An Improved Coupled Routing and Excess Storage (CREST) Distributed Hydrological Model and Its Verification in Ganjiang River Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Review of Distributed Hydrological Model
1.2. Brief Introduction of the Coupled Routing and Excess Storage (CREST) Model and Motivation of Model Improvement
1.3. Content of This Paper
2. Methodology
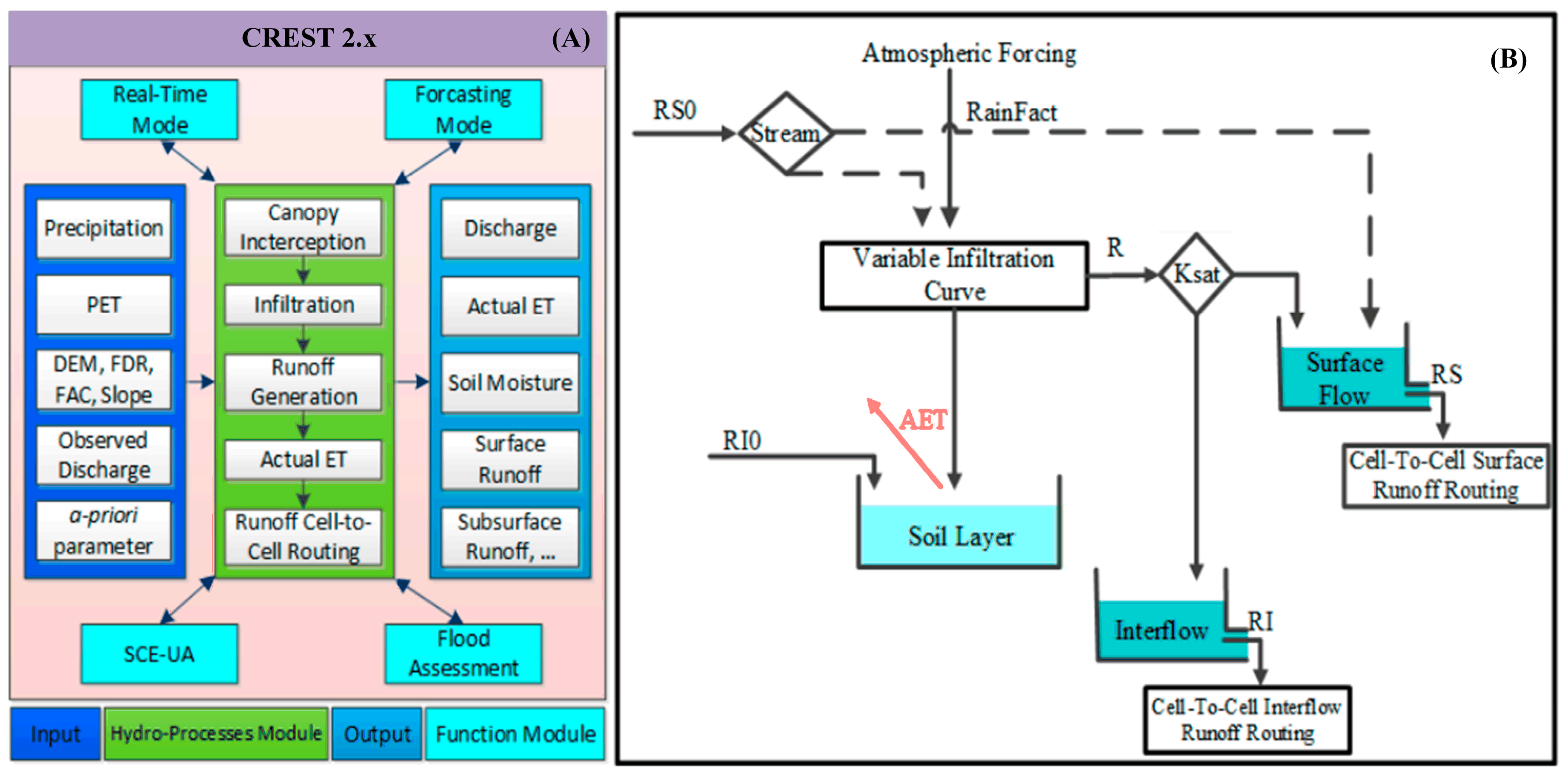
2.1. Traditional CREST Model—Version 2.x
2.2. Improved CREST Model—Version 3.0
2.2.1. Tension Water Storage Capacity Distribution Curve-Based Runoff Generation
2.2.2. Three Soil Layers-Based Soil Moisture and Evapotranspiration Computation
2.2.3. Free Water Reservoir-Based Separation of Three Runoff Components
2.2.4. Four Mechanisms-Based Cell-To-Cell Routing
2.3. Model Calibration
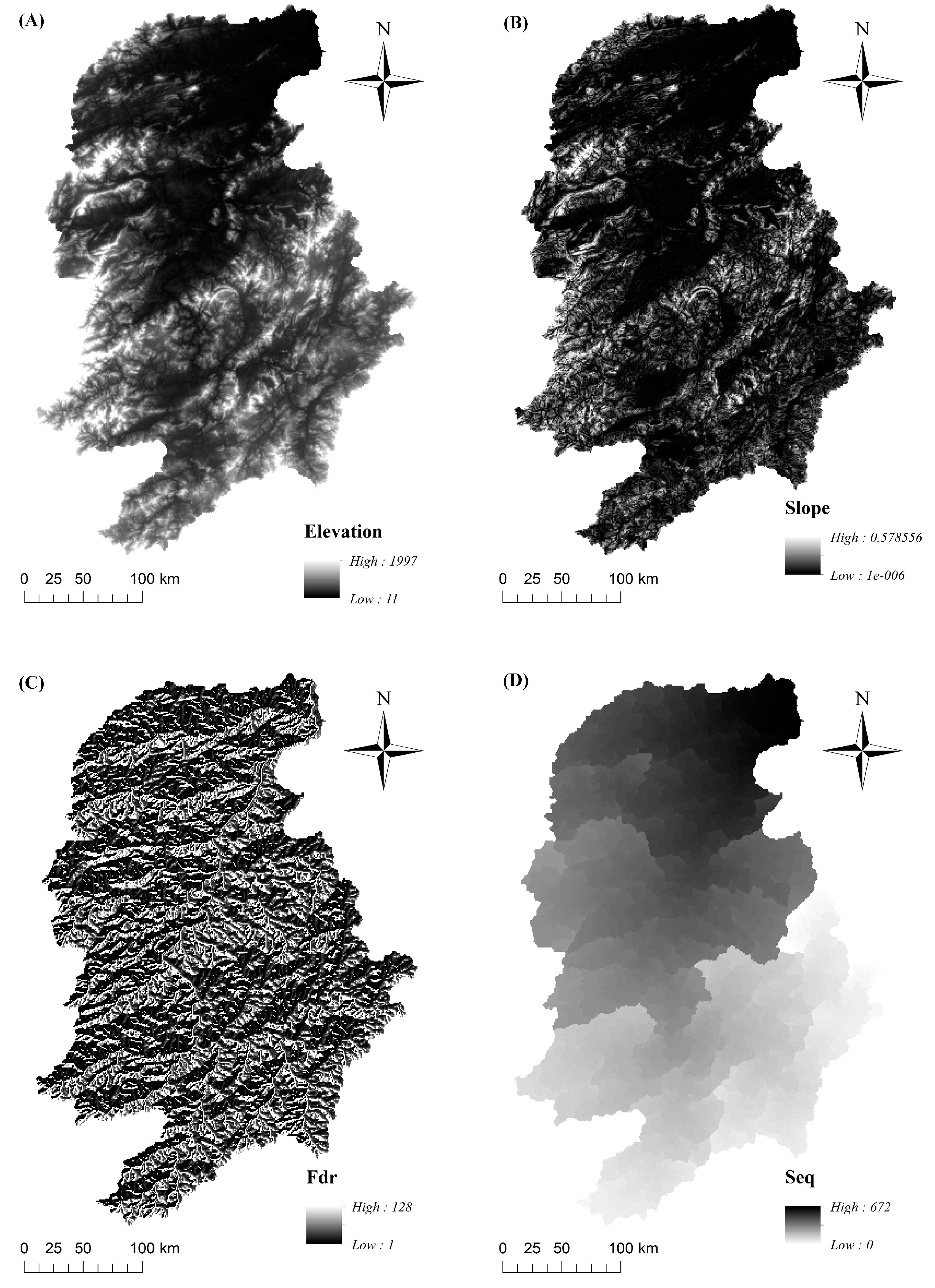
3. Study Area and Data Description
4. Results and Discussion
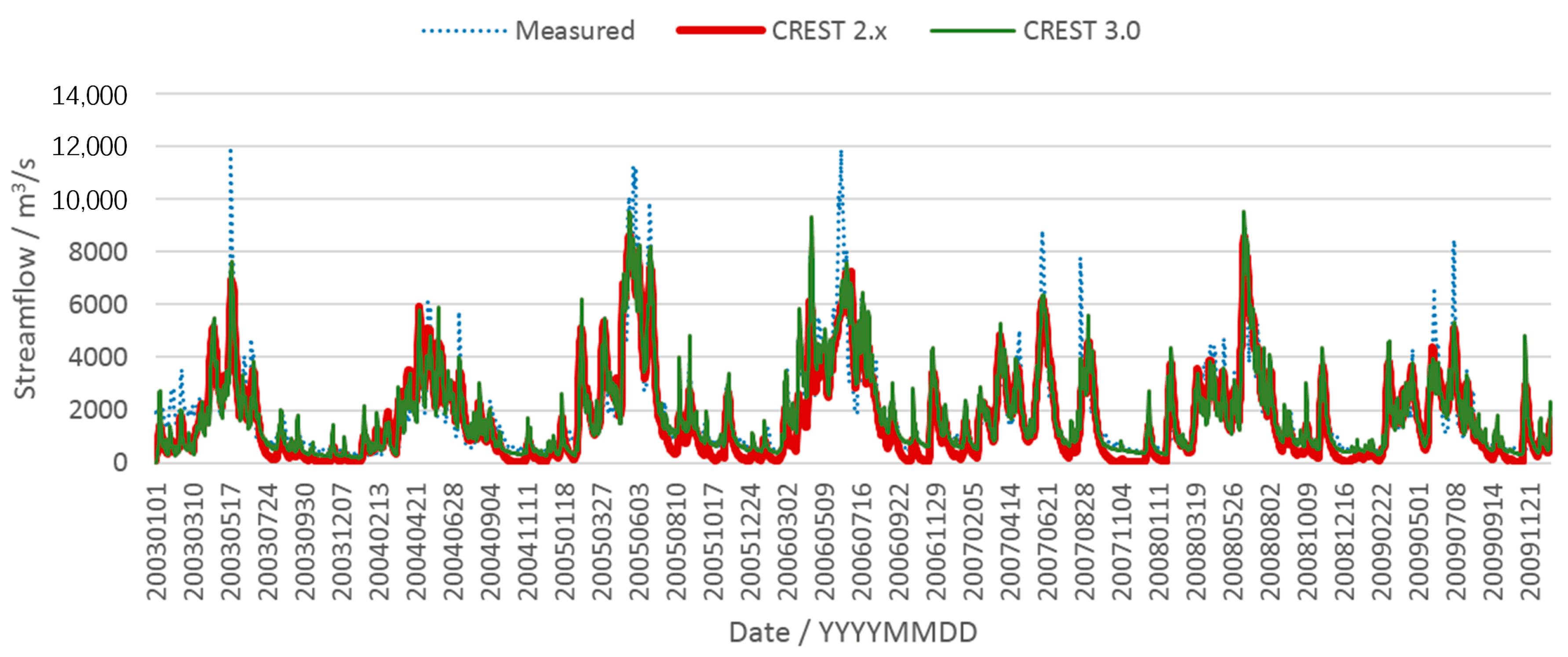
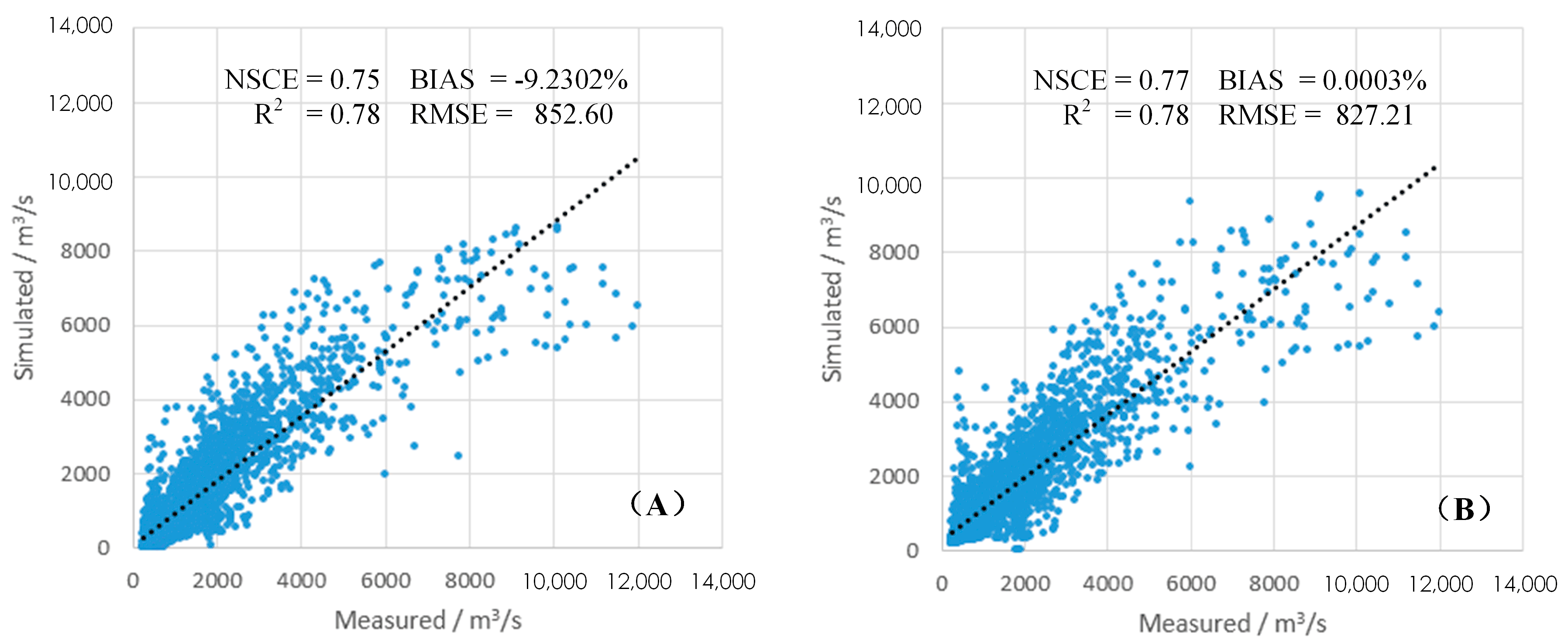
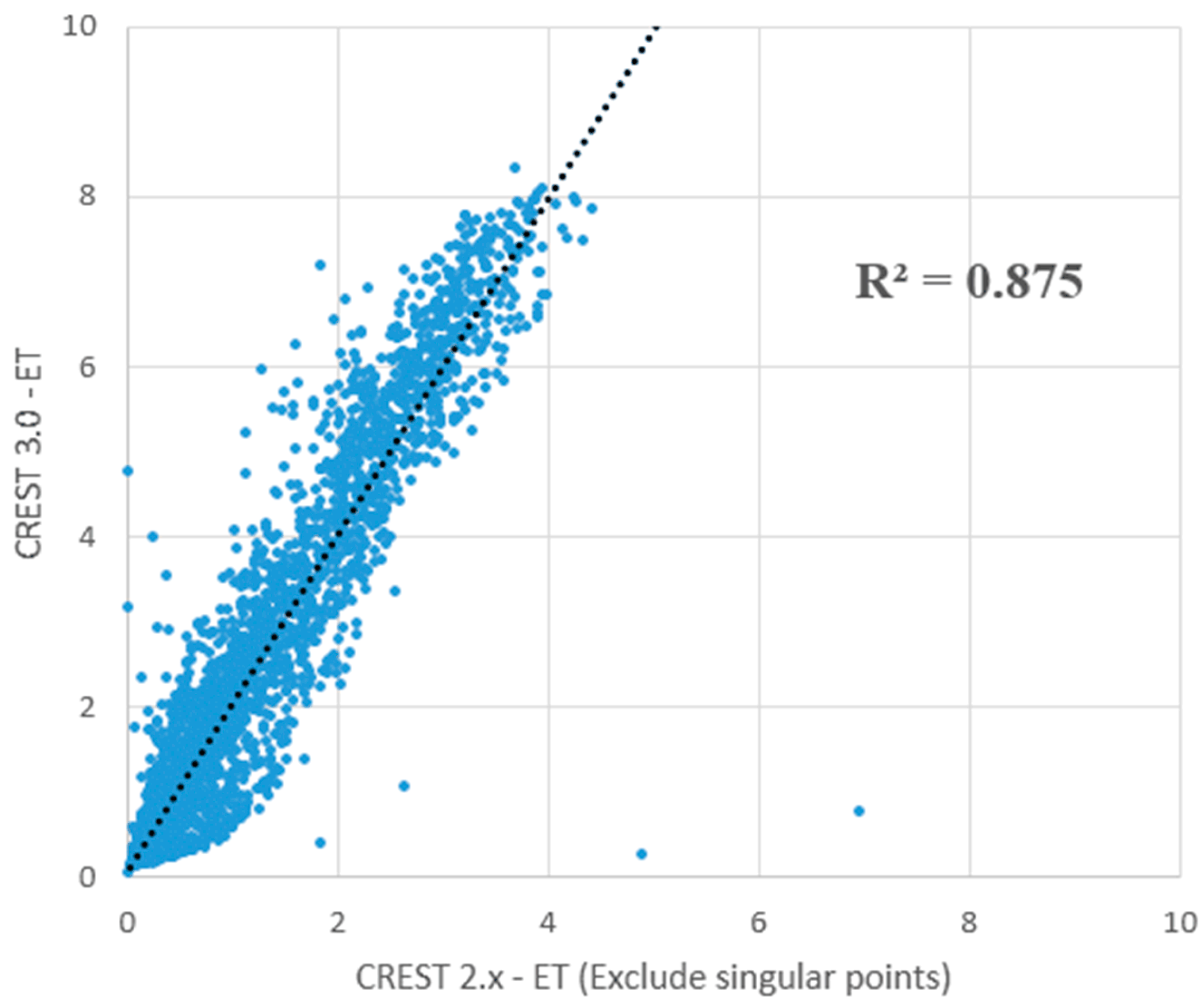
4.1. Comparison of Basin Outlet Discharge Simulations between CREST 2.x and 3.0
