Riverbed Clogging and Sustainability of Riverbank Filtration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Site Description
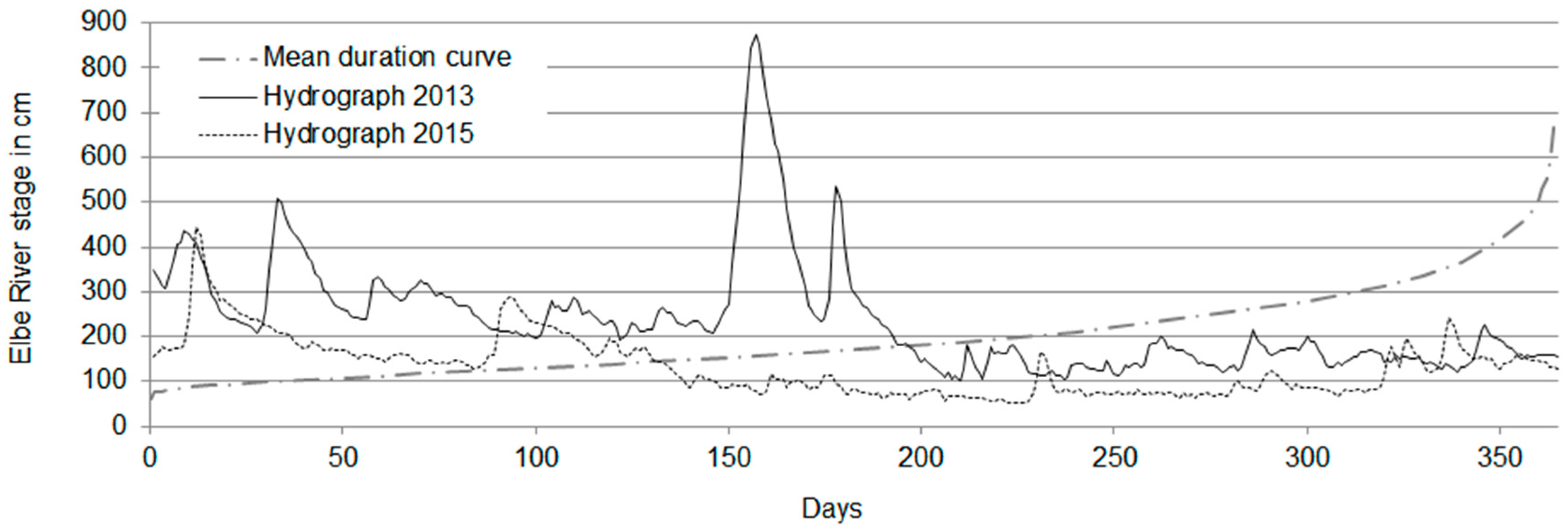
2.1.1. Elbe River
2.1.2. Elbe River Water Quality
2.1.3. Study Sites
2.2. Field Tests
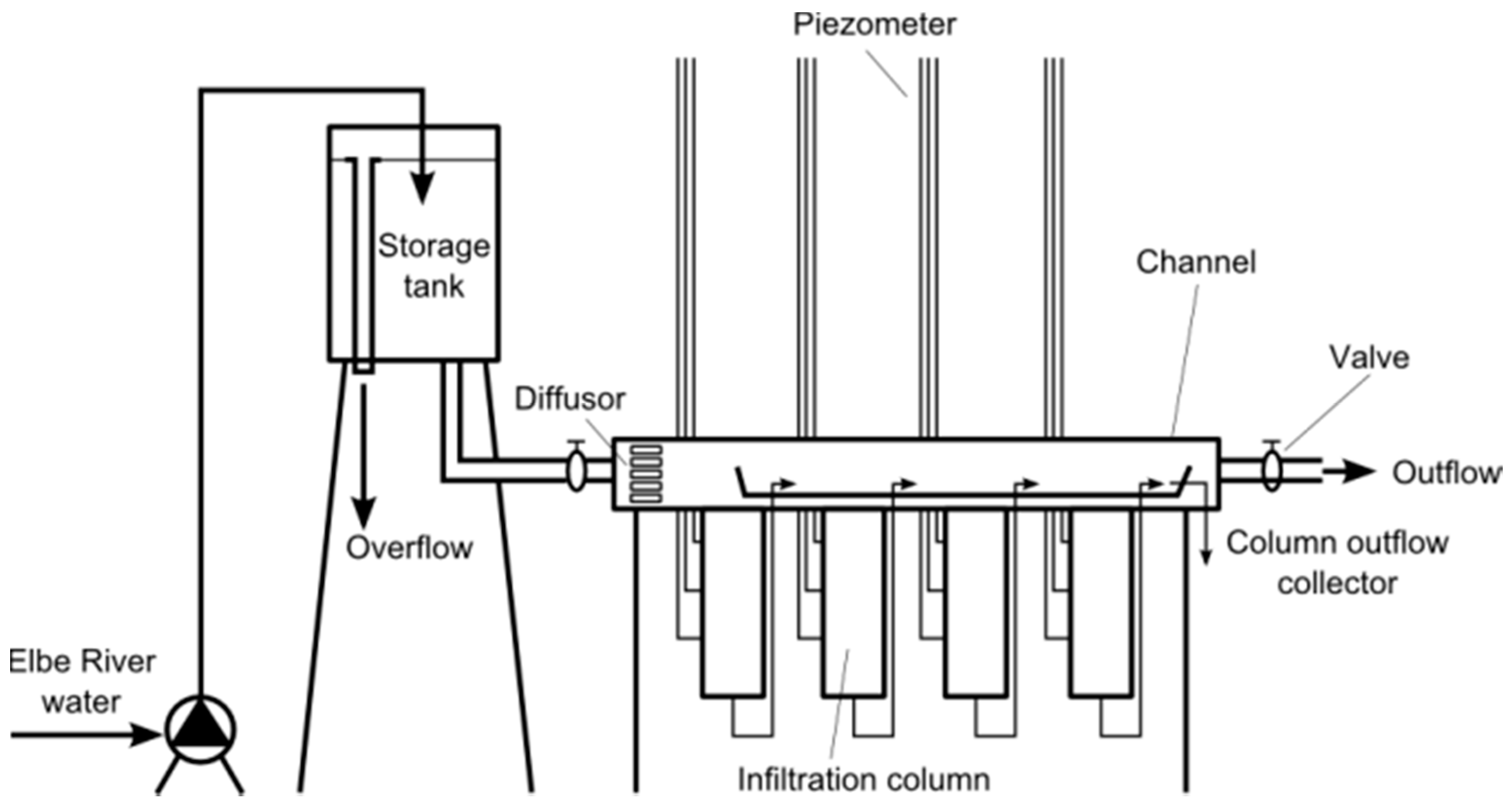
2.2.1. Infiltrometer
2.2.2. Channel Test
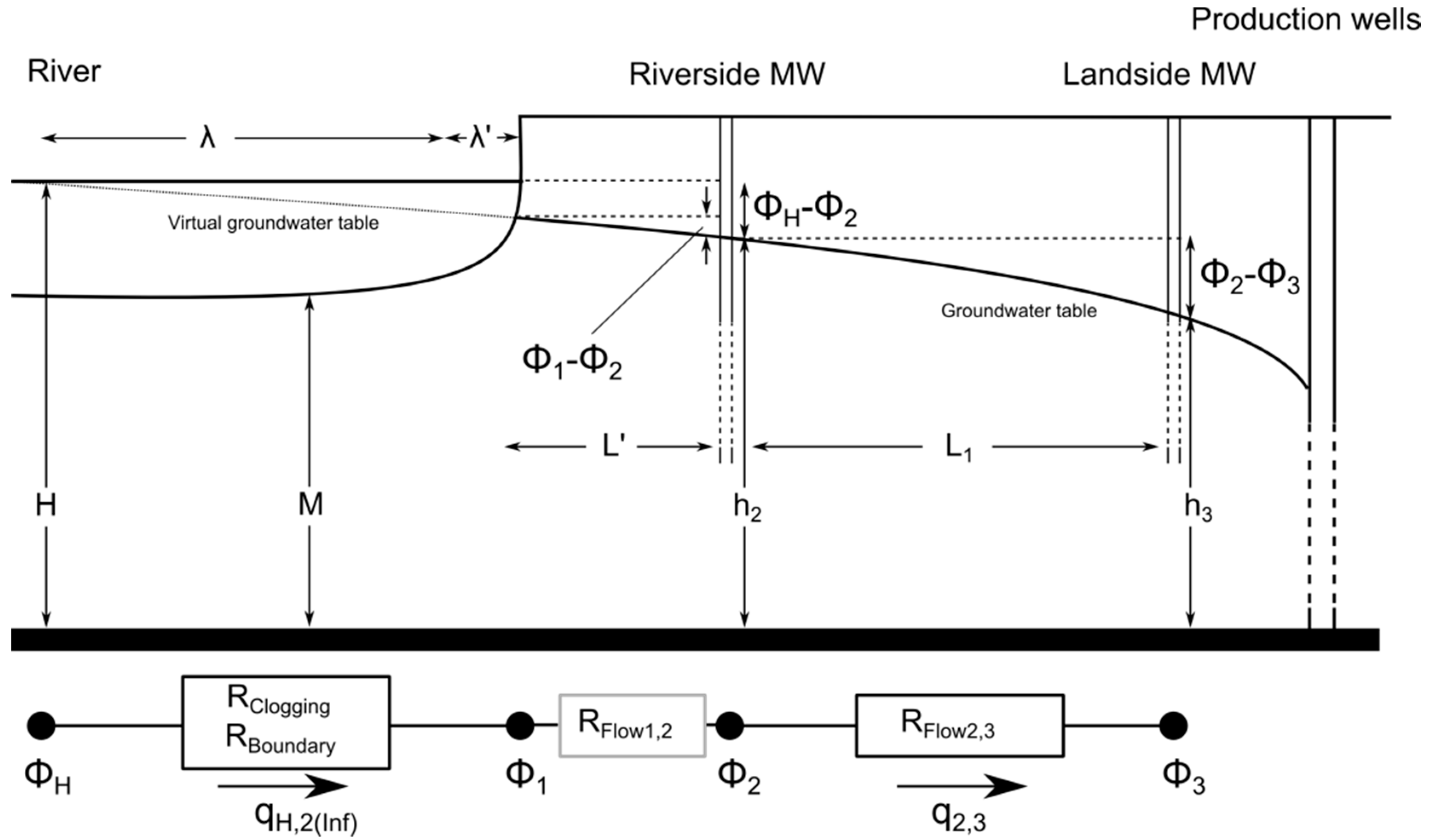
2.3. Analytical and Numerical Determination of Leakage Coefficients
