Riverbed Micromorphology of the Yangtze River Estuary, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
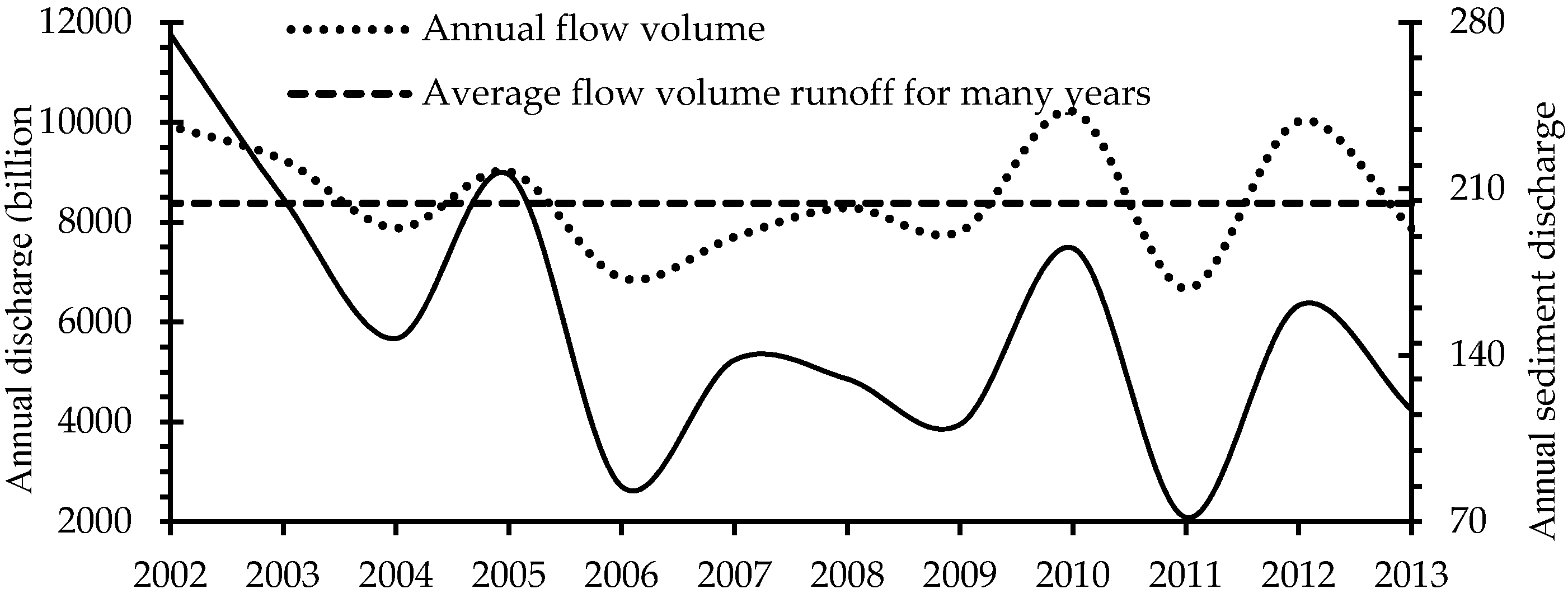
2.1. Study Area
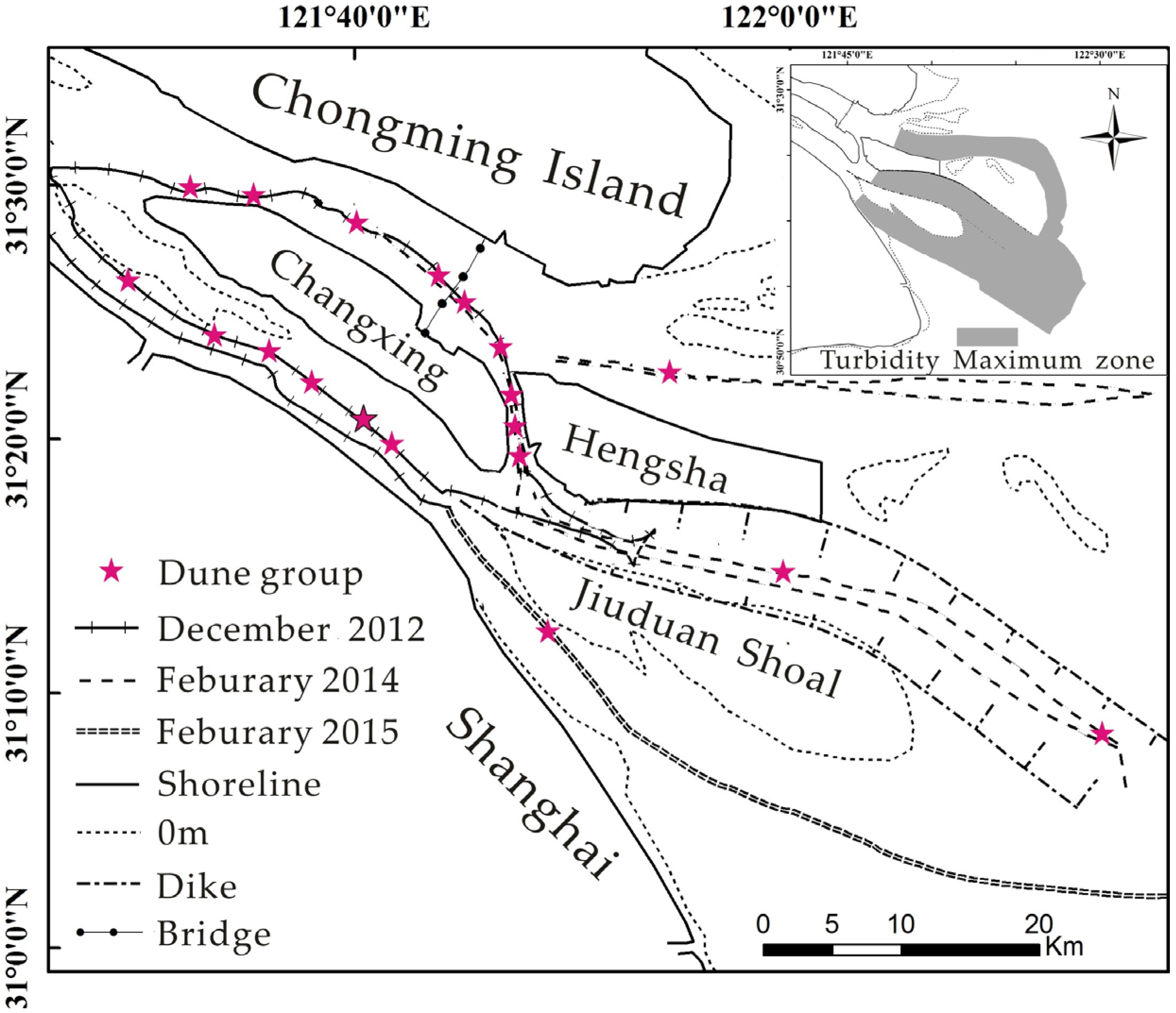
2.2. Riverbed Measurements
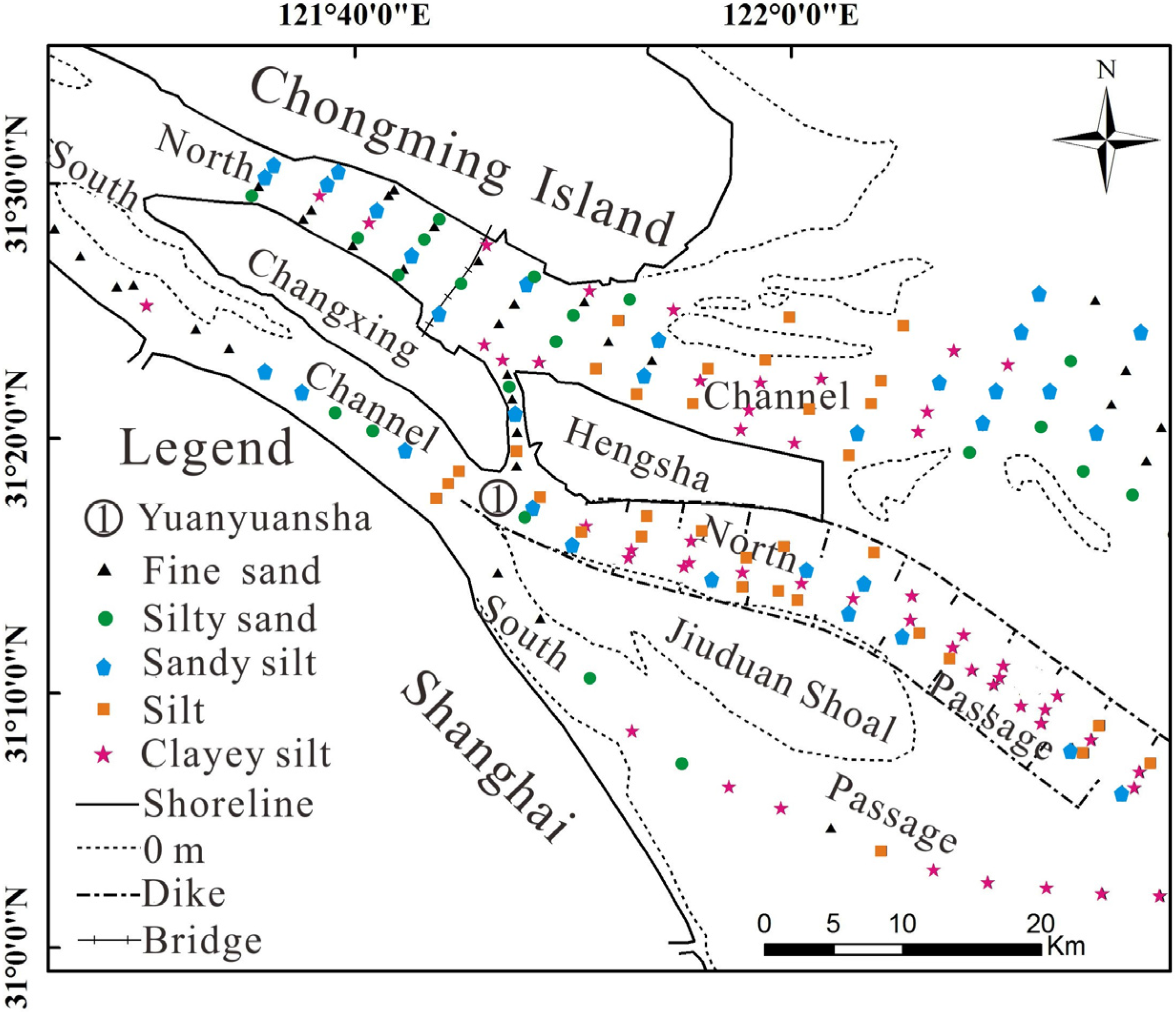
2.3. Field Sampling
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
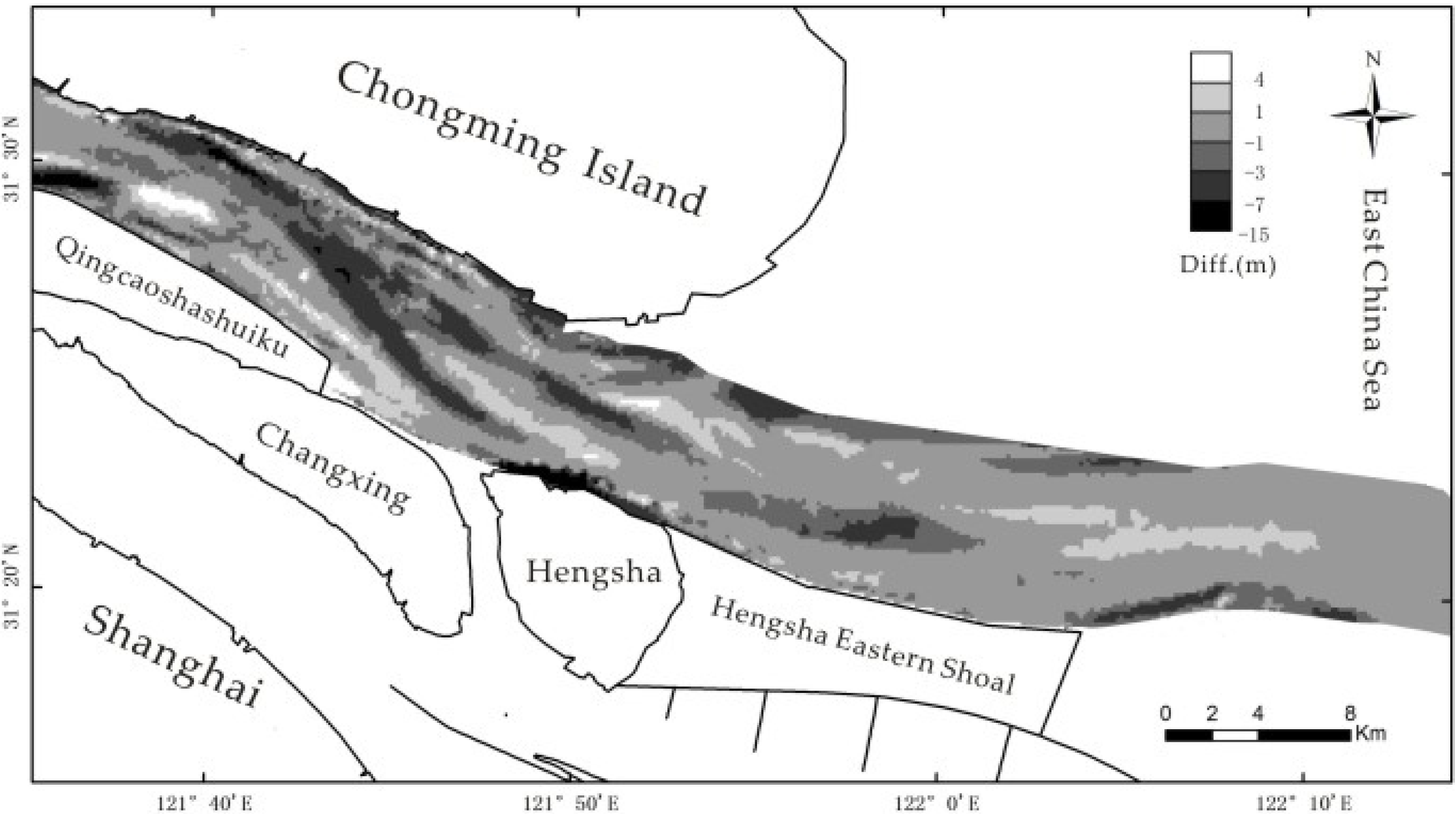
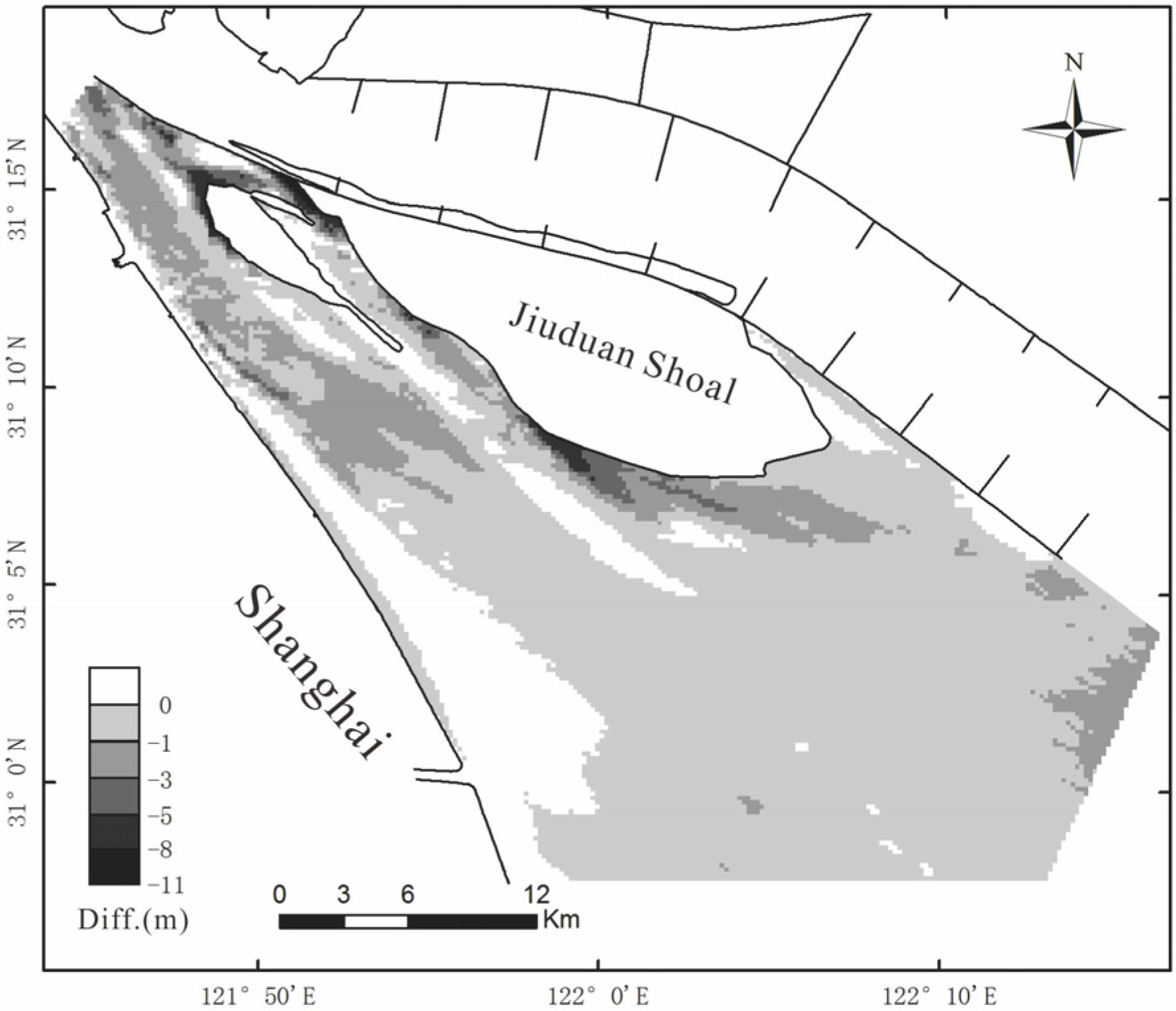
3.1. Channel-Bed Morphology Analysis
3.2. Types and Grain Size of Sediment
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing Dune Formation in the Yangtze River Estuary
4.2. Factors Influencing and Denotative of Dune Geometry
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashley, G.M. Classification of large-scale subaqueous bed forms: A new look at an old problem. J. Sediment. Res. 1990, 1, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, R.W.; Hoogendoorn, E.L. Erosion and deposition on migrating shoreface-attached ridges, Sable Island, Eastern Canada. Geosci Can. 1997, 24, 350–360. [Google Scholar]
- Knaapen, M.A.F.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Vriend, H.J.; Stolk, A. A new type of sea bed waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaschuk, R. A field study of turbulence and sediment dynamics over subaqueous dunes with flow separation. Sedimentology 2000, 47, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmink, J.J.; Dohmen-Janssen, C.M.; Lansink, J.; Naqshband, S.; van Duin, O.J.M.; Paarlberg, A.J.; Termes, P.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Understanding river dune splitting through flume experiments and analysis of a dune evolution model. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2014, 39, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, J.H. A flume study on the development and equilibrium morphology of current ripples in very fine sand. Sedimentology 1994, 41, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijin, L.C. Sediment transport part III: bedforms and alluvial roughness. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE. 1984, 110, 1733–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L.; Orfeo, O.; Hardy, R.J.; Kostaschuk, R.; Lane, S.N. Morphology and flow fields of three-dimensional dunes, Rio Parana, Argentina: Results from simultaneous multibeam echo sounding and acoustic Doppler current profiling. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, S.R.; Nelson, J.M.; Wolfe, S.R. Turbulence structure over two-dimensional bedforms: Implications for sediment transport. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 12729–12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.M.; Wolfe, S.R. Mean flow and turbulence over two-dimensional bedforms. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 3935–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsler, M.L.; Garcia, M.H. Sand dune geometry of large rivers during floods: Discussion. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASCE Task Force. Flow and transport over dunes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 127, 726–728. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J. The fluid dynamics of river dunes: A review and some future research directions. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, A.; Hulscher, S.; Van Damme, R.M.J. Simulating offshore sand waves. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, A.; Hulscher, S.; de Vriend, H.J. Modeling sand wave migration in shallow shelf seas. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelissen, R.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Knaapen, M.A.F.; Nemeth, A.; Bijker, R. Mathematical modeling of sandwave migration and the interaction with pipelines. Coast. Eng. 2003, 48, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catano-Lopera, Y.A.; Abad, J.D.; Garcia, M.H. Characterization of bedform morphology generated under combined flows and currents using wavelet analysis. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besio, G.; Blondeaux, P.; Brocchini, M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Idier, D.; Knaapen, M.A.F.; Ne´meth, A.A.; Roos, P.C.; Vittori, G. The morphodynamics of tidal sand waves: A model overview. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J.; Best, J.L.; Roden, J.E.; Bristow, C.S.; Klaassen, G.J. Morphological evolution and dynamics of a large, sand braid-bar, Jamuna River, Bangladesh. Sedimentology 2000, 47, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, F. Bed-form geometry in san-bed flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 1999, 125, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, M.M.; Best, J.L.; Yokokawa, M.; Sekiguchi, T.; Takagawa, T.; Garcia, M.H. A unified model for bedform development and equilibrium under unidirectional, oscillatory and combined-flows. Sedimentology 2014, 61, 2063–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Landeghem, K.J.J.; Wheeler, A.J.; Mitchell, N.C.; Sutton, G.D. Variations in sediment wave dimensions across the tidally dominated Irish Sea, NW Europe. Mar. Geol. 2009, 263, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veen, H.H.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Knaapen, M.A.F. Grain size dependency in the occurrence of sand waves. Ocean Dyn. 2006, 56, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, M.A.F. Sandwave migration predictor based on shape information. J. Geophys Res. 2005, 110, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Azcunaga, L.; Carbajal, N.; Montano-Ley, Y. Bed load transport of sediments and morphodynamics in the Northern gulf of California. