Influence of Irrigation Water Discharge Frequency on Soil Salt Removal and Rice Yield in a Semi-Arid and Saline-Sodic Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
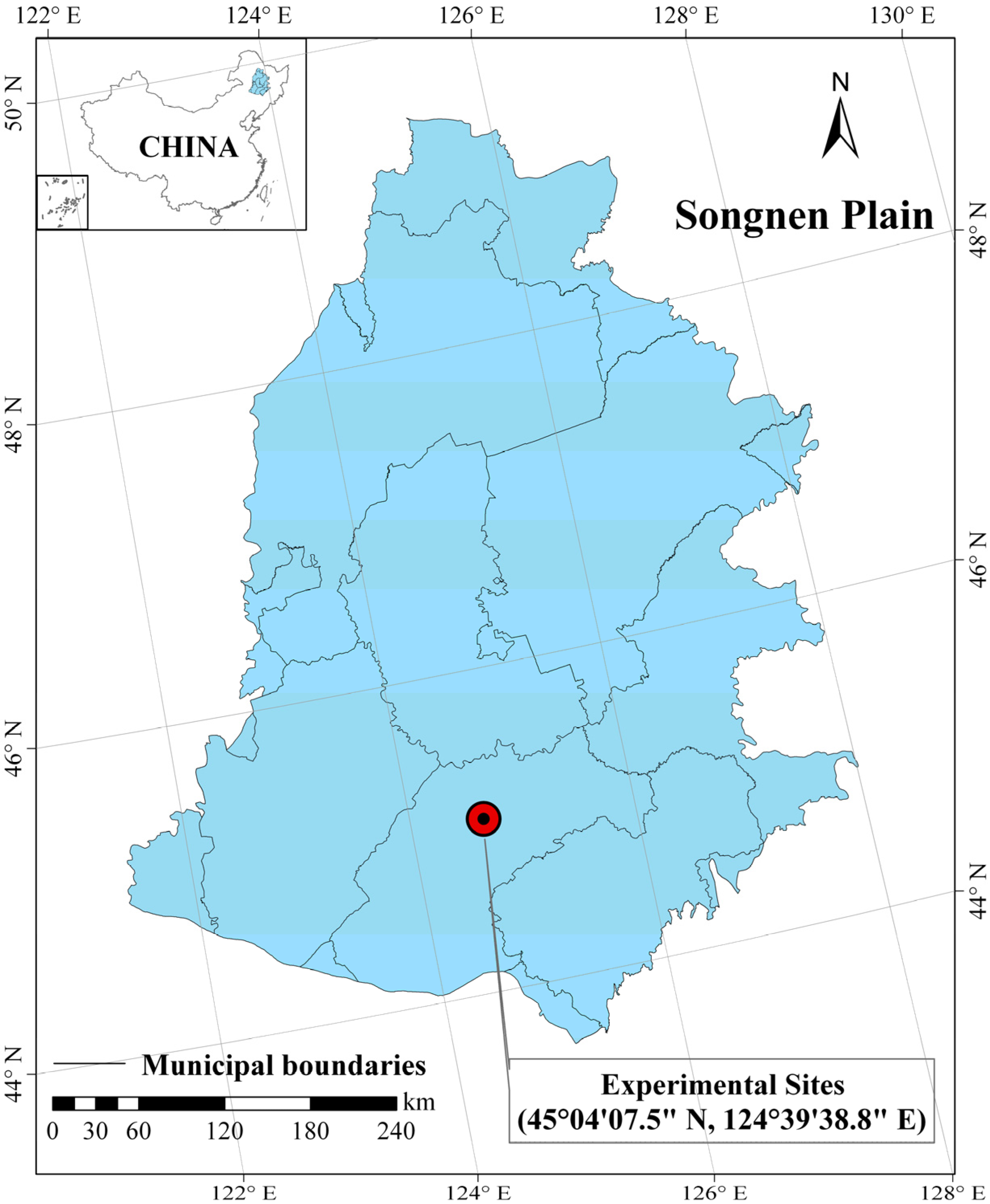
2.1. Study Site
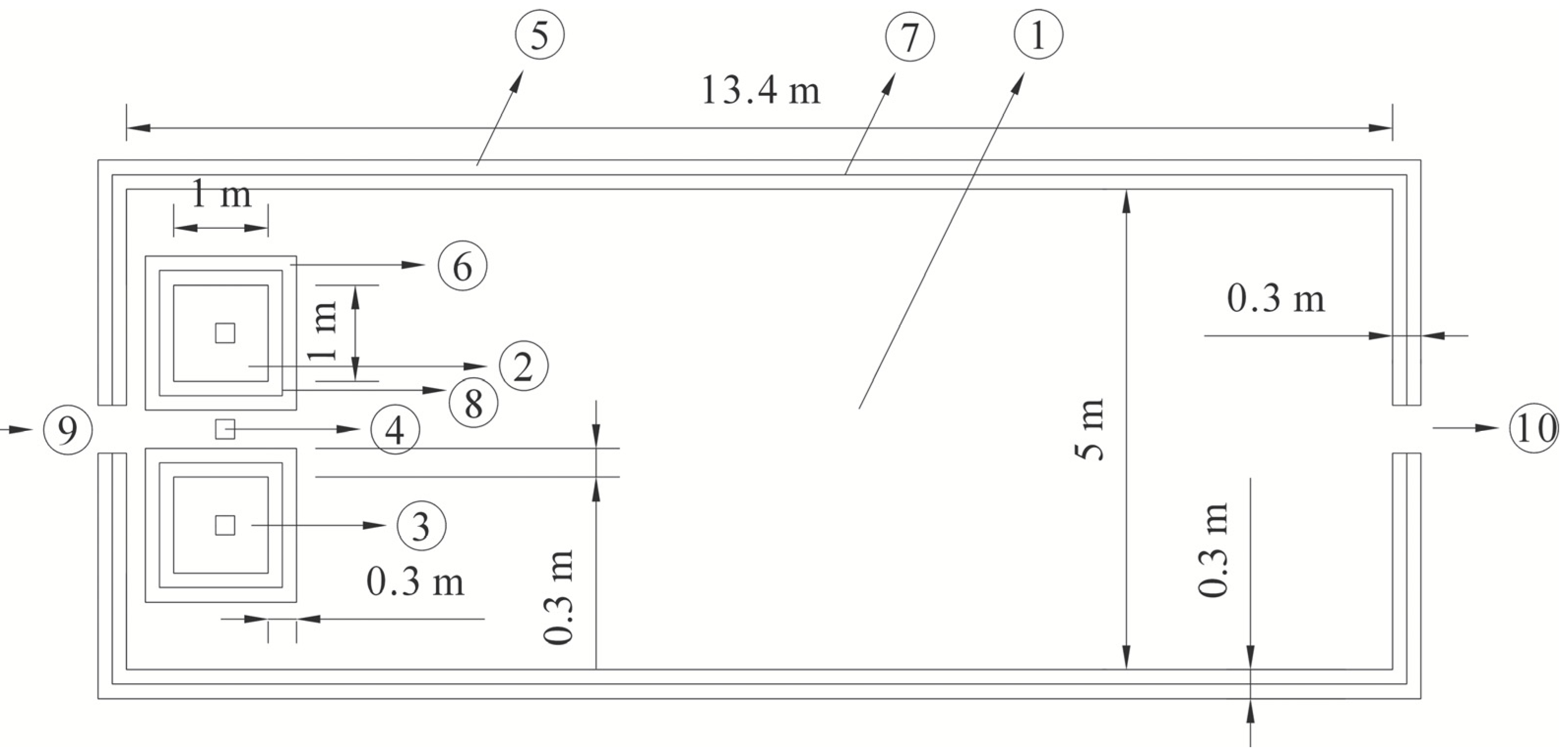
2.2. Experiment Design
| Treatments | PTS | RTS | RGS | TS | JBS | YRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-9-30 | 150 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| I-6-30 | 150 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| I-3-30 | 150 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| I-2-80 | 150 | 20 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Treatments | PTS | 5 June | 10 June | 20 June | 10 July | 20 July | 10 August | 20 August | 20 September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-9-30 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| I-6-30 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| I-3-30 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| I-2-80 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Soil and Water Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Salt, Electrical Conductivity and pH
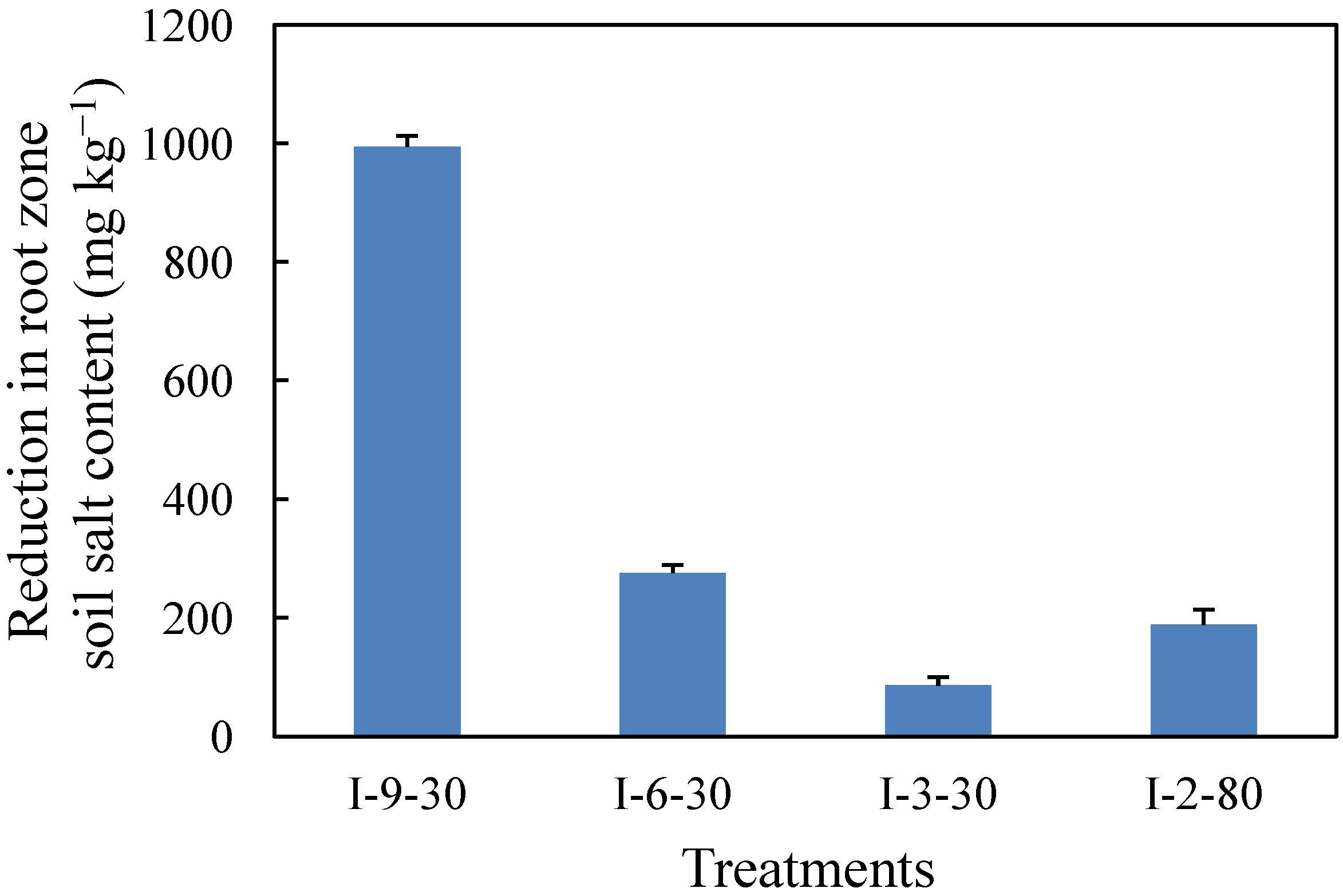
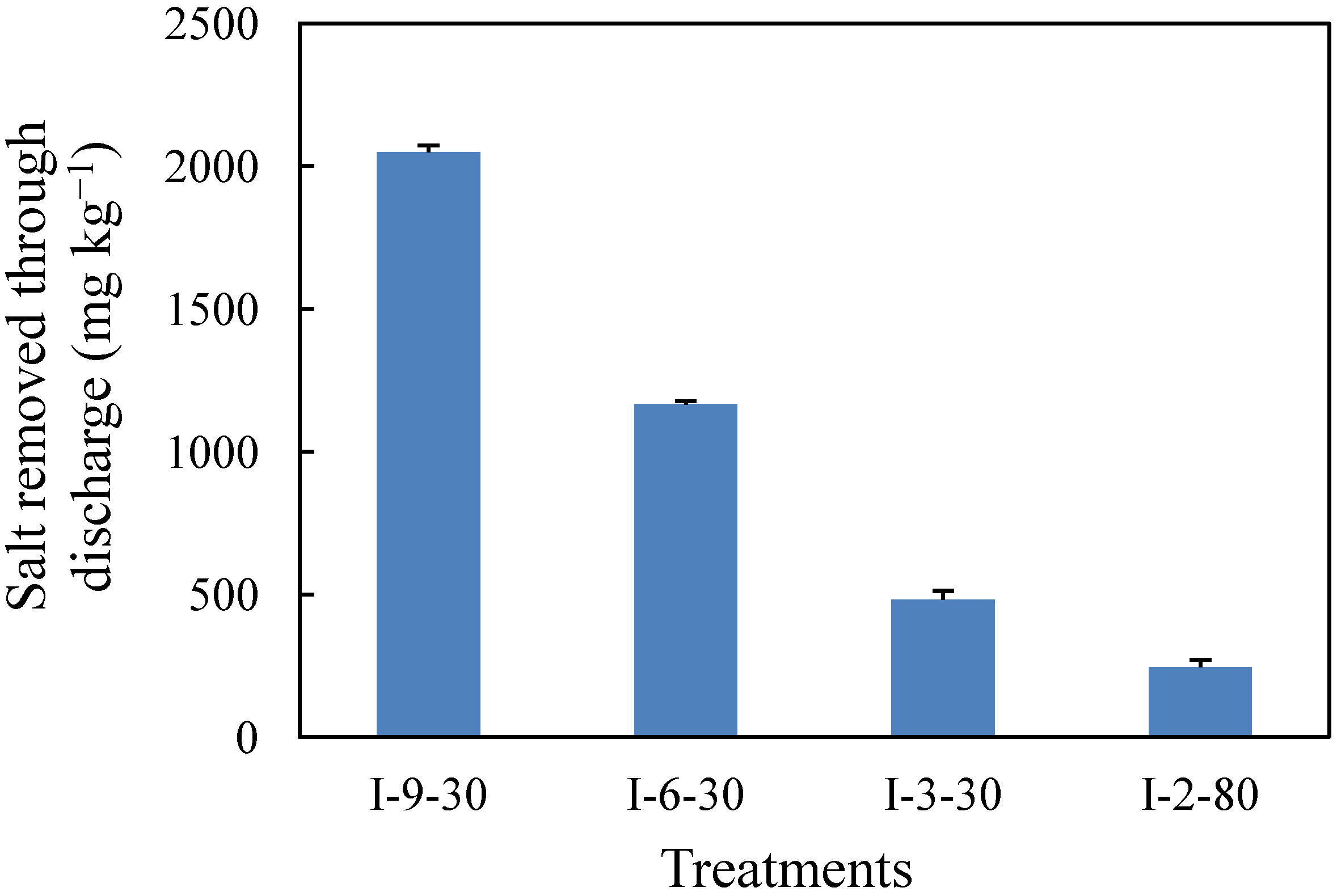
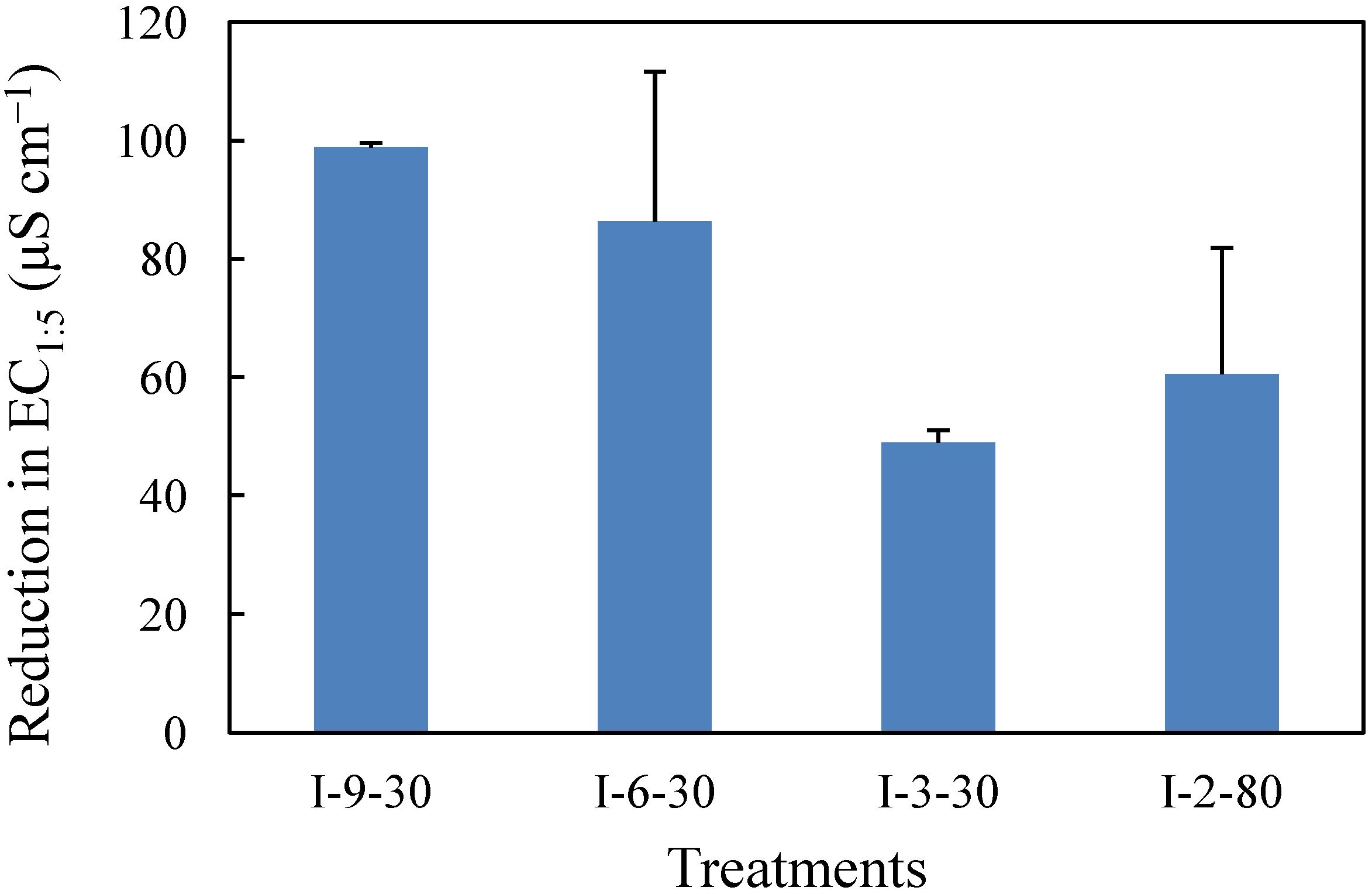
3.2. Rice Yield and Yield Components
| Treatments | Panicle number per plant | Spikelet per panicle | Seed setting rate (%) | 1000-grain weight (g) | Actual yield (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-9-30 | 20.7 ± 0.0 a | 84.7 ± 8.2 b | 72.7 ± 4.4 a | 19.2 ± 0.1 a | 6863.5 ± 57.5 b |
| I-6-30 | 21.7 ± 1.3 a | 86.9 ± 6.0 b | 74.6 ± 0.7 a | 19.8 ± 0.2 a | 6709.0 ± 152.0 b |
| I-3-30 | 19.5 ± 0.5 a | 97.8 ± 2.1 ab | 83.3 ± 0.4 a | 20.0 ± 0.0 a | 6328.0 ± 502.0 b |
| I-2-80 | 20.5 ± 1.5 a | 104.5 ± 3.4 a | 78.8 ± 7.5 a | 19.8 ± 1.0 a | 7686.5 ± 270.5 a |
3.3. Water Consumption