3. Results
3.1. Type of Clogging and Clogging Layer Thickness
3.2. Infiltration Resistance
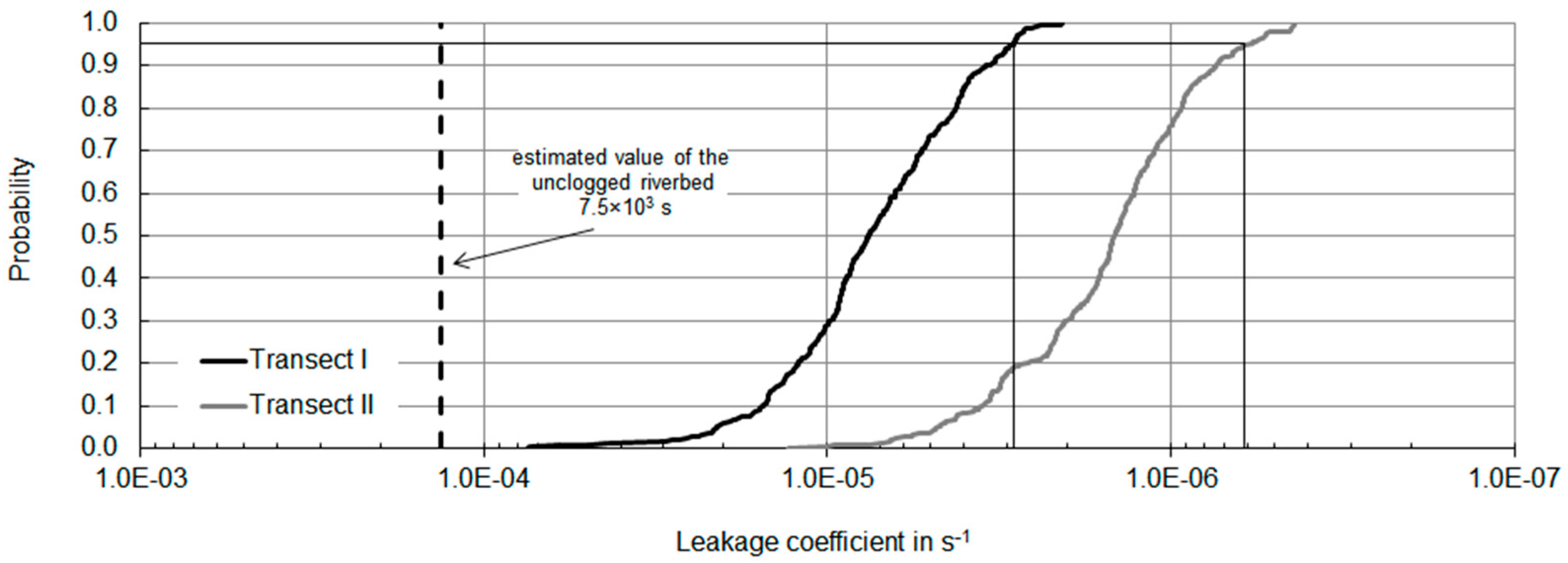
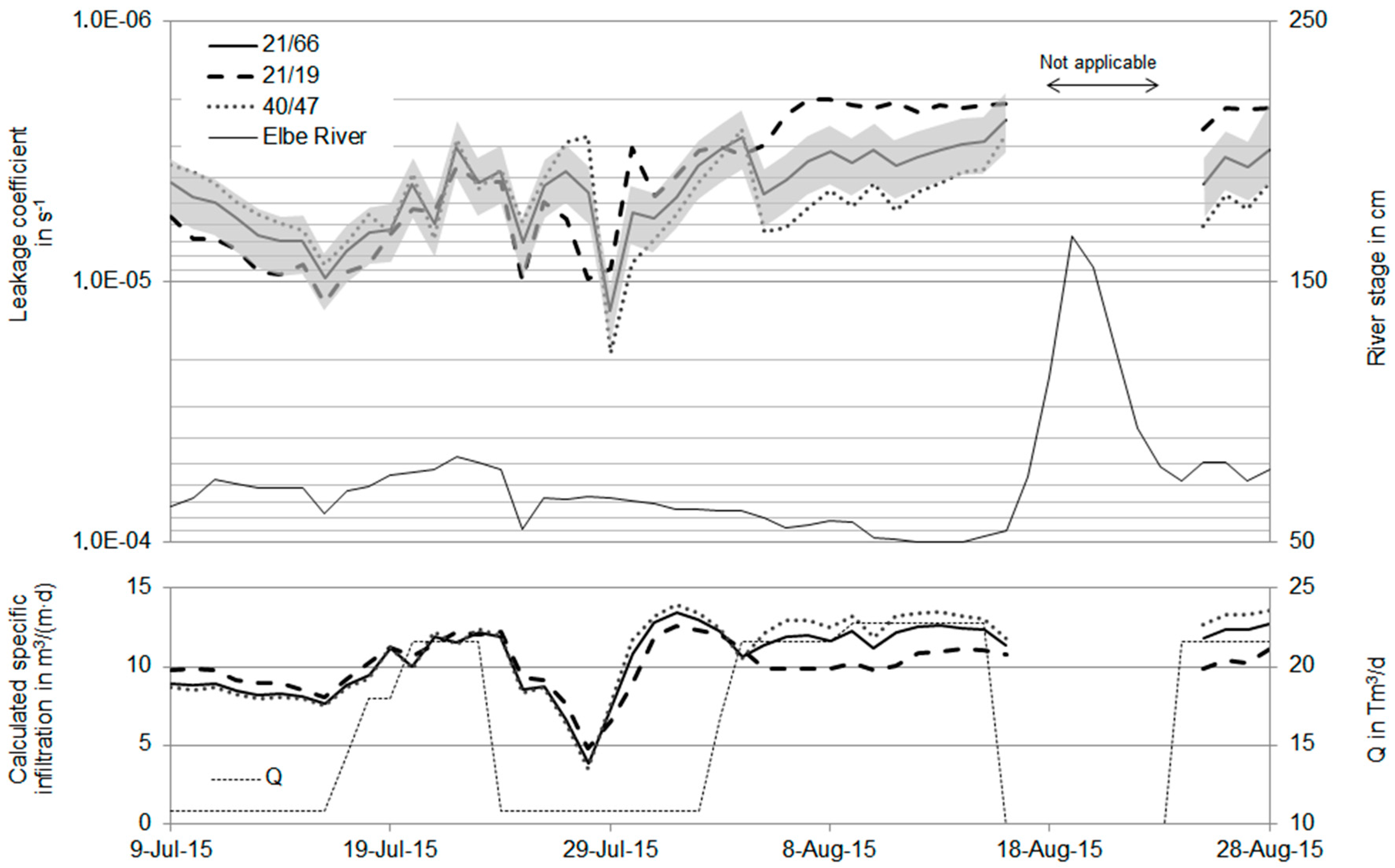
3.3. Comparison of Different Methods to Estimate the Leakage Coefficient
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hubbs, S.A. Changes in riverbed hydraulic conductivity and specific capacity at Louisville. In Riverbank Filtration Hydrology; Hubbs, S.A., Ed.; NATO Science Series IV; Earth and Environmental Sciences: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 199–220. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, J. Significance of hydrologic aspects on RBF performance. In Riverbank Filtration Hydrology; Hubbs, S.A., Ed.; NATO Science Series IV; Earth and Environmental Sciences: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Schälchli, U. Clogging of Surface Water Bed: Processes and Calculations. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rinck-Pfeiffer, S.; Ragusa, S.; Sztajnbok, P.; Vandevelde, T. Interrelationships between biological, chemical and physical processes as an analog to clogging in aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) wells. Water Resour. 2000, 34, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WSA; (The Waterways and Shipping Board, Magdeburg, Germany). Personal communication, 2016.
- IKSE International Commission for Protection of the Elbe River, Gradient, Flow Velocity and Travel Time Elbe River. The Elbe River and Its Catchment Basin (German). p. 212. Available online: http://www.ikse-mkol.org/uploads/media/IKSE-Elbe-und-ihr-Einzugsgebiet-2005-Kap5-2.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2016).
- DREWAG; (Dresden, Germany). Unpublished water quality data. 2011.
