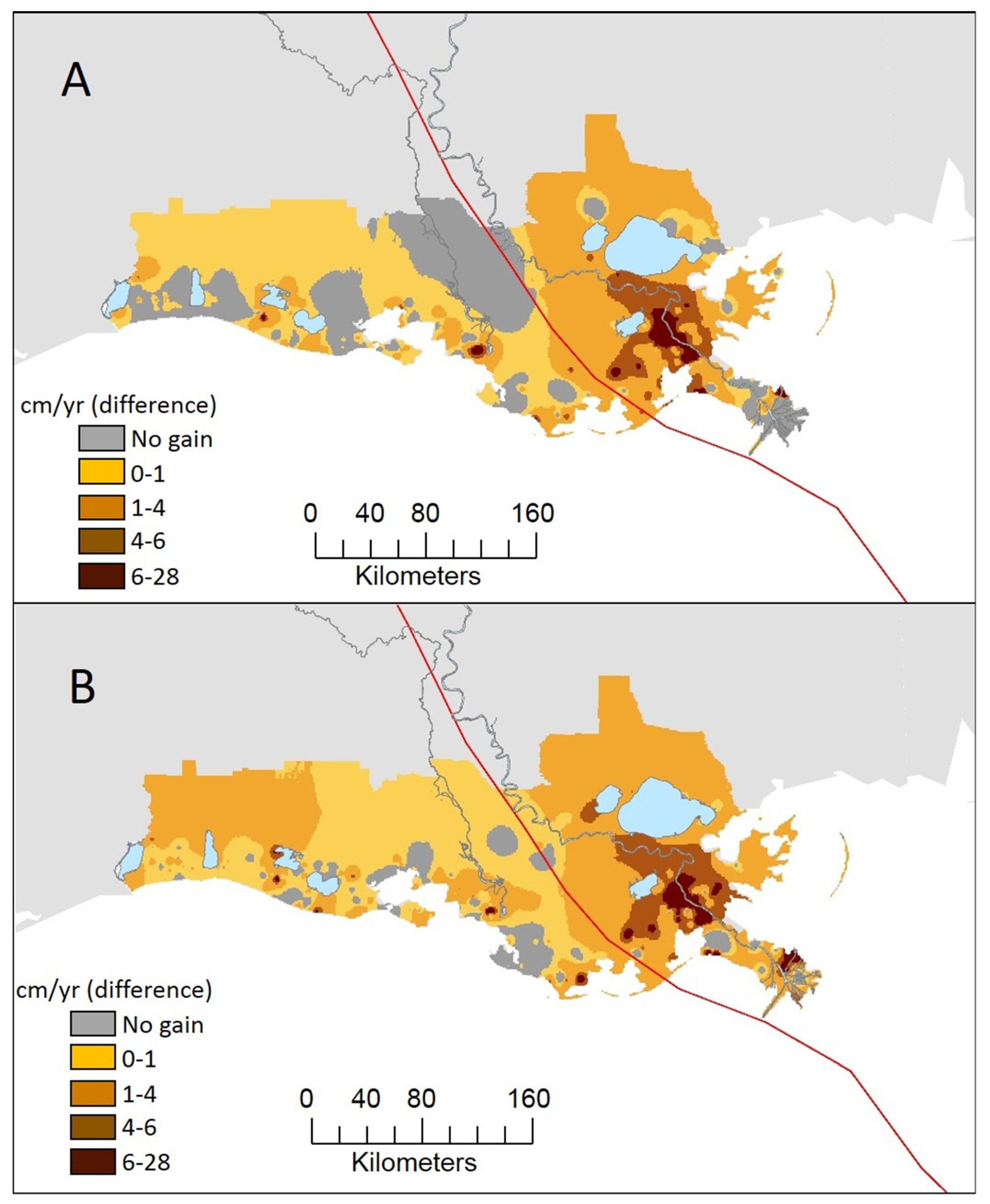
Wetland Accretion Rates Along Coastal Louisiana: Spatial and Temporal Variability in Light of Hurricane Isaac’s Impacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Research Problem
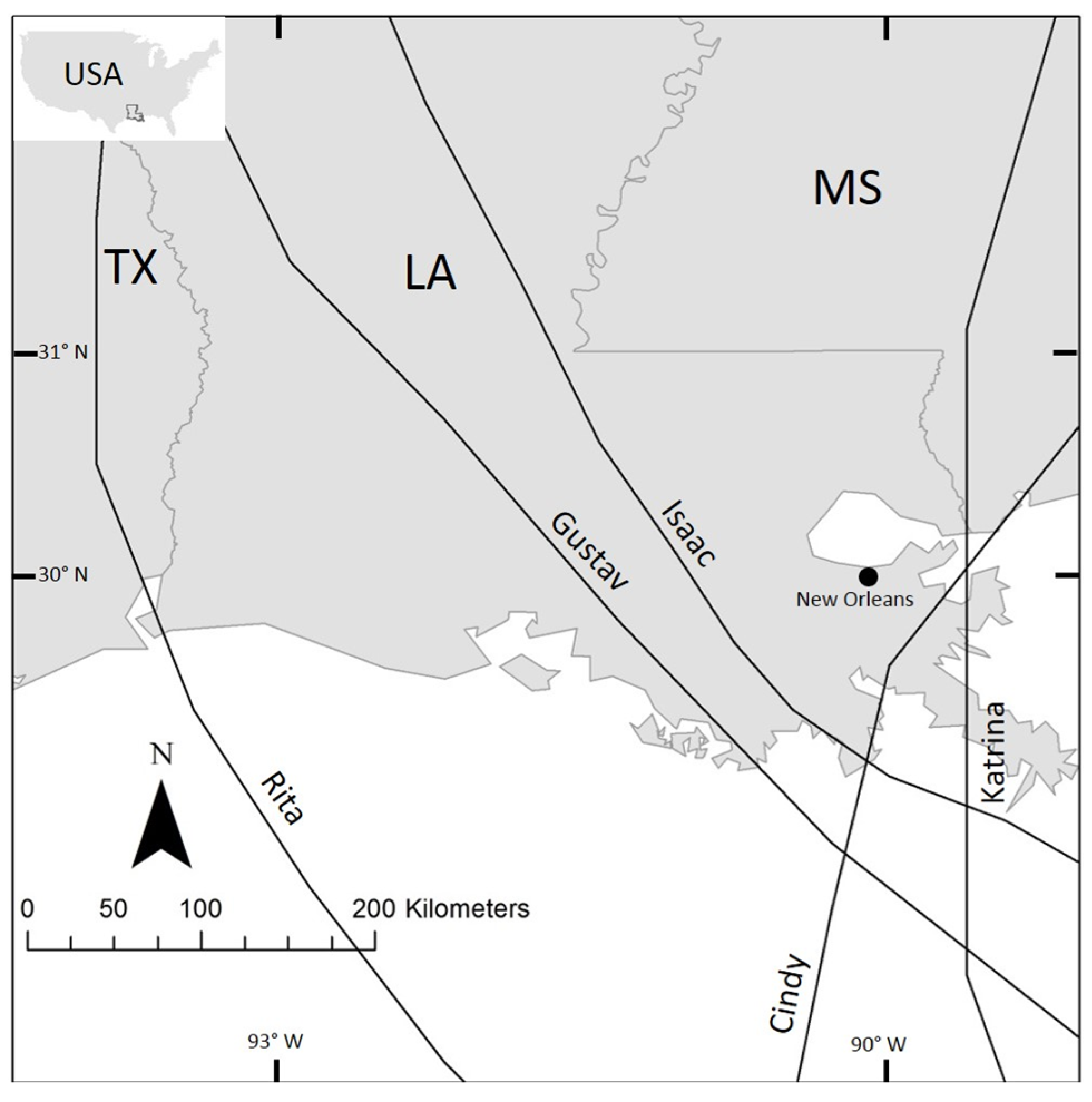
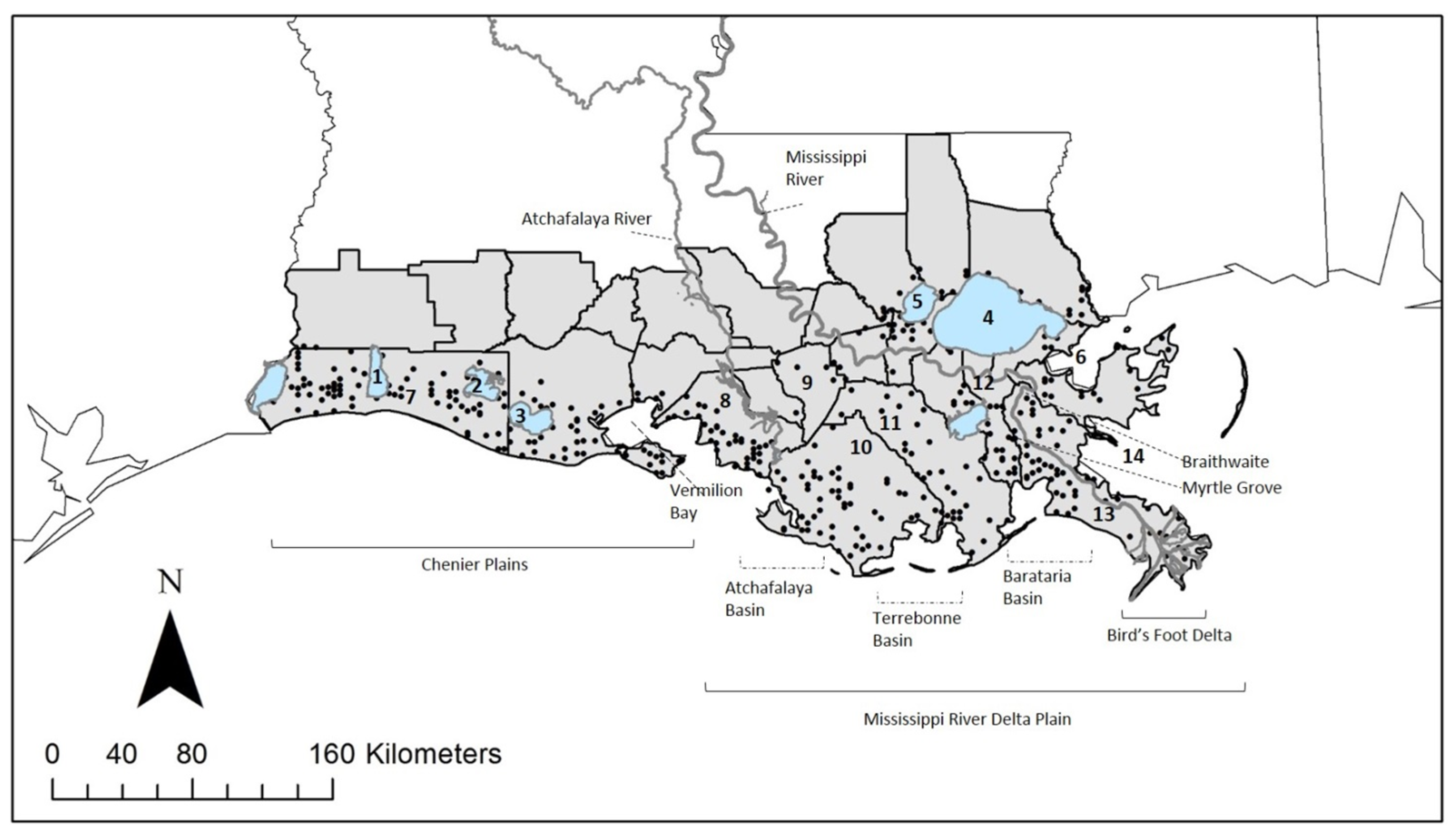
1.2. Study Area
1.3. Hurricane Isaac
2. Materials and Methods
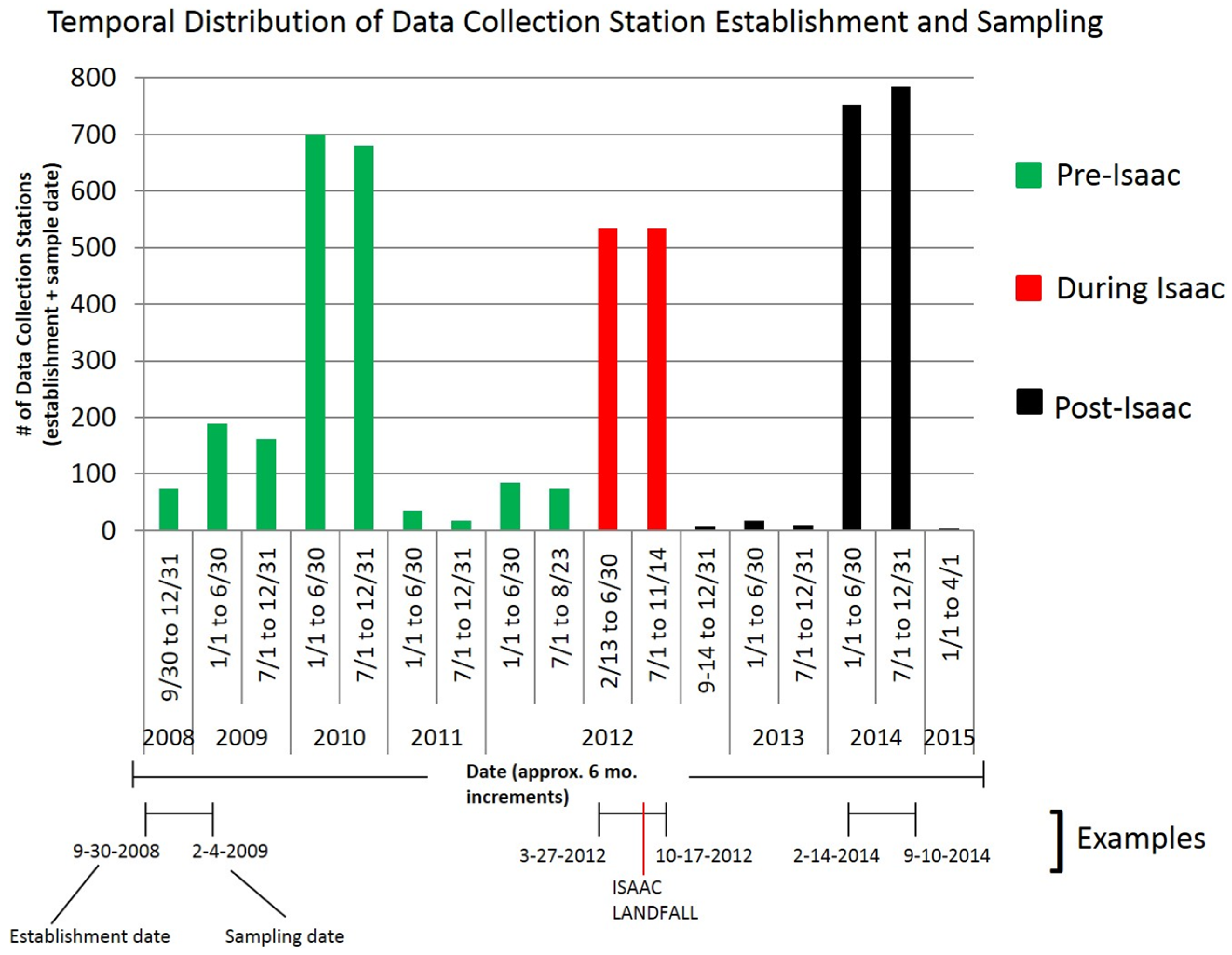
