A Simplified Model for Modular Green Roof Hydrologic Analyses and Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
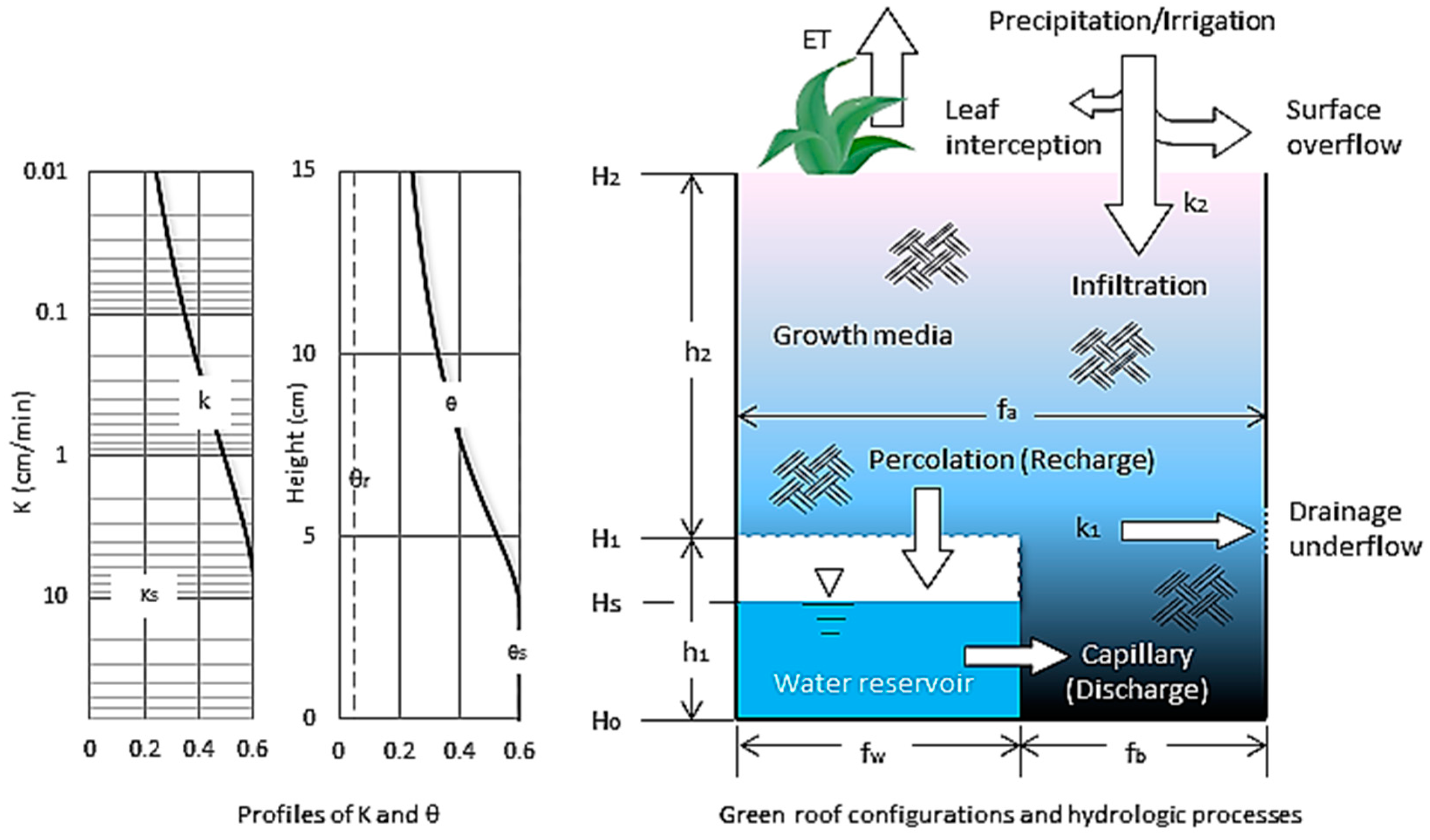
2.1. Typical Green Roof Configurations and Hydrologic Processes
2.2. Governing Equations
2.3. Green Roof Runoff Hydrograph Simulation
2.4. Computer Simulation
3. Calibration
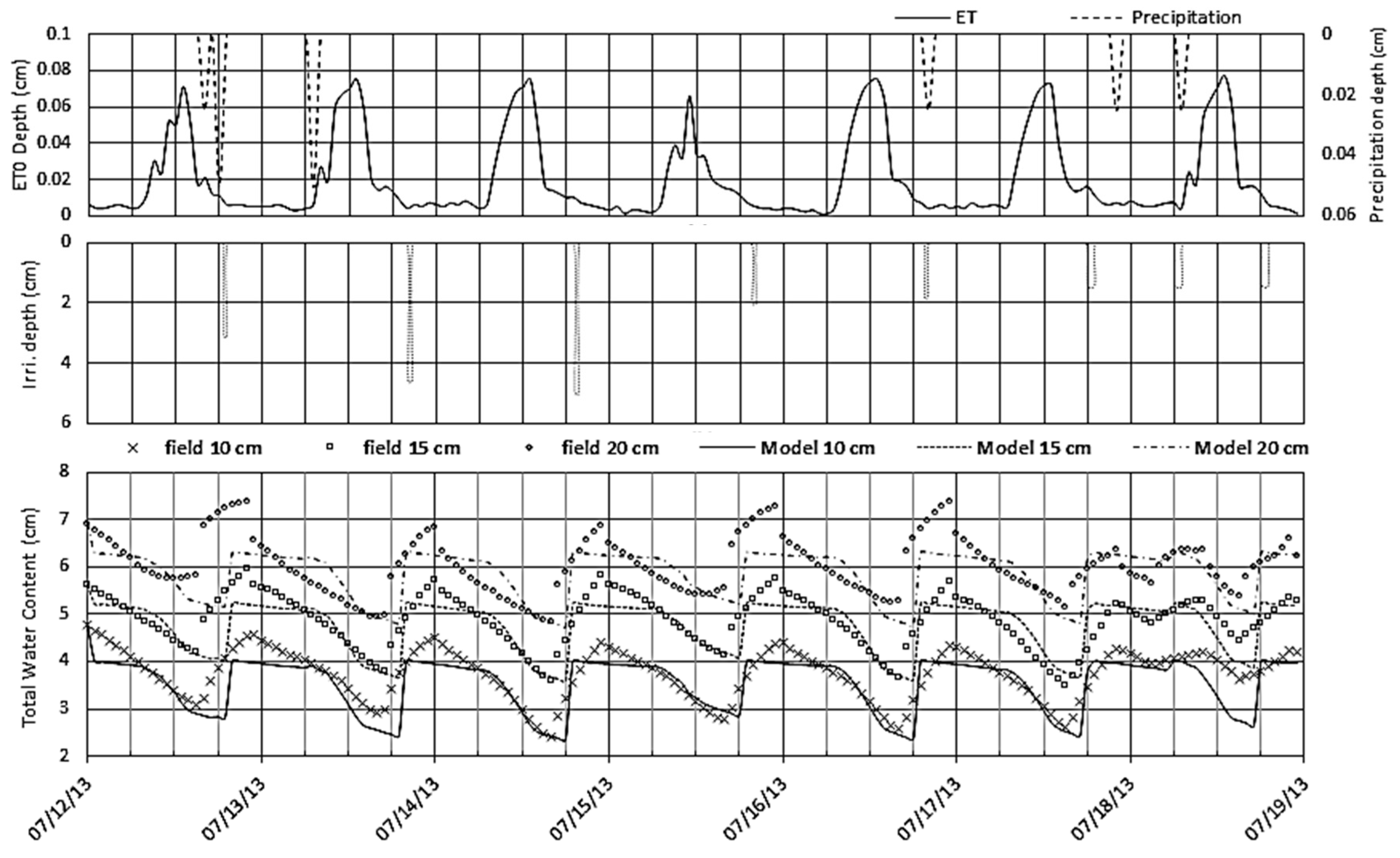
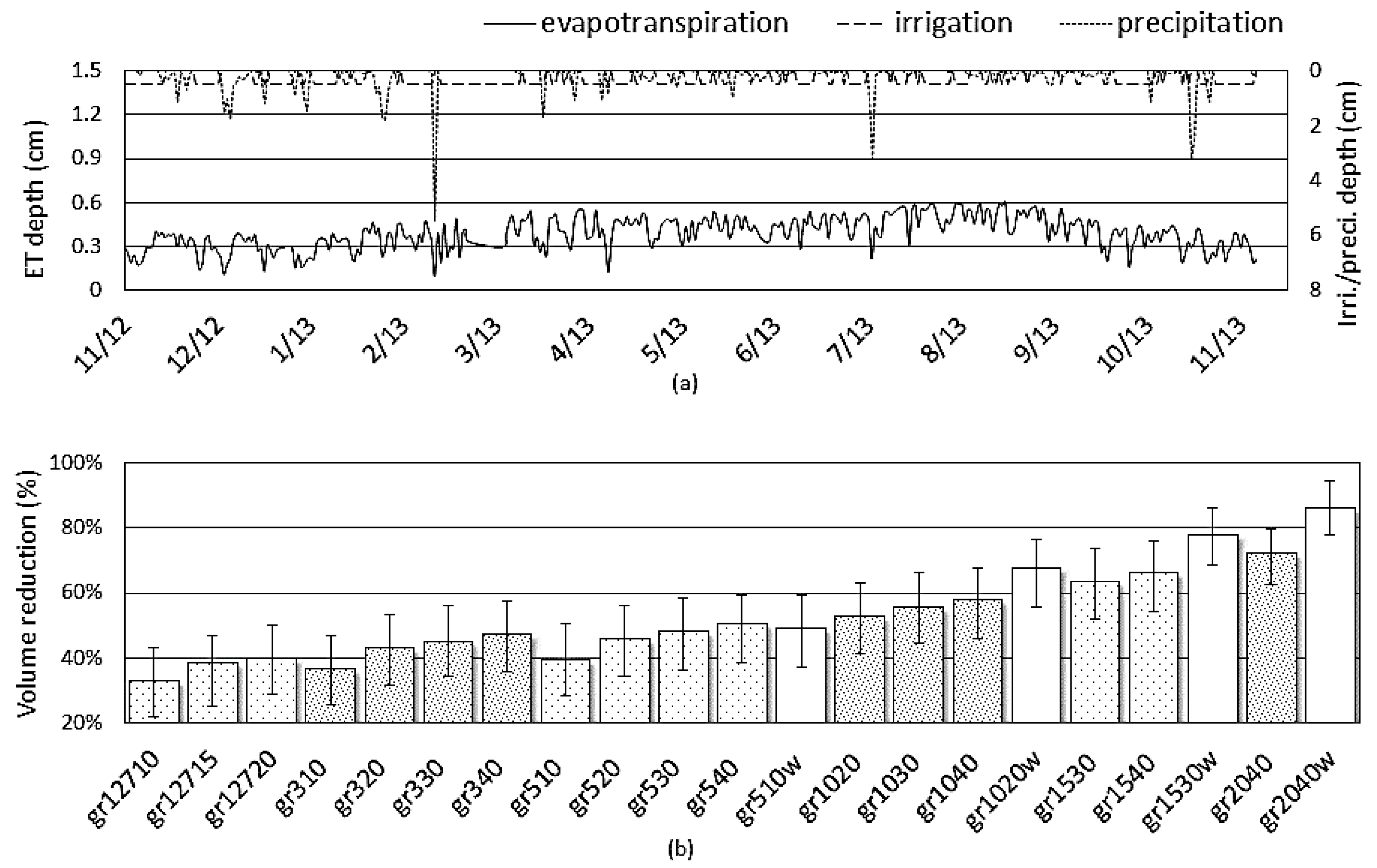
3.1. Pilot Green Roof Experimental Data
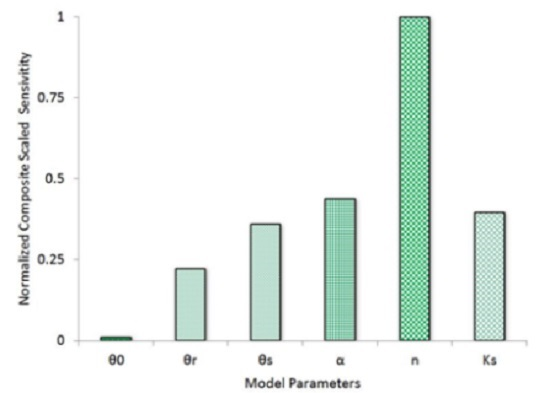
3.2. Calibration and Sensitivity of the Simplified Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Results of 21 Configurations
4.2. Hydrologic Performance Curves
4.3. Hydrologic Performance Simulation Results and Analyses
4.4. Long-Term Runoff Volume Reductions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- What is Green Infrastructure. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/green-infrastructure/what-green-infrastructure#Greenroofs (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Li, Y.L.; Babcock, R.W., Jr. Green roof hydrologic performance and modeling: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesuviano, G.; Stovin, V. A Generic hydrological model for a green roof drainage layer. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Guo, Y.P. Analytical probabilistic model for evaluating the hydrologic performance of green roofs. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.P.; Liu, S.G.; Baetz, B.W. Probabilistic rainfall-runoff transformation considering both infiltration and saturation excess runoff generation processes. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredo, K.; Montalto, F.; Goldstein, A. Observed and modeled performances of prototype green roof test plots subjected to simulated low- and high-intensity precipitations in a laboratory experiment. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burszta-Adamiak, E.; Mrowiec, M. Modelling of green roofs’ hydrologic performance using EPA’s SWMM. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, T.; Jackson, C.R. Vegetated roofs for stormwater management at multiple spatial scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, N.A.; Pang, J. Physically based green roof model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versini, P.A.; Ramier, D.; Berthier, E.; de Gouvello, B. Assessment of the hydrological impacts of green roof: From building scale to basin scale. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, L.; Mark, O.; Mikkelsen, P.S.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Jensen, M.B.; Binning, P.J. Modelling of green roof hydrological performance for urban drainaage applications. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3237–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovin, V.; Poe, S.; Berretta, C. A modelling study of long term green roof retention performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 131, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesuviano, G.; Sonnenwald, F.; Stovin, V. A two-stage storage routing model for green roof runoff detention. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Babcock, R.W., Jr. Modeling hydrologic performance of a green roof system with HYDRUS-2D. J. Environ. Eng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londra, P.A. Simultaneous determination of water retention curve and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity of substrates using a steady-state laboratory method. HortScience 2010, 45, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.C. Methods and Guidelines for Effective Model Calibration; Water Resources Investigation Report 98-4005; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1998.
- Walesh, S.G. Urban Surface Water Management; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Valparaiso, IN, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kasmin, H.; Stovin, V.R.; Hathway, E.A. Towards a generic rainfall-runoff model for green roofs. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, T.B.; Marasco, D.E.; Culligan, P.J.; McGillis, W.R. Hydrological performance of extensive green roofs in New York City: Observations and multi-year modeling of three full-scale systems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassman-Beck, E.; Voyde, E.; Simcock, R.; Hong, Y.S. 4 Living roofs in 3 locations: Does configuration affect runoff mitigation? J. Hydrol. 2013, 490, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED). LEED® for New Construction & Major Renovations. Available online: http://www.usgbc.org/Docs/Archive/General/Docs1095.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2016).
