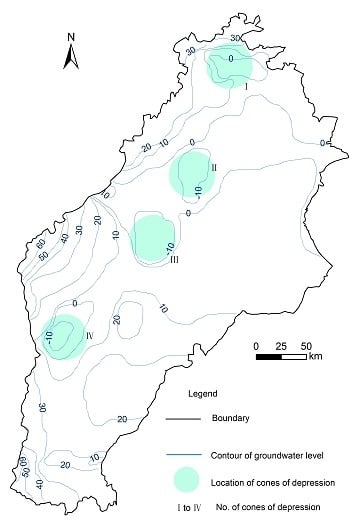
Long-Term Evolution of Cones of Depression in Shallow Aquifers in the North China Plain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Method of Completing Missing Values in Pumpage
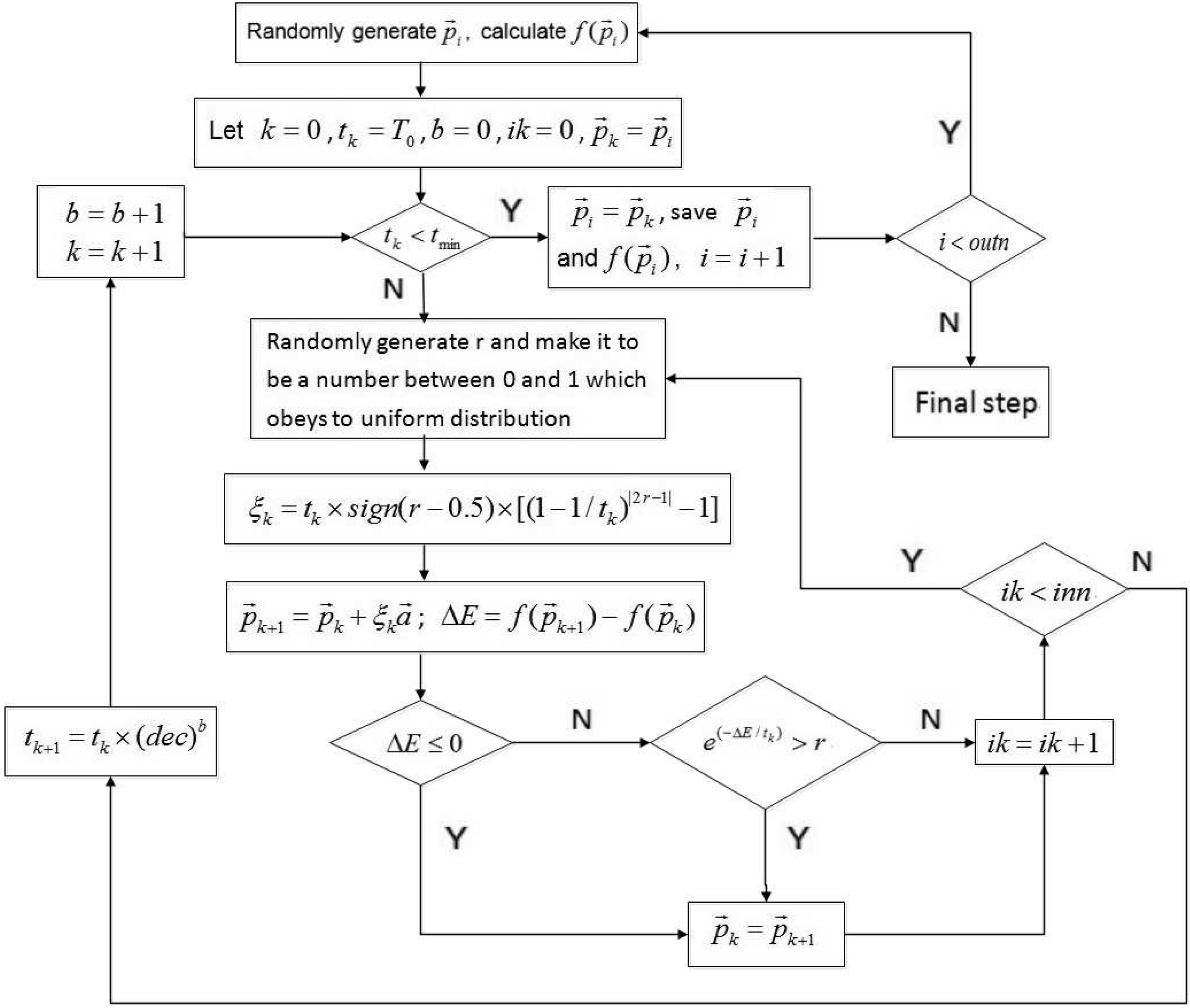
2.2. Inversion for Hydrogeological Parameters
3. Numerical Model
3.1. Site Descriptions and Hydrogeological Setting

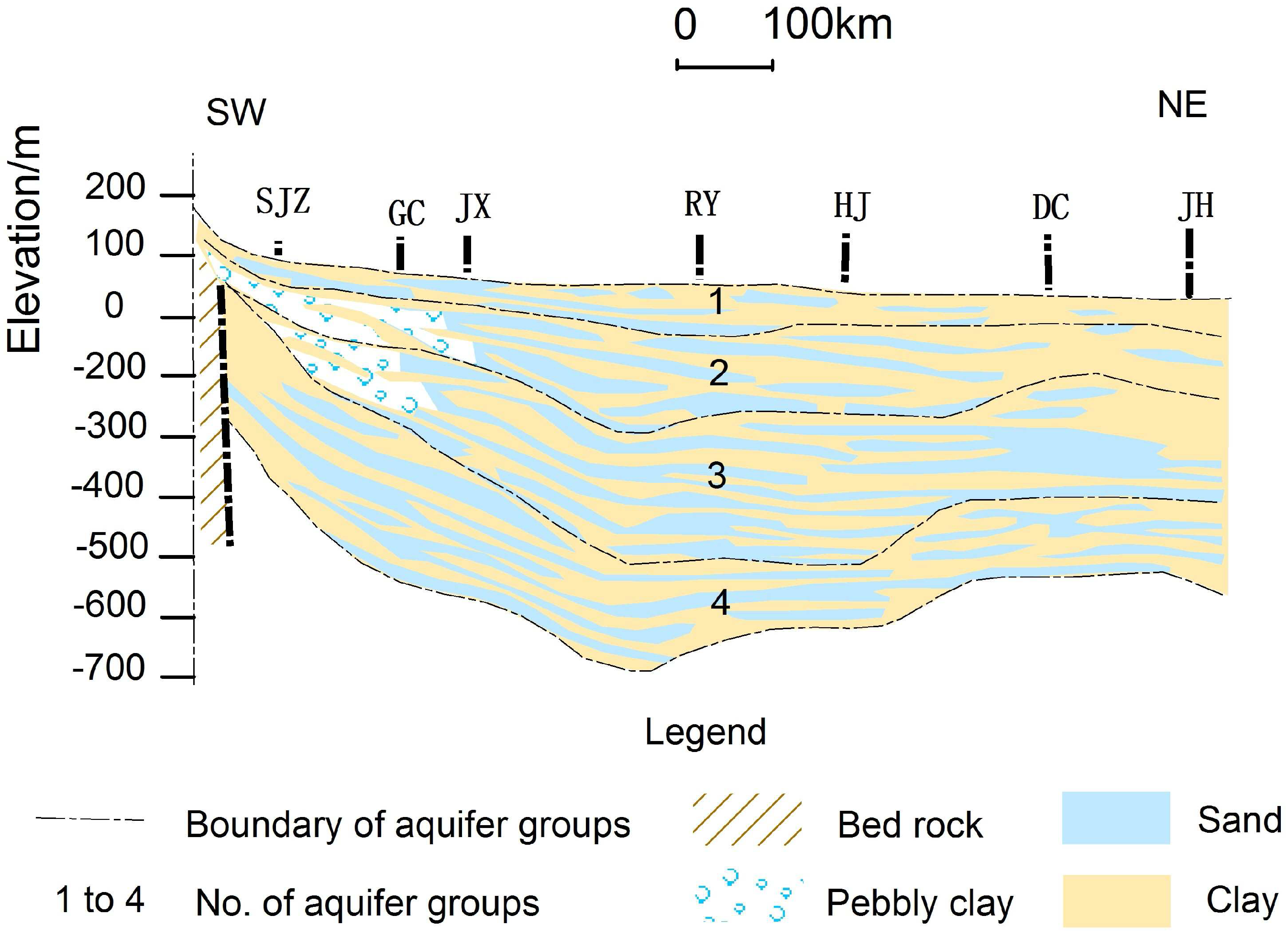
3.2. Model Discretization
3.3. Boundary Conditions
3.4. Recharge and Discharge

| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Area () | 2,090 | 1,203 | 16,437 | 846 | 27,758 | 1,068 | 5,132 | 183 | 379 | 654 |
| No. | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| Area () | 1,017 | 760 | 3,342 | 4,193 | 816 | 16,158 | 640 | 1,375 | 447 | 1,959 |
| No. | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | |||||
| Area () | 2,394 | 100 | 429 | 454 | 19,836 |
| Year | Population ( persons) | Industrial Output Value ( CNY) | Grains ( tons) | Vegetables ( tons) | Fruits ( tons) | Irrigated Area ( hectares) | Pumpage ( ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 739.6 | 85.9 | 55.2 | 131.6 | 4.5 | 149.0 | |
