Abstract
Sustaining good water quality in aquaculture ponds is vital. Without an aerator, the dissolved oxygen in ponds comes primarily from mass transfer at the water-ambient atmosphere interface. As sediment can seriously affect water quality, this study used indoor experiments to examine the nutrient (nitrogen and phosphorus) release mechanisms and fluxes from sediment in aquaculture ponds with moving water but no aeration. The results showed that the ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) concentration in the overlying water was inversely proportional to flow velocity and that a higher flow velocity tended to result in a lower concentration in the overlying water, a steeper vertical gradient of concentration within the bed sediments, and a faster release rate from the sediments. The sediment disturbed by flowing water released more nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N) and nitrite nitrogen (NO2-N) into the overlying water and NO2-N could become oxidized into NO3-N. In still water, NO3-N was released gradually and some anaerobic NO3-N was nitrified into NO2-N. Phosphorus release from the sediments was controlled by the adsorption–desorption balance, with the phosphorus concentration in the overlying water dropping gradually to a steady value from its initial maximum. The relationship between NH3-N release flux and flow rate is described by a cubic function.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of the aquaculture industry in recent years has led to abundant residual feed, metabolites, and excreta being deposited in pond sediments. The resulting 50- to 500-fold rise in the nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) concentrations in the sediments compared to those in the overlying water [1] vastly increases the likelihood that N and P will be released from the sediment-water interface and migrate into the water, potentially threatening the aquaculture environment and impacting aquaculture production. Given that the N and P released can also boost autotrophic growth in freshwater ecosystems, seriously affecting the biomass and population structures of aquatic species [2,3,4], a great deal of research has focused on the role played by N and P in aquaculture [5,6]. Most previous studies examined the changes in nutrition concentration in the sediment porewater and overlying water and measured the nutrient diffusion flux under still water conditions [7], but the water turbulence caused by storms, aeration, and bioturbation can have a significant impact on the release of N and P at the sediment-water interface [8]. The deposition and resuspension of sediments resulting from water turbulence can prompt the release of nutrients and metals into overlying water [9] and increase the exchange coefficient between the overlying water and sediments, thus accelerating the diffusion of any contaminants present in the sediments into the overlying water and boosting nutrient release. Reddy et al. [8] found that in Apoka Lake, which is located in the US state of Florida, under turbulent water conditions the nutrient concentrations in the overlying water resulting from the deposition and resuspension was dozens of times higher than those resulting from diffusion alone. In Denmark’s Arreso Lake, Sondergaard et al. [10] found that sediment resuspension led to 20- to 30-fold increases in the nutrient concentrations in the overlying water under similar conditions.
The dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration in water also influences the release of N and P at the sediment-water interface. Usui et al. [11] used 15N as a tracer to monitor the fate of nutrients in sediments in the Tama estuary, Japan. By comparing changes in the level of N2O, they showed that increasing the concentrations of NO3− and DO in the overlying water stimulated nitrification and denitrification. In a series of laboratory experiments, Baudo [12] demonstrated that while insoluble ferric hydroxide (Fe(OH)3) was converted into soluble Fe(OH)3,there was a massive release of iron bound phosphorus (Fe-P) into the water column under anaerobic conditions, one of the potential mechanisms leading to the eutrophication of shallow lakes. Although phosphorus release can occur under aerobic conditions, the amount released is generally thought to be much smaller than under anaerobic conditions. The aerobic release mechanism is primarily based on the mineralization of sediments and the aerobic decomposition of organic matter.
The objective of this study was therefore to determine precisely how the N and P release mechanisms in aquaculture sediments are influenced by water hydrodynamics and DO conditions. To this end, a series of experiments were conducted to simulate circular flow in the overlying water and measure the N and P released from sediments in an aquaculture pond that was not subject to aeration.
2. Experimental Apparatus and Method
2.1. Experimental Apparatus
The experimental apparatus is illustrated in Figure 1. The tank, made of clear poly(methyl-methacrylate) organic glass, was 50 cm long, 25 cm wide, and 35 cm high. It was wrapped in aluminum foil to deter algae growth and reproduction under light stimulation. The tank cover was equipped with a small hole to provide access for the DO meter probe and for water sampling; this was sealed with a rubber plug when not in use. Two vertical 10-cm-high glass plates were placed inside the tank, 5 cm away from the water inlet and outlet pipes, as shown in Figure 1. The sediments were placed between these two plates to protect the sediment surface from being washed away by the water flow. Three small 6-mm-diameter holes were drilled along one side of the tank, with the first being about 1 cm above the sediment surface and the others 3 cm and 6 cm, respectively, below the sediment surface, and rhizosphere soil solution collectors (Rhizon pipes) inserted horizontally into each to collect porewater samples. The structure of the Rhizon pipes is illustrated in Figure 2. The sample sediments for the laboratory experiments were taken from an aquaculture pond, containing three species of fish, namely black, grass, and silver carp, with a breeding density of about 6000 kg·ha−1. These sediments consisted of muddy fine sandy soils with a mean particle size of about 0.1 mm. Distilled water was used as the overlying water to eliminate any effects of algae and microorganism in natural water. In order to conduct synchronous measurements under different flow rates, five identical sets of the apparatus shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 were constructed, each with its own pump, to allow the circulation flow rates to be adjusted independently. Seen from Figure 1, the pipes, the valve, water pump, flow meter, and tank were composed of a water flow process. Along with the arrow direction, water in the tank flowed circularly, with the water pump adjusting the water flow rate.
