Heuristic Methods for Reservoir Monthly Inflow Forecasting: A Case Study of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Pearl River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sets
2.1. Study Area
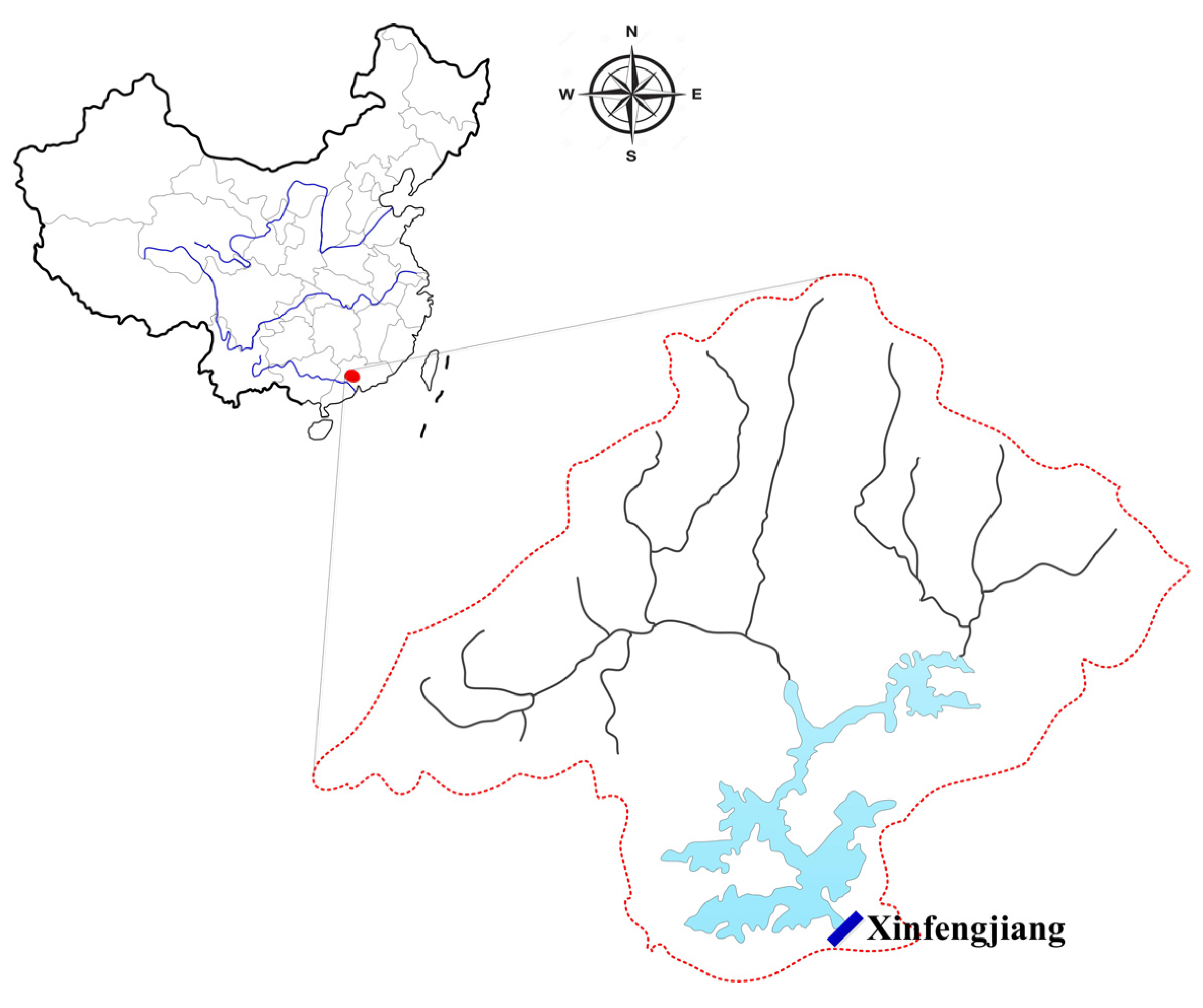
2.2. Division of Data
| Datasets | Statistic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xmean | Sd | Xmin | Xmax | Range | |
| Training set | 204.1 | 14.3 | 9.3 | 1506.0 | 1496.7 |
| Testing set | 192.1 | 13.9 | 24.5 | 1300.2 | 1275.7 |
| Validation set | 176.3 | 13.3 | 22.3 | 1496.4 | 1474.1 |
| Original data | 195.3 | 14.0 | 9.3 | 1506.0 | 1496.7 |
2.3. Data Preprocessing
3. Forecasting Methodology
3.1. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
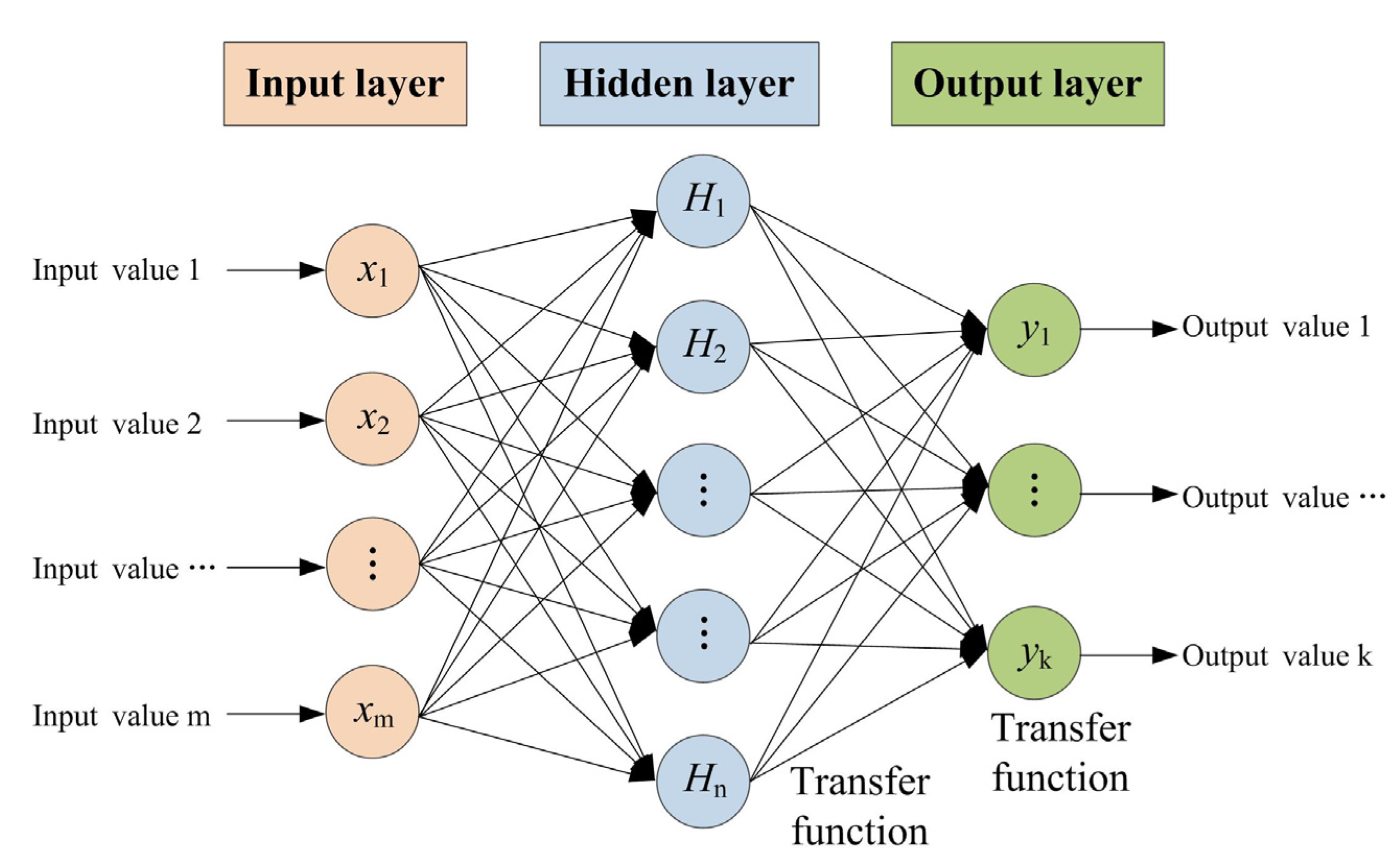
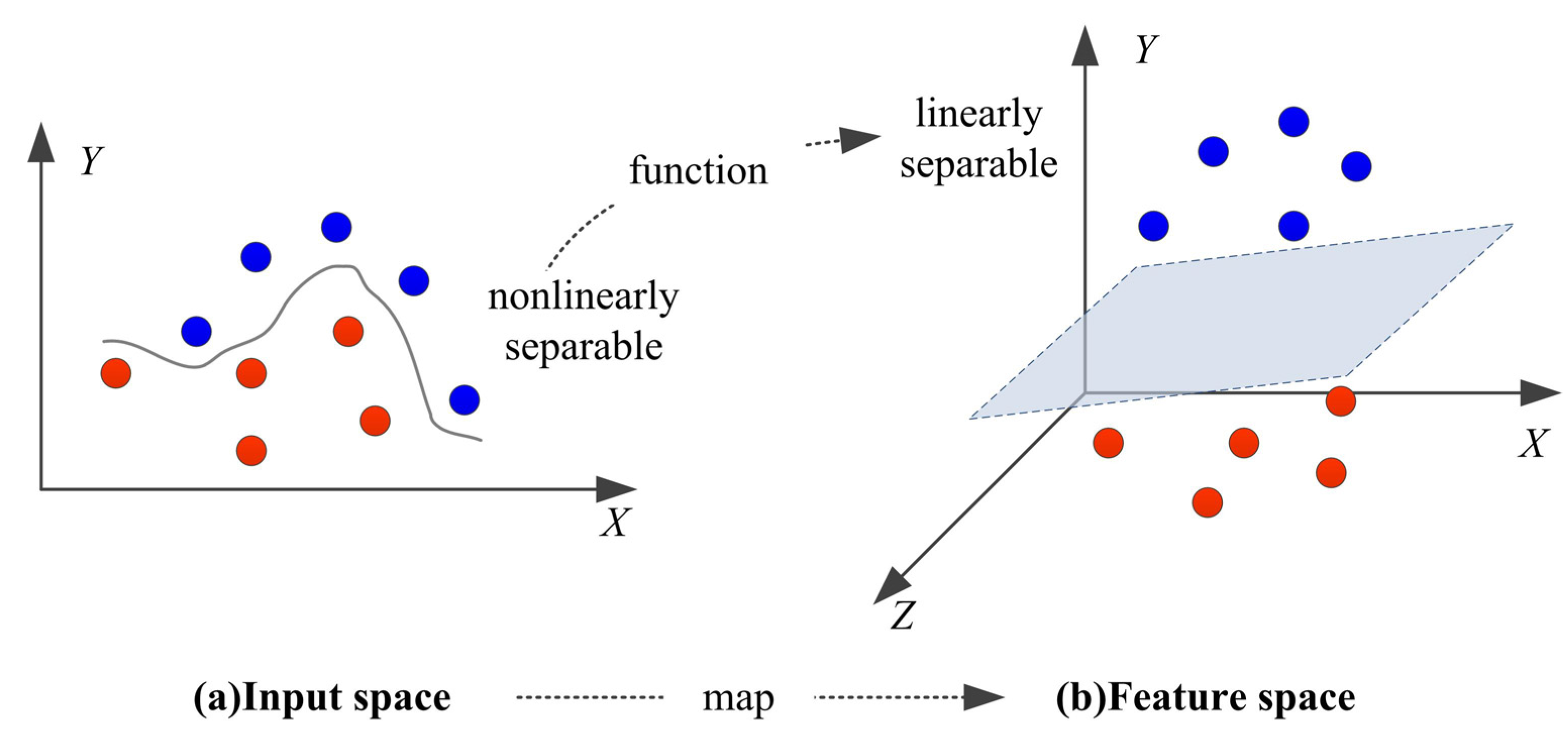
3.2. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
3.3. Genetic Algorithm (GA)

3.4. Hybrid Forecasting Method
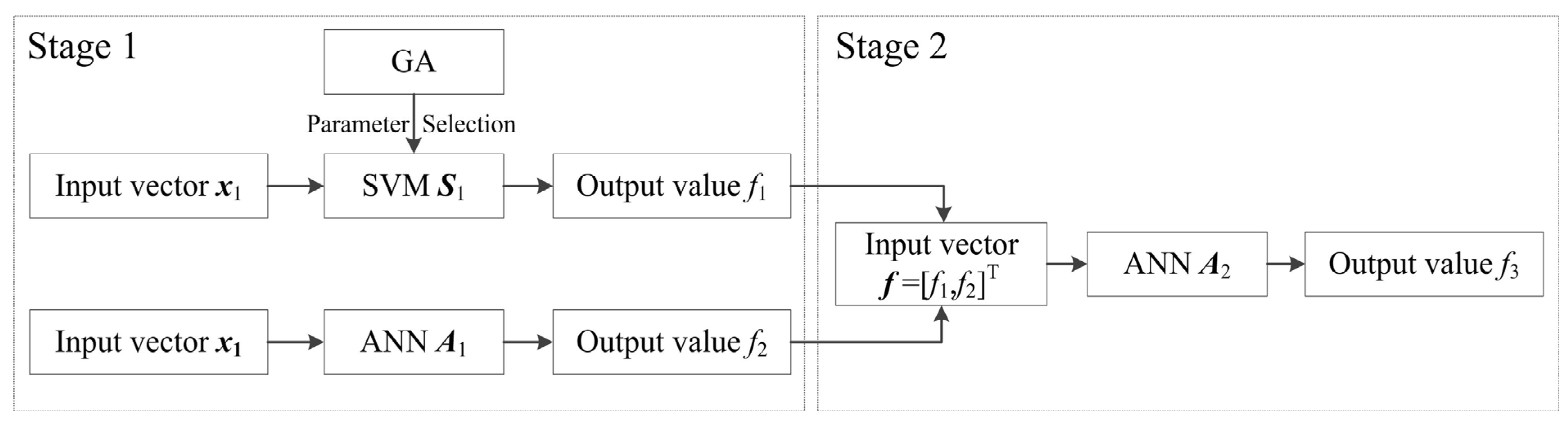
4. Statistical Measures
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Input Variables Determination
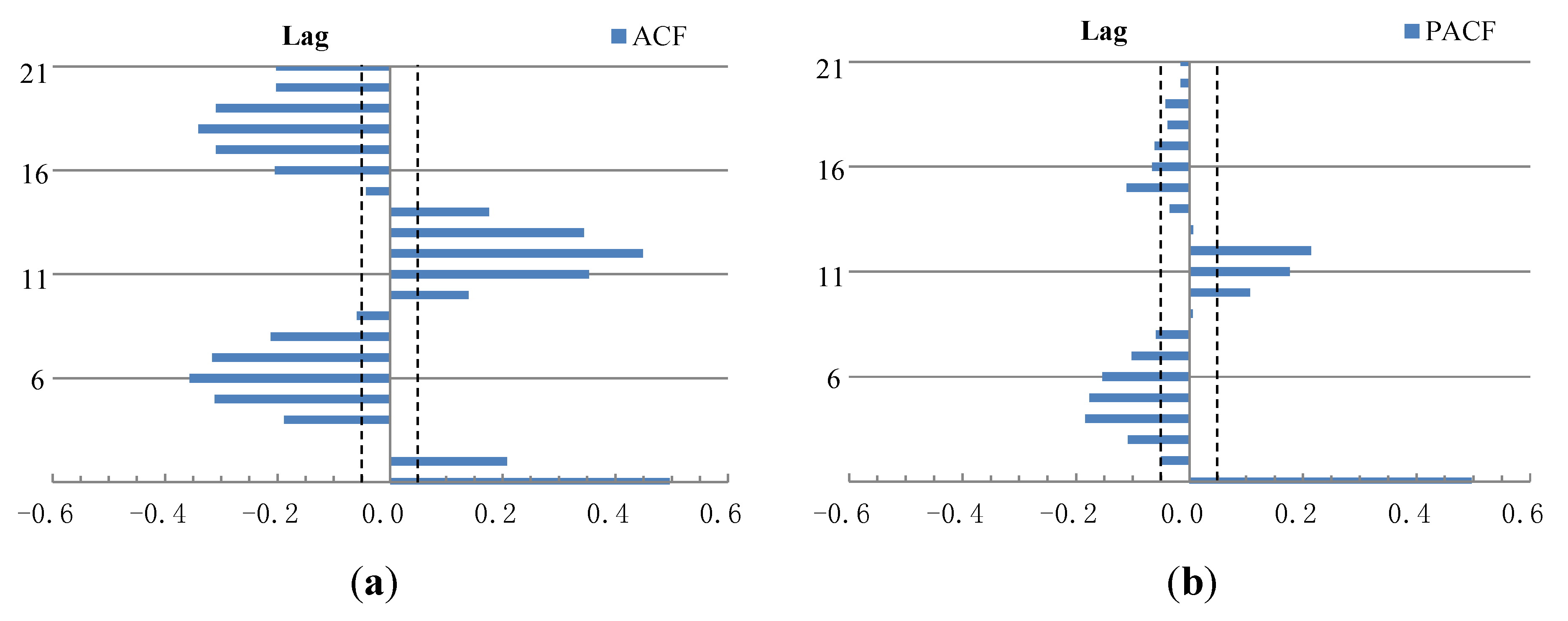
5.2. Development of Various Models
5.2.1. ANN Model A1 Development
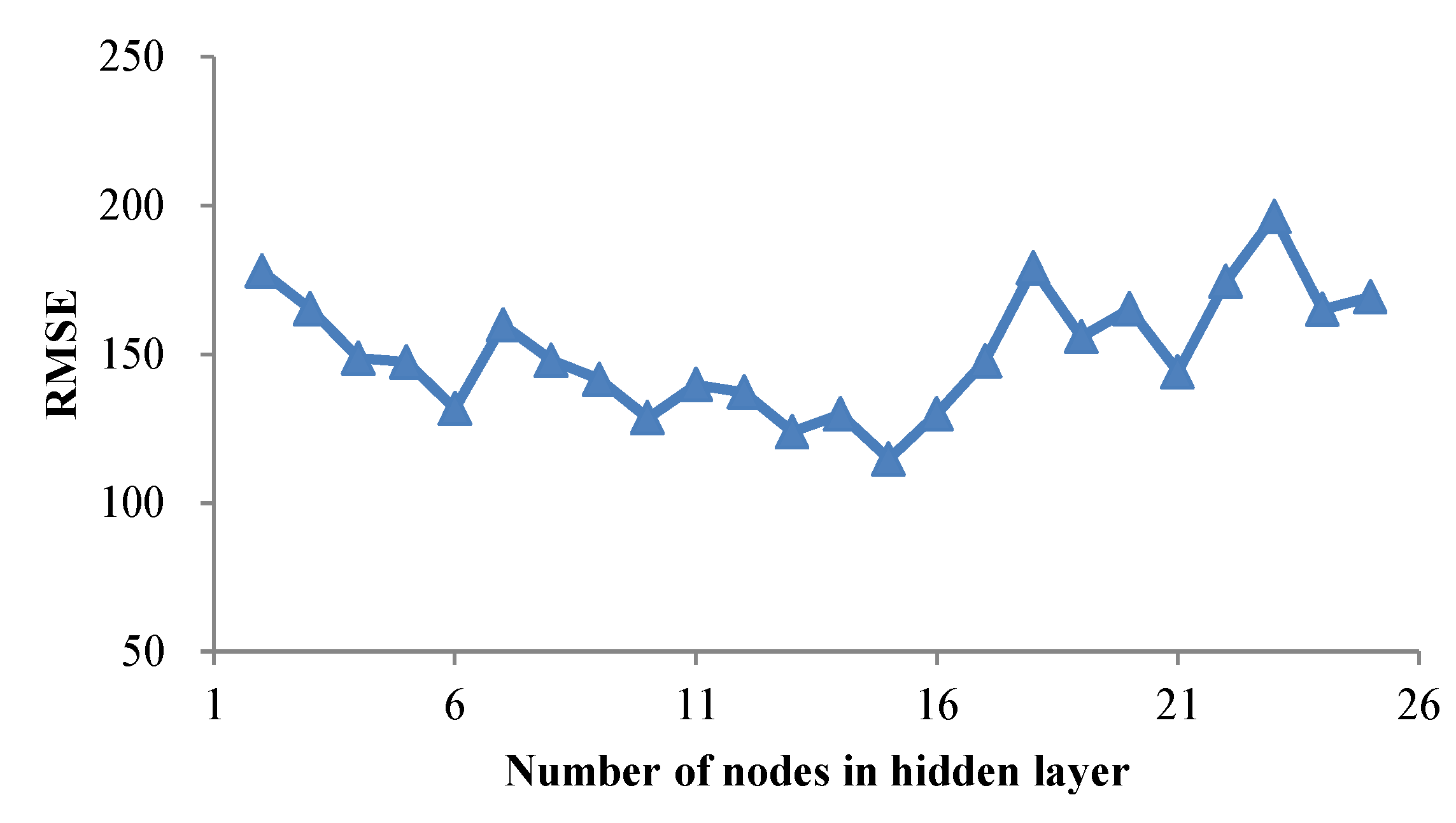
5.2.2. SVM Model S1 Development
| Trial No. | Optimal Parameters (C, ε, σ) | Training | Validation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | NS | R | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | NS | R | ||
| 1 | (10.653, 1.032, 0.078) | 151.00 | 59.19 | 87.85 | 0.49 | 0.70 | 153.90 | 70.23 | 93.03 | 0.42 | 0.64 |
| 2 | (9.827, 0.435, 0.064) | 144.82 | 54.29 | 85.60 | 0.53 | 0.73 | 133.07 | 61.87 | 82.54 | 0.56 | 0.75 |
| 3 | (2.783, 0.678, 0.125) | 152.46 | 61.54 | 88.08 | 0.48 | 0.69 | 152.51 | 66.38 | 89.44 | 0.43 | 0.65 |
