Utilization of Ion-Exclusion Chromatography for Water Quality Monitoring in a Suburban River in Jakarta, Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
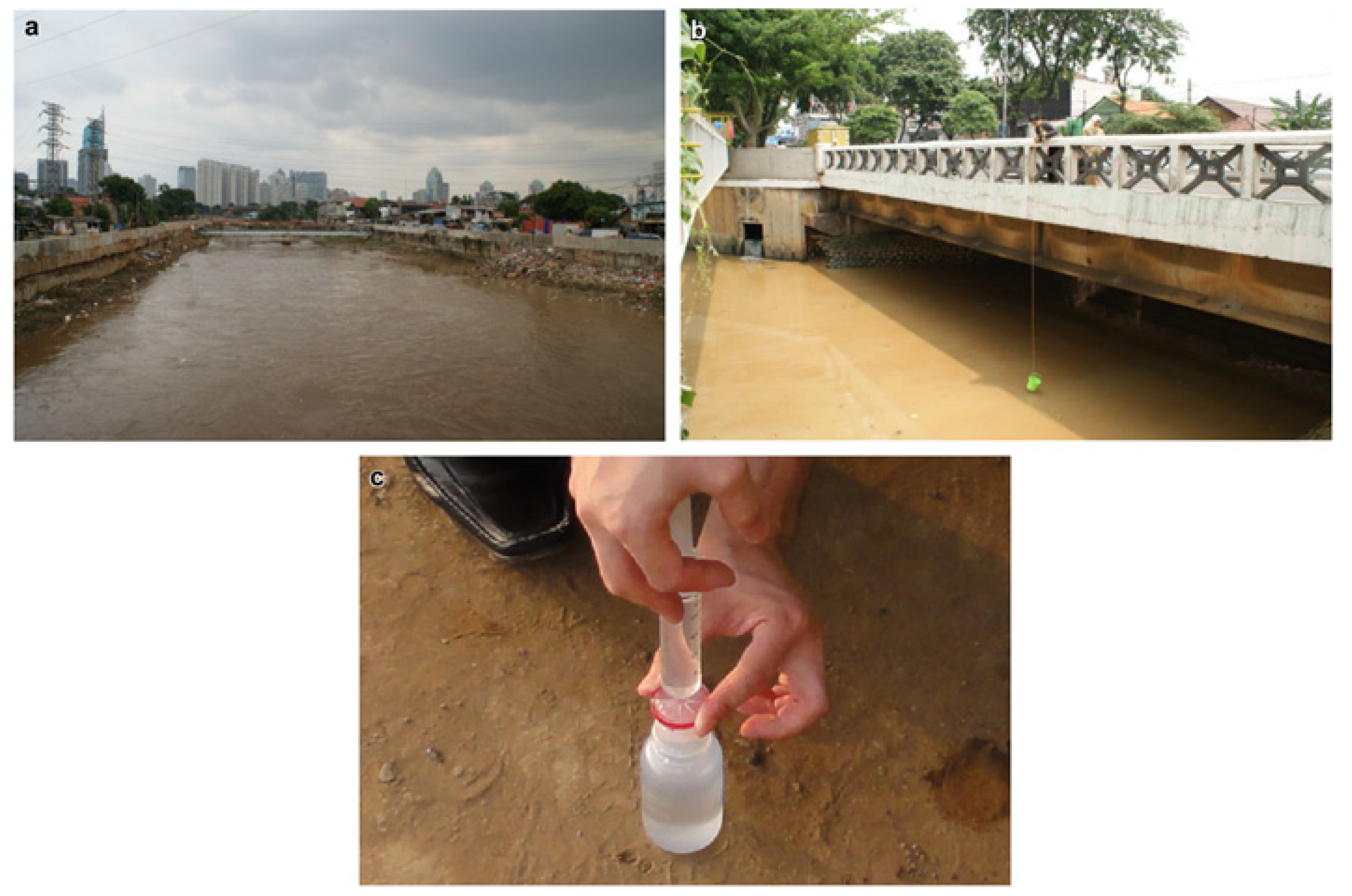

2. Materials and Methods
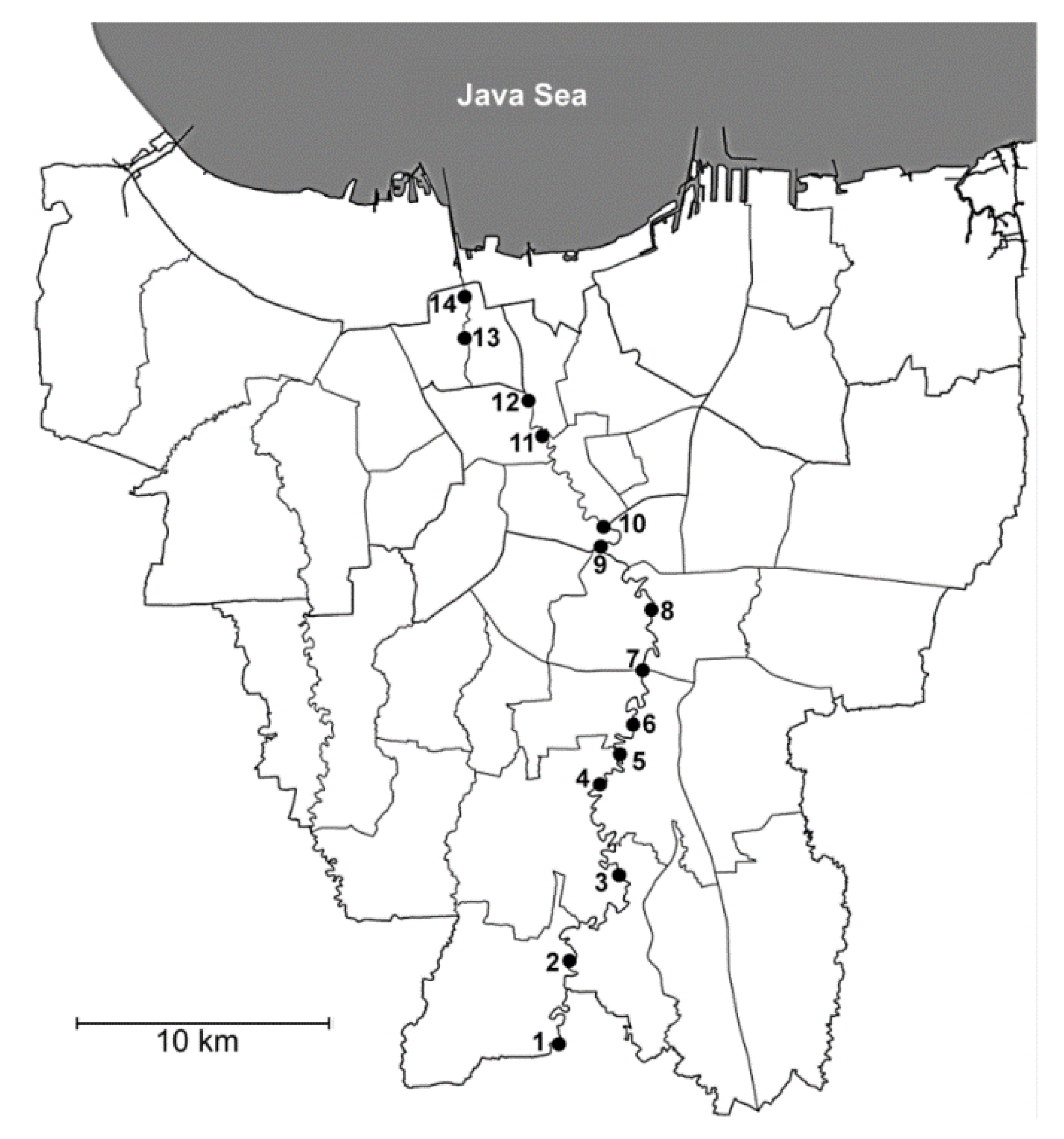
2.1. Water Sampling in the Ciliwung River
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Ion-Exclusion Chromatography
2.3.1. Ion Chromatograph
2.3.2. IEC of Bicarbonate Ion
2.3.3. IEC/CEC of Inorganic Anions and Cations
2.3.4. IEC-Post-Column Derivatization of Phosphate and Silicate Ions
2.4. Analyses of Other Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analytical Performances of the IEC System
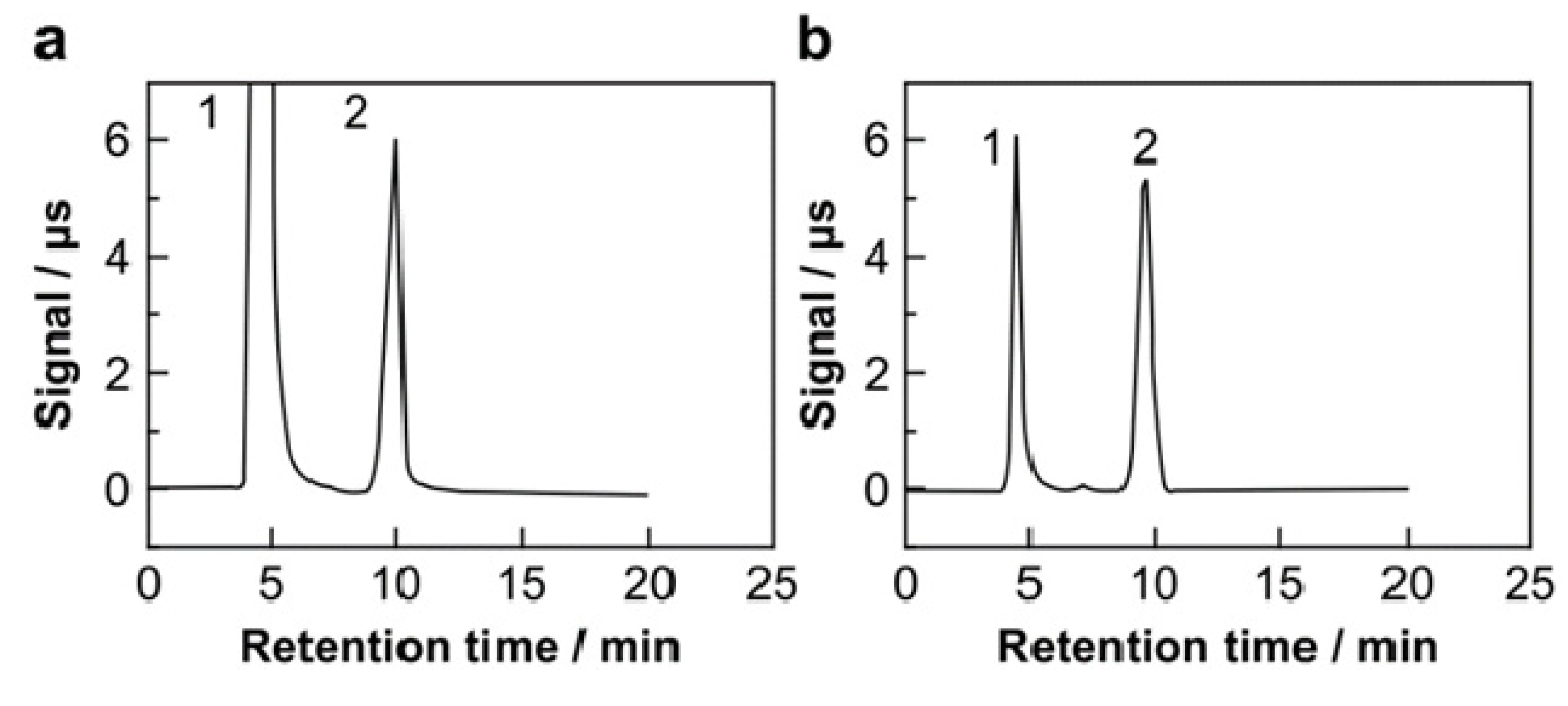
3.1.1. IEC for the Carbonate Ion
| Analyte | Lineality range (mg/L) | Correlation coefficient | Detection limits (mg/L) * | Relative standard deviation (%) | Methodology |
| Sulfate ion | 9.60–192 | 0.9993 | 0.874 | 0.330 | IEC/CEC for common inorganic ions |
| Chloride ion | 3.55–70.9 | 0.9999 | 0.138 | 0.240 | |
| Nitrate ion | 6.20–124 | 0.9958 | 0.211 | 0.210 | |
| Sodium ion | 2.30–46.0 | 0.9999 | 0.177 | 0.400 | |
| Ammonium ion | 1.80–18.0 | 0.9999 | 0.126 | 0.420 | |
| Potassium ion | 3.91–39.1 | 0.9928 | 0.403 | 0.620 | |
| Magnesium ion | 2.43–24.3 | 0.9995 | 0.102 | 0.250 | |
| Calcium ion | 4.01–40.1 | 0.9962 | 0.289 | 0.430 | |
| Bicarbonate ion | 0.610–6.10 | 0.9990 | 0.0311 | 0.500 | IEC for bicarbonate ion |
| Phosphate ion | 0.501–9.91 | 0.9900 | 0.0681 | 0.360 | IEC for phosphate and silicate ions |