| 1961 | 729.2 | 53.2 | 60.8 | 129.8 | 4.4 | 101.0 | 5.2 |
| 1962 | 732.2 | 41.9 | 79.2 | 161.1 | 8.3 | 108.0 | 10.8 |
| 1963 | 757.9 | 44.5 | 85.5 | 148.2 | 8.9 | 161.0 | 10.8 |
| 1964 | 776.3 | 49.4 | 97.5 | 115.4 | 9.9 | 207.0 | 10.8 |
| 1965 | 787.1 | 55.9 | 119.2 | 134.4 | 9.6 | 245.0 | 12.1 |
| 1966 | 782.0 | 69.0 | 110.2 | 116.0 | 10.5 | 252.0 | 10.8 |
| 1967 | 796.4 | 58.2 | 113.5 | 132.6 | 9.5 | 247.0 | 10.8 |
| 1968 | 794.7 | 61.4 | 127.4 | 121.4 | 10.8 | 256.0 | 10.8 |
| 1969 | 779.6 | 87.5 | 116.0 | 122.1 | 11.7 | 262.0 | 10.8 |
| 1970 | 784.3 | 97.1 | 140.9 | 144.8 | 9.1 | 278.0 | 10.8 |
| 1971 | 797.4 | 99.3 | 142.3 | 139.9 | 10.5 | 283.0 | 13.8 |
| 1972 | 809.2 | 105.3 | 117.8 | 145.9 | 12.5 | 276.0 | |
| 1973 | 826.0 | 113.1 | 152.9 | 144.0 | 10.4 | 289.0 | |
| 1974 | 836.8 | 123.3 | 170.7 | 156.3 | 14.8 | 308.0 | 22.7 |
| 1975 | 844.4 | 133.8 | 183.9 | 156.3 | 14.1 | 325.0 | 21.5 |
| 1976 | 845.1 | 141.2 | 170.4 | 173.9 | 14.7 | 331.0 | 22.8 |
| 1977 | 860.5 | 149.3 | 150.4 | 173.6 | 12.2 | 337.0 | |
| 1978 | 871.5 | 170.0 | 186.0 | 164.5 | 16.5 | 341.7 | 24.5 |
