Abstract
In this study, the contribution of liquid and powder detergents to the composition of domestic laundry graywater was evaluated. Dosages recommended by the manufacturers were used to prepare detergent solutions and generate laundry graywater. Solutions and graywater were characterized in terms of total solids (TS), total suspended solids (TSS), total dissolved solids (TDS), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total organic carbon (TOC), and concentration of Linear Alkylbenzene Sulfonates (LAS’s). Additionally, the effect of the type of detergent on the treatment performance was also assessed. The coagulation–flocculation process was selected as a potential alternative for treating domestic laundry graywater. Treatment performance was assessed based on the removals of TS, TSS, TDS, turbidity, COD, and electrical conductivity (EC). Optimum coagulant dosages and mixing conditions for flocculation were determined. The results indicate a differential contribution of the type of detergent to the domestic laundry graywater composition. Liquid detergents contributed with more COD and TOC and fewer solids and LAS’s, in comparison with powder detergents. Soiled clothes increased the solids and organic loads of laundry graywater; furthermore, the laundry process reduced the LAS concentration of graywater by 77% for the liquid detergent and 47% for the powder detergent. On the other hand, the coagulation–flocculation process was more effective in treating powder detergent graywater even though the liquid detergent graywater was less polluted. Removal efficiencies on the order of 95% for turbidity and 75% for TSS were achieved for powder detergent graywater; meanwhile, for liquid detergent graywater, the removals were 73% for turbidity and 51% for TSS.
1. Introduction
The use of detergents in washing and cleaning processes is so familiar and normal in our modern lifestyle that we do not pay attention to the way we use such substances. The indiscriminate and intensive use of detergents has caused the disposal of huge amounts of xenobiotic compounds into water and soil environments. Graywater from domestic laundry is one of the major contributors of surfactants contained in domestic wastewater. The washing process represents a complex interaction between soiled laundry, water, mechanical and thermal energy, and detergents. Graywater is a troublesome byproduct that has the potential to cause a number of undesirable effects in sewage treatment plants and in the environment. Virtually all of the clean water brought into the process is later released to the sewage system in the form of contaminated wastewater containing additional energy, soil from laundry, lint, dyes, finishing agents, and detergents. Detergent components are released into the wastewater either in an essentially unchanged form or as the products of reaction with other materials present [1].
Laundry graywater varies considerably in concentration and composition. These differences arise partly due to variations in laundry soil levels, although washing technology and the composition and amount of added detergent are also significant factors. Little doubt exists that laundry graywater must be generally regarded as a heavily contaminated medium; therefore, it should not be returned to receiving waters in untreated form [1]. Many new technologies have been developed to treat graywater [2,3,4]. The major difficulty in the treatment of graywater is the large variation in its composition. The chemical processes applied to graywater treatment include coagulation, photo-catalytic oxidation, ion exchange, and granular activated carbon [3]. In one study [5], the coagulation process and the magnetic ion exchange resin process were applied to shower graywater treatment. At optimal conditions, coagulation with aluminum salt reduced the chemical oxygen demand (COD) from 791 mg/L to 287 mg/L, the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) from 205 mg/L to 23 mg/L, the turbidity from 46.6 NTU to 4.28 NTU, the total nitrogen (TN) from 18 mg/L to 15.7 mg/L, and the phosphates (PO43−) from 1.66 mg/L to 0.09 mg/L. Chang et al. [6] also investigated the flocculation process for graywater treatment. The COD and the anionic surfactant concentration were reduced by 70% and 90%, respectively. The study demonstrated that the flocculation process alone is not able to reduce the organic substances to the required reuse standard, thereby necessitating the application of biological processes.
On the other hand, water resources have being intensively exploited and polluted, and it is estimated that, in a few years, the level of water stress will be high worldwide [7,8,9,10]. With the pressure on potable water supplies continuing to increase worldwide, interest in the use of alternative water sources, such as recycled wastewater, is also growing [11,12,13]. Graywater treatment and reuse is an important alternative that has recently received considerable attention because the treated effluents can be used as an additional water source to address the demand for clean water [9,14,15]. Graywater, if properly treated, can be reused for non-potable purposes in buildings, irrigation, and other uses that do not require potable water. The level of treatment required depends on the quality of the raw graywater, as well as the intended reuse application.