| Silicate ion | 0.510–10.1 | 0.9999 | 0.0955 | 1.10 |
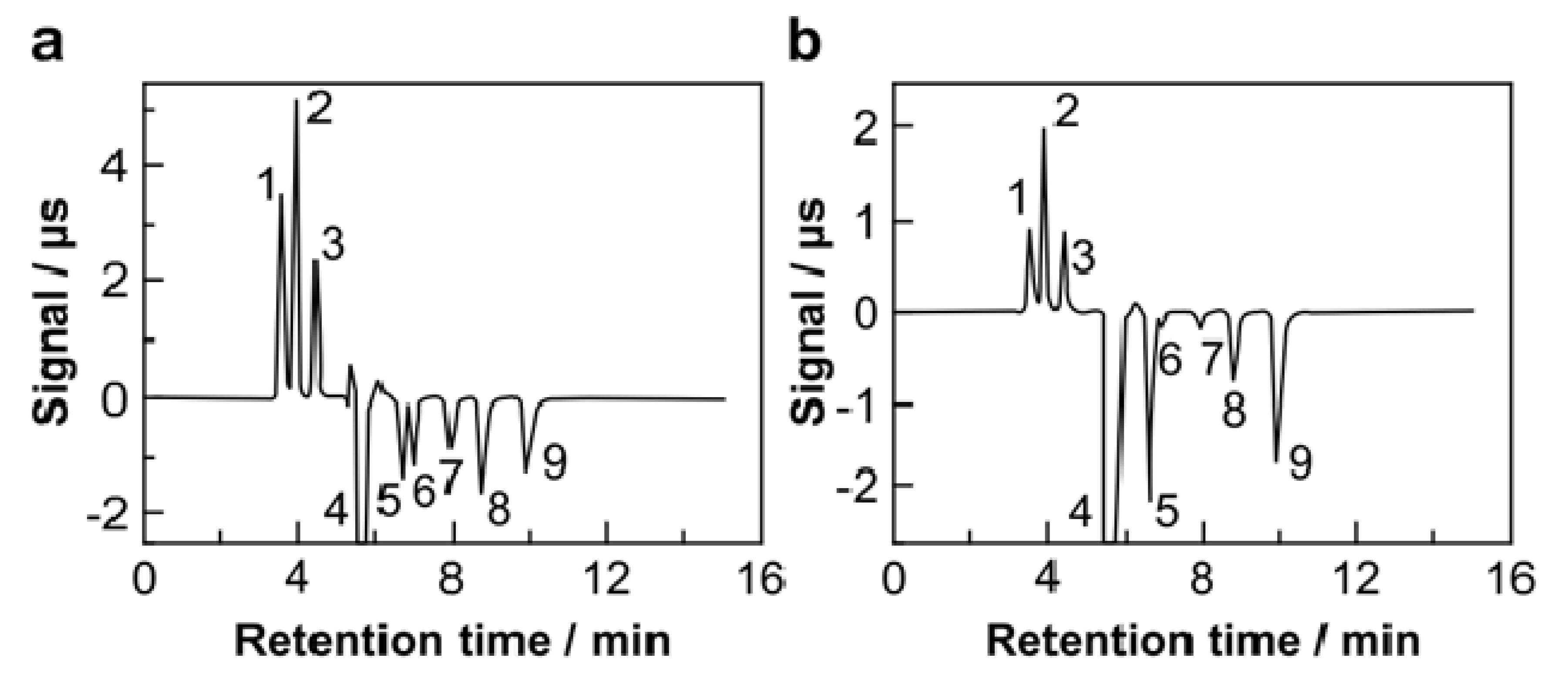
3.1.2. Simultaneous IEC/CEC for Common Inorganic Ions
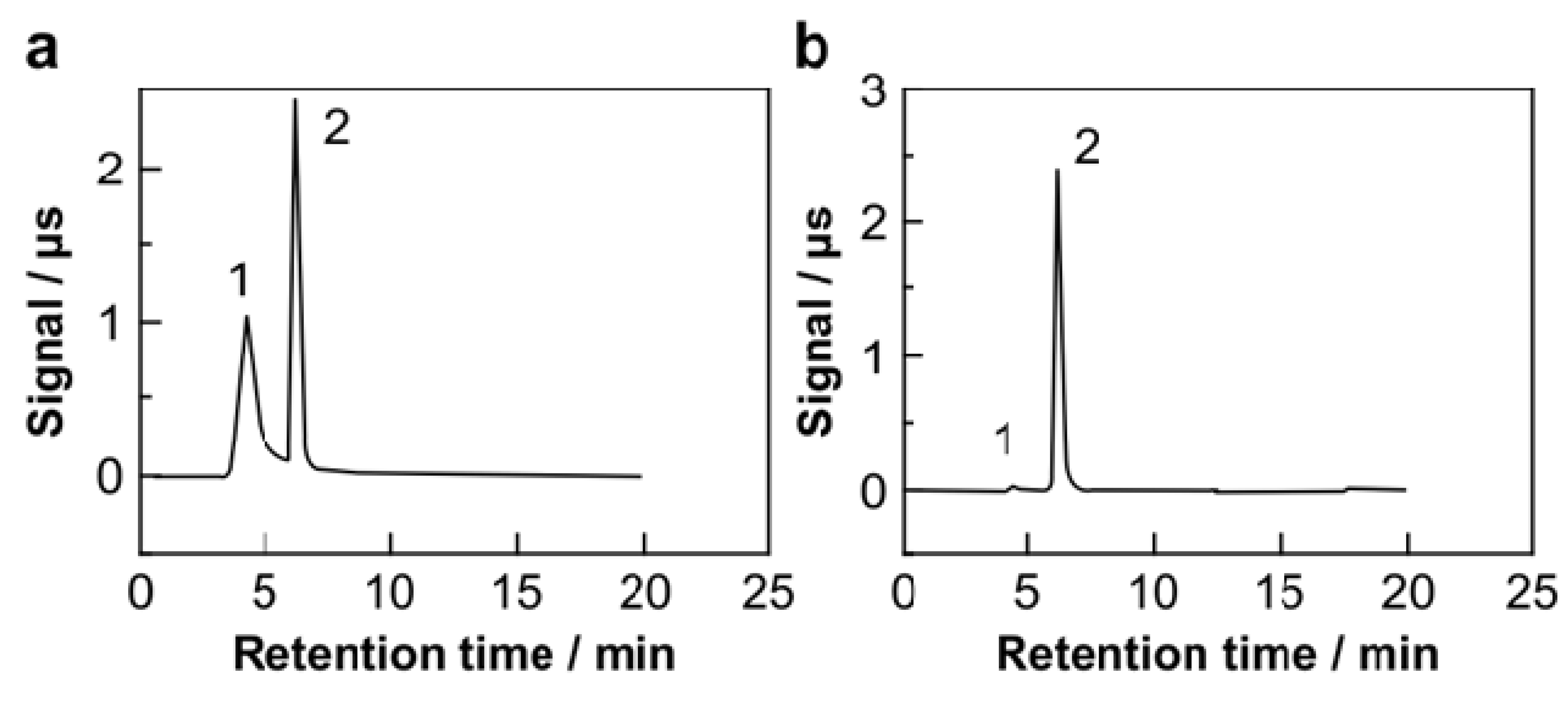
3.1.3. IEC for Phosphate and Silicate Ions
3.2. Transition of Ionic Composition in the Ciliwung River
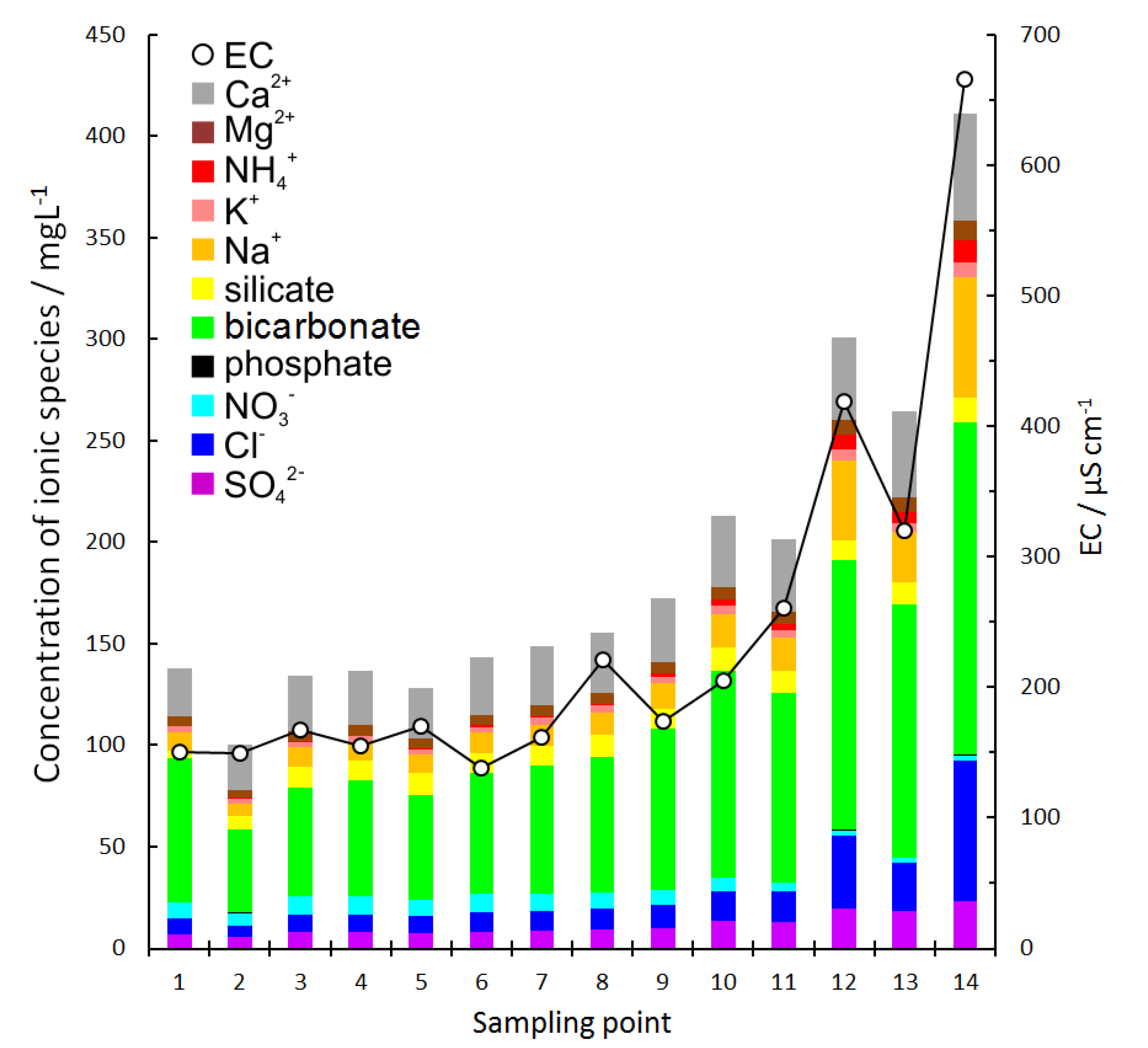
3.3. Changes in the Ionic Concentrations for Various Biological and Chemical Reactions
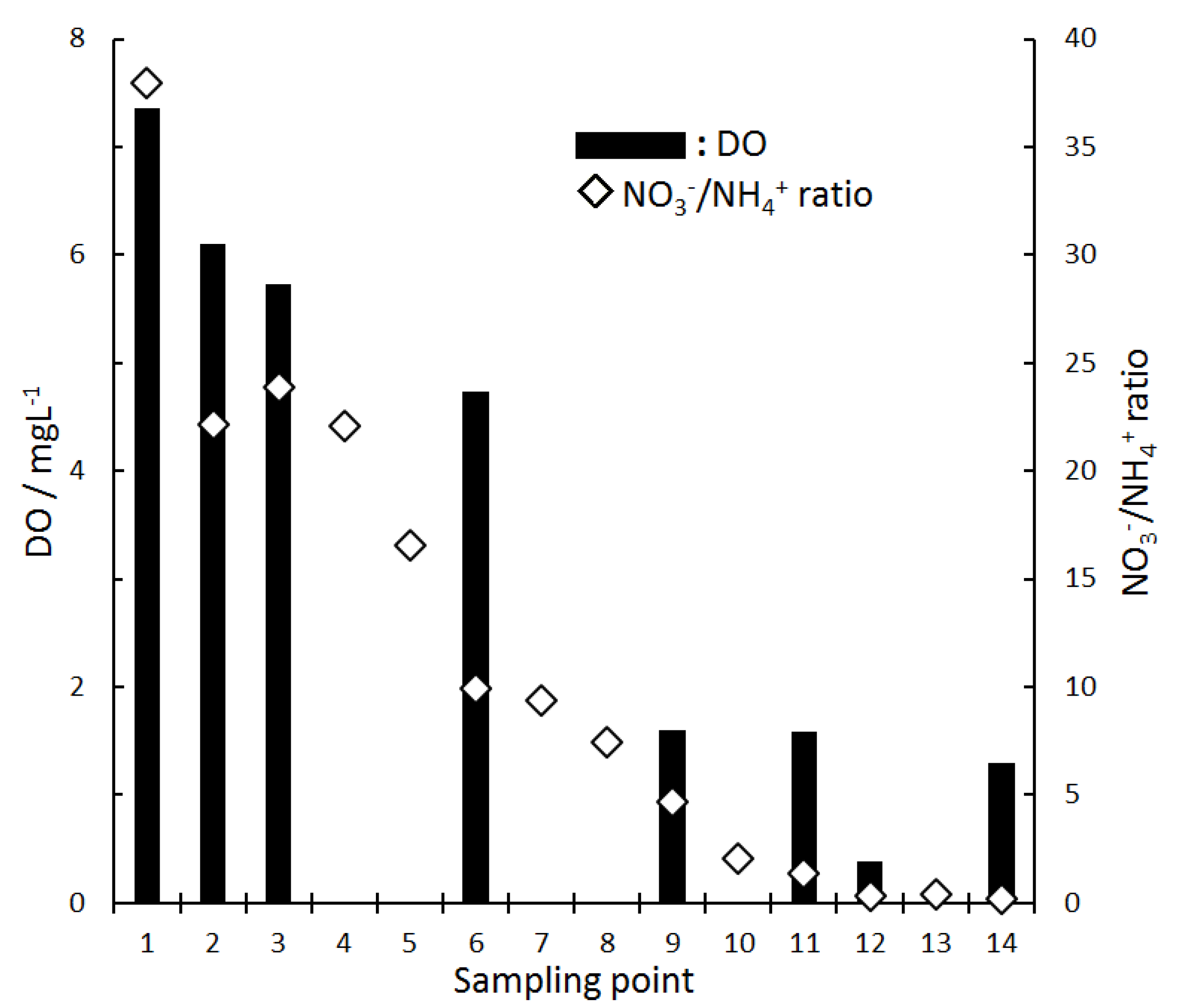
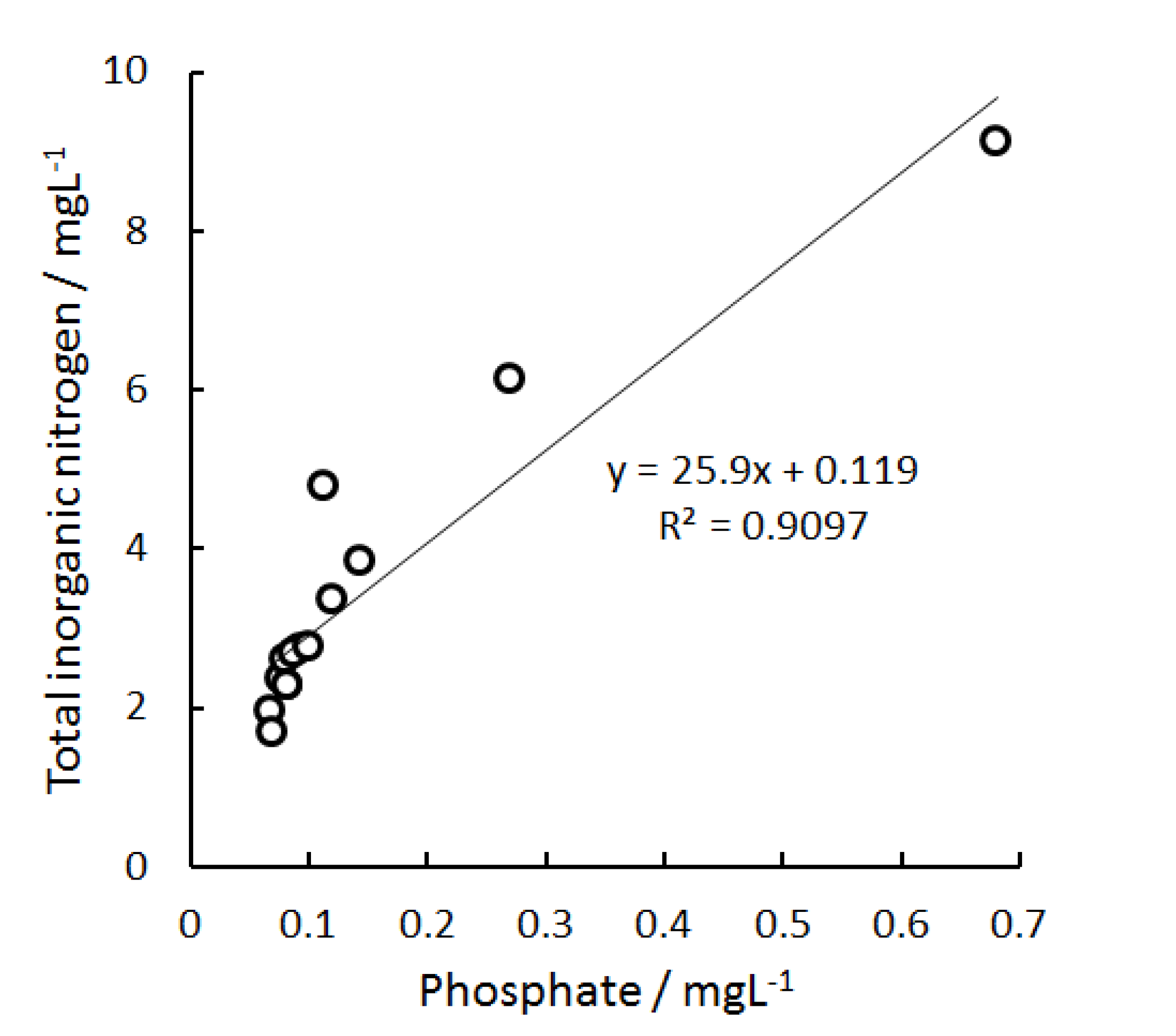
3.3.1. Inorganic Nitrogen Species and DO
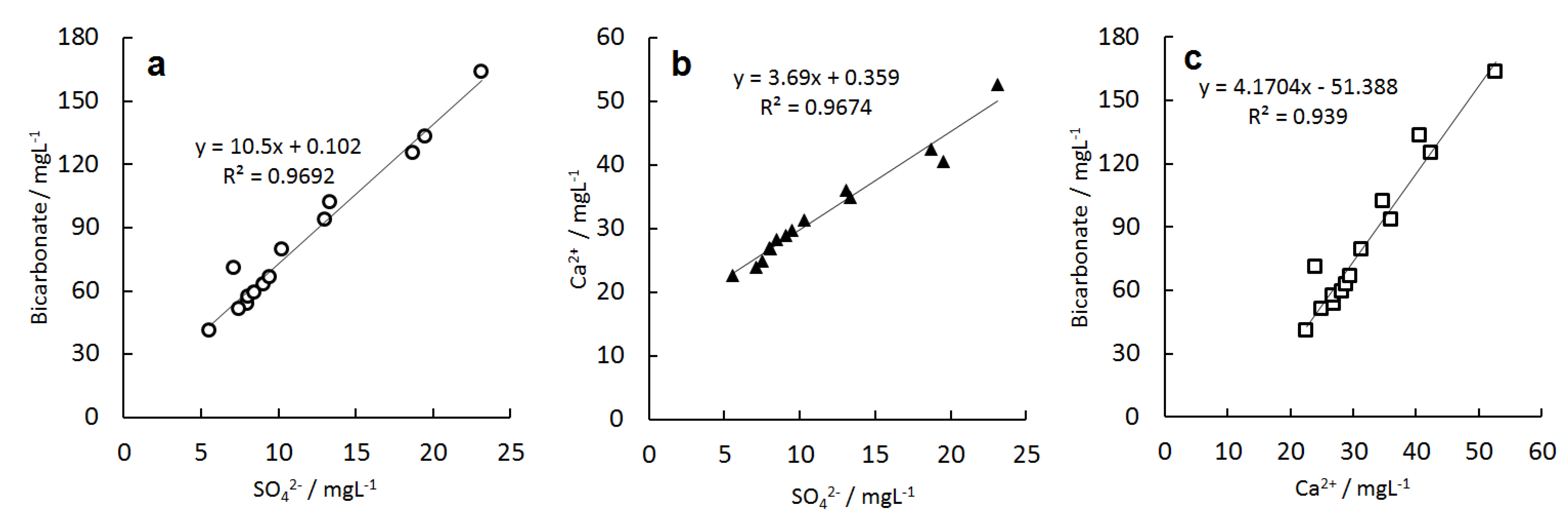
3.3.3. Bicarbonate, Sulfate, and Calcium Ions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of interest
References
- Brebbia, C.A.; Anagnostopoulos, P. Water Pollution: Modelling, Measuring and Prediction; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, D.A. Water-Quality Engineering in Natural Systems: Fate and Transport Processes in the Water Environment; Wiley-VCH: Weinhelm, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of the Environment, Institute for Global Environmental Strategies. Onsite wastewater treatment systems for improving water quality in Asian cities. Clean Asia Initiat. Newsl. 2013, 10, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. Study on the Waste Treatment Facility Bot Project in Dki Jakarta, the Republic of Indonesia; Study on Private-Initiative Infrastructure Projects in Developing Countries in FY2011; Ministry of Economy: Tokyo, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kido, M.; Wati, Y.; Syawal, M.S.; Sulastri.; Hosokawa, T.; Tanaka, S.; Saito, T.; Iwakuma, T.; Kurasaki, M. Comparison of general water quality of rivers in Indonesia and Japan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 156, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palupi, K.; Sumengen, S.; Inswiasri, S.; Agustina, L.; Nunik, S.; Sunarya, W.; Quraisyn, A. River water quality study in the vicinity of Jakarta. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 31, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takarina, N.D.; Adiwibowo, A. Impact of heavy metals contamination on the biodiversity of marine benthic organisms in Jakarta bay. J. Coast. Dev. 2011, 14, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Taurusman, A.A. Community structure of macrozoobenthic feeding guilds in responses to eutrophication in Jakarta Bay. Biodiversitas 2010, 11, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Meij, S.E.T.; Moolenbeek, R.G.; Hoeksema, B.W. Decline of the Jakarta Bay molluscan fauna linked to human impact. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 59, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Ishizuka, T. Elution behavior of acids in ion-exclusion chromatography using a cation-exchange resin. J. Chromatogr. 1979, 174, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Fritz, J.S. Separation of aliphatic carboxylic acids by ion-exclusion chromatography using a weak-acid eluent. J. Chromatogr. 