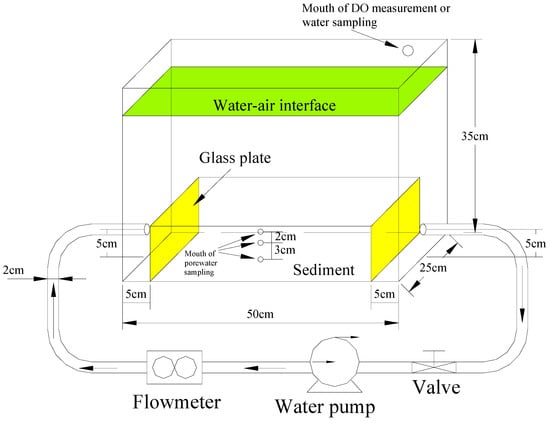
Figure 1.
Illustration of the experimental apparatus.
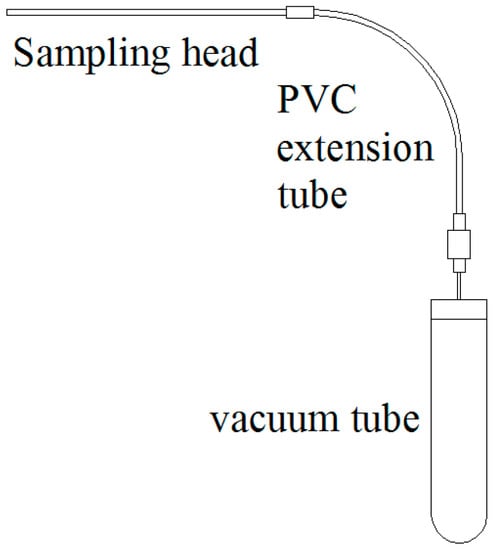
Figure 2.
Structure of the Rhizon pipes.
The geochemical processes of porewater govern important aspects of all lake and oceanic water environments, most notably the spatial distribution, migration, and transformation of chemical substances at the sediment-water interface as well as the early diagenetic process within sediments [13]. As part of the effort to develop a better understanding of how these processes function, some researchers have used balance sampling devices to collect in-situ porewater, while others have used specially designed sediment collectors to harvest clay cores or superficial sediments that are then layered, centrifuged or filter pressed to extract the porewater [14,15]. For laboratory experiments, porewater is often acquired via an anaerobic centrifugation approach [8,16,17], but this approach relies on strict operational procedures and can only be conducted in a nitrogenous environment to avoid oxidization effects. The chemical balance of the porewater is also all too easily influenced by factors such as the pH and temperature. The biggest shortcoming of the anaerobic centrifugation approach, however, is the resulting destruction of the biologic characteristics of porewater, making it unsuitable for long-term sampling. Giesler et al. [13] used a high-speed centrifugal method and a zero-tension lysimeter to measure the solute leaching loss, and found that the leaching loss was overestimated substantially. In contrast, measurements made using the type of Rhizon pipe utilized in this study, which has a 10-cm-long sampling head and a 12-cm-long PVC (polymer of vinyl chloride) extension tube, proved more effective than the lysimeter for collecting porewater samples within sediments because it minimizes sediment disturbance and changes in the porewater properties, isolates the sample from air, and is both inexpensive and reusable [18]. The head incorporates a negative-pressure joint and is connected to a vacuum tube in which the porewater sample is collected and stored (Figure 2).
2.2. Experimental Method
The sediment sample was collected in the summer of 2014 from an aquaculture farm in Guangzhou, China using a clamshell sampler and immediately sealed in a polyethylene plastic bucket for transport back to the laboratory. Upon arrival, large stones, organic detritus, benthos, and rubbish were removed, after which the sample was stirred and mixed evenly to form a rebonded sediment sample with average physicochemical properties for the sediments in that aquaculture pond, which is typical of those in the area. The space between the two glass plates in each tank was filled with rebonded sediment to a depth of 10 cm, level with the top of the glass retaining plates, and the sediment surface smoothed gently. During this process, the three Rhizon pipes were inserted at the appropriate depths in each tank. After the sediment had been allowed to settle for 15 days, distilled water was slowly poured into each tank until the overlying water depth reached about 18 cm.