Thus, the aim of this study is to show how the type of detergent contributes to domestic laundry graywater composition and how that affects treatment performance. To achieve these objectives numerous jar tests were conducted to assess the contribution of the type of detergent to graywater characteristics, select the proper coagulant and its dosage, and determine the optimum mixing intensity and mixing time for conducting the coagulation–flocculation process. The results indicate a differential contribution of the type of detergent to domestic laundry graywater composition. Soiled clothes increased the solids and organic loads of laundry graywater; furthermore, the laundry process reduced the LAS concentration. On the other hand, the coagulation–flocculation process was more effective in treating powder detergent graywater.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Contribution of the Type of Detergent to the Composition of Domestic Laundry Graywater
The effect of the type of detergent on the graywater characteristics was evaluated using liquid and powder detergents. Detergent solutions were prepared by dissolving the recommended dosage of commercial liquid and powder detergents (Ariel®) into deionized water (26.63 g/31.7 L and 23.25 g/31.7 L for liquid and powder detergents, respectively). The solutions were stored at 4 °C until they were characterized. Laundry graywater was prepared by conducting the washing process with the commercial liquid and powder detergents (Ariel®). The washing conditions for each type of detergent ensured homogeneous graywater discharges and characteristics. The amount of water used in each washing cycle and the detergent dosage were determined based on the instructions included in the detergent package (26.63 g/31.7 L for liquid detergent and 23.25 g/31.7 L for powder detergent, respectively). The type and amount of clothes were set to be as identical as possible for all washing cycles. Graywater samples of the first laundry discharge were taken and stored at 4 °C until they were characterized. Detergent solutions and laundry graywater samples were characterized based on the following parameters, total solids (TS), total suspended solids (TSS), total dissolved solids (TDS), total organic carbon (TOC), chemical oxygen demand (soluble: SCOD and particulate: XCOD), and four linear alkylbenzene sulfonates (LAS’s): sodium decylbenzene sulfonate (C10), sodium undecylbenzene sulfonate (C11), sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (C12), and sodium trydecylbenzene sulfonate (C13). TS, TSS, TDS, and COD were determined using standard methods [16]. The total organic carbon (TOC) was measured by using a TOC analyzer (Shimadzu TOC-5000A). The LAS concentrations were determined by solid-phase extraction (SPE) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). An LC10 series liquid chromatographer (Shimadzu) with a fluorescence detector, a Rheodyne Model 7125 injection valve (Rheodyne, Cotati, CA, USA) and a degasser was used. The separation was performed using a Wakopak® WS AS-Aqua column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 mm particle size; Wako Pure Chemicals). The mobile phase consisted on a mixture of acetonitrile and a sodium perchlorate aqueous solution at the ratio of 65/35 (v/v). The flow rate was set at 0.7 mL/min. The fluorescence excitation and emission wavelength were fixed at λex = 221 nm and λem = 284 nm, respectively, and the column temperature was set at 40 °C. Data acquisition and processing were performed using a LC solution system (Shimadzu). With the characterization results, the contribution of the type of detergent to the laundry graywater composition was assessed.
2.2. The Effect of the Type of Detergent on the Graywater Treatment Performance
The effect of the type of detergent on the graywater treatment performance by coagulation–flocculation was assessed based on the removal efficiencies of TSS, TDS, turbidity, electrical conductivity, and total COD. Turbidity and EC were determined by using a Hanna 2100AN turbidimeter and a Hanna HI 98130 potentiometer, respectively. Several jar tests were conducted to determine the optimum coagulation–flocculation conditions. The coagulant type and dosage, the mixing time and intensity for coagulation and flocculation, and the settling time were the variables evaluated. Table 1 summarizes the conditions under which the jar tests were performed. Optimum coagulation–flocculation conditions were determined based on the removal efficiencies obtained for the parameters previously mentioned. Additional analysis was conducted to assess the reuse potential of the treated graywater.

Table 1.
Jar tests conditions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Contribution of the Type of Detergent to the Domestic Laundry Graywater Composition
Figure 1 presents the bulk composition of the detergents solutions prepared based on the dosages recommended by the detergents producer. As seen, the powder detergent (PD) contained more solids than liquid detergent (LD), and the main fraction corresponded to dissolved solids (DS’s) in both detergents. The DS fraction in the liquid detergent was 81%, whereas, in the powder detergent, it was 94%. Regarding the COD load, the liquid detergent COD was 2.3 times greater than the powder detergent load. In both detergents, the soluble fraction (SCOD) was the main constituent, representing approximately 90%. On the other hand, the content of LAS’s was greater in the powder detergent solution, but the distribution of the four types of LAS’s was quite similar in both detergents. TOC load was similar in both detergent solutions.