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56. Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/x0490e/x0490e00.htm (accessed on 10 August 2016).
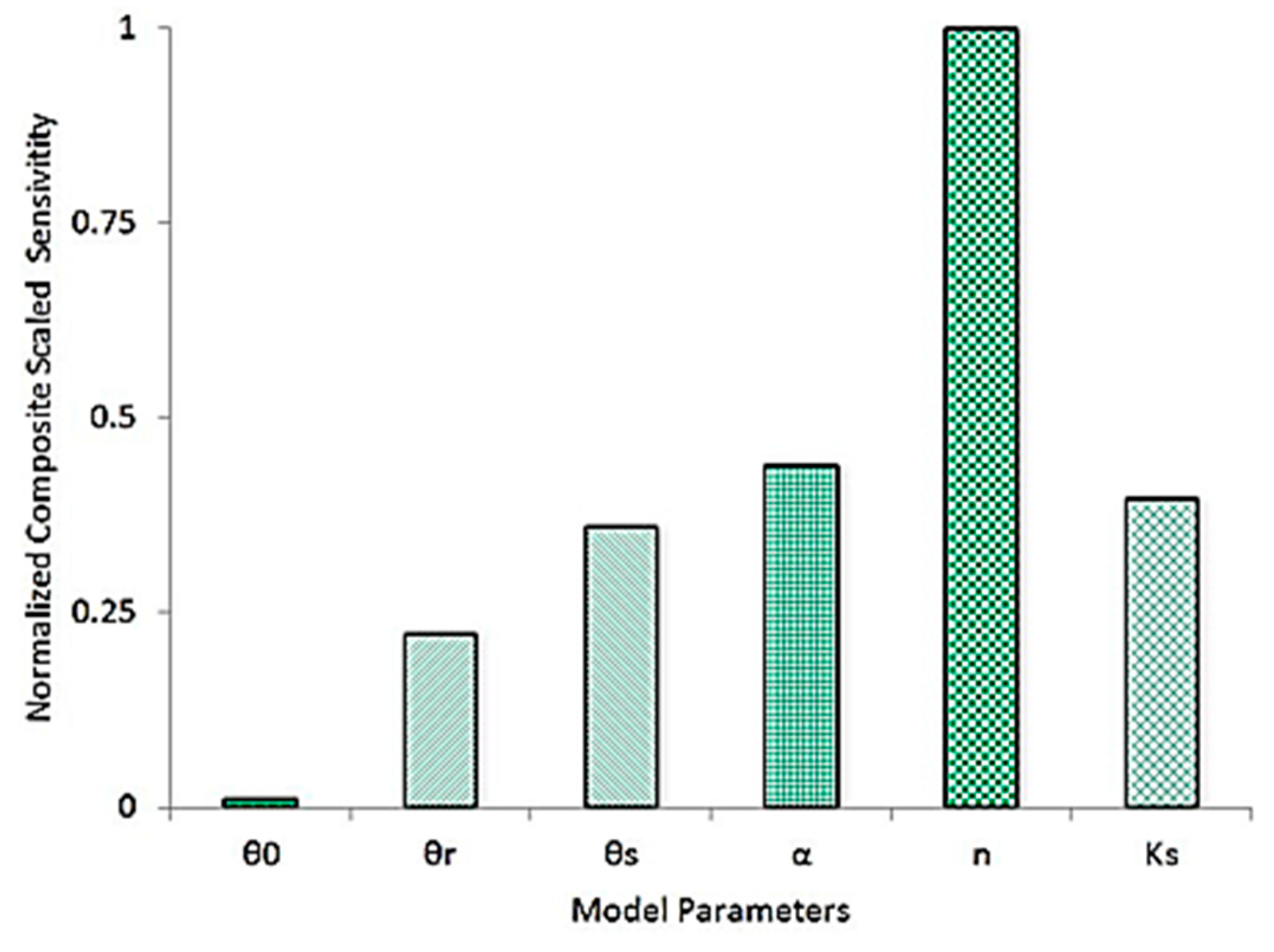

| Variable | θr | θs | α | n | Ks | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | cm3/cm3 | cm3/cm3 | cm−1 | - | cm/min | - |
| Lab Measurement | 0.05–0.16 | 0.55–0.82 | 0.19–0.37 | 1.71–2.17 | 8.00–10.00 | 0.50 |
| Calibration Simplified Model | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.29 | 1.80 | 10.00 | 0.50 |
| Design | H1 | H2 | fa | fb | fw | Ce | Ct | Cm | Rv * | Rp * | Rt * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm | cm | - | - | - | cm | cm | cm | % | % | % | |
| gr12710 | 1.27 | 10 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 2.12 | 3.4 | 5.52 | 12.77 | 33.52 | 1.01 |
| gr12715 | 1.27 | 15 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 2.83 | 5.43 | 8.26 | 17.05 | 36.60 | 1.55 |
| gr12720 | 1.27 | 20 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 3.43 | 7.58 | 11.01 | 20.08 | 40.59 | 1.97 |
| gr310 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2.61 | 2.88 | 5.49 | 18.20 | 36.12 | 2.07 |
| gr320 | 3 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4.03 | 6.95 | 10.98 | 26.76 | 40.85 | 2.13 |
| gr330 | 3 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5.03 | 11.44 | 16.47 | 31.33 | 53.24 | 2.71 |
| gr340 | 3 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5.82 | 16.14 | 21.96 | 34.18 | 65.05 | 3.54 |
| gr510 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3.14 | 2.35 | 5.49 | 23.14 | 28.19 | 1.49 |
| gr510w | 5 | 10 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 5.59 | 1.70 | 7.29 | 41.46 | 65.50 | 5.96 |
| gr520 | 5 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4.69 | 6.29 | 10.98 | 33.14 | 52.38 | 2.74 |
| gr530 | 5 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5.76 | 10.71 | 16.47 | 38.41 | 70.40 | 4.56 |