| Station Establishment and Sampling Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Pre Isaac | During Isaac | Post Isaac |
| # of Accretion Records (Data Collection Stations) | 1007 | 535 | 802 |
| Earliest Station Establishment | 9/30/2008 | 2/13/2012 | 9/14/2012 |
| Latest Station Establishment | 4/18/2012 | 6/5/2012 | 9/16/2014 |
| Earliest Sampling Date | 2/3/2009 | 9/3/2012 | 3/19/2013 |
| Latest Sampling Date | 8/23/2012 | 11/14/2012 | 4/1/2015 |
| Longest Sampling Period (Days) | 213 | 213 | 212 |
| Shortest Sampling Period (Days) | 64 | 141 | 62 |
| Average Sampling Period (Days) | 175 | 193 | 175 |
3. Results
| ACCRETION STATISTICS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Pre Isaac | During Isaac | Post Isaac |
| # of Sites | 272 | 188 | 278 |
| Mean (cm/year) | 2.89 | 4.04 | 2.38 |
| Standard Error | 0.18 | 0.33 | 0.21 |
| Mean, common sites (cm/year) | 2.85 | 4.39 | 2.13 |
| Median (cm/year) | 2.28 | 2.79 | 1.58 |
| Range (cm/year) | 0 to 35.08 | 0 to 28.84 | 0 to 46.58 |
| Standard Deviation | 2.98 | 4.48 | 3.49 |
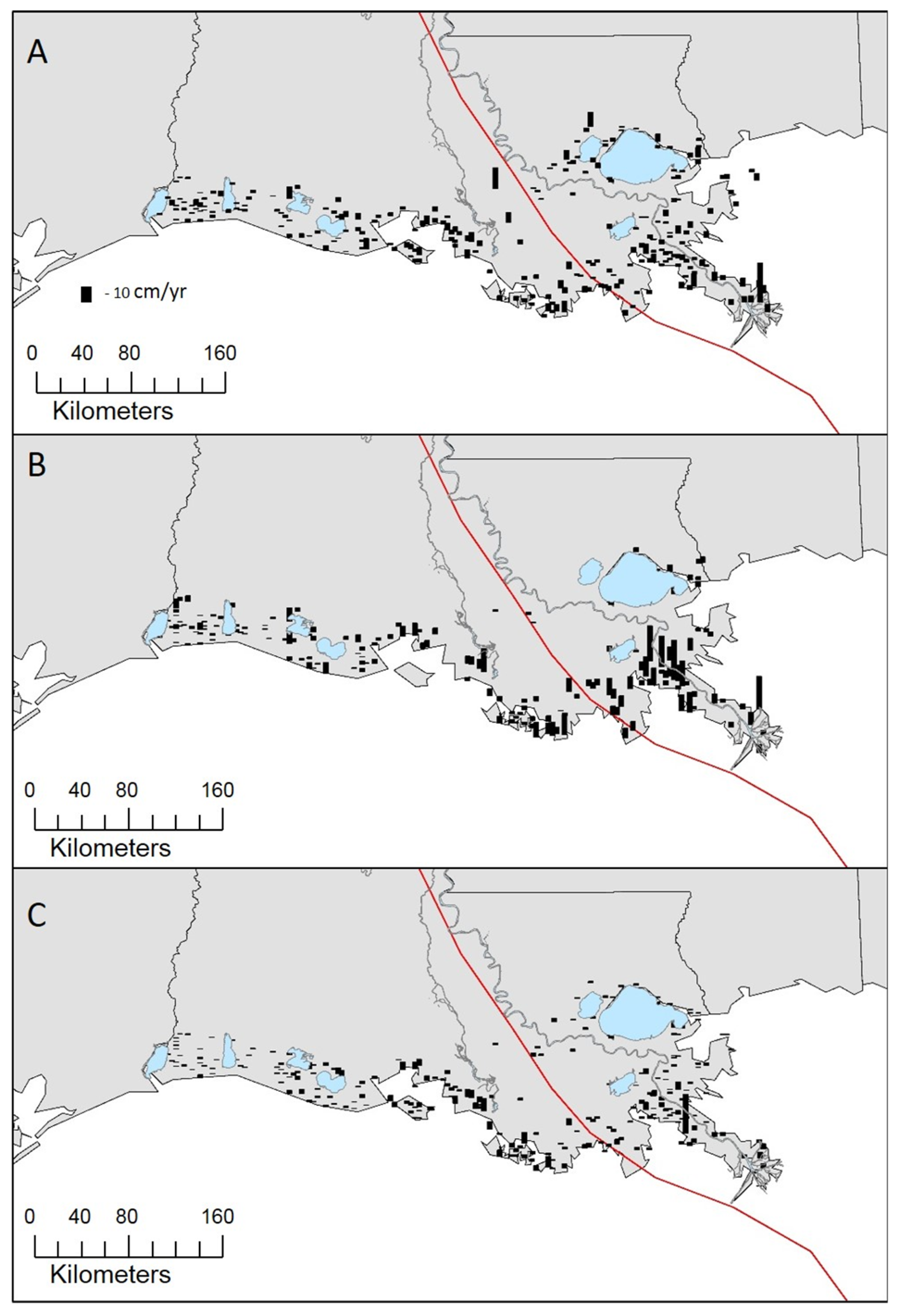
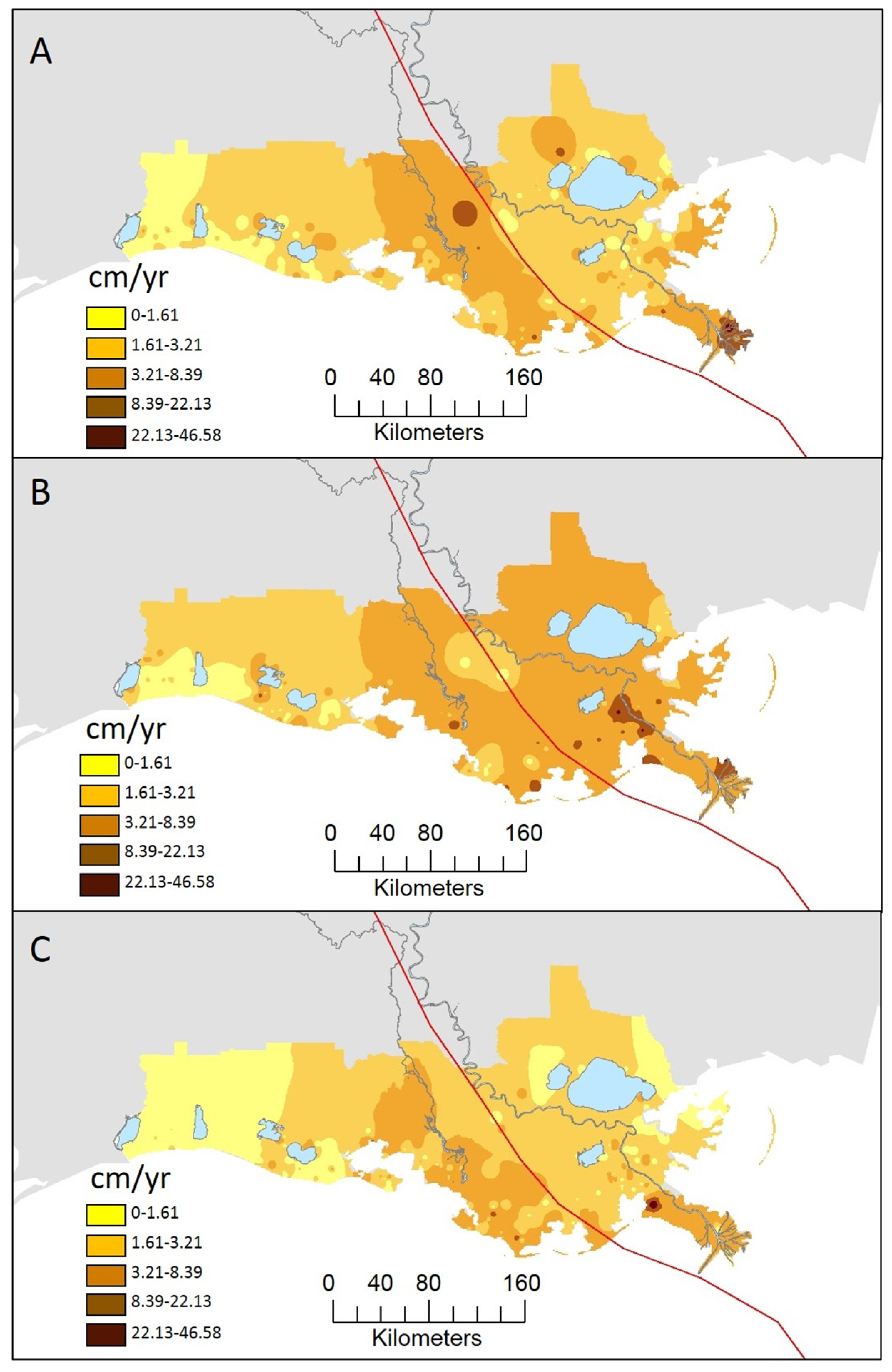

4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Variability in Accretion during Isaac Period
4.2. Temporal Variability in Accretion
4.3. The Role of Hurricanes as “Land-builders” for Coastal Louisiana
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couvillion, B.R.; Barras, J.A.; Steyer, G.D.; Sleavin, W.; Fischer, M.; Beck, H.; Trahan, N.; Griffin, B.; Heckman, D. Land area change in coastal Louisiana from 1932 to 2010. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3164, Scale 1:265,000; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2011; p. 12.
- Church, J.A.; Clark, P.U.; Cazenave, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Levermann, A.; Merrifield, M.A.; Milne, G.A.; Nerem, R.S.; Nunn, P.D.; et al. Sea level change. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 1137–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Barras, J.A.; Beville, S.; Britsch, D.; Hartley, S.; Hawes, S.; Johnston, J.; Kemp, P.; Kinler, Q.; Martucci, A.; Porthouse, J.; et al. Historical and Projected Coastal Louisiana Land Changes: 1978–2050; USGS Open File Report 03–334; U.S. Geoogca Survey: Lafayette, LA, USA, 2003; p. 39.