| 1979 | 897.1 | 189.6 | 172.8 | 181.3 | 15.2 | 340.8 | |
| 1980 | 904.3 | 213.4 | 186.0 | 175.9 | 14.9 | 340.3 | |
| 1981 | 919.2 | 219.0 | 180.7 | 172.8 | 14.8 | 341.3 | 26.2 |
| 1982 | 935.0 | 230.8 | 185.5 | 208.3 | 13.1 | 339.4 | 26.2 |
| 1983 | 950.0 | 256.8 | 201.5 | 199.1 | 17.0 | 343.3 | 26.2 |
| 1984 | 965.0 | 276.2 | 217.4 | 218.0 | 19.0 | 342.6 | 26.2 |
| 1985 | 981.0 | 324.2 | 219.7 | 204.0 | 17.9 | 338.4 | |
| 1986 | 1028.0 | 336.5 | 216.5 | 222.7 | 17.5 | 337.9 | |
| 1987 | 1047.0 | 387.6 | 227.0 | 241.1 | 21.5 | 337.9 | |
| 1988 | 1061.0 | 495.6 | 234.6 | 271.3 | 22.5 | 338.1 | |
| 1989 | 1075.0 | 602.7 | 239.2 | 331.0 | 25.7 | 338.4 | 27.0 |
| 1990 | 1086.0 | 625.9 | 264.6 | 356.1 | 26.4 | 335.1 | |
| 1991 | 1094.0 | 730.2 | 279.7 | 368.4 | 27.8 | 328.7 | 26.5 |
| 1992 | 1102.0 | 860.0 | 281.9 | 381.4 | 32.9 | 331.1 | |
| 1993 | 1112.0 | 1166.6 | 284.0 | 418.8 | 37.9 | 314.7 | 26.0 |
| Year | Population ( persons) | Industrial Output Value ( CNY) | Grain ( tons) | Vegetable ( tons) | Fruits ( tons) | Irrigated Area ( hectares) | Pumpage ( ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | 1,125.0 | 1,576.6 | 249.2 | 350.0 | 47.2 | 323.4 | |
