Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management in Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Elements | Old (1971–1998) and new (1998–present) paradigms and their implications in water resources management | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old Paradigms | Implication | New Paradigms | Implication | |
| Governance regime | Autocracy | Strong leadership character | Democracy | Participative leadership |
| Administrative rule | Centralization | Concentration on national administration | Decentralization | Domination by district and provincial administrations |
| Decision-making process | Top down | All decisions made based on administrator interests | Bottom up | All decisions made based on stakeholders aspiration |
| Budgetary system | Government allocation | Financial sources from debts offering by international institutions funding and government budget | Water users sharing participation | Financial sources from water users and water polluters pay principles and government budget |
| Role of water in regional development | Supporting factor | Risks to environmental imbalance | Limiting factor | Priority on water balance consideration |
| Management responsibility | Regional authority | Regionally economic development interests | River basin and regional authority | Sustainable development interests |
| Role of government in construction | Provider | Risks of corruption due to power authority | Enabler | Capacity building needs for strengthening government administration |
| Project setting up orientation | Partial approach | Regionally (or personally) economic development interests basis | Integrated approach | Environmental sustainability interests basis |
| Project interest | Supremacy instruction | To increase personal popularity | People aspiration | To solve water-related problems |
| Project preparation | Based on short term planning | Approved based on personal/local interests | Based on master plan | Approved based on comprehensive study |
2. Water Availability and Seasonality of Indonesia’s Climate
3. Water-Related Issues
3.1. Floods