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Q.; Kostaschuk, R.; Shi, Z. Tidal currents, Bed Sediments, and Bedforms at the South Branch and the South Channel of the Chajiang (Yangtze) Estuary, China: Implications for the ripple-dune transition. Estuaries 2004, 27, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cheng, H.; Li, J.; Dong, P. Temporal and spatial changes of dunes in the Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 77, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H. Bedforms and bed material transport pathways in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary. Geomorphology 2009, 104, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Singh, V.P.; Yang, T. Multiscale variability of sediment load and streamflow of the lower Yangtze River basin: Possible causes and implications. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X.; Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J. The impact of Three Gorges Dam on the downstream distribution and texture of sediments along the middle and lower Yangtze River (Changjiang) and its estuary, and subsequent sediment dispersal in the East China Sea. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Gupta, A. The Yangtze River: An introduction. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, S.B.; Li, M.; Xu, X.J. Effect of deposition and erosion within the main river channel and large lakes on sediment delivery to the estuary of the Yangtze River. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.; Shi, Y.; Quan, W.; Shen, X. Distribution of Macrocrustaceans in Relation to Abiotic and Biotic Variables across the Yangtze River Estuary, China. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Han, M.; Zhou, F. Transport of the suspended sediment in the Changjiang Estuary. Int. J. Sediment Res. 1993, 7, 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Shi, J.Z.; Hu, G.; Xiong, L. Circulation and mixing along the North Passage in the Changjiang River Estuary, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 148, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Wang, X.; Cao, Z.; Guan, W. Suspended sediment transport in the Deepwater Navigation Channel, Yangtze River Estuary, China, in the dry season 2009: 1. Observations over spring and neap tidal cycles. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 5555–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Shen, H.; Yang, Z.; Meades, R.H. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Weltje, G.J.; Zhang, J. Dynamics and spatial variability of near-bottom sediment exchange in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cao, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G. Biogeochemistry of bulk organic matter and biogenic elements in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; He, Q. A numerical model study of the transport time scale and change of estuarine circulation due to waterway constructions in the Changjiang Estuary, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 82, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, F.P. Nomenclature based on sand–silt–clay ratios. J. Sediment. Res. 1954, 24, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Li, J.; de Swart, H.E. Effects of navigational works on morphological changes in the bar area of the Yangtze River Estuary. Geomorphology 2012, 139, 205–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, N.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Hu, H.; Chen, Z. Sedimentary and morphological evolution of nearshore coast of Yangtze Estuary in the last 30 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 945–954. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J. Morphological Evolution of Mouth Bars of the Yangtze Estuarine Waterways in the Last 100 Years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 305–312. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, J. Tidal impact on the dynamic behavior of dissolved pharmaceuticals in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Wal, D.; Pye, K.; Neal, A. Long-term morphological change in the Ribble Estuary, northwest England. Mar. Geol. 2002, 189, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wal, D.; Pye, K. The use of historical bathymetric charts in a GIS to assess morphological change in estuaries. Geogr. J. 2003, 169, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Jin, X.L.; Li, J.B. Linear sand ridges on the outer shelf of the East China Sea. China Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 2517–2528. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, W.; Shen, H. Sediment properties and transportation in the turbidity maximum in Changjiang Estuary. Geogr. Res. 1994, 13, 51–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.X. On sandwaves in Yawosha channel of the Yangtze Estuary. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on River Sedimentation, Nanjing, China, 11–16 October 1983; Water Resources and Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 1983; pp. 650–661. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tang, J.; Miu, S. Study on evolution trend of North Channel of Yangtze River Estuary and influences of related projects. Yangtze River 2011, 42, 39–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Southard, J.B.; Boguchwal, A.L. Bed configurations in steady unidirectional water flows. Part 2. Synthesis of flume data. J. Sediment. Res. 1990, 60, 658–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, C.; Guo, J. Evolution of the upper reach of mouth bars in the North Channel of the Changjiang Estuary. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 2, 41–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, J.T.; Fu, G.; Xie, H. A thirteen-year record of bathymetric changes in the North Passage, Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary. Geomorphology 2013, 187, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaschuk, R.A.; Villard, P.V. Flow and sediment transport over large subaqueous dunes: Fraser River, Canada. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region | Height (m) | Length (m) | Windward Side Angle (°) | Lee Side Angle (°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | |
| Upper and middle reaches of the SC | 3.12 | 0.89 | 127.89 | 19.3 | 13.78 | 5.74 | 29.0 | 9.02 |
| Upper and middle reaches of the NC | 2.4 | 1.11 | 106.72 | 25.5 | 9.05 | 4.40 | 20.6 | 7.47 |
| Mouth bar of the NC | 1.84 | 0.72 | 95.18 | 15.43 | 12.16 | 5.14 | 19.65 | 9.84 |
| Middle reach of the NP | 0.74 | 0.48 | 94.27 | 39.41 | 3.49 | 1.65 | 4.19 | 1.81 |
| Lower reach of the NP | 0.53 | 0.33 | 14.56 | 11.11 | 15.51 | 5.85 | 4.34 | 2.85 |
| Upper reach of the SP | 0.57 | 0.35 | 20.07 | 14.83 | 3.50 | 1.82 | 7.42 | 3.40 |
| Reach | Main Type | Medium Size (Micrometer) | Content of Fine Sand (%) | Content of Silt (%) | Content of Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle and upper reaches of the South Channel | Fine sand | 130–178 | >73 | 4–18 | <8 |
| Lower reach of the South Channel | Silty sand | 94–123 | 60–65 | 30–35 | <6 |
| Sandy silt | 45–56 | 22–39 | 52–71 | 8 | |
| Yuanyuansha waterway | silt | 37–51 | 13–18 | 68–74 | 13–18 |
| Sandy sit | 23–72 | 32–38 | 47–55 | <18 | |
| Hengsha Passage | Fine sand | 130–200 | >80 | 10–16 | <4 |
| Upper reach of the North Passage | Clayey silt | 17–23 | 3–10 | 66–72 | 20–27 |
| Middle reach of the North Passage | Clayey silt | 10–24 | 2–4 | 64–72 | 24–34 |
