Modeling and Optimization of New Flocculant Dosage and pH for Flocculation: Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hybrid Copolymer
2.3. Characterization of Hybrid Copolymer
2.4. Wastewater Source
2.5. Wastewater Flocculation

2.6. Response Surface Methodology
| Variables (Factors) | Symbol | Real values of coded levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low level (−1) | Center level (0) | High level (+1) | ||
| Dose (mg/L) | X1 | 50 | 100 | 150 |
| pH | X2 | 5 | 7 | 9 |

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Spectra
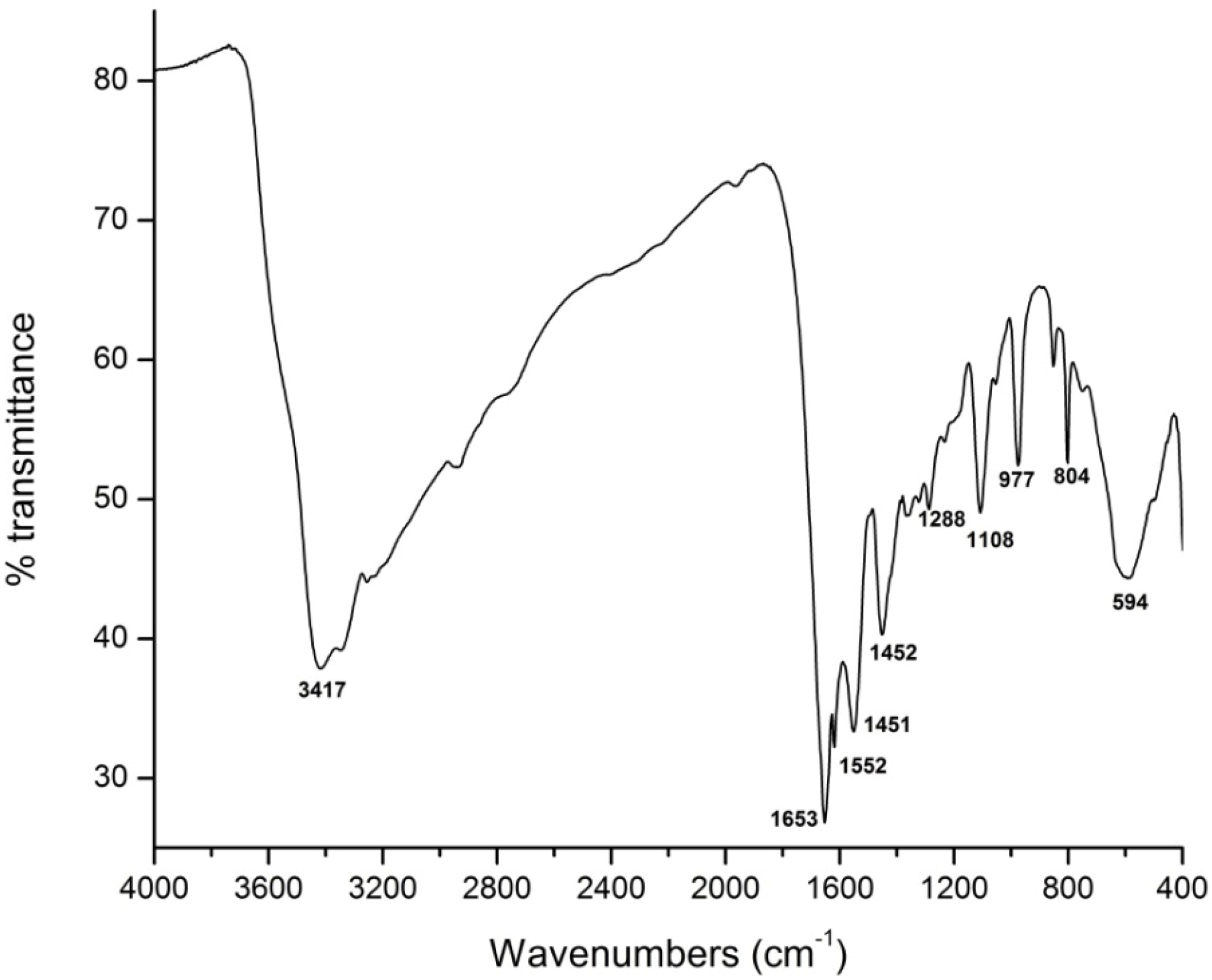
3.2. Morphological Analysis
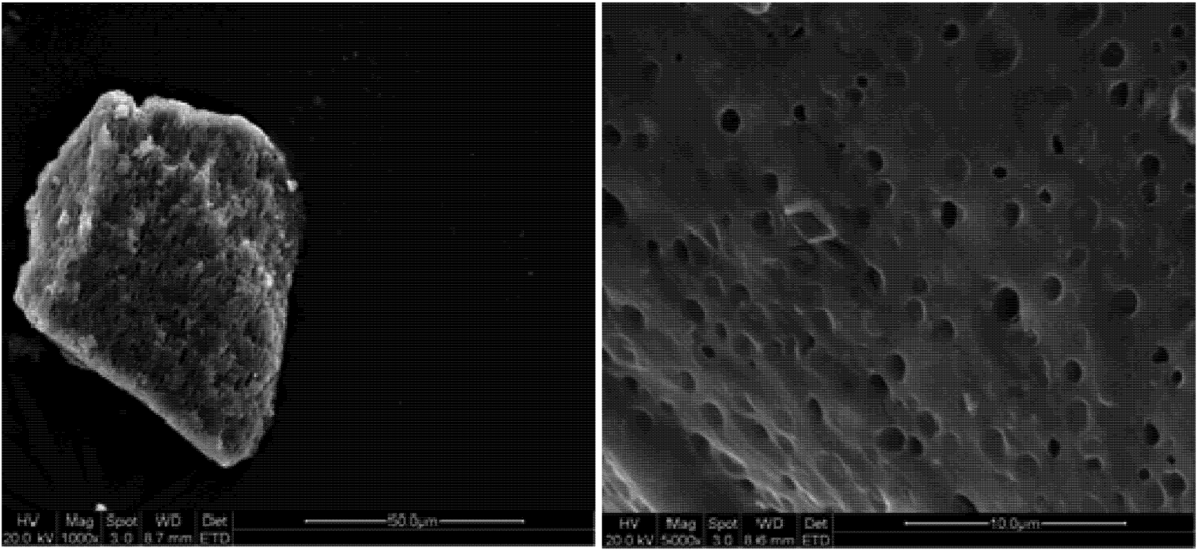

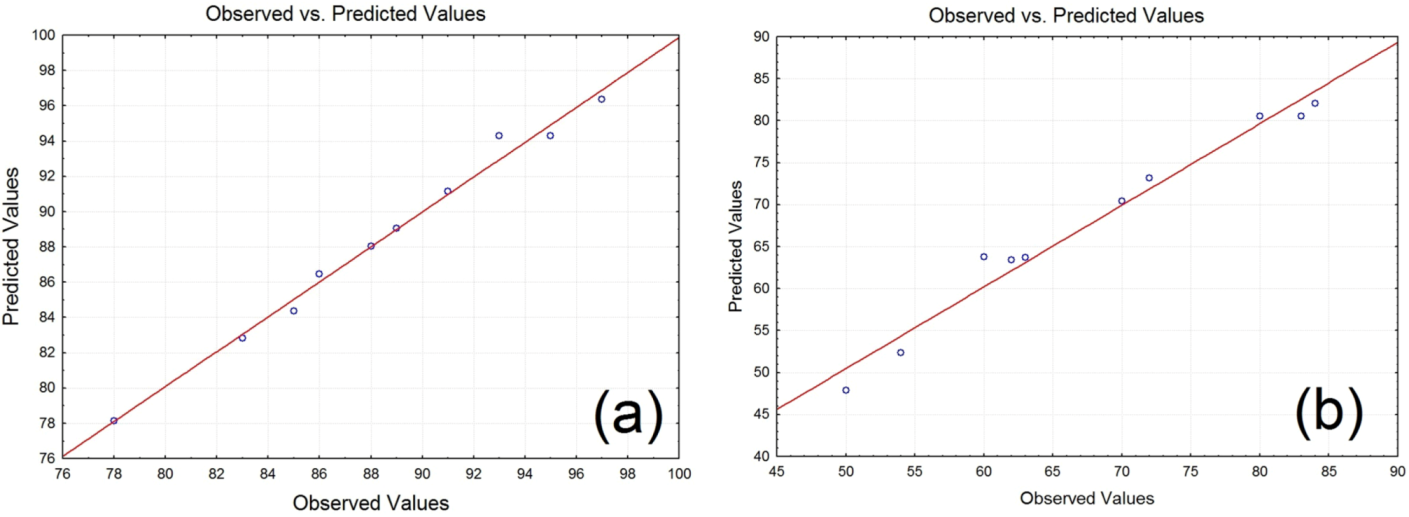
3.3. Statistical Analysis
| Run No. | Coded variables | Real variables | Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | pH | Dose (mg/L) | pH | Turbidity Removal (%) | COD Removal (%) | |
| 1 | 1 | −1 | 150 | 5 | 91 | 72 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 50 | 9 | 78 | 50 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 7 | 93 | 83 |
| 4 | −1 | −1 | 50 | 5 | 83 | 54 |
| 5 | 0 | −1 | 100 | 5 | 89 | 70 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 150 | 7 | 97 | 84 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 150 | 9 | 86 | 63 |
| 8 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 9 | 85 | 62 |
| 9 | −1 | 0 | 50 | 7 | 88 | 60 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 7 | 95 | 80 |
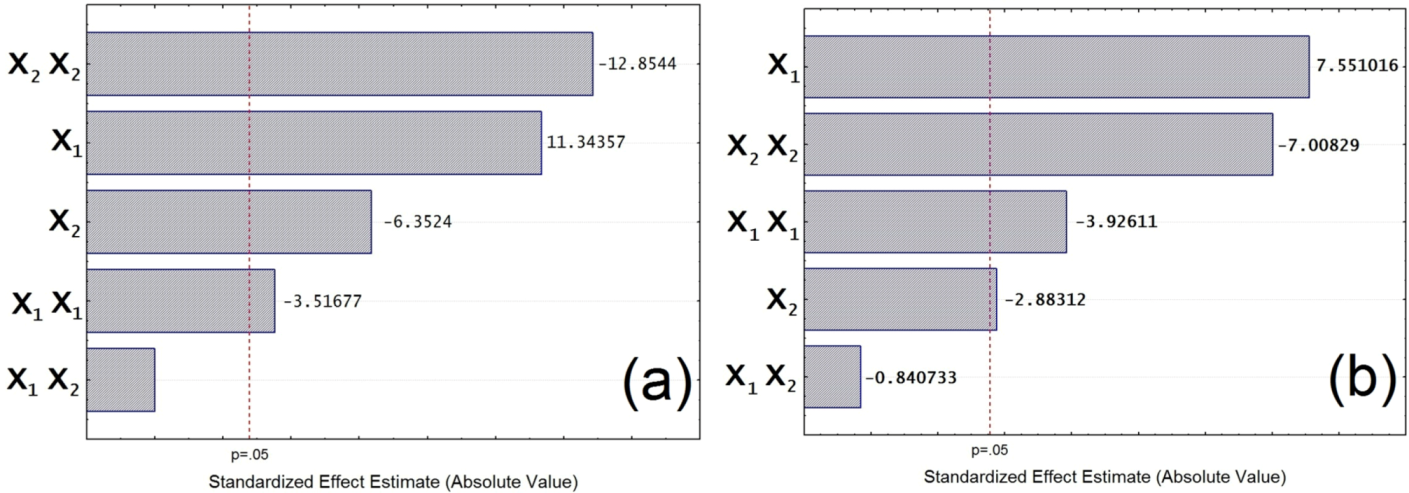
