Simulating the Effects of Agricultural Management on Water Quality Dynamics in Rice Paddies for Sustainable Rice Production—Model Development and Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Site
2.2. APEX-Paddy Model
2.2.1. Evapotranspiration
2.2.2. Puddling Simulation
2.2.3. Transplanting Simulation
2.3. Model Calibration and Validation
3. Results and Discussion
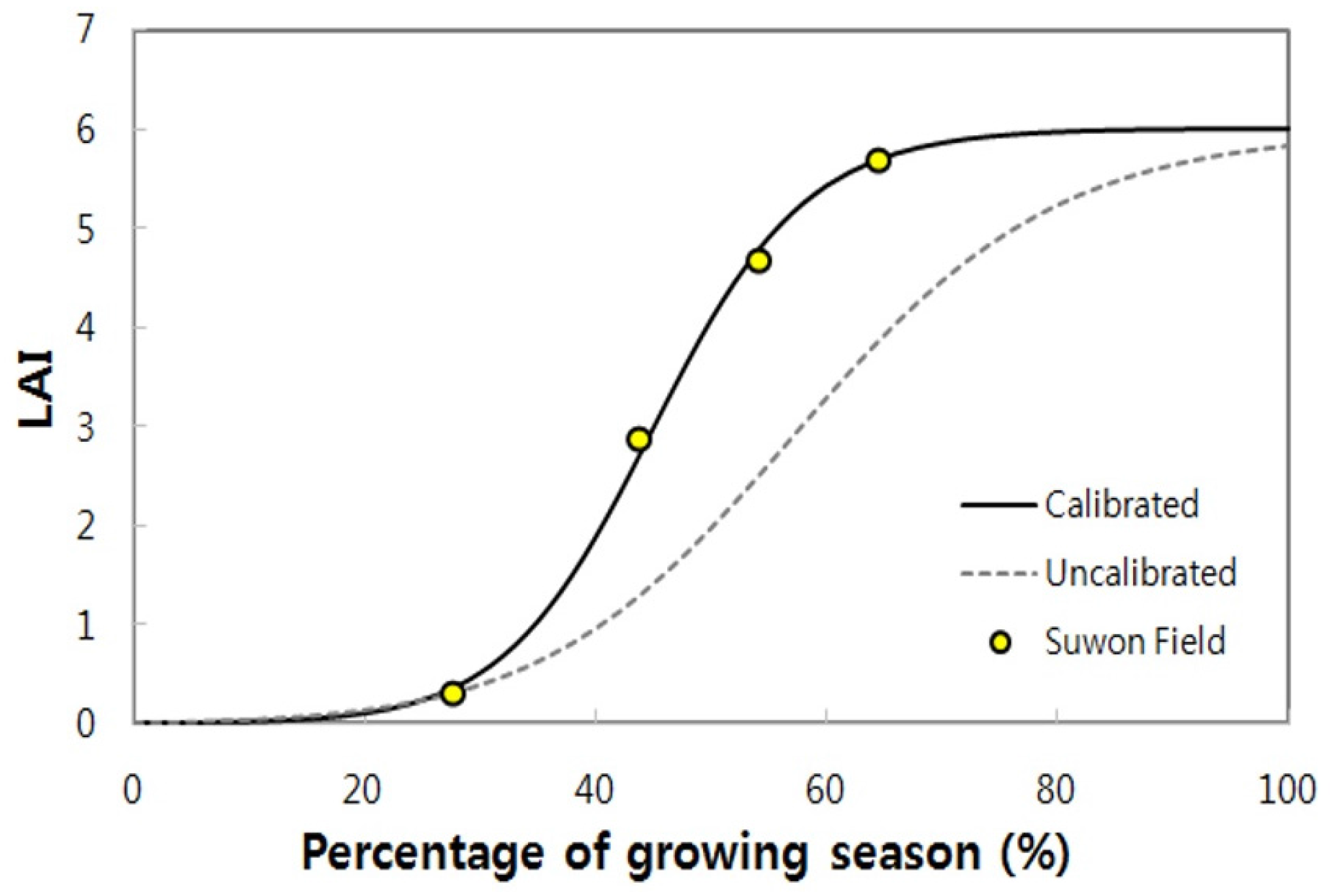
3.1. Characterization of Paddy Rice for APEX Simulation
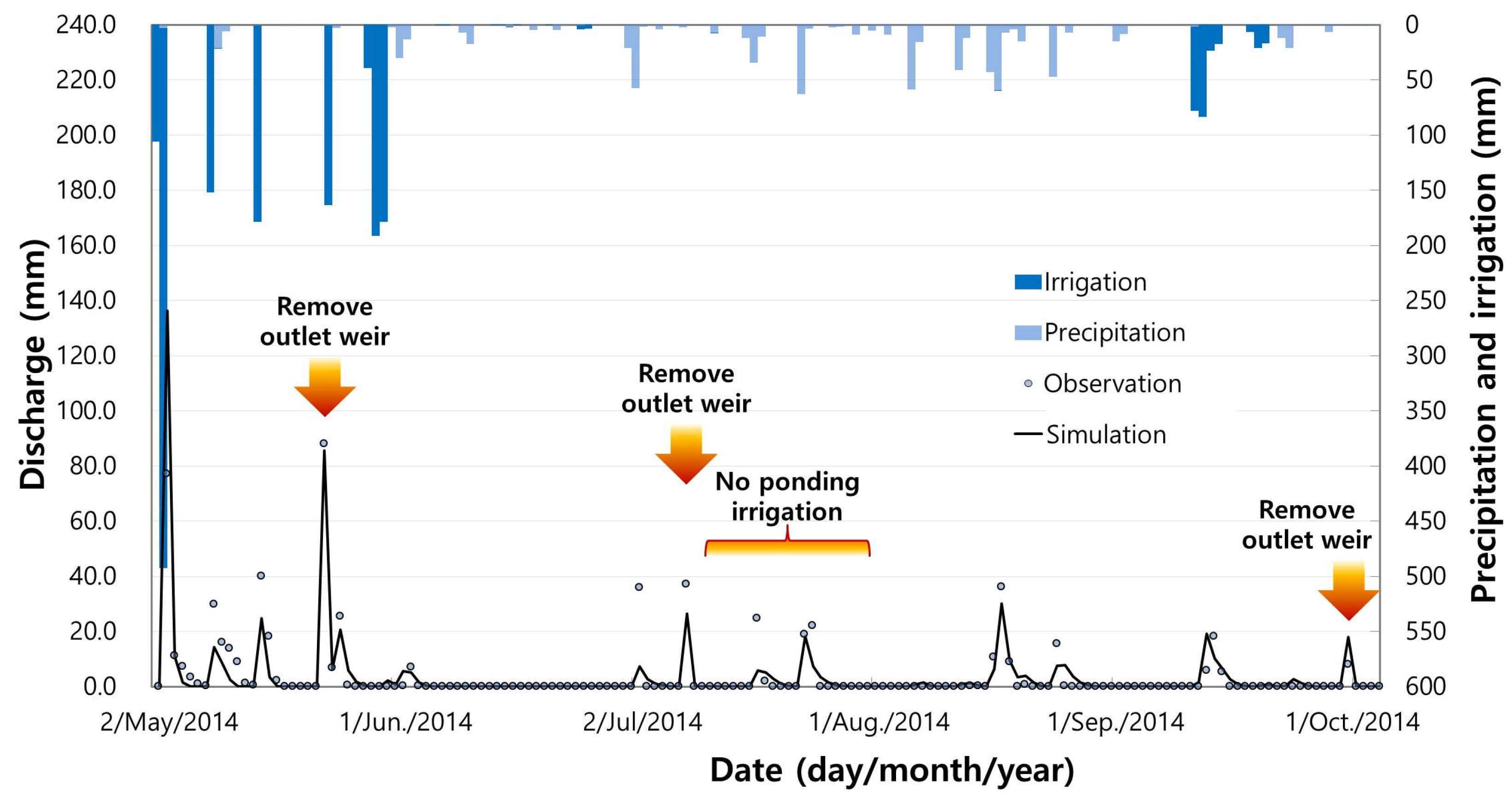
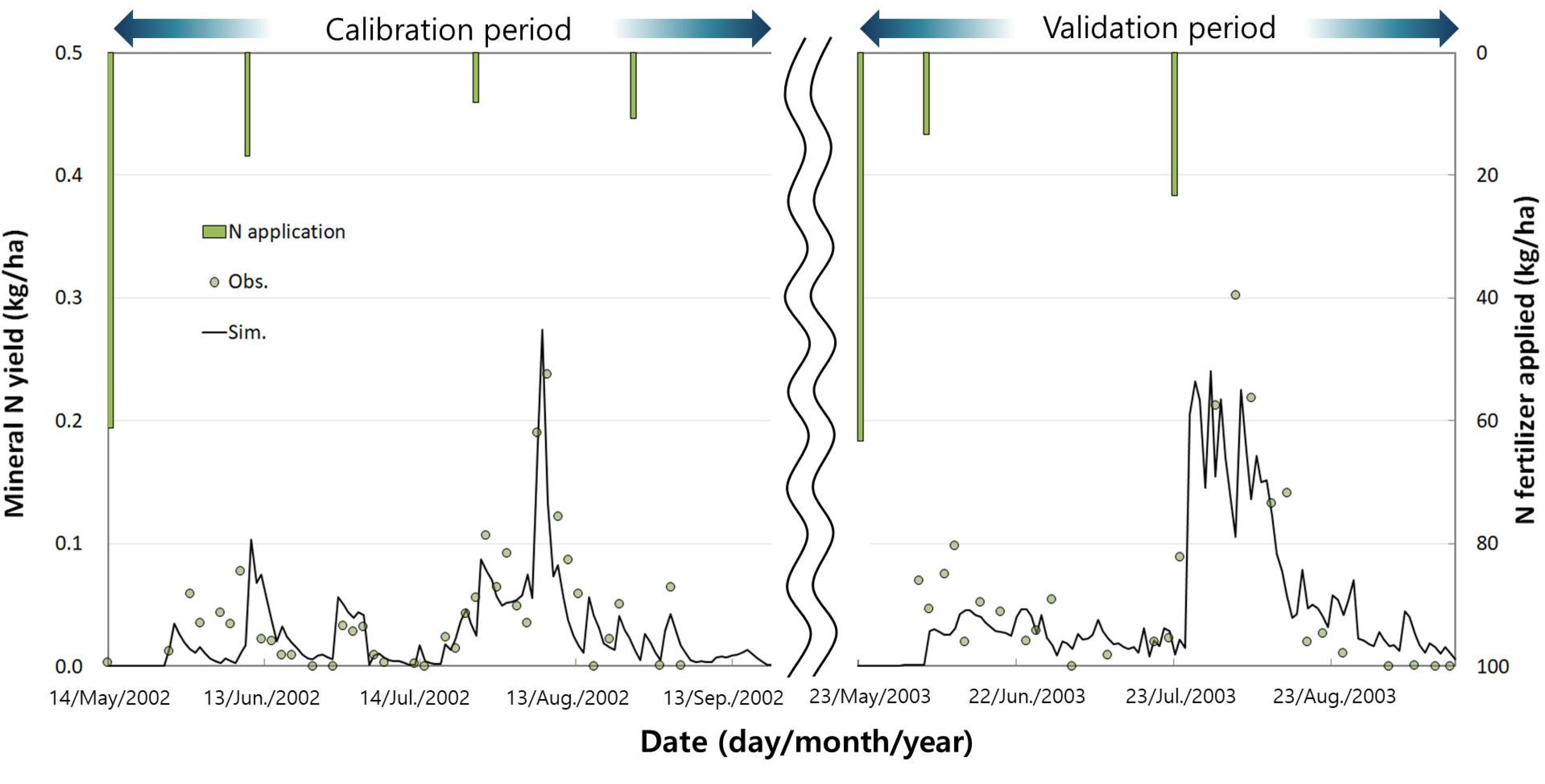
3.2. Effects of Paddy Management on Water and Nitrogen Balance
3.3. Performance of APEX-Paddy over APEX1501
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, M.S.; Park, S.W.; Lee, J.J.; Yoo, K.H. Applying SWAT for TMDL programs to a small watershed containing rice paddy fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 79, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MARFA). The 2013 Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Survey; Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs: Sejong-si, Korea, 2013.
