Tracing the Nitrate Sources of the Yili River in the Taihu Lake Watershed: A Dual Isotope Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
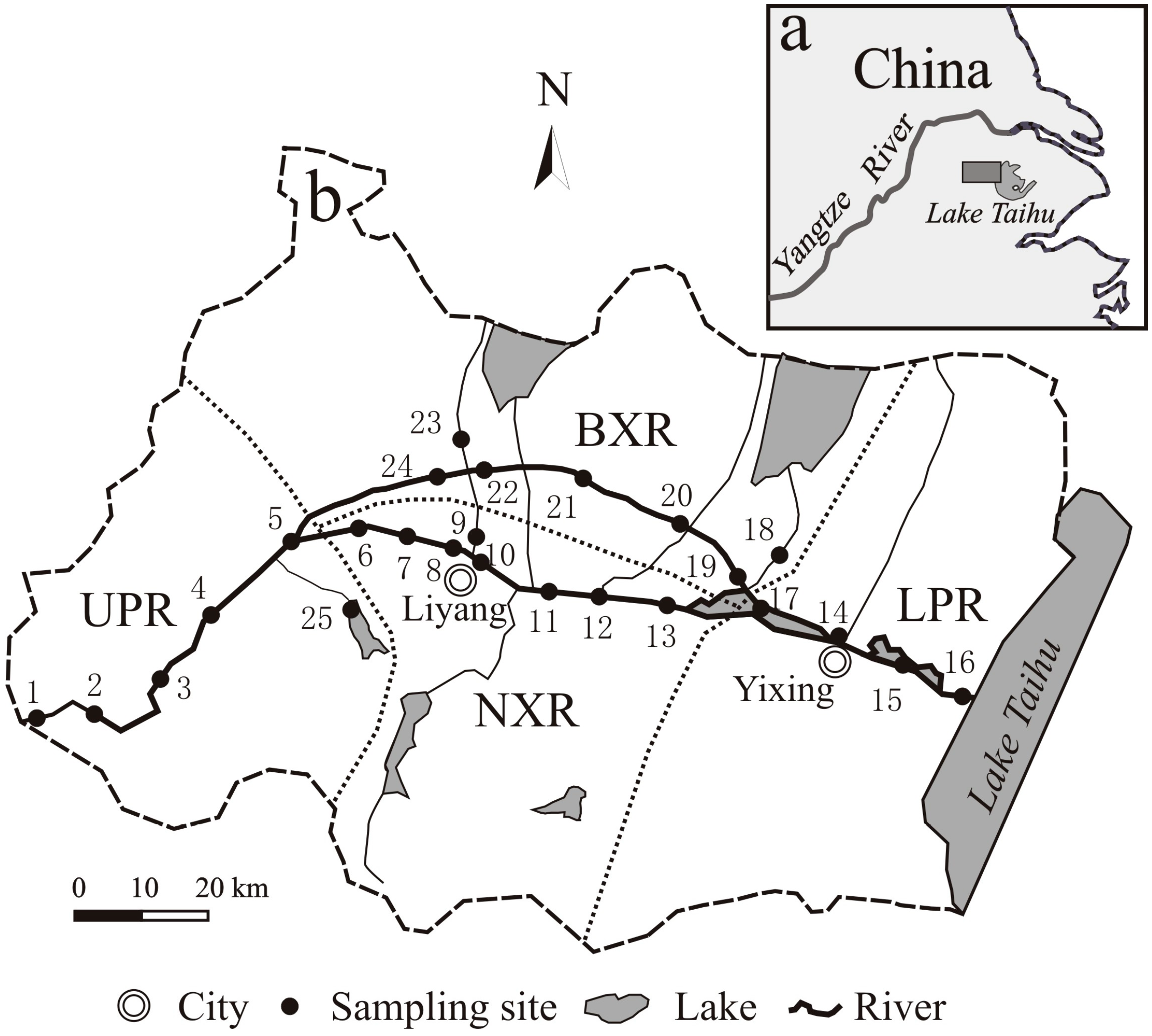
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Major Elements and Isotopic Composition
| Location | Cl− | NO3− | δ15N-NO3− | δ18O-NO3− | δ18O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | mgN/L | ‰ | ‰ | ‰ | |
| Wet season (July 2010) | |||||
| UPR(n = 6) | 15.02 ± 7.36 | 1.62 ± 0.39 | 8.6 ± 2.1 | 13.3 ± 6.1 | −7.6 ± 0.3 |
| NXR(n = 8) | 31.75 ± 4.89 | 2.58 ± 0.74 | 8.7 ± 3.5 | 6.9 ± 3.4 | −7.9 ± 0.1 |
| BXR(n = 7) | 39.67 ± 8.59 | 1.57 ± 0.42 | 7.5 ± 3.7 | 5.9 ± 2.1 | −8.0 ± 0.2 |
| LPR(n = 4) | 30.28 ± 10.97 | 2.61 ± 0.65 | 10.5 ± 2.4 | 6.0 ± 3.7 | −8.0 ± 0.1 |
| Mean(n = 25) | 29.95 ± 11.38 | 2.07 ± 0.74 | 8.4 ± 2.9 | 8.2 ± 4.7 | −8.0 ± 0.2 |
| Dry season (March 2010) | |||||
| UPR(n = 6) | 28.70 ± 17.75 | 0.75 ± 0.35 | 7.5 ± 2.1 | 12.1 ± 3.6 | −3.1 ± 0.4 |
| NXR(n = 8) | 120.14 ± 55.67 | 1.69 ± 0.16 | 10.6 ± 2.1 | 9.1 ± 2.1 | −4.2 ± 1.8 |
| BXR(n = 7) | 176.18 ± 18.86 | 1.46 ± 0.41 | 11.9 ± 3.0 | 5.4 ± 1.8 | −5.8 ± 0.3 |
| LPR(n = 4) | 150.31 ± 77.30 | 1.84 ± 0.46 | 12.7 ± 2.1 | 8.3 ± 1.8 | −5.4 ± 1.7 |
| Mean(n = 25) | 113.88 ± 73.19 | 1.40 ± 0.47 | 10.2 ± 3.1 | 8.8 ± 3.2 | −4.4 ± 1.8 |
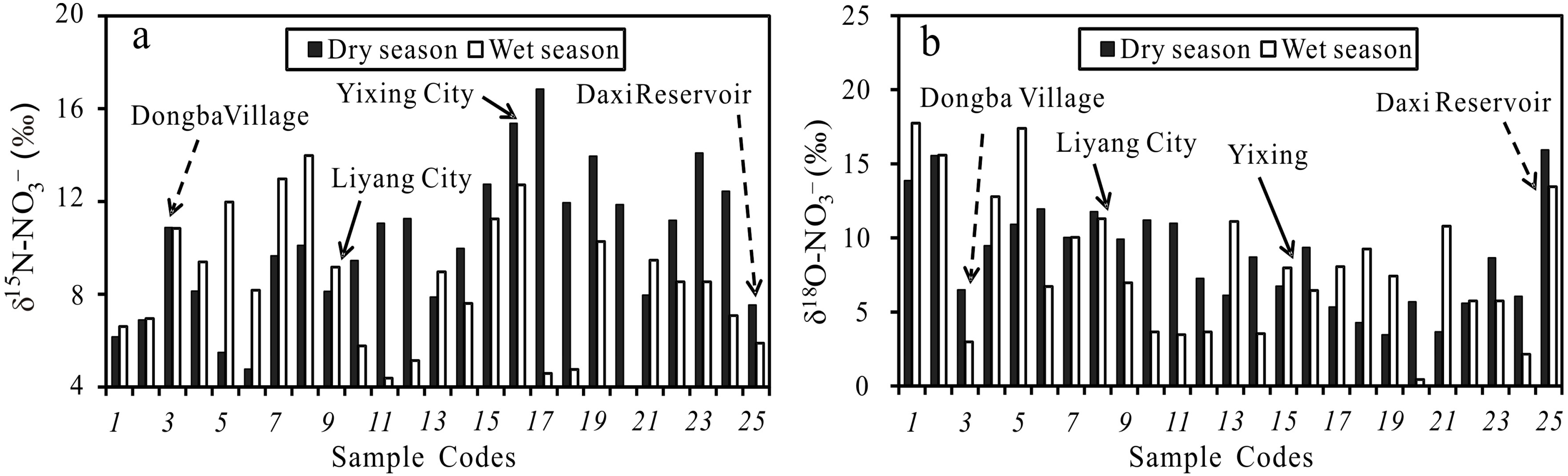
3.2. Identification of Nitrate Sources
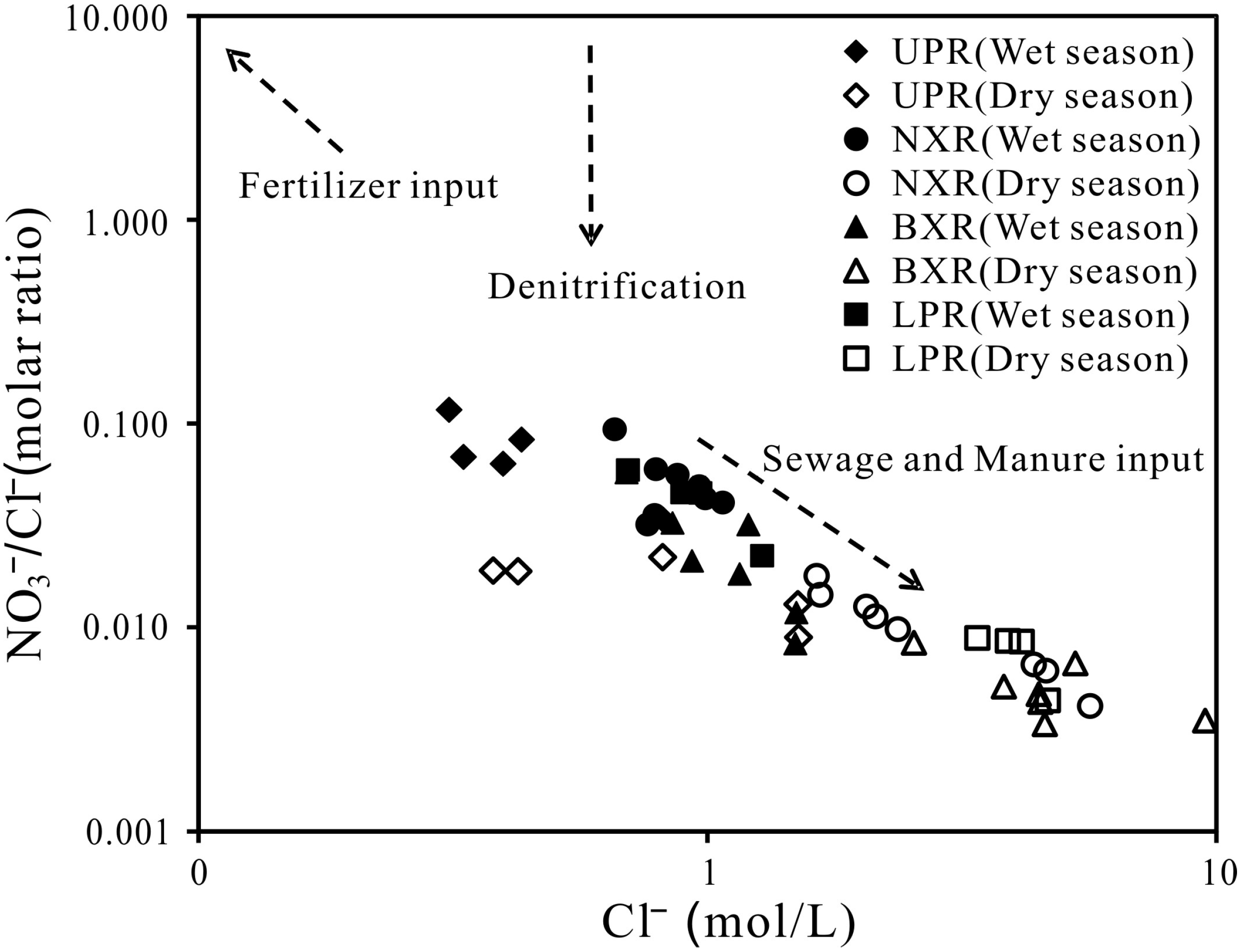
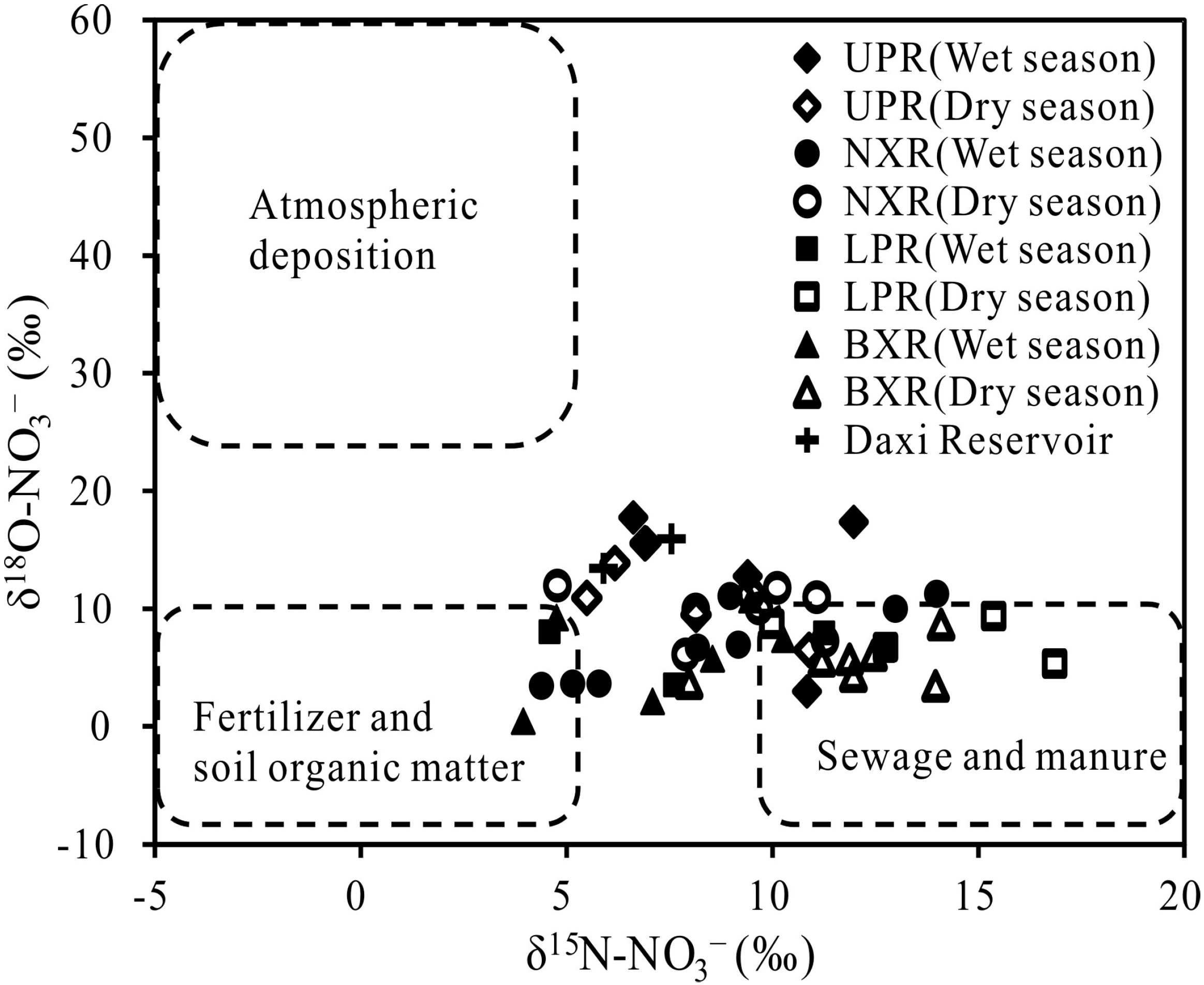
