Identifying Seasonal Groundwater Recharge Using Environmental Stable Isotopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
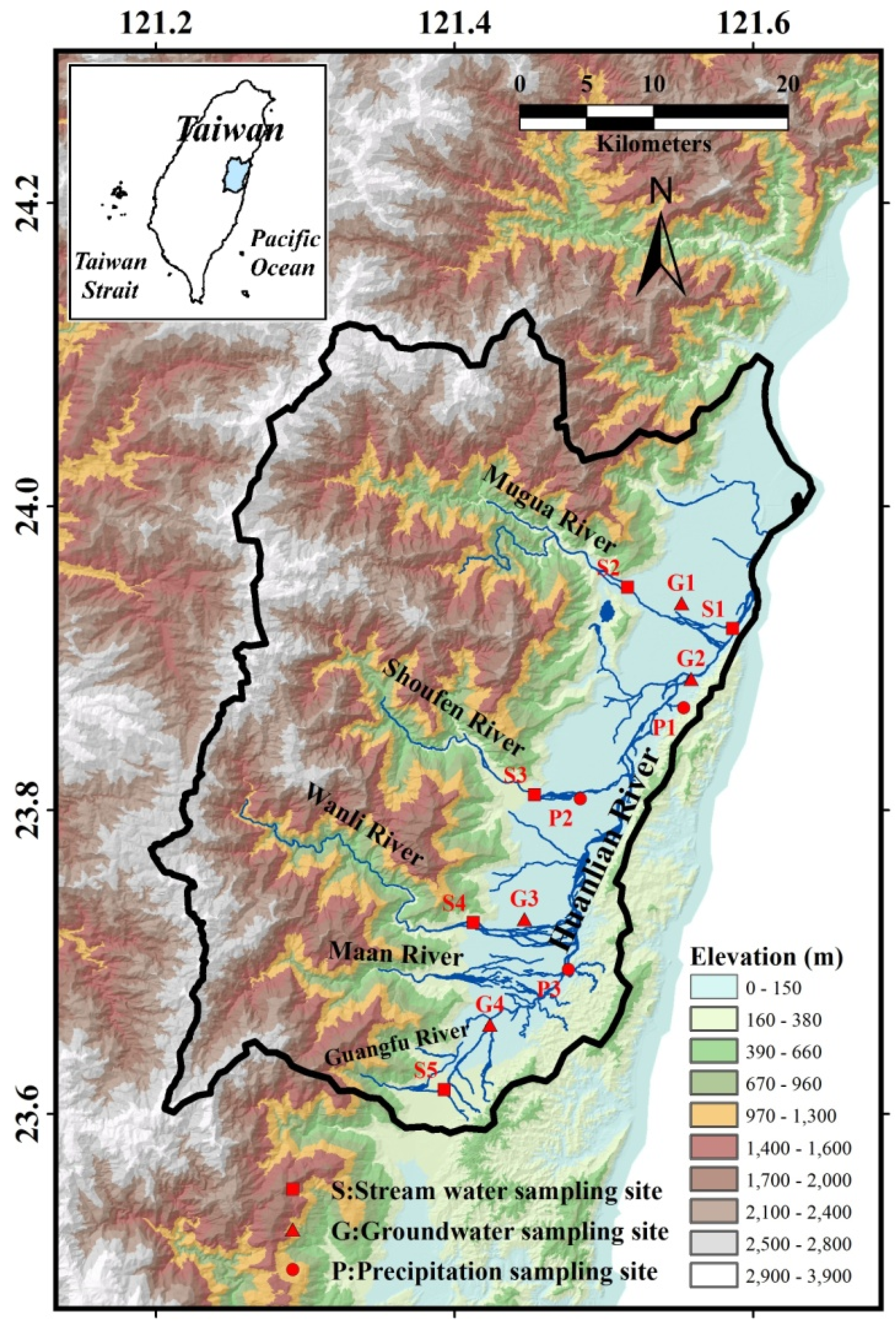
3. Sampling and Analytical Method
| Site | Longitude | Latitude | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 121.59 | 23.92 | 7 |
| S2 | 121.52 | 23.95 | 96 |
| S3 | 121.45 | 23.81 | 140 |
| S4 | 121.41 | 23.73 | 143 |
| S5 | 121.39 | 23.62 | 160 |
| P1 | 121.55 | 23.87 | 76 |
| P2 | 121.48 | 23.81 | 91 |
| P3 | 121.48 | 23.70 | 106 |
| G1 | 121.55 | 23.94 | 52 |
| G2 | 121.56 | 23.89 | 18 |
| G3 | 121.45 | 23.73 | 110 |
| G4 | 121.42 | 23.66 | 116 |
4. Results and Discussion
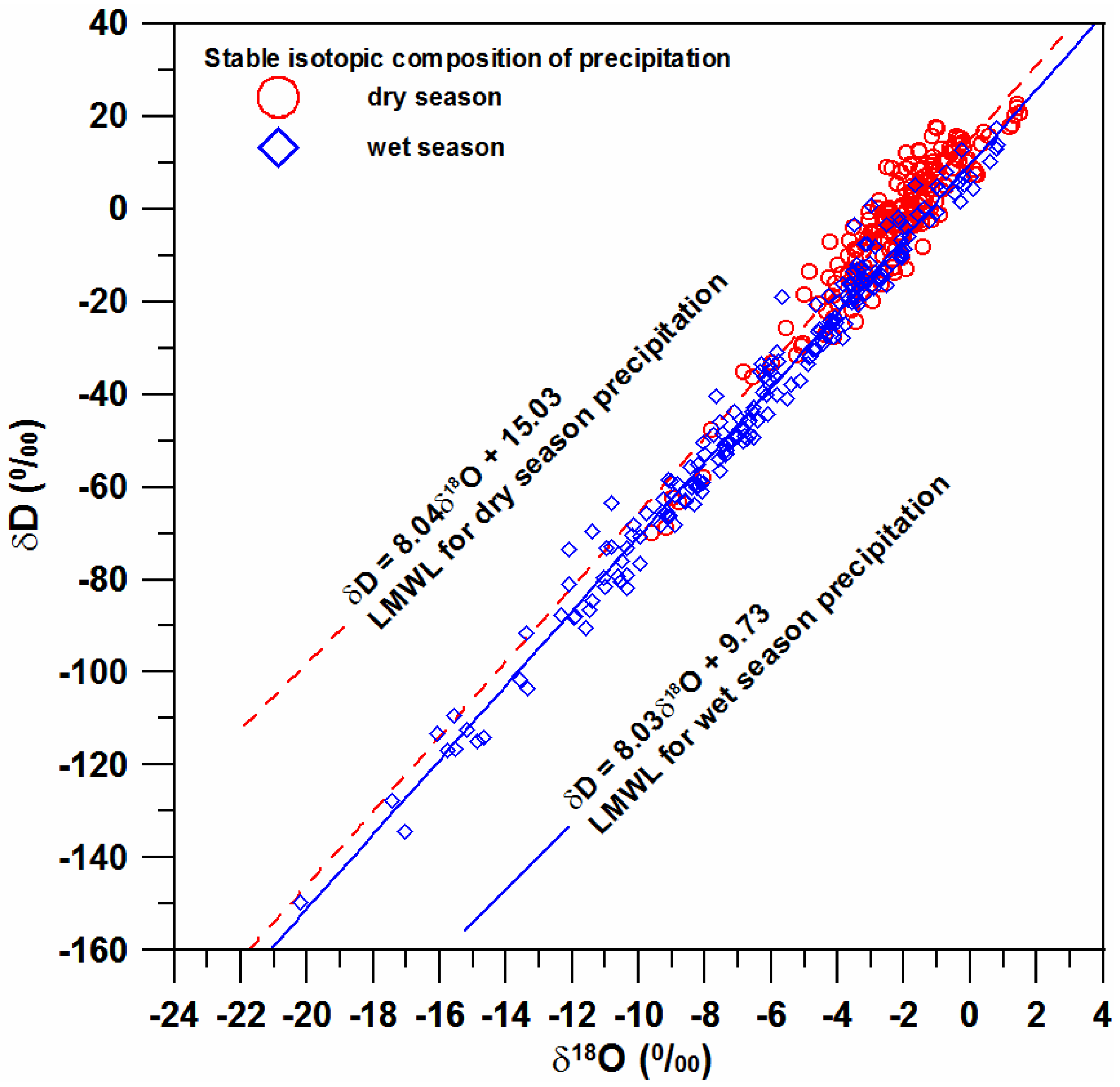
4.1. Isotopic Compositions of Precipitation
4.2. Isotopic Compositions of River Water


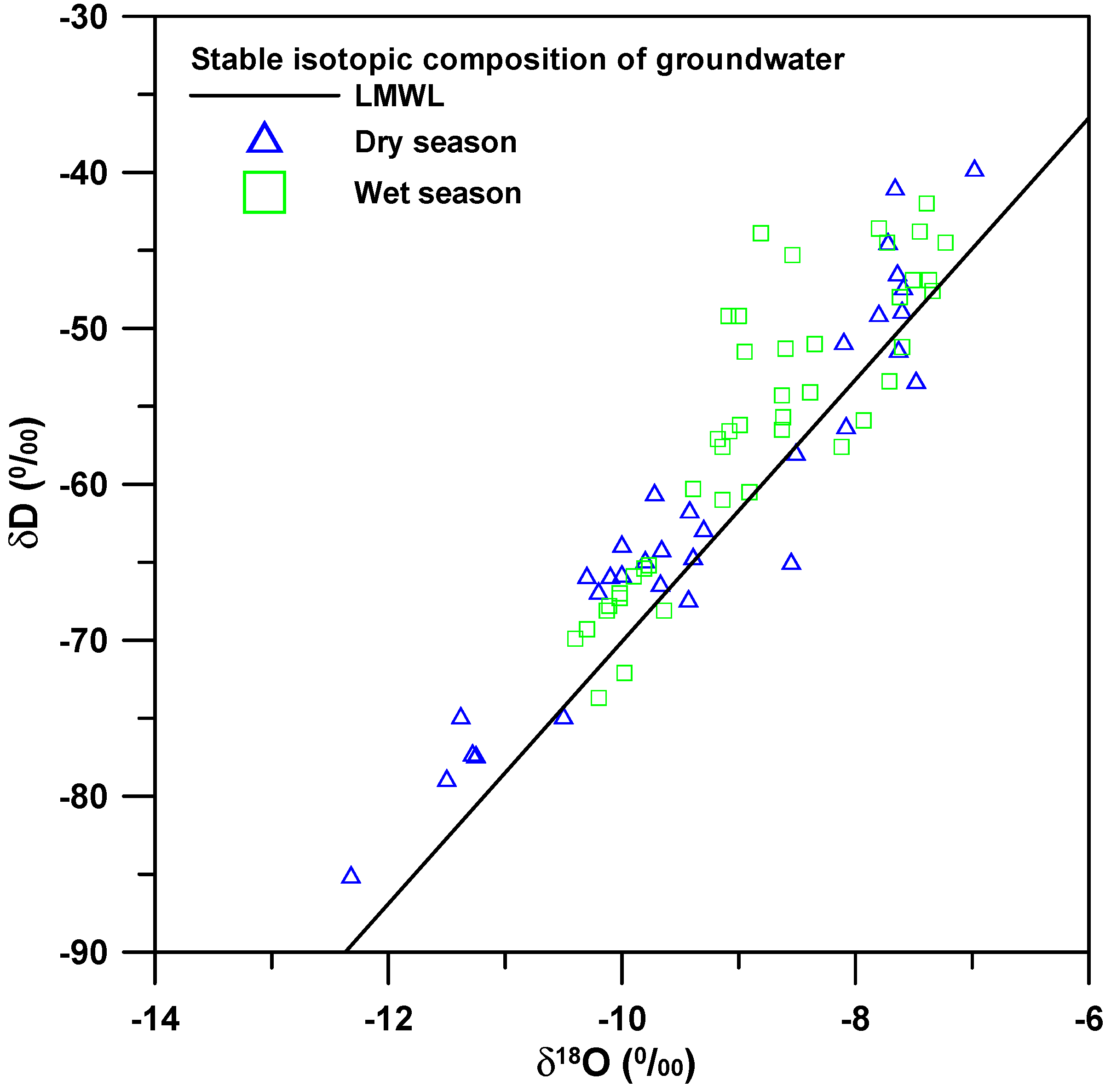
4.3. Isotopic Compositions of Groundwater
4.4. Mass Balance Analysis
| Weighted Average: | Precipitation | River Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Season | Wet Season | Dry Season | Wet Season | |
| Ratio | 0.19 | 0.81 | 0.14 | 0.86 |
| n (used for average) | 185 | 200 | 41 | 64 |
| δD (‰) | −3.7 ± 16.1 | −40.6 ± 32.8 | −62.9 ± 6.5 | −66.2 ± 10.6 |
| δ18O (‰) | −2.3 ± 1.9 | −6.3 ± 4.1 | −9.6 ± 0.7 | −9.8 ± 1.2 |
| d-excess (‰) | 14.7 ± 5.6 | −9.5 ± 4.6 | 13.5 ± 3.2 | 12.1 ± 3.5 |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrology; Lewis Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vandenschrick, G.; van Wesemael, B.; Frot, E.; Pulido-Bosch, A.; Molina, L.; Stiévenard, M.; Souchez, R. Using stable isotope analysis (δD and δ18O) to characterise the regional hydrology of the Sierra de Gador, south east Spain. J. Hydrol. 2002, 265, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, R.D.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Jani, R.A.; Gupta, S.K. Distribution of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in shallow groundwaters from Southern India: Influence of a dual monsoon system. J. Hydrol. 