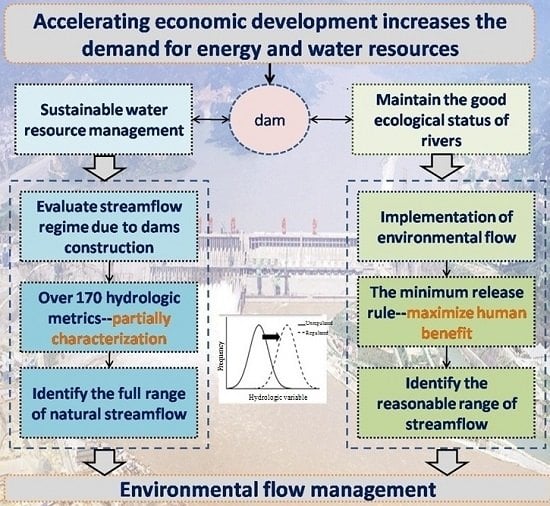
Hydrologic Alteration Associated with Dam Construction in a Medium-Sized Coastal Watershed of Southeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Method
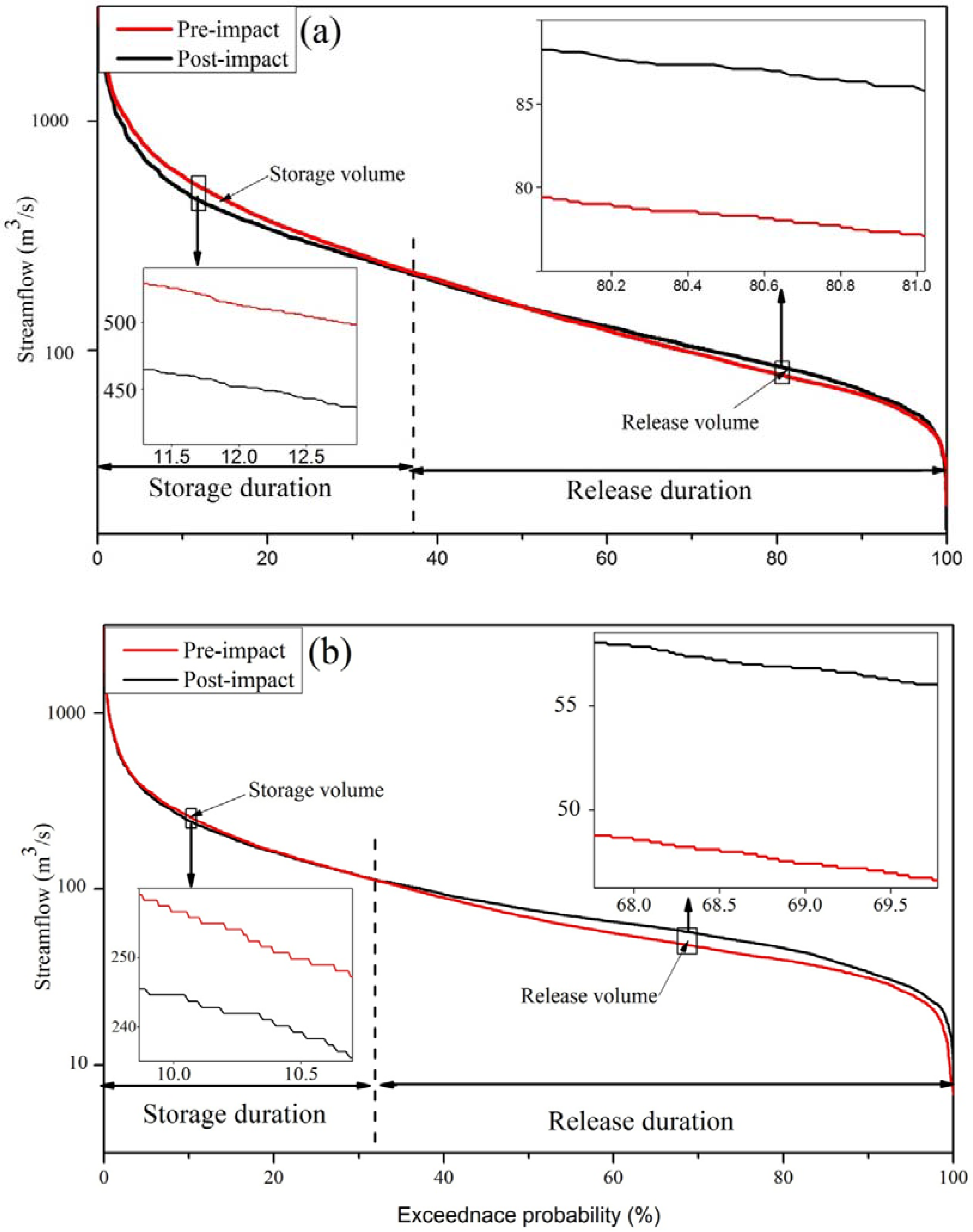
2.3.1. Flow Duration Curve Analysis (FDC)
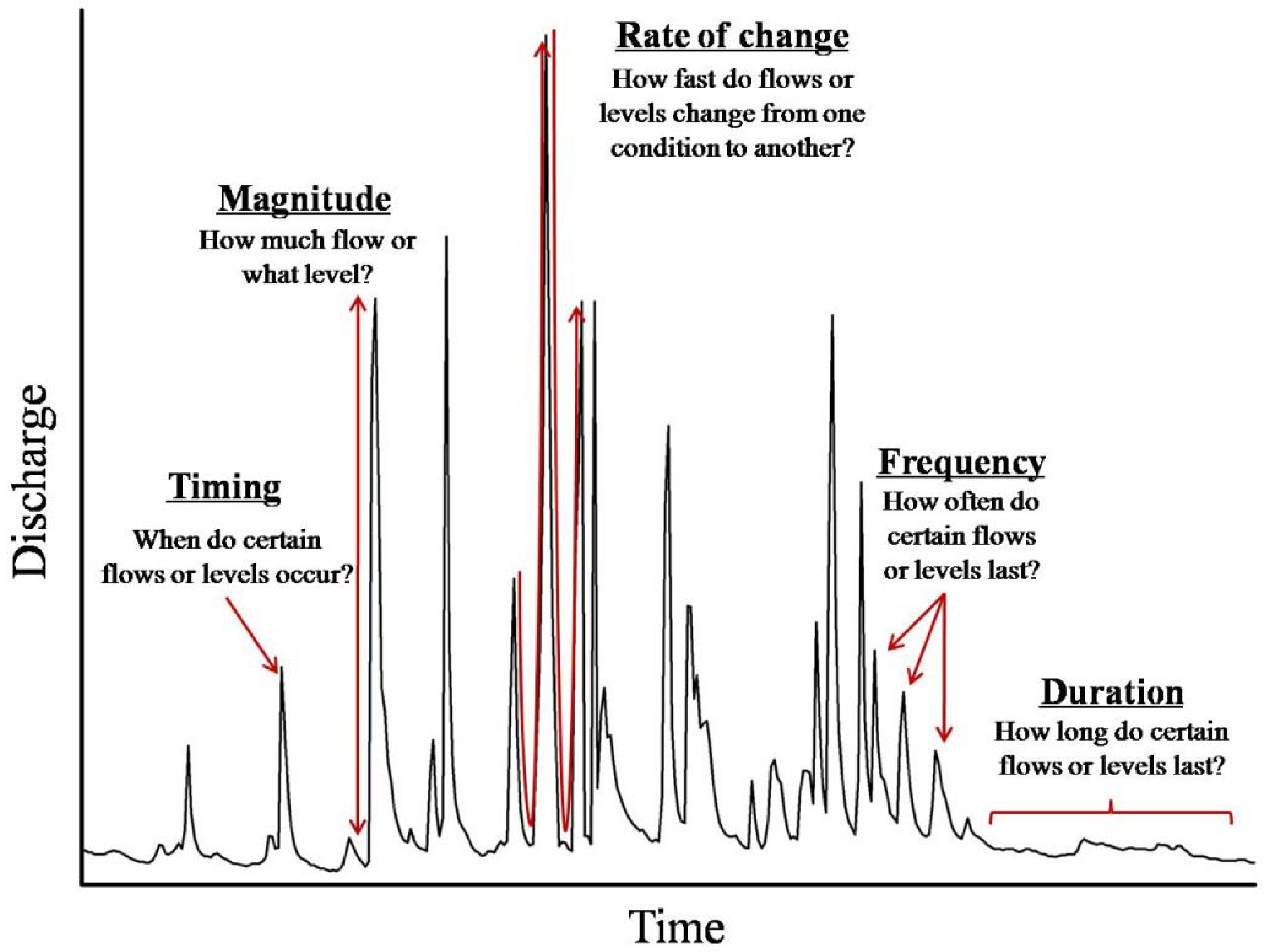
2.3.2. Indicators of Hydrologic Alteration (IHA)
2.3.3. Range of Variability Approach (RVA)
2.3.4. Method for Measuring Environmental Flow
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
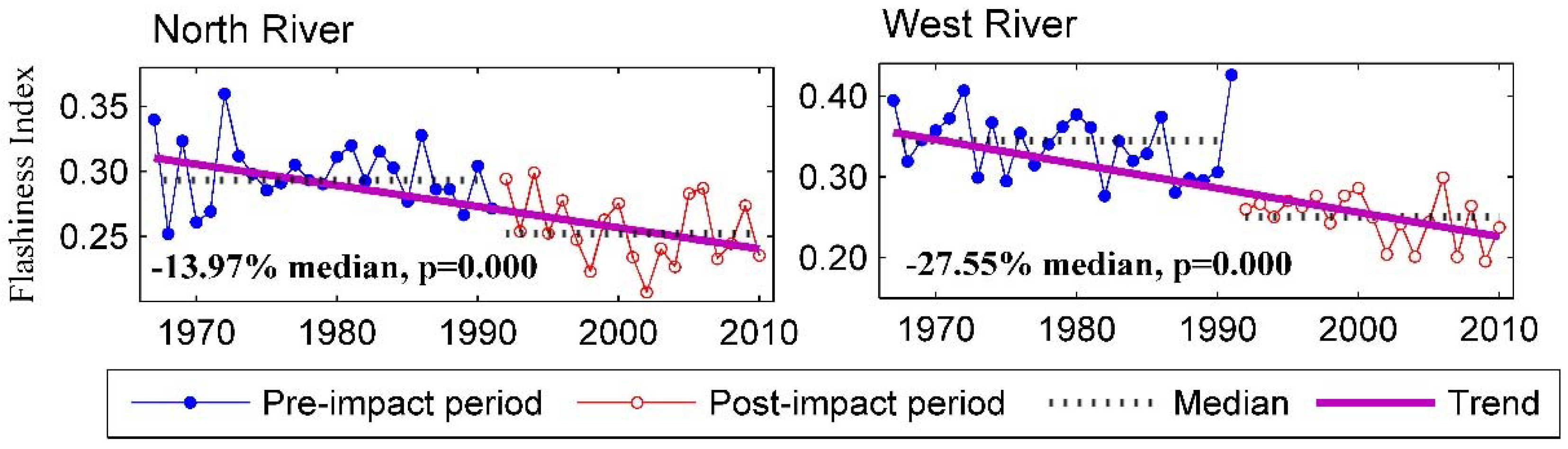
3.1. Overall Hydrologic Impact Assessment
3.2. Hydrologic Regime Changein a Full Range
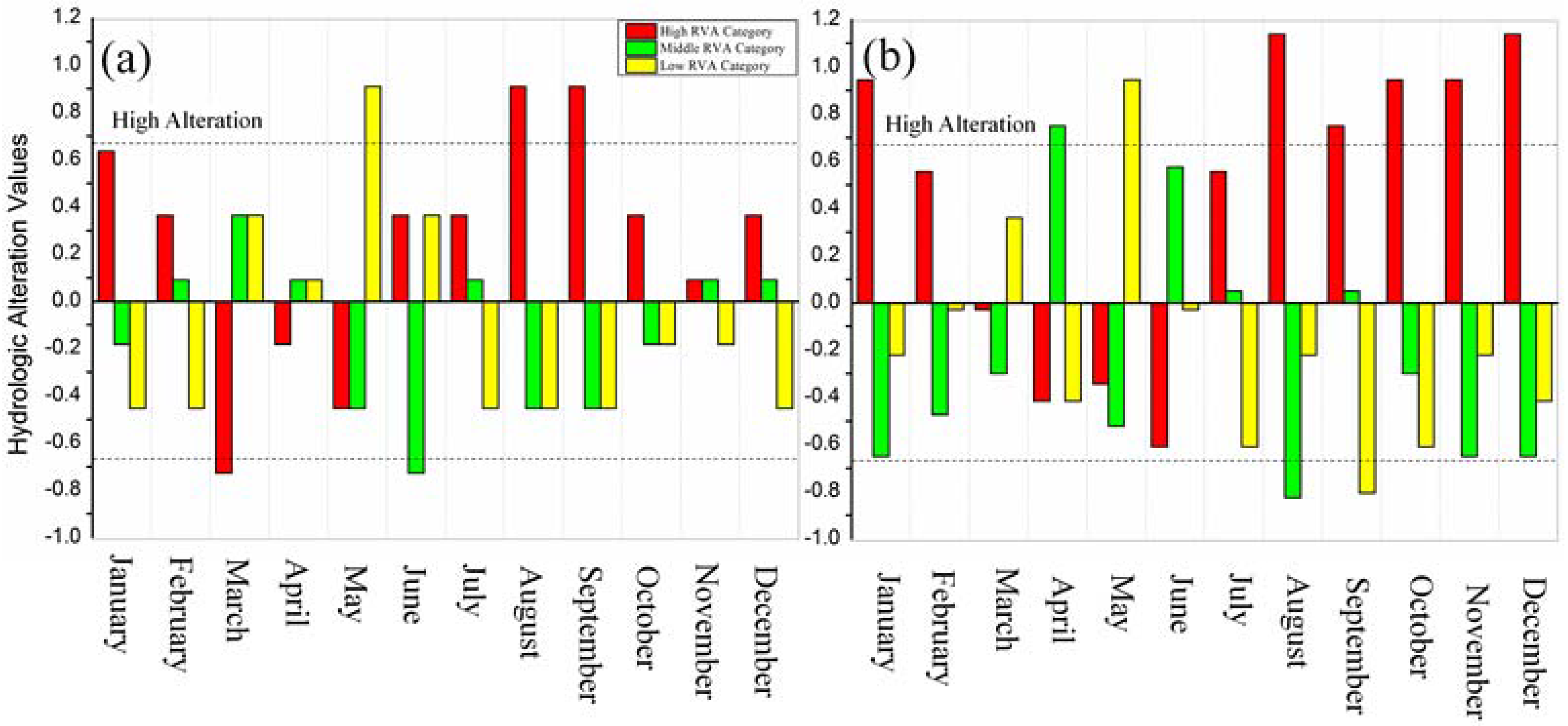
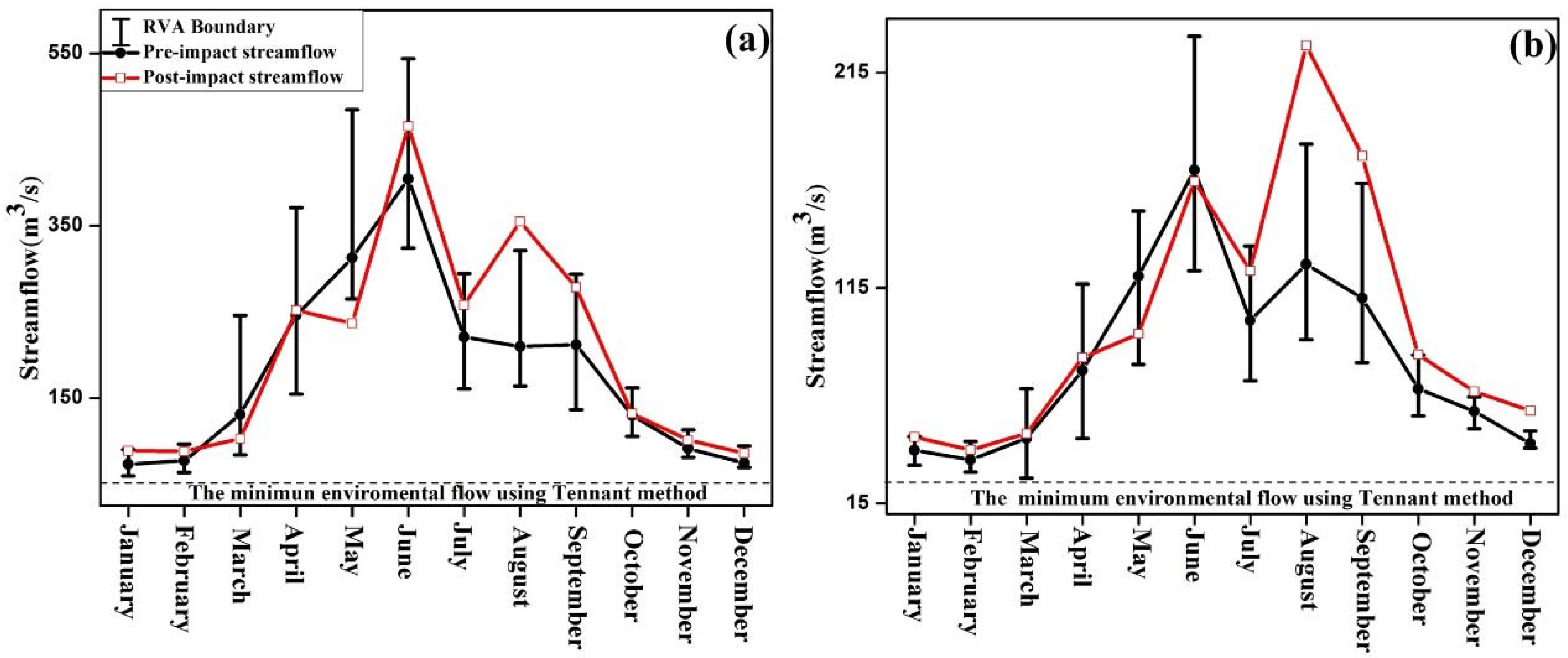
3.2.1. Magnitude of Monthly Streamflow Regime
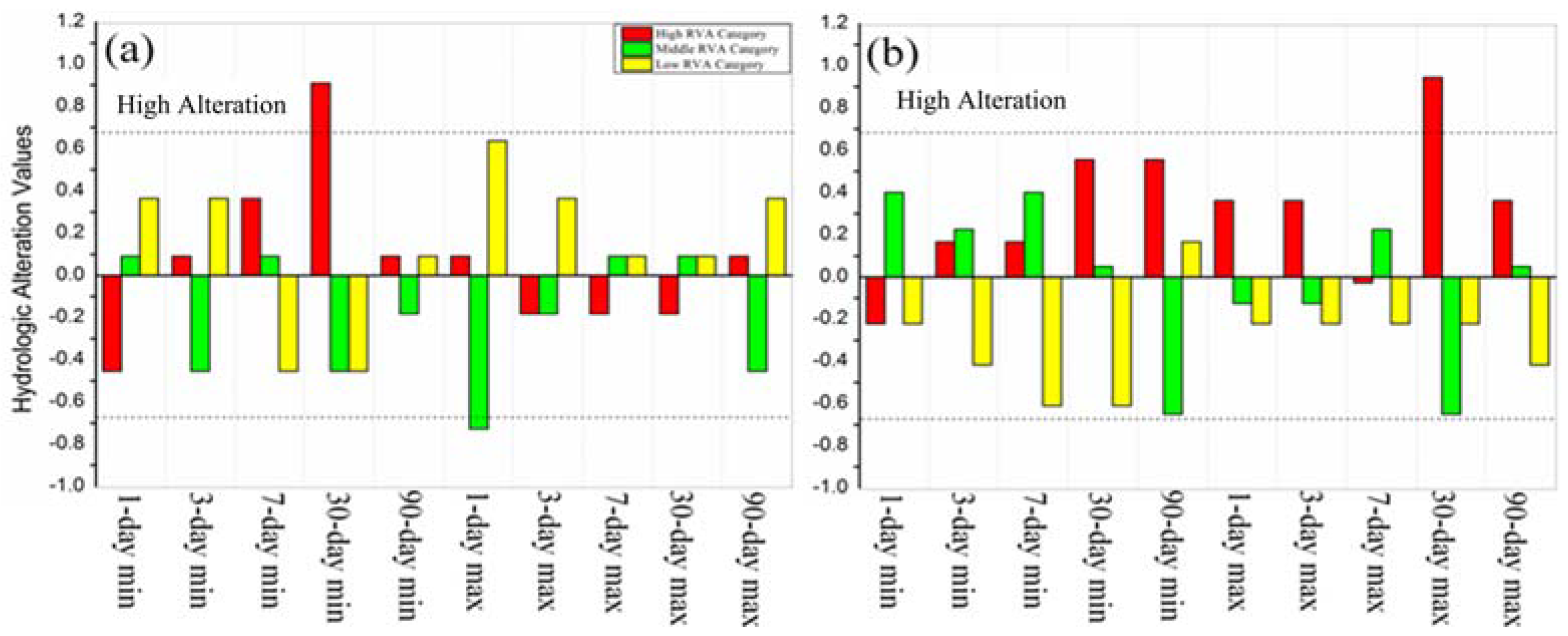
3.2.2. Magnitude, Duration and Timing of Extreme Streamflow Regime
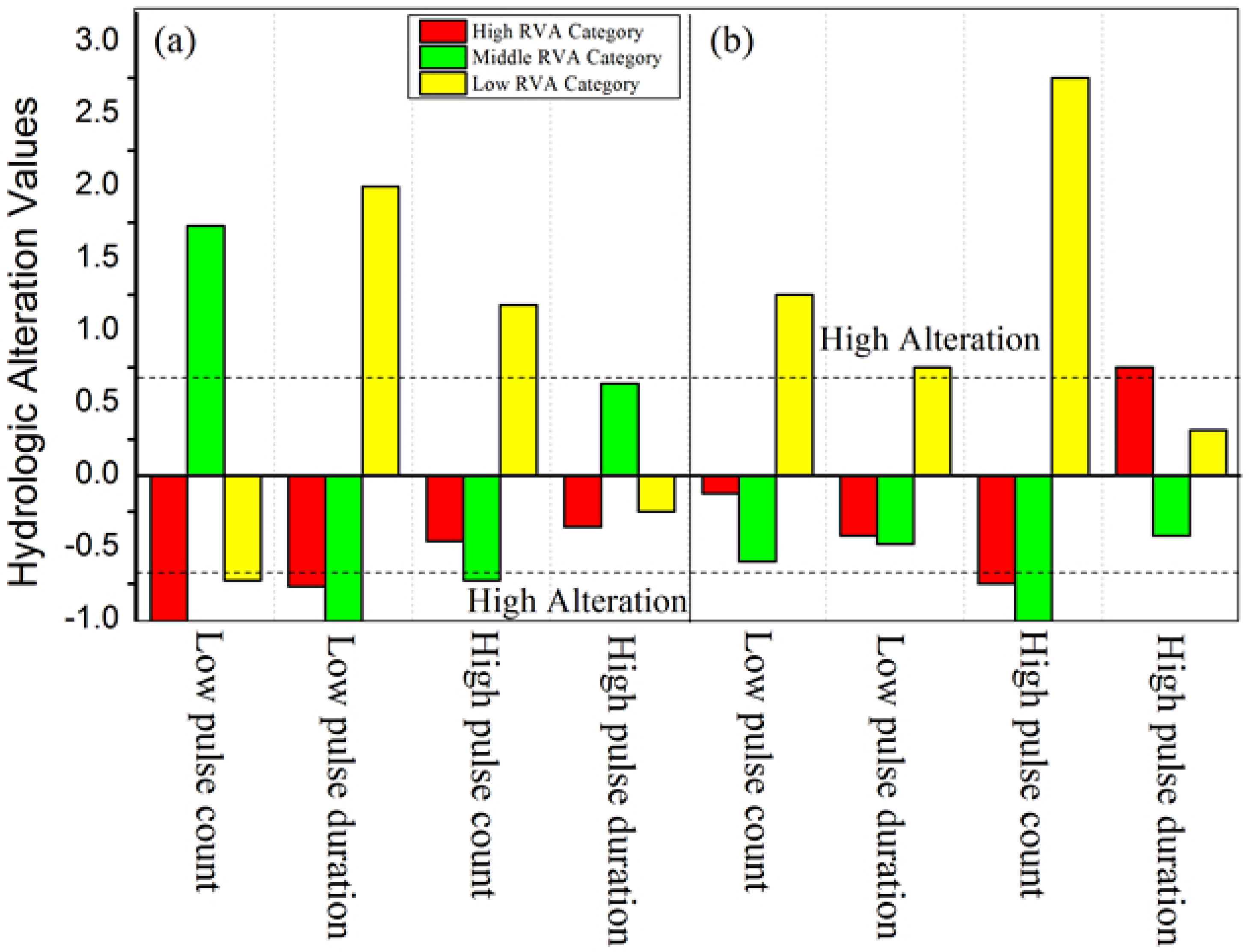
3.2.3. Frequency and Duration of High and Low Pulses
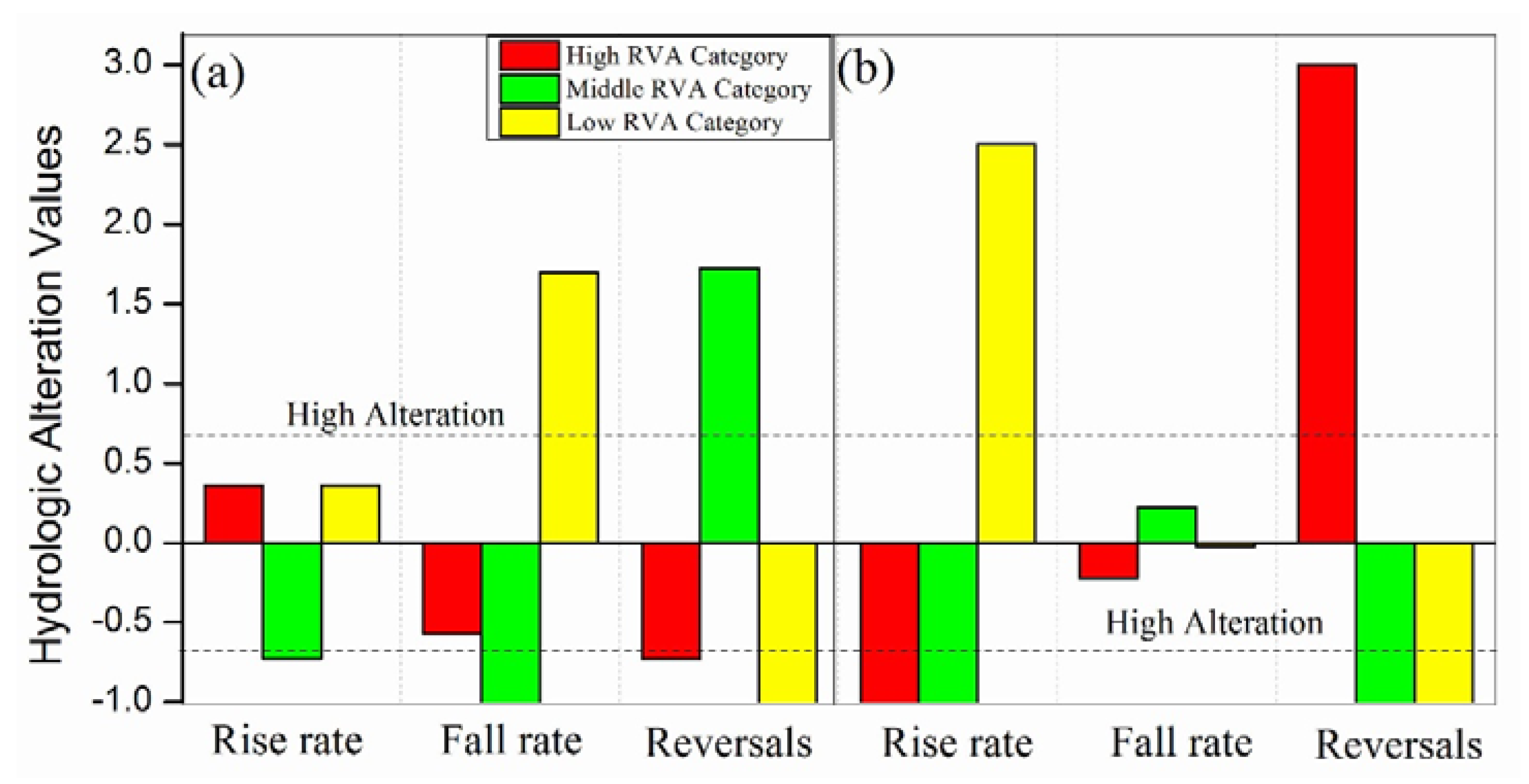
3.2.4. Rate and Frequency of Streamflow Regime Change
3.3. The Possible Suitable Range of Streamflow Regime
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Impact of Streamflow Regulation on Flow Regimes
4.2. Magnitude of Monthly Streamflow Regime
4.3. Magnitude, Duration and Timing of Extreme Streamflow Regime
4.4. Pulse, Rate and Frequency Change
4.5. Feasible Streamflow Regime in JRW
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Spark, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime: A paradigm for river conservation and restoration. BioScience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripl, W. Water: The bloodstream of the biosphere. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2003, 358, 1921–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Feng, Y.; Hong, H.S. Hydrologic response to climate change and human activities in a subtropical coastal watershed of southeast China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Andrew, T.; Warner, J.L.; Meyer, K. A collaborative and adaptive process for developing environmental flow recommendations. River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Olden, J.D.; Merritt, D.M.; Pepin, D.M. Homogenization of regional river dynamics by dams and global biodiversity implications. PNAS 2007, 104, 5732–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.K. Multi-scale entropy analysis of Mississippi River flow. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2008, 22, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Yang, T.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Hao, Z.C. Hydrologic alteration along the middle and upper East River (Dongjiang) basin, South China: A visually enhanced mining on the results of RVA method. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 24, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, D.; Zhao, T.T.G.; Yang, H.B. Changes in the eco-flow metrics of the upper Yangtze River from 1961 to 2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448–449, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flug, M.; Seiz, H.L.H.; Scott, J.F. Multicriteria decision analysis applied to Glen Canyon dam. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2000, 126, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, C.M.; Stoudt, R.T. Dam-induced modifications to upper Allegheny River streamflow patterns and their biodiversity implications. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2002, 38, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.T.; Wu, F.C. Assessment of hydrologic alterations caused by Chi-Chi diversion weir in Chou-Shui Creek, Taiwan: Opportunities for restoring natural flow conditions. River Res. Appl. 2004, 20, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Liu, S.L.; Deng, L.; Dong, S.K.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.F.; Yang, J.J. Landscape change and hydrologic alteration associated with dam construction. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 16, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, K.H.; Daniels, M.D. Damming the prairie: Human alteration of Great Plains river regimes. J. Hydrol. 2012, 444–445, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losos, E.; Hayes, J.; Phillips, A.; Wilcove, D.; Alkire, C. Taxpayer-subsidized resource extraction harm species: Double jeopardy. Bioscience 1995, 45, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trush, W.J.; McBain, S.M.; Leopold, L.B. Attributes of an alluvial river and their relation to water policy and management. PNAS 2000, 97, 11858–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManamay, R.Y.; Orth, D.J.; Dolloff, C.A. Revisiting the homogenization of dammed rivers in the southeastern US. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, S.E.; Arthington, A.H. Basic principles and ecological consequences of altered flow regimes for aquatic biodiversity. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B.; Mount, J.F. Homogenous rivers, homogeneous fauna. PNAS 2007, 104, 5711–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, R.; Nilsson, C.; Renofalt, B. Fragmentation of riparian floras in rivers with multiple dams. Ecology 2000, 81, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovanec, A.; Schiemer, F.; Waibacher, H.; Spolwind, R. Rehabilitation of a heavily modified river section of the Danube in Vienna (Austria): Biological assessment of landscape linkages on different scales. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2002, 87, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Stanford, J.A. Riverine flood plains: Present state and future trends. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J.D.; Poff, N.L. Redundancy and the choice of hydrologic indices for characterizing stremflow regimes. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D. River rehabilitation for conservation of fish biodiversity in monsoonal Asia. Ecol. Soc. 2005, 10, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.W.; Wang, G.X.; Deng, W.; Li, S.N. The influence of dams on ecohydrological conditions in the Huaihe River basin, China. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 33, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilhofer, P.; de Moura, R.M. Hydrological changes in the northern Pantanal caused by the Manso dam: Impact analysis and suggestions for mitigation. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Q. Assessment of the flow regime alterations in the lower Yellow River, China. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 10, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgarter, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, R.; Richter, B.D. Application of the indicators of hydrologic alteration software in environmental flow setting. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.Q.; You, J.Y.; Sparks, R.; Demissie, M. Impact of human activities to hydrologic alterations on the Illiois River. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.M.; Sieber, J.; Archfield, S.A.; Smith, M.P.; Apse, C.D.; Huber-Lee, A. Relations among storage, yield and instream flow. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W05403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. Assessment of flow regulation effects by dams in the Han River, Korea, on the downstream flow regimes using SWAT. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2012, 138, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Western, A.W.; McMahon, T.A.; Zhang, L. Impact of forest cover changes on annual stramflow and flow duration curves. J. Hydrol. 2013, 483, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreman, M.C.; Ferguson, A.J.D. Environmental flows and the European Water Framework Directive. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E. Instream flow science for sustainable reiver management. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, I.G.; Biggs, B.J.F. Application of the ‘natural flow paradigm’ in a New Zealand context. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Richter, B.; Arthington, A.; Bunn, S.E.; Naiman, R.J.; Kendy, E.; Acreman, M.; Apse, C.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Freeman, M.; et al. The ecological limits of hydrologic alteration (ELOHA): A new framework for developing regional environmental flow standards. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halleraker, J.H.; Sundt, H.; Alfredsen, K.T.; Dangelmaier, G. Application of multiscale environmental flow methodologies as tools for optimized management of a Norwegian regulated nation salmon water course. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, H.I.; Smith, B.T. Sustainable reservoir operation: Can we generate hydropower and preserve ecosystem values? River Res. Appl. 2008, 24, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Thomas, G.A. Restoring environmental flows by modifyingdam operations. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Naiman, R.J.; Latterell, J.J.; Pettit, N.E.; Olden, J.D. Flow variability and thebiophysical vitality of river systems. C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.A.; Yang, Z.F.; Petts, G.E. Reservoir operating rules to sustain environmental flows in regulated rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W08509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.A.; Yang, Z.F.; Petts, G.E. Optimizing environmental flows below dams. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Poff, N.L.; Naiman, R.J. The challenge of providing environmental flow rules to sustain river systems. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D. Re-thinking environmental flows: From allocations and reserves to sustainability boundaries. River Res. Appl. 2010, 26, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magilligan, F.J.; Nislow, K.H. Long-term changes in regional hydrologic regime following impoundment in a humid-climate watershed. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyron, M.; Neumann, K. Hydrologic alterations in theWabash river watershed, USA. River Res. Appl. 2008, 24, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.H.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Z.H. Restoration of the lower reaches of the Tarim River in China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.J.; Liu, J.T. Impact of large dams on downstream fluvial sedimentation: An example of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) on the Changjiang (Yangtze River). J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räsänen, T.A.; Koponen, J.; Lauri, H.; Kummu, M. Downstream hydrological impacts of hydropower development in the Upper Mekong Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3495–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Q.; Opp, C.; Hennig, T.; Marold, U. Impacts and Implications of major changes caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.M.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J.; Zhang, W. Energy’s thirst for water in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11760–11768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, X.H. The Influence of dam and lakes on the Yangtze River streamflow: Long-range correlation and complexity analyses. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, L.H.; Dong, L.H.; Zhang, J. Effects of Three Gorges reservoir on the hydrologic droughts at the downstream Yichang station during 2003–2011. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3891–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commissionon Dams (WCD). Dams and Development: A New Framework for Decision-Making; Report of the World Commissionon Dams; Earthscan Publishing: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Deitch, M.J.; Merenlender, A.M.; Feirer, S. Cumulative effects of small reservoirs and streamflow in Northern coastal California catchments. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 5101–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). WWF’s Dams Initiative: Rivers at Risk. Available online: http://wwf.panda.org/what_we_do/footprint/water/dams_initiative/ (accessed on 1 July 2012).
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Hong, H. Streamflow variability response to climate change and cascade dams development in a coastal China watershed. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 166, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Braun, D.P.; Powell, J. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1998, 14, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G. River utilization and the preservation of migratory fish life. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1961, 18, 225–244. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, D.L. Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation and related environmental resources. Fisheries 1976, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, I.; Yang, D.Q. Streamflow characteristics and changes in Kolyma basin in Siberia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteau, M.; Assani, A.A.; Mesfioui, M. Application of multivariate statistical analysis methods to the dams hydrologic impact studies. J. Hydrol. 2009, 371, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Walker, J.F.; Day, J.C.; Kallio, R. The Influence of Man on Hydrological Systems; Wolman, M.G., Riggs, H.C., Eds.; Surface Water Hydrology, Geological Society of America, Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford, J.A.; Ward, J.V.; Liss, W.J.; Frissell, C.A.; Williams, R.N.; Lichatowich, J.A.; Coutant, C.C. A general protocol for restoration of regulated rivers. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. 