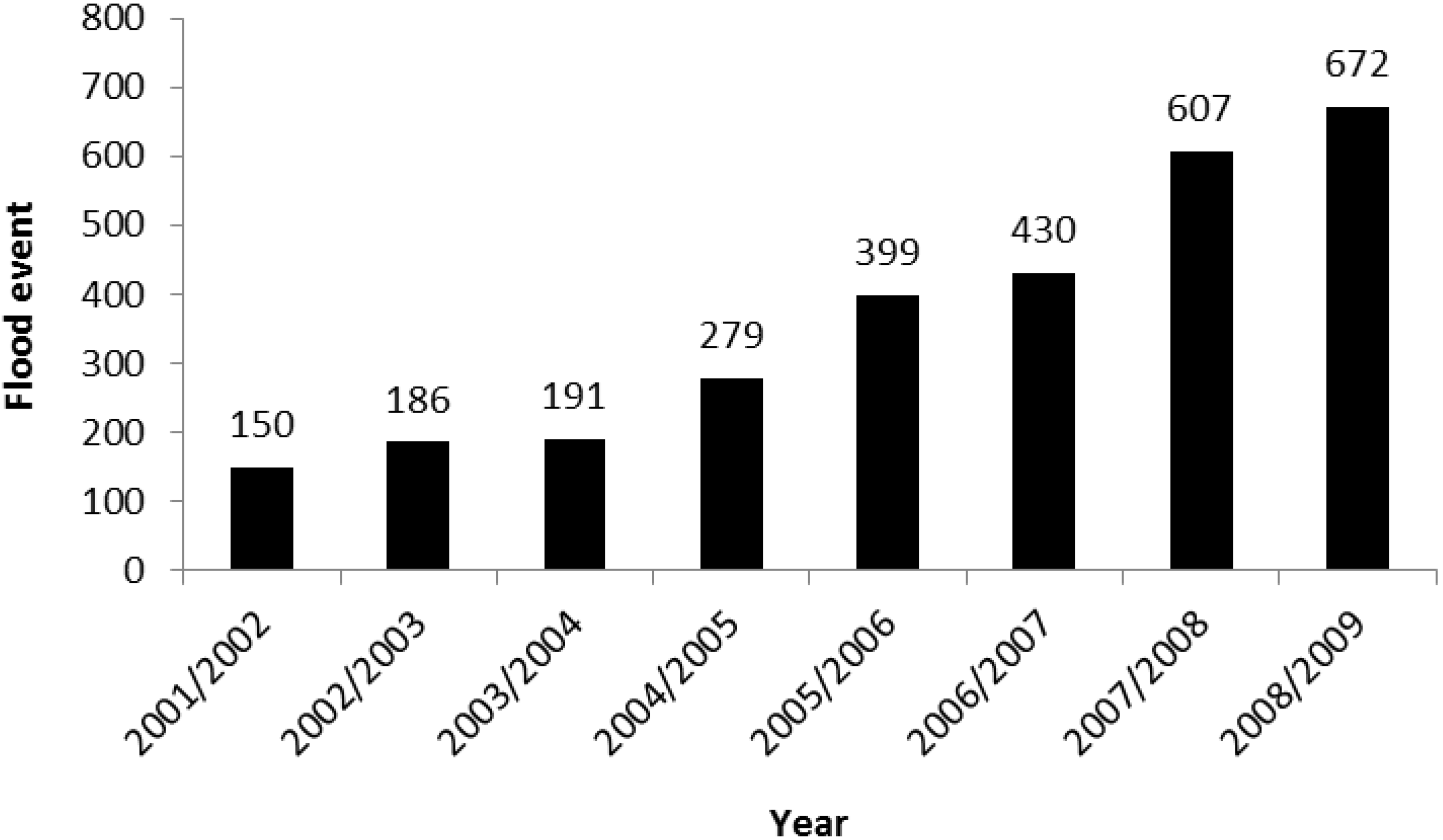
3.2. Droughts
3.3. Soil Erosion and Sludge Production
3.4. Lack of Adequate Water Storage
3.5. Watersheds Degradation
3.6. Threats on Water Availability and Sustainability
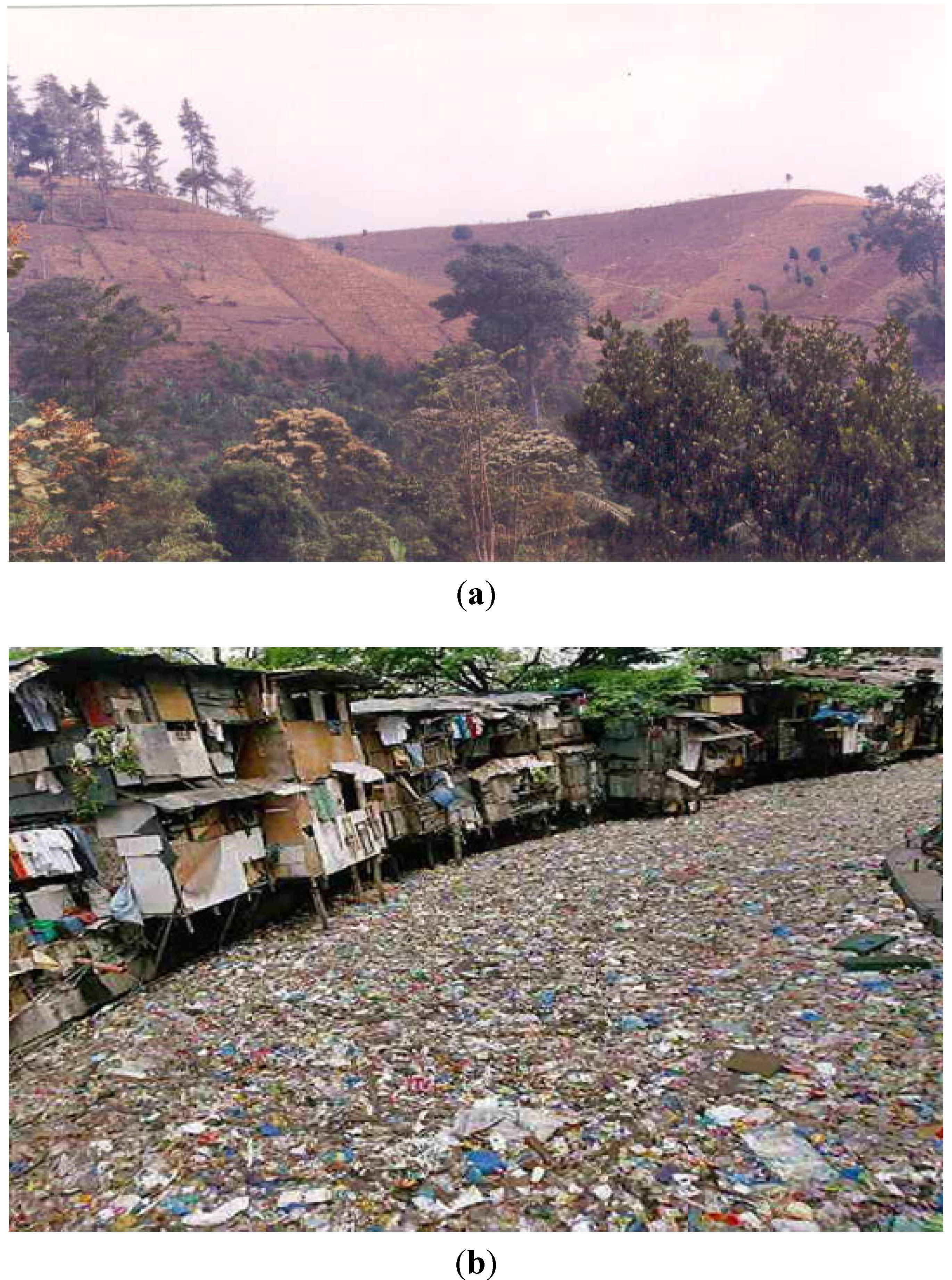

3.7. Water Quality Problems
4. A Brief Description of the Major Tasks Involved in the Implementation of IWRM
4.1. Coordinating Perspectives in Water Management
4.2. The IWRM Pilot Projects and Reasons behind Program Delays
4.3. Coordination Instruments and Water Coordinating Agency
4.4. Constraints and Weaknesses
5. Challenges of Developing the Future IWRM
5.1. Enabling Environment
5.2. Institutional Frameworks
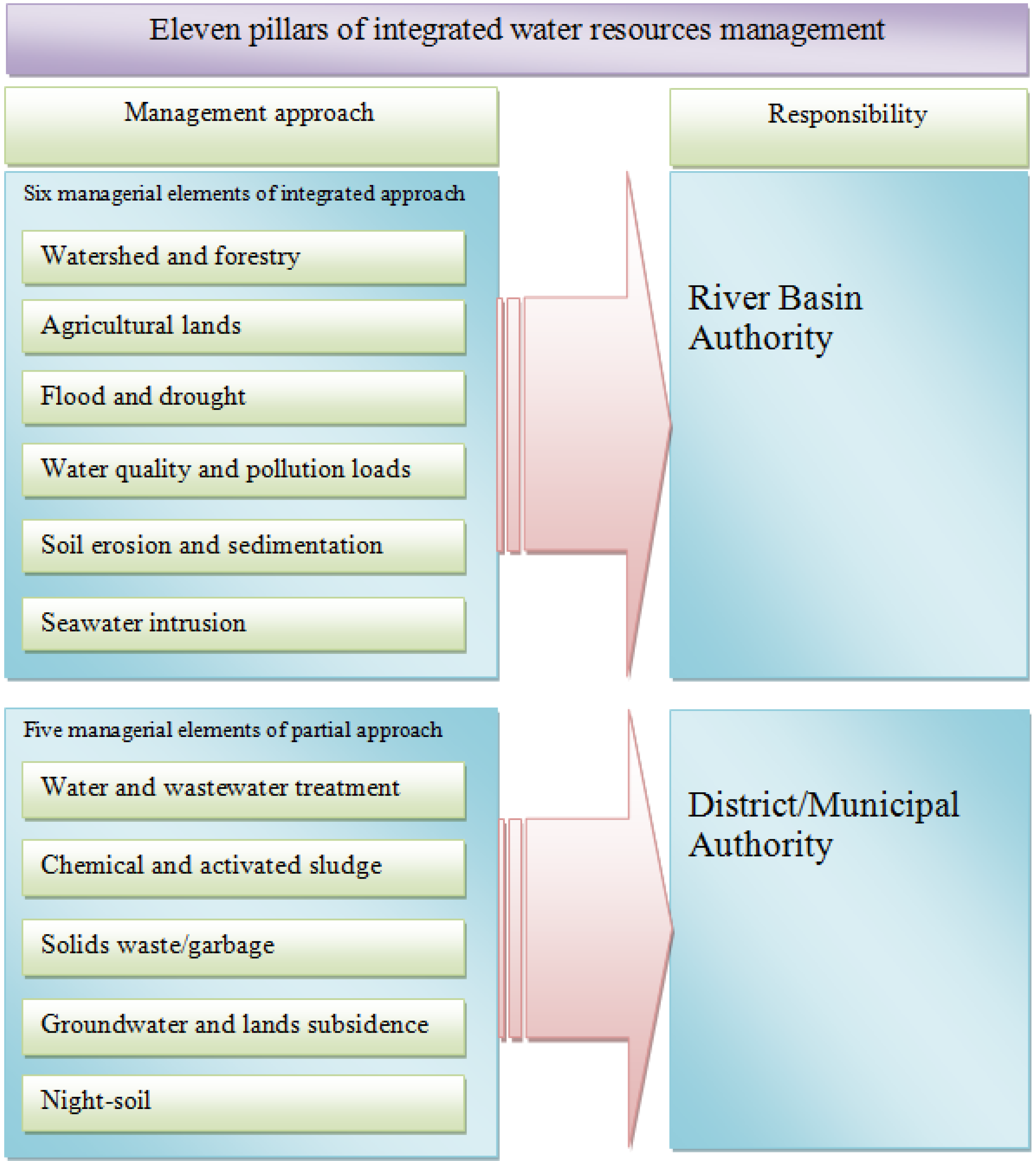
5.3. Management Instruments
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thou, A.D.M. Community and Social Responses to Land Use Transformations in the Nairobi Rural-Urban Fringe, Kenya. Available online: http://factsreports.revues.org/435 (accessed on 11 July 2014).
- Fulazzaky, M.A.; Gany, A.H.A. Challenges of soil erosion and sludge management for sustainable development in Indonesian. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R. Environmental restoration of invaded ecosystems: How much versus how often? J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, C. Organization of Water Management in France: Capacity Building for Better Water Management; International Office for Water: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bearden, B.L. The legal regime of the Mekong River: A look back and some proposals for the way ahead. Water Policy 2010, 12, 798–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brils, J. Sediment monitoring and the European Water Framework Directive. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanità 2008, 44, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- zerol, G.; Newig, J. Evaluating the success of public participation in water resources management: Five key constituents. Water Policy 2008, 10, 639–655. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Climate Change and Human Health: Risks and Responses; McMichael, A.J., Campbell-Lendrum, D.H., Corvalán, C.F., Ebi, K.L., Githeko, A.K., Scheraga, J.D., Woodward, A., Eds.