Regional Climate Change Impacts on Irrigation Vulnerable Season Shifts in Agricultural Water Availability for South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection of Historical and Representative Concentration Pathway Climate Change Scenarios
2.3. Vulnerable Irrigation Season Modeling with Climate Change
2.4. Water Resources Balance Model for Reservoirs
2.5. Reservoir Operation Model
2.6. Irrigation Water Requirement Model
2.7. Elements of the Irrigation Vulnerability Assessment Model
2.8. Definition of the Vulnerable Seasons of Paddy Irrigation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Climate Change Variability
3.2. Analysis of Agricultural Water Supply and Demand Balance
3.3. Assessment of the Vulnerable Seasons of Paddy Irrigation
3.4. Shifts of Vulnerable Irrigation Seasons under Climate Change
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Working group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, P. Impact of climate change and variability on irrigation requirements: A global perspective. Clim. Chang. 2002, 54, 269–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Wisser, D.; Eisner, S.; Florke, M.; Gerten, D.; Haddeland, I.; Hanasaki, N.; Masaki, Y.; Portmann, F.T.; Stacke, T.; et al. Multimodel projections and uncertainties of irrigation water demand under climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4626–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumbelow, K.; Georgakakos, A. Consideration of climate variability and change in agricultural water resources planning. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2007, 133, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minville, M.; Brissette, F.; Leconte, R. Impacts and uncertainty of climate change on water resource management of the Peribonka river system (Canada). J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2010, 136, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S. Impact of climate change on irrigation water demand of dry season Boro rice in northwest Bangladesh. Clim. Chang. 2011, 105, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Ahmadi, B.; Zahmatkesh, Z. Developing an agricultural planning model in a watershed considering climate change impacts. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Q.; Huang, W.; Ho, C.H.; Li, R.; Tang, Z. Projected climate regime shift under future global warming from multi-model, multi-scenario CMIP5 simulations. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainuddin, M.; Kirby, M.; Chowdhury, R.A.R.; Shah-Newaz, S.M. Spatial and temporal variations of, and the impact of climate change on, the dry season crop irrigation requirements in Bangladesh. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, I.M.; Hengst, J.C.; Goll, A.; Hollermann, B.; Diekkruger, B. Future of water supply and demand in the middle Draa Valley, Morocco, under climate and land use change. Water 2016, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraniwar, S.D.; Smout, I.K. Multilevel approach for optimizing land and water resources and irrigation deliveries for tertiary units in large irrigation schemes. II: Application. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, I.; Miura, A.; Hitomi, T.; Hamada, K.; Shiratani, E. Runoff nitrogen from a large sized paddy field during a crop period. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, P.E.; Papamichail, D.M. Optimization model of an irrigation reservoir for water allocation and crop planning under various weather conditions. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, A.; Lopez-Fuster, P.; Fereres, E. Improving on-farm water management through an irrigation scheduling service. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Srivastava, D.K.; Arya, D.S. Improved planning model for canal scheduling of rotational irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Lei, X.; Cai, S.; Wang, X. Hedging rules for water supply reservoir based on the model of simulation and optimization. Water 2016, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, D.R.; Hutchinson, P.D. Modeling water demands of irrigation projects. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1983, 109, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.J.; Kumar, D.N. Evolving strategies for crop planning and operation of irrigation reservoir system using multi-objective differential evolution. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J. Estimating irrigation water demand using an improved method and optimizing reservoir operation for water supply and hydropower generation: A case study of the Xinfengjiang reservoir in southern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhong, P.A.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Optimal hedging rules for water supply reservoir operations under forecast uncertainty and conditional value-at-risk criterion. Water 2017, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, B.; Panda, S.N.; Mull, R. Simulation of water harvesting potential in rainfed ricelands using water balance model. Agric. Syst. 2001, 69, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraniwar, S.D.; Smout, I.K. Allocation of scarce water resources using deficit irrigation in rotational systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Tingsanchali, T. Optimization and simulation of reservoir operation with sediment evacuation: A case study of the Tarbela Dam, Pakistan. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 730–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi-Jalal, M.; Haddad, O.B.; Karney, B.W.; Marino, M.A. Reservoir operation in assigning optimal multi-crop irrigation areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Maeda, S.; Kawachi, T. Stochastic multiobjective optimization model for allocating irrigation water to paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2007, 5, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nys, E.; Le Gal, P.Y.; Raes, D.; Ana, E. WaDI (Water Delivery for Irrigation): A simulation tool to address strategic interaction of water demand and supply in irrigation schemes. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, L.D.; Webb, J.A.; Nathan, R.J.; Etchells, T.; Malano, H.M. Evaporation from water supply reservoirs: An assessment of uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, F.J.; Wilks, D.S.; Gurovich, L.; Bambach, N. Impacts of climate change on irrigated agriculture in the Maipo basin, Chile: Reliability of water rights and changes in the demand for irrigation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2012, 138, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahraman, B.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Optimal allocation of water from a single purpose reservoir to an irrigation project with pre-determined multiple cropping patterns. Irrig. Sci. 2002, 21, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.K.; Haden, V.R.; Joyce, B.A.; Purkey, D.R.; Jackson, L.E. Irrigation demand and supply, given projections of climate and land-use change, in Yolo County, California. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharian, E.; Burian, S.J.; Bardsley, T.; Strong, C. Incorporating potential severity into vulnerability assessment of water supply systems under climate change conditions. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04015051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Hong, E.M.; Choi, J.Y. Has climate change already affected the spatial distribution and temporal trends of reference evapotranspiration in South Korea? Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 150, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Choi, J.Y. Development of an irrigation vulnerability assessment model in agricultural reservoirs utilizing probability theory and reliability analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 142, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Nam, W.H.; Kim, J.T. Decision support system for the real-time operation and management of an agricultural water supply. Irrig. Drain. 2016, 65, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, C.; Garcia-Bolanos, M.; Mateos, L. Patterns of variability in large-scale irrigation schemes in Mauritania. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 112, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.D.; Lin, M.C.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, S.F.; Wen, T.H.; Hsieh, H.I. A spatial aggregation index for effective fallow decision in paddy irrigation demand planning. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.M.; Nam, W.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Projected irrigation requirements for upland crops using soil moisture model under climate change in South Korea. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Hoang, V.N.; Seo, B. Cost and environmental efficiency of rice farms in South Korea. Agric. Econ. 2012, 43, 367–376. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.; Jeong, C. Nonparametric statistical temporal downscaling of daily precipitation to hourly precipitation and implications for climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J.I.; Gibson, W.P.; Doggett, M.K.; Taylor, G.H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P.P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.A.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.K.; Cho, C.H.; Baek, H.J. Assessing changes in observed and future projected precipitation extremes in South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.B.; Jo, S.; Suh, M.S.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, D.K.; Hong, S.Y.; Min, S.K.; Park, S.C.; Kang, H.S.; Shim, K.M. Changes of precipitation extremes over South Korea projected by the 5 RCMs under RCP scenarios. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 52, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kite, G. Use of time series analysis to detect climatic change. J. Hydrol. 1989, 111, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudelsee, M. Climate time series analysis. In Classical Statistical and Bootstrap Methods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Hamer, W.; Love, D.; Owen, R.; Booij, M.J.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Potential water supply of a small reservoir and alluvial aquifer system in southern Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth 2008, 33, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukalla, A.D.; Haile, A.M.; Schultz, B. Optimum irrigation and pond operation to move away from exclusively rainfed agriculture: The Boru Dodota Spate Irrigation Scheme, Ethiopia. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H. Sustainability and Operations Evaluation of Agricultural Reservoirs Based on Probability Theory. Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University, Korea, 2013. (In Korean). [Google Scholar]
- Ashofteh, P.S.; Haddad, O.B.; Marino, M.A. Climate change impact on reservoir performance indexes in agricultural water supply. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.W.; Coles, N.A. An artificial catchment rainfall-runoff collecting system: Design efficiency and reliability potential considering climate change in Western Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 121, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, M. Automatic calibration of the tank model. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1979, 24, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Singh, V.P. Tank model using kalman filter. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Kang, M.S.; Song, I.; Jun, S.M. Water balance in irrigation reservoirs considering flood control and irrigation efficiency variation. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2016, 142, 04016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry (MAF). Design Standard of Agricultural Improvement Project: Irrigation; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Seoul, Korea, 1998. (In Korean)
- Veihmeyer, F.J. Evapotranspiration. In Handbook of Applied Hydrology; Chow, V.T., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, R.M. Timeliness of irrigation. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1995, 9, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oad, R.; Sampath, R.K. Performance measure for improving irrigation management. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1995, 9, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smout, I.K.; Goraniwar, S.D. Multilevel approach for optimizing land and water resources and irrigation deliveries for tertiary units in large irrigation schemes. I: Method. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldt, A.L.; Eisenhauer, D.E.; Martin, D.L.; Wilmes, G.J. Water conservation practices for a river valley irrigated with groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 38, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, C.S.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Knox, J.W.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A. Predicting the impacts of climate change—A case study of paddy irrigation water requirements in Sri Lanka. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 93, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, W.O. Guidelines for Predicting Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Paper No. 24; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Water Resources and Development Service: Rome, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.E.; Burman, R.D.; Allen, R.G. Evapotranspiration and irrigation water requirement. In ASCE Manual No. 70; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Doorenbos, J.; Kassam, A.H. Yield Response to Water; FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Paper No. 33; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Water Resources and Development Service: Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, T.; Tanji, K.K. Soil physical properties in relationship to drainage. In Physical and Chemical Processes of Soil Related to Paddy Drainage; Maruyama, T., Tanji, K.K., Eds.; Shinzansha Sci. & Tech.: Tokyo, Japan, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, G.A.; Kwon, H.J. Evaluation of paddy water storage dynamics during flood period in South Korea. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 2007, 11, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage, Paper No. 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Water Resources and Development Service: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Water Resources Cooperation. Dam Design Manual; Korea Water Recourses Cooperation: Taejeon, Korea, 2004. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.J. A spatial reasoning approach to estimating paddy rice water demand in Hwanghaenam-do, North Korea. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoo, S.H.; Engel, B.A. A real-time online drought broadcast system for monitoring soil moisture index. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 16, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.H.; Hayes, M.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Tadesse, T.; Wilhite, D.A. Drought hazard assessment in the context of climate change for South Korea. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
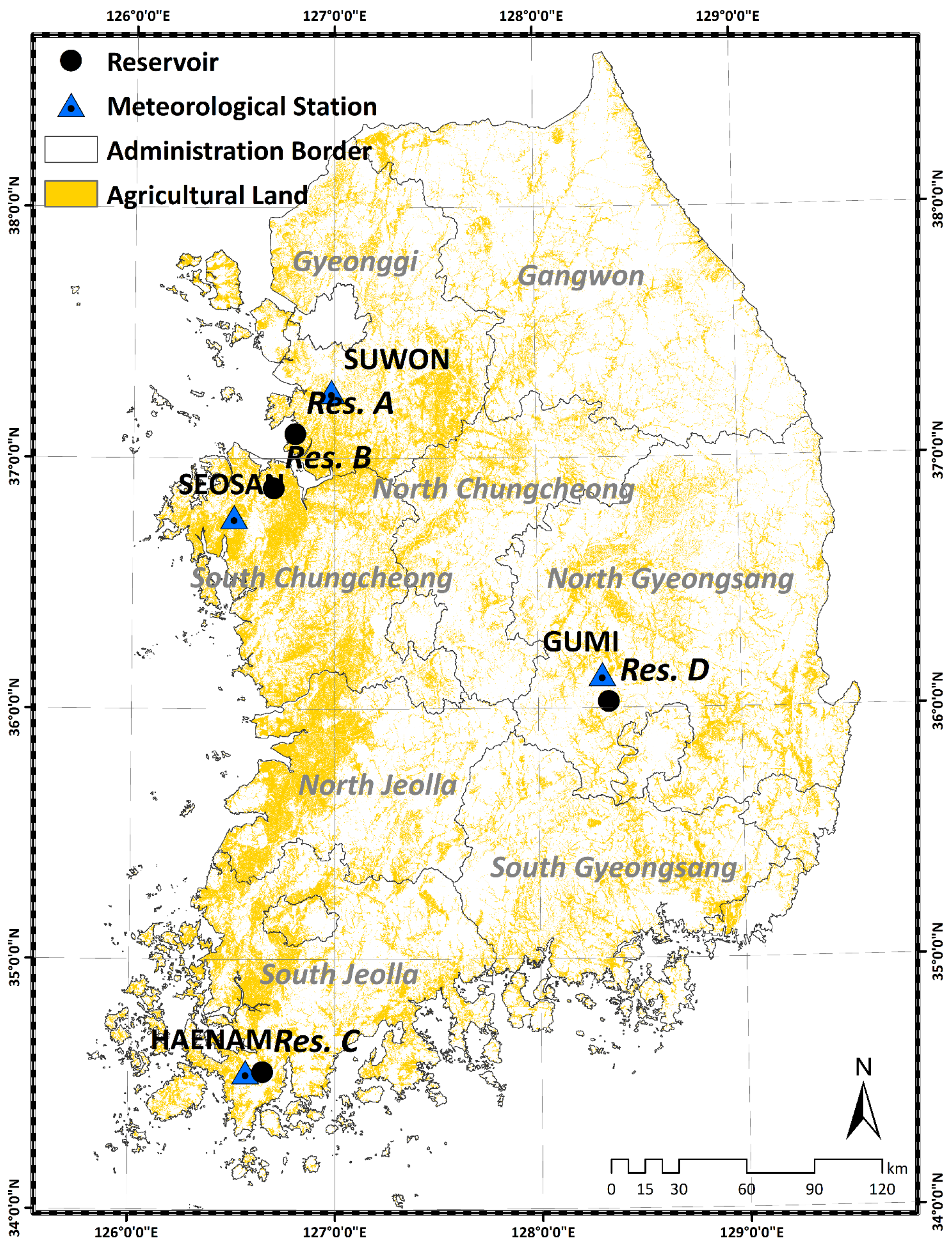
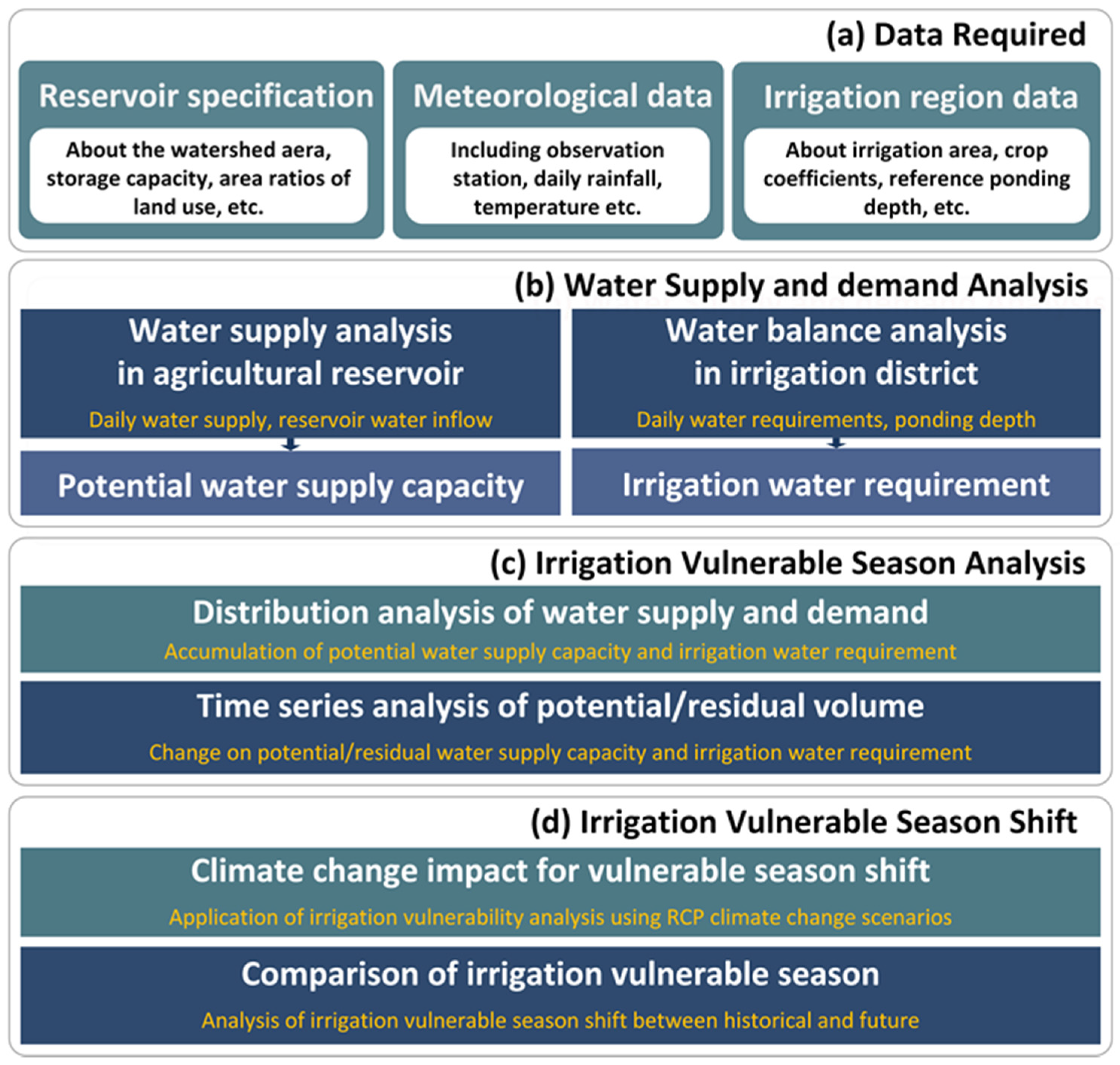
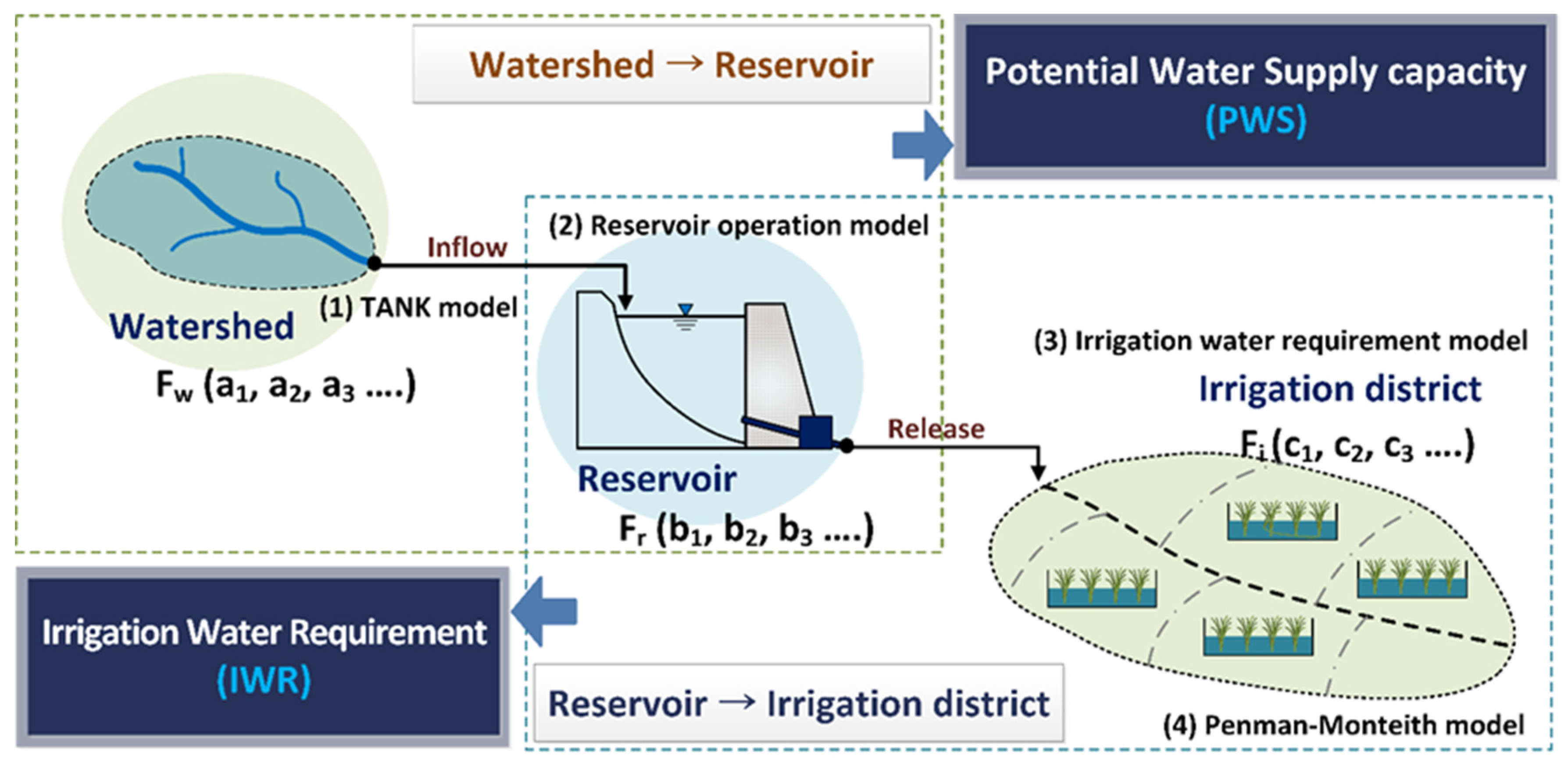
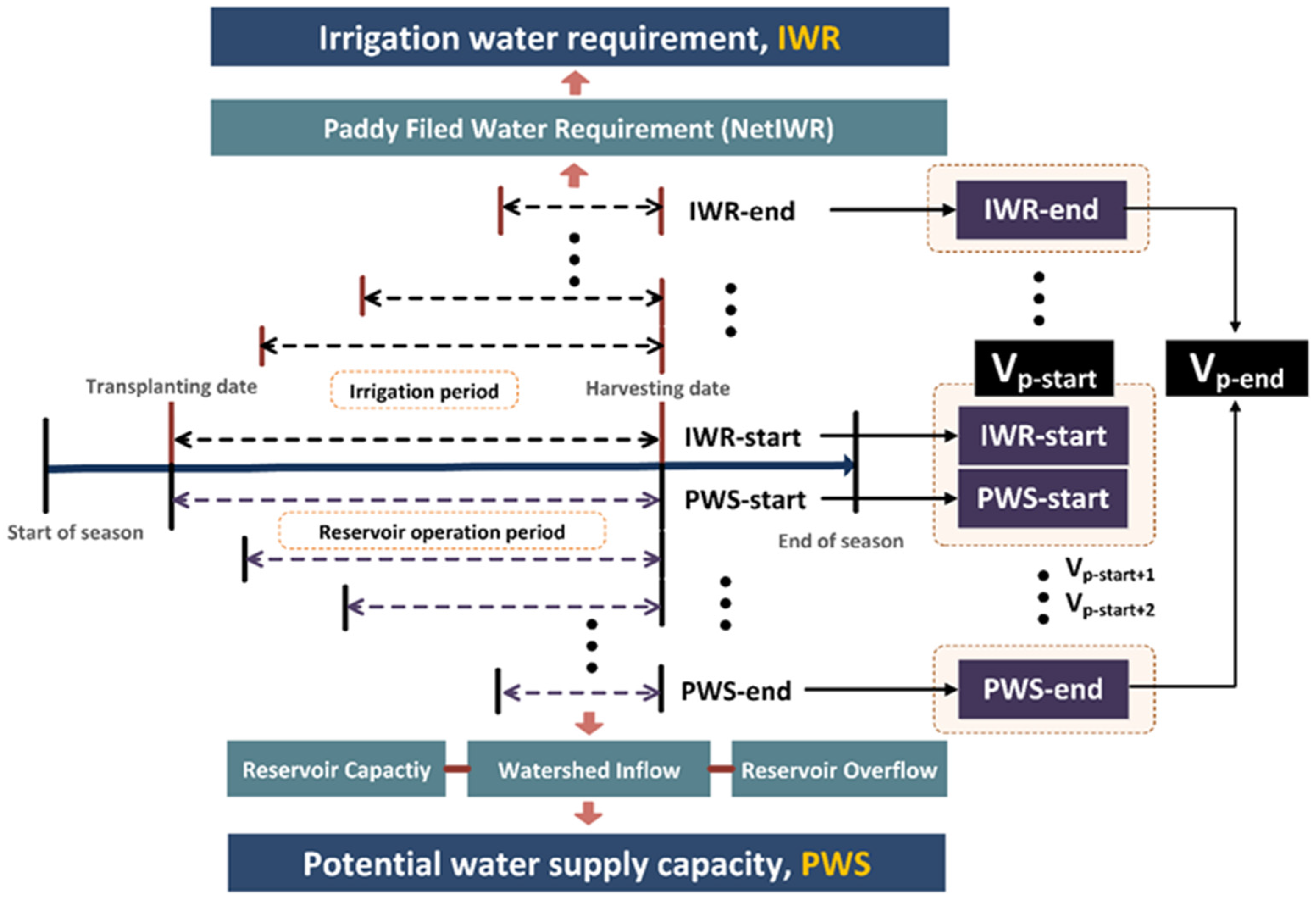

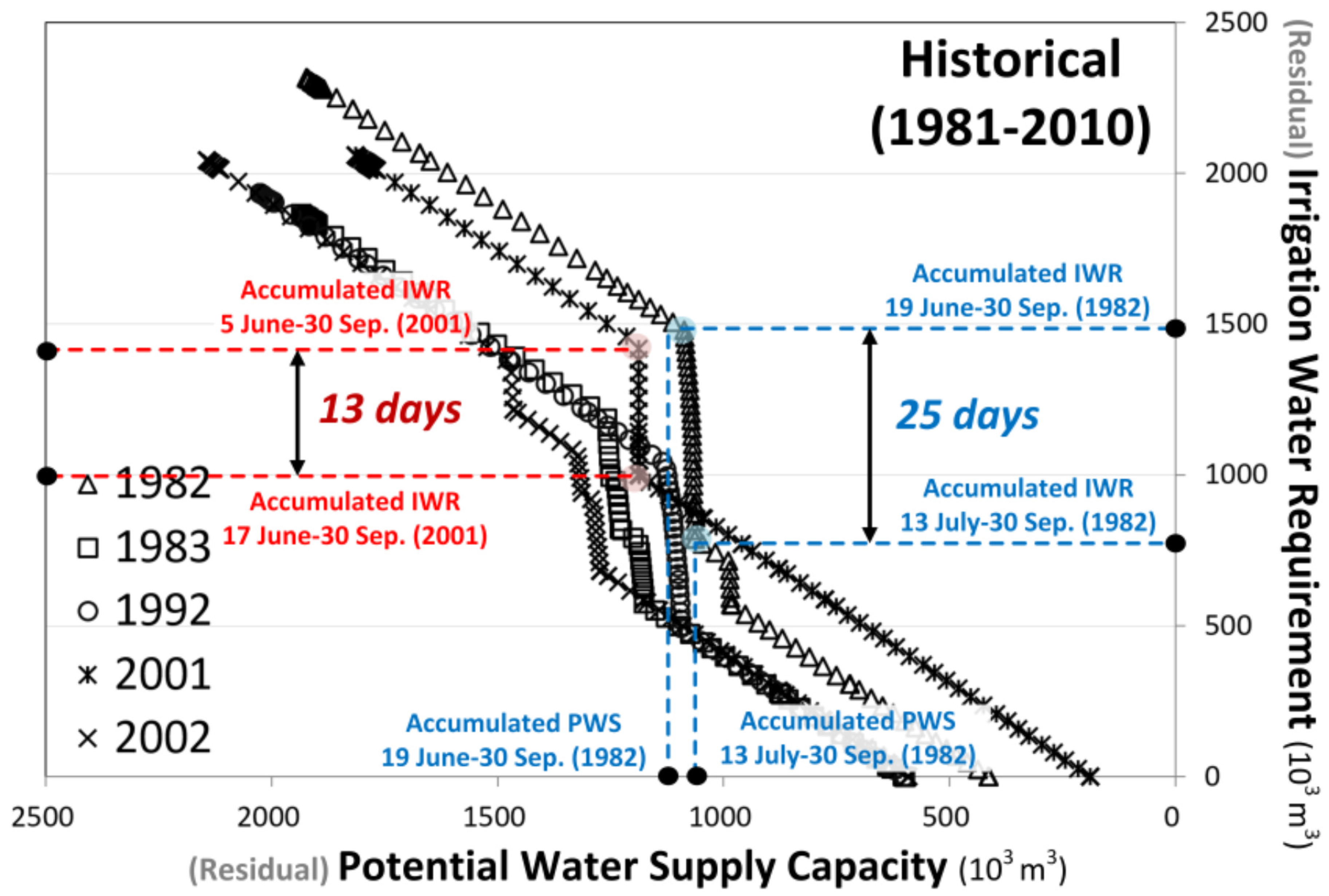
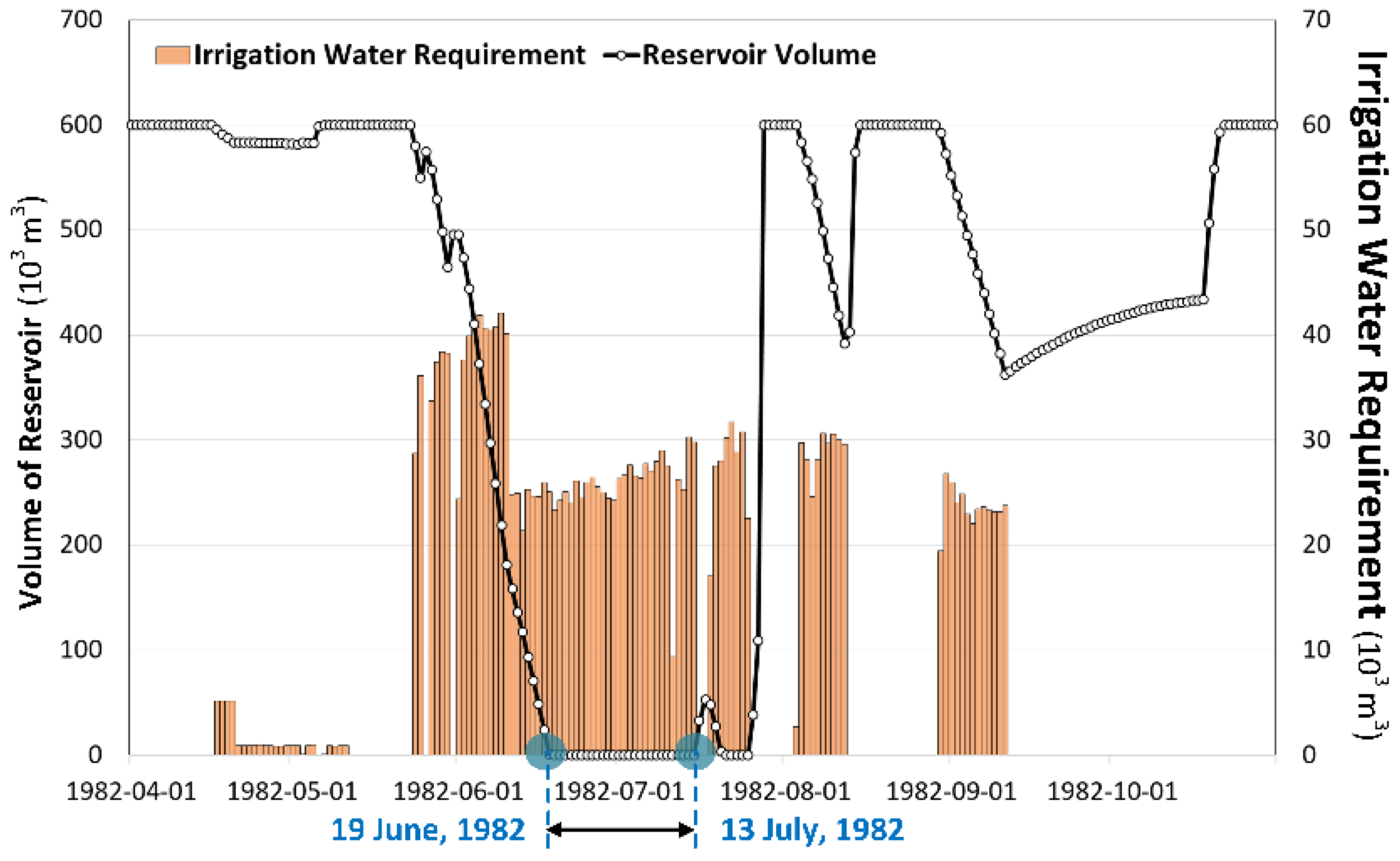
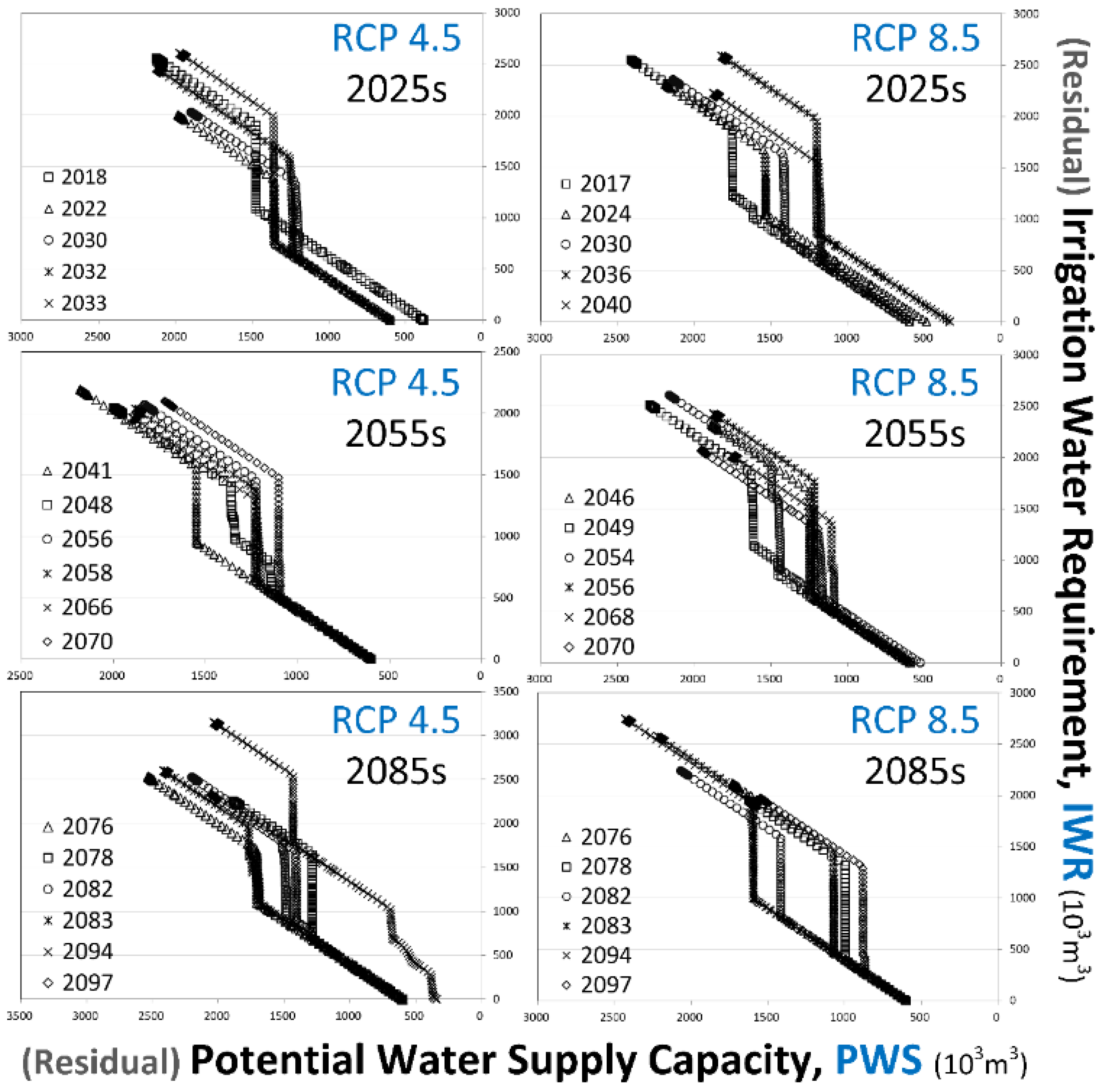
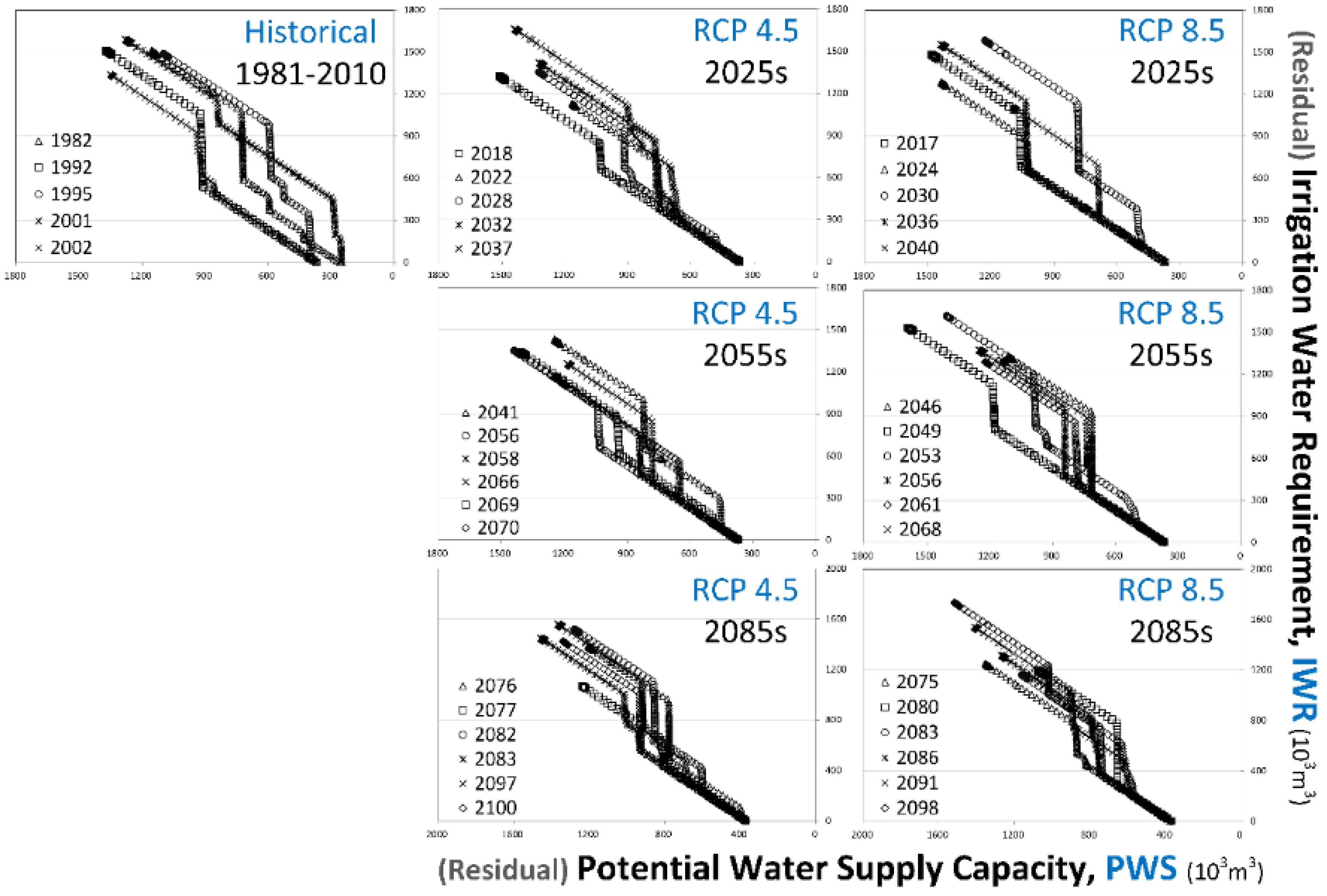

| Region | Meteorological Station | Reservoir Name | Symbol | Effective Storage Capacity (103 m3) | Watershed Area (ha) | Irrigated Area (ha) | Design Frequency of Drought (Year) | Construction Year (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central region | Suwon | Myeoku | Res. A | 600 | 830 | 246 | 5 | 1945 |
| Seosan | Songak | Res. B | 463 | 254 | 161 | 3 | 1958 | |
| Southern region | Haenam | Baekho | Res. C | 826 | 570 | 370 | 3 | 1958 |
| Gumi | Duman | Res. D | 369 | 470 | 149 | 3 | 1972 |
| Classification | Period | Source | Climate Model | Climate Data Items |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical | 1981–2010 | KMA (Korea Meteorological Administration) | Observed data | Daily maximum/minimum temperature, precipitation, solar radiation, relative humidity and sunshine duration |
| RCP 2025s | 2011–2040 | RCP scenarios (RCP 4.5 and 8.5, source of KMA) | HadGEM3-RA | |
| RCP 2055s | 2041–2070 | |||
| RCP 2085s | 2071–2100 |
| Date | 30 May | 1 June–20 June | 21 June–31 July | 1 August–10 August | 11 August–10 September | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth stages | Transplanting | Effective Tillering | Non-effective Tillering (Forced Drainage) | Head development | Heading | Grain filling and ripening |
| Ponding water depth (mm) | 30 | 30 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 30 |