| Lower reach of the North Passage | silt | 10–20 | <5 | 64–70 | 26–36 |
| Upper reach of the South Passage | Fine sand | 136–204 | >95 | 1–4 | <1 |
| Middle and lower reaches of the South Passage | Clayey silt | 6–13 | <1 | 55–60 | 37–43 |
| Upper and middle reaches of the North Channel | Fine sand | 105–237 | >80 | 10 | <6 |
| Silty sand | 61–201 | 48–76 | 20–45 | <12 | |
| Mouth bar of the North Channel | silt | 15–30 | 10–20 | 65–75 | 10–20 |
| Clayey silt | 7–18 | 2–15 | 60–70 | 20–30 |
| Dune regime | Height (m) | Length (m) | Windward Side Angle (°) | Lee Side Angle (°) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | Mean | |
| South Channel(1997.12) [28] | 1.3 | 0.5 | 51.6 | 13.7 | 7.5 | 3.8 | 11.8 | 5.6 |
| South Channel(2006.2) [27] | 1.4 | 0.6 | 55.7 | 14.1 | 6.5 | 3.2 | 11.0 | 5.0 |
| South Channel(2012.12) | 3.12 | 0.89 | 127.89 | 19.3 | 13.78 | 5.74 | 29 | 9.02 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Y.J.; Li, J.; Zheng, S.; Xu, W. Riverbed Micromorphology of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Water 2016, 8, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050190
Wu S, Cheng H, Xu YJ, Li J, Zheng S, Xu W. Riverbed Micromorphology of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Water. 2016; 8(5):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050190
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shuaihu, Heqin Cheng, Y. Jun Xu, Jiufa Li, Shuwei Zheng, and Wei Xu. 2016. "Riverbed Micromorphology of the Yangtze River Estuary, China" Water 8, no. 5: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050190
APA StyleWu, S., Cheng, H., Xu, Y. J., Li, J., Zheng, S., & Xu, W. (2016). Riverbed Micromorphology of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Water, 8(5), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050190