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fulazzaky, M.A.; Akil, H. Development of data and information system to improve water resources management in Indonesia. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulazzaky, M.A.; Sutardi, S. Integrated Water Resources Management in View of Environmental Sustainability Aspects; Penerbit UTHM: Batu Pahat, Malaysia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Indonesia (GOI). Indonesian Law No. 7/2004 on Water Resources; Indonesian Law and Regulation Document; GOI: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Directorate General of Water Resources (DGWR). Water Resources Conservation Problems in Indonesia. In Ministerial Coordination Meeting amongst the Ministries of Public Works, Forestry, and Environment; DGWR Official Document; DGWR: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, V.I.; Krantzberg, G. Great Lakes: Lesson in Participatory Governance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, B. Planning and management of shared waters: Hydropolitics and hydropsychology—Two sides of the same coin. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2014, 30, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulsink, F.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Booij, M.J. The water footprint of Indonesian provinces related to the consumption of crop products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Mallory, S.J.L. The importance of operating rules and assessments of beneficial use in water resource allocation policy and management. Water Policy 2009, 11, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfai, M.A.; King, L.; Singh, L.P.; Mardiatno, D.; Sartohadi, J.; Hadmoko, D.S.; Dewi, A. Natural hazards in Central Java Province, Indonesia: An overview. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M. Flood risk impact factor for comparatively evaluating the main causes that contribute to flood risk in urban drainage areas. Water 2014, 6, 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- Santato, S.; Bender, S.; Schaller, M. The European Floods Directive and Opportunities Offered by Land Use Planning; CSC Report 12; Climate Service Center: Hamburg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pretty, J. Agricultural sustainability: Concepts, principles and evidence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.; Reggiani, P.; Roo, A.D.; Bates, P.; Sprokkereef, E. Flood forecasting and warning at the river basin and at the European scale. Nat. Hazards 2005, 36, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, L.A.; Lutz, B.D.; Doyle, M.W. Characterization of drought in the South Atlantic, United States. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.; Verulkar, S.B.; Mandal, N.P.; Variar, M.; Shukla, V.D.; Dwivedi, J.L.; Singh, B.N.; Singh, O.N.; Swain, P.; Mall, A.K.; et al. Drought yield index to select high yielding rice lines under different drought stress severities. Rice 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Malack, M.H.; Abuzaid, N.S.; Bukhari, A.A.; Essa, M.H. Characterization, utilization, and disposal of municipal sludge: The state of-the-art. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2002, 27, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, E.Z.; Lee, T.; McBride, M.; Bossard, S.; Chase, L.; Bouldin, D.; Czymmek, K. Considerations for Dairy Farms Regarding Use of Sewage Sludges, Sludges Products and Septage; Cornell Waste Management Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.; Jackson, R.H.; Yuan, Z.; Jackson, M.W.; Sun, B. The effects of sediment-laden waters on irrigated lands along the lower Yellow River in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 84, 858–865. [Google Scholar]
- Fulazzaky, M.A. Problems and restoration activities for eutrophicated lakes and reservoirs in Indonesia. In Proceeding of the 56th IEC-ICID Meeting and 19th ICID Congress, Beijing, China, 10–18 September 2005.
- Maherali, H.; DeLucia, E.H. Influence of climate-driven shifts in biomass allocation on water transport and storage in ponderosa pine. Oecologia 2001, 129, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukistijono, S. Erosion and sedimentation in Brantas upper reach and its countermeasures. In Proceeding of the First International Workshop on Water and Sediment Management on Brantas River Basin, Batu-Malang, Indonesia, 28–29 July 2005.