3.4. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)


| Response | Source | Sum of Squares | df | F value | p value | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidity removal | X1 | 104.17 | 1 | 128.68 | 0.0003 | significant |
| X2 | 32.67 | 1 | 40.35 | 0.0031 | significant | |
| X1X2 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.00 | 1.0000 | not significant | |
| X1X1 | 10.01 | 1 | 12.37 | 0.0245 | significant | |
| X2X2 | 133.76 | 1 | 165.24 | 0.0002 | significant | |
| COD removal | X1 | 504.17 | 1 | 57.02 | 0.0016 | significant |
| X2 | 73.50 | 1 | 8.31 | 0.0449 | significant | |
| X1X2 | 6.25 | 1 | 0.71 | 0.4478 | not significant | |
| X1X1 | 136.30 | 1 | 15.41 | 0.0172 | significant | |
| X2X2 | 434.30 | 1 | 49.12 | 0.0022 | significant |
| Response | Probability | R2 | Adj. R2 | Pred. R2 | Adeq. precision | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidity removal | 0.0005 | 0.9892 | 0.9758 | 0.9466 | 26.169 | 1.02 |
| COD removal | 0.0032 | 0.9726 | 0.9383 | 0.7469 | 14.859 | 4.39 |
3.5. Analysis of Flocculation Process
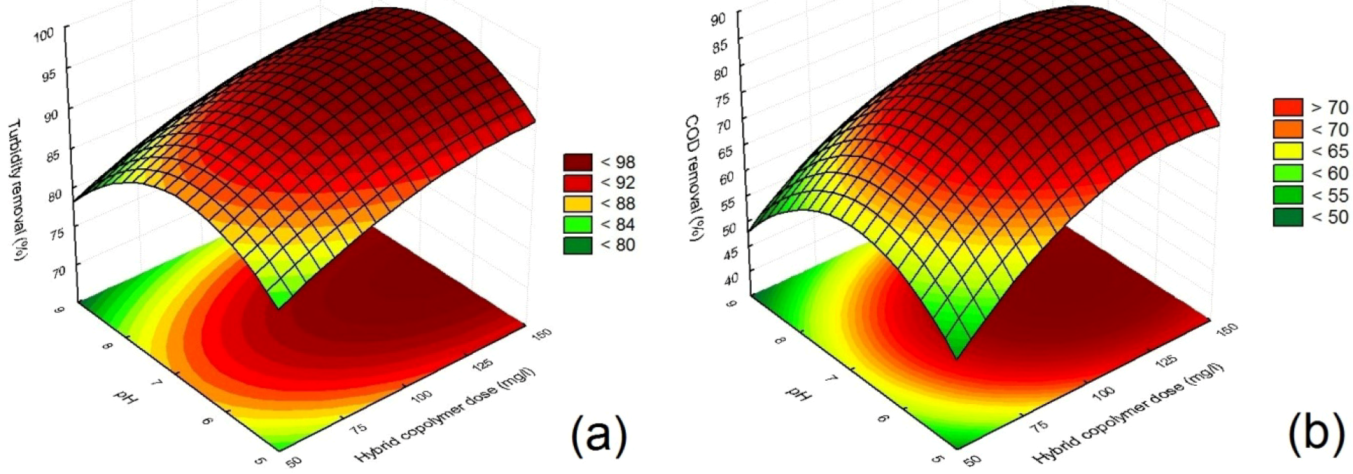
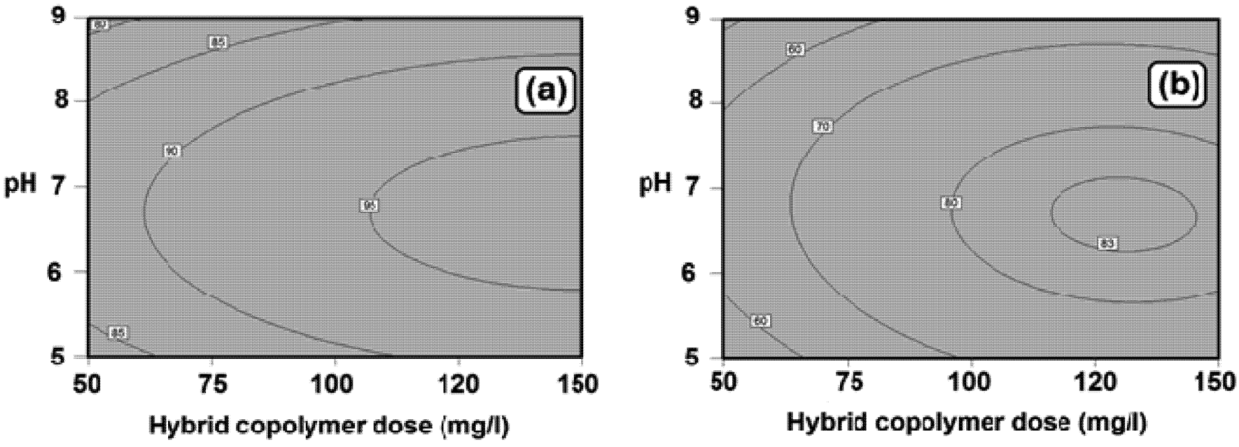
3.6. Optimization Conditions and Verification
- Find: (Dose and pH)
- Maximize removal process = f (Dose and pH)
- Subjected to the constraint: removal process ≤ 100%
- Parameter ranges: −1 ≤ Dose ≤ +1 and −1 ≤ pH ≤ +1
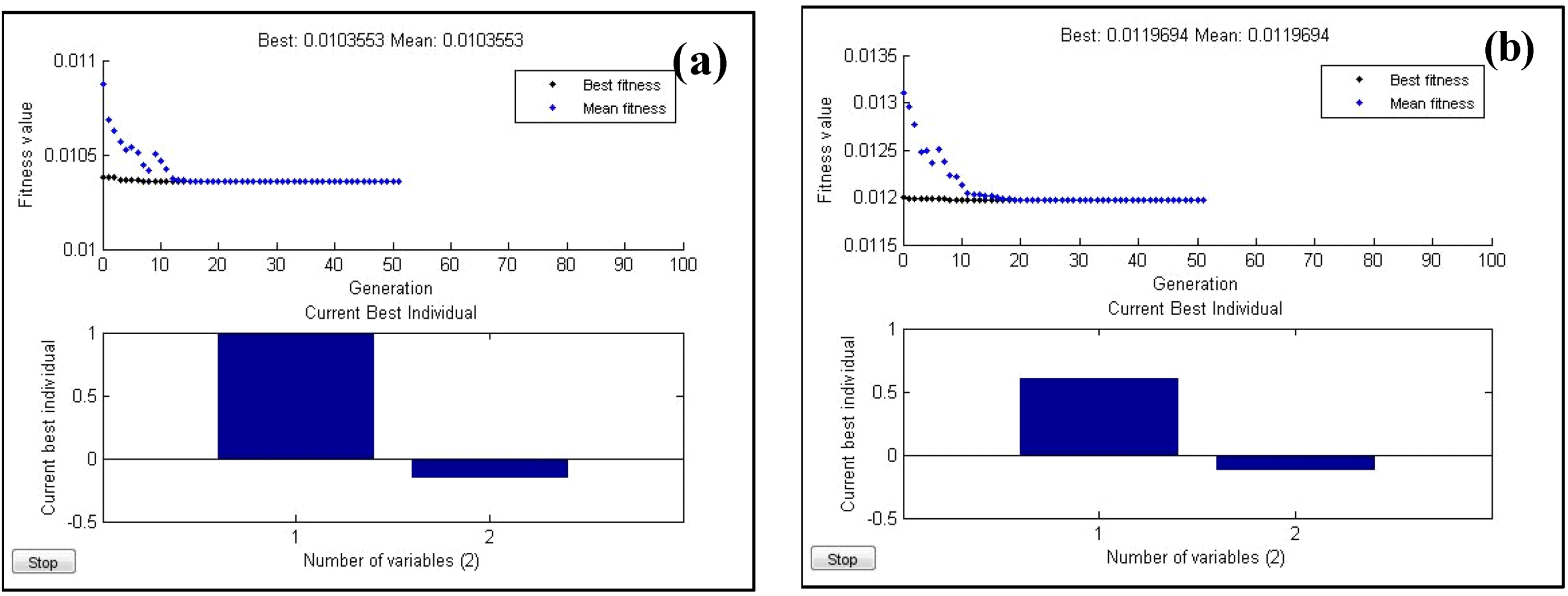