| 4 | (9.425, 0.823, 0.081) | 118.66 | 70.48 | 82.44 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 96.60 | 75.73 | 74.36 | 0.77 | 0.89 |
| 5 | (11.803, 1.254, 0.708) | 147.80 | 64.17 | 88.98 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 154.22 | 74.28 | 94.58 | 0.41 | 0.65 |
5.2.3. ANN Model A2 Development
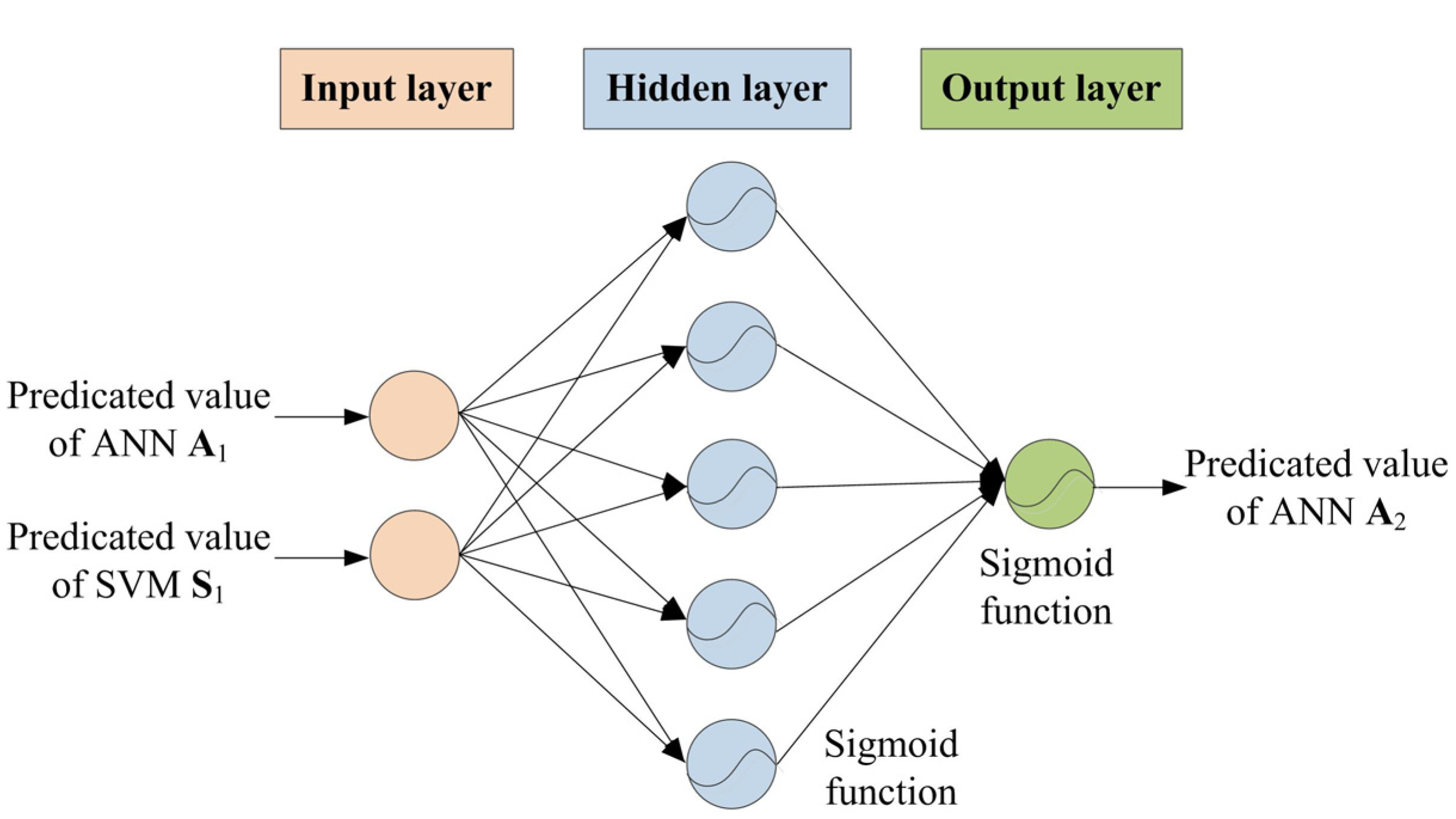
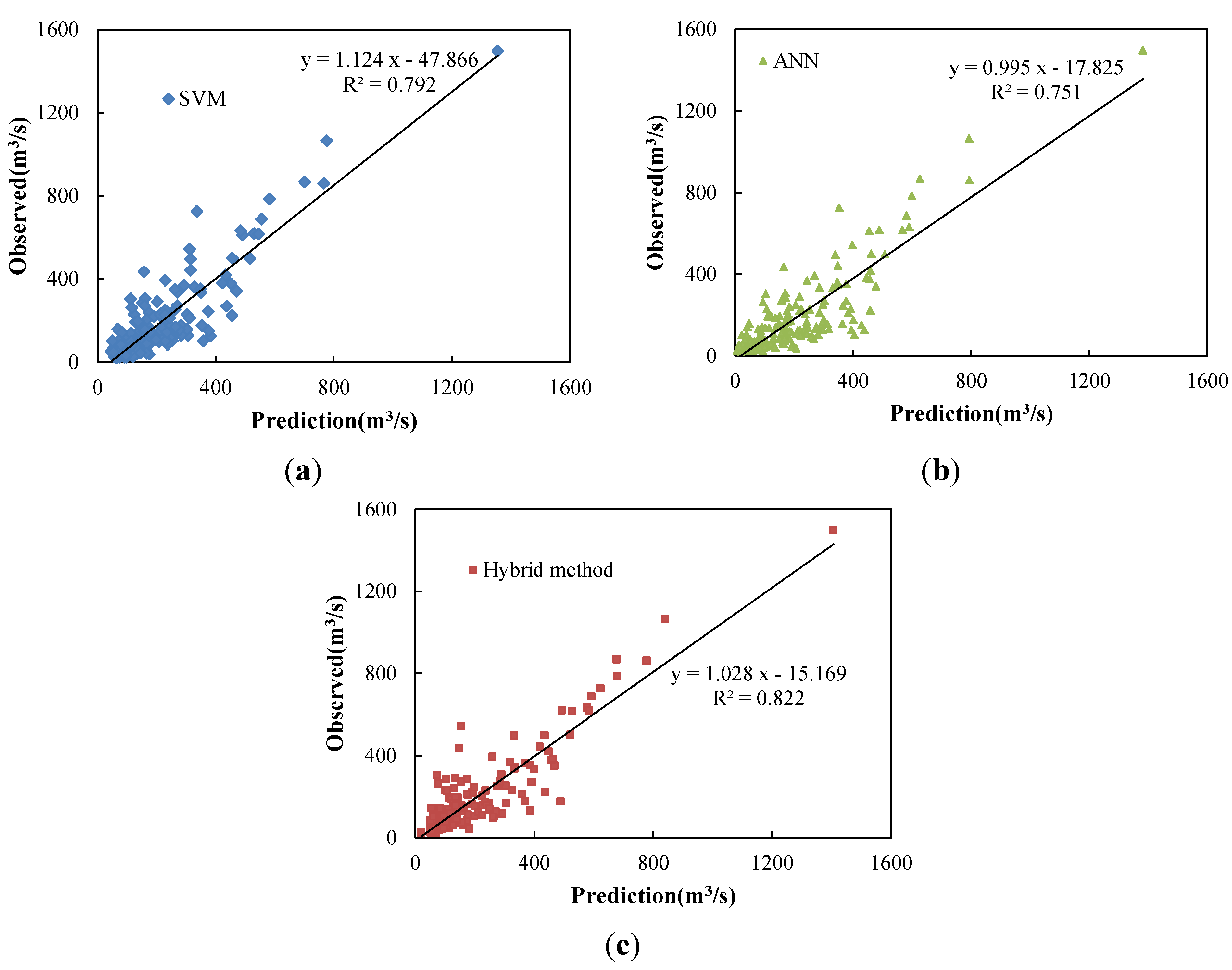
5.3. Comparison and Discussion
| Models | Training | Validation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | NS | R | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | NS | R | |
| SVM | 118.66 | 70.48 | 82.44 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 96.60 | 75.73 | 74.36 | 0.77 | 0.89 |
| ANN | 118.60 | 55.20 | 79.73 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 102.09 | 63.68 | 73.49 | 0.74 | 0.87 |
| Hybrid Method | 95.86 | 48.28 | 62.44 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 85.72 | 49.78 | 58.33 | 0.82 | 0.91 |
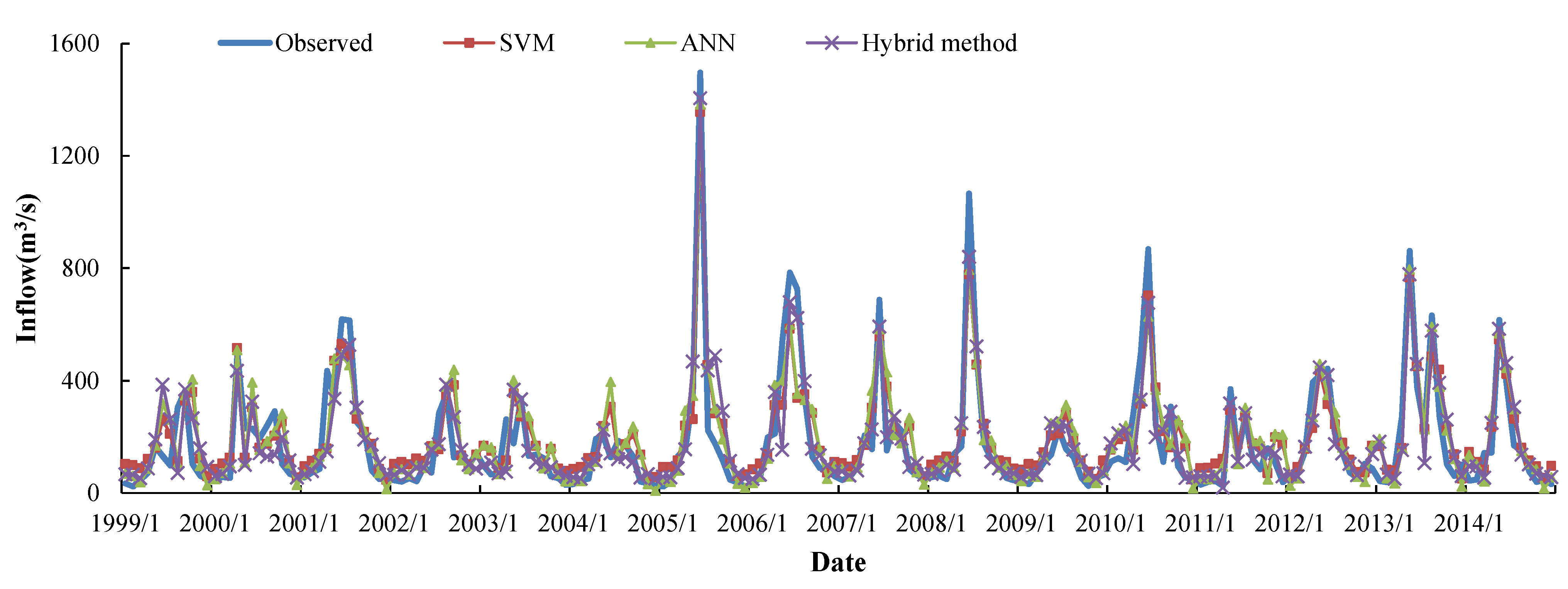
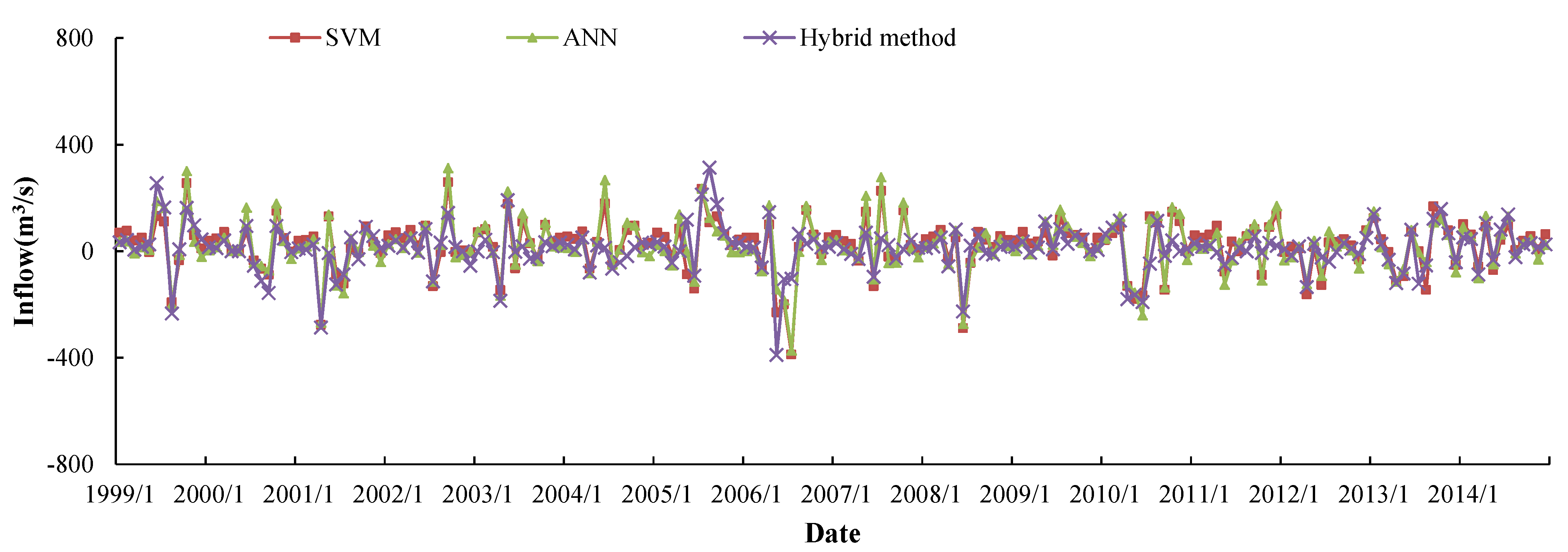
| Peak No. | Date | Observed | Forecast Peak | Relative Error (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak | SVM | ANN | Hybrid Method | SVM | ANN | Hybrid Method | ||
| 1 | 1999/9 | 362.0 | 327.9 | 346.9 | 369.5 | −9.4 | −4.2 | 2.1 |
| 2 | 2000/4 | 497.9 | 516.0 | 507.5 | 434.9 | 3.6 | 1.9 | −12.7 |
| 3 | 2001/6 | 618.1 | 530.3 | 488.4 | 492.9 | −14.2 | −21.0 | −20.3 |
| 4 | 2002/8 | 352.6 | 349.1 | 376.7 | 386.2 | −1.0 | 6.8 | 9.5 |
| 5 | 2003/6 | 336.2 | 272.0 | 285.6 | 334.4 | −19.1 | −15.1 | −0.5 |
| 6 | 2004/5 | 202.8 | 237.3 | 236.8 | 225.8 | 17.0 | 16.8 | 11.3 |
| 7 | 2005/6 | 1496.4 | 1355.5 | 1381.3 | 1405.7 | −9.4 | −7.7 | −6.1 |
| 8 | 2006/6 | 783.8 | 583.2 | 598.1 | 679.5 | −25.6 | −23.7 | −13.3 |
