Using Pressure and Alteration Indicators to Assess River Morphological Quality: Case Study of the Prahova River (Romania)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
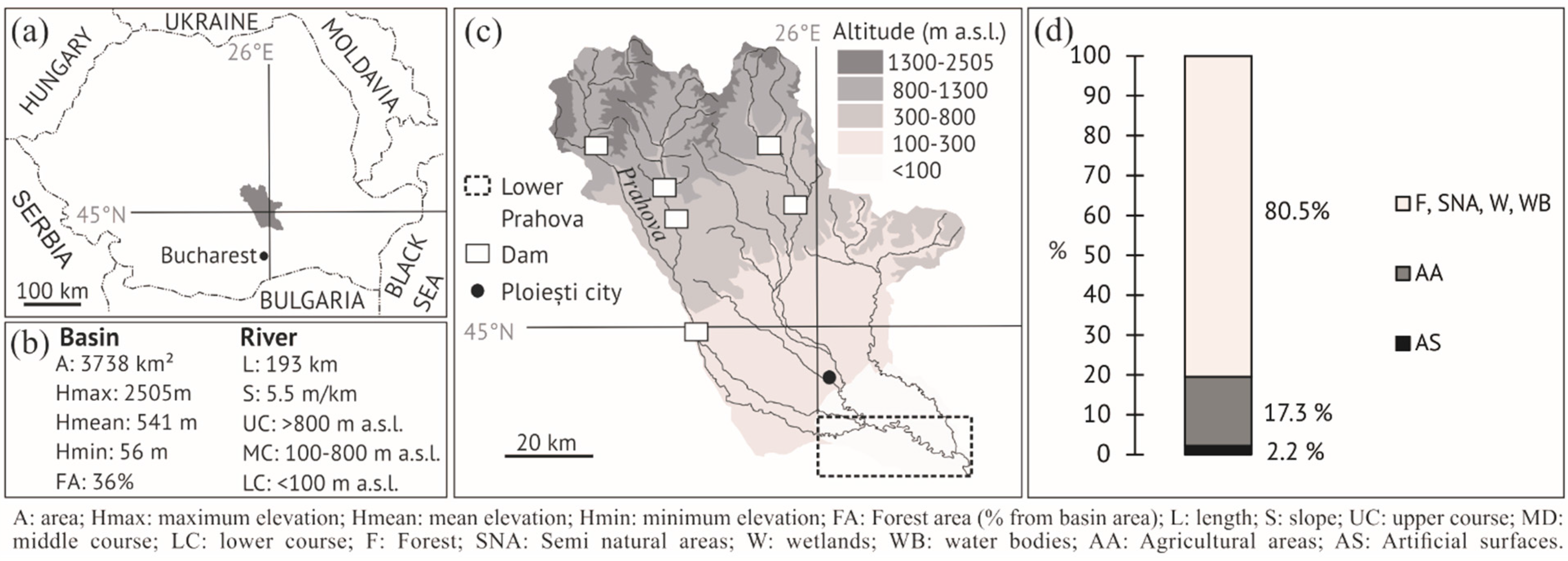
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
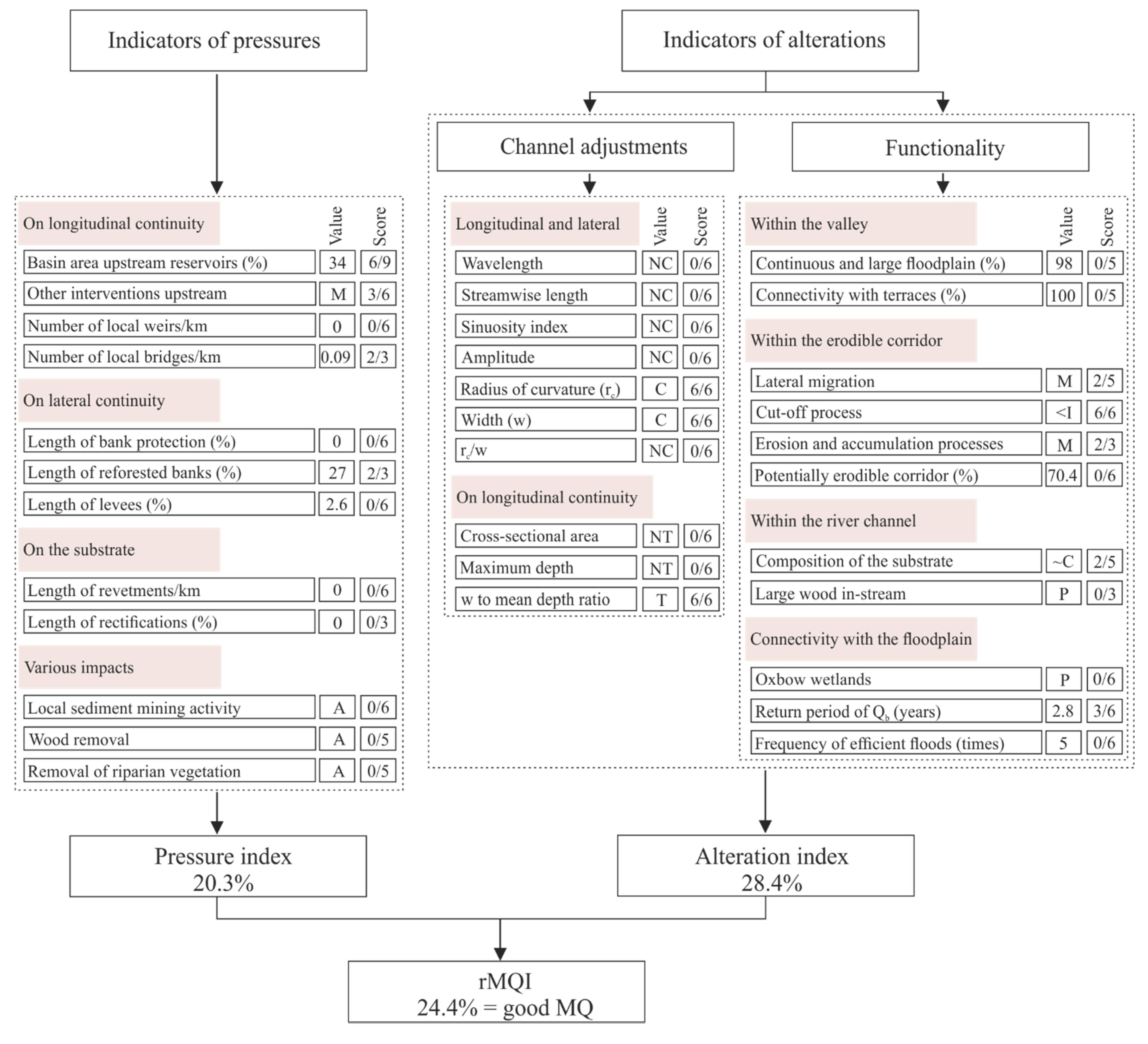
3.2. Revisited Morphological Quality Index
3.2.1. Human Pressure Indicators Linked to Disturbed River Morphology

3.2.2. Change/Trend of Channel Adjustment Indicators
3.2.3. Indicators for Meandering Functionality
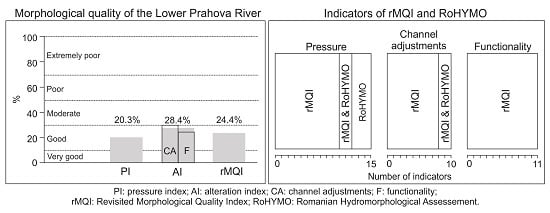
4. Results: Level of Pressure and Alteration of Lower Prahova River
| Indicator | Mean | Standard Deviation | Median | Change Mann-Whitney Test α = 0.05 | ||||
| 1954 | 2005 | 1954 | 2005 | 1954 | 2005 | Two-Tailed (p-value) | Upper-Tailed (p-value) | |
| Wavelength (m) | 540 | 544 | 261 | 296 | 516 | 492 | 0.759 | -- |
| Length (m) | 1209 | 1203 | 558 | 626 | 1011 | 1049 | 0.736 | -- |
| Sinuosity index | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 0.871 | -- |
| Amplitude (m) | 506 | 483 | 244 | 268 | 427 | 409 | 0.434 | -- |
| Radius of curvature (rc) (m) | 178 | 151 | 83 | 78 | 164 | 124 | 0.029 | 0.007 |
| Width (w) (m) | 53 | 44 | 19 | 15 | 50 | 42 | 0.014 | 0.015 |
| rc/w | 3.4 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 0.781 | -- |
| Indicator | Mean | Standard Deviation | Median | Trend Mann-Kendall Test α = 0.05 | ||||
| 1966–2010 | Two-Tailed (p-value) | Lower-Tailed (p-value) | ||||||
| Cross-sectional area (m2) | 152 | 11.6 | 149 | 0.088 | -- | |||
| Maximum depth (m) | 3.2 | 0.2 | 3.2 | 0.544 | -- | |||
| Width–to–mean–depth ratio | 28.6 | 6 | 28 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Indicator | Value (m3/s) | Return period (Log Pearson III, 1961–2010) | ||||||
| Qb (m3/s) | 280 | 2.8 years | ||||||
| Q10 (m3/s) | 550 | 1966, 1972, 1975, 1997, 2005 | ||||||
5. Discussion
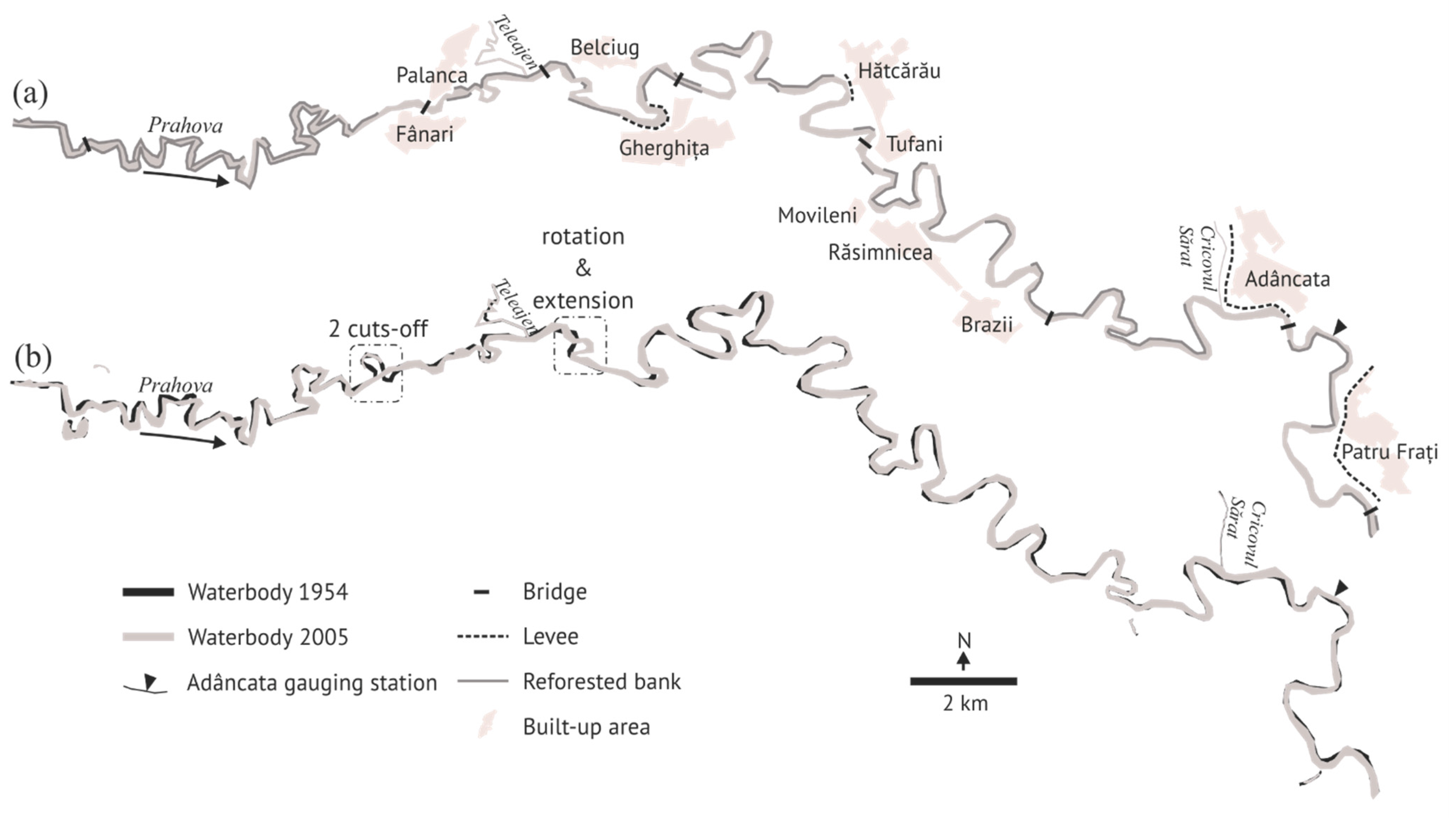