| gr540 | 5 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 6.58 | 15.38 | 21.96 | 41.41 | 79.13 | 6.69 |
| gr1020 | 10 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 6.72 | 4.26 | 10.98 | 48.76 | 83.48 | 10.74 |
| gr1020w | 10 | 20 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 11.00 | 3.59 | 14.59 | 81.93 | 94.95 | 71.12 |
| gr1030 | 10 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7.98 | 8.49 | 16.47 | 55.77 | 89.55 | 22.37 |
| gr1040 | 10 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8.90 | 13.06 | 21.96 | 59.82 | 91.88 | 30.99 |
| gr1530 | 15 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 10.15 | 6.32 | 16.47 | 72.48 | 93.78 | 56.49 |
| gr1530w | 15 | 30 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 16.23 | 5.65 | 21.88 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.98 |
| gr1540 | 15 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 11.21 | 10.75 | 21.96 | 77.72 | 94.84 | 68.07 |
| gr2040 | 20 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 13.47 | 8.49 | 21.96 | 93.24 | 98.27 | 89.10 |
| gr2040w | 20 | 40 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 21.36 | 7.82 | 29.18 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.98 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Babcock, R.W. A Simplified Model for Modular Green Roof Hydrologic Analyses and Design. Water 2016, 8, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080343
Li Y, Babcock RW. A Simplified Model for Modular Green Roof Hydrologic Analyses and Design. Water. 2016; 8(8):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080343
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanling, and Roger W. Babcock. 2016. "A Simplified Model for Modular Green Roof Hydrologic Analyses and Design" Water 8, no. 8: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080343
APA StyleLi, Y., & Babcock, R. W. (2016). A Simplified Model for Modular Green Roof Hydrologic Analyses and Design. Water, 8(8), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080343