| 9 | 2007/6 | 687.5 | 555.7 | 581.4 | 592.1 | −19.2 | −15.4 | −13.9 |
| 10 | 2008/6 | 1066.0 | 776.5 | 792.3 | 840.5 | −27.2 | −25.7 | −21.2 |
| 11 | 2009/6 | 228.2 | 211.5 | 252.4 | 236.1 | −7.3 | 10.6 | 3.5 |
| 12 | 2010/6 | 867.5 | 701.4 | 626.7 | 677.5 | −19.2 | −27.8 | −21.9 |
| 13 | 2011/5 | 369.6 | 293.5 | 244.1 | 319.3 | −20.6 | −34.0 | −13.6 |
| 14 | 2012/6 | 442.3 | 315.6 | 348.7 | 419.6 | −28.6 | −21.2 | −5.1 |
| 15 | 2013/5 | 860.9 | 766.5 | 794.2 | 778.3 | −11.0 | −7.7 | −9.6 |
| 16 | 2014/5 | 616.2 | 544.8 | 567.0 | 584.9 | −11.6 | −8.0 | −5.1 |
| Average (absolute) | 15.2 | 15.5 | 10.6 | |||||
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, T.; Zhao, J. Joint and respective effects of long and short-term forecast uncertainties on reservoir operations. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.C.; Chang, L.C.; Chang, F.J. Using a hybrid genetic algorithm-simulated annealing algorithm for fuzzy programming of reservoir operation. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3162–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouz, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Moridi, A. Probabilistic reservoir operation using bayesian stochastic model and support vector machine. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Yao, Y.; Ma, C.; Guo, Q. Reservoir operation rules for controlling algal blooms in a tributary to the impoundment of three gorges dam. Water 2014, 6, 3200–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.W.; Wu, C.L.; Li, Y.S. Comparison of several flood forecasting models in Yangtz River. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2005, 10, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lin, K.; Wei, X. A two-stage method of quantitative flood risk analysis for reservoir real-time operation using ensemble-based hydrologic forecasts. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk A 2014, 29, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.W.; Wu, C.A. Hybrid model coupled with singular spectrum analysis for daily rainfall prediction. J. Hydroinform. 2010, 12, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Lin, J.Y.; Sun, Y.G.; Chau, K.W. Long-term prediction of discharges in Manwan hydropower using adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference systems models. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2005, 3612, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, S.W.; Weber, F.A. Detection of long-term change in hydroelectric reservoir inflows: Bridging theory and practice. J. Hydrol. 2012, 470, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W.; Li, Y.S. Methods to improve neural network performance in daily flows prediction. J. Hydrol. 2009, 372, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.R. Flood Management in California. Water 2012, 4, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttil, N.; Chau, K.W. Machine learning paradigms for selecting ecologically significant input variables. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 20, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, P.; Haché, M.; Fortin, V.; Bobée, B. Improving daily reservoir inflow forecasts with model combination. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2005, 10, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Lund, J.R.; Jenkins, M.W.; Marques, G.F.; Ritzema, R.S. Climate change, urbanization, and optimal long-term floodplain protection. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W. Data-driven models for monthly streamflow time series prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2010, 23, 1350–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Banihabib, M.E.; Behbahani, S.M.R. Comparison of the ARMA, ARIMA and the autoregressive artificial neural network models in forecasting the monthly inflow of Dez dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Chau, K.W.; Cheng, C.T.; Qiu, L. A comparison of performance of several artificial intelligence methods for forecasting monthly discharge time series. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taormina, R.; Chau, K.W. Neural network river forecasting with multi-objective fully informed particle swarm optimization. J. Hydroinform. 2015, 17, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Chen, G.R.; Huang, P.Y. Effective typhoon characteristics and their effects on hourly reservoir inflow forecasting. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, M.C.; Venancio, A.; Kahya, E. Flow forecast by SWAT model and ANN in Pracana basin, Portugal. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2009, 40, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidifarzad, B.; Nourani, V.; Aalami, M.; Chau, K.W. Multi-site calibration of linear reservoir based geomorphologic rainfall-runoff models. Water 2014, 6, 2690–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chau, K.W. Intelligent manipulation and calibration of parameters for hydrological models. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 28, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Ou, C.P.; Chau, K.W. Combining a fuzzy optimal model with a genetic algorithm to solve multi-objective rainfall-runoff model calibration. J. Hydrol. 2002, 268, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, M.T.; Yurekli, K.; Pal, M. Performance evaluation of artificial neural network approaches in forecasting reservoir inflow. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: A review of modeling issues and applications. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2000, 15, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taormina, R.; Chau, K.W.; Sethi, R. Artificial neural network simulation of hourly groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer system of the venice lagoon. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Cimen, M. A wavelet-support vector machine conjunction model for monthly streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Yu, S.P.; Liu, G.M. Multi-step-ahead predictor design for effective long-term forecast of hydrological signals using a novel wavelet neural network hybrid model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4981–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Karbassi, A.R.; Moghaddamnia, A.; Han, D.; Zokaei-Ashtiani, M.H.; Farokhnia, A.; Gousheh, M.G. Assessment of input variables determination on the SVM model performance using PCA, Gamma test, and forward selection techniques for monthly stream flow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2011, 40, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Chen, G.R.; Wu, M.C.; Chou, Y.C. Effective forecasting of hourly typhoon rainfall using support vector machines. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazartseren, B.; Hildebrandt, G.; Holz, K.P. Short-term water level prediction using neural networks and neuro-fuzzy approach. Neurocomputing 2003, 55, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, P.; Anctil, F.; Bobee, B. Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using artificial neural networks with stopped training approach. J. Hydrol. 2000, 230, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, B.; Li, C.; Yang, Z. A structurally simplified hybrid model of genetic algorithm and support vector machine for prediction of chlorophyll a in reservoirs. Water 2015, 7, 1610–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lung, W.S. A hybrid neural-genetic algorithm for reservoir water quality management. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.H.; Wu, J.; Lu, H.Y.; Wang, J.Z. A case study on a hybrid wind speed forecasting method using bp neural network. Knowl. Based Syst. 2011, 24, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalaiah, K.; Deo, M.C. River stage forecasting using artificial neural networks. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1998, 3, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvisi, S.; Mascellani, G.; Franchini, M.; Bardossy, A. Water level forecasting through fuzzy logic and artificial neural network approaches. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S.; Kisi, O.; Singh, V.P. Daily water level forecasting using wavelet decomposition and artificial intelligence techniques. J. Hydrol. 2015, 520, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, C.T.; Liao, S.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Shen, J.J. Daily reservoir inflow forecasting combining QPF into ANNs model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 6, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Cheng, C.T.; Chau, K.W. Using support vector machines for long-term discharge prediction. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Yang, S.L.; Lei, Y.P. Quantifying the anthropogenic and climatic impacts on water discharge and sediment load in the Pearl River (Zhujiang), China (1954–2009). J. Hydrol. 