- Maclean, J.; Hardy, B.; Hettel, G. Rice Almanac, 4th ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Banos, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.H.; Yoon, C.G.; Jung, K.W.; Jang, J.H. HSPF-Paddy simulation of water flow and quality for the Saemangeum watershed in Korea. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.; Song, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, K.; Jang, J.R.; Kang, M.S. Long-term evaluation of the BMPs scenarios in reducing nutrient surface loads from paddy rice cultivation in Korea using the CREAMS-PADDY model. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawara, O.; Hirayma, K.; Kunimatsu, T. A study on pollutant loads from the forest and rice paddy fields. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, Y. Potential pollution and recommended critical levels of phosphorus in paddy soils of the southern Lake Tai area, China. Geoderma 2003, 115, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Masumoto, T.; Matsui, H.; Kato, T.; Sato, Y. Prospects for multifuctionality of paddy rice cultivation in Japan and other countries in monsoon Asia. Paddy Water Environ. 2006, 4, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Hannaway, D.; Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, L. A rice growth and productivity model. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2009, 57, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, A.; Soler, C.; Ali, H.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Anothai, J. Application of the CSM-CERES-Rice model for evaluation of plant density and nitrogen management of fine transplanted rice for an irrigated semiarid environment. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inao, K.; Watanabe, H.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Capri, E. Simulation models of pesticide fate and transport in paddy environment for ecological risk assessment and management. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2008, 42, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, N.; Lamers, M.; Nguyen, V.V.; Streck, T. Modeling the fate of pesticides in paddy rice-fish pond farming systems in northern VieQNam. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Spurlock, F.; Gill, S.; Goh, K.S. Modeling complexity in simulating pesticide fate in a rice paddies. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 53, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inao, K.; Hojyo, T.; Annoh, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Saito, T.; Parka, H.D. Predicting the behavior of paddy pesticides in a river basin using a simulation model (PADDY-Large): Application to a tributary of the Chikuma River under rice cultivation. Pestic. Sci. 2011, 36, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, R.; Kato, T.; Jeong, J. SWAT model improvement for discharge process in rice paddies. In Proceedings of the PAWEES-INWEPF Joint International Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Izaurralde, R.C. The APEX Model; BRC Report No. 2005-02; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Texas Agricultural Extension Service, Texas A&M University: Temple, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, D.K.; Yagow, G.; Saleh, A.; Barnes, P.L.; Rosenthal, W.; Krug, E.C.; Hauck, L.M. Sediment and nutrient modeling for TMDL development and implementation. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 967–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Roh, K.A.; Lee, N.J.; Seo, M.C.; Koh, M.H. Nutrient load balance in large-scale paddy fields during rice cultivation. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2005, 38, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.Y.; Seo, M.C.; Kim, M.K. Linking hydro-meteorological factors to the assessment of nutrient loadings to streams from large-plotted paddy rice fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Izaurralde, R.C. The APEX model. In Watershed Models; Singh, V.P., Frevert, D.K., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 437–482. [Google Scholar]
- Rural Development Administration (RDA). Crop Test Report; Rural Development Adiministration: Wanju-gun, Korea, 2002; p. 11.