2003, 271, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Edwards, T.W.D.; Birks, S.J.; St Amour, N.A.; Buhay, W.M.; McEachern, P.; Wolfe, B.B.; Peters, D.L. Progress in isotope tracer hydrology in Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammons, C.H.; Poulson, S.R.; Pellicori, D.A.; Reed, P.J.; Roesler, A.J.; Petrescu, E.M. The hydrogen and oxygen isotopic composition of precipitation, evaporated mine water, and river water in Montana, USA. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasch, K.W.; Bryson, J.R. Distinguishing sources of ground water recharge by using δ2H and δ18O. Ground Water 2007, 45, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Pan, G.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J. Recharge source and hydrogeochemical evolution of shallow groundwater in a complex alluvial fan system, southwest of North China Plain. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilweil, V.M.; Solomon, D.K.; Gingerich, S.B.; Verstraeten, I.M. Oxygen, hydrogen, and helium isotopes for investigating groundwater systems of the Cape Verde Islands, West Africa. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hou, G.; Su, X.; Wang, D.; Dong, J.; Hao, Y.; Wang, X. Isotopes (δD and δ18O) in precipitation, groundwater and surface water in the Ordos Plateau, China: Implications with respect to groundwater recharge and circulation. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, B.; Singh, S.; Singh, I.B. Investigation on the hydrodynamics of Ganga Alluvial Plain using environmental isotopes: A case study of the Gomati River Basin, northern India. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R. The isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Fritz, P., Fontes, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1980; pp. 21–47. [Google Scholar]