| Treatments | P | I | ET | DP | D | ΔW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-9-30 | 466.4 | 530.0 | 546.5 ± 37.5 a | 90.5 ± 2.5 a | 363.2 ± 40.5 a | −3.8 |
| I-6-30 | 466.4 | 440.0 | 533.5 ± 14.5 a | 93.5 ± 1.5 a | 285.7 ± 13.0 b | −6.3 |
| I-3-30 | 466.4 | 320.0 | 570.0 ± 63.0 a | 90.0 ± 15.0 a | 120.7 ± 36.0 c | 5.7 |
| I-2-80 | 466.4 | 340.0 | 586.5 ± 59.5 a | 90.5 ± 3.5 a | 124.4 ± 5.1 c | 5.0 |
3.4. Rice Water Use Efficiency
| Treatments | IWUE (kg ha−1 mm−1) | WUE (kg ha−1 mm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| I-9-30 | 13.0 ± 0.1 c | 12.6 ± 0.8 a |
| I-6-30 | 15.2 ± 0.3 c | 12.6 ± 0.1 a |
| I-3-30 | 19.8 ± 1.6 b | 11.3 ± 2.1 a |
| I-2-80 | 22.6 ± 0.8 a | 13.2 ± 0.9 a |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Li, X.B. The changes on quality and production capacity of farmland in the main agricultural regions during recent 20 years [in Chinese]. Geogr. Geo. Inf. Sci. 2011, 27, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Kong, X.B.; Wu, Z.K.; Shi, J.R.; Zhang, Q.P. Spatial distribution characteristics of potential productivity of arable land in main crop production area in China [in Chinese]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J. The Alkili-saline land and agricultural sustainable development of the Western Songnen Plain in China [in Chinese]. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2000, 20, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Han, D.M.; Tang, C.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Ma, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Tanji, K.K. Nature and extent of agricultural salinity. In Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management; ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering Practices NO. 71; Tanji, K.K., Ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, D.L. Sodic soil reclamation: Modelling and field study. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1225–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Pitman, M.G.; Laüchli, A. Global impact of salinity and agricultural ecosystems. In Salinity: Environment-Plants-Molecules; Laüchli, A., Lüttge, U., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Noble, A.D.; Schubert, S.; Thomas, R.J.; Arslan, A. Sodicity-induced land degradation and its sustainable management: Problems and prospects. Land Degrad. Dev. 2006, 17, 661–676. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, W.W.; Moore, D.P.; Alban, A.L. Improvement of a solonetzic (slick spot) soil by deep plowing, subsoiling and amendments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1972, 36, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Oster, J.D.; Shainberg, I.; Abrol, I.P. Reclamation of salt affected soils. In Agricultural Drainage; Skaggs, R.W., van Schilfgaarde, J., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy-Crop Science Society of America-Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1999; pp. 659–691. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelgawad, A.; Arslan, A.; Awad, F.; Kadouri, F. Deep Plowing Management Practice for Increasing Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Verch, Cotton, Wheat and Intensified Corn Using Saline and Non-Saline Irrigation Water. In Proceedings of the 55th IEC Meeting of the International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID), Moscow, Russia, 9–10 September 2004; pp. 67–78.
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.D. Crop and irrigation management strategies for saline-sodic soils and waters aimed at environmentally sustainable agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 323, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Sharma, B.R.; Bruggeman, A.; Choukr-Allah, R.; Karajeh, F. Non-conventional water resources and opportunities for water augmentation to achieve food security in water scarce countries. Agric. Water Manage 2007, 87, 2–22. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.C.; Deng, W.; Li, Q.S.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhang, G.X. Techniques of controlling secondary soil salinization in the west of songnen plain [in Chinese]. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2002, 22, 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.Z.; Sun, G.Y. Desalinization process through cultivating rice in heavy salinized meadow soil containing saline-alkaline patches [in Chinese]. Ecol. Env. 2004, 13, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.P.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.B.; Geng, Y.H.; Wang, S.H.; Li, C.L. Theoretical and technological problems in the development of planting paddy in saline-alkali land of Songnen Plain [in Chinese]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2012, 34, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, C.L.; Abrol, I.P. Effect of river sand on the permeability of a sodic soil. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1976, 24, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, N.; Qureshi, R.H.; Qadir, M. Amelioration of a calcareous saline-sodic soil by gypsum and forage plants. Land Degrad. Dev. 1990, 2, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, R.; Abrol, I.P. Reclaiming effect of rice grown in sodic soils. Soil Sci. 1977, 124, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Van Asten, P.J.A.; van’t Zelfde, J.A.; van der Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Hammecker, C. The effect of irrigated rice cropping on the alkalinity of two alkaline rice soils in the Sahel. Geoderma 2004, 119, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ceuppens, J.; Wopereis, M.C.S. Impact of non-drained irrigated rice cropping on soil salinization in the Senegal River Delta. Geoderma 1999, 92, 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Shi, Y.L.; Wang, R.Y. The resource of saline soil in the Northeast China [in Chinese]. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 35, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.M.; Wang, Z.C. Characterizing salt-affected soils of Songnen Plain using saturated paste and 1:5 soil-to-water extraction methods. Arid Land Res. Manage 2010, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.H.; Lesch, S.M.; Grieve, C.M. Rice growth and yield respond to changes in water depth and salinity stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 59, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.M.; Peng, S.Z.; Yang, J.S. Soil salt dynamics of rice field under different controlled irrigation conditions [in Chinese]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 23, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Menete, M.Z.L.; van Es, H.M.; Brito, R.M.L.; DeGloria, S.D.; Famba, S. Evaluation of system of rice intensification (SRI) component practices and their synergies on salt-affected soils. Field Crops Res. 2008, 109, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.M.; Liang, Z.W.; Wang, Z.C.; Huang, L.H.; Ma, H.Y.; Liu, M.; Gu, X.Y. Effect of irrigation water depth on rice growth and yield in a saline-sodic soil in Songnen Plain, China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 530–534. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X. Measures for securing water safety of main grain production base and wetland ecological safety in Northeast China [in Chinese]. China Water Resour. 2012, 15, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.X.; Deng, W.; Hu, J.M.; Zhou, D.M. Studies on changes of air temperature and precipitation for last 50 years in Songnen Plain [in Chinese]. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2007, 28, 355–358. [Google Scholar]