- Mockus, V. National Engineering Handbook Section 4, Hydrology; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses, a Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Deptment Agriculture, U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Vu, S.H.; Watanabe, H.; Takagi, K. Application of FAO-56 for evaluating evapotranspiration in simulation of pollutant runoff from paddy rice field in Japan. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stockle, C.O.; Williams, J.R.; Rosenberg, N.J.; Jones, C.A. A method for estimating the direct and climate effects of rising atmospheric carbon dioxide on growth and yield of crops: Part I-Modification of the EPIC model for climate change analysis. Agric. Syst. 1992, 38, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, A.; Eguchi, S.; Kato, T.; Kasuya, M.; Ono, K.; Miyata, A.; Tase, N. Development and evaluation of a paddy module for improving hydrological simulation in SWAT. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 137, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.E.; Burman, R.D.; Allen, R.G. Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Water Requirements; ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practice No. 70; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Steglich, E.M. Agricultural Policy/Environmental Extender Model: Theoretical Documentation Version 0806; BRC Report No. 2008-17; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Texas Agricultural Extension Service, Texas A&M University: Temple, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models; part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, N.; Kamewada, K.; Iwasaki, S. Quality changes of agricultural water passing through paddy fields. Bull. Tochigi Prefect. Agric. Exp. Stn. 2005, 55, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Somura, H.; Takeda, I.; Mori, Y. Influence of puddling procedures on the quality of rice paddy drainage water. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute Technical Report No. 406; Texas Water Resources Institute, Texas A&M University: Temple, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tolson, B.A.; Shoemaker, C.A. Dynamically dimensioned search algorithm for computationally efficient watershed model calibration. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W01413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Park, S.W. Development and application of total maximum daily loads simulation system using nonpoint source pollution model. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 36, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Hauck, L.M.; Dugas, W.A. Application of a watershed model to evaluate management effects on point and nonpoint source polution. Trans. ASAE 2001, 43, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steglich, E.M.; Williams, J.W. Agricultural Policy and Environmental Extender Model User’s Manual Version 0604; BRC Report No. 2008-16; Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, Texas Agricultural Extension Service, Texas A&M University: Temple, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jeong, J. APEX-CUTE 4 User Manual; Texas A&M AgriLife Research, Blackland Research and Extension Center, Texas A&M University: Temple, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Statstics Korea. Available online: http://www.kostat.go.kr/ (accessed on 12 February 2016).




| Date | Operation | Amounts |
|---|---|---|
| 1 May | Pesticide application | 30 kg/ha |
| 5 May | Fertilizer application | 61 kg N/ha, 42 kg P/ha |
| 5 May | Ploughing | 100 mm depth |
| 10 May | Irrigate | 100 mm ponding |
| 15 May | Puddling | 80 mm depth |
| 19 May | lower water depth | 25 mm ponding |
| 20 May | Transplanting | 125 stalks/ha |
| 20 May | Irrigate | 60 mm ponding |
| 30 May | Pesticide application | 30 kg/ha |
| 10 June | Fertilizer application | 24.2 kg N/ha |
| 20 July | Stop irrigation and drain water | |
| 25 July | Fertilizer application | 12.1 kg N/ha |
