engineering Applications, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 471–478. ISBN 0521602750. [Google Scholar]
- Julien, P.Y.; Lan, Y. Rheology of hyperconcentrations. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1991, 117, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Aode, H. A laboratory study of rheological properties of mudflows in Hangzhou Bay, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2009, 24, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Ng, C.O.; Shen, H.T.; Wang, S.Y. Rheological properties and incipient motion of cohesive sediment in the Haihe Estuary of China. China Ocean Eng. 2002, 16, 483–498. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Garcia, M.H. A Herschel-Bulkley model for mud flow down a slope. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 374, 305–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, T.; Blom, C. Rhelogy of cohesive sediments: Comparison between a natural and an artificial mud. J. Hydraul. Res. 1998, 36, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.J. Understanding fluid mud in a dynamic environment. Geo-Mar. Lett. 1991, 11, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z. Acoustic observations of fluid mud and interfacial waves, Hangzhou Bay, China. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, A.J. Mudshore dynamics and controls. In Muddy Coasts of the World: Processes, Deposits and Function, 1st ed.; Healy, T., Wang, Y., Healy, J.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 19–60. ISBN 0-444-510192. [Google Scholar]
- Faas, R.W.; Wartel, S.I. Rheological properties of sediment suspensions from Eckernforde and Kieler Forde bays, western Baltic Sea. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2006, 21, 24–41. [Google Scholar]
- Granboulan, J.; Feral, A.; Villerot, M.; Jouanneau, J.M. Study of the sedimentological and rheological properties of fluid mud in the fluvio-estuarine system of the Gironde estuary. Ocean Coast. Manag. 1989, 12, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, C.; Winterwerp, J.C. Erosion of fluid mud layers. I: Entrainment model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; Kranenburg, C. Erosion of fluid mud layers. II: Experiments and model validation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C. On the flocculation and settling velocity of estuarine mud. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1339–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankers, P.J.T.; Winterwerp, J.C. Hindered settling of mud flocs: Theory and validation. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, D.B. Shear rheology of hard-sphere, dispersed, and aggregated suspensions, and filler-matrix composites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickel, J.J.; Powell, R.L. Fluid mechanics and rheology of dense suspensions. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Llewellin, E.W.; Mader, H.M. The rheology of suspensions of solid particles. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 2010, 466, 1201–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P. Structural similarity and transition from Newtonian to non-Newtonian behavior for clay-water suspensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 3971–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossum, J.O. Flow of clays. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2012, 204, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.M.; Dougherty, T.J. A mechanism for non-Newtonian flow in suspensions of rigid spheres. J. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.S.; Christiansen, E.B.; Baer, A.D. Rhelogy of concentrated suspensions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1971, 15, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabak, T.; Yucel, O. Shear viscosity behavior of highly concentrated suspensions at low and high shear rates. Rheol. Acta 1986, 25, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M. Particle packing and rtheological property of highly-concentrated ceramic suspensions: Phi determination and viscosity prediction. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 5503–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, F.; Guazzelli, É.; Pouliquen, O. Unifying suspension and granular rheology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 188301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trulsson, M.; Andreotti, B.; Claudin, P. Transition from the viscous to inertial regime in dense suspensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 118305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, D.; Acrivos, A. The rheological properties of suspensions of rigid particles. AIChE J. 1976, 22, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P.; Ancey, C. Rheophysical classification of concentrated suspensions and granular pastes. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 59, 4445–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P. Rheophysics of pastes: A review of microscopic modelling approaches. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Eineneue Bestimmung der Moleküldimensionen. Ann. Phys. 1906, 19, 289–306. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Effect of Brownian motion on bulk stress in a suspension of spherical particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 83, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, R. The viscosity of suspensions of rigid spheres. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1952, 3, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, W.B.; Sperry, P.R. Effect of microstructure on the viscosity of hard sphere dispersions and modulus of composites. Prog. Org. Coat. 1994, 23, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemada, D.; Berli, C. Energy of interaction in colloids and its implications in rheological modeling. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 51–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A. Viscosity of high crystal content melts: Dependence on solid fraction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Molen, I.; Paterson, M. Experimental deformation of partially melted granite. Contrib. Mineral. Pet. 1979, 70, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, A.; Richet, P. Rheology of crystal-bearing silicate melts: An experimental study at high viscosity. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 4215–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.W. Flocculation and Transport of Cohesive Sediment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Helos and Rodos Introduction. Available online: http://www.sympatec.com/EN/LaserDiffraction/RODOS.html (accessed on 1 January 2016).
- Brookfield Rheometers. Available online: http://www.brookfieldengineering.com/products/rheometers (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- Wiederseiner, S.; Andreini, N.; Epely-Chauvin, G.; Ancey, C. Refractive-index and density matching in concentrated particle suspensions: A review. Exp. Fluids 2011, 50, 1183–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D. Transport characteristics of suspensions: VIII. A note on the viscosity of Newtonian suspensions of uniform spherical particles. J. Colloid Sci. 1965, 20, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| The Proposed Equation | Einstein Equation | Batchelor Formula | Roscoe Formula | Krieger and Dougherty Formula | Chong Formula | Dabak Formula | Liu Formula | Costa Formula | Boyer Formula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.93 | 0.59 |
| NRMSE | 0.03 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 2.82 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.14 |
| Einstein Equation | Batchelor Formula | Roscoe Formula | Krieger and Dougherty Formula | Chong Formula | Dabak Formula | Liu Formula | Boyer Formula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| NRMSE | 0.46 | 0.45 | 130.40 | 4.07 | 8.60 | 11.11 | 12.99 | 5.16 |
| Einstein Equation | Batchelor Formula | Roscoe Formula | Krieger and Dougherty Formula | Chong Formula | Dabak Formula | Liu Formula | Boyer Formula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 |
| NRMSE | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.26 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, D. Dependence of Sediment Suspension Viscosity on Solid Concentration: A Simple General Equation. Water 2017, 9, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070474
Zhu Z, Wang H, Peng D. Dependence of Sediment Suspension Viscosity on Solid Concentration: A Simple General Equation. Water. 2017; 9(7):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070474
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhongfan, Hongrui Wang, and Dingzhi Peng. 2017. "Dependence of Sediment Suspension Viscosity on Solid Concentration: A Simple General Equation" Water 9, no. 7: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070474
APA StyleZhu, Z., Wang, H., & Peng, D. (2017). Dependence of Sediment Suspension Viscosity on Solid Concentration: A Simple General Equation. Water, 9(7), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070474