- Seckler, D. The New Era of Water Resources Management: From Dry to Wet Water Savings; Research Report 1; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jalota, S.K.; Prihar, S.S. Reducing Soil Water Evaporation with Tillage and Straw Mulching; IOWA State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tuong, T.P. Productive water use in rice production: opportunities and limitations. In Water Use and Production; Kikham, M.B., Ed.; The Haworth Press Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999; pp. 241–264. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, G.B.S.; Sood, A.; Jalota, S.K.; Choudhury, B.U.; Sharma, P.K. Yield, evapotranspiration and water productivity of rice (Oryza sativa L.)–wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) system in Punjab-India as influenced by transplanting date of rice and weather parameters. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu, B.S.; Khera, K.L.; Prihar, S.S.; Singh, B. Irrigation needs and yield of rice on a sandy loam soil as affected by continuous and intermittent submergence. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 1980, 50, 492–496. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.B.; Aujla, T.S.; Sandhu, B.S.; Khera, K.L. Effect of transplanting date and irrigation regime on growth, yield and water use in rice (Oryza sativa) in northern India. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 1996, 66, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tabbal, T.P.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Bhuyian, S.I.; Sibayan, E.B.; Satter, M.A. On-farm strategies for reducing water input in irrigated rice: Case studies in Philippines. Agric. Water Manage 2002, 56, 93–112. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.C.; Wang, D.L. Effects of various salt-alkaline mixed stresses on Aneurolepidium chinense (Trin.) Kitag. Plant Soil 2005, 271, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, Z.C. The alkalization parameters and their influential factors of saline-sodic soil in the Songnen Plain [in Chinese]. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2006, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chen, B.C.; Shen, Q.R. Studies on the changes of pH value and alkalization of heavily saline soil in seabeach during its desalting process [in Chinese]. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2000, 37, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G.; Rehman, M.Z.; Saifullah; Sabir, M. Reclamation and salt leaching efficiency for tile drained saline-sodic soil using marginal quality water for irrigating rice and wheat crops. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, Y.H. Water-Saving irrigation technique for well-irrigated rice in saline-alkali waterlogged lowland of Songnen Plain [in Chinese]. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2002, 24, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.J.; Huang, Z. Influence of Irrigation Water Discharge Frequency on Soil Salt Removal and Rice Yield in a Semi-Arid and Saline-Sodic Area. Water 2013, 5, 578-592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020578
Chen Y, Zhang G, Xu YJ, Huang Z. Influence of Irrigation Water Discharge Frequency on Soil Salt Removal and Rice Yield in a Semi-Arid and Saline-Sodic Area. Water. 2013; 5(2):578-592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020578
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yueqing, Guangxin Zhang, Y. Jun Xu, and Zhigang Huang. 2013. "Influence of Irrigation Water Discharge Frequency on Soil Salt Removal and Rice Yield in a Semi-Arid and Saline-Sodic Area" Water 5, no. 2: 578-592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020578
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhang, G., Xu, Y. J., & Huang, Z. (2013). Influence of Irrigation Water Discharge Frequency on Soil Salt Removal and Rice Yield in a Semi-Arid and Saline-Sodic Area. Water, 5(2), 578-592. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020578