| Model | Optimized Technique | Optimal Dose (mg/L) | Optimal pH | Best predicted Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turbidity removal | Desirable function | 137 | 6.68 | 96.40 |
| Genetic algorithm | 150 | 6.69 | 96.56 | |
| COD removal | Desirable function | 137 | 6.68 | 83.50 |
| Genetic algorithm | 130 | 6.74 | 83.54 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Wang, J.P.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ge, X.W.; Yu, H.Q. Optimization of coagulation–flocculation process for a paper-recycling wastewater treatment using response surface methodology. Colloid. Surf. A 2007, 302, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, S.; Tshukudu, T.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, P.; He, Q. Investigations of coagulation–flocculation process by performance optimization, model prediction and fractal structure of flocs. Desalination 2011, 269, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, R.; Dahiya, R. COD and BOD removal from domestic wastewater generated in decentralised sectors. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E.; Teng, T.T.; Morad, N.; Poh, B.T.; Mahalingam, M. Flocculation activity of novel ferric chloride–polyacrylamide (FeCl3-PAM) hybrid polymer. Desalination 2011, 266, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qian, J.; Shen, Z. A novel flocculant of Al(OH)3-polyacrylamide ionic hybrid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Shi, B. The characteristics of composite flocculants synthesized with inorganic polyaluminium and organic polymers. In Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment VII, Proceedings of the 10th Gothenburg symposium 2002, Gothenburg, Sweden, June 17–19, 2002; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2002; pp. 