| 1995 | 1,251.1 | 1,493.3 | 259.8 | 397.3 | 45.2 | 292.4 | 25.5 |
| 1996 | 1,259.4 | 1,590.6 | 237.4 | 403.2 | 49.5 | 301.9 | 27.3 |
| 1997 | 1,240.0 | 1,819.7 | 237.5 | 408.8 | 52.9 | 323.3 | 25.5 |
| 1998 | 1,245.6 | 1,947.0 | 239.3 | 403.8 | 57.5 | 323.7 | 25.5 |
| 1999 | 1,257.2 | 2,183.5 | 201.0 | 419.8 | 57.8 | 322.1 | 25.5 |
| 2000 | 1,363.6 | 2,842.0 | 144.2 | 466.3 | 63.7 | 322.7 | 27.2 |
| 2001 | 1,385.1 | 3,270.1 | 104.9 | 491.0 | 68.8 | 322.7 | 27.2 |
| 2002 | 1,423.2 | 3,620.2 | 82.3 | 507.4 | 75.6 | 219.7 | 24.2 |
| 2003 | 1,456.4 | 4,410.8 | 58.0 | 486.7 | 80.5 | 178.9 | 25.4 |
| 2004 | 1,492.7 | 5,733.3 | 70.2 | 444.1 | 86.9 | 186.7 | 26.8 |
| 2005 | 1,538.0 | 6,946.2 | 94.9 | 373.1 | 89.6 | 181.5 | 24.9 |
| 2006 | 1,581.0 | 8,210.0 | 109.2 | 341.2 | 84.4 | 181.5 | 24.3 |
| 2007 | 1,633.0 | 9,648.4 | 102.1 | 340.1 | 86.4 | 173.6 | 24.2 |
| 2008 | 1,695.0 | 10,413.1 | 125.5 | 321.3 | 85.1 | 172.0 | 22.9 |
| 2009 | 1,755.0 | 11,039.1 | 124.8 | 320.3 | 120.1 | 218.7 | 21.8 |
| 2010 | 1,962.0 | 13,699.8 | 115.7 | 290.8 | 115.2 | 211.4 | 21.2 |