- Lam, N.S.N.; Arenas, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.B. An estimate of population impacted by climate change along the U.S. Coast. J. Coastal Res. 2009, SI 56, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Qiang, Y.; Lam, N.S.N. Modeling land use and land cover changes in a vulnerable coastal region using artificial neural networks and cellular automata. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Day, J.N. Wetland surface elevation, vertical accretion, and subsidence at three Louisiana estuaries receiving diverted Mississippi River water. Wetlands 2006, 26, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R.; Reed, D.J.; Day, J.W., Jr. Estimating shallow subsidence in microtidal salt marshes of the southeastern United States: Kaye and Barghoorn revisited. Mar. Geol. 1995, 128, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, S.; Ramsey, K.E. Relative sea-level rise in Louisiana and the Gulf of Mexico: 1908–1988. J. Coastal Res. 1990, 6, 323–342. [Google Scholar]
- Kolker, A.S.; Allison, M.A.; Hameed, S. An evaluation of subsidence rates and sea-level variability in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L21404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H.; Buresh, R.J. Sedimentation-rates determined by 137Cs dating in a rapidly accreting salt-marsh. Nature 1978, 275, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaune, R.D.; Baumann, R.H.; Gosselink, J.G. Relationships among vertical accretion, coastal submergence, and erosion in a Louisiana Gulf-Coast marsh. J. Sediment Petrol. 1983, 53, 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Delaune, R.D.; Whitcomb, J.H.; Patrick, W.H.; Pardue, J.H.; Pezeshki, S.R. Accretion and canal impacts in a rapidly subsiding wetland. 1. 137Cs and 210Pb techniques. Estuaries 1989, 12, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, R.H.; Day, J.W.; Miller, C.A. Mississippi deltaic wetland survival—Sedimentation versus coastal submergence. Science 1984, 224, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brantley, C.G.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Lane, R.R.; Hyfield, E.; Day, J.N.; Ko, J.-Y. Primary production, nutrient dynamics, and accretion of a coastal freshwater forested wetland assimilation system in Louisiana. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.A.; Allison, M.A. An equilibrium profile model for retreating marsh shorelines in southeast Louisiana. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 80, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, J.C. Vertical Accretion Rates in Coastal Louisiana: A Review of the Scientific Literature; United States Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2010; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Nyman, J.A.; Crozier, C.R.; Delaune, R.D. Roles and patterns of hurricane sedimentation in an estuarine marsh landscape. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R.; Reed, D.J.; Day, J.W.; Steyer, G.D.; Boumans, R.M.; Lynch, J.C.; McNally, D.; Latif, N. The influence of Hurricane Andrew on sediment distribution in Louisiana coastal marshes. J. Coastal Res. 1995, SI 21, 280–294. [Google Scholar]
- Tweel, A.W.; Turner, R.E. Landscape-scale analysis of wetland sediment deposition from four tropical cyclone events. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.H. Dynamic changes of the Holocene Mississippi River Delta Plain: The delta cycle. J. Coastal Res. 1997, 13, 605–627. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, R.A.; Taylor, M.J.; Byrnes, M.R. Coastal morphodynamics and Chenier-Plain evolution in southwestern LA, USA: A geomorphic model. Geomorphology 2007, 88, 367–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, C.E.; Visser, J.M.; Mouton, E.; Linscombe, J.; Hartley, S.B. Vegetation Types in Coastal Louisiana in 2013. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3290, 1 Sheet, Scale 1:550,000; United States Geological Survey: Lafayette, LA, USA, 2014.
- Berg, R. Hurricane Isaac (al092012) 21 August–1 September 2012; Technical report for National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Weather Service: Miami, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hurricane Isaac with and without 2012 100-Year HSDRRS Evaluation; Technical report for United States Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 230.
- Demas, A. Mississippi River Flows Backwards Due to Isaac; United States Geological Survey Newsroom: Reston, VA, USA, 2012.
- Liu, K.B.; McCloskey, T.A.; Ortego, S.; Maiti, K. Sedimentary signature of Hurricane Isaac in a Taxodium swamp on the western margin of Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana, USA. In Sediment Dynamics from the Summit to the Sea; Xu, Y.J., Allison, M.A., Bentley, S.J., Collins, A.L., Erskine, W.D., Golosov, V., Horowitz, A.J., Stone, M., Eds.; International Association of Hydrological Sciences: Wallingford, UK, 2014a; pp. 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.B.; McCloskey, T.A.; Bianchette, T.A.; Keller, G.; Lam, N.S.N.; Cable, J.E.; Arriola, J. Hurricane Isaac storm surge deposition in a coastal wetland along Lake Pontchartrain, southern Louisiana. J. Coastal Res. 2014, SI70, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority. Coastal Information Management System. Available online: http://cims.coastal.louisiana.gov/default.aspx (accessed on 11 June 2015).
- Steyer, G.D. Coastal Reference Monitoring System (CRMS). United States Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2010–3018; United States Geological Survey: Lafayette, LA, USA, 2010; p. 2.