- Nestler, W.; Socher, M.; Grischek, T.; Schwan, M. River Bank Infiltration in the Upper Elbe River Valley: Hydrochemical Aspects; IAHS Publ.: Vienna, Austria, 1991; pp. 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Grischek, T.; Schoenheinz, D.; Eckert, P.; Ray, C. Sustainability of river bank filtration: Examples from Germany. In Groundwater Quality Sustainability; Maloszewski, P., Witczak, S., Malina, G., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012; pp. 213–227. [Google Scholar]
- Banscher, E. Contribution to the Evaluation of Clogging Processes along Streams. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Dresden, Department of Water Sciences, Dresden, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, W.; Banscher, E. On the methodology for riverbank filtration site investigation. Z. Angew. Geol. 1976, 22, 149–154. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Heeger, D. Investigation of Clogging Processes in Rivers. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Department of Math & Natural Sciences, Dresden, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Grischek, T.; Macheleidt, W.; Nestler, W. River bed specifics and their effect on bank filtration efficiency. In Management of Aquifer Recharge for Sustainability; Dillon, P., Ed.; Balkema Publ.: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Grischek, T. Management of RBF along the Elbe River. Ph.D. Thesis, Dresden University of Technology, Department of Water Sciences, Dresden, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M. The Influence of High Infiltration Rates, Suspended Sediment Concentration and Sediment Grain Size on River and Lake Bed Clogging. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Berlin, Faculty III-Process Sciences, Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heeger, D.; (WW Dresden-Tolkewitz, Germany). Unpublished technical report. 1988.
- Beyer, W.; (Methodology for Riverbank Filtration Site Investigation, Dresden University of Technology, Department of Water Sciences, Dresden, Germany). Unpublished work. 1974.
- Busch, K.F.; Luckner, L.; Tiemer, K. Textbook Hydrogeology—Geohydraulics (German), 3rd ed.; Gebrueder Borntraeger: Berlin/Stuttgart, Germany, 1993; pp. 186–211. [Google Scholar]
- Beims, U. One dimensional flow. In Textbook Hydrogeology—Groundwater Exploration; Bahlke, K.D., Beims, U., Heers, F.W., Hölting, B., Homrighausen, R., Matthess, G., Eds.; Gebrueder Borntraeger: Berlin/Stuttgart, Germany, 2000; pp. 130–195. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Nogaro, G.; Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Montuelle, B.; Boisson, J.-C.; Gibert, J. Chironomid larvae stimulate biogeochemical and microbial processes in a riverbed covered with fine sediment. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 70, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.N. Groundwater–Surface Water Interactions in the Hyporheic Zone; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2005; No. SC030155/SR1. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, H.; Kloep, F.; Wilzcek, S.; Pusch, M.T. A river’s liver—Microbial processes within the hyporheic zone of a large lowland river. Biogeochemistry 2005, 76, 349–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemisch, K. Hydrodynamic Effects of Ships in Canals; Mitt. Franzius-Inst.: Hannover, Germany, 1990; p. 295. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Landon, M.K.; Rus, D.L.; Harvey, F.E. Comparison of instream methods for measuring hydraulic conductivity in sandy streambeds. Ground Water 2001, 39, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberry, D.O.; LaBaugh, J.W. Field Techniques for Estimating Water Fluxes between Surface Water and Ground Water; U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 4–D2; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; p. 128.