| 2011 | 2,019.0 | 14,513.6 | 121.8 | 293.3 | 120.9 | 209.3 | 20.9 |
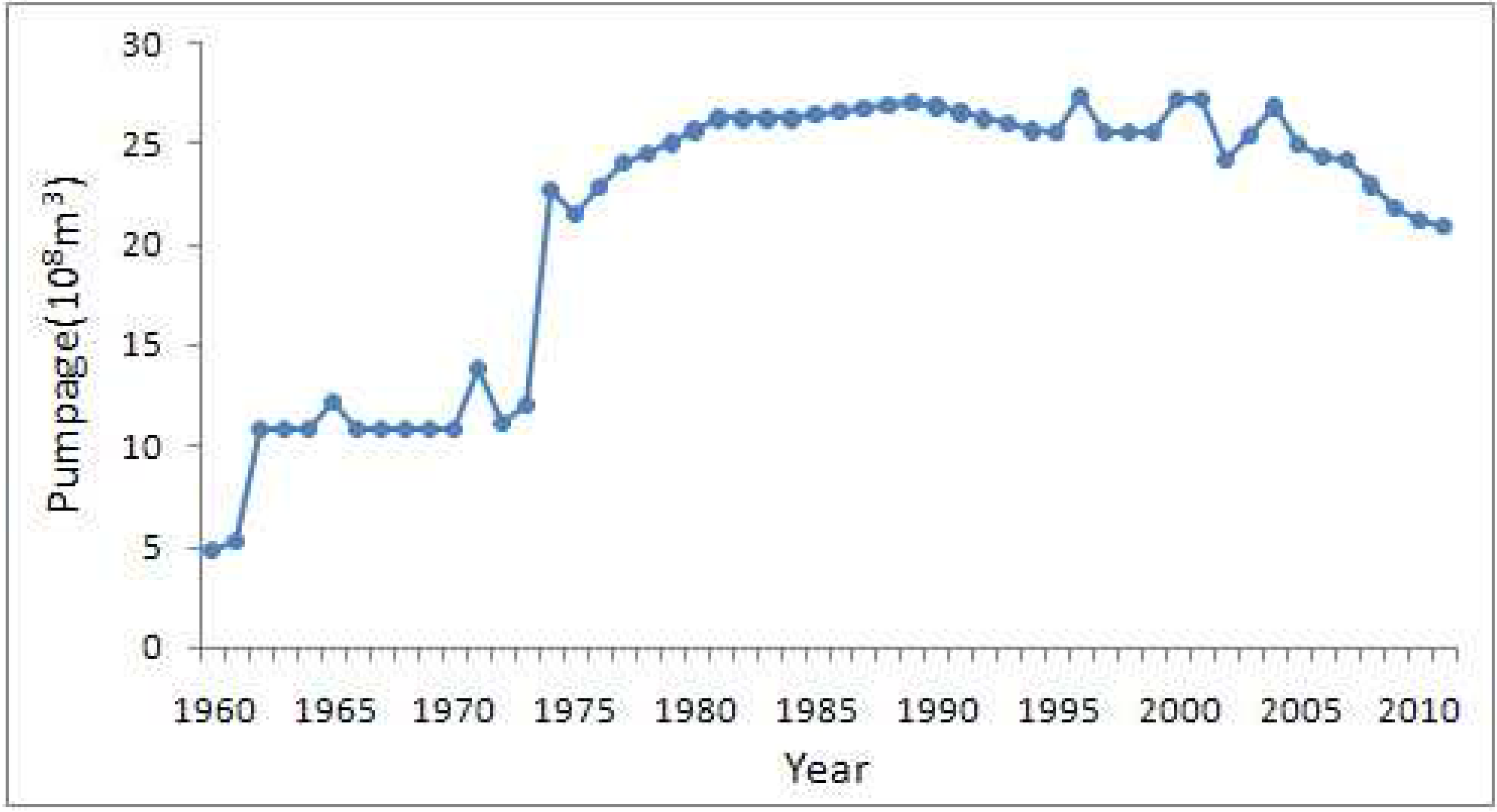
3.5. Model Calibration
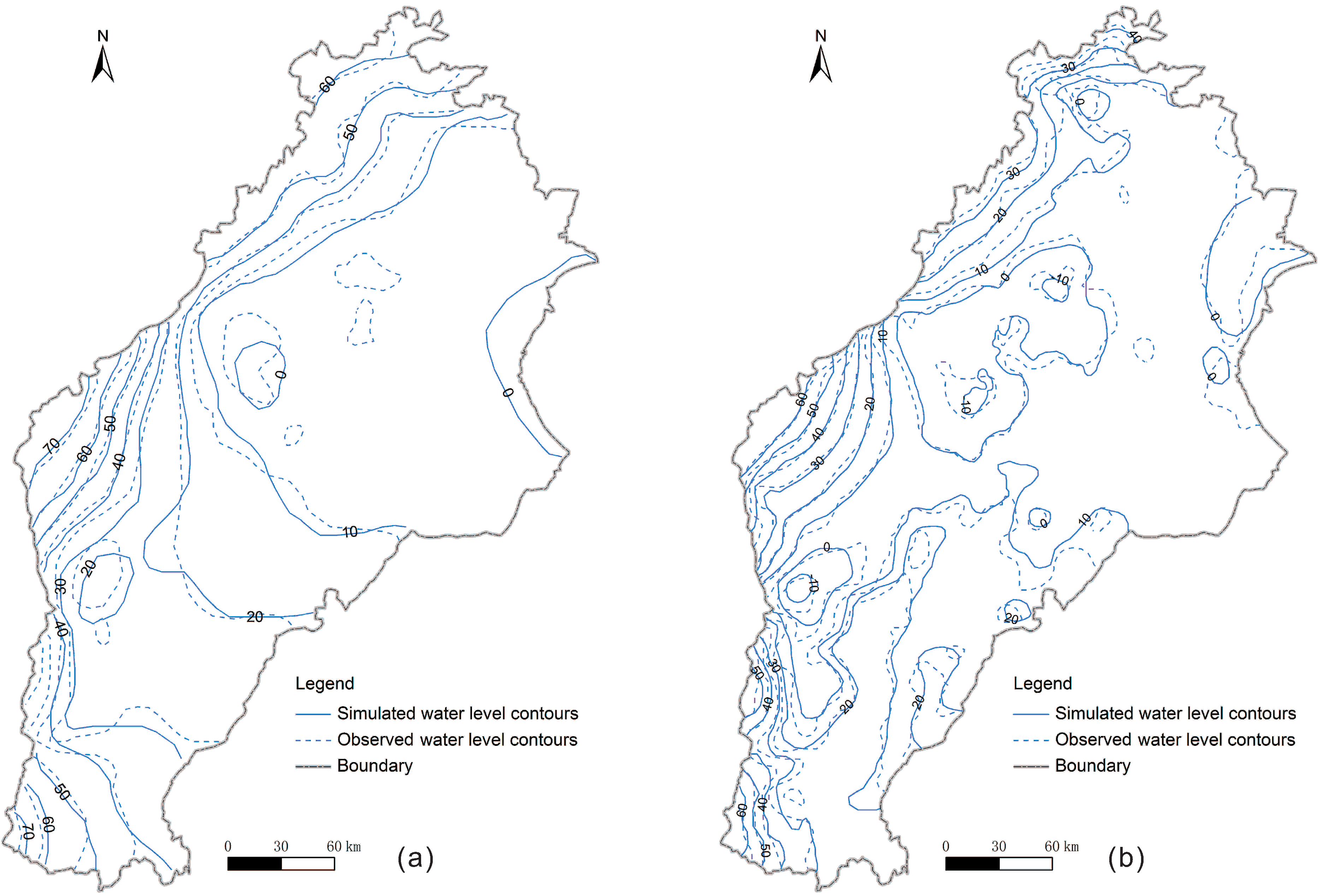
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Cone of Depression in Beijing

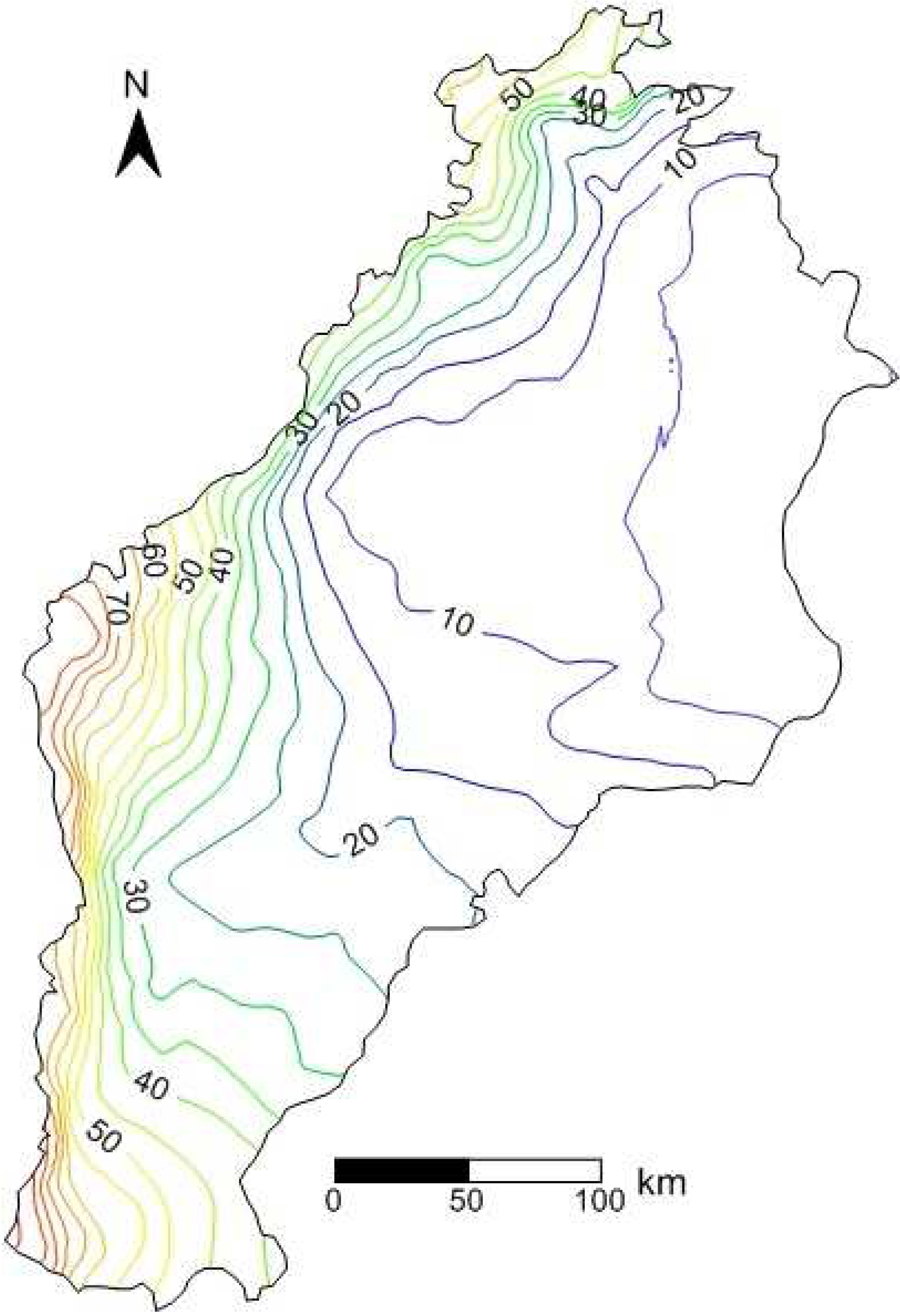
4.2. Cone of Depression in Bazhou
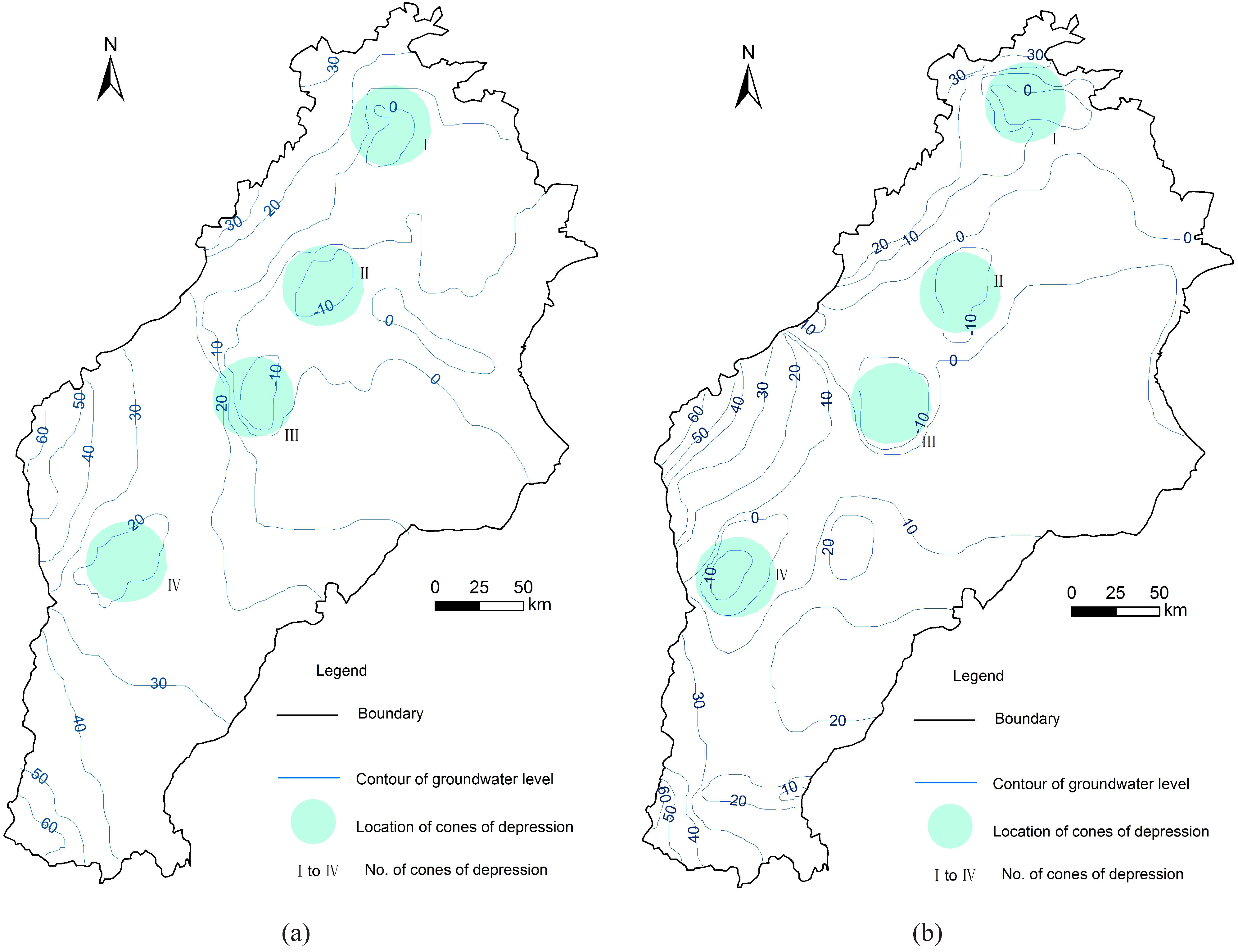
4.3. Cone of Depression in Lixian
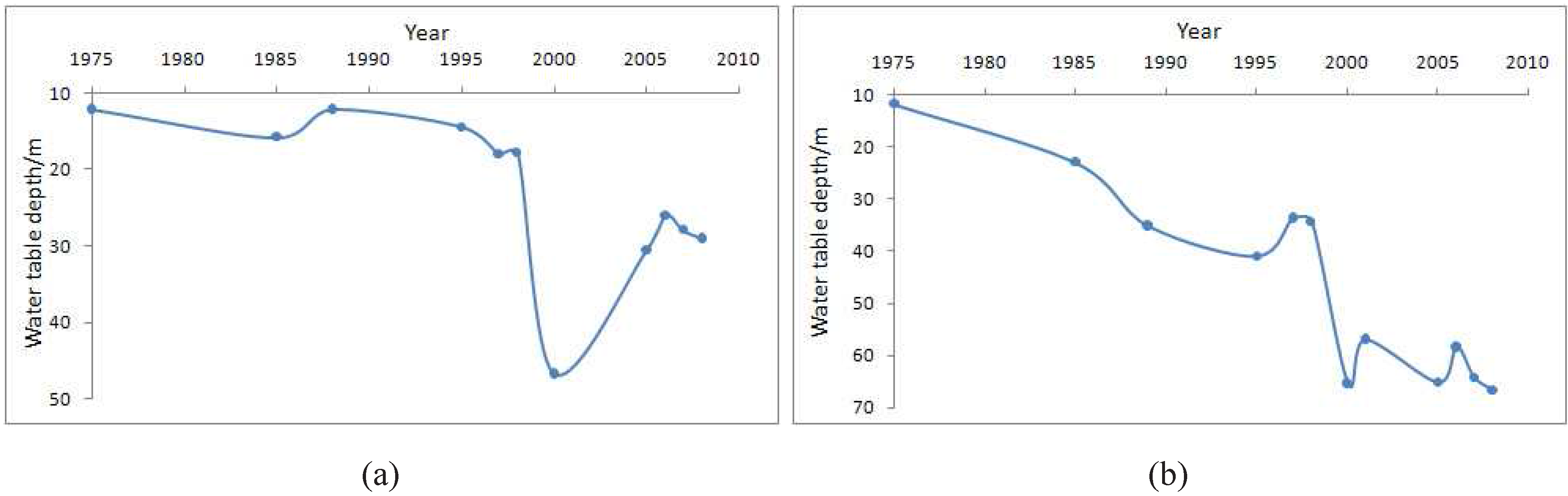
4.4. Cone of Depression in Ningbolong
4.5. Evaluation of the Exploitation Limitation Strategy
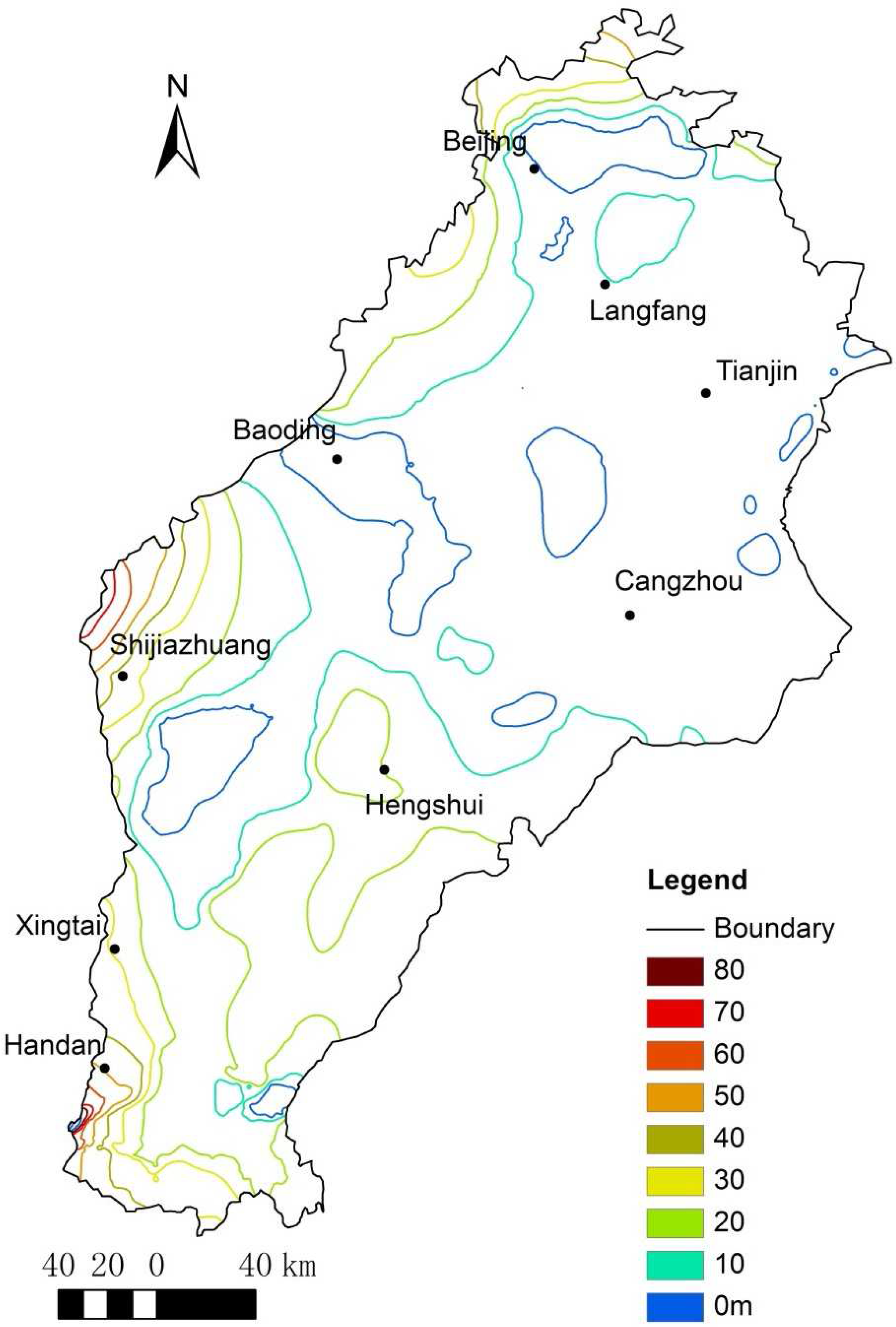
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- De Vries, J.J.; Simmers, I. Groundwater recharge: An overview of processes and challenges. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; van Beek, L.P.H.; van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.T.M.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, E. Aquifer overexploitation: What does it mean? Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 254–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almedeij, J.; Al-Ruwaih, F. Periodic behavior of groundwater level fluctuations in residential areas. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vigna, F.; Mazza, R.; Capelli, G. Detecting the flow relationships between deep and shallow aquifers in an exploited groundwater system, using long-term monitoring data and quantitative hydrogeology: The Acque Albule Basin case (Rome, Italy). Hydrol. Process. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.A.; Voss, C.I. Controls on groundwater flow in the Bengal Basin of India and Bangladesh: Regional modeling analysis. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1561–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.S.; Liu, C.M. Groundwater dynamic drift and response to different exploitation in the North China Plain: A case study of luancheng county, Hebei Province [in Chinese]. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2002, 57, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.B.; Sun, H.; Zhai, P.Y.; Dong, X.D. Study on formation mechanism of cones of depression [in Chinese]. Ground Water 2012, 34, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S.; Fei, Y.H.; Qian, Y.; Jian, M.; Han, Z.T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.J. Discussion on evolution characteristics and formation mechanism of deep groundwater depression cone in Cangzhou region [in Chinese]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2013, 27, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, J. Groundwater resources in the North China Plain. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1988, 12, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.L.; Zheng, C.M.; Scanlon, B.R.; Liu, J.; Li, W.P. Use of flow modeling to assess sustainability of groundwater resources in the North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.H.; Miao, J.X.; Zhang, Z.J.; Chen, Z.Y.; Song, H.B.; Yang, M. Analysis on evolution of groundwater depression cones and its leading factors in North China Plain [in Chinese]. Resour. Sci. 2009, 31, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.M.; Zheng, H.X. South-to-North water transfer schemes for China. Water Res. Dev. 2002, 18, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General program of the South-to-North water transfer project. China Water Resour. 2003, 1B, 3–6.