The sediments were cultured for 7 days under different circulation flow rates. During this period, porewater samples from within the sediments and in the overlying water were collected using vacuum pipes at the same time every day. The resulting 5 mL samples were then used to test ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), nitrite nitrogen (NO2−), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−), and soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) via an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Due to its strong specificity, high sensitivity, good repeatability, simple operation, and freedom from radioactive contamination [19], ELISA is capable of testing hundreds of samples very quickly, greatly facilitating the collection and analysis of this type of data. The pH of the overlying water was measured by a pH meter (Acme Meter Corp, Springfield, IL, USA), while overlying water temperatures (T) and DO concentration were measured by a YSI ProODO optical dissolved oxygen instrument (YSI Inc., Yellow Springs, OH, USA). Oxidation-reduction potentials (ORP) of the overlying water were tested by a Model oxidization-reduction potential meter.
To determine the mean flow velocity in the overlying water, the mean water depth in each of the experimental tanks was calculated as:
where h is the mean overlying water depth; V is the water volume of the tank (= 27.5 L); W is the width of the tank (= 25 cm); L is the length of the tank (= 50 cm); l is the distance from the plate to the nearest side wall of the tank (= 5 cm); and hp is the height of the glass plate (= 10 cm).
The mean flow velocity in the overlying water was calculated as:
where v is the mean flow velocity in the overlying water; and Q is the flow rate in the pipe.
Based on Equations (1) and (2), the mean overlying water depth h was calculated to be 0.2 m and the mean flow velocities in the overlying water in the five tanks were calculated to be 0, 0.47, 0.54, 0.57, and 0.61 cm·s−1, respectively.
3. Results
As stated above, the release of N and P from sediments can be affected by a number of external factors [20], including organic matter supplements [21,22,23]; temperature, DO, pH, and ORP [24]; and the physical properties of the sediments [25]. We will therefore analyze these factors before moving on to discuss the effect of the flow velocity of the overlying water on the N and P release rates from the sediments.
3.1. Changes in the External Factors Affecting the Overlying Water during Culture Periods
3.1.1. Water Temperature
Water circulation driven by pumps inevitably emits some heat, slightly raising the water temperature. In our experiments, water temperature was measured daily and the results are shown in Figure 3. The water temperature in the still-water tank (i.e., with no pumping) was lower, as it was only influenced by air temperature, but the water temperatures in the other four tanks (v = 0.47, 0.54, 0.57, and 0.61 cm·s–1) were very similar. Water temperature is known to indirectly influence P release in sediments [26], with a high temperature boosting the activity of some substances and accelerating physical, chemical, and biological reactions such as the diffusion and degradation of organic matter. Microorganisms can also decompose organic P in sediments into inorganic P and convert insoluble phosphorus compounds into soluble ones and higher metabolic rates can accelerate the degradation of organic matter [27], thus promoting P release from sediments. For N release, Liu et al. [28] reported that water temperature can influence degradation speed, when temperatures drop too low, the degradation of N in deeper-sediments can cease altogether. Based on a series of experiments on sediment contaminant release, Huang et al. [29] found that a high temperature accelerates the emission of dissolved contaminants considerably. Ogilivie et al. [30] agreed, pointing out that rising temperatures not only favor ammonification and nitrification but also enhance ammonifying and nitrifying bacterial activity.
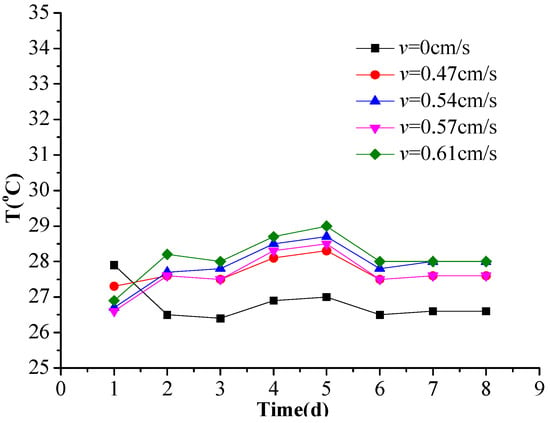
Figure 3.
Plot of overlying water temperature for different flow rates during the experiment.
3.1.2. DO and ORP
The DO levels in the overlying water and the corresponding ORP values are presented in Figure 4a,b, respectively. ORP is a measure of the relative degree of water oxidizability or reducibility. Wetzel et al. [31] and Seiki et al. [32] showed that the DO content in the overlying water is an important factor influencing ORP. As the data in Figure 4a shows, even when the culture tanks were sealed and not aerated, the existence of an air-filled space above the overlying water provided some air re-aeration through water surface entrainment caused by the circulating water flow, as indicated by the declining concentrations of DO over the first two days and the subsequent increases later in the experiment, which contrast markedly with the DO concentrations in the still-water tank, which declined monotonically throughout. Interestingly, the data in Figure 4b show that the ORP was consistently negative, ranging from −60 to −100, implying that the culture water environment favors the reduction of ORP.
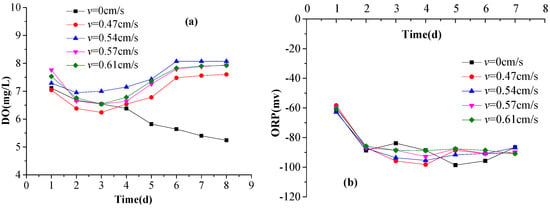
Figure 4.