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kasiri, M.; Khataee, A. Photooxidative decolorization of two organic dyes with different chemical structures by UV/H2O2 process: Experimental design. Desalination 2011, 270, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, F.M.; Rahman, N.N.N.A.; Ahmad, A. COD reduction in semiconductor wastewater by natural and commercialized coagulants using response surface methodology. Water Air Soil Poll. 2008, 195, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woon, S.; Querin, O.; Steven, G. Structural application of a shape optimization method based on a genetic algorithm. Struct. Multidiscip. Opitm. 2001, 22, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.L.; Gunst, R.F.; Hess, J.L. Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments: With Applications to Engineering and Science; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 356752. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, D. Applying hybrid coagulants and polyacrylamide flocculants in the treatment of high-phosphorus hematite flotation wastewater (HHFW): Optimization through response surface methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretsch, E.; Bühlmann, P.; Badertscher, M. Structure Determination of Organic Compounds: Tables of Spectral Data; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafari, S.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Zinatizadeh, A.A. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize coagulation–flocculation treatment of leachate using poly-aluminum chloride (PAC) and alum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, L.; Dilbaghi, N. Optimization of process variables for decolorization of Disperse Yellow 211 by Bacillus subtilis using Box–Behnken design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wantala, K.; Khongkasem, E.; Khlongkarnpanich, N.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Kim, K.W. Optimization of As(V) adsorption on Fe-RH-MCM-41-immobilized GAC using Box-Behnken design: Effects of pH, loadings, and initial concentrations. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 5, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, P.; Srivastava, V.C.; Kumar, A. Optimization of an azo dye batch adsorption parameters using Box–Behnken design. Desalination 2009, 249, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Vahabzadeh, F.; Bonakdarpour, B.; Mofarrah, E.; Mehranian, M. Application of the central composite design and response surface methodology to the advanced treatment of olive oil processing wastewater using Fenton’s peroxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.K.; Kang, L.S. Response surface methodological approach to optimize the coagulation–flocculation process in drinking water treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 2011, 89, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.J.; Duff, S.J.B. Coagulation and precipitation of a mechanical pulping effluent—I. Removal of carbon, colour and turbidity. Water Res. 1996, 30, 781–792. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.H.; Teng, T.T.; Omar, A. Removal of dyes and industrial dye wastes by magnesium chloride. Water Res. 2000, 34, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dawood, A.S.; Li, Y. Modeling and Optimization of New Flocculant Dosage and pH for Flocculation: Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater. Water 2013, 5, 342-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020342
Dawood AS, Li Y. Modeling and Optimization of New Flocculant Dosage and pH for Flocculation: Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater. Water. 2013; 5(2):342-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020342
Chicago/Turabian StyleDawood, Ammar Salman, and Yilian Li. 2013. "Modeling and Optimization of New Flocculant Dosage and pH for Flocculation: Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater" Water 5, no. 2: 342-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020342
APA StyleDawood, A. S., & Li, Y. (2013). Modeling and Optimization of New Flocculant Dosage and pH for Flocculation: Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater. Water, 5(2), 342-355. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020342