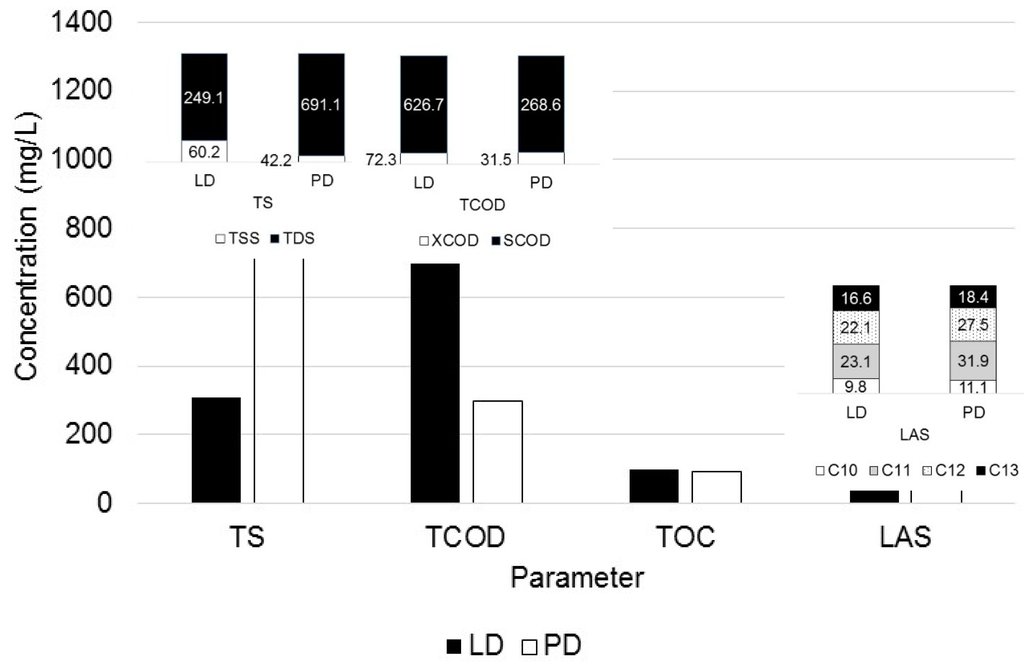
Figure 1.
Composition of liquid (LD) and powder detergent (PD) in recommended dosages. TS: total solids; TCOD: total chemical oxygen demand; TOC: total organic carbon; LAS: linear alkylbenzene sulfonates.
Table 2 summarizes the bulk graywater composition of both detergents based on analysis of 16 samples. The graywater composition was observed to exhibit great variability, as denoted by the significant standard deviation of the parameters values, especially in the case of powder detergent graywater. The great variability of the graywater composition has been reported by several researchers [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. During the laundry process, not only the detergents but also the soil from the clothes contributed to the domestic graywater composition, as seen in Figure 2. Nevertheless, the contribution of the soil was lower than that of the detergents. A differential contribution was observed with regard to detergent type; liquid detergent contributed 83% of TS, 82% of TOC, and 99% of COD, whereas the powder detergent contributed 92% of TS, 86% of TOC, and 63% of COD. Regarding the surfactants contain, the laundry process caused a reduction in LAS’s in the graywater. The LAS reduction, relative to the composition of the detergents solutions, was approximately 77% for the liquid detergent and 47% for the powder detergent. This reduction seems to be associated with the LAS adsorption onto the fibers of the clothes, which are partially desorbed during the rinse cycle. Furthermore, the laundry process not only reduced the LAS’s contained in the detergents but also modified their distribution due to the differential adsorption onto the clothes fibers. The sodium undecylbenzene sulfonate (C11) was less adsorbed onto the fibers; consequently, its proportion in graywater increased for both detergents. It is important to note that the quality of the water source used during the laundry process can also contribute to the composition of graywater, especially in the case of hard water.

Table 2.
Bulk characterization of graywater for two types of detergent (n = 16).
