Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
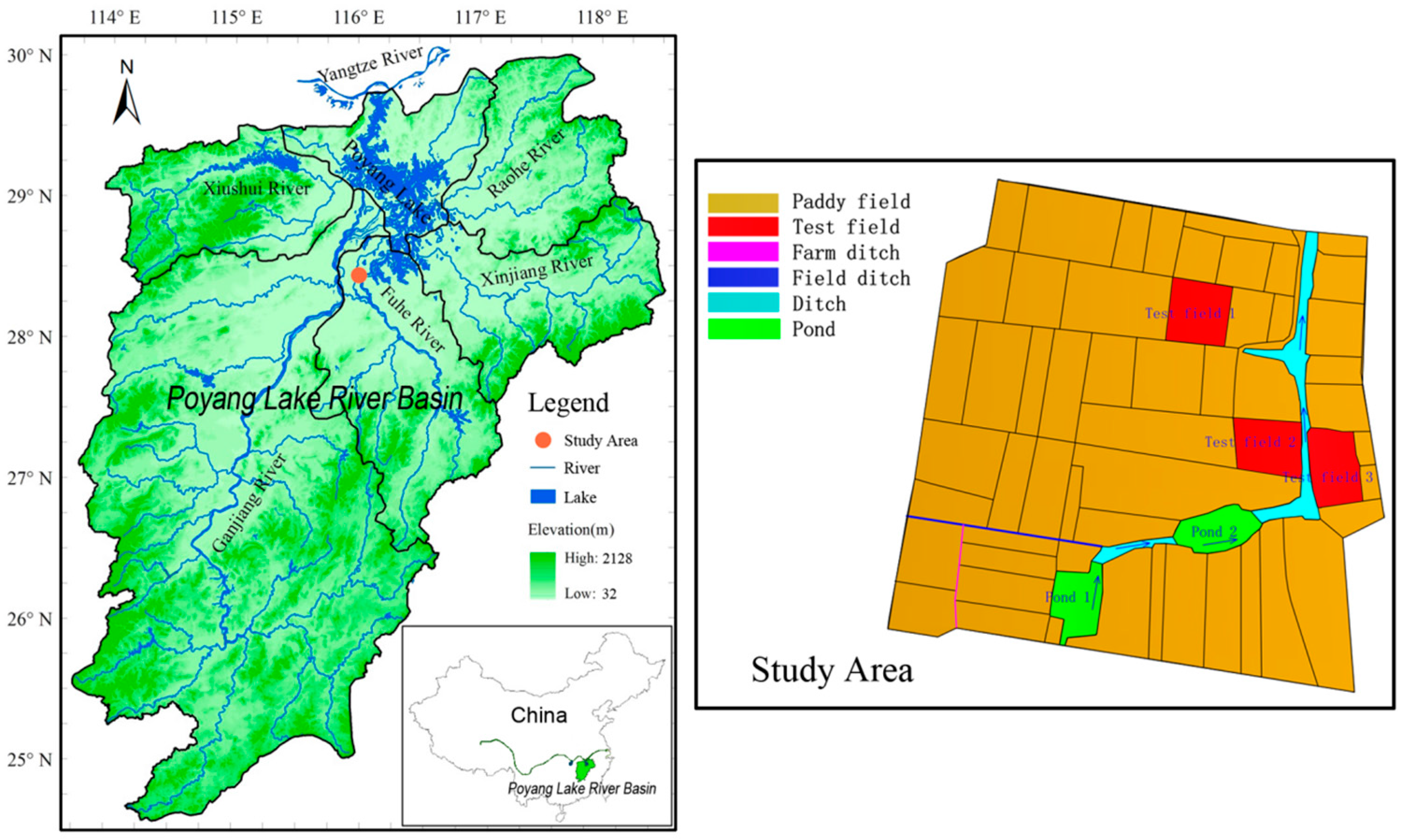
2.1. Study area Overview
2.2. Construction of Purification Technology
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Water-Fertilizer Comprehensive Regulation Technique in Rice Paddies
2.3.2. Ecological Restoration by Eco-Channel–Pond–Wetland System
2.4. Measured Variables and Methods
2.4.1. Measured Variables
2.4.2. Formulas
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect on Water Conservation
3.2. Effect on Yield
3.3. Effect on Pollutant Reduction
3.3.1. Effect of Efficient Use of Water and Fertilizers on Pollutant Reduction
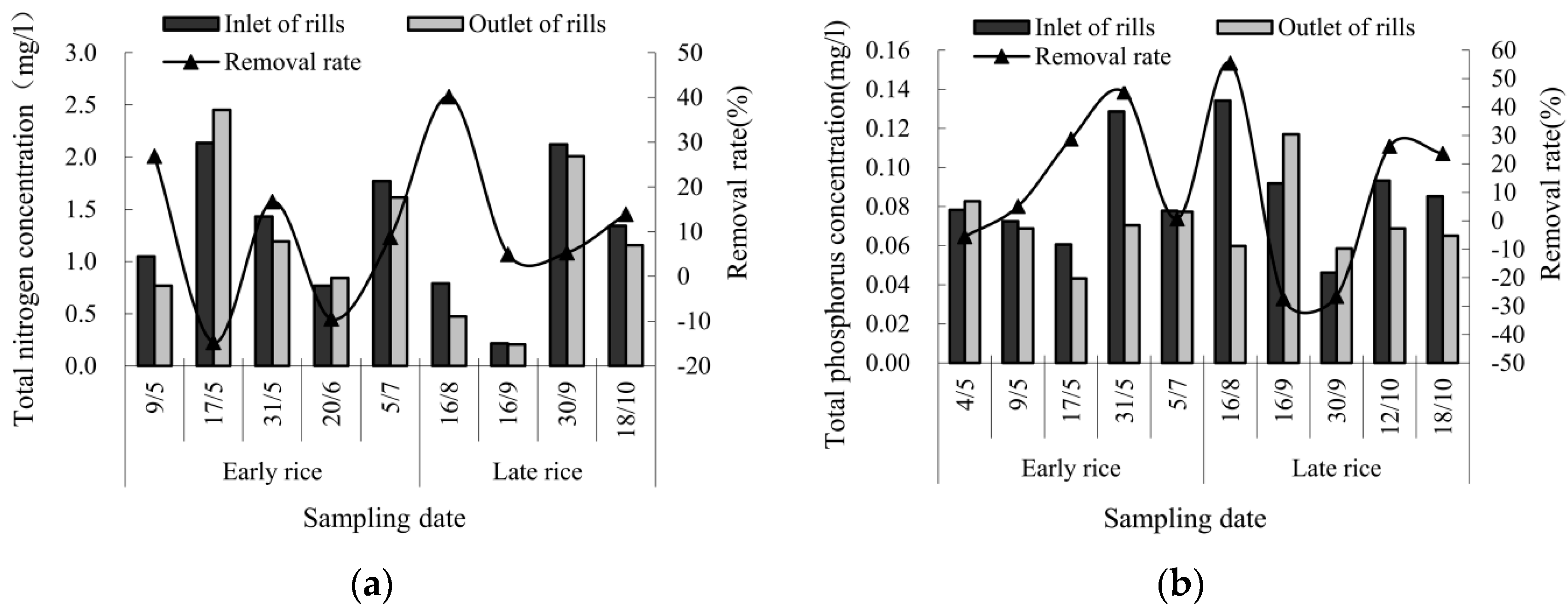
3.3.2. Effect of Eco-Channels on Pollutant Reduction
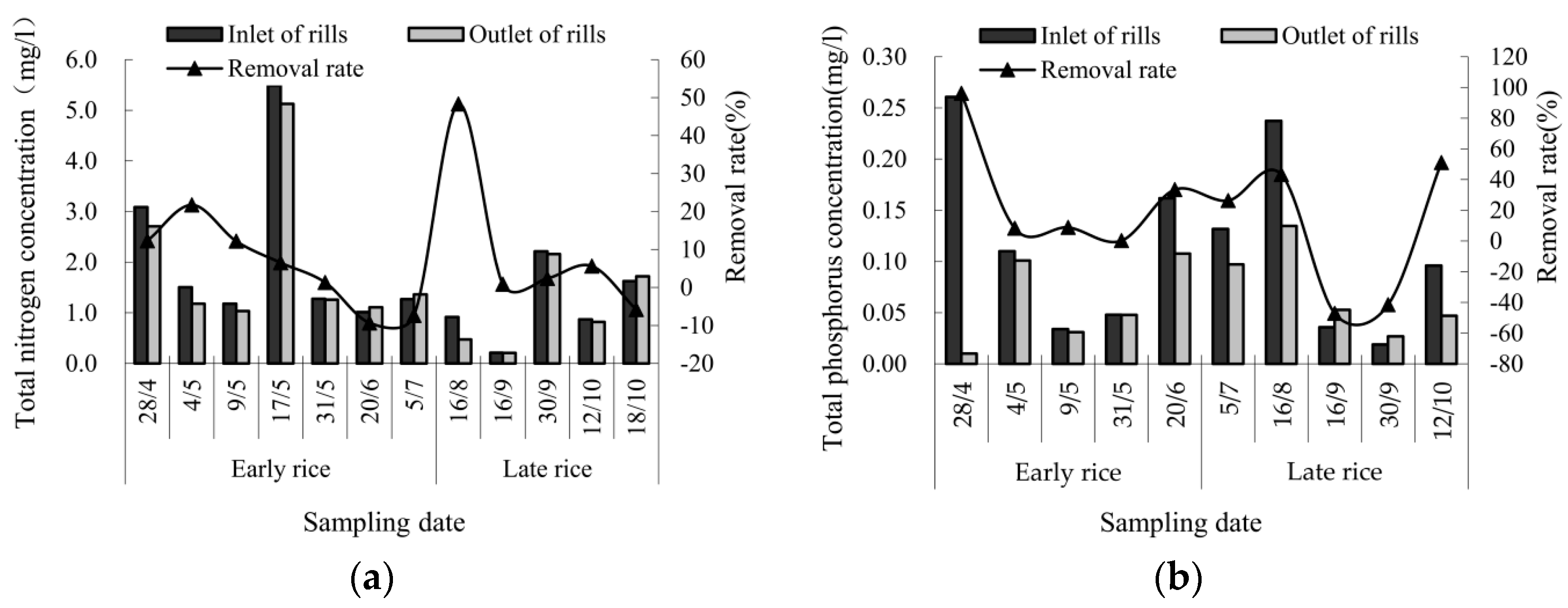
3.3.3. Effect of Pond Wetlands on Pollutant Reduction
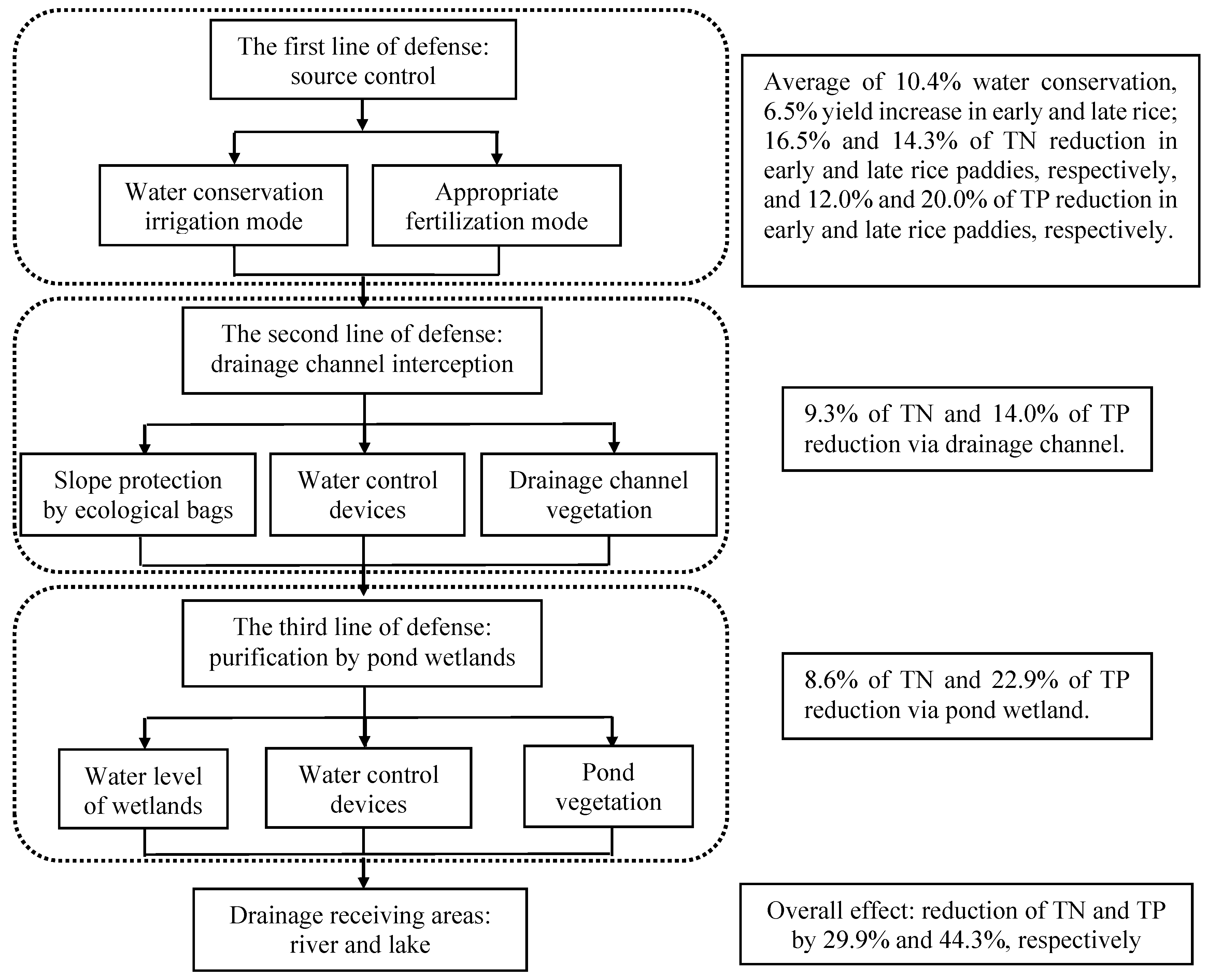
3.4. Comprehensive Effects of the Poyang Lake Basin Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Ecological Restoration Integrated Technique
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, H.J.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhong, J.Y.; Lou, Q.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y.Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xu, H.X.; Jiang, X.Y. Denitrification occurring on suspended sediment in a large, shallow, subtropical lake (Poyang Lake, China). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jin, S.G.; Tenzer, R.; Feng, J.L. Water storage variations in the Poyang Lake Basin estimated from GRACE and satellite altimetry. Geodesy Geodyn. 2016, 7, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Zhen, L.; Miah, M.G. Comparison of the ecosystem services provided by China’s Poyang Lake wetland and Bangladesh’s Tanguar Haor wetland. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, L.; Li, F.; Huang, H.Q.; Dilly, O.; Liu, J.Y.; Wei, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Cao, X.C. Household’s willingness to reduce pollution threats in the Poyang Lake region, southern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 110, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.X.; Fu, Y.C.; Ruan, B.Q.; Ge, H.F.; Zhao, N.N. Agricultural non-point source pollution in the Yongding River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ji, X.T.; Ouyang, W.; Zhao, X.C.; Lai, X.H. Dilemma analysis of China agricultural non-point source pollution based on peasants’ household surveys. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Z.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, Q.H.; Wu, H.Y. Study of landscape patterns of variation and optimization based on non-point source pollution control in an estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.B.; Su, B.L.; Li, R.R.; Yang, W.Z.; Shen, M.M. A field-scale observation method for non-point source pollution of paddy fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Liu, J.Z.; Shen, R.F.; Fu, B.J. Mitigation of nonpoint source pollution in rural areas: From control to synergies of multi ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissman, A.R.; Carpenter, S.R. Progress on nonpoint pollution: Barriers & opportunities. Daedalus 2015, 144, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ribaudo, M.O.; Heimlich, R.; Claassen, R.; Peter, M. Least-cost management of nonpoint source pollution: Source reduction versus interception strategies for controlling nitrogen loss in the Mississippi Basin. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 37, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, L.X.; Yang, L.Z.; Zhang, F.S.; Norse, D.; Zhu, Z.L. Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: Causes and mitigation measures. Ambio 2012, 41, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Yang, L.Z. Strategies for controlling agricultural non-point source pollution: Reduce-retain-restoration (3R) theory and its practice. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.Z.; Liu, G.H.; Ma, L.; Yang, L.Z.; Li, Y.D. The effects of contour hedges and reduced tillage with ridge furrow cultivation on nitrogen and phosphorus losses from sloping arable land. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Z.; Feng, Y.F.; Shi, W.M.; Xue, L.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Song, X.F.; Chang, Z.Z. Review of the advances and development trends in agricultural non-point source pollution control in China. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric. 2013, 21, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Grismer, M.E.; O’Geen, A.T.; Lewis, D. Vegetative Filter Strips for Nonpoint Source Pollution Control in Agriculture; Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of California: Oakland, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Tang, X.Q.; Li, Q.Y.; Yang, W.J.; Jin, F.; Tang, M.Z.; Scholz, M. Review of ecological engineering solutions for rural non-point source water pollution control in Hubei Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1561–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.J.; Peng, S.Z.; Luo, Y.F.; Xu, J.Z.; Yang, S.H. A paddy eco-ditch and wetland system to reduce non-point source pollution from rice-based production system while maintaning water use efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Z.; Wang, F.W.; Liu, W.; Tang, C.L.; Wu, C.X.; Wu, Y.H. Nutrient removal by up-scaling a hybrid floating treatment bed (HFTB) using plant and periphyton: From laboratory tank to polluted river. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audet, J.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Andersen, P.M.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Johansen, J.R.; Larsen, S.E.; Kjaergaard, C.; Elsgaard, L. Nitrous oxide fluxes in undisturbed riparian wetlands located in agricultrual catchments: Emission, uptake and controlling factors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Hu, Z.L.; Yang, L.Z.; Graham, B.; Kerr, P.G. The removal of nutrients from non-point source wastewater by a hybrid bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, N.; Ruan, X.H.; Xu, J.; Pan, Z.R. Estimating the optimal width of buffer strip for nonpoint source pollution control in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Ecol. Model. 2014, 276, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzon, I.; Helenius, J. Agricultural drainage ditches, their biological importance and functioning. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xiao, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Luo, Q.; Wu, J.S. Effect of novel constructed drainage ditch on the phosphorus sorption capacity of ditch soils in an agricultural headwater catchment in subtropical central China. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, R.; Moore, M.T.; Farris, J.L.; Gopalan, M. Evidence for the use of low-grade weirs in drainage ditches to improve nutrient reductions from agriculture. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 221, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for Irrigation Experiment SL13-2015; Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method HJ 636-2012; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method GB/T 11893-1989; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989. (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen-Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry HJ 535-2009; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009. (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water Quality-Determination of Nitrate-Nitrogen-Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry HJ/T 346-2007; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Dai, J.F.; Cui, Y.L.; Cai, X.L.; Brown, L.C.; Shang, Y.H. Influence of water management on the water cycle in a small watershed irrigation system based on a distribution hydrologic model. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhong, X.H.; Lampayan, R.M.; Singleton, G.R.; Huang, N.R.; Liang, K.M.; Peng, B.L.; Tian, K. Grain yield, water productivity and nitrogen use efficiency of rice under different water management and fertilizer-N inputs in South China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 184, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.H.; Hayashi, K.; Agbisit, R.; Villegas-Pangga, G. Evaluation of fertilizer and water management effect on rice performance and greenhouse gas intensity in different seasonal weather of tropical climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, J.H.; Walker, T.W.; Anders, M.M.; Smith, M.C.; Avila, L.A. Farmer adaptation of intermittent flooding using multiple-inlet rice irrigation in Mississippi. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, L.F.D.; Mezzomo, R.F.; Avila, L.A.; Massey, J.H.; Marchesan, E.; Zanella, R.; Peixoto, S.C.; Refatti, J.P.; Cassol, G.V.; Marques, M. Imazethapyr and imazapic runoff under continuous and intermittent irrigation of paddy rice. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.N.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. Nitrogen removal in an ecological ditch receiving agricultural drainage in subtropical central China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumwimba, M.N.; Zhu, B.; Suanon, F.; Muyembe, D.K.; Dzakpasu, M. Long-term impact of primary domestic sewage on metal/loid accumulation in drainage ditch sediments, plants, and water: Implications for phytoremediation and restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, J.F.; Martin, J.F.; Granata, T.; Bouchard, V.; Quigley, M.; Brown, L. Effects of wetland depth and flow rate on residence time distribution characteristics. Ecol. Eng. 2004, 23, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Q.; Cui, Y.L.; Dong, B.; Luo, Y.F.; Liu, F.P.; Zhao, S.J.; Wu, H.R. Test study of the optimal design for hydraulic performance and treatment performance of free water surface flow constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.Q.; Cui, Y.L.; Dong, B.; Liu, F.P. Test study of the hydraulic performance of constructed wetlands planted with three different aquatic plant species. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizio, B.; Davide, T. Five year water and nitrogen balance for a constructed surface flow wetland treating agricultural drainage waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 3, 56–78. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Mateos, D.; Pedrocchi, C.; Comin, F.A. Effects of wetland construction on water quality in a semi-arid catchment degraded by intensive agricultural use. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Mao, Z.; Dong, B.; Gao, X.R. Experimental research on reduction of agricultural non-point source pollution using pond wetland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 130–135, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.W.; Mao, Z. Construction and effect of water-saving and pollution prevention irrigation system. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 137–145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Irrigation Method | Rice Season | Re-Greening Stage | Early Tillering Stage | Late Tillering Stage | Jointing–Booting Stage | Heading and Flowering Stage | Milky Stage | Yellow Ripening Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flooding irrigation | Early rice | 0-20-40 | 0-20-50 | 0-20-50 Late paddy sunning | 0-20-50 | 0-20-50 | 0-20-50 | 0-30 Late drying |
| Late rice | 0-20-40 | 0-20-50 | 0-20-50 Late paddy sunning | 0-20-50 | 0-20-50 | 0-20-50 | 0-30 Late drying | |
| Intermittent irrigation | Early rice | 0-20-30 Drying for 4 days | 0-20-50 Drying for 4 days | 0-20-50 Late paddy sunning | 0-20-50 Drying for 4 days | 0-20-50 Drying for 4 days | 0-20-50 Drying for 4 days | 0-20-30 Late drying |
