Use of Multi-Carbon Sources by Zooplankton in an Oligotrophic Lake in the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
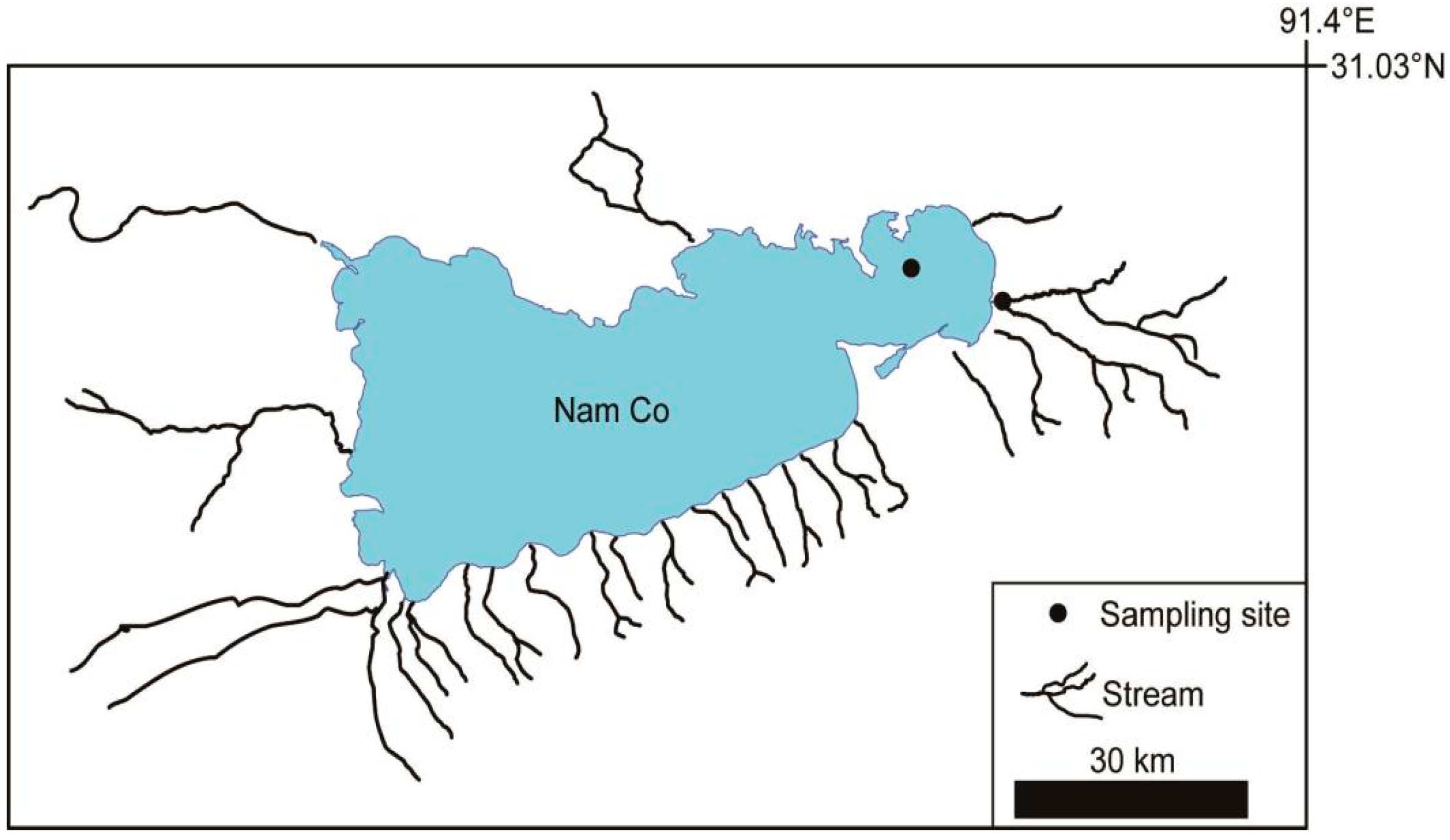
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Radiocarbon and Stable Carbon Isotope Analysis
2.4. Isotope Modeling for Multiple Food Sources
3. Results
3.1. Isotope Signature
3.2. Contribution of Potential Carbon Sources to Zooplankton
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jansson, M.; Persson, L.; de Roos, A.M.; Jones, R.I.; Tranvik, L.J. Terrestrial carbon and intraspecific size-variation shape lake ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipale, S.; Kankaala, P.; Tiirola, M.; Jones, R.I. Whole-lake 13C additions reveal seasonal shifts between multiple food source contributions to zooplankton diet. Ecology 2008, 89, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kluijver, A.; Ning, J.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Gulati, R.D.; Middelburg, J.J. Macrophytes and periphyton carbon subsidies to bacterioplankton and zooplankton in a shallow eutrophic lake in tropical China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Pace, M.L.; van de Bogert, M.C.; Kitchell, J.L.; Hodgson, J.R. Differential support of lake food webs by three types of terrestrial organic carbon. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Cole, J.J.; Pace, M.L.; van de Bogert, M.; Bade, D.L.; Bastviken, D. Ecosystem subsidies: terrestrial support of aquatic food webs from 13C addition to contrasting lakes. Ecology 2005, 86, 2737–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kitchell, J.L.; Pace, M.L.; Solomon, C.T.; Weidel, B. Strong evidence for terrestrial support of zooplankton in small lakes based on stable isotopes of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, J.; Berggren, M.; Ask, J.; Bystrom, P.; Jonsson, A.; Laudon, H. Terrestrial organic matter support of lake food webs: Evidence from lake metabolism and stable hydrogen isotopes of consumers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, M.L.; Cole, J.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kitchell, J.F.; Hodgson, J.R.; van de Bogert, M.C. Whole lake carbon-13 additions reveal terrestrial support of aquatic food webs. Nature 2004, 427, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, M.L.; Carpenter, S.R.; Cole, J.J.; Coloso, J.J.; Kitchell, J.F.; Hodgson, J.R. Does terrestrial organic carbon subsidize the planktonic food web in a clear water lake? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, E.; Battin, T.J.; Fellman, J.; Neel, S.O.; Spencer, R.G. Storage and release of organic carbon from glaciers and ice sheets. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.; Vogel, J.G.; Crummer, K.G.; Lee, H.; Sickman, J.O.; Osterkamp, T.E. The effect of permafrost thaw on old carbon release and net carbon exchange from tundra. Nature 2009, 459, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, P.J.; Eglinton, T.I.; McIntyre, C.P.; Zimov, N.; Davydova, A.; Vonk, J.E. Utilization of ancient permafrost carbon in headwaters of Arctic fluvial networks. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, E.; Fellman, J.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Hernes, P.J.; Edward, R.; D’Amore, D. Glaciers as a source of ancient and labile organic matter to the marine environment. Nature 2009, 462, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, M.P.; Das, S.B.; Xu, L.; Charette, M.A.; Wadham, J.L.; Kujawinski, E.B. Organic carbon export from the Greenland ice sheet. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 109, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.G.; Guo, W.; Raymond, P.A.; Dittmar, T.; Hood, E.; Fellman, J. Source and biolability of ancient dissolved organic matter in glacier and lake ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 142, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Richter, A.; Bol, R.; Garnett, M.H.; Baumler, R.; Xu, X. Heterotrophic microbial communities use ancient carbon following glacial retreat. Biol. Lett. 2007, 3, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, G.A.; Fasching, C.; Wilhelm, L.; Niggemann, J.; Steier, P.; Dittmar, T. Biogeochemically diverse organic matter in Alpine glaciers and its downstream fate. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hågvar, S.; Ohlson, M. Ancient carbon from a melting glacier gives high 14C age in living pioneer invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellman, J.B.; Hood, E.; Raymond, P.A.; Hudson, J.; Bozeman, M.; Arimitsu, M. Evidence for the assimilation of ancient glacier organic carbon in a proglacial stream food web. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, D.M. Carbon-13 and carbon-14 abundances in Alaskan aquatic organisms: Delayed production from peat in arctic food webs. Science 1983, 219, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Cao, J.; Hansen, J.; Yao, T.; Joswia, D.; Wang, N. Black soot and the survival of Tibetan glaciers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22114–22118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; You, Q.; Flügel, W.A.; Pepin, N.; Yao, T. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, T.; Jiao, N.; Liu, X.; Kang, S.; Luo, T. Seasonal dynamics of the bacterial community in Lake Namco, the largest Tibetan lake. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J. Stable isotopes dissect aquatic food webs from the top to the bottom. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraco, N.; Bauer, J.E.; Cole, J.J.; Petsch, S.; Raymond, P. Millennial-aged organic carbon subsidies to a modern river food web. Ecology 2010, 91, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, L.; Bull, I.D.; Gates, P.J.; Evershed, R.P. A simple modification of a silicic acid lipid fractionation protocol to eliminate free fatty acids from glycolipid and phospholipid fractions. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2009, 78, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschker, H.T.S.; Kromkamp, J.C.; Middelburg, J.J. Biomarker and carbon isotopic constraints on bacterial and algal community structure and functioning in a turbid, tidal estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga, E.; Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Masiello, C.A.; Krusche, A.V.; Hedges, J.I.; Quay, P.D. Young organic matter as a source of carbon dioxide outgassing from Amazonian rivers. Nature 2005, 436, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNichol, A.P.; Aluwihare, L.I. The power of radiocarbon in biogeochemical studies of the marine carbon cycle: Insights from studies of dissolved and particulate organic carbon (DOC and POC). Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigah, P.K.; Minor, E.C.; Werne, J.P.; Leigh McCallister, S. An isotopic (Δ14C, δ13C, and δ15N) investigation of the composition of particulate organic matter and zooplankton food sources in Lake Superior and across a size-gradient of aquatic systems. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3663–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y. Major Ionic Features and Their Sources in the Nam Co Basin over the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. 2008, 29, 3009–3016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, N.F.; Uchida, M.; Shibata, Y.; Tayasu, I. Carbon storage reservoirs in watersheds support stream food webs via periphyton production. Ecology 2014, 95, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Altitude | pH | Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | Chlorophyll-a | Salinity | POC | DOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4730 m a.s.l. | 9.9 | 0.37 mg/L | 0.003 mg/L | 0.26 μg/L | 0.98 g/L | 1.32 mg/L | 11.93 mg/L |
| Sources | δ13C | ∆14C |
|---|---|---|
| Zooplankton | −26.3 ± 0.9 | −45.3 |
| Phytoplankton | −29.9 | −36.1 |
| Submersed plant | −15.0 ± 0.3 | −44.1 |
| POC bulk | −25.6 ± 0.6 | −247.3 |
| DOC bulk 1 | −22.9 | −70.2 |
| POC allo | −24.5 ± 1.0 | −120.6 |
| DOC allo 1 | −23.3 | −158.3 |
| DIC | 0.6 | −36.1 |
| Sources | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|
| Phytoplankton | 73.9 (67–81) |
| Submersed plant | 18.3 (11–25) |
| POC allo | 4.7 (0–10) |
| DOC allo | 3.1 (0–7) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, E.; He, H.; Su, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z. Use of Multi-Carbon Sources by Zooplankton in an Oligotrophic Lake in the Tibetan Plateau. Water 2016, 8, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120565
Hu E, He H, Su Y, Jeppesen E, Liu Z. Use of Multi-Carbon Sources by Zooplankton in an Oligotrophic Lake in the Tibetan Plateau. Water. 2016; 8(12):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120565
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, En, Hu He, Yaling Su, Erik Jeppesen, and Zhengwen Liu. 2016. "Use of Multi-Carbon Sources by Zooplankton in an Oligotrophic Lake in the Tibetan Plateau" Water 8, no. 12: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120565
APA StyleHu, E., He, H., Su, Y., Jeppesen, E., & Liu, Z. (2016). Use of Multi-Carbon Sources by Zooplankton in an Oligotrophic Lake in the Tibetan Plateau. Water, 8(12), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120565