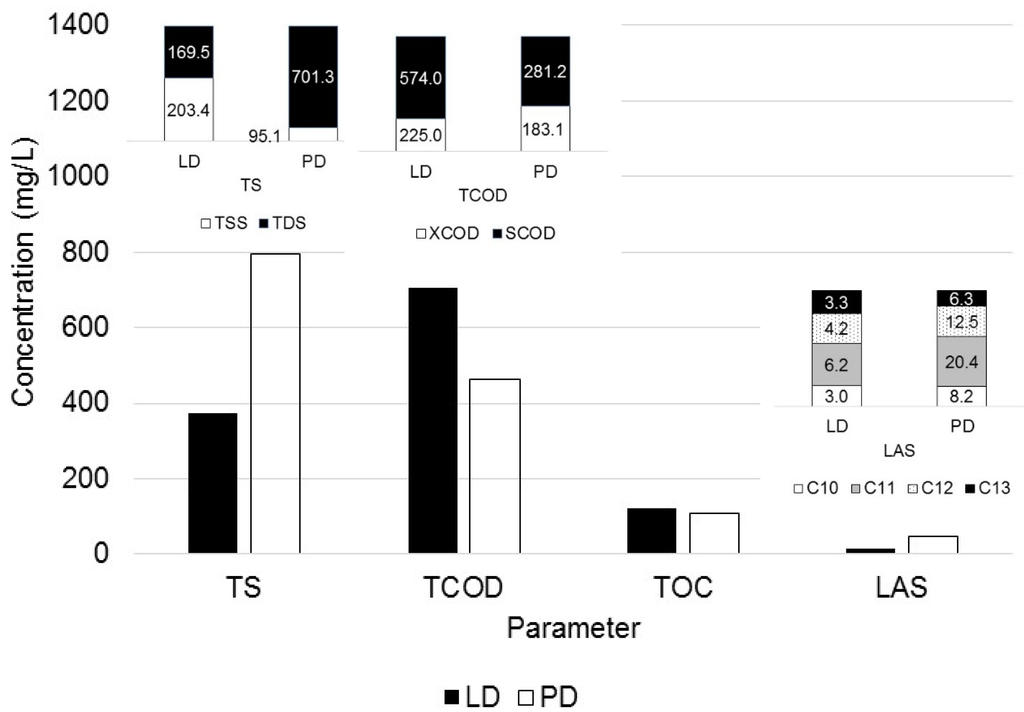
Figure 2.
Composition of laundry graywater for LD and PD.
Since detergents are the main contributor to graywater composition and their contribution is differential depending on the type, it is very important to take into account the way detergents are used and dosed. Detergent overdosing during the laundry process will adversely impact the aquatic environment when graywater is discharged into water bodies without treatment. Undoubtedly, laundry graywater is regarded as heavily contaminated; therefore, it should be treated before it is disposed into receiving waters. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effect of direct raw graywater discharges into the receiving water bodies, especially related to the dilution and self-purifying effects with emphasis on the presence of xenobiotic organic compounds (XOCs), which are hazardous micropollutants in graywater. Since conventional wastewater treatments are not efficient to remove XOCs, future studies should consider chemical treatments, especially advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) that have been found to be effective in mineralizing recalcitrant organic compounds in wastewater [25].
3.2. The Effect of the Type of Detergent on the Graywater Treatment Performance
3.2.1. Coagulant Selection and Dosage Determination
Several jar tests with aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)2) and ferric chloride (FeCl3) were conducted to select the appropriate coagulant for graywater. For aluminum sulfate, well-formed flocs at pH in the range of 6–10 were observed. This result was advantageous because pH adjustment of graywater was not required. On the contrary, the use of ferric chloride required pH adjustment and caused dispersion of the graywater constituents inhibiting settling and increasing turbidity. Thus, aluminum sulfate was selected as coagulant. Similar results were reported in [26].
