Characteristics of DOM and Removal of DBPs Precursors across O3-BAC Integrated Treatment for the Micro-Polluted Raw Water of the Huangpu River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set-up

| Water quality | Minimum | Maximum | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 4.0 | 27.5 | 16.2 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 20 | 127 | 44 |
| pH | 7.1 | 7.7 | 7.4 |
| UV254 (cm−1) | 0.143 | 0.193 | 0.159 |
| DOC (mg/L) | 5.64 | 7.29 | 6.78 |
| TOC (mg/L) | 8.10 | 11.52 | 9.16 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 4.6 | 9.0 | 6.5 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 0.26 | 2.53 | 1.72 |
2.2. Water Sampling and Pretreatment
2.3. Determination of Distribution Ranges of the Molecular Weight Fraction
2.4. Analysis of the Trihalomethane Formation Potential
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DOM Size Fraction of Raw Water
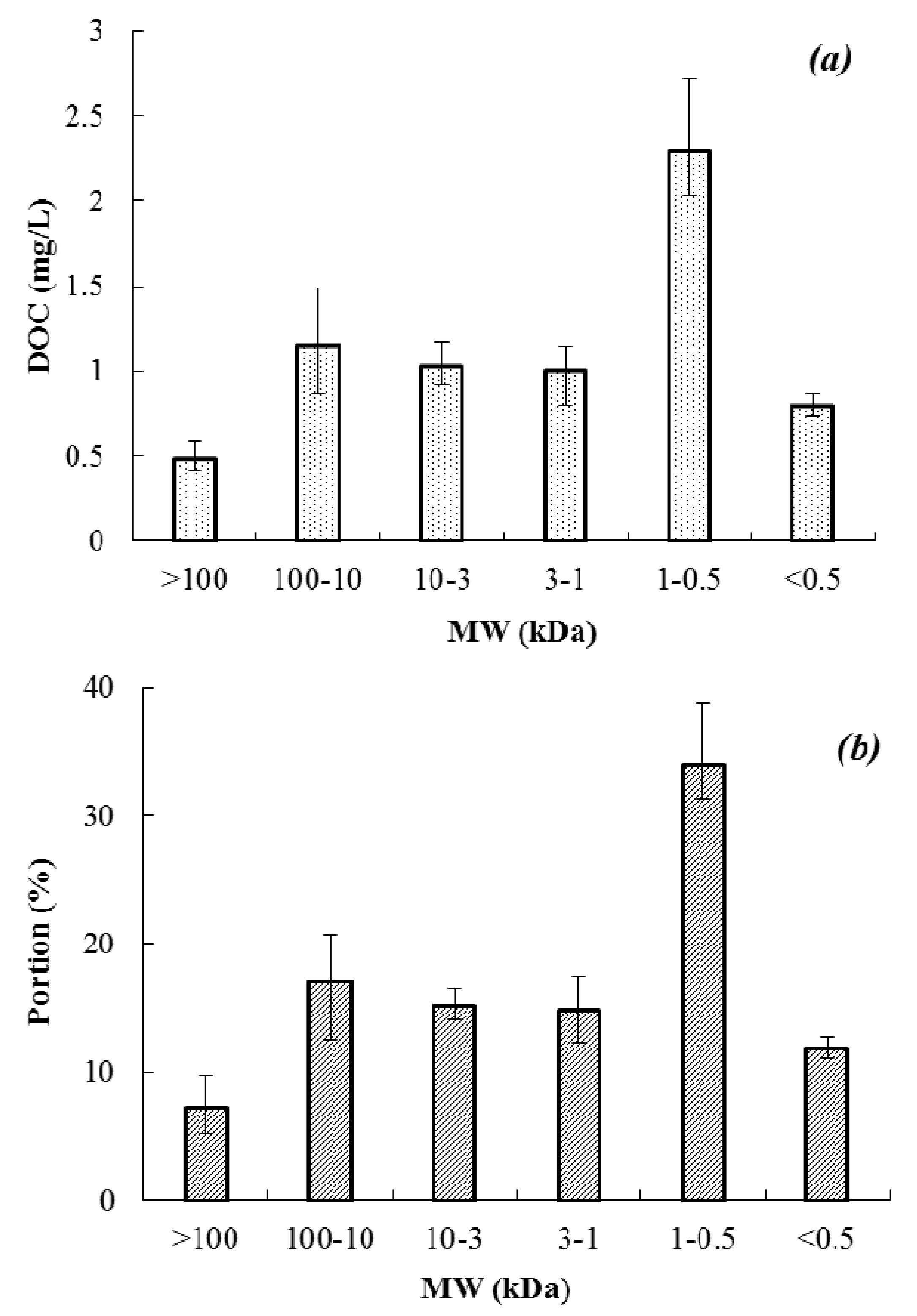
3.2. Overall DOC Removal

3.3. Effects of Unit Process on MW Fraction Distribution
| MW ranges (kDa) | Sampling 1 | Sampling 2 | Sampling 3 | Sampling 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOC (mg/L) | Portion (%) | DOC (mg/L) | Portion (%) | DOC (mg/L) | Portion (%) | DOC (mg/L) | Portion (%) | |
| >100 | 0.572 ± 0.003 | 8 | 0.197 ± 0.002 | 4 | 0.075 ± 0.002 | 2 | 0.078 ± 0.002 | 2 |
| 10–100 | 1.336 ± 0.006 | 20 | 0.496 ± 0.003 | 10 | 0.272 ± 0.003 | 6 | 0.473 ± 0.004 | 14 |
| 3–10 | 1.117 ± 0.004 | 17 | 0.717 ± 0.001 | 14 | 0.366 ± 0.003 | 8 | 0.101 ± 0.002 | 3 |
| 1–3 | 1.063 ± 0.003 | 16 | 1.212 ± 0.003 | 25 | 1.328 ± 0.005 | 29 | 1.088 ± 0.004 | 32 |
| 0.5–1 | 1.785 ± 0.007 | 26 | 1.189 ± 0.004 | 24 | 1.088 ± 0.003 | 24 | 0.892 ± 0.004 | 27 |
| <0.5 | 0.839 ± 0.003 | 13 | 1.118 ± 0.003 | 23 | 1.415 ± 0.003 | 31 | 0.731 ± 0.002 | 22 |
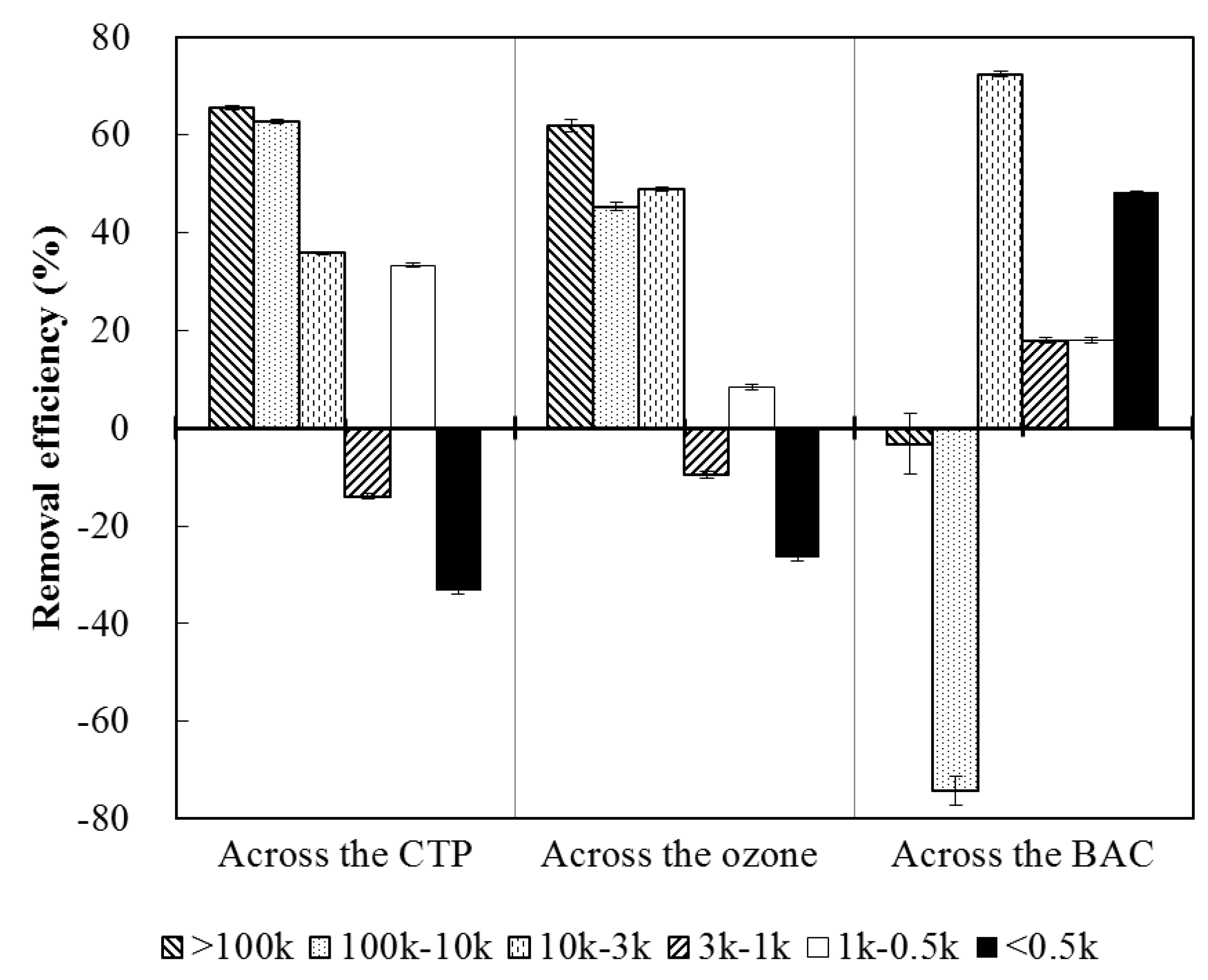
3.4. The Removal of Trichloromethane Formation Potential

| parameters | Across the CTP (%) | Across the ozone (%) | Across the BAC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOC | 27 | 8 | 26 |
| THMFP | 55 | 20 | 27 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, S. Multivariate statistical study of organic pollutants in Nanjing reach of Yangtze River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Hu, Z.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y. Distribution of organochlorine pesticides in surface water and sediments from Qiantang River, East China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, K.L.; Ulrich, E.M.; Hites, R.A. Differential toxicity and environmental fates of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter from drinking water by advanced oxidation process. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, C.; Bell, K.; Ibrahim, E.; Verges, D.; Amy, G.; Lechevallier, M. Impact of enhanced and optimized coagulation on removal of organic matter and its biodegradable fraction in drinking water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, C.; Kaplan, L.A.; Fobinson, J.; Zhu, H.; Lechevallier, M. Fluctuation of dissolved organic matter in river used for drinking water and impacts on conventional treatment plant performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4258–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, A.D.; Lekkas, T.D.; Golfinopoulos, S.K. Kinetics of the formation and decomposition of chlorination by-products in surface water. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 100, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, S.; Manuel, J.R. Disinfection by products (DBPs) in drinking water and predictive model for their occurrence: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 321, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; He, W.; Han, H. Changes in different organic matter fractions during conventional treatment and advanced treatment using resin isolation. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Braun, K.; Fabris, R.; Hoefel, D.; Morran, J.; Monis, P.; Drikas, M. Comparison of drinking water treatment process streams for optimal bacteriological water quality. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3934–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.M.; Mezyk, S.P.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L. Reactivity of effluent organic matter (EfOM) with hydroxyl radical as a function of molecular weight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5714–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanly, L.M.; Chiang, K.; Amal, R.; Chow, C.; Drikas, M. A study on the removal of humic acid using advanced oxidation process. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeldt, E.J.; Linden, K.G. Degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals bisphenol A, ethinyl estradiol, and estradiol during UV photolysis and advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5476–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Leal, M.; Li, Q. Degradation of natural organic matter by TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation and its effect on fouling of low-pressure membranes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lim, M.; Fabris, R.; Chow, C.; Chiang, K.; Drikas, M.; Amal, R. Removal of humic acid using TiO2 photocatalytic process—Fractionation and molecular weight characterization studies. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heringa, M.B.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Reus, A.A.; Krul, C.A.M.; Metz, D.H.; Jpelaar, G.F. Formation and removal of genotoxic activity during UV/H2O2-GAC treatment of drinking water. Water Res. 2011, 45, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, F.J.; Acero, J.L.; Real, F.J.; Roldan, G.; Rodriguez, E. Ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes applied to the removal of the pharmaceuticals amoxicillin, naproxen, metoprolol and phenacetin from water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedna, M.; Marshall, W.E.; Husseiny, A.A.; Goktepe, I.; Rao, R.M. The use of nutshell carbons in drinking water filters for removal of chlorination by-products. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Gao, N.; Yin, D.; Deng, P.; Templeton, M.R. Ozone-biological activated carbon integrated treatment for removal of precursors of halogenated nitrogenous disinfection by-products. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, R.; Amiri, F.; Wilson, S.; Garvey, E.; Metcalfe, C.; Ishida, C.; Lin, K. Comparing methods to remove emerging contaminants and disinfection by-product precursors at pilot scale. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2011, 60, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Gao, N.; Sun, X.; Xia, S.; Simonot, M.O.; Causserand, C.; Rui, M.; Wu, H. Characteristics of organic material in Huangpu River and treatability with O3-BAC process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, G.; Yapsakli, K.; Mertoglu, B.; Tufan, D.; Saatci, A. Evaluation of biological activated carbon (BAC) process in wastewater treatment secondary effluent for reclamation purposes. Desalination 2011, 265, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Yang, K.; Wu, A.; Yuan, W. Water supply development and sources water area protection in Shanghai: Patterns, problems and prospects. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 20, 651–659. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Ye, T.; Li, D.; Hu, C.; Lin, Y.; Xia, S.; Tian, F.; Gao, N. Measurement of dissolved organic nitrogen in drinking water treatment plant: Size fraction, fate, and relation to water quality parameters. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasner, S.W.; Westerhoff, P.; Chen, B.Y.; Rittmann, B.E.; Nam, S.N.; Amy, G. Impact of wastewater treatment processes on organic carbon, organic nitrogen, and DBP precursors in effluent organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2911–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard for Drinking Water Quality (GB5749-2006); (in Chinese). Ministry of Health of P.R. China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Wu, Y.; Lu, X. Removal characteristics of dissolved organic by combined process containing ozonation-BAC and chlorine treatment. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2012, 44, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, G. Pilot studies on ozone-biological activated carbon process for treating micro-polluted raw water in Huangpu River. Technol. Water Treat. 2007, 33, 53–56. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Westerhoff, P. Formation of organic chloramines during water disinfection—Chlorination versus chloramination. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gu, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Leung, K.M.Y. Disinfection characteristics of the dissolved organic fractions at seven of a conventional drinking water treatment plant in Southern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA)American Water Works Association (AWWA)The World Economic Forum (WEF)Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X. Study on analysis method of halomethanes by liquid-liquid extraction and gas chromatography in drinking water. J. Harbin Univ. Commer. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2007, 27, 296–299. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Bose, P.; Peckhow, D.A. The effect of ozonation on natural organic matter removal by alum coagulation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, P.; Chang, E.; Chang, P.; Huang, C. Effects on pre-ozonation on the removal of THM precursors by coagulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5735–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapsakli, K.; Cecen, F. Effect of type of granular activated carbon on DOC biodegradation in biological activated carbon filters. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, M.; Lin, T. Molecular weight distribution of organics during drinking water treatment. J. PLA Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 10, 160–164. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shu, S.; Yan, M.; Su, D.; Gao, N. Influence of ozonation/BAC on molecular weight distribution of organic matter. China Environ. Sci. 2007, 27, 638–641. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Han, W. Comparison of AC/O3-BAC and O3-BAC processes for removing organic pollutants in secondary effluent. Chemosphere 2006, 61, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, J. Water quality characteristics along the course of the Huangpu River (China). J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Lu, X. Characteristics of DOM and Removal of DBPs Precursors across O3-BAC Integrated Treatment for the Micro-Polluted Raw Water of the Huangpu River. Water 2013, 5, 1472-1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041472
Wu Y, Zhu G, Lu X. Characteristics of DOM and Removal of DBPs Precursors across O3-BAC Integrated Treatment for the Micro-Polluted Raw Water of the Huangpu River. Water. 2013; 5(4):1472-1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041472
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yifeng, Guangcan Zhu, and Xiwu Lu. 2013. "Characteristics of DOM and Removal of DBPs Precursors across O3-BAC Integrated Treatment for the Micro-Polluted Raw Water of the Huangpu River" Water 5, no. 4: 1472-1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041472
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhu, G., & Lu, X. (2013). Characteristics of DOM and Removal of DBPs Precursors across O3-BAC Integrated Treatment for the Micro-Polluted Raw Water of the Huangpu River. Water, 5(4), 1472-1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041472