5.1. Interpretation of Morphological Quality of the Lower Prahova River
5.2. Usefulness of rMQI for River Morphological Quality Assessment in Romania
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Directive 2000/60/EC. Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. Available online: http://faolex.fao.org/cgi-bin/faolex.exe?rec_id=017501&database=faolex&search_type=link&table=result&lang=eng&format_name=@ERALL (accessed on 9 June 2015).
- Fehér, J.; Gáspár, J.; Szurdine Veres, K.; Kiss, A.; Kristensen, P.; Peterlin, M.; Globevni, L.; Kirn, T.; Semerádová, S.; Künitzer, A.; et al. Hydromorphological Alterations and Pressures in European Rivers, Lakes, Transitional and Coastal Waters; ETC/ICM: Prague, Czech Republic, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Newson, M.D.; Large, A.R.G. ‘Natural’ rivers, ‘hydromorphological quality’ and river restoration: A challenging new agenda for applied fluvial geomorphology. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 1606–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, I.P.; Diamond, M.; Gurnell, A.M.; Hall, K.A.; Jenkins, A.; Milner, N.J.; Naylor, L.A.; Sear, D.A.; Woodward, G.; Ormerod, S.J. Integrating ecology with hydromorphology: A priority for river science and management. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2009, 19, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, P.J.; Holmes, N.T.H.; Raven, P.J. Developing standards approaches for recording and assessing river hydromorphology: The role of the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2010, 20, S55–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standardization. European Standard EN14614; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussetini, M. A method for the assessment and analysis of the hydromorphological conditions of Italian streams: The Morphological Quality Index (MQI). Geomorphology 2013, 180–181, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.; Fryirs, K.A. Geomorphology and River