1996, 12, 391–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, W.L. Damage control: Restoring the physical integrity of America’s rivers. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2001, 91, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.B.; Richards, R.P.; Loftus, T.T.; Kramer, J.W. A new flashiness index: Characteristics and applications to Midwestern rivers and streams. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 40, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.T.; Wu, F.C. Feasible diversion and instream flow release using range of variability approach. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magilligan, F.J.; Nislow, K.H. Changes in hydrologic regime by dams. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Satio, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, X. Interannual and seasonal variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) water discharge over the past 50 years: Connections to impacts from ENSO events and dams. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 50, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Tao, X.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, X. A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration caused by dam construction in the middle and lower Yellow River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3829–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
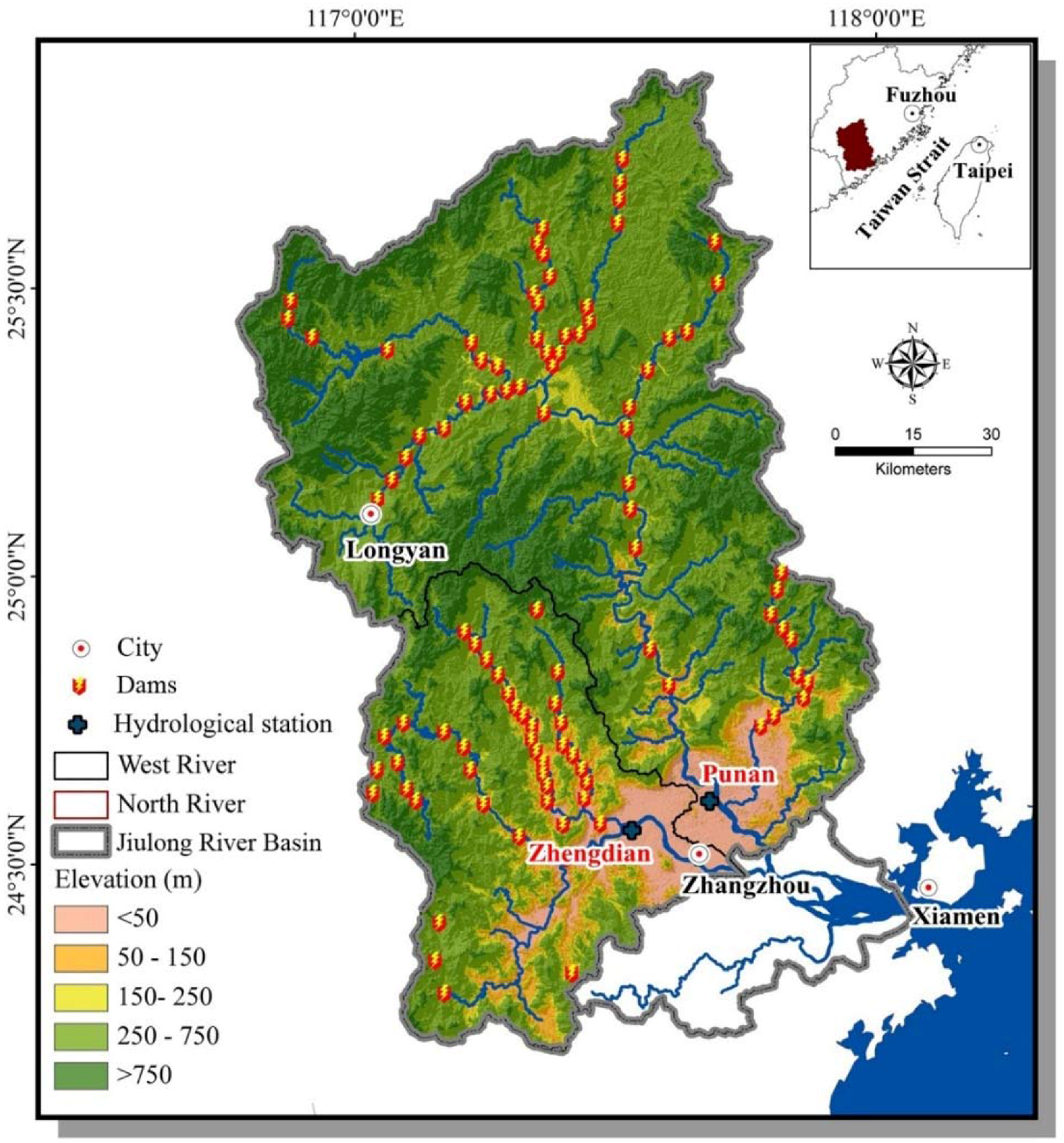

| Station | Longitude | Latitude | Discharge Area (km2) | Length(km) | Number of Dams Upstream from Stations | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Punan (North River) | 117.67° E | 24.61° N | 9640 | 274 | 87 | 1967–1999 | 2000–2010 |
| Zhengdian (West River) | 117.53° E | 24.56° N | 3940 | 172 | 37 | 1967–1994 | 1995–2010 |
| Two Reaches | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | April | May | Jun. | Jul. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North River | 10.5 | −12.1 | −37.7 | −10.1 | −33.4 * | 6.4 | 21.6 | 17.4 | 10.7 | 6.2 | 4.8 | 10.7 |
| West River | 18.7 * | −13.3 | −14.1 | −19.1 | −23.2 | −8 | 30.3 | 54.2 * | 25.3 | 28 | 11.1 | 20.9 * |
| Two Reaches | Pre-Impact Min Q | Post-Impact Min Q | Pre-Impact Max Q | Post-Impact Max Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NorthRiver | 34.0 | 33.0 | 171.0 | 189.0 |