(a) Dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations; and (b) oxidation-reduction potentials (ORP), in the overlying water during the experiment.
3.1.3. pH
For all the flow rates tested, the culture water pH was effectively independent of flow rate varying only from 6.5 to 7.0 (Figure 5), indicating a weak acidity, although pH did tend to decrease with culture time. The pH is known to have a significant impact on P morphology [33], however, as iron, aluminum, and cadmium in water and sediments are highly likely to react with soluble inorganic P in acidic solutions, forming non-dissolvable deposits, while anions of phosphate are more likely to be absorbed by bauxite, kaolinite, and/or montmorillonite, as well as by newly precipitated Fe(OH)3 and aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) colloids. The deposition-dissolution and adsorption–dissolution processes have a major influence on the physiochemical dynamics (in this case, the solubility and biological cycle) of P compounds. pH also plays an important role in N release from sediments, with the optimum pH for sediment nitration being about 7.5 [34]. If the pH of the water increases, the rate of nitrification rises, leading to higher levels of free ammonia nitrogen. However, when the pH exceeds 7.5, the nitrification rate becomes almost independent of the free ammonia nitrogen concentration. During this experiment, the pH in the overlying water was kept weakly acid, with a pH below the optimum value, thus limiting the activity of the enzymes in the nitrifying bacteria and reducing the nitrification activity.
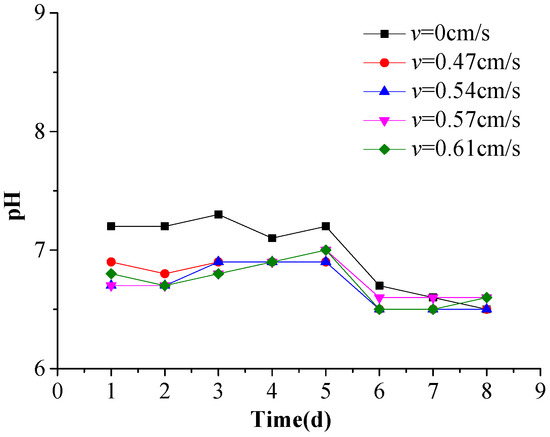
Figure 5.
Variations in the pH of the overlying water during the experiment.
3.2. Effects of Flow Rate on NH3-N Concentration
Figure 6 shows how the NH3-N concentrations in the porewater and overlying water varied during the course of the experiment. For any given flow rate, the NH3-N concentration near the surface of the sediment was lower than that at greater depths, while for a given depth, the NH3-N concentration at a faster flow rate was lower than that at a slower flow rate. This is because the sediments were disturbed more by higher flow rates, thus releasing more NH3-N into the overlying water and introducing more oxygen into the sediments to oxidize NH3-N. The NH3-N concentration gradient between the 6-cm- and 3-cm-deep sediments was steeper than the gradient between the 1-cm-deep sediment and the overlying water, demonstrating the effect of flow rate on NH3-N release from the sediments. The gradient around the 3 cm depth was greatest because the sediments at this depth were both releasing NH3-N upward and receiving DO from shallower sediments. In addition, the NH3-N concentration in the 1-cm-deep sediments decreased gradually, ultimately achieving a steady state. This may be because the NH3-N concentration gradient was becoming less steep, leading to a reduced release rate. Further, the NH3-N concentration increased with time for any given flow condition, although a higher flow rate tended to be accompanied by a lower NH3-N concentration. This is probably because higher flow rates would likely stir up the sediments more, thus encouraging the release of nutrients.
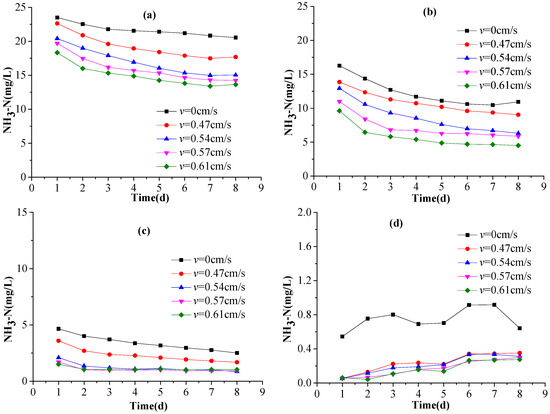
Figure 6.
The concentrations of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) in the sediment at depths of: (a) 6 cm; (b) 3 cm; (c) 1 cm; and (d) in the overlying water, throughout the experiment.
The release flux of NH3-N from the sediments can be calculated as:
where J is the sediment release flux (mg L−1·day−1); and C(t) and C(t+1) are the measured NH3-N concentrations in the sediment porewater on days t and t + 1, respectively.