Once the coagulant was selected, the next step was to set the appropriate coagulant dosage. This was determined by conducting jar tests and evaluating the removal of parameters such as TS, TSS, turbidity, COD, and EC. The results are shown in Figure 3. As seen, the pH of both graywaters decreased as coagulant dosage increased. A pH adjustment of the graywater was not required. The best coagulation performance was obtained for the powder detergent graywater. For TS, the best removal was obtained at a dosage of 205.0 mg/L aluminum sulfate for both graywaters. The removal efficiencies achieved were 42% for the powder detergent and 26% for the liquid detergent graywater. For TSS, the greatest removal was observed at a dosage of 274.0 mg/L aluminum sulfate, but it was not so different for that obtained with 205.0 mg/L aluminum sulfate. The removal efficiencies were 51% for powder detergent and only 8% for liquid detergent graywater. Turbidity exhibited maximum removal efficiencies at a coagulant dosage of 205.0 mg/L aluminum sulfate with values of 65% for powder detergent graywater and 54% for liquid detergent. The COD removal was approximately 60% for powder detergent graywater and 50% for liquid detergent for dosages between 68.0 mg/L and 205.0 mg/L aluminum sulfate; however, at the dosage of 342.0 mg/L, the removal efficiency was approximately 80% for powder detergent graywater. This result is an outlier, so it might not be representative. For electrical conductivity, the removal efficiencies were approximately 33% for powder detergent and 5% for liquid detergent graywater, irrespective of the coagulant dosage. Based on these results, the optimum coagulant dosage was set at 205.0 mg/L aluminum sulfate for both graywaters. It was clear that the type of detergent influenced the coagulation performance. This dosage is greater than those values reported in [5], which were in the order of 24 mg/L aluminum sulfate; however, it is important to remark that the organic loads of graywater used in this study (COD: 1500 ± 406 mg/L for powder detergent and 1086 ± 511 mg/L for liquid detergent graywater) were much higher than that reported by them (791 mg/L). Furthermore, in this study, the pH of the graywater was not adjusted in comparison with the pH of 4.5 they used in their experiments, and the removal efficiencies were on the same order: 60%. An adjustment of process pH may signify a problem in practical applications.
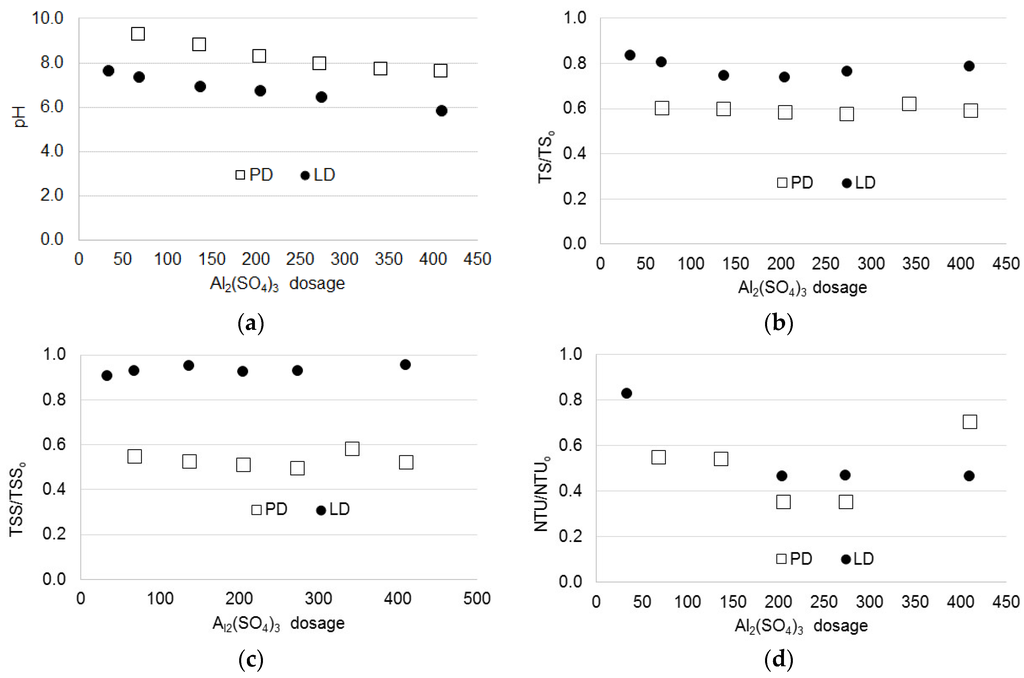
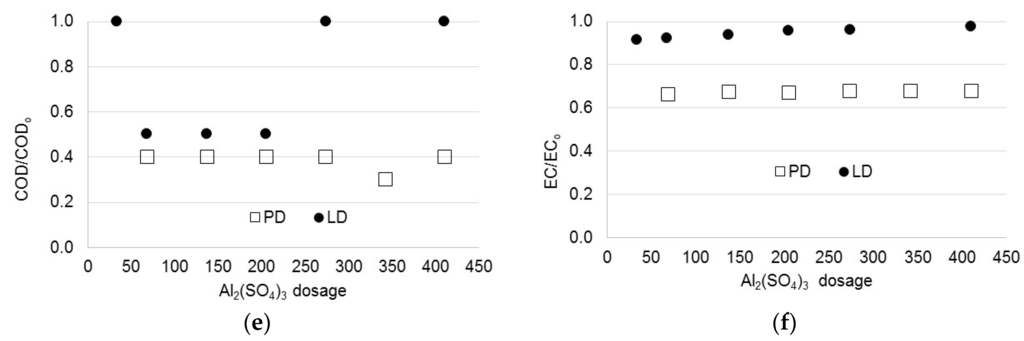
Figure 3.