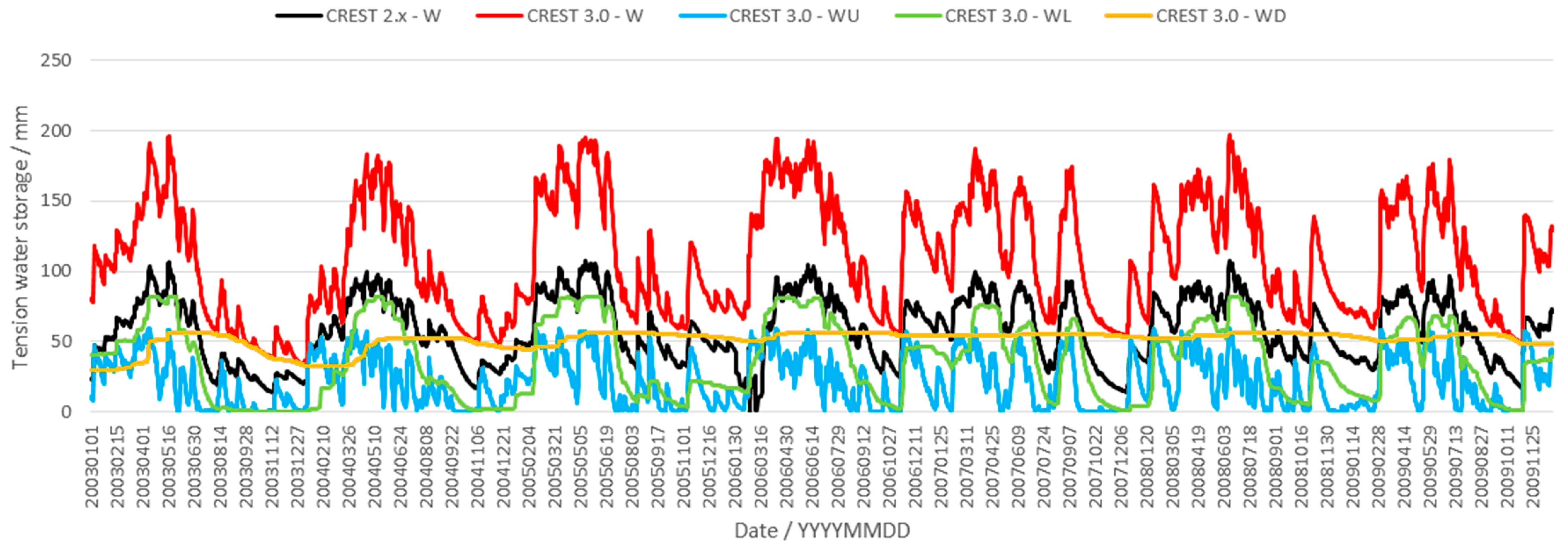
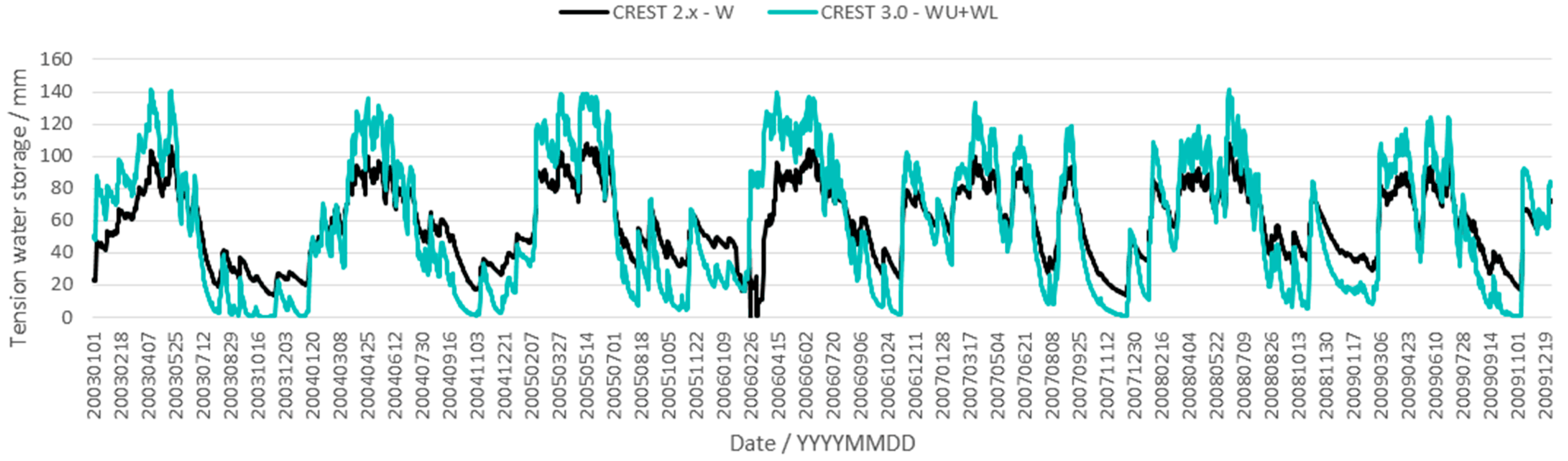
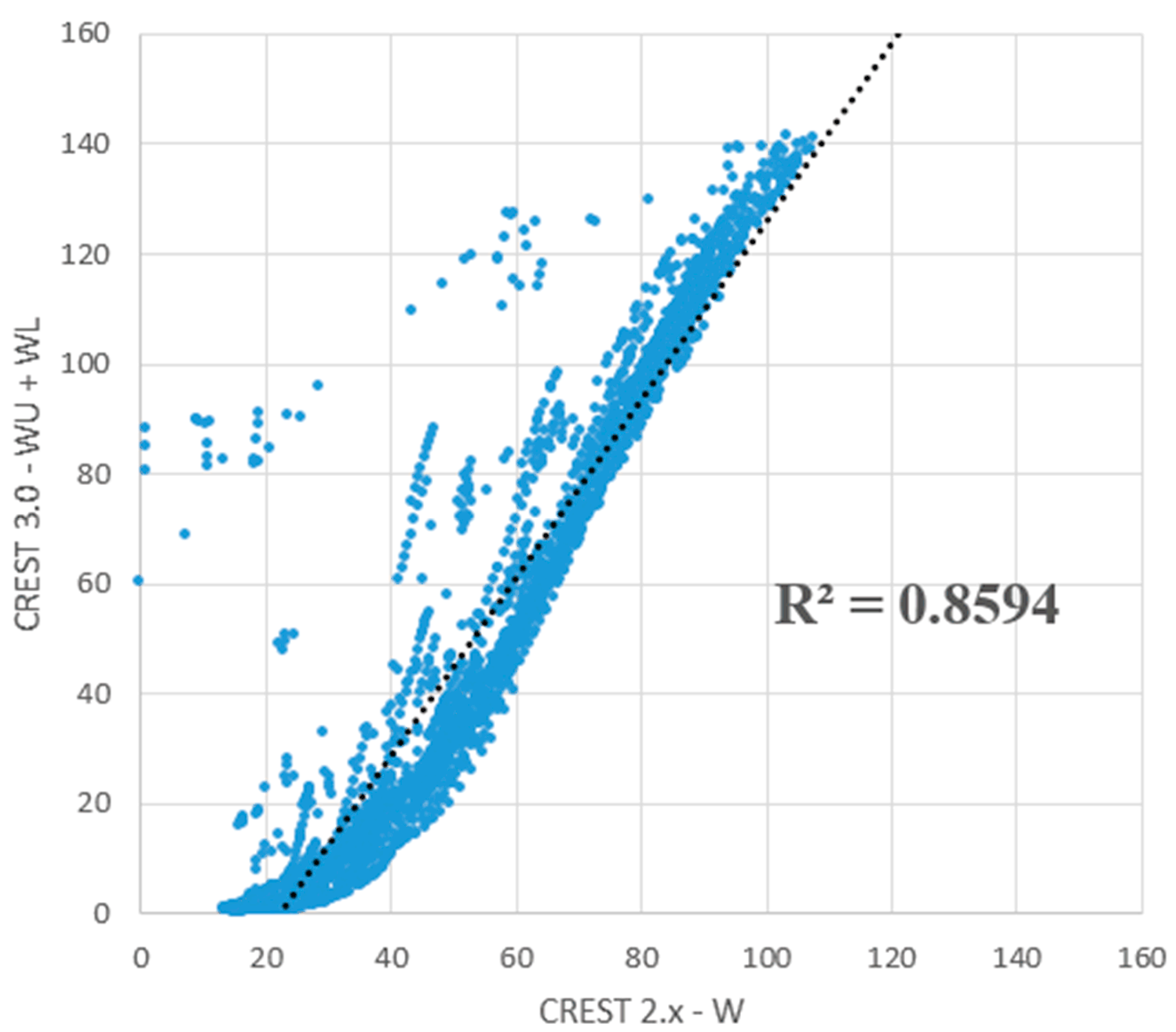
4.2. Comparison of Areal Mean Soil Moisture Simulations between CREST 2.x and 3.0
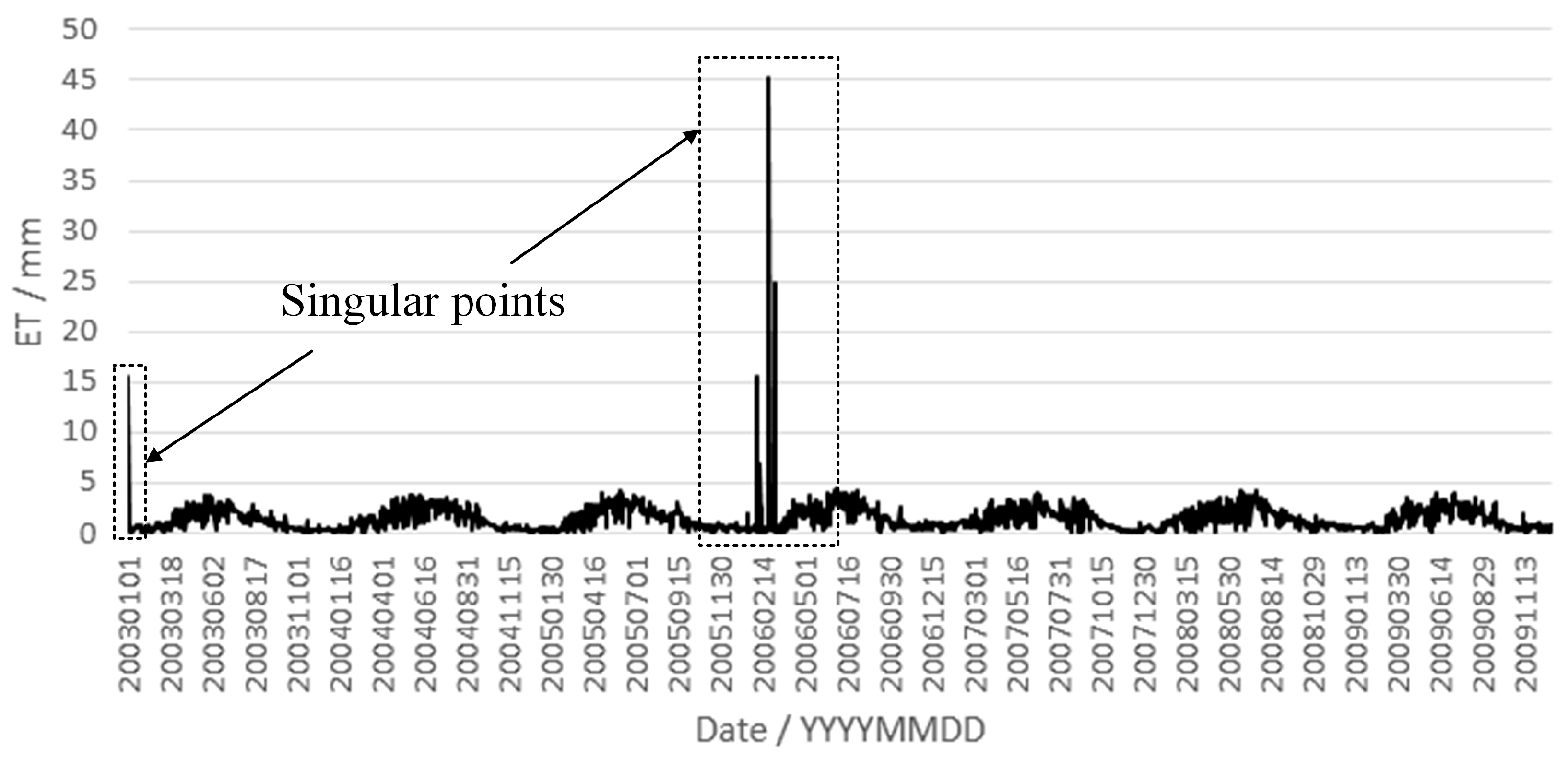
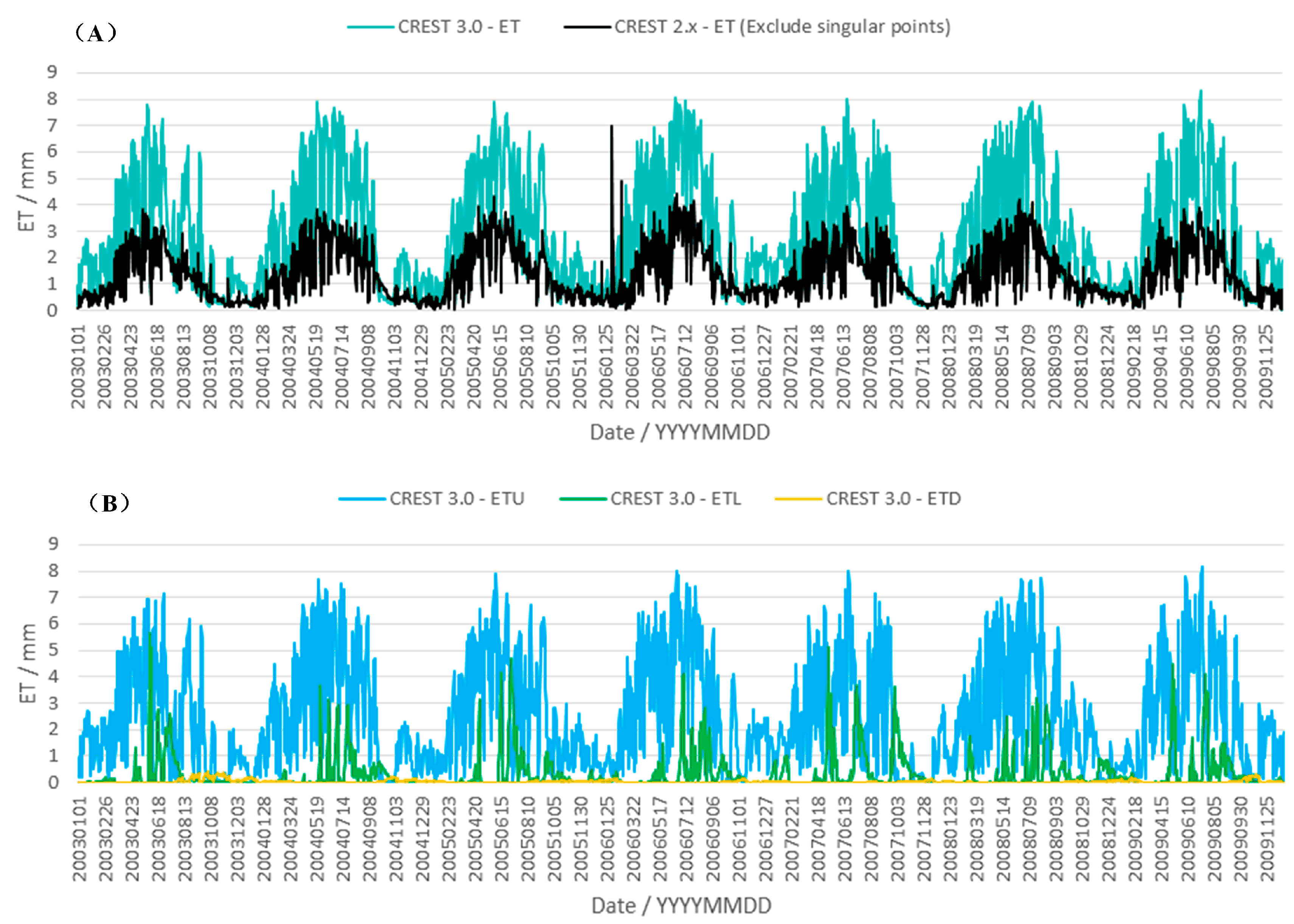
4.3. Comparison of Areal Mean Actual Evapotranspiration Simulations between CREST 2.x and 3.0
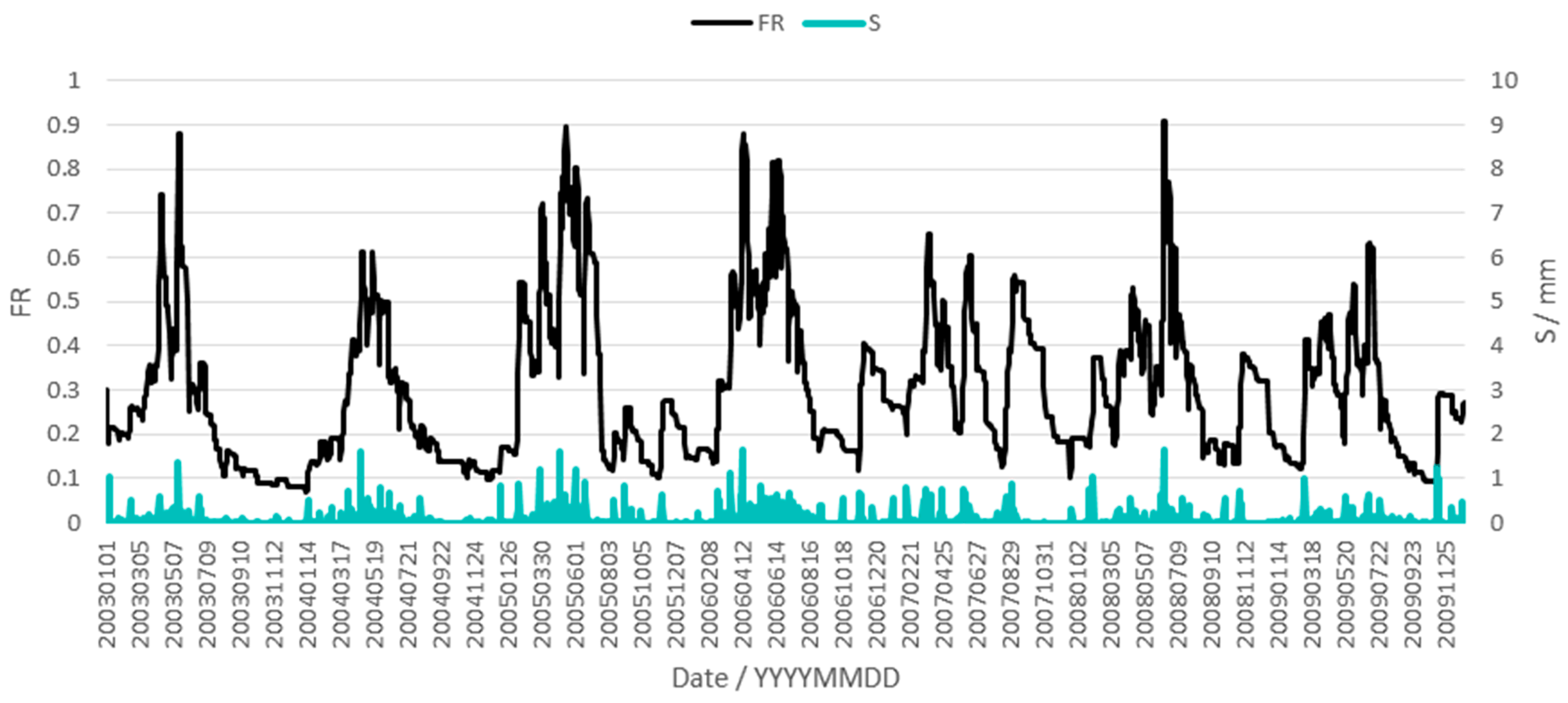
4.4. Analysis of Areal Mean Runoff Generation Area and Free Water Storage Simulations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, D.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, J.H. Multiobjective Automatic Parameter Calibration of a Hydrological Model. Water 2017, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarapica, L.; Todini, E. TOPKAPI: A model for the representation of the rainfall-runoff process at different scales. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Todini, E. Towards a comprehensive physically-based rainfall-runoff model. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 6, 859–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, A.; Alila, Y.; Beckers, J.; Toews, D. Application of the distributed hydrology soil vegetation model to redfish creek, British Columbia: Model evaluation using internal catchment data. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Xie, Z.H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H.W.; Su, F.G.; Liang, X.; Ren, L.L. An application of the VIC-3L land surface model and remote sensing data in simulating streamflow for the Hanjiang River basin. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oconnell, P.E.; Todini, E. Modelling of rainfall, flow and mass transport in hydrological systems: An overview. J. Hydrol. 1996, 175, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, P. Overview of Ecohydrological Models and Systems at the Watershed Scale. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 9, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Vivoni, E.R.; Ogden, F.L.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Mirus, B.; Gochis, D.; Downer, C.W.; Camporese, M.; Davison, J.H.; Ebel, B.A.; et al. An overview of current applications, challenges, and future trends in distributed process-based models in hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooge, J.C.L. Looking for hydrologic laws. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalew, S.; van Griensven, A.; Ray, N.; Kokoszkiewicz, L.; Betrie, G.D. Distributed computation of large scale SWAT models on the Grid. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 41, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Zhu, A.X.; Qin, C.Z. Estimation of theoretical maximum speedup ratio for parallel computing of grid-based distributed hydrological models. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 60, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Zhu, A.X.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhu, T.X.; Qin, C.Z. A layered approach to parallel computing for spatially distributed hydrological modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 51, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, Z.J.; Bao, H.J.; Yu, Z.B. Application of a Developed Grid-Xinanjiang Model to Chinese Watersheds for Flood Forecasting Purpose. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, Z.J.; Yu, Z.B.; Zhang, K. A priori parameter estimates for a distributed, grid-based Xinanjiang model using geographically based information. J. Hydrol. 2012, 468, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Storm, B.; Refsgaard, A. Recent developments of the Systeme Hydrologique Europeen (SHE) towards the MIKE SHE. In Modelling and Management of Sustainable Basin-scale Water Resource Systems; IAHS Publications 231; IAHS Publications: Wallingford, UK, 1995; pp. 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Q.H.; Yang, D.W.; Yang, H.B.; Li, Z. Establishing a rainfall threshold for flash flood warnings in China’s mountainous areas based on a distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, S.; Rahimpour, M.; Zounemat-Kermani, M. Numerical modeling based on a finite element method for simulation of flow in furrow irrigation. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiyama, K.; Okada, T. Automatic mesh generation method for shallow-water flow-analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1992, 15, 1037–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloschl, G.; Sivapalan, M. Scale issues in hydrological modeling—A review. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 251–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.D. Modelling effects of soil structure on the water balance of soil-crop systems: A review. Soil Tillage Res. 1998, 48, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, D.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Cordier, M.O. Parameterisation of hydrological models: A review and lessons learned from studies of an agricultural catchment (Naizin, France). Agronomie 2002, 22, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietroniro, A.; Leconte, R. A review of Canadian remote sensing and hydrology, 1999–2003. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hong, Y.; Li, L.; Gourley, J.J.; Khan, S.I.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Adler, R.F.; Policelli, F.S.; Habib, S.; Irwn, D.; et al. The coupled routing and excess storage (CREST) distributed hydrological model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based multi-satellite precipitation analysis over the Wangchu basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B43V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, K. CREST User manual Version 2.1-Fortran; The University of Oklahoma (OU) HyDROS Lab: Norman, OK, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Hao, Z. Refining a distributed linear reservoir routing method to improve performance of the CREST model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 22, 04016061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, H.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Gourley, J.J.; Flamig, Z.L.; Hong, Y.; Arthur, A.; Kolar, R. Estimating a-priori kinematic wave model parameters based on regionalization for flash flood forecasting in the Conterminous United States. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The University of Oklahoma, Hydrometeorology and Remote Sensing Laboratory. 2017. Website of CREST Model. Available online: http://hydro.ou.edu/research/crest/ (accessed on 15 June 2017).