The results obtained using Equation (3) are shown in Figure 7. The NH3-N release fluxes at the three depths exhibited a similar pattern: NH3-N was released quickly in the first 1–2 days, but then the release slowed, gradually becoming stable. The initial rapid release is likely due to the greater NH3-N concentration gradient between the overlying water (0 mg·L−1) and the sediments; as time progresses, the NH3-N concentration in the overlying water increases so the concentration gradient gradually decreases, leading to a slower NH3-N release rate. For the higher flow rates, the sediments are disturbed more strongly, resulting in a higher initial release rate that is once again followed by a steady rate, which indicates the decreasing effect of flow rate on NH3-N release. For the first few days, the flowing-water tanks released more NH3-N than the still-water tank, but as time elapsed, the release flux in the flowing-water tanks tended to approach that in the still-water tank. Such decreasing trends in NH3-N release rate can be well modeled using regression equations (Table 1), as indicated by the high values obtained for R2, which ranged from 0.895 to 0.995.
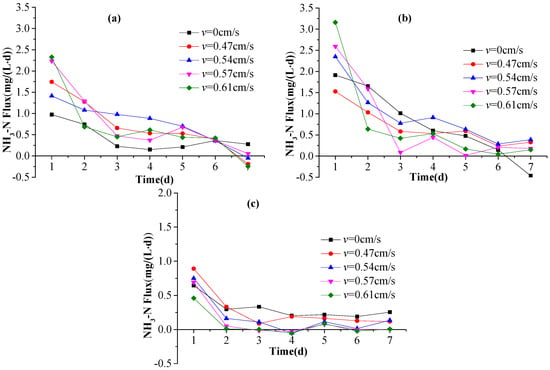
Figure 7.
The release flux of NH3-N during the course of the experiment measured at depths of: (a) 6 cm; (b) 3 cm; and (c) 1 cm within the sediments.

Table 1.
The regression equations for the NH3-N release flux.
The generic format of these regression equations consists of a cubic function expressed as:
where y is the NH3-N release flux from the sediments at day x (mg·L−1·day−1); and a, b1, b2, and b3 are the regression coefficients.
A positive value for y indicates that NH3-N is released from the sediment into the overlying water, whereas a negative value means that NH3-N is absorbed from the overlying water back into the sediment. Because the overlying water in these experiments was distilled and free of nutrients, the sediments, which were rich in NH3-N, initially released a large amount of NH3-N into the overlying water. However, once a balance in the NH3-N between the sediments and the overlying water had been achieved, the release from the sediments to the overlying water slowed or even ceased. Once this “balance point” was reached, the NH3-N in the overlying water began to be absorbed back into the sediments.
3.3. Effects of Flow Rate on NO3-N Concentration
Under flowing-water conditions, a lower flow rate corresponded to a higher NO3-N concentration for any given sediment depth, while a lower depth had a lower NO3-N concentration for the same test day (Figure 8). The NO3-N concentrations in the overlying water and at a sediment depth of 1 cm increased with time, whereas the NO3-N concentrations 3 cm and 6 cm below the surface of the sediments decreased after the initial increase. Under the still-water condition, the NO3-N concentration at a depth of 6 cm decreased monotonically with time.
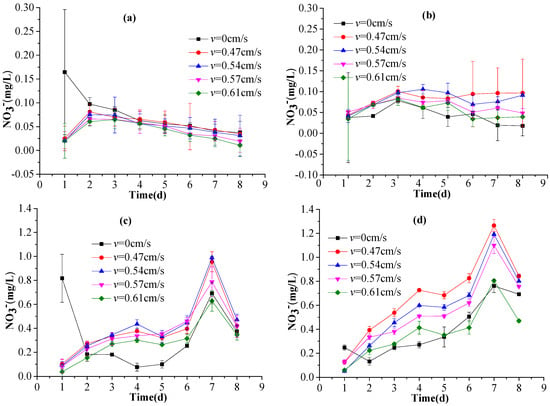
Figure 8.
Nitrate (NO3-N) concentrations at depths of: (a) 6 cm; (b) 3 cm; and (c) 1 cm within the sediments; and (d) in the overlying water, during the experiment.
One possible explanation for this observation is that because the sediment was disturbed by the water flow, more NO3-N and NO2-N was released from the sediments into the overlying water and NO2-N was more likely to be oxidized into NO3-N. This is also probably true for the 1-cm-deep sediments, which were soaked by the overlying water. As time progressed, the NO3-N concentration in the overlying water and in the 1-cm-deep sediments increased, reducing the concentration gradient between the sediments and the overlying water. Comparing the DO variations (Figure 4a) with the NO3-N variations (Figure 8), a lower DO generally corresponded to a higher NO3-N concentration regardless of the flow rate or sediment depth, indicating that some NO2-N had probably been gradually oxidized into NO3-N due to aeration from the overlying water. This transformation process is supported by the variations in the NH3-N concentration (Figure 6). The NO3-N concentrations in the 3-cm- and 6-cm-deep sediments exhibited flipped “V-shaped” variation trends for the test flow rates, possibly as a result of the dynamic exchange of NO3-N between the upper and lower sediment levels. At the beginning of the experiment, the deep sediments released NO3-N, leading to a decreased concentration and an increasing release rate.