Effect of coagulant dosage (mg/L) on bulk parameters removals for both graywaters. PD: Powder detergent; LD: Liquid detergent.
3.2.2. Determination of Optimum Mixing Conditions for Flocculation
Optimum mixing intensity and mixing time for flocculation were determined by conducting numerous jar tests. The results are plotted in Figure 4 and Figure 5 for powder detergent and liquid detergent graywater, respectively. For powder detergent graywater, the best removal efficiencies were observed at a mixing intensity of 10 rpm and mixing time of 20 min, especially for turbidity and TSS, with removal efficiencies of 95% and 75%, respectively. The removals of TDS and EC were approximately 34% and 33%, respectively, irrespective of the mixing time and the mixing intensity.
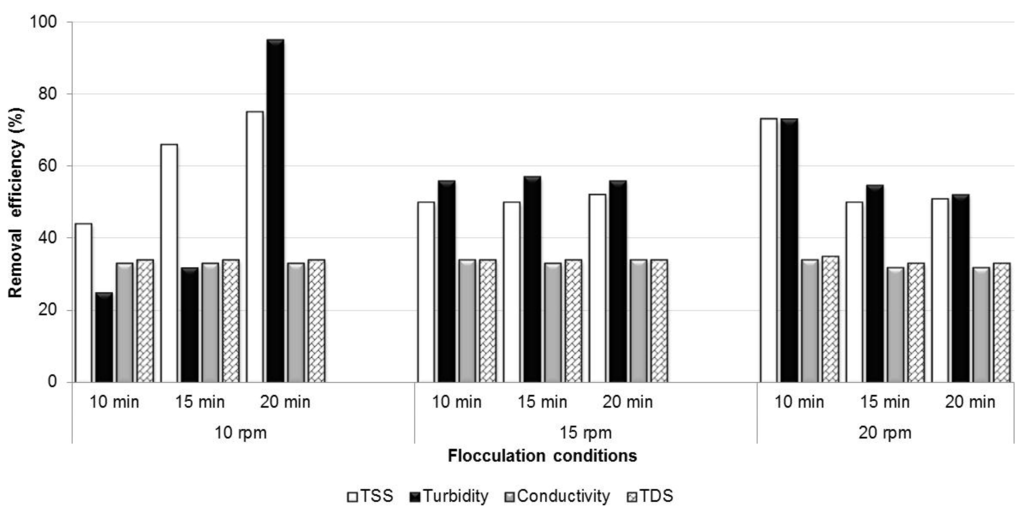
Figure 4.
Optimum conditions for flocculation of powder detergent graywater.
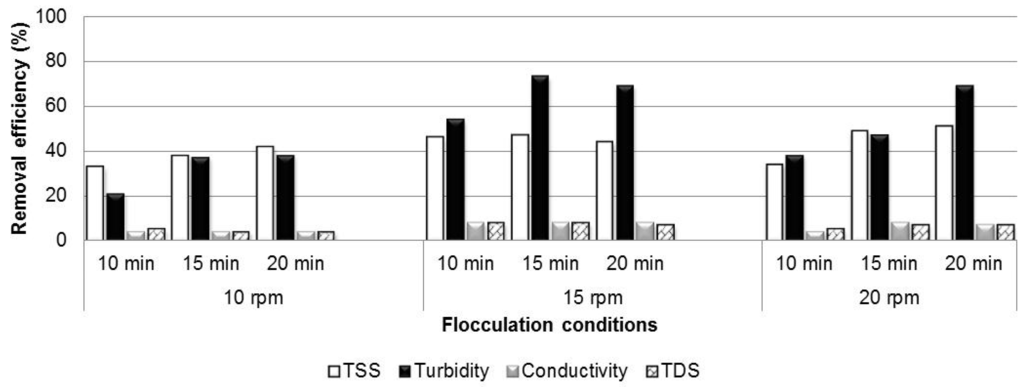
Figure 5.