1986, 361, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikedo, M.; Mori, M.; Kurachi, K.; Hu, W.; Tanaka, K. Selective and simultaneous determination of phosphate and silicate ions in leaching process waters for ceramics glaze raw materials of natural origin by ion-exclusion chromatography coupled with UV-detection after postcolumn derivatization. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, N.; Kozaki, D.; Masuda, W.; Nakagoshi, N.; Hasebe, K.; Mori, M.; Tanaka, K. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of phosphate and silicate ions in river water by using ion-exclusion chromatographic separation and post-column derivatization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 116, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kozaki, D.; Nakatani, N.; Mori, M.; Nakagoshi, N.; Tanaka, K. Development of water quality monitoring system for sequential determination of ionic nutrients by ion-exclusion chromatography with spectrophotometric detection on cation- and anion-exchange resin columns in parallel using water eluent. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2012, 30, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, M.; Tanaka, K.; Helaleh, M.I.H.; Xu, Q.; Ikedo, M.; Ogura, Y.; Sato, S.; Hu, W.; Hasebe, K.; Haddad, P.R. High-speed simultaneous ion-exclusion/cation-exchange chromatography of anions and cations on a weakly acidic cation-exchange resin column. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 997, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, M.; Tanaka, K.; Satori, T.; Ikedo, M.; Hu, W.; Itabashi, H. Influence of acidic eluent for retention behaviors of common anions and cations by ion-exclusion/cation-exchange chromatography on a weakly acidic cation-exchange resin in the H+-form. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1118, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K. Study on water quality monitoring by advanced ion-exclusion chromatography. Bunseki Kagaku 2006, 55, 275–289. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozaki, D.; Goto, R.; Masuda, W.; Saito, D.; Nakatani, N.; Nakagoshi, N.; Mori, M.; Tanaka, K. Application of ion-exclusion/cation-exchange chromatography to water quality monitoring of sub-urban river. Bunseki Kagaku 2008, 57, 651–658. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Ikedo, M.; Hu, W.; Helaleh, M.I.H.; Xu, Q.; Itabashi, H.; Tanaka, K. High-speed ion-exclusion chromatography of dissolved carbon dioxide on a small weakly acidic cation-exchangeresin column with ion-exchange enhancement columns of conductivity detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1092, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.S.; Gjerde, D.T. Ion Chromatography, 4th ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinhelm, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Japanese Standards Association. JIS K0102 Testing Methods for Industrial Wastewater; Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2008. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Japanese Standards Association. JIS K0127 General Rules for IonChromatography; Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2013. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Part. 4110 Determination of Anions by Ion Chromatography; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency website. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/waterscience/ftp/basins/ training/tutorial/hcyclepx.htm (accessed on 21 November 2013).
- International Organization for Standardization website. Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/home.html (accessed on 21 November 2013).
- Butler, J.N. Carbon Dioxide Equilibria and Their Applications; CRC-Press: Florida, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: An Introduction Emphasizing Chemical Equilibria in Natural Water, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus transport by world rivers. Am. J. Sci. 1982, 282, 401–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; McCauley, E. The nitrogen-phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N.; Justic, D.; Dortch, Q. Global patterns of dissolved N, P, and Si in large river. Biogeochemistry 2003, 64, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.B.; Finlay, J.C. Patterns of hydrologic control over stream water total nitrogen to total phosphorus ratios. Biogeochemistry 2010, 99, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, C.; Cann, M. Environmental Chemistry, 3rd ed.; W.H. Freeman Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.K. Water Pollution; A P H Publishing Corporation: New Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Karamouz, M.; Moridi, A.; Nazif, S. Water Engineering and Management; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pena, M.A.; Katsev, S.; Oguz, T.; Gilbert, D. Modeling dissolved oxygen dynamics and hypoxia. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 933–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.R.; Murphy, K.L. Estimation of nitrifying biomass and kinetics in wastewater. Water Res. 1980, 14, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K. Determination of bicarbonate ion in biological nitrification process water by ion-exclusion chromatography with coulometric detection. Bunseki Kagaku 1981, 30, 358–362. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.E. Taphonomy A Process Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles, R. Denitrification. Microbiol. Rev. 1982, 46, 43–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin, H.J.; Michaels, J.T.; Beaulaton, C.M.; Graham, W.F.; Dutt, W.; Steinbach, P.; Losordo, T.M.; Schrader, K.K.; Main, K.L. Comparing denitrification rates and carbon sources in commercial scale upflow denitrification biological filters in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2008, 38, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, H.; Odagiri, M.; Ito, T.; Okabe, S. Microbial community structures and in situ sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing activities in biofilms developed on mortar specimens in a corroded sewer system. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4729–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamdrup, B.; Canfield, D.E. Pathways of carbon oxidation in continental margin sediments off central Chile. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1629–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozaki, D.; Ozaki, T.; Nakatani, N.; Mori, M.; Tanaka, K. Utilization of Ion-Exclusion Chromatography for Water Quality Monitoring in a Suburban River in Jakarta, Indonesia. Water 2014, 6, 1945-1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6071945
Kozaki D, Ozaki T, Nakatani N, Mori M, Tanaka K. Utilization of Ion-Exclusion Chromatography for Water Quality Monitoring in a Suburban River in Jakarta, Indonesia. Water. 2014; 6(7):1945-1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6071945
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozaki, Daisuke, Takashi Ozaki, Nobutake Nakatani, Masanobu Mori, and Kazuhiko Tanaka. 2014. "Utilization of Ion-Exclusion Chromatography for Water Quality Monitoring in a Suburban River in Jakarta, Indonesia" Water 6, no. 7: 1945-1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6071945
APA StyleKozaki, D., Ozaki, T., Nakatani, N., Mori, M., & Tanaka, K. (2014). Utilization of Ion-Exclusion Chromatography for Water Quality Monitoring in a Suburban River in Jakarta, Indonesia. Water, 6(7), 1945-1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6071945