- Folse, T.M.; Sharp, L.A.; West, J.L.; Hymel, M.K.; Troutman, J.P.; McGinnis, T.E.; Weifenbach, D.; Boshart, W.M.; Rodrigue, L.B.; Richardi, D.C.; Wood, W.B.; Miller, C.M. A Standard Operating Procedures Manual for the Coastwide Reference Monitoring System-Wetlands: Methods for Site Establishment, Data Collection, and Quality Assurance/Quality Control (Revised); Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2014; p. 228.
- Cahoon, D.R.; Lynch, J.C.; Knaus, R.M. Improved cryogenic coring device for sampling wetland soils. J. Sediment Res. 1996, 66, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, P.A.; Goodchild, M.F.; Maguire, D.J.; Rhind, D.W. Geographic Information Systems and Science, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2001; p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, W.R. Computer movie simulating urban growth in Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R. Recent accretion in two managed marsh impoundments in coastal Louisiana. Ecol. Appl. 1994, 4, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahoon, D.R.; Turner, R.E. Accretion and canal impacts in a rapidly subsiding wetland. 2. Feldspar marker horizon technique. Estuaries 1989, 12, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander-Bloch, B. Plaquemines after Hurricane Isaac: A Year Later, Residents Redefine What Home Means. Available online: http://www.nola.com/environment/index.ssf/2013/08/plaquemines_after_hurricane_is_3.html (accessed on 6 October 2015).
- Falcini, F.; Khan, N.S.; Macelloni, L.; Horton, B.P.; Lutken, C.B.; McKee, K.L.; Santoleri, R.; Colella, S.; Li, C.; Volpe, G.; D’Emidio, M.; Salusti, A.; Jerolmack, D.J. Linking the historic 2011 Mississippi River flood to coastal wetland sedimentation. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Baustian, J.J.; Swenson, E.M.; Spicer, J.S. Wetland sedimentation from Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Science 2006, 314, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweel, A.W.; Turner, R.E. Contribution of tropical cyclones to the sediment budget for coastal wetlands in Louisiana, USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baustian, J.J.; Mendelssohn, I.A. Hurricane-induced sedimentation improves marsh resilience and vegetation vigor under high rates of relative sea level rise. Wetlands 2015, 35, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.A.; Mendelssohn, I.A. Functional assessment of differential sediment slurry applications in a deteriorating brackish marsh. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, J.A.; Walters, R.J.; Delaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Marsh vertical accretion via vegetative growth. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaseanu-Lovejoy, M.; Kranenburg, C.; Barras, J.A.; Brock, J.C. Land loss due to recent hurricanes in coastal Louisiana, USA. J. Coastal Res. 2013, SI 63, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, N.C.; Fitzgerald, D.M.; Hughes, Z.J.; Georgiou, I.Y.; Kulp, M.A.; Miner, M.D.; Smith, J.M.; Barras, J.A. Hurricane-induced failure of low salinity wetlands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14014–14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.A.; Barras, J.A. Hurricane impacts on coastal wetlands: A half-century record of storm-generated features from southern Louisiana. J. Coastal Res. 2011, 27, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnqvist, T.E.; Paola, C.; Parker, G.; Liu, K.B.; Mohrig, D.; Holbrook, J.M.; Twilley, R.R. Comment on Wetland sedimentation from hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Science 2007, 316, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchette, T.A.; Liu, K.-b.; Qiang, Y.; Lam, N.S.-N. Wetland Accretion Rates Along Coastal Louisiana: Spatial and Temporal Variability in Light of Hurricane Isaac’s Impacts. Water 2016, 8, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010001
Bianchette TA, Liu K-b, Qiang Y, Lam NS-N. Wetland Accretion Rates Along Coastal Louisiana: Spatial and Temporal Variability in Light of Hurricane Isaac’s Impacts. Water. 2016; 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchette, Thomas A., Kam-biu Liu, Yi Qiang, and Nina S.-N. Lam. 2016. "Wetland Accretion Rates Along Coastal Louisiana: Spatial and Temporal Variability in Light of Hurricane Isaac’s Impacts" Water 8, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010001
APA StyleBianchette, T. A., Liu, K.-b., Qiang, Y., & Lam, N. S.-N. (2016). Wetland Accretion Rates Along Coastal Louisiana: Spatial and Temporal Variability in Light of Hurricane Isaac’s Impacts. Water, 8(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8010001