Optimum conditions for flocculation of liquid detergent graywater.
For the liquid detergent graywater, in general, optimum removal efficiencies were observed at a mixing intensity of 15 rpm. Regarding turbidity, the highest removal efficiency (73%) was obtained at a mixing time of 15 min. For TSS, the highest removal was 51% obtained at a mixing intensity of 20 rpm and a mixing time of 20 min; however, at 15 rpm and a mixing time of 15 min, the removal efficiency was quite similar—approximately 47%. The removals for EC and TDS were notably low, i.e., no greater than 8% in all cases. Based on these results, a mixing intensity of 15 rpm and a mixing time of 15 min were selected as the optimum flocculation conditions for liquid detergent graywater.
Similarly to coagulation, the type of detergent influenced the flocculation process performance. It was not expected that the coagulation–flocculation process would remove significant amounts of TDS and EC; however, Figure 4 and Figure 5 contrast the removal differences not only in TSS, but also in TDS an EC depending on the type of graywater. Thus, the coagulation–flocculation process was more effective with powder detergent graywater. This result might have been expected because liquid detergent contains anticoagulants to improve detergent performance. However, this constituent affected the coagulation–flocculation process performance.
Table 3 summarizes the optimum coagulation–flocculation conditions and the treatment performance for both graywaters. If wastewater reuse standards from different countries reported in [3] are considered, the graywater characteristics after treatment obtained in this study do not meet such standards. However, the coagulation–flocculation process appears to be a potential pre-treatment alternative for treating graywater due to the reasonable removal efficiencies observed for both powder and liquid detergent graywater. It is important to remark that the scope of this work was to assess the contribution of the type of detergent to graywater characteristics and its effect on the treatment performance, rather than the efficacy of the coagulation–flocculation process as a treatment alternative to meet wastewater reuse standards.

Table 3.
Optimum conditions for the graywater coagulation–flocculation process.
Several treatment processes have been proposed to treat graywater and meet the quality requirements for reuse. The current preferred treatments for graywater reuse are physical and biological/natural systems. However, because of the XOC concern, chemical systems such as coagulation, adsorption, and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have recently been considered and have been successful for low- to moderate-strength graywater [25]. Since laundry graywater is a high-load graywater, a chemical system integrated by the coagulation–flocculation process and an advanced oxidation process could be a potential alternative to remove XOCs and meet the quality requirements for reuse. Coagulation–flocculation is ideal as a pre-treatment to reduce the graywater load, and the AOP is ideal for mineralizing recalcitrant organic compounds; therefore, studies in this respect should be conducted. The results obtained in this work could be useful when future studies on chemical treatment are conducted.
4. Conclusions
The type of detergent and the way these compounds are used during the laundry process must be taken into consideration when graywater is disposed into receiving water bodies or when it is reused as a sustainable solution to face the increase in water demand, water shortages, and environmental pollution. The type of detergent affects significantly not only the efficacy of the laundry process but also, and more importantly, the characteristics of the graywater that must be disposed or reused. Detergent overdosing can cause laundry graywater to heavily contaminate water bodies if it is not properly treated before disposal.
Detergent constituents, rather than soiled clothing, are the main contributors to graywater composition. Liquid and powder detergents are different in composition and contribute differentially to graywater characteristics. Powder detergents generate more polluted graywater. The laundry process increases the solids and organic loads of graywater, but reduces the concentration of surfactants.
Detergent type influences treatment performance of graywater. The coagulation–flocculation process was more effective with the powder detergent graywater even though the liquid detergent graywater was less polluted. Constituents such as anticoagulants present in liquid detergents affected the coagulation–flocculation process performance.
Turbidity removal efficiencies on the order of 95% and 73% for powder detergent and liquid detergent graywater, respectively, and total suspended solids removals of 75% and 51% for powder detergent and liquid detergent graywater, respectively, were achieved. Even though these efficiencies are significant, the coagulation–flocculation process must be complemented with an additional treatment process before laundry graywater is disposed into receiving waters or reused in non-potable water uses.