For the still-water tank, because there was no flow turbulence NO3-N was likely to have continued to be released gradually throughout with some anaerobic NO3-N being nitrified into NO2-N, leading to a monotonic decreasing trend for NO3-N (Figure 8). Chong [35] found that the nitrate release rate in deep water is slower than that in shallow water, which implies that the nutrient cycle in deep water is slower because there is less vertical mixing. This finding is supported by our experimental results, which confirmed that stronger vertical mixing in shallower water can induce more nutrient release. The overlying water temperature was relatively higher on the 4th and 5th days (Figure 3), while the NO3-N concentrations were somewhat reduced on those days (Figure 8b–d). In contrast, from the 6th day onward, the overlying water temperature decreased but the NO3-N concentrations started to increase. This indicates that the NO3-N concentration in the sediments is likely negatively related to water temperature, which is consistent with the findings reported by previous studies. For example, Anthony and Lewis [36] examined the release of endogenous nitrogen in an oligotrophic lake, and found that the release rate of NH3-N at the sediment-water interface was positively correlated with water temperature while the NO3-N concentration in the overlying water was negatively correlated with water temperature. The NO3-N variations with time can once again be expressed as regression equations (Table 2), with high values of R2, ranging from 0.769 to 0.973.

Table 2.
The regression equations for theNO3-N concentrations.
These regression equations can be expressed as the following generic form:
where y is the NO3-N concentration on day x; and a and b are regression coefficients.
3.4. Effects of Flow Rate on SRP Concentration
Under anaerobic conditions, the degradation of organic matter was positively correlated with the SRP release flux, which in turn was negatively correlated with the DO concentration [37]. For a given sediment depth, a higher flow rate corresponded to a lower SRP concentration, whereas for a given testing day a deeper depth had a lower SRP concentration (Figure 9).The SRP concentrations in the overlying water and in the 1-cm-deep sediments increased monotonically with time, although the concentrations in the 3-cm- and 6-cm-deep sediments decreased after their initial increase. This increasing-decreasing pattern in the SRP concentrations for the 3-cm- and 6-cm-deep sediments suggests that the P release in the sediments was likely controlled by an adsorption–desorption process. At the beginning, the overlying water had a low P content and so the sediments began to release P in an attempt to restore equilibrium. Once the P content in the overlying water increased sufficiently, the P release from the sediments achieved a dynamic balance. The maximum P release from the sediments was achieved at a relatively early stage. Figure 9d shows that under the still-water condition the sediments released P into the overlying water quite rapidly, and overall the P release was affected significantly by the hydrodynamic conditions.
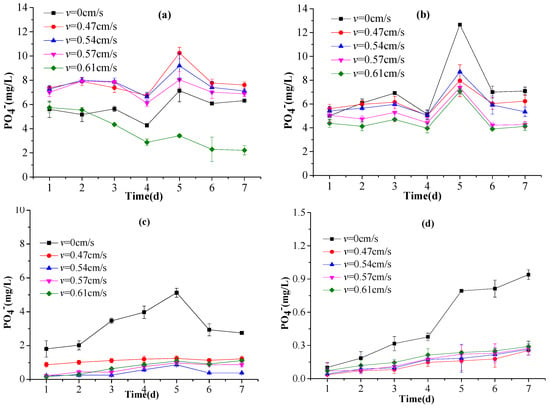
Figure 9.
The concentrations of phosphate (PO4−) at depths of: (a) 6 cm; (b) 3 cm; and (c) 1 cm within the sediments; and (d) in the overlying water, during the experiment.
4. Discussion
The levels of NH3-N, NO3-N, and PO4− are generally used to indicate water quality in aquaculture ponds. Figure 10 shows the seven day average values of these three variables in the overlying water measured in this study under different water velocity conditions. As Figure 10a shows, the NH3-N concentrations in the overlying water decreased with increasing water velocity. When the overlying water was still, the NH3-N concentration was more than 3-fold higher than was the case when the water was moving at any of the flow rates tested, and the NH3-N concentrations decreased with increasing water velocity, although this trend slowed as the water velocity increased. Figure 10c shows that this was also true for PO4−: when the overlying water was still, the concentration was once again almost 3-fold higher than when the overlying water was moving, but unlike NH3-N, when the water was flowing the PO4− concentrations increased with increasing water velocity. Similar results were reported for earlier studies by Luo et al. [38], Duan et al. [39], Larned and Atkinson [40], and Zhu et al. [41]. For example, Larned and Atkinson found that with increasing water velocity, the rate of NH3-N and PO4− uptake were positively correlated with velocity by D. cavernosa, which indicates that the NH3-N and PO4− concentrations when the overlying water maintains a certain velocity are lower than those found in still overlying water. Zhu et al. found that sediment resuspension does not always increase phosphorus concentration in overlying water in shallow lakes, which means there is an effect threshold of water velocity on the lowest or highest concentrations of phosphorus. In this study, we conducted experimental measurements for a relatively coarse scale of five water velocities in the overlying water. A more detailed examination of what happens when the water velocities are within the narrow range of 0 to 0.47 cm/s, where the data shown in Figure 10 indicate major changes appear to occur, could provide useful experimental data that better explains the observed trends in nutrient concentrations.