Management: Applications of the River Styles Framework; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brierley, G.J.; Fryirs, K.A.; Boulton, A.; Cullum, C. Working with change: The importance of evolutionary perspectives in framing the trajectory of river adjustment. In River Futures: An Integrative Scientific Approach to River Repair. Society for Ecological Restoration International; Brierley, G., Fryirs, K.A., Eds.; Society for Ecological Restoration International, Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liébault, F.; Piégay, H. Causes of 20th Century channel narrowing in mountain and piedmont rivers of Southeastern France. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Rinaldi, M.; Buijse, A.D.; Gurnell, A.M.; Mosselman, E. A review of assessment methods for river hydromorphology. Environm. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2079–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungwirth, M.; Muhar, S.; Schmutz, S. Re-Establishing and assessing ecological integrity in riverine landscapes. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollero, A.; Ibisate, A.; Gonzalo, L.E.; Acin, V.; Ballarin, D.; Diaz, E.; Domenech, S.; Gimeno, M.; Granado, D.; Horacio, J.; et al. The IHG index for hydromorphological quality assessment of rivers and streams: Updated version. Limnetica 2011, 30, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Chandesris, A.; Mengin, N.; Malavoi, R.N.; Souchon, Y.; Pella, H.; Wasson, J.G. Système Relationnel d’Audit de l’Hydromorphologie des Cours d’Eau; CEMAGREF: Lyon, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gob, F.; Bilodeau, C.; Thommeret, N.; Belliard, J.; Albert, M.B.; Tamisier, V.; Baudoin, J.M.; Kreutzenberger, K. Un outil de caractérisation hydromorphologique des cours d’eau pour l’application de la DCE en France (CARHYCE). Géomorphol. Relief Process. Environ. 