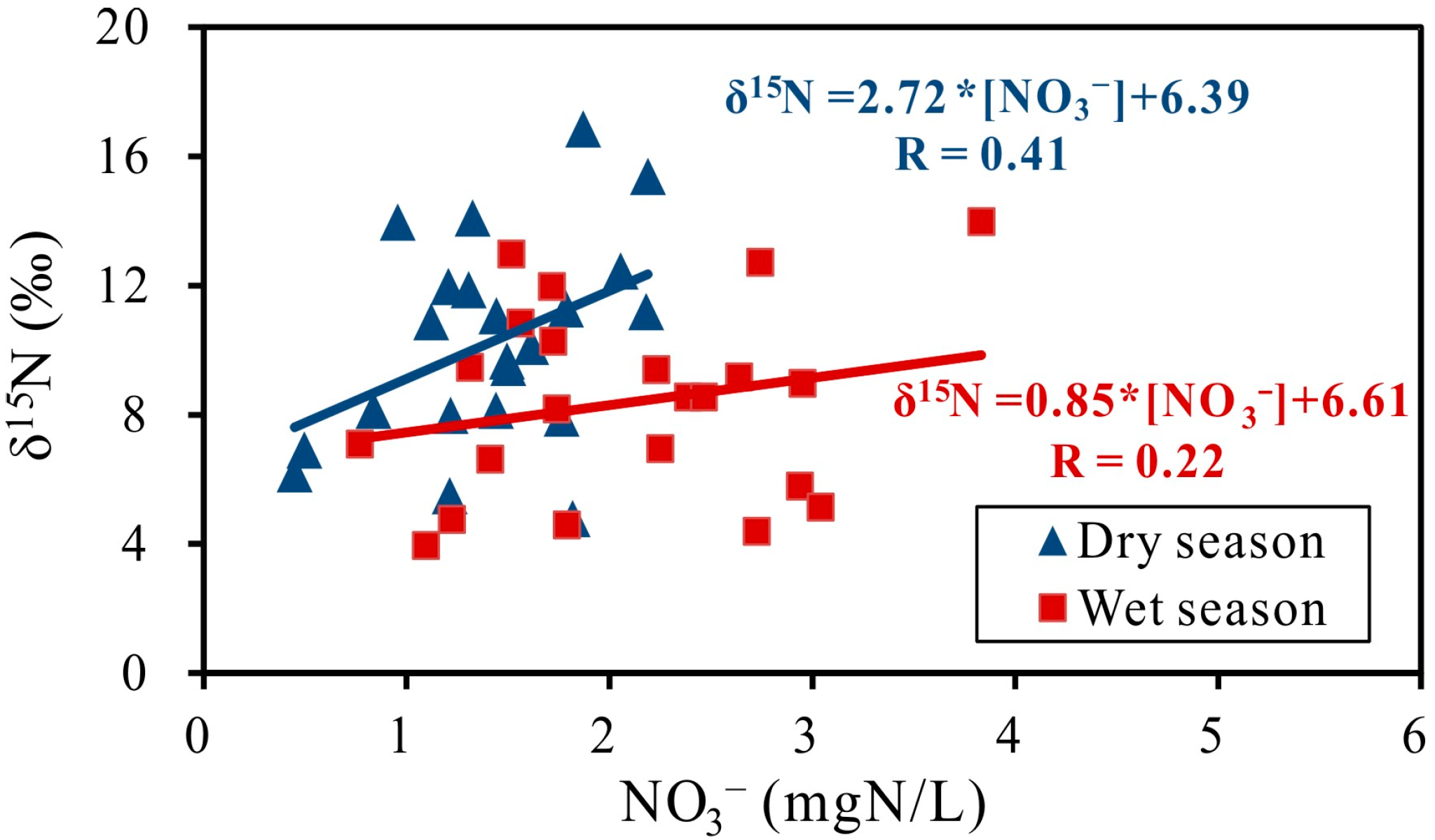
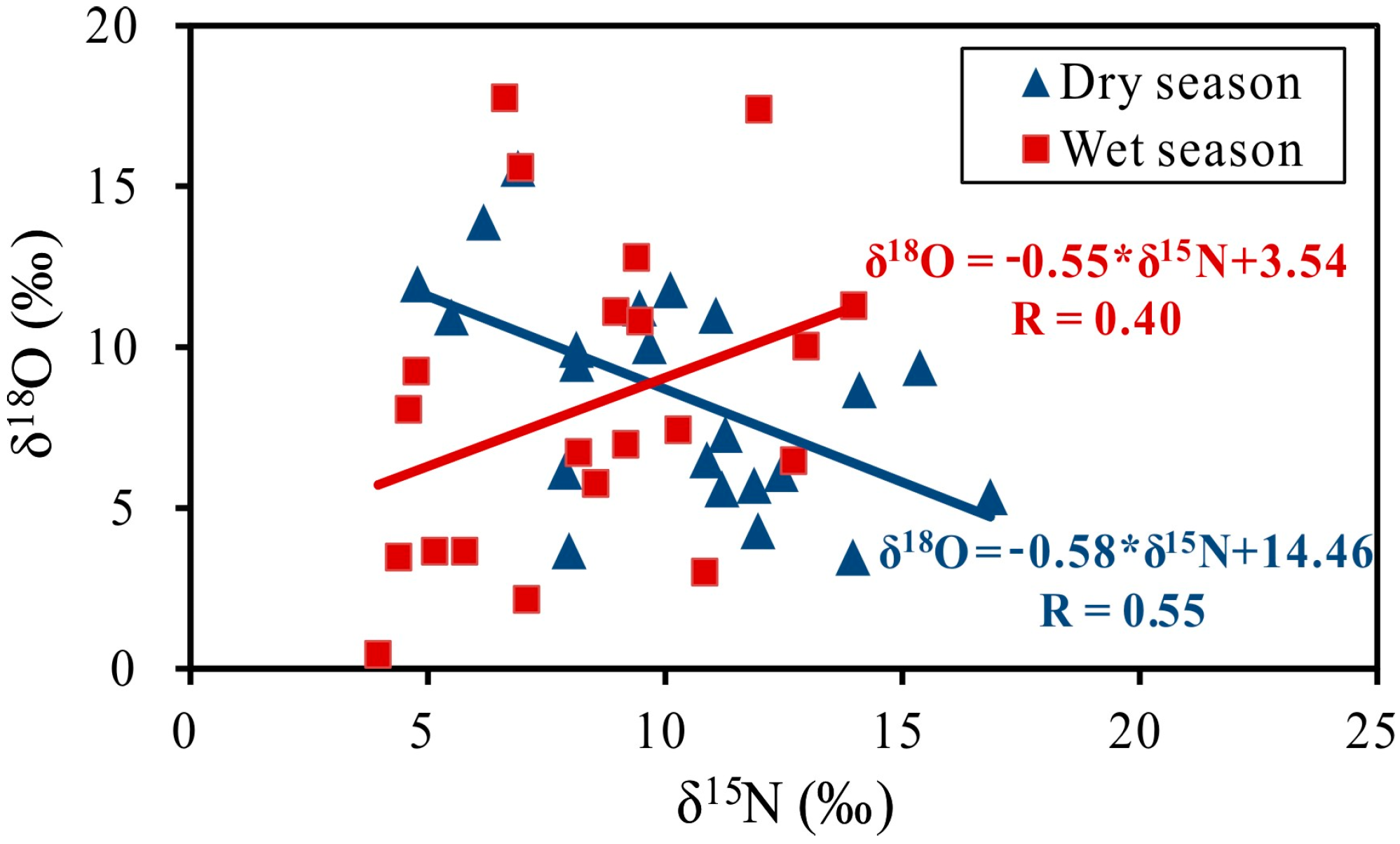
| Location | Contribution of Different Nitrate Source (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Deposition | Organic Matter or Fertilizer | Manure and Sewage | |
| Dry season | |||
| UPR | 35.5 | 31.7 | 32.8 |
| BXR | 3.5 | 43.6 | 52.9 |
| NXR | 20.5 | 31.2 | 48.3 |
| LPR | 16.5 | 23.6 | 59.9 |
| Wet season | |||
| UPR | 48.0 | 10.6 | 41.4 |
| BXR | 15.0 | 55.9 | 29.1 |
| NXR | 19.0 | 44.1 | 36.9 |
| LPR | 15.0 | 38.1 | 46.8 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McIsaac, G.F.; David, M.B.; Gertner, G.Z.; Goolsby, D.A. Eutrophication: Nitrate flux in the Mississippi River. Nature 2001, 414, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.N.; Dentener, F.J.; Capone, D.G.; Boyer, E.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Asner, G.P.; Cleveand, C.C.; Green, P.A.; Holland, E.A.; et al. Nitrogen cycles: Past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 2004, 70, 153–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N&P) management strategy. Water Res. 2010, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daisuke, K.; Takashi, O.; Nobutake, N.; Masanobu, M.; Kazuhiko, T. Utilization of ion-exclusion chromatography for water quality monitoring in a suburban river in Jakarta, Indonesia. Water 2014, 6, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G.H. Dietary