- Nakayama, T.; Yang, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Zhang, X.Y. Simulation of groundwater dynamics in the North China Plain by coupled hydrology and agricultural models. Hydrol. Processes 2006, 20, 3441–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, R.W.; Bolstad, P.V.; Manson, S.M. Spatio-temporal trend analysis of long-term development patterns (1900–2030) in a southern appalachian county. Landsc. Urban Plan 2012, 104, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, H. RIPGIS-NET: A GIS tool for riparian groundwater evapotranspiration in MODFLOW. Ground Water 2012, 50, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visocky, A.P. Impact of lake Michigan allocations on the Cambrian-Ordovician aquifer system. Ground Water 1982, 20, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, S.J.; Casino, B. Competitive versus efficient extraction of a common property resource: The groundwater case. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2001, 25, 1117–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, J.Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, Y. A simplified numerical model of 3-D groundwater and solute transport at large scale area. J. Hydrodyn. 2010, 22, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, L.X.; Duan, Z.G.; Zhang, J.L. Assessing the impacts of South-to-North water transfer project with decision support systems. Decis. Support Syst. 2007, 42, 1989–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, C.; Lei, Y. Ground water sustainability: Methodology and application to the North China Plain. Ground Water 2008, 46, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.K.; Moiwo, J.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Han, S.M.; Yang, Y.M. Agricultural water-saving and sustainable groundwater management in Shijiazhuang irrigation district, North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.M.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, M.; Yang, J.Q.; Zhou, D.; Yang, Z.S.; Zheng, F.D. Influence of south to north water transfer on groundwater dynamic change in Beijing plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Shi, D.H.; Ren, F.H.; Yin, Z.Z.; Sun, J.C.; Zhang, C.Y. Evolution of quaternary groundwater system in North China Plain. Sci. China Ser. D 1997, 3, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Shao, J.L.; Song, X.F.; Zhang, Y.B.; Huo, Z.B.; Zhou, X.Y. Application of MODFLOW and geographic information system to groundwater flow simulation in North China Plain, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Lin, L. Research on groundwater regulation and recovery in North China Plain after the implementation of South-to-North water transfer [in Chinese]. Resour. Sci. 2009, 31, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.; Gardumo, H.; Evans, R.; Olson, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Han, Z.S. Quaternary aquifer of the North China Plain–Assessing and achieving groundwater resource sustainability. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, K.; Tang, C.; Song, X.; Kondoh, A.; Sakura, Y.; Yu, J.; Kaneko, S. Characteristics of chemistry and stable isotopes in groundwater of Chaobai and Yongding River basin, North China plain. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; McClelland, J.L. Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations Inthe Microstructure of Cognition; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 318–362. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Yang, C.C. A fast global optimization algorithm for regularized migration imaging. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Han, S.P.; Fei, Y.H.; Wang, J.S.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, Y. Laboratory study on the relationship between soil mass deformation and water seepage in North China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 2195–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Ma, C. A study on the environmental geology of the middle route project of the South-North water transfer. Eng. Geol. 1999, 51, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Luo, G.Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.M.; Li, T.S.; Jiang, X.Q. Study on sustainable utilization of groundwater in North China Plain [in Chinese]. Resour. Sci. 2009, 3, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.H. Groudwater in Hebei Province [in Chinese]; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M.G.; Harbaugh, A.W. A Modular Three-Dimensional Finite Diffe Rence Groundwater Flow Model. In Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations of the USGS; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Harbaugh, A.W.; Banta, E.R.; Hill, M.C.; McDonald, M.G. MODFLOW-2000, The U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model User Guide to Modularization Concepts and the Ground-Water Flow Process; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Fei, Y.H. Atlas of Groundwater Sustainable Utilization in NorthChina Plain [in Chinese]; Zhang, Z.J., Fei, Y.H., Eds.; Sinomaps Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Song, X.F.; Wang, Q.X.; Xiao, G.Q.; Liu, C.M.; Liu, J.R. Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.M.; Kim, N.W.; Lee, J.; Sophocleous, M. Assessing distributed groundwater recharge rate using integrated surfacewater–groundwater modeling: Application to Mihocheon watershed. S. KoreaI1 Moon. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susan, K.J. Applications of hydrologic information automatically extracted from digital elevation models. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Z. Study on Numerical Simulating Methods for Delineation of Groundwaterresource Protection Area [in Chinese]; Dissertation, The China Academy of Science: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2003; Annual Data. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/statisticaldata/yearlydata/ (accessed on 7 April 2013).
- Zhang, Z.H.; Shen, Z.L.; Xue, Y.Q.; Ren, F. Groundwater Environment Evolution in the North China Plain [in Chinese]; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hebei Water, People’s Government of Hebei Province, 2013. In Groundwater Bullitin 2008. Available online: http://www.hebwater.gov.cn/ (accessed on 7 April 2013).
- Haihe River Water Conservancy Commission, 2013. Haihe River Water Resources Bulletin 1998–2010. Available online: http://www.chinawater.net.cn (accessed on 7 April 2013).
- Tamanyu, S.; Muraoka, H.; Ishii, T. Geological interpretation of groundwater level lowering in the North China Plain. S. Bull. Geol. Surv. Jpn. 2009, 60, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J. Investigation and Evaluation of Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater in North China Plain [in Chinese]; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- He, P. Analysis ongroundwater overdraft status and its countermeasure in Langfang City [in Chinese]. Ground Water 2009, 31, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Changjiang Water Resources Commission of the Ministry of Water Resources. The South-to-North water transfer project planning (2001 revision) [in Chinese]. China Water Resour. 2003, 1B, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Long-Term Evolution of Cones of Depression in Shallow Aquifers in the North China Plain. Water 2013, 5, 677-697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020677
Zhang Y, Li G. Long-Term Evolution of Cones of Depression in Shallow Aquifers in the North China Plain. Water. 2013; 5(2):677-697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020677
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuan, and Guomin Li. 2013. "Long-Term Evolution of Cones of Depression in Shallow Aquifers in the North China Plain" Water 5, no. 2: 677-697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020677
APA StyleZhang, Y., & Li, G. (2013). Long-Term Evolution of Cones of Depression in Shallow Aquifers in the North China Plain. Water, 5(2), 677-697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020677