2014, 1, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyzga, B.; Zawiejska, J.; Radecki-Pawlik, A.; Hajdukiewicz, H. Environmental change, hydromorphological reference conditions and the restoration of Polish Carpathian Rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2012, 37, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scottish Environment Protection Agency. Supporting Guidance (WAT-SG-21). Environmental Standards for River Morphology. Available online: http://www.sepa.org.uk/media/152194/wat_sg_21.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2015).
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M. The morphological quality index (MQI) for stream evaluation and hydromorphological classification. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 1, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vernier, G.; Peeters, A.; Castelain, L.; Henrotte, C.; Halleux, M.; Regnier, M.; Rivière, A.; Latli, A.; Damman, R. Conception d’un outil d’aide à la décision pour la restauration hydromorphologique des masses d’eau en Région Wallonne. Rapport scientifique du projet WALPHY LIFE-Environnement (LIFE07 ENV/B/000038). Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/life/project/Projects/index.cfm?fuseaction=home.showFile&rep=file&fil=WALPHY_Rapport_Geomorphologie_Def.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2015).
- Şerban, P.; Rădulescu, D. Abiotic criteria for the heavily modified water bodies designation. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on River Restoration, Zagreb, Croatia, 17–21 May 2004; pp. 355–365.
- Gălie, A.; Popescu, V.; Moldovan, C. Assessment of the ecological status using different quality elements in the Prut River Basin (Work Package 6). Available online: http://www.seehydropower.eu/download_deliverables/ (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Tecuci, I.; Moldoveanu, M. The assessment of hydromorphological status of Romanian rivers. Air Water Compon. Environ. 