- Zhao, E.Y.; Gao, C.X.; Jiang, X.G.; Liu, Z.X. Land surface temperature retrieval from AMSR-E passive microwave data. Opt. Express 2017, 25, A940–A952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Vu, T.; Veettil, A.V.; Entekhabi, D. Drought monitoring with soil moisture active passive (SMAP) measurements. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodiguez-Fernandez, N.J.; Sabater, J.M.; Richaume, P.; de Rosnay, P.; Kerr, Y.H.; Albergel, C.; Drusch, M.; Mecklenburg, S. SMOS near-real-time soil moisture product: Processor overview and first validation results. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5201–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felfelani, F.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Pokhrel, Y.N. Natural and human-induced terrestrial water storage change: A global analysis using hydrological models and GRACE. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Gourley, J.J.; Adler, R.F.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Policelli, F.; Habib, S.; Irwin, D. Satellite remote sensing and hydrologic modeling for flood inundation mapping in lake Victoria basin: Implications for hydrologic prediction in ungauged basins. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Adler, R.F.; Hong, Y.; Tian, Y.; Policelli, F. Evaluation of global flood detection using satellite-based rainfall and a hydrologic model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1268–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q. A Global Optimization Strategy for Efficient and Effective Calibration of Hydrologic Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Hydrology and Water Resources, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshianz, S.; Gupta, V. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Gupta, V.; Sorooshian, S. A shuffled complex evolution approach for effective and efficient global minimization. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1993, 76, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V. Optimal use of the SCE-UA global optimization method for calibrating watershed models. J. Hydrol. 1994, 158, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.; Zhang, M.; Liang, K.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; He, X.; Hong, Y.; Zuo, D.; et al. Improving water quantity simulation & forecasting to solve the energy-water-food nexus issue by using heterogeneous computing accelerated global optimization method. Appl. Energy 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.; Lei, T.; Liang, K.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; He, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zuo, D.; Bao, Z.; et al. A multi-core CPU and many-core GPU based fast parallel shuffled complex evolution global optimization approach. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2016, 28, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.; Liang, K.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; He, X.; Hu, Y.; Amo-Boateng, M. Accelerating the SCE-UA global optimization method based on multi-core CPU and many-core GPU. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 8483728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.; He, X.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liang, K.; Zhang, M. Computer aided numerical methods for hydrological model calibration: An overview and recent development. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.; He, X.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Hong, Y.; Zuo, D.; Ren, M.; Lei, T.; Liang, K. Fast hydrological model calibration based on the heterogeneous parallel computing accelerated shuffled complex evolution method. Eng. Optim. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, G.; He, X.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Liang, K.; Hong, Y. A heterogeneous computing accelerated SCE-UA global optimization method using OpenMP, CUDA and OpenACC. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Li, Z.; Xue, X.; Hu, Q.; Yong, B.; Hong, Y. A study of substitutability of TRMM remote sensing precipitation for gauge-based observation in Ganjiang River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 340–346. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Long, D.; Guo, X.; Yong, B.; Zhang, W.; Hong, Y. Statistical and hydrological comparisons between TRMM and GPM level-3 products over a midlatitude basin: Is day-1 IMERG a good successor for TMPA 3B42V7? J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Toward improved calibration of hydrologic models: Multiple and noncommensurable measures of information. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Physical Meaning | Range and Unit |
|---|---|---|
| KC | Potential evapotranspiration correction coefficient | 0.1–2 |
| B | Power of tension water storage capacity distribution curve | 0.1–2 |
| C | Deeper soil layer evapotranspiration coefficient | 0.01–0.5 |
| WUM | Upper soil layer water capacity | 5–60 (mm) |
| WLM | Lower soil layer water capacity | 10–90 (mm) |
| WDM | Deep soil layer water capacity | 35–150 (mm) |
| IM | Impervious area ratio | 0.01–0.5 |
| SM | Free water capacity | 1–60 (mm) |
| EX | Power of free water storage capacity distribution curve | 0.01–2 |
| KG | Free water storage to groundwater outflow coefficient | 0–1 |
| KI | Free water storage to interflow outflow coefficient | 0–1 |
| KRF | Velocity coefficient for river channel flow | 0–100 |
| KOF | Velocity coefficient for overland flow | 0–10 |
| KIF | Velocity coefficient for interflow | 0–1 |
| KGF | Velocity coefficient for ground water flow | 0–0.1 |
| Model | Error Statistics Indicator | Value |
|---|---|---|
| CREST 2.x | NSCE | 0.75 |
| BIAS | −9.2302% | |
| R2 | 0.78 | |
| RMSE | 852.60 | |
| CREST 3.0 | NSCE | 0.77 |
| BIAS | 0.0003% | |
| R2 | 0.78 | |
| RMSE | 827.21 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kan, G.; Tang, G.; Yang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; He, X.; Liang, K.; He, L.; Li, Z.; et al. An Improved Coupled Routing and Excess Storage (CREST) Distributed Hydrological Model and Its Verification in Ganjiang River Basin, China. Water 2017, 9, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110904
Kan G, Tang G, Yang Y, Hong Y, Li J, Ding L, He X, Liang K, He L, Li Z, et al. An Improved Coupled Routing and Excess Storage (CREST) Distributed Hydrological Model and Its Verification in Ganjiang River Basin, China. Water. 2017; 9(11):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110904
Chicago/Turabian StyleKan, Guangyuan, Guoqiang Tang, Yuan Yang, Yang Hong, Jiren Li, Liuqian Ding, Xiaoyan He, Ke Liang, Lian He, Zhansheng Li, and et al. 2017. "An Improved Coupled Routing and Excess Storage (CREST) Distributed Hydrological Model and Its Verification in Ganjiang River Basin, China" Water 9, no. 11: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110904
APA StyleKan, G., Tang, G., Yang, Y., Hong, Y., Li, J., Ding, L., He, X., Liang, K., He, L., Li, Z., Hu, Y., & Cui, Y. (2017). An Improved Coupled Routing and Excess Storage (CREST) Distributed Hydrological Model and Its Verification in Ganjiang River Basin, China. Water, 9(11), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110904