| Slope of Potential Volume | Comparison of Elements | Irrigation State |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 45 degrees | PWS 1 > IWR 2 | Excessive irrigation |
| 45 degrees | PWS = IWR | Appropriate irrigation water supply |
| More than 45 degrees | PWS < IWR | Shortage of irrigation water supply or water-saving irrigation |
| Region | Meteorological Station | Factors | Historical (1981–2010) | RCP 4.5 Scenario | RCP 8.5 Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | ||||
| Central region | Suwon | PREC 1 | 1312 | 1576 | 1673 | 1849 | 1604 | 1806 | 1823 |
| TEMP 2 | 12.1 | 13.2 | 14.1 | 14.7 | 13.4 | 15.2 | 17.3 | ||
| Seosan | PREC | 1286 | 1516 | 1642 | 1734 | 1539 | 1652 | 1775 | |
| TEMP | 11.9 | 12.7 | 13.7 | 14.3 | 12.9 | 14.7 | 16.9 | ||
| Southern region | Haenam | PREC | 1325 | 1678 | 1774 | 1917 | 1619 | 1778 | 1942 |
| TEMP | 13.5 | 14.3 | 15.3 | 15.9 | 14.5 | 16.3 | 18.3 | ||
| Gumi | PREC | 1073 | 1394 | 1414 | 1486 | 1318 | 1478 | 1484 | |
| TEMP | 12.6 | 13.6 | 14.5 | 15.1 | 13.9 | 15.6 | 17.7 | ||
| Region | Reservoir Symbol | Factors | Historical (1981–2010) | RCP 4.5 Scenario | RCP 8.5 Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | ||||
| Central region | Res. A (Myeoku) | RI 1 | 6627 (1535) | 5107 (1626) | 7145 (1911) | 6176 (2112) | 5908 (1742) | 6317 (1645) | 6910 (1831) |
| RF 2 | 5084 (1649) | 3505 (1766) | 5718 (2027) | 4593 (2252) | 4431 (1838) | 4794 (1770) | 5348 (2046) | ||
| ETc 3 | 1469 (60) | 1579 (121) | 1531 (87) | 1606 (140) | 1539 (84) | 1643 (94) | 1709 (138) | ||
| ER 4 | 1559 (258) | 1331 (342) | 1570 (298) | 1429 (334) | 1361 (262) | 1368 (267) | 1427 (270) | ||
| Res. B (Songak) | RI | 1896 (574) | 1534 (463) | 2070 (546) | 1843 (701) | 1729 (494) | 1801 (463) | 1942 (489) | |
| RF | 900 (592) | 535 (473) | 1115 (572) | 868 (755) | 753 (469) | 822 (456) | 949 (545) | ||
| ETc | 942 (41) | 1004 (73) | 982 (62) | 1032 (87) | 974 (63) | 1039 (67) | 1087 (91) | ||
| ER | 971 (217) | 918 (214) | 1071 (197) | 993 (214) | 915 (180) | 922 (173) | 962 (164) | ||
| Southern region | Res. C (Baekho) | RI | 4497 (1368) | 4672 (1218) | 5333 (1147) | 5227 (1608) | 5075 (1138) | 4951 (1356) | 5890 (1361) |
| RF | 2348 (1263) | 2585 (1372) | 3323 (1372) | 3207 (1766) | 3092 (1322) | 2846 (1481) | 3959 (1635) | ||
| ETc | 3347 (174) | 3382 (241) | 3433 (212) | 3477 (223) | 3345 (163) | 3647 (227) | 3754 (221) | ||
| ER | 3593 (773) | 4103 (679) | 4357 (722) | 4365 (703) | 4099 (556) | 4184 (757) | 4557 (639) | ||
| Res. D (Gumi) | RI | 2868 (939) | 2984 (686) | 3366 (630) | 3270 (990) | 3254 (876) | 3227 (634) | 3594 (919) | |
| RF | 1856 (996) | 1954 (795) | 2392 (699) | 2252 (1014) | 2312 (939) | 2235 (686) | 2657 (1072) | ||
| ETc | 961 (48) | 900 (50) | 904 (45) | 1020 (76) | 981 (48) | 1043 (54) | 1095 (68) | ||