2014, 2014, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Aquaproiect. Atlasul Cadastrului Apelor din Romania; Ministerul Mediului: Bucharest, Romania, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- European Environmental Agency. Corine Land Cover 2000. Available online: http://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/corine-land-cover-2000-clc2000-seamless-vector-database (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Ioana-Toroimac, G. La Dynamique Hydrogéomorphologique de la riviere Prahova: Fonctionnement Actuel, évolution récente et conséquences géographiques. Ph.D. Thesis, University Lille 1 Sciences and Technologies, Lille, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Armaş, I.; Osaci-Costache, G.; Braşoveanu, L. Forest landscape history using diachronic cartography and GIS. Case study: Subcarpathian Prahova Valley, Romania. In Planning and Designing Sustainable and Resilient Landscapes; Crăciun, C., Boştenaru-Dan, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2014; pp. 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Catană, S. Studiu Hidrogeografic al Bazinului râului Teleajen. Aplicaţii ale SIG şi Teledetecţiei. Ph.D Thesis, University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Statistics. Recensământul populaţiei şi locuinţelor 2011. Judeţul Ialomiţa. Judeţul Prahova. Available online: http://www.rpl2011.djsct.ro/ (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Schumm, S.A. The Fluvial System; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Armaş, I.; Gogoaşe Nistoran, D.E.; Osaci-Costache, G.; Braşoveanu, L. Morphodynamic evolution patterns of Subcarpathian Prahova River (Romania). Catena 2012, 100, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bîrsan, M.; Zaharia, L.; Chendeş, V.; Brănescu, E. Seasonal trends in Romanian streamflow. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4496–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E.; Amoros, C. (Eds.) Fluvial Hydrosystems; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1996.