nitrates, nitrites, and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2011, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.X.; Yin, X.B.; Liu, G.; Liu, G.J. Tracing nitrogen sources and cycle in freshwater through nitrogen and oxygen isotopic research. In Wastewater Reuse and Management; Sharma, S.K., Sanghi, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2013; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Durka, W.; Schulze, E.D.; Gebauer, G.; Voerkelius, S. Effects of forest decline on uptake and leaching of deposited nitrate determined from 15N and 18Omeasurements. Nature 1994, 372, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Boyer, E.W.; Goodale, C.; Jaworski, N.A.; Breemen, N.V.; Howarth, R.W. Sources of nitrate in rivers draining sixteen watersheds in the northeastern U.S.: Isotopic constraints. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57/58, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Bottea, J.; de Baets, B.; Accoe, F.; Nestler, A.; Taylor, P.; van Cleemput, O.; Berglund, M.; Boeckx, P. Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface and groundwater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, C.; Elliott, E.M.; Wankel, S.D. Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Michener, R., Lajtha, K., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 375–449. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, M.; Robbie, G.; Catherine, E.C.; Robert, M.K.; Wolfram, M. Simplifying and improving the extraction of nitrate from freshwater for stable isotope analyses. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panno, S.V.; Hackley, K.C.; Kelly, W.R.; Hwang, H.H. Isotopic evidence of nitrate sources and denitrification in the Mississippi River, Illinois. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panno, S.V.; Kelly, W.R.; Hackley, K.C.; Hwang, H.H.; Martinsek, A.T. Sources and fate of nitrate in the Illinois river basin, Illinois. J. Hydrol. 2008, 359, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Bong, Y.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.J. Tracking the sources of nitrate in the Han River watershed in Korea, using δ15N-NO3− and δ18O-NO3− values. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 395, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Chetelat, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, F. Assessment of the sources of nitrate in the Changjiang River, China using a nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 144, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Q.; Nie, Z.Y.; He, M.M.; Guo, R.; Zhu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Stephan, K. Application of 15N-18O double stable isotope tracer technique in an agricultural nonpoint polluted river of the Yangtze Delta Region. Eenviron. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6972–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Nutrient and other environmental controls of harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the freshwater-marine continuum. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 216–241. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.H. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and nitrogen fixation in lacustrine and estuarine ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, B.; Teubner, K.; Dokulil, M.T. Longterm dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Hao, Y. Monitoring pollutant ingoing gross of rivers in Taihu valley of Jiangsu province. Environ. Monit. China 2005, 21, 52–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Townsend-Small, A.; McCarthy, M.J.; Brandes, J.A.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Gardner, W.S. Stable isotopic composition of nitrate in Lake Taihu, China, and major inflow rivers. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, W.; Lam, M.H.W.; Liu, G.; Yin, X. Identification of nitrate sources in Taihu Lake and its major inflow rivers in China, using δ15N-NO3− and δ18O-NO3− values. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, P. Strategy of water pollution prevention in Taihu Lake and its effects analysis. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Statistical Bureau of Jiangsu Province. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook. 2013. Available online: http://www.jssb.gov.cn/2014nj/nj20.htm (accessed on 25 November 2014). [Google Scholar]
- Lis, G.P.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hendry, M.J. High-precision laser spectroscopy D/H and 18O/16O measurements of microliter natural water samples. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; van Wilgenburg, S.L.; Larson, K.; Hobson, K.A. A groundwater isoscape (δD, δ18O) for Mexico. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlvin, M.R.; Altabet, M.A. Chemical conversion of nitrate and nitrite to nitrous oxide for nitrogen and oxygen isotopic analysis in freshwater and seawater. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5589–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, D.R.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D. Analysis of water movement through an unsaturated soil zone in Jeju Island, Korea using stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2007, 345, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jia, G.; Chen, J. Nitrate sources and watershed denitrification inferred from nitrate dual isotopes in the Beijiang River, South China. Biogeochemistry 2009, 94, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.Y.; Kendall, C.; Silva, S.R.; Battaglin, W.A.; Campbell, D.H. Nitrate stable isotopes: Tools for determining nitrate sources among different land uses in the Mississippi River Basin. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1874–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.R.; Ging, P.B.; Lee, R.W.; Ebbert, J.C.; Tesoriero, A.J.; Inkpen, E.L. Forensic applications of nitrogen and oxygen isotopes in tracing nitrate sources in urban environments. Environ. Forensics 2002, 3, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Bollwerk, S.M.; Mansfeldt, T.; Hutter, B.; Veizer, J. The oxygen isotope composition of nitrate generated by nitrification in acid forest floors. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2743–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Wassenaar, L.I. Isotopic characterization of nitrate sources and transformations in Lake Winnipeg and its contributing rivers, Manitoba, Canada. J. Great Lakes Res. 2012, 38, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengis, M.; Schiff, S.L.; Harris, M.; English, M.C.; Aravena, R.; Elgood, R.J.; MacLean, A. Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing groundwater NO3− elimination in a riparian zone. Ground Water 1999, 37, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, J.; Sigman, D.M.; Needoba, J.A.; Harrison, P.J. Coupled nitrogen and oxygenisotope fractionation of nitrate during assimilation by cultures of marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, T.; Hiscock, K.M.; Dennis, P.F.; Grischek, T. A dual isotope approach to identify denitrification in groundwater at a river-bank infiltration site. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3070–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, J.; Strebel, O.; Voerkelius, S.; Schmidt, H.L. Using isotope fractionation of nitrate-nitrogen and nitrate-oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Du, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Zhang, L. Denitrification in sediments of typical rivers in Taihu Basin. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2012, 32, 1866–1873. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, D.L.; Koch, P.L. Incorporating concentration dependence in stable isotope mixing models. Oecologica 2002, 130, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, H.; Wu, J. Tracing the Nitrate Sources of the Yili River in the Taihu Lake Watershed: A Dual Isotope Approach. Water 2015, 7, 188-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010188
Zeng H, Wu J. Tracing the Nitrate Sources of the Yili River in the Taihu Lake Watershed: A Dual Isotope Approach. Water. 2015; 7(1):188-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010188
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Haiao, and Jinglu Wu. 2015. "Tracing the Nitrate Sources of the Yili River in the Taihu Lake Watershed: A Dual Isotope Approach" Water 7, no. 1: 188-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010188
APA StyleZeng, H., & Wu, J. (2015). Tracing the Nitrate Sources of the Yili River in the Taihu Lake Watershed: A Dual Isotope Approach. Water, 7(1), 188-201. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010188