| ER | 862 (207) | 1199 (277) | 1392 (283) | 923 (189) | 940 (176) | 951 (160) | 1023 (178) | ||
| Region | Reservoir Symbol | Factors | Historical (1981–2010) | RCP 4.5 Scenario | RCP 8.5 Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | ||||
| Central region | Res. A (Myeoku) | PWS 1 | 2135 (224) | 2222 (297) | 2095 (261) | 2234 (240) | 2101 (234) | 2164 (252) | 2218 (368) |
| IWR 2 | 1822 (274) | 2068 (400) | 1812 (284) | 2011 (443) | 2045 (289) | 2115 (317) | 2100 (331) | ||
| Res. B (Songak) | PWS | 1356 (170) | 1343 (149) | 1405 (122) | 1402 (133) | 1343 (118) | 1369 (110) | 1404 (159) | |
| IWR | 1234 (238) | 1318 (241) | 1151 (197) | 1262 (273) | 1293 (207) | 1350 (214) | 1336 (212) | ||
| Southern region | Res. C (Baekho) | PWS | 2627 (392) | 2737 (241) | 2739 (343) | 2774 (290) | 2709 (268) | 2808 (266) | 2699 (332) |
| IWR | 2310 (561) | 2376 (529) | 2265 (511) | 2295 (456) | 2330 (436) | 2472 (488) | 2246 (519) | ||
| Res. D (Gumi) | PWS | 1327 (139) | 1405 (150) | 1351 (123) | 1394 (113) | 1319 (133) | 1364 (176) | 1314 (208) | |
| IWR | 1243 (221) | 1214 (214) | 1153 (151) | 1247 (214) | 1181 (214) | 1228 (199) | 1186 (246) | ||
| Region | Reservoir Symbol | Historical (1981–2010) | RCP 4.5 Scenario | RCP 8.5 Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | 2025s | 2055s | 2085s | |||
| Central region | Res. A (Myeoku) | 22 (6.0) | 26 (4.9) | 26 (5.3) | 32 (5.9) | 31 (6.4) | 37 (7.1) | 31 (2.3) |
| Res. B (Songak) | 24 (8.5) | 25 (5.1) | 27 (6.7) | 34 (11.7) | 26 (8.3) | 31 (6.0) | 37 (9.4) | |
| Southern region | Res. C (Baekho) | 21 (5.9) | 14 (4.4) | 15 (3.5) | 18 (2.9) | 18 (2.5) | 20 (5.6) | 25 (5.0) |
| Res. D (Gumi) | 25 (3.5) | 19 (4.9) | 20 (4.1) | 27 (4.5) | 19 (5.7) | 28 (3.0) | 26 (3.0) | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, W.-H.; Kim, T.; Hong, E.-M.; Choi, J.-Y. Regional Climate Change Impacts on Irrigation Vulnerable Season Shifts in Agricultural Water Availability for South Korea. Water 2017, 9, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100735
Nam W-H, Kim T, Hong E-M, Choi J-Y. Regional Climate Change Impacts on Irrigation Vulnerable Season Shifts in Agricultural Water Availability for South Korea. Water. 2017; 9(10):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100735
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Won-Ho, Taegon Kim, Eun-Mi Hong, and Jin-Yong Choi. 2017. "Regional Climate Change Impacts on Irrigation Vulnerable Season Shifts in Agricultural Water Availability for South Korea" Water 9, no. 10: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100735
APA StyleNam, W.-H., Kim, T., Hong, E.-M., & Choi, J.-Y. (2017). Regional Climate Change Impacts on Irrigation Vulnerable Season Shifts in Agricultural Water Availability for South Korea. Water, 9(10), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100735