| Late rice | 0-20-40 Drying for 3 days | 0-20-50 Drying for 3 days | 0-20-50 Late paddy sunning | 0-20-50 Drying for 3 days | 0-20-50 Drying for 3 days | 0-20-50 Drying for 3 days | 0-20-30 Late drying |
| Rice Season | Treatment | Rainfall/ m3·ha−1 | Displacement/ m3·ha−1 | Rainfall Utilization Rate/% | Irrigation Amount/ m3·ha−1 | Yield/ kg·ha−1 | Irrigation Water Use Efficiency/ kg·m−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early rice | W1F2 | 4266.21 | 2560.13 | 40.0 | 1994.88 | 7756.01 | 4.03 |
| W0F1 | 4266.21 | 3022.15 | 29.2 | 2243.06 | 7354.39 | 3.37 | |
| Late rice | W1F2 | 1196.06 | 85.00 | 92.9 | 3891.40 | 8442.78 | 2.15 |
| W0F1 | 1196.06 | 114.01 | 90.5 | 4327.49 | 7938.40 | 1.81 | |
| Total | W1F2 | 5462.27 | 2645.13 | 51.6 | 5886.28 | 16,390.38 | 2.78 |
| W0F1 | 5462.27 | 3136.16 | 42.6 | 6570.55 | 15,386.22 | 2.34 |
| Rice Season | Treatment | Ear Length/cm | Effective Panicle/ 104·ha−1 | Total Grains | Seed Setting Rate/% | 1000-Grain Weight/g | Yield/kg·ha−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early rice | W1F2 | 20.65aA | 234.59aA | 150.84aA | 86.97aA | 28.73aA | 8042.13aA |
| W0F1 | 20.07aA | 226.82bA | 145.66bB | 84.70bB | 28.25bB | 7567.62bB | |
| Late rice | W1F2 | 20.44aA | 345.23aA | 127.73aA | 92.43aA | 23.34aA | 8348.25aA |
| W0F1 | 20.15bA | 340.12bA | 122.42bB | 89.43bB | 22.67bB | 7818.60bB | |
| Average | W1F2 | 20.55aA | 289.91aA | 139.29aA | 89.70aA | 26.04aA | 8195.19aA |
| W0F1 | 20.11bA | 283.47bA | 134.04bB | 87.07bB | 25.46bB | 7693.11bB |
| Rice Season | Treatment | Nitrogen/kg·ha−1 | Phosphorus/kg·ha−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia Nitrogen (NH4+-N) | Nitrate Nitrogen (NO3−-N) | Total Nitrogen (TN) | Total Phosphorus (TP) | ||
| Early rice | W1F2 | 4.66bB | 0.25bB | 5.27bB | 0.22bA |
| W0F1 | 5.62aA | 0.29aA | 6.31aA | 0.25aA | |
| Late rice | W1F2 | 0.04bB | 0.011bA | 0.06bB | 0.004bA |
| W0F1 | 0.05aA | 0.012aA | 0.07aA | 0.005aA | |
| Nutrient Elements | Location | Collection Date of Water Sample | Average Removal Rate/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 April | 4 May | 9 May | 17 May | 31 May | 20 June | 3 July | 5 July | |||
| TN/mg·L−1 | Inlet of Wetland 1 | 3.07 | 1.50 | 1.14 | 5.14 | 1.36 | 1.02 | 1.05 | 1.19 | 11.3 |
| Outlet of Wetland 1 | 2.71 | 1.17 | 1.09 | 4.48 | 1.29 | 0.76 | 1.07 | 1.06 | ||
| Inlet of Wetland 2 | 2.14 | 1.46 | 1.69 | 5.12 | 1.28 | 1.12 | 2.37 | 1.37 | 11.3 | |