- Ikeda, I. Sedimentary controls on channel migration and origin of point bars in sand-bedded meandering rivers. In River Meandering; Ikeda, S., Parker, G., Eds.; American Geophysical Union Water Resources Monograph 12, American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- National Agency for Cadaster and Land Registration. Geoportal. Viewer. Available online: http://geoportal.ancpi.ro/geoportal/viewer/index.html (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Dobre, R.; Grecu, F.; Zaharia, L. Évolution 2D de la bande active de la Haute Prahova (Roumanie) durant les 150 dernières années. Géomorphol. Relief Process. Environ. 2010, 3, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice, J.C. Channel Patterns and Terraces of the Loup River in Nebraska; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1964.
- Brierley, G.; Fryirs, K.A.; Jain, V. Landscape connectivity: The geographic basis of geomorphic applications. Area 2006, 38, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, J.; James, L.A. Changing fluvial systems. Phys. Geogr. 2013, 34, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Fort, M.; Arnaud-Fassetta, G. La part respective des facteurs hydroclimatiques et anthropiques dans l’évolution récente (1956–2000) de la bande active du Haut Guil, Queyras, Alpes françaises du Sud. Méditerranée 2004, 1–2, 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Surian, N.; Ziliani, L.; Comiti, F.; Lenzi, M.A.; Mao, L. Channel adjustments and alteration of sediment fluxes in gravel-bed rivers of North-Eastern Italy: potential and limitations for channel recovery. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliani, L.; Surian, N. Evolutionary trajectory of channel morphology and controlling factors in a large gravel-bed river. Geomorphology 2012, 173–174, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnock, D. Water resource management problems in Romania. GeoJournal 1979, 3, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ragomirescu, Ş.; Dragomirescu, S. Hydro-Electricity in the Romanian Carpathians. GeoJournal 1993, 29, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Şerban, P.; Gălie, A. Managementul apelor Principii şi reglementări europene; Tipored: Bucharest, Romania, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Salit, F.; Ioana-Toroimac, G. In-Stream gravel mining in alluvial rivers: Geomorphological impact and European Legislation. In Proceeding of the 3rd International Geography Symposium–GEOMED, Kemer, Turkey, 10–13 June 2013; pp. 201–210.
- Van der Brugge, R.; Rotmans, J.; Loorbach, D. The transition in Dutch water management. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2005, 5, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, S. De l’aménagement au ménagement des cours d’eau : Le bassin de la Loire, miroir de l’évolution des rapports entre aménagement fluvial et environnement. Cybergeo Eur. J. Geogr. 2010, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, P.; Guangchun, L.; Cai, L. From Stockholm to Rio II: The natural and institutional landscapes through which rivers flow. In River Conservation and Management; Boon, P.J., Raven, P.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2012; pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Louckova, B. Eastern Europe perspective on the environmental aspects in current flood risk management: The example of the Czech Republic. In The Global Water System in Anthropocene. Challenges for Science and Governance; Bhaduri, A., Bogardi, J., Marx, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2014; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Knighton, D. Fluvial Forms and Processes; Arnold: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, T.; Blanka, V. River channel response to climate- and human-induced hydrological changes: Case study on the meandering Hernád River, Hungary. Geomorphology 2012, 175–176, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickin, E.J.; Nanson, G.C. The character of channel migration of the Beatton River, Northeast British Columbia, Canada. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1975, 86, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfankuch, D.J. Stream Reach Inventory and Channel Stability Evaluation; U.S.D.A. Forest Service, Region 1: Missoula, MT, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, K. Rivers: Form and Process in Alluvial Channels; Methuen: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. River Variability and Complexity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kiss, T.; Fiala, K.; Sipos, G. Alterations of channel parameters in response to river regulation works since 1840 on Lower Tisza River (Hungary). Geomorphology 2008, 98, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollero, A. Channel changes and floodplain management in the meandering middle Ebro River, Spain. Geomorphology 2010, 117, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdaleno, F.; Fernandez-Yuste, J.A. Meander dynamics in a changing river corridor. Geomorphology 2011, 130, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibisate, A.; Diaz, E.; Ollero, A.; Acin, V.; Granado, D. Channel response to multiple damming in a meandering river, middle and lower Aragon (Spain). Hydrobiologia 2013, 712, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.A.; Marcus, W.A. The human role in changing fluvial systems: Retrospect, inventory and prospect. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juracek, K. Historical channel-bed elevation change as a result of multiple disturbances, Soldier Creek, Kansas. Phys. Geogr. 2004, 25, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigon, E.; Moretto, J.; Rainato, R.; Lenzi, M.A.; Zorzi, A. Evaluation of the morphological quality index in the Cordevole River (BI, Italy). J. Agric. Eng. 2013, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Rădoane, M.; Obreja, F.; Cristea, I.; Mihăilă, D. Changes in the channel-bed level of the eastern Carpathian rivers: Climatic vs. human control over the last 50 years. Geomorphology 2013, 193, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.D.; Lienert, J.; Schuwirth, N.; Reichert, P. How to make river assessments comparable: A demonstration for hydromorphology. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 32, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.; Florsheim, J.L.; Wohl, E.; Collins, B.D. Feedback in Human-Landscape system. Environ. Manag. 2013, 53, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environmental Agency. WISE WFD database. Available online: http://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/wise_wfd (accessed on 5 January 2015).
- Song, X.; Frostell, B. The DPSIR Framework and a pressure-oriented water quality monitoring approach to ecological river restoration. Water 2012, 4, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanian Waters National Administration. Planul de Management al Spațiului Hidrografic Buzău-Ialomița. Available online: http://www.rowater.ro/dabuzau (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Romanian Waters National Administration. Istoric. Cum a apărut şi s-a dezvoltat gospodărirea apelor? Available online: http://www.rowater.ro/Lists/Istoric/AllItems.aspx (accessed on 18 January 2015).
- Sear, D.; Newson, M.; Hill, C.; Old, J.; Branson, J. A method for applying fluvial geomorphology in support of catchment-scale river restoration planning. Aquat. Conserve. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2009, 19, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, C.P. The human-landscape system: Challenges for geomorphologists. Phys. Geogr. 2014, 35, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Surian, N.; Comiti, F.; Bussettini, M. Guidebook for the Evaluation of Stream Morphological Conditions by the Morphological Quality Index (MQI); Istituto Superiore per Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale: Rome, Italy, 2012.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Zaharia, L.; Minea, G. Using Pressure and Alteration Indicators to Assess River Morphological Quality: Case Study of the Prahova River (Romania). Water 2015, 7, 2971-2989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062971
Ioana-Toroimac G, Zaharia L, Minea G. Using Pressure and Alteration Indicators to Assess River Morphological Quality: Case Study of the Prahova River (Romania). Water. 2015; 7(6):2971-2989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062971
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoana-Toroimac, Gabriela, Liliana Zaharia, and Gabriel Minea. 2015. "Using Pressure and Alteration Indicators to Assess River Morphological Quality: Case Study of the Prahova River (Romania)" Water 7, no. 6: 2971-2989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062971
APA StyleIoana-Toroimac, G., Zaharia, L., & Minea, G. (2015). Using Pressure and Alteration Indicators to Assess River Morphological Quality: Case Study of the Prahova River (Romania). Water, 7(6), 2971-2989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062971