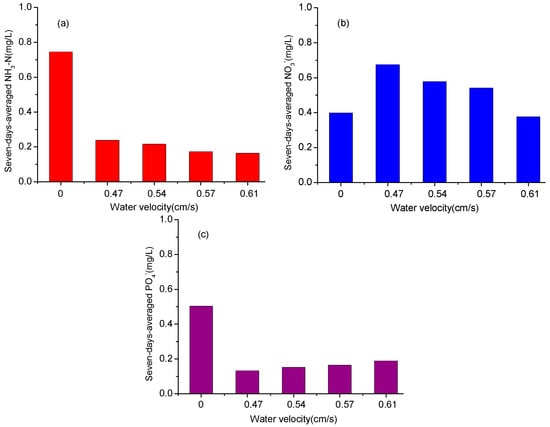
Figure 10.
The seven-day-averaged concentrations in the overlying water for: (a) NH3-N, (b) NO3-N and (c) PO4−.
Our findings demonstrate that in aquaculture ponds, although the water velocity is important for the removal of NH3-N and PO4−, it has little effect on the removal of NO3-N (Figure 10b). It does, however, provide a useful way to monitor the effects of hydrodynamic disturbance on nutrient release from the pond sediments into the overlying water.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the effects of flow rate on nutrient release at the aquaculture pond sediment-water interface using laboratory experiments conducted in sealed anaerobic culture model tanks. The results revealed that:
- Flow rate influenced ORP in the overlying water (pH = 6.5 to 7.0) slightly. Although the experiments were implemented under nonaerated conditions, the water could become re-aerated at certain flow rates.
- For the flowing-water conditions, a steep vertical gradient was observed in the NH3-N concentration between the overlying water and the porewater. A higher flow rate was found to correspond to a lower NH3-N concentration in the overlying water, a larger gradient in the NH3-N concentration in the sediments, and a faster release rate of nutrients from the sediments. The trends in NH3-N concentrations were well described by a cubic function.
- The NO3-N concentrations in the overlying water and sediments tended to increase during the first five culture days, but then declined from the 6th day onward. For the still-water condition, because there was no flow turbulence NO3-N continued to be released, with some anaerobic NO3-N likely nitrified to NO2-N. The trends observed in the NO3-N concentration were well described by an e-based exponential function.
- The P release from the sediments was controlled by an adsorption–desorption process. The maximum P release rate from the sediments was achieved at an early stage.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (#CARS-46-17), the National Key Technology R&D Program (#2012BAD25B04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (#51579106) and the Open Research Fund Program of Key Laboratory of Tropical & Subtropical Fishery Resource Application & Cultivation. Also, the primary author appreciates the research opportunity of taking up a visiting professorship at the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department of Old Dominion University, Virginia, USA.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to this work. Specifically, Xiangju Cheng focused on the analysis of the experimental data and contributed to writing the paper; Dantong Zhu conducted the laboratory measurement, analyzed the experimental data and created the graphics; Xixi Wang organized the writing and structure of the paper; and Deguang Yu and Jun Xie provided the laboratory space and developed the specialized equipment and instruments needed for this experimental research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Henderson-Seller, B.; Markland, D.H.R. Decaying Lakes: The Origins and Control of Cultural Eutrophication; John Wiley and Sons: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 5–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hecky, R.E.; Kilham, P. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: A review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 797–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippart, C.J.M.; Cadee, G.C.; Van Raaphorst, W.; Riegman, R. Long-term phytoplankton-nutrient interactions in a shallow coastal sea: Algal community structure, nutrient budgets, and denitrification potential. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, B.; Duan, W.; Li, W.; Luo, P.; Razafindrabe, B.H.N. Source Apportionment of Annual Water Pollution Loads in River Basins by Remote-Sensed Land Cover Classification. Water 2016, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.W.; Boyd, C.E. Chemical budgets for organically fertilized fish ponds in the dry tropics. J. World Aqua. Soc. 1995, 26, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nairn, R.W.; Mitsch, W.J. Phosphorus removal in created wetland ponds receiving river overflow. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 14, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, L. Diffusion of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface and in seawater at aquaculture areas of Daya Bay, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 1557–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; Fisher, M.M.; Ivanoff, D. Resuspension and diffusive flux of nitrogen and phosphorus in a hypereutrophic lake. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnejais, L.H.; Martin, W.R.; Bothner, M.H. The release of dissolved nutrients and metals from coastal sediments due to resuspension. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondergaard, M.; Kristensen, P.; Jeppesen, E. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind exposed Lake Arreso. Den. Hydrobiol. 1992, 228, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, T.; Koike, I.; Ogura, N. N2O production, nitrification and denitrification in an estuarine sediment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudo, R.; Giesy, J.P.; Muntau, H. (Eds.) Sediments: Chemistry and Toxicity of In-place Pollutants; Lewis Publishers: Boston, MI, USA, 1990; pp. 131–144.