| Outlet of Wetland 2 | 2.14 | 1.00 | 1.35 | 3.51 | 1.20 | 1.02 | 2.44 | 1.44 | ||
| TP/mg·L−1 | Inlet of Wetland 1 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 21.3 |
| Outlet of Wetland 1 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.11 | ||
| Inlet of Wetland 2 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.37 | 29.4 | |
| Outlet of Wetland 2 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.24 | ||
| Nutrient Elements | Location | Collection Date of Water Sample | Average Removal Rate/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 July | 25 July | 16 August | 26 September | 30 September | 12 October | 18 October | |||
| TN/mg·L−1 | Inlet of Wetland 1 | 4.14 | / | 0.96 | 0.22 | 2.18 | 0.89 | 1.89 | 5.6 |
| Outlet of Wetland 1 | 4.00 | / | 0.81 | 0.22 | 2.21 | 0.87 | 1.63 | ||
| Inlet of Wetland 2 | 4.34 | 4.86 | 0.69 | 0.22 | 2.18 | 0.83 | 1.73 | 6.1 | |
| Outlet of Wetland 2 | 4.21 | 4.25 | 0.67 | 0.22 | 2.08 | 0.77 | 1.52 | ||
| TP/mg·L−1 | Inlet of Wetland 1 | 0.26 | / | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 18.8 |
| Outlet of Wetland 1 | 0.21 | / | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.13 | ||
| Inlet of Wetland 2 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 22.3 | |
| Outlet of Wetland 2 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.10 | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, S.; Shi, H.; Pan, X.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Xie, H. Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China. Water 2017, 9, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100745
Cai S, Shi H, Pan X, Liu F, Cui Y, Xie H. Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China. Water. 2017; 9(10):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100745
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Shuo, Hong Shi, Xiaohua Pan, Fangping Liu, Yuanlai Cui, and Hengwang Xie. 2017. "Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China" Water 9, no. 10: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100745
APA StyleCai, S., Shi, H., Pan, X., Liu, F., Cui, Y., & Xie, H. (2017). Integrating Ecological Restoration of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Poyang Lake Basin in China. Water, 9(10), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100745