| West River | 64.5 | 50.5 | 211.5 | 215.0 |
| Two Reaches | 1-Day Min | 3-Day Min | 7-Day Min | 30-Day Min | 90-Day Min | 1-Day Max | 3-Day Max | 7-Day Max | 30-Day Max | 90-Day Max | BFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North River | −20.3 | −5.9 | 7.2 | 10.4 | −0.4 | −9.6 | −7.4 | −6.6 | −7.5 | −8.2 | 18.8 * |
| West River | 8 | 11.7 | 13.7 | 12.7 | 7.1 | 6 | −2.1 | −0.2 | 8 | 9.8 | 17.7 |
| Two Reaches | Low Pulse Count | Low Pulse Duration | High Pulse Count | High Pulse Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North River | 101.8 ** | −62.1 ** | −21.4 * | 19.2 * |
| West River | −15.5 | −29.0 | −37.1 ** | 6.7 |
| Two Reaches | Rise Rate | Fall Rate | Number of Reversals |
|---|---|---|---|
| North River | −26.9 * | 28.3 * | 40.7 ** |
| West River | −61.0 ** | 0.8 | 46.4 ** |
| Hydrologic Parameters | North River | West River | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVA Range | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | RVA Range | Pre-Impact | Post-Impact | |
| Rise rate | 16.0~33.5 | 24.0 | 17.6 | 10.1~19.8 | 15.2 | 5.9 |
| Fall rate | −17.5~−12.2 | −15.0 | −19.2 | −8.4~−5.5 | −7.1 | −7.2 |
| Number of Reversals | 103.0~137.0 | 119.9 | 168.7 | 98.3~108.8 | 106.7 | 156.2 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J. Hydrologic Alteration Associated with Dam Construction in a Medium-Sized Coastal Watershed of Southeast China. Water 2016, 8, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080317
Zhang Z, Huang Y, Huang J. Hydrologic Alteration Associated with Dam Construction in a Medium-Sized Coastal Watershed of Southeast China. Water. 2016; 8(8):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080317
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenyu, Yaling Huang, and Jinliang Huang. 2016. "Hydrologic Alteration Associated with Dam Construction in a Medium-Sized Coastal Watershed of Southeast China" Water 8, no. 8: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080317
APA StyleZhang, Z., Huang, Y., & Huang, J. (2016). Hydrologic Alteration Associated with Dam Construction in a Medium-Sized Coastal Watershed of Southeast China. Water, 8(8), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080317