- Djajadiredja, E.A.; Ibrahim, A.B. Effect of land-use change on sedimentation rate at upper Citarum river basin. In Proceeding of the First International Workshop on Water and Sediment Management on Brantas River Basin, Batu-Malang, Indonesia, 28–29 July 2005.
- National Statistic Board (NSB). Environmental Statistic of Indonesia Annual Statistic Publication; NSB Publications: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Koottatep, T. Night soil treatment and management. In Proceeding of the International Training Course on Water Management, Water Supply and Sanitation, Hat Yai, Thailand, 19 July–6 August 1999.
- Gleditsch, N.P. Whither the weather? Climate change and conflict. J. Peace Res. 2012, 49, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglione, A.; Merz, R.; Bloschl, G. On the role of the runoff coefficient in the mapping of rainfall to flood return periods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulazzaky, M.A. Water quality evaluation system to assess the Brantas river water. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 3019–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulazzaky, M.A. Water quality evaluation system to assess the status and the suitability of the Citarum river water to different uses. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 168, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reba, M.L.; Daniels, M.; Chen, Y.; Sharpley, A.; Bouldin, J.; Teague, T.G.; Daniel, P.; Henry, C.G. A statewide network for monitoring agricultural water quality and water quantity in Arkansas. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 45A–49A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.L. Water and Health: Challenges in ASEAN Countries and Singapore’s Experience. In Proceedings of the Conference on Globalising Asia: Health Law, Governance and Policy-Issues, Approaches and Gaps, Bangkok, Thailand, 27–29 October 2011.