- Giesler, R.; Lundström, U.S.; Grip, H. Comparison of soil solution chemistry assessment using zero-tension lysimeters or centrifugation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Reddy, K.R.; Fisher, M.M. Phosphorus flux between sediment and overlying water in lake Okeechobee, Florida: Spatial and temporal variations. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugo, P.; Bertolin, A.; Moretto, L.M. Monitoring sulphur species and metal ions in salt-marsh pore-waters by using an in-situ sampler. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1998, 73, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Reddy, K.R.; Graetz, D.A. Phosphorus geochemistry in the sediment-water column of a hypereutrophic lake. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Reddy, K.R. Role of Eh and pH on phosphorus geochemistry in sediments of Lake Okeechobee, Florida. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeberg-Elverfeldt, J.; Schlüter, M.; Feseker, T.; Kölling, M. Rhizon sampling of porewaters near the sediment-water interface of aquatic systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2005, 3, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.J.; Fadly, A.M.; Okazaki, W. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses. Avian Dis. 1979, 23, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.W. Pollution Characteristics of the Sediment of the Hangzhou Section of the Grand Canal, China, and Its Pollution Releasing Mechanism and Ecological Effects. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, Z.W.; de Giesen, N.; Zhu, D.J. The Influence of a Eutrophic Lake to the River Downstream: Spatiotemporal Algal Composition Changes and the Driving Factors. Water 2015, 7, 2184–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.H.; Lomstrin, E.; Sorensen, J. Benthic NH4+ and NO3− following sedimentation of a spring phytoplankton bloom in Aarhus Bight Denmark. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 61, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloth, N.P.; Blackburn, H.; Hansen, L.S.; Risgaard-Petersen, N.; Lomstein, B.A. Nitrogen cycling in sediments with different organic loading. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 116, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, W.M.; Boynton, W.R. External and internal factors regulating metabolic rates of an estuarine benthic community. Oecologia 1982, 51, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, K.; Rasmussen, M.B.; Jensen, A. Effect of bioturbation on microbial nitrogen transformations in the sediment and fluxes of ammonium and nitrate to the overlying water. Ecol. Bull. 1983, 35, 193–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L.; Jansson, M. Principles of Lake Sedimentology; Springer-Verlag: Berlin and Heidelberg, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- D’Angelo, E.M.; Reddy, K.R. Diagenesis of organic matter in a wetland receiving hypereutrophic lake water: I. Distribution of dissolved nutrients in the soil and water column. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Chen, Z.L.; Liu, J. Effects of environmental factors on NH4+ release in tidal flat sediments along the Yangtze Delta. Res. Environ. Sci. 2002, 15, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.L.; Sun, Y.J.; Li, X.P.; Liu, L.K.; Yu, J. The simulation test of pollutants release from sediments of urban river. Adv. Chem. Technol. Water Wastewater Treat. CCS Int. Conf. 2008, 3, 733–739. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie, B.; Nedwell, D.B.; Harrison, R.M.; Robinson, A.; Sage, A. High nitrate, muddy estuaries as nitrogen sinks: The nitrogen budget of the River Colne estuary (United Kingdom). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 150, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology; W B Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Seiki, T.; Iazwa, H.; Date, E. Benthic nutrient remineralization and oxygen consumption in the coastal area of Hiroshima Bay. Water Res. 1989, 23, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvanovics, V. Seasonal variation of phosphorous release from the sediments of shallow lake. Water Res. 1988, 22, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, E.A.; Mitchell, N.L.; Lamberti, G.A. Factors regulating nitrification in aquatic sediments: Effects of organic carbon, nitrogen availability, and pH. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.Y. Dynamics of Dissolved Oxygen and Benthic Release of Nutrients in the Bottom Water Layer in Shallow versus Deep Areas in Hong Kong Waters. Ph.D. Thesis, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, J.L.; Lewis, W.M., Jr. Low boundary layer response and temperature dependence of nitrogen and phosphorus releases from toxic sediments of an oligotrophic lake. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktorsson, L.; Almroth-Rosell, E.; Tengberg, A. Benthic phosphorus dynamics in the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Aquat. Geochem. 2012, 18, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Razafindrabe, B.H.N.; Nover, D.; Yamashiki, Y. Spatiotemporal trend analysis of recent river water quality conditions in Japan. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 2819–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.L.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Luo, P.P.; Nover, D.; Hu, M.C. Modeling suspended sediment sources and transport in the Ishikari River basin, Japan, using SPARROW. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larned, S.T.; Atkinson, M.J. Effects of water velocity on NH4 and PO4 uptake and nutrient-limited growth in the macroalga Dictyosphaeria cavernosa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 157, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Effects of hydrodynamics on phosphorus concentrations in water of Lake Taihu, a large, shallow, eutrophic lake of China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).