Regarding that laundry graywater is a high load graywater, a chemical system integrated by coagulation–flocculation and an advance oxidation process could be an interesting alternative to remove the XOCs and meet the quality requirements for reuse. The coagulation–flocculation process can be used as a pre-treatment to reduce the graywater load, and the AOP can be used to mineralize recalcitrant organic compounds. Studies in this respect must be conducted to evaluate their effectiveness and reliability. Because the coagulation–flocculation performance is affected by the type of detergent and its characteristics, the results obtained in this work could be useful at the time of conducting future studies on chemical treatment.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Tecnológico de Monterrey.
Author Contributions
Miguel Ángel López Zavala conceived, designed, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. Eunice Espinoza Estrada prepared the tables and figures and analyzed the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Smulders, E. Laundry Detergents; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Diaper, C.; Dixon, A.; Butler, D.; Fewkes, A.; Parsons, S.A.; Stephenson, T. Small scale water recycling systems—Risk assessment and modelling. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wichmann, K.; Otterpohl, R. Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedler, E.; Kovalio, R.; Galil, N.I. On-site grey water treatment and reuse in multi-story buildings. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pidou, M.; Avery, L.; Stephenson, T.; Jeffrey, P.; Parsons, S.A.; Liu, S.; Memon, F.A.; Jefferson, B. Chemical solutions for graywater recycling. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Wagner, M.; Cornel, P. Treatment of grey water for urban reuse. In Proceedings of the Advanced Sanitation Conference, Aachen, Germany, 12–13 March 2007.
- López Zavala, M.A.; Suárez Pérez, L.B.; Reynoso-Cuevas, L.; Funamizu, N. Pre-filtration for enhancing direct membrane filtration of graywater from washing machine discharges. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 64, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabelnika, K.; Kõiva, M.; Kasaka, K.; Jenssenb, P.D.; Mandera, Ü. High-strength graywater treatment in compact hybrid filter systems with alternative substrates. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 49, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Cheng, C.Y.; Leite, D. Development of an experimental system for graywater reuse. Desalination 2012, 285, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, C.; Sampaio, A.; Bentes, I. Possibilities of graywater reuse in non-potable in situ urban applications, according with its quality and quantity. WSEAS Trans. Environ. Dev. 2010, 7, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Revitt, D.M.; Eriksson, E.; Donner, E. The implications of household graywater treatment and reuse for municipal wastewater flows and micropollutants loads. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Koning, J.; Joksimovic, D.; Savic, D.; Wintgens, T. Wastewater, reuse in Europe. Desalination 2006, 187, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Fu, P. Wastewater reuse potential analysis: Implications for China’s water resources management. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2746–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Kaplan, D.; Baker, K. Removal of chemical and microbiological contaminants from domestic graywater using a recycled vertical flow bioreactor (RVFB). Ecol. Eng. 2007, 31, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidou, M.; Memon, F.A.; Stephenson, T.; Jefferson, B.; Jeffrey, R. Greywater recycling: Treatment options and applications. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Eng. Sustain. 2007, 160, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA; AWWA: Denver, CO, USA; WEF: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, J.; Levine, L.; Yorio, N.; Hummerick, M. Response of graywater recycling systems based on hydroponic plant growth to three classes of surfactants. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, E.; Auffarth, K.; Henze, M.; Ledin, A. Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water 2002, 4, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledin, A.; Eriksson, E.; Henze, M. Aspects of groundwater recharge using grey wastewater. In Decentralized Sanitation and Reuse: Concepts, Systems and Implementation; Lens, P., Zeeman, G., Lettinga, G., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, F. Wastewater treatment by graywater separation: Outline for a biologically based graywater purification plant in Sweden. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Greywater reuse systems for toilet flushing in multistory buildings—Over ten years’ experience in Berlin. Urban Water 2000, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Butler, D.; Friedler, E. At-source domestic wastewater quality. Urban Water 1999, 1, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D. The effect of reformulation of household powder laundry detergents on their contribution to heavy metals levels in wastewater. Water Environ. Res. 1998, 70, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santala, E. Microbiological graywater treatment and recycling in an apartment building. In Proceedings of the AWT 98—Advanced Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse, Milan, Italy, 14–16 September 1998; pp. 319–324.
- Boyjoo, Y.; Pareek, V.K.; Ang, M. A review of graywater characteristics and treatment processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1403–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budd, G. Coagulation applications for new treatment goals. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2004, 96, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).