- Hansnata, E. Water management in Indonesia: Lessons from Australia. In Economics, Politics and Public Policy in East Asia and the Pacific; East Asia Forum: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, C.; Erickson, J.; Noordewier, T.; Sheldon, A.; Kline, M. Collaborative environmental planning in river management: An application of multi-criteria decision analysis in the White River Watershed in Vermont. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 84, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, G.A.; Martins, H. Multi-criteria decision analysis in natural resource management: A critical review of methods and new modeling paradigms. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 230, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braden, J.B.; Jolejole-Foreman, M.C.; Schneider, D.W. Humans and the water environment: The need for coordinated data collection. Water 2014, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kerssens, P.J.M.; van Urk, A. Experimental studies on sedimentation due to water withdrawal. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1986, 112, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian Development Bank (ADB). Integrated Citarum Water Resources Management Investment Program; Project 1; Compliance Review Panel: Manila, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Forestry (MOF). National Movement for Forests and Lands Rehabilitation: Works Plan 2003–2007; MOF: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Duane, T.P.; Opperman, J.J. Comparing the conservation effectiveness of private water transactions and public policy reforms in the conserving California landscapes initiative. Water Policy 2010, 12, 913–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, U. Multiple conceptions of sustainable urban water systems: Problem or asset? Water Policy 2010, 12, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischhendler, I.; Heikkila, T. Does integrated water resources management support institutional change? The case of water policy reform in Israel. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol15/iss1/art4/ (accessed on 11 July 2014).
- Kakabadse, N.K.; Rozuel, C.; Lee-Davies, L. Corporate social responsibility and stakeholder approach: A conceptual review. Int. J. Bus. Gov. Ethics 2005, 1, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.K.; Sato, N. Deforestation, land conversion and illegal logging in Bangladesh: The case of the Sal (Shorea robusta) forests. iForest 2012, 5, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, Z.Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.W. Assessment of surface water quality at large watershed scale: Land-use, anthropogenic, and administrative impacts. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnsawasdi, R.; Roongtawanreongsri, S. Economic as a tool for sustainable water, wastewater and solid waste management. In Proceeding of the International Training Course on Water Management, Water Supply and Sanitation, Hat Yai, Thailand, 19 July–6 August 1999.
- Jones, N.; Evangelinos, K.; Gaganis, P.; Polyzou, E. Citizens’ perceptions on water conservation policies and the role of social capital. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulazzaky, M.A.; Wahyudi, S.I. Participating the farmers on operation and maintenance of the irrigation networks system in Central Java, Yogyakarta and West Nusa Tenggara Provinces. In Proceeding of the 4th Asian Regional Conference and 10th International Seminar on Participatory Irrigation Management, Tehran, Iran, 2–5 May 2007.
- Bryan, B.A.; Kandulu, J.M. Designing a policy mix and sequence for mitigating agricultural non-point source pollution in a water supply catchment. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 875–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R. Capturing benefits from water entitlement trade in salinity affected areas: A role for trading houses? Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. Soc. 2002, 46, 347–366. [Google Scholar]
- Munawir, M.; Suhardi, S.; Salim, S.; Suyanto, A.; Vermeulen, S. Action-Learning to Develop and Test Upstream-Downstream Transactions for Watershed Protection Services: A Diagnostic Report from Segara River Basin, Indonesia; Centre for Water Resources and Environment—Institute for Social and Economic Research, Education & Information: Jakarta, Indonesia; International Institute for Environment and Development: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Samani, Z.; Skaggs, R.K. The multiple personalities of water conservation. Water Policy 2008, 10, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fulazzaky, M.A. Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management in Indonesia. Water 2014, 6, 2000-2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072000
Fulazzaky MA. Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management in Indonesia. Water. 2014; 6(7):2000-2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072000
Chicago/Turabian StyleFulazzaky, Mohamad Ali. 2014. "Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management in Indonesia" Water 6, no. 7: 2000-2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072000
APA StyleFulazzaky, M. A. (2014). Challenges of Integrated Water Resources Management in Indonesia. Water, 6(7), 2000-2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6072000