- Zipfel, K. Groundwater Recovery along Rivers with Self-Sealing Riverbed. Ph.D. Thesis, Karlsruhe University, Karlsruhe, Germany, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, C.; Grischek, T.; Kumar, P.; Ray, C. Potential for riverbank filtration in India. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2011, 13, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodeif, K.; Grischek, T.; Bartak, R.; Wahaab, R.; Herlitzius, J. Potential of river bank filtration (RBF) in Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pholkern, K.; Srisuk, K.; Grischek, T.; Soares, M.; Schäfer, S.; Archwichai, L.; Saraphirom, P.; Pavelic, P.; Wirojanagud, W. Riverbed clogging experiments at potential river bank filtration sites along the Ping River, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7699–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


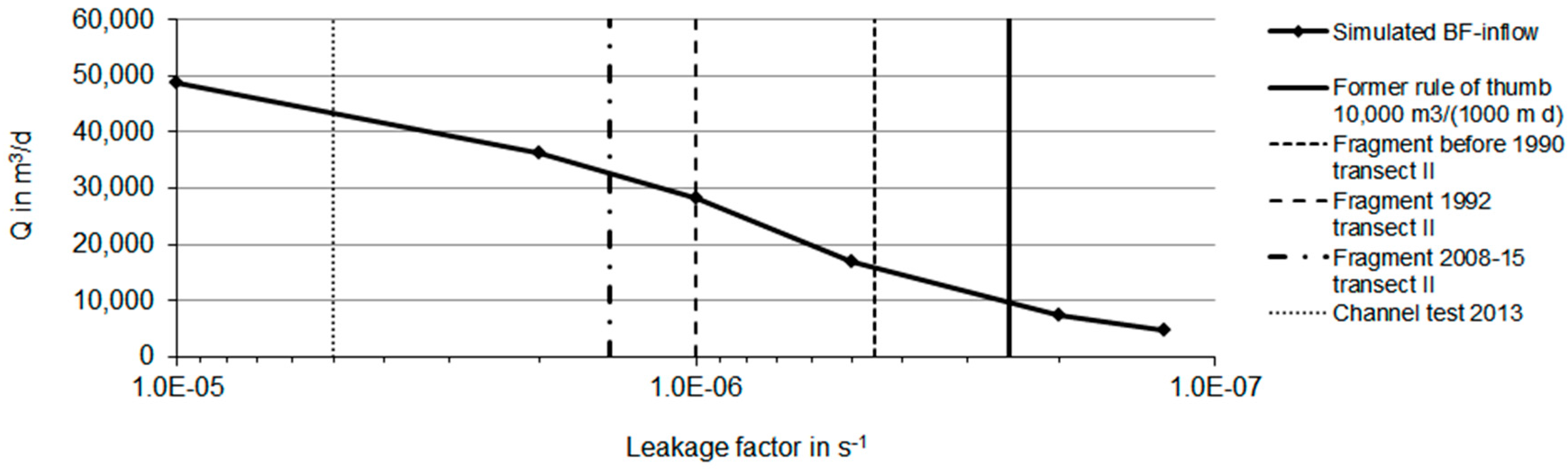
| Method | Parameter | Before 1990 | 1991–1993 | 2008–2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragment Approach | Leakage coefficient in s−1 | 0.45 *,# | 1 | 1.5 * |
| Cross comparison in % | 30 | 67 | 100 | |
| Channel Test | Leakage coefficient in s−1 | 0.2–2.0 x | 2.4 $,+ | 5 $,y |
| Cross comparison in % | 4–40 | 48 | 100 |
| Site | q in m3/(m·day) | Channel | Infiltrometer | Fragment Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD Tolkewitz | 9.7 | 5 | n.d. | 1 (0.4–1.3) |
| Meissen–Siebeneichen | 1.5 | 3 (2–10) | 200 (125–500) | n.d. * |
| Torgau–Ost | 15.8 | 10 (2.5–20) | 250 (125–1000) | 100 (5–200) |
| Distance from River/Distance between MW in (m) | 21/66 | 21/19 | 40/47 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median L in s−1 | 4.2 × 10−6 | 4.0 × 10−6 | 4.6 × 10−6 |
| Cross Comparison in % | 100 | 94 | 110 |
| MAE in % (excl. 4–16 August 2015) | 0 | 23 | 16 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grischek, T.; Bartak, R. Riverbed Clogging and Sustainability of Riverbank Filtration. Water 2016, 8, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120604
Grischek T, Bartak R. Riverbed Clogging and Sustainability of Riverbank Filtration. Water. 2016; 8(12):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120604
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrischek, Thomas, and Rico Bartak. 2016. "Riverbed Clogging and Sustainability of Riverbank Filtration" Water 8, no. 12: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120604
APA StyleGrischek, T., & Bartak, R. (2016). Riverbed Clogging and Sustainability of Riverbank Filtration. Water, 8(12), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120604