- Darling, W.G.; Armannsson, H. Stable isotopic aspects of fluid flow in the Krafla, Namafijall and Theistareykir geothermal systems of northeast Iceland. Chem. Geol. 1989, 76, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Matsubaya, O. Stable isotopic studies of Japanese geothermal system. Geothermics 1977, 5, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Wenner, D.B.; Lee, I. Using H- and O-isotopic data for estimating the relative contributions of rainy and dry season precipitation to groundwater: Example from Cheju Island, Korea. J. Hydrol. 1999, 222, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.R.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; Fei, L.Y.; Chen, C.T.A.; Hwong, J.L. Stable isotopic characteristic of Taiwan’s precipitation: A case study of western Pacific monsoon region. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Resource Agency (WRA). Investigation of Water Resource in Hualien; Ministry of Economic Affairs: Taipei, Taiwan, 1997; p. 265.
- Water Resource Agency (WRA). Investigation of Groundwater Resource in Hualien Alluvial Valley; Ministry of Economic Affairs: Taipei, Taiwan, 2005; p. 395.
- Water Resource Agency (WRA). Conjunctive Utilization of Surface Water with Groundwater for Hualien Area; Ministry of Economic Affairs: Taipei, Taiwan, 2010; p. 525.
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Guidebook on Nuclear Techniques in Hydrology; IAEA Technical Reports Series No. 91; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1983; p. 439. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, S.; Mayeda, T. Variation of 18O content of waters from natural sources. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1953, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.L.; Shepherd, T.J.; Durham, J.J.; Rouse, J.E.; Moore, G.R. Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis. Anal. Chem. 1982, 54, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Peng, T.R. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of Taipei precipitation: 1990–1998. West. Pac. Earth Sci. 2001, 1, 429–442. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, T.R.; Wang, C.H.; Lai, T.C.; Ho, S.K. Using hydrogen, oxygen, and tritium isotopes to identify hydrological factors contributing to landslides in a mountainous area, central Taiwan. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes for the characteristics of groundwater recharge: A case study from the Chih-Pen Creek basin, Taiwan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtesever, Y.; Gat, J.R. Atmospheric waters. In Stable Isotope Hydrology: Deuterium and Oxygen-18 in the Water Cycle; IAEA Technical Report Series No. 210; Gat, J.R., Gonfiantini, R., Eds.; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1981; pp. 103–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.Y.; Peng, T.R.; Liu, T.K.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, C.C. Study of stable isotopes for highly deformed aquifers in the Hsinchu-Miaoli area, Taiwan. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, H.-F.; Lin, H.-I.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsu, K.-C.; Wu, C.-S. Identifying Seasonal Groundwater Recharge Using Environmental Stable Isotopes. Water 2014, 6, 2849-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6102849
Yeh H-F, Lin H-I, Lee C-H, Hsu K-C, Wu C-S. Identifying Seasonal Groundwater Recharge Using Environmental Stable Isotopes. Water. 2014; 6(10):2849-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6102849
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Hsin-Fu, Hung-I Lin, Cheng-Haw Lee, Kuo-Chin Hsu, and Chi-Shin Wu. 2014. "Identifying Seasonal Groundwater Recharge Using Environmental Stable Isotopes" Water 6, no. 10: 2849-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6102849
APA StyleYeh, H.-F., Lin, H.-I., Lee, C.-H., Hsu, K.-C., & Wu, C.-S. (2014). Identifying Seasonal Groundwater Recharge Using Environmental Stable Isotopes. Water, 6(10), 2849-2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6102849