2012, 452, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.S.; Chen, S.T.; Chang, I.F. Support vector regression for real-time flood stage forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.F.; Chen, G.R.; Huang, P.Y.; Chou, Y.C. Support vector machine-based models for hourly reservoir inflow forecasting during typhoon-warning periods. J. Hydrol. 2009, 372, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W.; Li, Y.S. River stage prediction based on a distributed support vector regression. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-T.; Feng, Z.-K.; Niu, W.-J.; Liao, S.-L. Heuristic Methods for Reservoir Monthly Inflow Forecasting: A Case Study of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Pearl River, China. Water 2015, 7, 4477-4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7084477
Cheng C-T, Feng Z-K, Niu W-J, Liao S-L. Heuristic Methods for Reservoir Monthly Inflow Forecasting: A Case Study of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Pearl River, China. Water. 2015; 7(8):4477-4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7084477
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chun-Tian, Zhong-Kai Feng, Wen-Jing Niu, and Sheng-Li Liao. 2015. "Heuristic Methods for Reservoir Monthly Inflow Forecasting: A Case Study of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Pearl River, China" Water 7, no. 8: 4477-4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7084477
APA StyleCheng, C.-T., Feng, Z.-K., Niu, W.-J., & Liao, S.-L. (2015). Heuristic Methods for Reservoir Monthly Inflow Forecasting: A Case Study of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Pearl River, China. Water, 7(8), 4477-4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7084477