| 1 August | Irrigate | 80 mm ponding |
| 20 September | Stop irrigation and drain water | |
| 30 September | Harvest |
| Measure | Output Response | Performance Evaluation Criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very Good | Good | Satisfactory | Not Satisfactory | ||
| R2 | Flow a | R2 > 0.85 | 0.75 < R2 ≤ 0.85 | 0.60 < R2 ≤ 0.75 | R2 ≤ 0.60 |
| N | R2 > 0.80 | 0.60 < R2 ≤ 0.70 | 0.30 < R2 ≤ 0.60 | R2 ≤ 0.30 | |
| NSE | Flow | NSE > 0.80 | 0.70 < NSE ≤ 0.80 | 0.50 < NSE ≤ 0.70 | NSE ≤ 0.50 |
| N/P | NSE > 0.65 | 0.50 < NSE ≤ 0.65 | 0.35 < NSE ≤ 0.50 | NSE ≤ 0.35 | |
| PBIAS | Flow | PBIAS ≥ ±5 | ±5 > PBIAS ≥ ±10 | ±10 > PBIAS ≥ ±15 | PBIAS ≥ ±15 |
| N/P | PBIAS ≥ ±10 | ±10 > PBIAS ≥ ±20 | ±20 > PBIAS ≥ ±30 | PBIAS ≥ ±30 | |
| Parameters | Description | For Upland Rice | For Paddy Rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLAP1 | First point on optimal leaf area development curve. | 30.01 | 28.01 |
| DLAP2 | Second point on optimal leaf area development curve. | 70.95 | 51.95 |
| RWPC1 | Fraction of root weight at emergence. | 0.40 | 0.47 |
| RWPC2 | Fraction of root weight at maturity. | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| PPLP1 | Plant Population for Crops & Grass—1st Point on curve. | 125.60 | 65.30 |
| PPLP2 | Plant Population for Crops & Grass—2nd Point on curve. | 250.95 | 130.95 |
| Item | Location | Period | No. of Measure (Day) | Rainfall (mm) | Irrigation (mm) | Discharge (mm) | R2 | NSE | PBIAS (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs. | Sim. | |||||||||
| APEX1501 | ||||||||||
| Calibration | Icheon | 2002 | 127 | 882.0 | 1291.8 | 670.4 | 1222.0 | 0.57 | −1.91 (not satisfactory) | −80.9 (not satisfactory) |
| APEX-PADDY | ||||||||||
| Calibration | Icheon | 2002 | 127 | 882.0 | 1291.8 | 670.4 | 733.8 | 0.88 (very good) | 0.87 (very good) | −14.6 (satisfactory) |
| Validation | Icheon | 2003 | 86 | 984.7 | 893.1 | 539.4 | 526.4 | 0.80 (good) | 0.65 (satisfactory) | 9.6 (good) |
| Gimje | 2014 | 156 | 737.8 | 887.0 | 606.8 | 568.8 | 0.77 (good) | 0.70 (good) | 10.8 (satisfactory) | |
| Class | Year | #Measures | Total Load a (kg/ha) | Peak Load (kg/ha) | R2 | NSE | PBIAS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APEX1501 | 2002 | 39 | 2.68 | 1.21 | 0.02 | −14.4 | −52.9 |
| APEX-Paddy | 2002 | 39 | 1.39 | 0.18 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 2.1 |
| 2003 | 27 | 1.17 | 0.22 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 4.5 | |
| Observed | 2002 | 39 | 1.76 | 0.24 | |||
| 2003 | 27 | 1.31 | 0.30 |
| Location | Observed Rice Yield (ton/ha) | Estimated Rice Yield (ton/ha) | PBIAS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | St. Dev. | Average | St. Dev. | ||
| Icheon | 6.53 | 0.32 | 6.27 | 0.43 | 4.02% |
| Gimje | 7.19 | 0.34 | 7.13 | 0.60 | 0.75% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.-K.; Jeong, J.; Kim, M.-K. Simulating the Effects of Agricultural Management on Water Quality Dynamics in Rice Paddies for Sustainable Rice Production—Model Development and Validation. Water 2017, 9, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110869
Choi S-K, Jeong J, Kim M-K. Simulating the Effects of Agricultural Management on Water Quality Dynamics in Rice Paddies for Sustainable Rice Production—Model Development and Validation. Water. 2017; 9(11):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110869
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Soon-Kun, Jaehak Jeong, and Min-Kyeong Kim. 2017. "Simulating the Effects of Agricultural Management on Water Quality Dynamics in Rice Paddies for Sustainable Rice Production—Model Development and Validation" Water 9, no. 11: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110869
APA StyleChoi, S.-K., Jeong, J., & Kim, M.-K. (2017). Simulating the Effects of Agricultural Management on Water Quality Dynamics in Rice Paddies for Sustainable Rice Production—Model Development and Validation. Water, 9(11), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9110869






